e66351236daa365a56555c5437844990.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62

E – Commerce (B 2 C) Kazadi, Mujinga Karaya, Jecinta Safrillah, Nur Sukrislismono, Yohanes 1

e - Commerce Objectives: • Introduction of e-commerce • The spread e-commerce in the world • The domain name • E-commerce payment system • Comparison of ecommerce in developed and developing countries 2

Definitions e - Commerce What is E-Commerce: the online transaction of business, featuring linked computer systems of the vendor, host, and buyer. Electronic transactions involve the transfer of ownership or rights to use a good or service. Source Export. Gov Type of E-Commerce : Business to Consumer (B 2 C) Business to Business (B 2 B) Consumer to Consumer (C 2 C) Peer to Peer (P 2 P) Mobile Commerce (M-Commerce) Source : Loudon, Kenneth C and Traver, Carol G “E-commerce”, Pearson, New Jersey, 2007 3
Type of e-commerce Business to Business (B 2 B) • refer businesses focus on electronically selling to other business • the largest form of e-commerce ( over 1. 5 trillion in transaction in US in 2005) • Net market place model : e-distributors, e-procurement companies, exchanges, etc • Private industrial network model : single firm network, industrywide network Consumer to Consumer (C 2 C) • Refer a way for consumers to electronically sell to each other • Example : e-Bay • generate > $44 billion in gross merchandise volume around the world 4

Type of e-commerce Peer to Peer (P 2 P) • Share files and computer resources directly • Example : Nepster. com, kazaa, grokster Mobile Commerce(M-commerce) • refers to the use of wireless digital devices to enable transaction on the Web. • Involved cell phone, Blackberry, PC • Used most widely in Japan & Europe 5

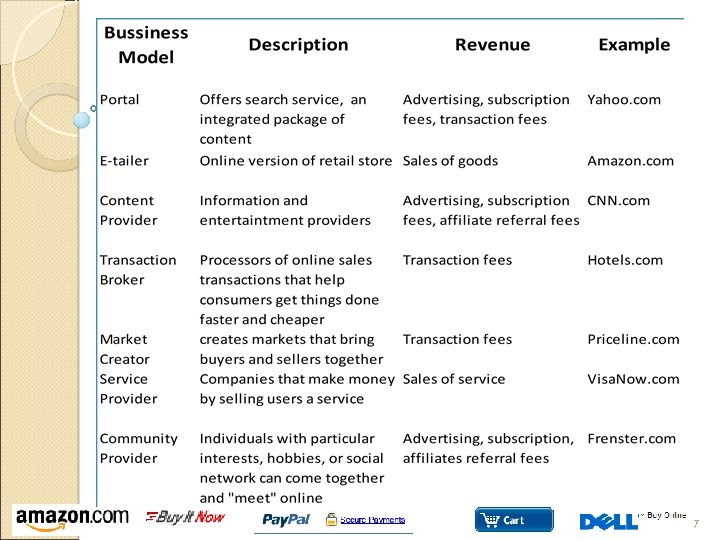
Type of e-commerce e - Commerce Business to Consumer (B 2 C) • activities of E-businesses serving end consumers with products and/or services. Source (http: //en. wikipedia. org) • Grows exponentially since 1995 • Most consumers are likely to encounter Business Models: Portal (Ex. Google. com, Yahoo. com, etc) E-Tailer (Ex. Amazon. com, Walmart. com, etc) Content Provider (Ex. Sportline. com, CNN. com, etc) Transaction Broker (Ex. Hotels. com, Travelocity. com, etc) Market Creator (Ex. Ebay. com, Priceline. com) Service Provider ( Ex. Visa. Now. com, Blue. Flag. com, etc) Community Provider (Ex. Ivillage. com, Friendster. com) Source : Loudon, Kenneth C and Traver, Carol G “E-commerce”, Pearson, New Jersey, 2007 6
7

