 E C 4 N IT TA N S U B U S D R U G S , A L C O H O L , T O B A C O E S U B
E C 4 N IT TA N S U B U S D R U G S , A L C O H O L , T O B A C O E S U B
 EQS UNIT 4 PAGE 41 IN YOUR NOTEBOOK 1. What are some of the reasons teens use drugs? What are the solutions to these reasons? 2. How does substance abuse affect a person’s health triangle? 3. Explain how a person’s family is affected when there is an addict in the family. 4. Explain how alcohol impairs driving.
EQS UNIT 4 PAGE 41 IN YOUR NOTEBOOK 1. What are some of the reasons teens use drugs? What are the solutions to these reasons? 2. How does substance abuse affect a person’s health triangle? 3. Explain how a person’s family is affected when there is an addict in the family. 4. Explain how alcohol impairs driving.
 VOCABULARY Carcinogen- Cancer causing Use at least 6 of the words to write a short story about a teen and drug use. Your story should be a minimum of 6 sentences. Euphoria-a state of intense happiness and self-confidence Psychoactive-a substance having a profound or significant effect on mental processes Nicotine- highly toxic and addictive substance found in tobacco products Stimulant- something that temporarily quickens some vital process or the functional activity of the nervous system Depressant- something that temporarily slows some vital process or the functional activity of the nervous system Sedative- tranquilizing, sleep inducing Paranoia- baseless or excessive suspicion of the motives of others, Inhibitions- restrain from a behavior that is wrong or goes against your morals and values Distorted- not truly or completely representing the facts or reality; misrepresented; false
VOCABULARY Carcinogen- Cancer causing Use at least 6 of the words to write a short story about a teen and drug use. Your story should be a minimum of 6 sentences. Euphoria-a state of intense happiness and self-confidence Psychoactive-a substance having a profound or significant effect on mental processes Nicotine- highly toxic and addictive substance found in tobacco products Stimulant- something that temporarily quickens some vital process or the functional activity of the nervous system Depressant- something that temporarily slows some vital process or the functional activity of the nervous system Sedative- tranquilizing, sleep inducing Paranoia- baseless or excessive suspicion of the motives of others, Inhibitions- restrain from a behavior that is wrong or goes against your morals and values Distorted- not truly or completely representing the facts or reality; misrepresented; false
 O D TH AT M FO N OR OR A ? H E D/ G T R N U R R TU A E D H UC DY A T R O O T B IS T CE E S HE A H AN TH F T W ST S B E N O SU NG IO A HA CT C UN F IN D .
O D TH AT M FO N OR OR A ? H E D/ G T R N U R R TU A E D H UC DY A T R O O T B IS T CE E S HE A H AN TH F T W ST S B E N O SU NG IO A HA CT C UN F IN D .
 DRUG USE AND HEALTH All Medicines are drugs, but not all drugs are medicines. Medicine misuse involves using a medicine in ways other than the intended use. Drug Abuse is intentionally taking a medication or drug for non-medical reasons. Drug overdose is a strong and sometime fatal reaction to taking a large amount of a drug. Substance Abuse is any unnecessary or intentional use of chemical substances for non-medical purposes.
DRUG USE AND HEALTH All Medicines are drugs, but not all drugs are medicines. Medicine misuse involves using a medicine in ways other than the intended use. Drug Abuse is intentionally taking a medication or drug for non-medical reasons. Drug overdose is a strong and sometime fatal reaction to taking a large amount of a drug. Substance Abuse is any unnecessary or intentional use of chemical substances for non-medical purposes.
 REASON TEENS EXPERIMENT WITH DRUGS Boredom Media Environment Stress What else?
REASON TEENS EXPERIMENT WITH DRUGS Boredom Media Environment Stress What else?
 DRUG ABUSE AND YOUR HEALTH TRIANGLE How does drug abuse affect each? Physical, Mental/ Emotional, Social
DRUG ABUSE AND YOUR HEALTH TRIANGLE How does drug abuse affect each? Physical, Mental/ Emotional, Social
 DRUGS AND THE TEEN BRAIN IN 22 MINUTESVIDEO a. Why are drugs more dangerous for teens than adults? b. What can you do to protect your developing brain during adolescence? c. When someone has a drug addiction, do you think they control the drug or the drug controls them? At what point, if any, do you think the drug takes control of their brain? d. As research reveals new information about drugs do you think any laws should change? Drinking age? Cigarette laws? Marijuana laws?
DRUGS AND THE TEEN BRAIN IN 22 MINUTESVIDEO a. Why are drugs more dangerous for teens than adults? b. What can you do to protect your developing brain during adolescence? c. When someone has a drug addiction, do you think they control the drug or the drug controls them? At what point, if any, do you think the drug takes control of their brain? d. As research reveals new information about drugs do you think any laws should change? Drinking age? Cigarette laws? Marijuana laws?
 REASONS TEENS USE DRUGS For your assigned reason come up with solutions to the influence: WHAT CAN THE TEEN DO? (Blue) WHAT CAN THE SCHOOL DO? (Green) WHAT CAN THE COMMUNITY DO? (Red) WHAT CAN THE GOVERNMENT DO? (Purple)
REASONS TEENS USE DRUGS For your assigned reason come up with solutions to the influence: WHAT CAN THE TEEN DO? (Blue) WHAT CAN THE SCHOOL DO? (Green) WHAT CAN THE COMMUNITY DO? (Red) WHAT CAN THE GOVERNMENT DO? (Purple)
 N O L SS C A T E D R U G 2 E G O R IE S
N O L SS C A T E D R U G 2 E G O R IE S
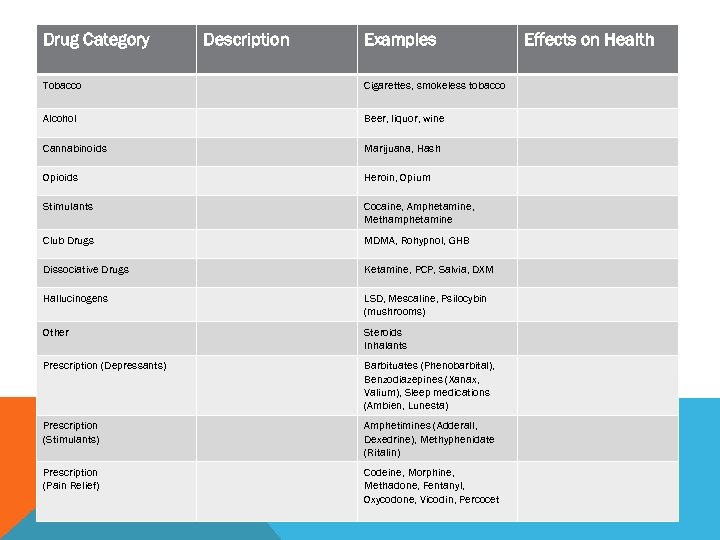 Drug Category Description Examples Tobacco Cigarettes, smokeless tobacco Alcohol Beer, liquor, wine Cannabinoids Marijuana, Hash Opioids Heroin, Opium Stimulants Cocaine, Amphetamine, Methamphetamine Club Drugs MDMA, Rohypnol, GHB Dissociative Drugs Ketamine, PCP, Salvia, DXM Hallucinogens LSD, Mescaline, Psilocybin (mushrooms) Other Steroids Inhalants Prescription (Depressants) Barbituates (Phenobarbital), Benzodiazepines (Xanax, Valium), Sleep medications (Ambien, Lunesta) Prescription (Stimulants) Amphetimines (Adderall, Dexedrine), Methyphenidate (Ritalin) Prescription (Pain Relief) Codeine, Morphine, Methadone, Fentanyl, Oxycodone, Vicodin, Percocet Effects on Health
Drug Category Description Examples Tobacco Cigarettes, smokeless tobacco Alcohol Beer, liquor, wine Cannabinoids Marijuana, Hash Opioids Heroin, Opium Stimulants Cocaine, Amphetamine, Methamphetamine Club Drugs MDMA, Rohypnol, GHB Dissociative Drugs Ketamine, PCP, Salvia, DXM Hallucinogens LSD, Mescaline, Psilocybin (mushrooms) Other Steroids Inhalants Prescription (Depressants) Barbituates (Phenobarbital), Benzodiazepines (Xanax, Valium), Sleep medications (Ambien, Lunesta) Prescription (Stimulants) Amphetimines (Adderall, Dexedrine), Methyphenidate (Ritalin) Prescription (Pain Relief) Codeine, Morphine, Methadone, Fentanyl, Oxycodone, Vicodin, Percocet Effects on Health
 TOBACCO PRODUCTS Tobacco plant, an addictive and toxic drug (nicotine) Examples: Cigarettes, cigars, pipes, smokeless tobacco.
TOBACCO PRODUCTS Tobacco plant, an addictive and toxic drug (nicotine) Examples: Cigarettes, cigars, pipes, smokeless tobacco.
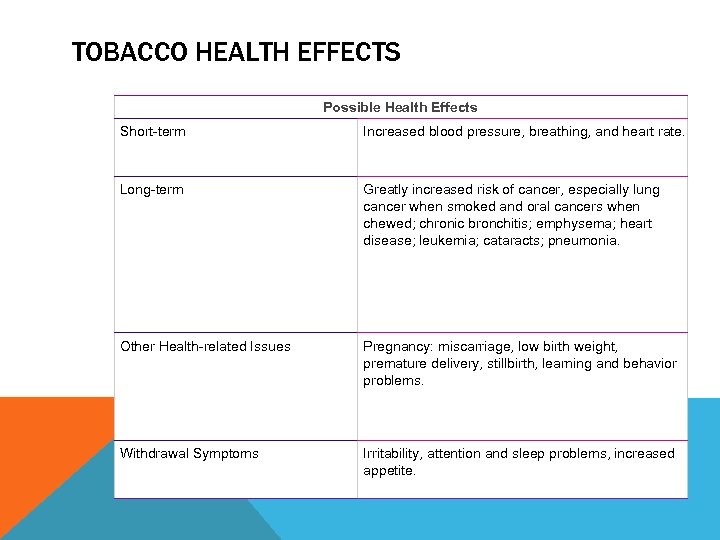 TOBACCO HEALTH EFFECTS Possible Health Effects Short-term Increased blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate. Long-term Greatly increased risk of cancer, especially lung cancer when smoked and oral cancers when chewed; chronic bronchitis; emphysema; heart disease; leukemia; cataracts; pneumonia. Other Health-related Issues Pregnancy: miscarriage, low birth weight, premature delivery, stillbirth, learning and behavior problems. Withdrawal Symptoms Irritability, attention and sleep problems, increased appetite.