e - Commerce Objectives: • Introduction of e-commerce • The spread e-commerce in the world • The domain name • E-commerce payment system • Comparison of ecommerce in develop and developing countries 8
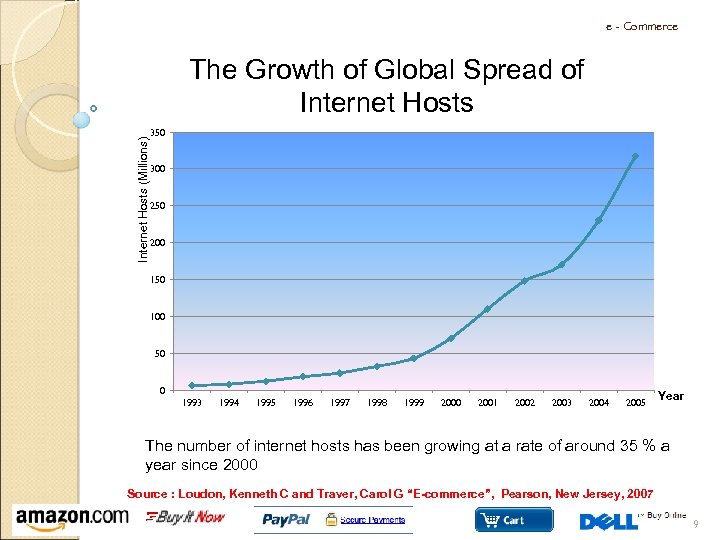
e - Commerce Internet Hosts (Millions) The Growth of Global Spread of Internet Hosts 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Year The number of internet hosts has been growing at a rate of around 35 % a year since 2000 Source : Loudon, Kenneth C and Traver, Carol G “E-commerce”, Pearson, New Jersey, 2007 9
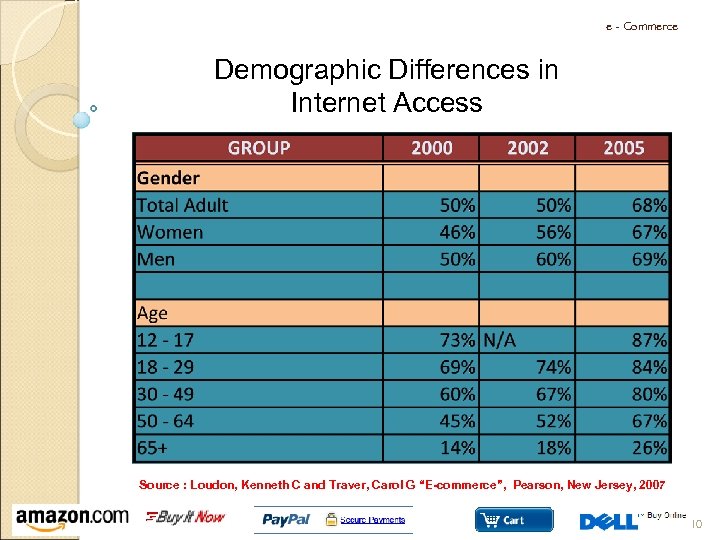
e - Commerce Demographic Differences in Internet Access Source : Loudon, Kenneth C and Traver, Carol G “E-commerce”, Pearson, New Jersey, 2007 10
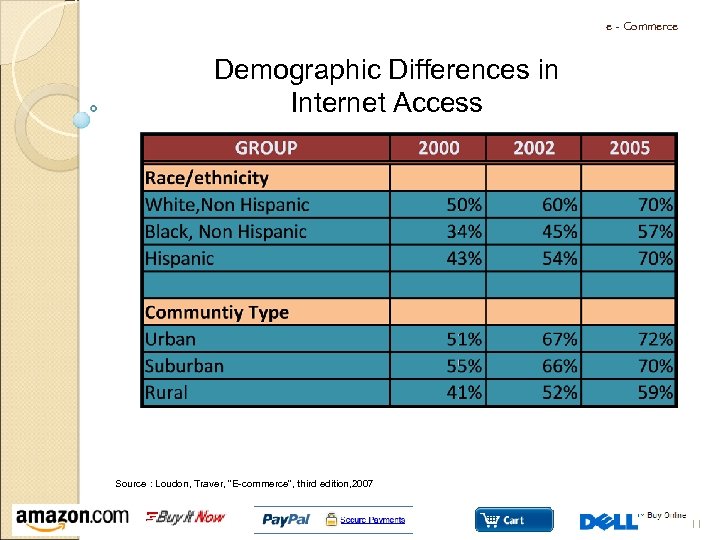
e - Commerce Demographic Differences in Internet Access Source : Loudon, Traver, “E-commerce”, third edition, 2007 11
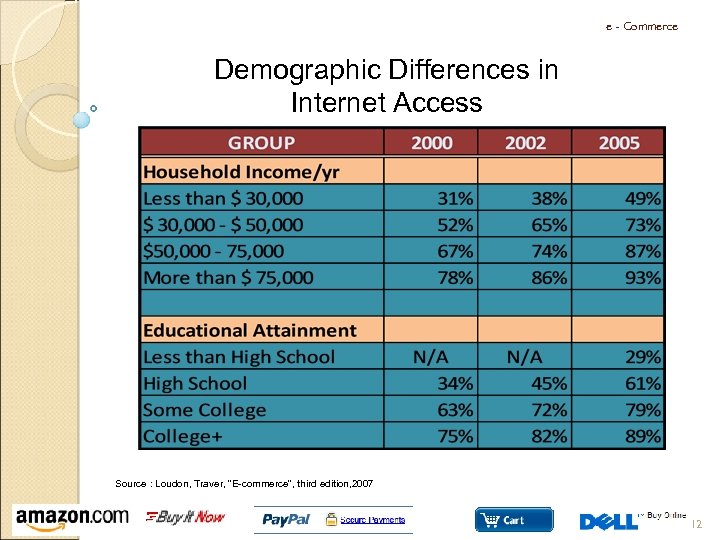
e - Commerce Demographic Differences in Internet Access Source : Loudon, Traver, “E-commerce”, third edition, 2007 12
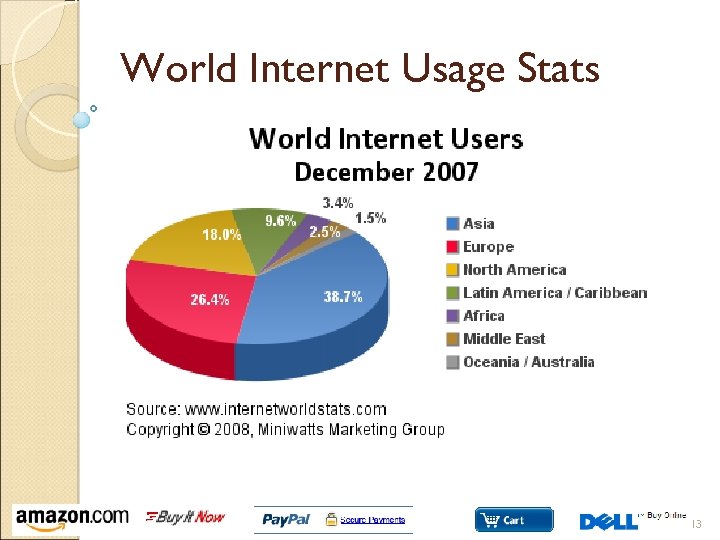
World Internet Usage Stats 13
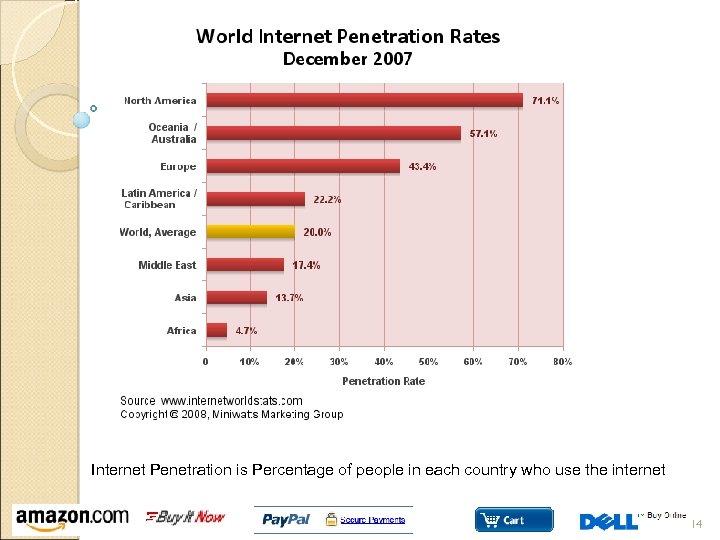
Internet Penetration is Percentage of people in each country who use the internet 14
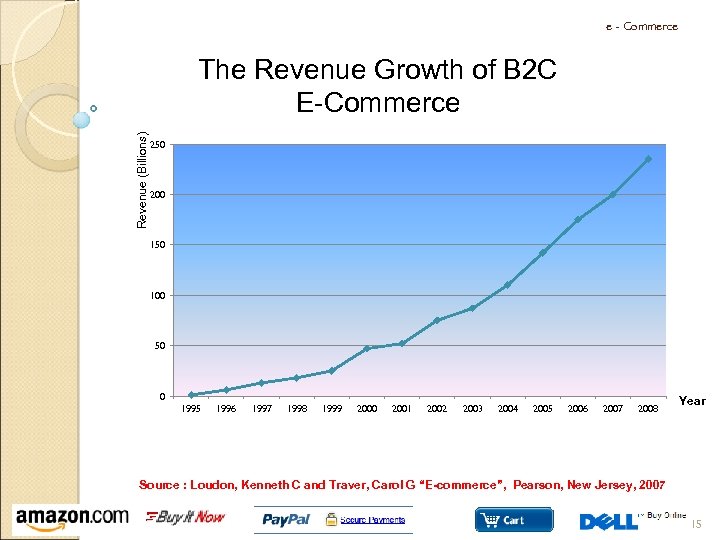
e - Commerce Revenue (Billions) The Revenue Growth of B 2 C E-Commerce 250 200 150 100 50 0 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 Year Source : Loudon, Kenneth C and Traver, Carol G “E-commerce”, Pearson, New Jersey, 2007 15
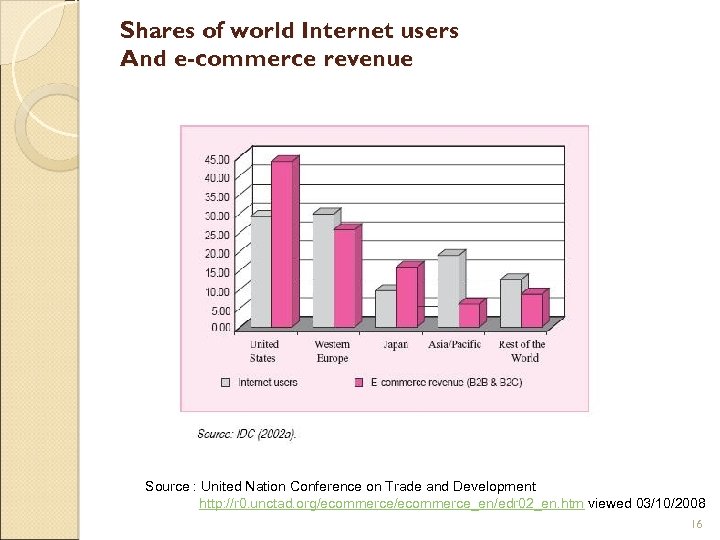
Shares of world Internet users And e-commerce revenue Source : United Nation Conference on Trade and Development http: //r 0. unctad. org/ecommerce_en/edr 02_en. htm viewed 03/10/2008 16
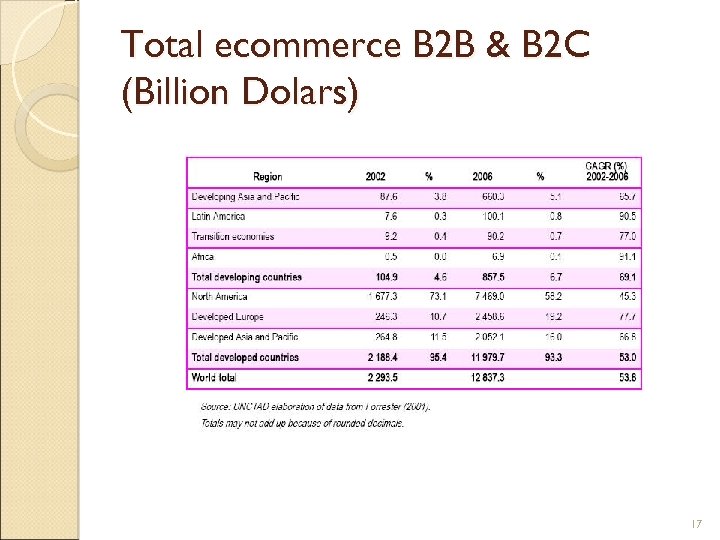
Total ecommerce B 2 B & B 2 C (Billion Dolars) 17
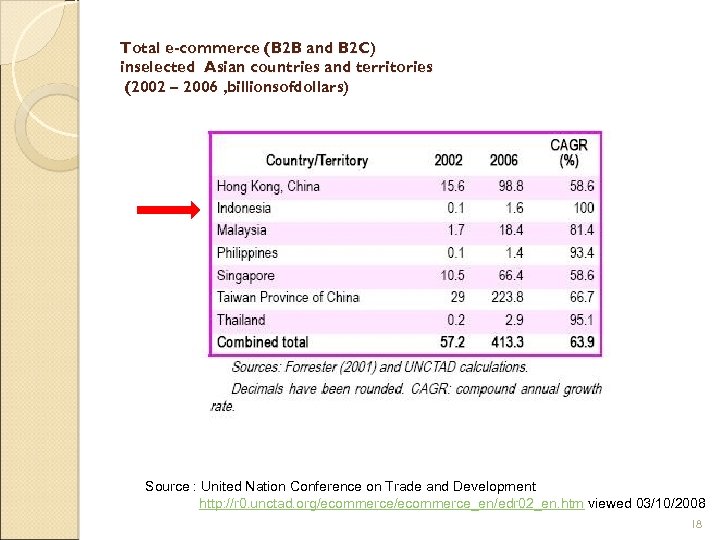
Total e-commerce (B 2 B and B 2 C) inselected Asian countries and territories (2002 – 2006 , billionsofdollars) Source : United Nation Conference on Trade and Development http: //r 0. unctad. org/ecommerce_en/edr 02_en. htm viewed 03/10/2008 18
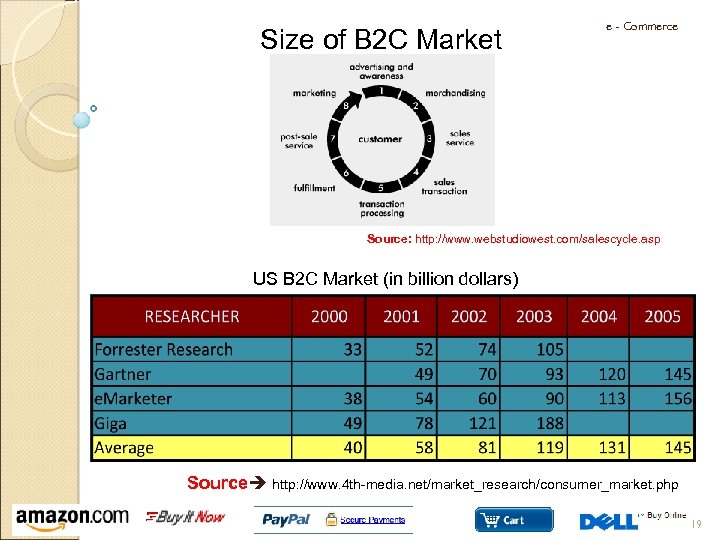
Size of B 2 C Market e - Commerce Source: http: //www. webstudiowest. com/salescycle. asp US B 2 C Market (in billion dollars) Source http: //www. 4 th-media. net/market_research/consumer_market. php 19
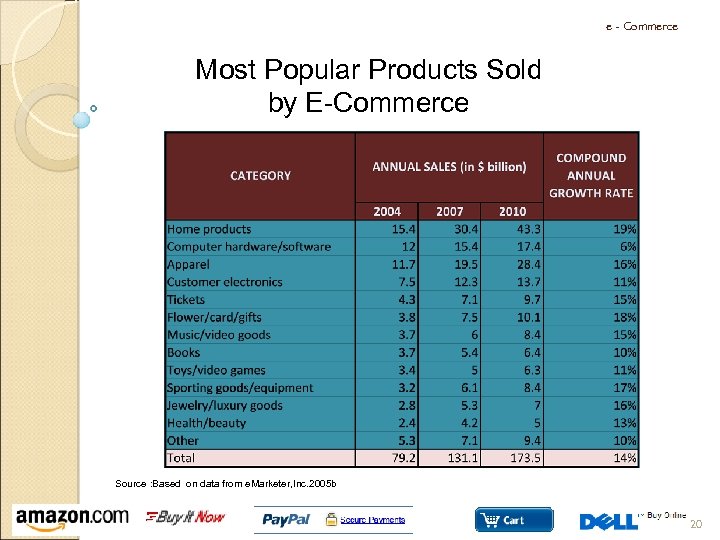
e - Commerce Most Popular Products Sold by E-Commerce Source : Based on data from e. Marketer, Inc. 2005 b 20