TOBACCO HEALTH EFFECTS Possible Health Effects Short-term Increased blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate. Long-term Greatly increased risk of cancer, especially lung cancer when smoked and oral cancers when chewed; chronic bronchitis; emphysema; heart disease; leukemia; cataracts; pneumonia. Other Health-related Issues Pregnancy: miscarriage, low birth weight, premature delivery, stillbirth, learning and behavior problems. Withdrawal Symptoms Irritability, attention and sleep problems, increased appetite.
 ALCOHOL Ethanol, a powerfully addictive drug. A depressant. Examples: Beer, wine, spirits (vodka), liquors.
ALCOHOL Ethanol, a powerfully addictive drug. A depressant. Examples: Beer, wine, spirits (vodka), liquors.
 ALCOHOL HEALTH EFFECTS Brain: Alcohol interferes with the brain’s communication pathways, and can affect the way the brain looks and works. These disruptions can change mood and behavior, and make it harder to think clearly and move with coordination. Heart: Drinking a lot over a long time or too much on a single occasion can damage the heart, causing problems including: Cardiomyopathy – Stretching and drooping of heart muscle Arrhythmias – Irregular heart beat Stroke High blood pressure Research also shows that drinking moderate amounts of alcohol may protect healthy adults from developing coronary heart disease. Liver: Heavy drinking takes a toll on the liver, and can lead to a variety of problems and liver inflammations including: Steatosis, or fatty liver Alcoholic hepatitis Fibrosis Cirrhosis Pancreas: Alcohol causes the pancreas to produce toxic substances that can eventually lead to pancreatitis, a dangerous inflammation and swelling of the blood vessels in the pancreas that prevents proper digestion. Cancer: Drinking too much alcohol can increase your risk of developing certain cancers, including cancers of the: Mouth Esophagus Throat Liver Breast Immune System: Drinking too much can weaken your immune system, making your body a much easier target for disease. Chronic drinkers are more liable to contract diseases like pneumonia and tuberculosis than people who do not drink too much. Drinking a lot on a single occasion slows your body’s ability to ward off infections – even up to 24 hours after getting drunk.
ALCOHOL HEALTH EFFECTS Brain: Alcohol interferes with the brain’s communication pathways, and can affect the way the brain looks and works. These disruptions can change mood and behavior, and make it harder to think clearly and move with coordination. Heart: Drinking a lot over a long time or too much on a single occasion can damage the heart, causing problems including: Cardiomyopathy – Stretching and drooping of heart muscle Arrhythmias – Irregular heart beat Stroke High blood pressure Research also shows that drinking moderate amounts of alcohol may protect healthy adults from developing coronary heart disease. Liver: Heavy drinking takes a toll on the liver, and can lead to a variety of problems and liver inflammations including: Steatosis, or fatty liver Alcoholic hepatitis Fibrosis Cirrhosis Pancreas: Alcohol causes the pancreas to produce toxic substances that can eventually lead to pancreatitis, a dangerous inflammation and swelling of the blood vessels in the pancreas that prevents proper digestion. Cancer: Drinking too much alcohol can increase your risk of developing certain cancers, including cancers of the: Mouth Esophagus Throat Liver Breast Immune System: Drinking too much can weaken your immune system, making your body a much easier target for disease. Chronic drinkers are more liable to contract diseases like pneumonia and tuberculosis than people who do not drink too much. Drinking a lot on a single occasion slows your body’s ability to ward off infections – even up to 24 hours after getting drunk.
 CANNABINOIDS (MARIJUANA) A plant whose leaves, buds, and flowers are smoked or ingested for their intoxicating effects. Examples: Weed, hashish, Wax Known as the “Gateway Drug”, people that use marijuana are 15 times more likely to move on to other drugs.
CANNABINOIDS (MARIJUANA) A plant whose leaves, buds, and flowers are smoked or ingested for their intoxicating effects. Examples: Weed, hashish, Wax Known as the “Gateway Drug”, people that use marijuana are 15 times more likely to move on to other drugs.