e - Commerce Objectives: • Introduction of e-commerce • The spread e-commerce in the world • The domain name • E-commerce payment system • Comparison of B 2 C in developed and developing countries 21

134. 124. 1. 234 ? ? ? Domain Name is the name of a specific host that maintains a website and related sub-sites. A domain name consists of a string of alphanumeric ASCII characters, separated by periods, which is used to find a host on a network domain name effectively serves, at one and the same time, as a branding or identification device for a business, an organization or a person, and as the functional mechanism to locate its website Examples : amazon. com, pln. co. id, global. net, umsl. edu 22
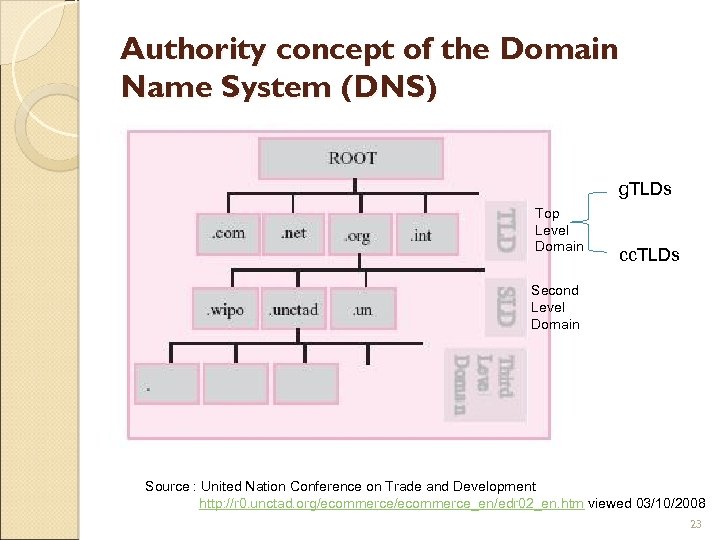
Authority concept of the Domain Name System (DNS) g. TLDs Top Level Domain cc. TLDs Second Level Domain Source : United Nation Conference on Trade and Development http: //r 0. unctad. org/ecommerce_en/edr 02_en. htm viewed 03/10/2008 23
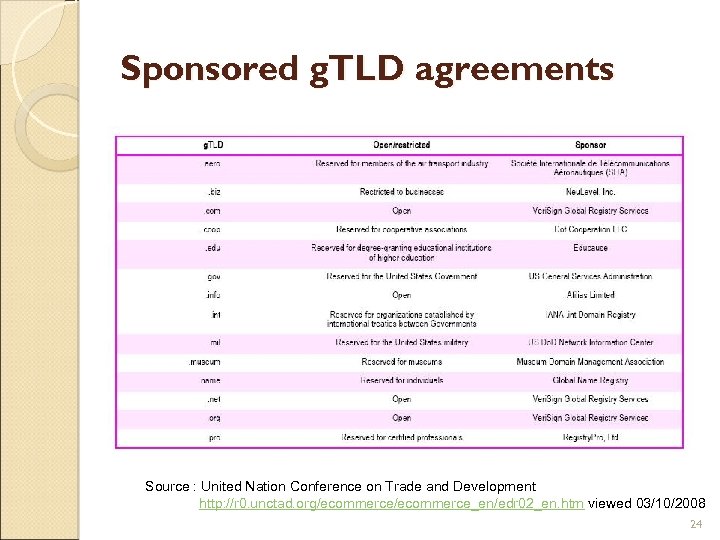
Sponsored g. TLD agreements Source : United Nation Conference on Trade and Development http: //r 0. unctad. org/ecommerce_en/edr 02_en. htm viewed 03/10/2008 24
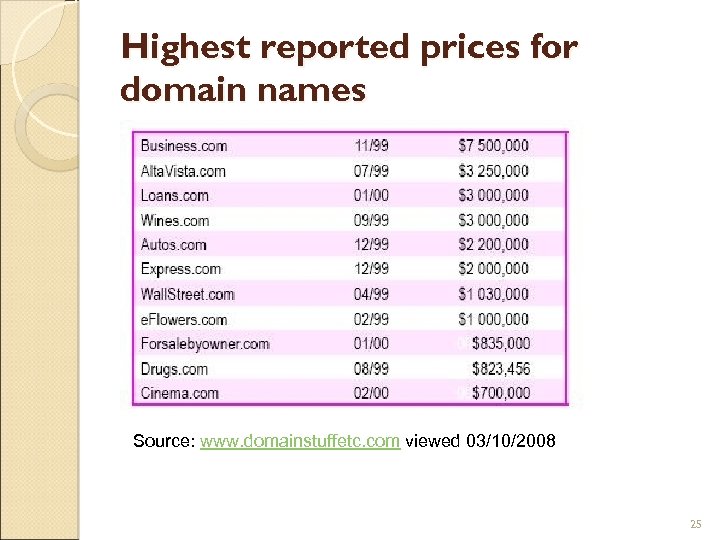
Highest reported prices for domain names Source: www. domainstuffetc. com viewed 03/10/2008 25
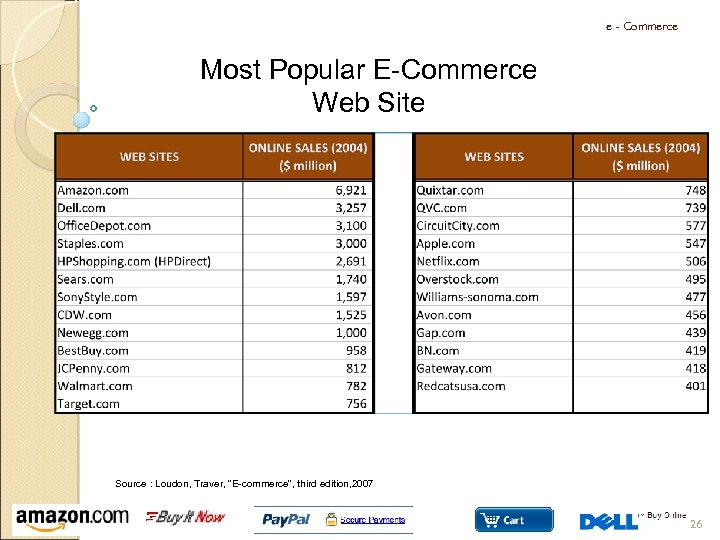
e - Commerce Most Popular E-Commerce Web Site Source : Loudon, Traver, “E-commerce”, third edition, 2007 26