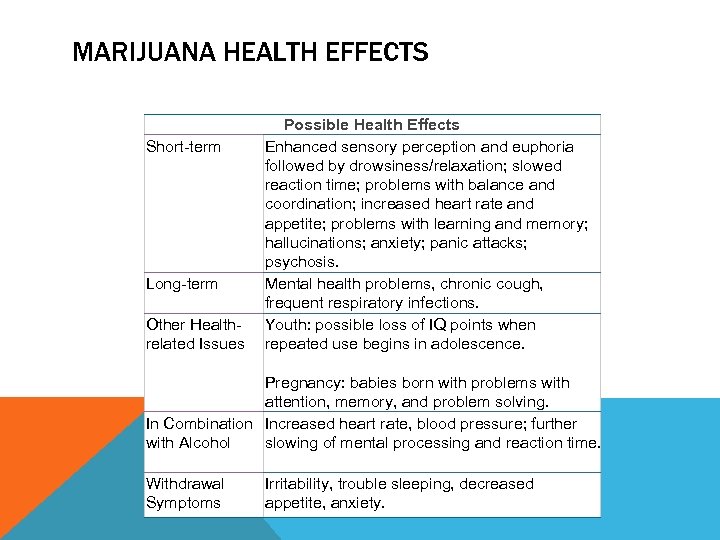 MARIJUANA HEALTH EFFECTS Short-term Long-term Other Healthrelated Issues Possible Health Effects Enhanced sensory perception and euphoria followed by drowsiness/relaxation; slowed reaction time; problems with balance and coordination; increased heart rate and appetite; problems with learning and memory; hallucinations; anxiety; panic attacks; psychosis. Mental health problems, chronic cough, frequent respiratory infections. Youth: possible loss of IQ points when repeated use begins in adolescence. Pregnancy: babies born with problems with attention, memory, and problem solving. In Combination Increased heart rate, blood pressure; further with Alcohol slowing of mental processing and reaction time. Withdrawal Symptoms Irritability, trouble sleeping, decreased appetite, anxiety.
MARIJUANA HEALTH EFFECTS Short-term Long-term Other Healthrelated Issues Possible Health Effects Enhanced sensory perception and euphoria followed by drowsiness/relaxation; slowed reaction time; problems with balance and coordination; increased heart rate and appetite; problems with learning and memory; hallucinations; anxiety; panic attacks; psychosis. Mental health problems, chronic cough, frequent respiratory infections. Youth: possible loss of IQ points when repeated use begins in adolescence. Pregnancy: babies born with problems with attention, memory, and problem solving. In Combination Increased heart rate, blood pressure; further with Alcohol slowing of mental processing and reaction time. Withdrawal Symptoms Irritability, trouble sleeping, decreased appetite, anxiety.
 OPIATES Narcotics, feelings of euphoria, derived from opium plants, medically used for pain relief. Examples: Morphine, codeine, oxycodane, heroin.
OPIATES Narcotics, feelings of euphoria, derived from opium plants, medically used for pain relief. Examples: Morphine, codeine, oxycodane, heroin.
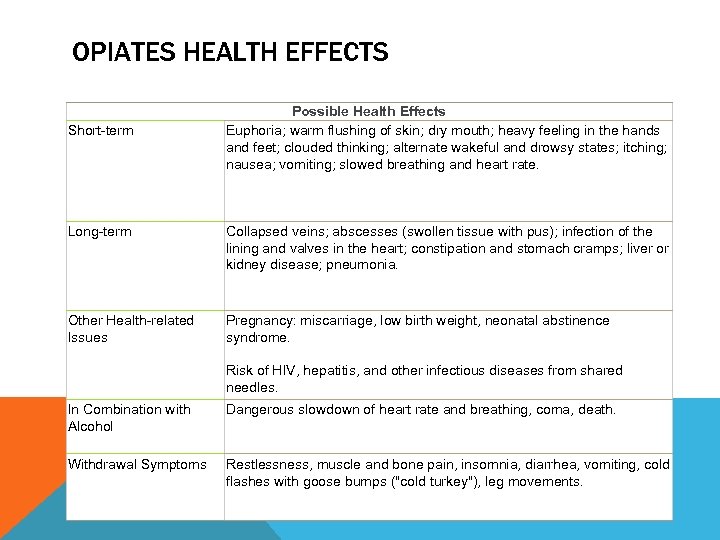 OPIATES HEALTH EFFECTS Short-term Possible Health Effects Euphoria; warm flushing of skin; dry mouth; heavy feeling in the hands and feet; clouded thinking; alternate wakeful and drowsy states; itching; nausea; vomiting; slowed breathing and heart rate. Long-term Collapsed veins; abscesses (swollen tissue with pus); infection of the lining and valves in the heart; constipation and stomach cramps; liver or kidney disease; pneumonia. Other Health-related Issues Pregnancy: miscarriage, low birth weight, neonatal abstinence syndrome. Risk of HIV, hepatitis, and other infectious diseases from shared needles. In Combination with Alcohol Dangerous slowdown of heart rate and breathing, coma, death. Withdrawal Symptoms Restlessness, muscle and bone pain, insomnia, diarrhea, vomiting, cold flashes with goose bumps ("cold turkey"), leg movements.
OPIATES HEALTH EFFECTS Short-term Possible Health Effects Euphoria; warm flushing of skin; dry mouth; heavy feeling in the hands and feet; clouded thinking; alternate wakeful and drowsy states; itching; nausea; vomiting; slowed breathing and heart rate. Long-term Collapsed veins; abscesses (swollen tissue with pus); infection of the lining and valves in the heart; constipation and stomach cramps; liver or kidney disease; pneumonia. Other Health-related Issues Pregnancy: miscarriage, low birth weight, neonatal abstinence syndrome. Risk of HIV, hepatitis, and other infectious diseases from shared needles. In Combination with Alcohol Dangerous slowdown of heart rate and breathing, coma, death. Withdrawal Symptoms Restlessness, muscle and bone pain, insomnia, diarrhea, vomiting, cold flashes with goose bumps ("cold turkey"), leg movements.
 STIMULANTS Psychoactive drugs that speed up the central nervous system. Examples: methamphetamines, cocaine, crack, amphetamine
STIMULANTS Psychoactive drugs that speed up the central nervous system. Examples: methamphetamines, cocaine, crack, amphetamine
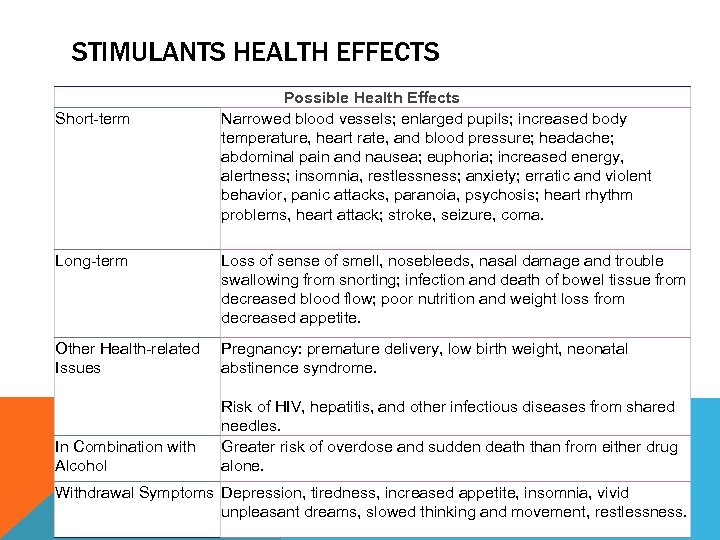 STIMULANTS HEALTH EFFECTS Short-term Possible Health Effects Narrowed blood vessels; enlarged pupils; increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure; headache; abdominal pain and nausea; euphoria; increased energy, alertness; insomnia, restlessness; anxiety; erratic and violent behavior, panic attacks, paranoia, psychosis; heart rhythm problems, heart attack; stroke, seizure, coma. Long-term Loss of sense of smell, nosebleeds, nasal damage and trouble swallowing from snorting; infection and death of bowel tissue from decreased blood flow; poor nutrition and weight loss from decreased appetite. Other Health-related Issues Pregnancy: premature delivery, low birth weight, neonatal abstinence syndrome. In Combination with Alcohol Risk of HIV, hepatitis, and other infectious diseases from shared needles. Greater risk of overdose and sudden death than from either drug alone. Withdrawal Symptoms Depression, tiredness, increased appetite, insomnia, vivid unpleasant dreams, slowed thinking and movement, restlessness.
STIMULANTS HEALTH EFFECTS Short-term Possible Health Effects Narrowed blood vessels; enlarged pupils; increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure; headache; abdominal pain and nausea; euphoria; increased energy, alertness; insomnia, restlessness; anxiety; erratic and violent behavior, panic attacks, paranoia, psychosis; heart rhythm problems, heart attack; stroke, seizure, coma. Long-term Loss of sense of smell, nosebleeds, nasal damage and trouble swallowing from snorting; infection and death of bowel tissue from decreased blood flow; poor nutrition and weight loss from decreased appetite. Other Health-related Issues Pregnancy: premature delivery, low birth weight, neonatal abstinence syndrome. In Combination with Alcohol Risk of HIV, hepatitis, and other infectious diseases from shared needles. Greater risk of overdose and sudden death than from either drug alone. Withdrawal Symptoms Depression, tiredness, increased appetite, insomnia, vivid unpleasant dreams, slowed thinking and movement, restlessness.