e - Commerce Objectives: • Introduction ecommerce as new business concept • How does ecommerce Spread in the world • The domain name • E-commerce payment system • Comparison of ecommerce in developed and developing country 27
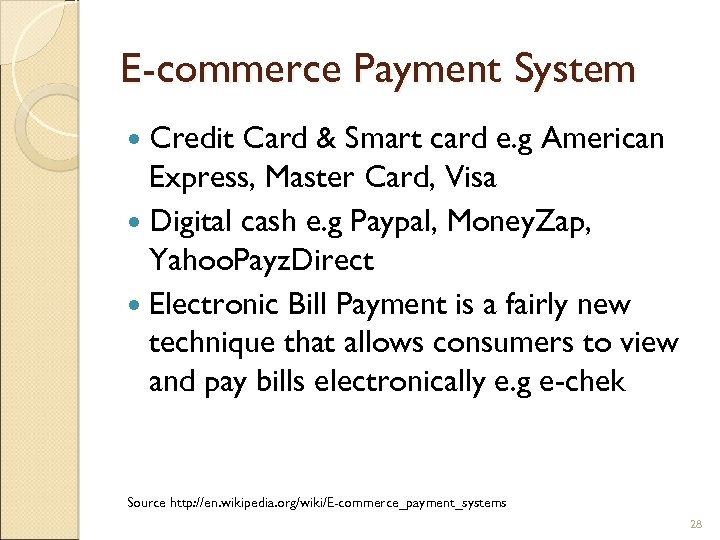
E-commerce Payment System Credit Card & Smart card e. g American Express, Master Card, Visa Digital cash e. g Paypal, Money. Zap, Yahoo. Payz. Direct Electronic Bill Payment is a fairly new technique that allows consumers to view and pay bills electronically e. g e-chek Source http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/E-commerce_payment_systems 28
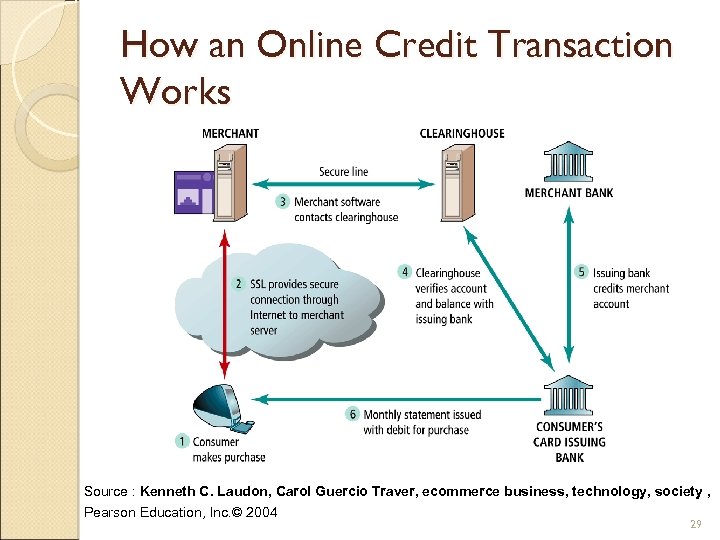
How an Online Credit Transaction Works Source : Kenneth C. Laudon, Carol Guercio Traver, ecommerce business, technology, society , Pearson Education, Inc. © 2004 29

Limitations of Online Credit Card Payment Systems Security – neither merchant nor consumer can be fully authenticated Cost – for merchants, around 3. 5% of purchase price plus transaction fee of 2030 cents per transaction Social equity – many people do not have access to credit cards (young adults, plus almost 100 million other adult Americans who cannot afford cards or are considered poor risk) 30
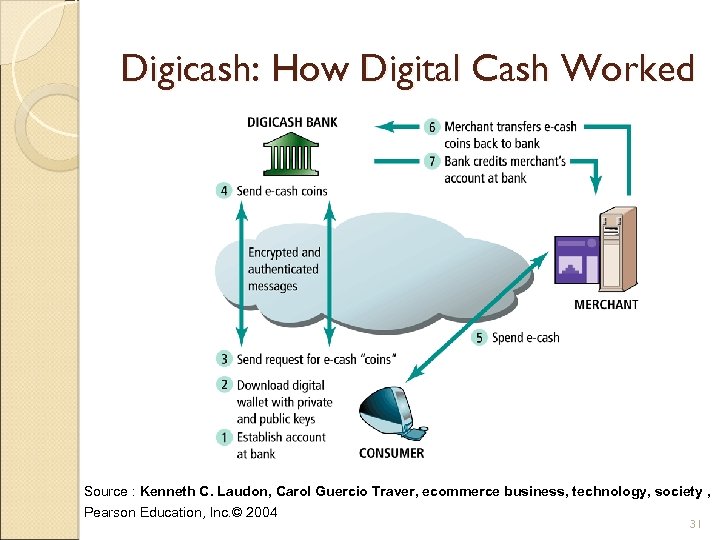
Digicash: How Digital Cash Worked Source : Kenneth C. Laudon, Carol Guercio Traver, ecommerce business, technology, society , Pearson Education, Inc. © 2004 31

Digital Cash One of the first forms of alternative payment systems Not really “cash” – rather, are forms of value storage and value exchange that have limited convertibility into other forms of value, and require intermediaries to convert Many of early examples have disappear; concepts survive as part of P 2 P payment systems 32
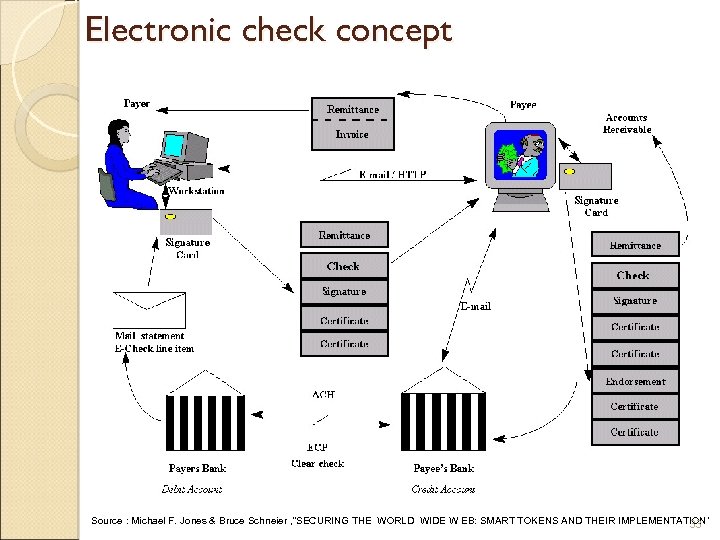
Electronic check concept Source : Michael F. Jones & Bruce Schneier , “SECURING THE WORLD WIDE W EB: SMART TOKENS AND THEIR IMPLEMENTATION’ 33

e - Commerce Objectives: • Introduction of e-commerce • The spread e-commerce in the world • The domain name • E-commerce payment system • Comparison of B 2 C in developed and developing countries 34