 CLUB DRUGS Psychoactive drugs that tend to be abused by teens and young adults at bars, nightclubs, concerts, and parties. Examples: MDMA, Rohypnol, GHB
CLUB DRUGS Psychoactive drugs that tend to be abused by teens and young adults at bars, nightclubs, concerts, and parties. Examples: MDMA, Rohypnol, GHB
 DISSOCIATIVE DRUGS A class of hallucinogen, which distort perceptions of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment – dissociation – from the environment and self. This is done through reducing or blocking signals to the conscious mind from other parts of the brain. Examples: Ketamine, PCP, Salvia, DXM
DISSOCIATIVE DRUGS A class of hallucinogen, which distort perceptions of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment – dissociation – from the environment and self. This is done through reducing or blocking signals to the conscious mind from other parts of the brain. Examples: Ketamine, PCP, Salvia, DXM
 HALLUCINOGENS Alter moods, thoughts, perception. Euphoria or paranoia. Examples: Psilocybin (mushrooms), LSD, Mescaline
HALLUCINOGENS Alter moods, thoughts, perception. Euphoria or paranoia. Examples: Psilocybin (mushrooms), LSD, Mescaline
 INHALANTS Substances whose fumes are sniffed or inhaled. Depresses the central nervous system. Causes brain damage. Examples: Solvents, aerosols, glue, paint, gasoline.
INHALANTS Substances whose fumes are sniffed or inhaled. Depresses the central nervous system. Causes brain damage. Examples: Solvents, aerosols, glue, paint, gasoline.
 ANABOLIC STEROIDS Synthetic substances similar to male hormones. Examples: Anadrol, Oxandrin, Durabolin, HCG
ANABOLIC STEROIDS Synthetic substances similar to male hormones. Examples: Anadrol, Oxandrin, Durabolin, HCG
 PRESCRIPTION DRUGS Medicines dispensed only with written approval of a licensed physician
PRESCRIPTION DRUGS Medicines dispensed only with written approval of a licensed physician
 PRESCRIPTION DEPRESSANTS Prescribed Sedatives that slow down the central nervous system. Examples: Barbituates (Phenobartial), Benzodiazephines (Xanax, Ativan, Vallium), Sleep medications (Ambien, Lunesta)
PRESCRIPTION DEPRESSANTS Prescribed Sedatives that slow down the central nervous system. Examples: Barbituates (Phenobartial), Benzodiazephines (Xanax, Ativan, Vallium), Sleep medications (Ambien, Lunesta)
 PRESCRIPTION STIMULANTS Prescribed medicines that stimulate the central nervous system
PRESCRIPTION STIMULANTS Prescribed medicines that stimulate the central nervous system
 PRESCRIPTION PAIN RELIF Prescribed medicines for pain relief
PRESCRIPTION PAIN RELIF Prescribed medicines for pain relief
 GRAPHIC ORGANIZER 1. Hallucinogens (Mushrooms, LSD) 2. Cannabis 3. Stimulants (Non Prescription) 4. Stimulants (Prescription) Description Categorize/ Organize Effects on health 5. Steroids 6. Club Drugs (Ecstasy, GHB, Rohypnol) 7. Dissociative Drugs (Ketamine, DXM, PCP) 8. Drugabuse. gov Drugfreeworkld. org Prescription Pain Relief (oxycontin, vicodin) Kidhealth. org 9. Prescription (Depressants) 10. Opioids (Heroin, opium) 11. Inhalants 12. Alcohol 13. Tobacco
GRAPHIC ORGANIZER 1. Hallucinogens (Mushrooms, LSD) 2. Cannabis 3. Stimulants (Non Prescription) 4. Stimulants (Prescription) Description Categorize/ Organize Effects on health 5. Steroids 6. Club Drugs (Ecstasy, GHB, Rohypnol) 7. Dissociative Drugs (Ketamine, DXM, PCP) 8. Drugabuse. gov Drugfreeworkld. org Prescription Pain Relief (oxycontin, vicodin) Kidhealth. org 9. Prescription (Depressants) 10. Opioids (Heroin, opium) 11. Inhalants 12. Alcohol 13. Tobacco

 DISCOVERY HEALTH- LIFE ON DRUGS VIDEO HOSTED BY ROBIN WILLIAMS https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=h. WSAs. Dn 60 iw Describe how each user functions Driving Marijuana Meth Cocaine Heroin Building a book case House Fire X X Strength Test
DISCOVERY HEALTH- LIFE ON DRUGS VIDEO HOSTED BY ROBIN WILLIAMS https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=h. WSAs. Dn 60 iw Describe how each user functions Driving Marijuana Meth Cocaine Heroin Building a book case House Fire X X Strength Test
 CHP. 15. 1 REVIEW QUESTIONS Read pages 299 -301 Answer Review Questions #1 -5
CHP. 15. 1 REVIEW QUESTIONS Read pages 299 -301 Answer Review Questions #1 -5
 3 PEND N DE O L S CAL ES I C H E M E N C Y A N D F A M IL Y R O L E S
3 PEND N DE O L S CAL ES I C H E M E N C Y A N D F A M IL Y R O L E S
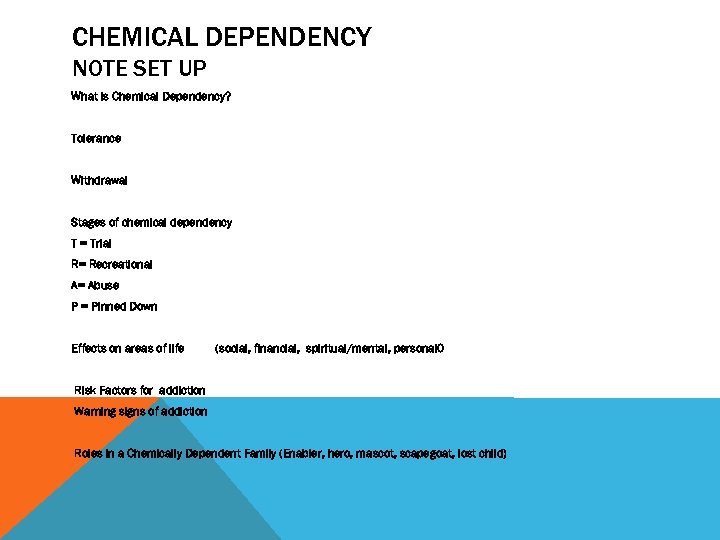 CHEMICAL DEPENDENCY NOTE SET UP What is Chemical Dependency? Tolerance Withdrawal Stages of chemical dependency T = Trial R= Recreational A= Abuse P = Pinned Down Effects on areas of life (social, financial, spiritual/mental, personal 0 Risk Factors for addiction Warning signs of addiction Roles in a Chemically Dependent Family (Enabler, hero, mascot, scapegoat, lost child)
CHEMICAL DEPENDENCY NOTE SET UP What is Chemical Dependency? Tolerance Withdrawal Stages of chemical dependency T = Trial R= Recreational A= Abuse P = Pinned Down Effects on areas of life (social, financial, spiritual/mental, personal 0 Risk Factors for addiction Warning signs of addiction Roles in a Chemically Dependent Family (Enabler, hero, mascot, scapegoat, lost child)
 CHEMICAL DEPENDENCY/ DRUG ADDICT The person is controlled physically (the body expects the drug) or psychologically (there is a mental craving) by the drug An addict will do anything to get the drug, the addict is no long taking the drug to have fun, but feels like they don’t have the choice An addict’s body has built a tolerance to the drug and will experience withdrawal symptoms without the drug. Tolerance- needing more and more of the drug to get the same high. Body DOES NOT get used to the drug, just loses warning signs. Withdrawal- symptoms people feel when they don’t get the drug they are addicted to https: //ed. ted. com/featured/Hm 9 X 3 Yrt
CHEMICAL DEPENDENCY/ DRUG ADDICT The person is controlled physically (the body expects the drug) or psychologically (there is a mental craving) by the drug An addict will do anything to get the drug, the addict is no long taking the drug to have fun, but feels like they don’t have the choice An addict’s body has built a tolerance to the drug and will experience withdrawal symptoms without the drug. Tolerance- needing more and more of the drug to get the same high. Body DOES NOT get used to the drug, just loses warning signs. Withdrawal- symptoms people feel when they don’t get the drug they are addicted to https: //ed. ted. com/featured/Hm 9 X 3 Yrt
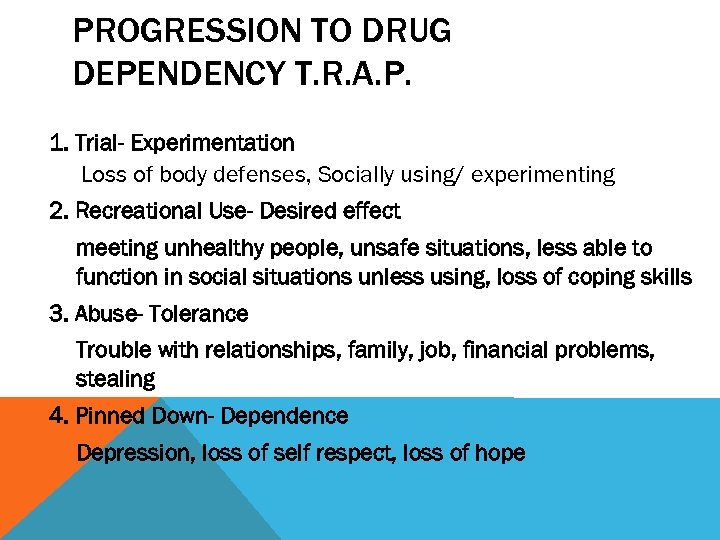 PROGRESSION TO DRUG DEPENDENCY T. R. A. P. 1. Trial- Experimentation Loss of body defenses, Socially using/ experimenting 2. Recreational Use- Desired effect meeting unhealthy people, unsafe situations, less able to function in social situations unless using, loss of coping skills 3. Abuse- Tolerance Trouble with relationships, family, job, financial problems, stealing 4. Pinned Down- Dependence Depression, loss of self respect, loss of hope
PROGRESSION TO DRUG DEPENDENCY T. R. A. P. 1. Trial- Experimentation Loss of body defenses, Socially using/ experimenting 2. Recreational Use- Desired effect meeting unhealthy people, unsafe situations, less able to function in social situations unless using, loss of coping skills 3. Abuse- Tolerance Trouble with relationships, family, job, financial problems, stealing 4. Pinned Down- Dependence Depression, loss of self respect, loss of hope