E-Commerce in Indonesia Background: Þ More than 16, 700 islands, Þ Population of almost 225 million Þ 4 th most populous country in the world. Gross National Income: US$1, 280 Þ Total area of the country is 9. 8 million sq km Þ Land size: 1. 9 sq km – Þ Population Density is 118 persons per sq km. Þ Þ Source: http: //countrystudies. us/indonesia/28. htm 35
Map of Indonesia
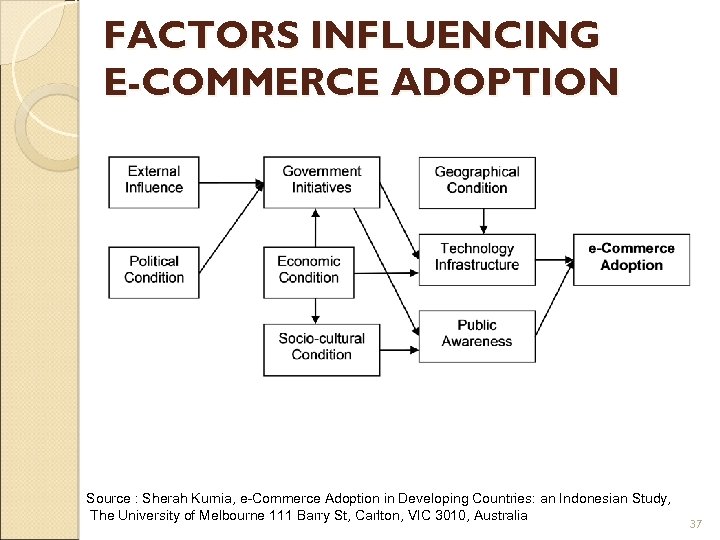
FACTORS INFLUENCING E-COMMERCE ADOPTION Source : Sherah Kurnia, e-Commerce Adoption in Developing Countries: an Indonesian Study, The University of Melbourne 111 Barry St, Carlton, VIC 3010, Australia 37
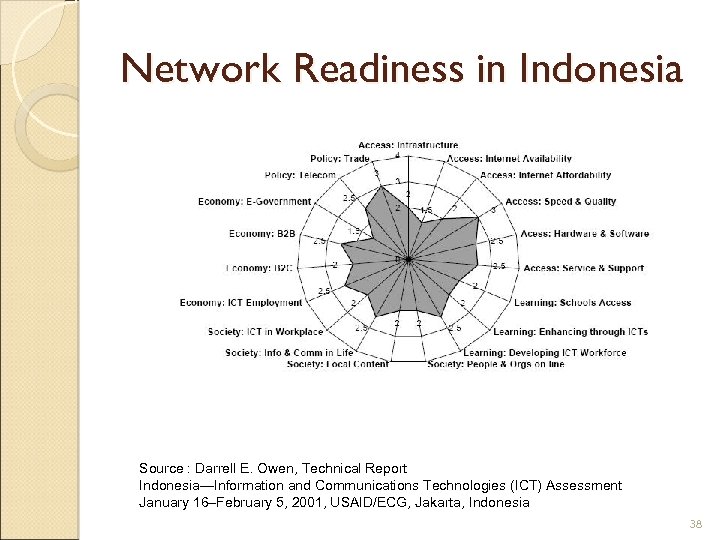
Network Readiness in Indonesia Source : Darrell E. Owen, Technical Report Indonesia—Information and Communications Technologies (ICT) Assessment January 16–February 5, 2001, USAID/ECG, Jakarta, Indonesia 38
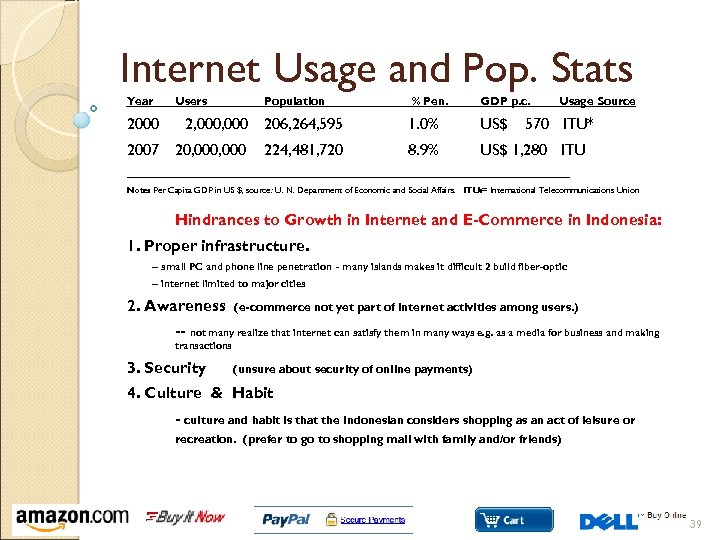
Internet Usage and Pop. Stats Year 2000 2007 Users Population 2, 000 206, 264, 595 20, 000 224, 481, 720 % Pen. GDP p. c. Usage Source 1. 0% US$ 8. 9% US$ 1, 280 ITU 570 ITU* __________________________________ Note: Per Capita GDP in US $, source: U. N. Department of Economic and Social Affairs. ITU: = International Telecommunications Union Hindrances to Growth in Internet and E-Commerce in Indonesia: 1. Proper infrastructure. -- small PC and phone line penetration - many islands makes it difficult 2 build fiber-optic -- internet limited to major cities 2. Awareness (e-commerce not yet part of internet activities among users. ) -- not many realize that internet can satisfy them in many ways e. g. as a media for business and making transactions 3. Security (unsure about security of online payments) 4. Culture & Habit - culture and habit is that the Indonesian considers shopping as an act of leisure or recreation. (prefer to go to shopping mall with family and/or friends) 39
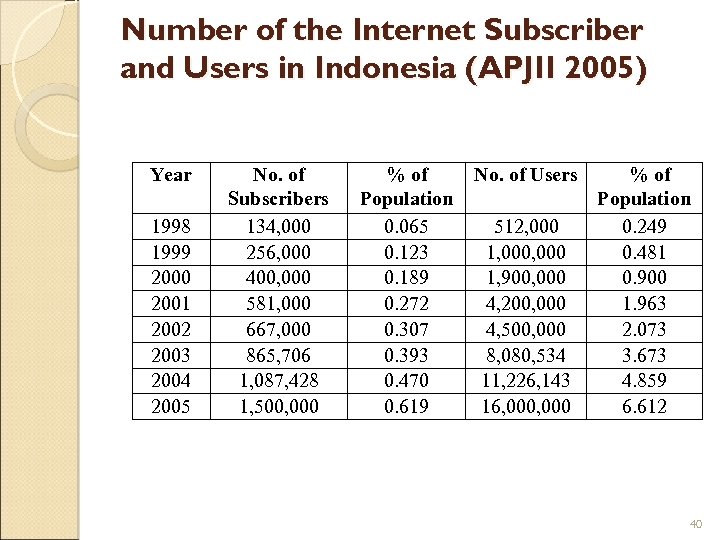
Number of the Internet Subscriber and Users in Indonesia (APJII 2005) Year 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 No. of Subscribers 134, 000 256, 000 400, 000 581, 000 667, 000 865, 706 1, 087, 428 1, 500, 000 % of Population 0. 065 0. 123 0. 189 0. 272 0. 307 0. 393 0. 470 0. 619 No. of Users 512, 000 1, 900, 000 4, 200, 000 4, 500, 000 8, 080, 534 11, 226, 143 16, 000 % of Population 0. 249 0. 481 0. 900 1. 963 2. 073 3. 673 4. 859 6. 612 40

E-Commerce in Indonesia Geography =>Composed of thousand of islands, is a big challenge in developing a fiberoptic-based global infrastructure. Aware of this, Indonesia government announced a national infrastructure concept called Nusantara 21 is a reflection of Indonesia's vision of entering information era as an important part of the global community. 41
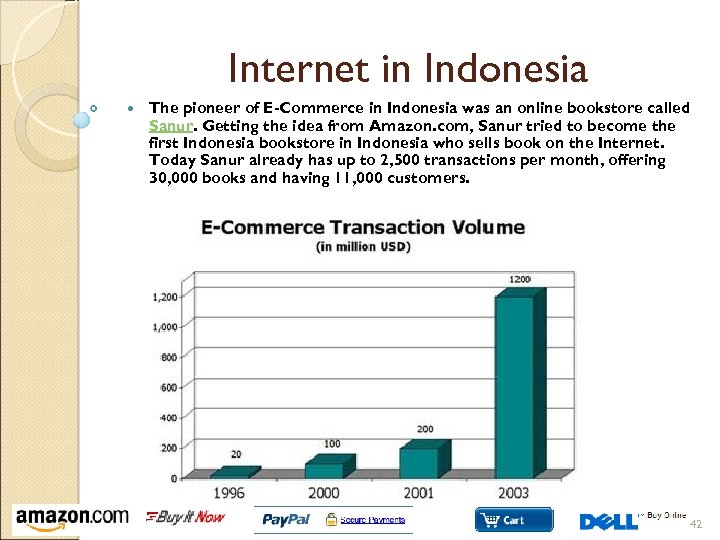
Internet in Indonesia The pioneer of E-Commerce in Indonesia was an online bookstore called Sanur. Getting the idea from Amazon. com, Sanur tried to become the first Indonesia bookstore in Indonesia who sells book on the Internet. Today Sanur already has up to 2, 500 transactions per month, offering 30, 000 books and having 11, 000 customers. 42
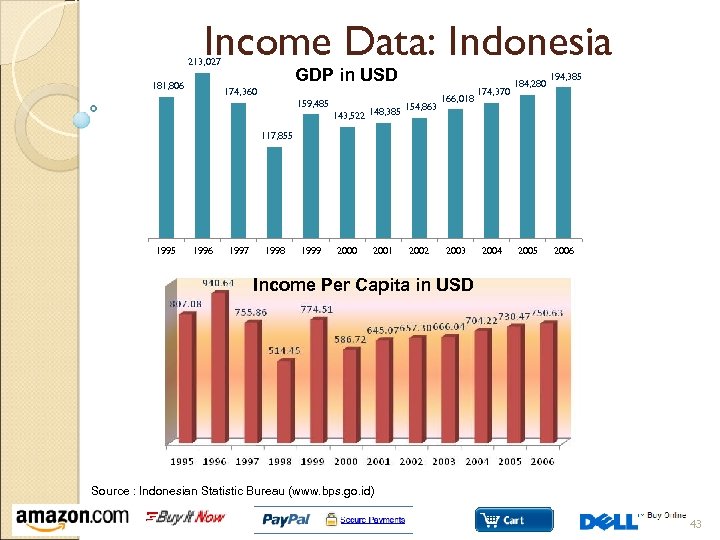
Income Data: Indonesia 213, 027 181, 806 GDP in USD 174, 360 159, 485 143, 522 148, 385 154, 863 166, 018 174, 370 184, 280 194, 385 117, 855 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Income Per Capita in USD Source : Indonesian Statistic Bureau (www. bps. go. id) 43
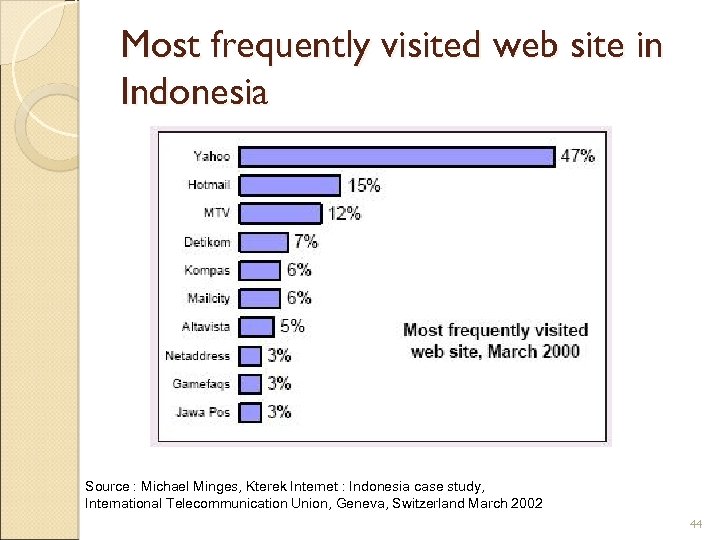
Most frequently visited web site in Indonesia Source : Michael Minges, Kterek Internet : Indonesia case study, International Telecommunication Union, Geneva, Switzerland March 2002 44

How ecommerce survive in Indonesia Internet Banking Online Trading B 2 C 45

klikbca. com Typo WWWKLIKBCA. COM KILKBCA. COM CLIKBCA. COM KLICKBCA. COM KLIKBAC. COM 46
Online Trading 47

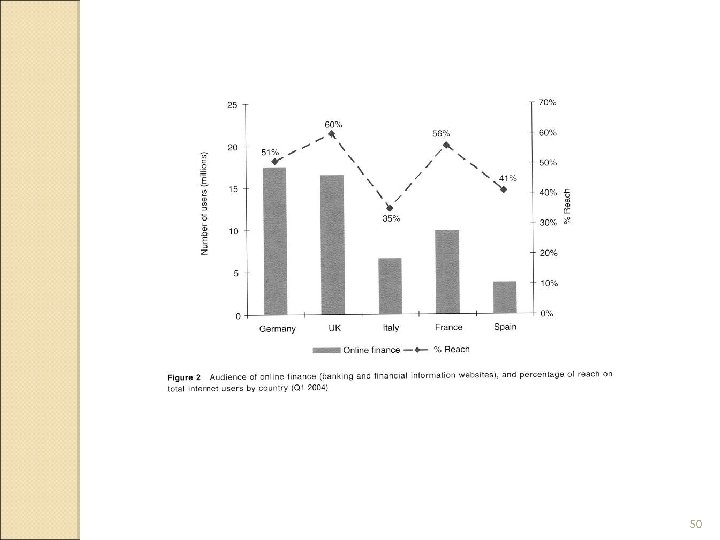
Online banking in Europe 48

Who uses online banking in Europe UK , Germany and France have the highest number of people using online banking Italy and Spain have the smallest number because these are emerging market. Source: Journal of Financial Services Marketing. London: Jun 2005. Vol. 9, Iss. 4; pg. 329, 15 pgs 49
50

WHO USES ONLINE BANKING People with high formal education are more likely to use online banking Adoption rates of online banking decreases from north to south and from rich to poor 51
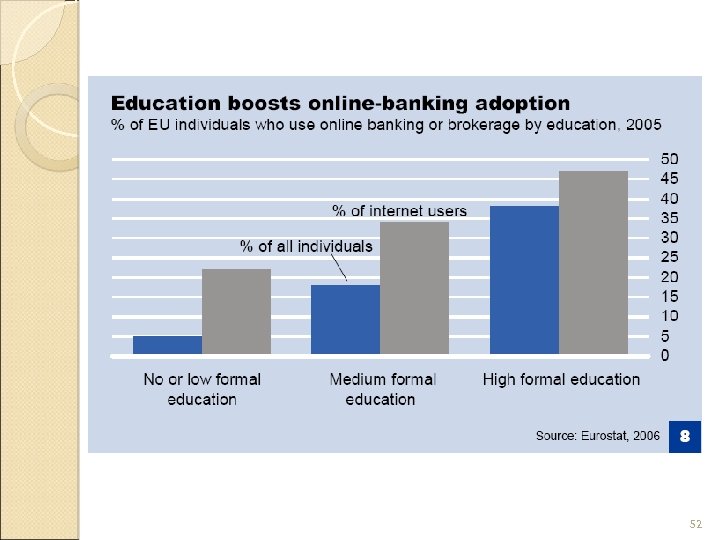
52
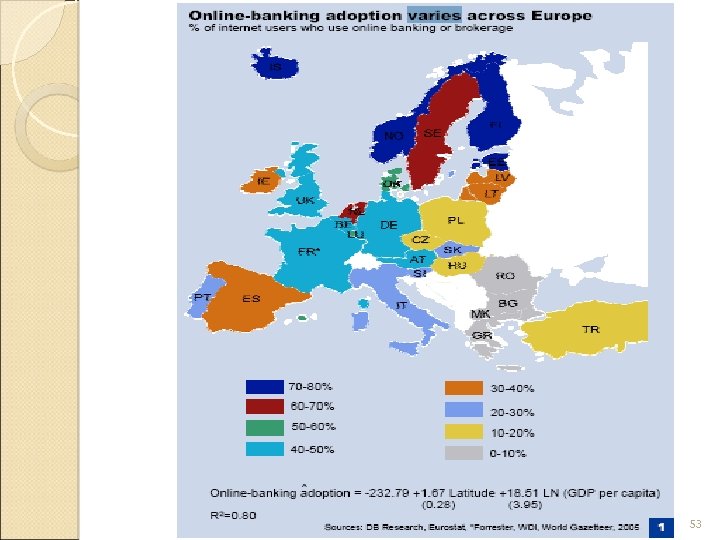
53

why do people choose not to use online banking? Most people who do not use online banking are concern about security Though using online banking is cheaper, most people are concern about the possibility to ask questions 54
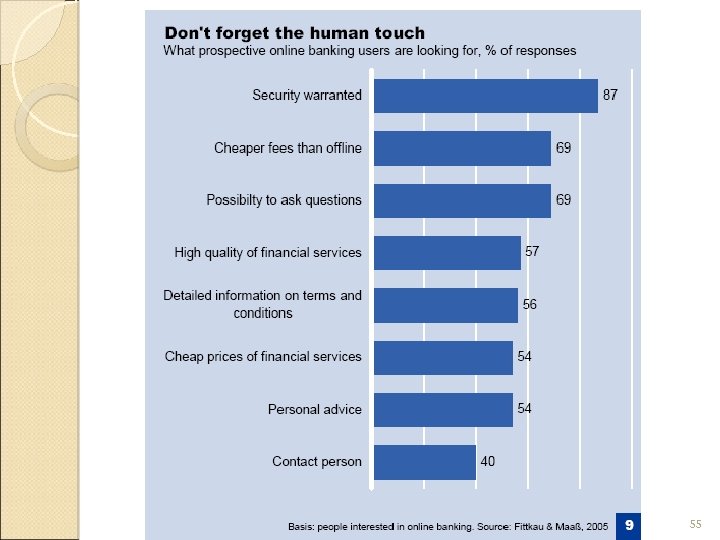
55

How do banks address security issues? Barclays bank in UK implement the use of the chip-and-pin device ◦ What is the chip-and-pin device? ◦ How is it used? ◦ When is it used? ◦ http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=X 7 pj. UIx. Ko Ec 56
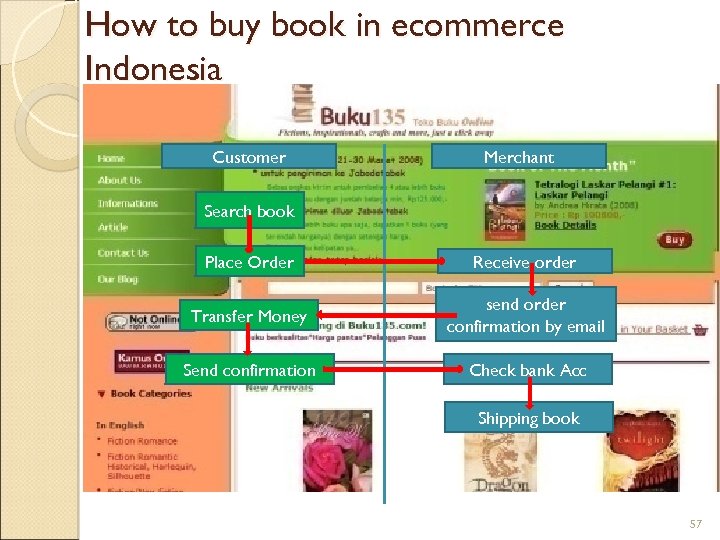
How to buy book in ecommerce Indonesia Customer Merchant Search book Place Order Receive order Transfer Money send order confirmation by email Send confirmation Check bank Acc Shipping book 57
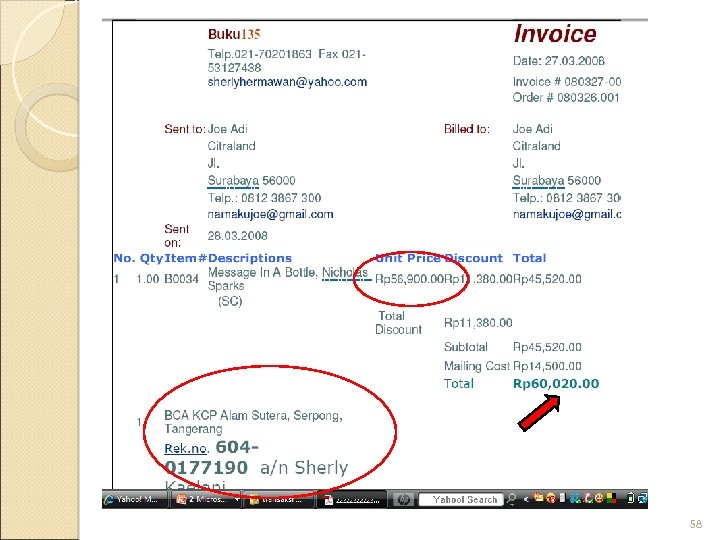
58

Conclusion There is opportunity for growth for ecommerce if the following issues are addressed : ◦ Improve security for internet user to build trust ◦ Educate population to accept the internet usage to become part of the culture ◦ Better infrastructure to speed up response time ◦ Make internet access affordable 59

References Loudon, Kenneth C and Traver, Carol G “E-commerce”, Pearson, New Jersey, 2007 Barbesino, Paolo, Camerani, Roberto, and Gaudino, Alessandra, “Digital finance in Europe: Competitive dynamics and online behaviour” Journal of Financial Services Marketing, Vol. 9, 4, 2001, pp 329 -343 E-commerce Guide, http: //www. 4 thmedia. net/market_research/consumer_market. php, viewed March 7, 2008 Indonesian Statistic Bureau, http: //www. bps. go. id, viewed March 30, 2008. http: //countrystudies. us/indonesia/28. htm, viewed on March 12, 2008. http: //www. internetworldstats. com/asia/id. htm, viewed on March 12, 2008. Meyer, Thomas, “Online banking : What we learn from the differences in Europe” www. dbresearch. com, viewed March 15, 2008. 60

http: //www. apjii. or. id/dokumentasi/statistik. php? lang=eng, viewed on March 20, 2008. http: //www. isoc. org/inet 2000/cdproceedings/7 c/7 c_3. htm#s 3, viewed on March 20, 2008. Kanchana, Kariyawasam, “Information & Communications Technology Law”, Abingdon, Mar 2008. Vol. 17, Iss. 1; p. 51 Zahid Hussain, James Wallace, Rana Tassabehji, Osman Khan. , “International Journal of Electronic Business. ”, Geneva, 2007. Vol. 5, Iss. 3; pg. 315 Alemayehu Molla, Richard Heeks, “Information Society”, New York, Mar 2007. Vol. 23, Iss. 2; p. 95 Richard Duncombe, Alemayehu Molla, “International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation”, London, Aug 2006. Vol. 7, Iss. 3; p. 185 Alemayehu Molla, Paul S Licker, “Information & Management”, Amsterdam, Sep 2005. Vol. 42, Iss. 6; p. 877 Andreas B Eisingerich, Tobias Kretschmer, “Harvard Business Review”, Boston, Mar 2008. Vol. 86, Iss. 3; p. 20 Jing Tan, Katherine Tyler, Andrea Manica, “Information & Management. Amsterdam”, Apr 2007. Vol. 44, Iss. 3; p. 332 61

Thank you 62
e66351236daa365a56555c5437844990.ppt