 ADDICTION: RISK FACTORS Unable to express/cope with emotions appropriately Having a mental health disorder Using drugs at a young age (teen years) Lack of Self-respect Having friends who use drugs Access to drugs rejected by peers having a family member who is an addict uninvolved with extra curricular activities Family problems Lack of respect for authority
ADDICTION: RISK FACTORS Unable to express/cope with emotions appropriately Having a mental health disorder Using drugs at a young age (teen years) Lack of Self-respect Having friends who use drugs Access to drugs rejected by peers having a family member who is an addict uninvolved with extra curricular activities Family problems Lack of respect for authority
 WARNING SIGNS OF ADDICTION Regular hangovers, difficulty concentrating, change in sleeping habits Slurred speech Red eyes, use of eye drops Change in eating habits sloppy appearance stealing money, asking for money lacking energy and motivation ditching, lack of effort in school Mood changes gang involvement
WARNING SIGNS OF ADDICTION Regular hangovers, difficulty concentrating, change in sleeping habits Slurred speech Red eyes, use of eye drops Change in eating habits sloppy appearance stealing money, asking for money lacking energy and motivation ditching, lack of effort in school Mood changes gang involvement
 HOW ADDICTION AFFECTS THE FAMILY https: //www. bhpalmbeach. com/recovery-articles/impact -substance-abuse-and-addiction-families Family Roles- Enabler. Mascot, Hero, Lost child, Scapegoat Enable- Allowing the user to use (excuses, ignoring, giving the user money, covering up for the user)
HOW ADDICTION AFFECTS THE FAMILY https: //www. bhpalmbeach. com/recovery-articles/impact -substance-abuse-and-addiction-families Family Roles- Enabler. Mascot, Hero, Lost child, Scapegoat Enable- Allowing the user to use (excuses, ignoring, giving the user money, covering up for the user)
 “TWEAK” EXCERPT DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. What are some of the reasons Nic started using drugs? Support your answer with evidence from the text 2. Did he have any risk factors for drug dependency? 3. What questions do have after reading the text? (Questions to evoke thinking, conversation) 4. How was Nic’s life affected by drug abuse? 5. What could have prevented his drug abuse? 6. Predict what the future holds for Nic.
“TWEAK” EXCERPT DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. What are some of the reasons Nic started using drugs? Support your answer with evidence from the text 2. Did he have any risk factors for drug dependency? 3. What questions do have after reading the text? (Questions to evoke thinking, conversation) 4. How was Nic’s life affected by drug abuse? 5. What could have prevented his drug abuse? 6. Predict what the future holds for Nic.
 ALCOHOL CORNELL NOTE SET UP Consequences- short/ long term Mixing alcohol and drugs -Marijuana -Cocaine -Sedatives Alcohol Poisoning- causes/ signs/ effects BAC and impairment Drinking and Driving DUI consequences Drinking and Pregnancy
ALCOHOL CORNELL NOTE SET UP Consequences- short/ long term Mixing alcohol and drugs -Marijuana -Cocaine -Sedatives Alcohol Poisoning- causes/ signs/ effects BAC and impairment Drinking and Driving DUI consequences Drinking and Pregnancy
 L N SO L ES H O A L C O 4
L N SO L ES H O A L C O 4
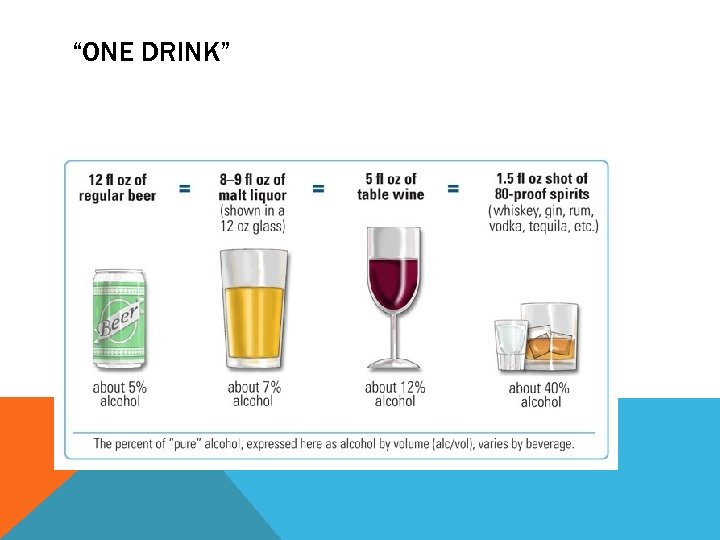 “ONE DRINK”
“ONE DRINK”
 SHORT TERM CONSEQUENCES Slurred speech Drowsiness Vomiting Diarrhea Upset stomach Headaches Breathing difficulties Distorted vision and hearing Impaired judgment/ lowered inhibitions Decreased perception and coordination Unconsciousness Anemia (loss of red blood cells) Coma Blackouts (memory lapses, where the drinker cannot remember events that occurred while under the influence)
SHORT TERM CONSEQUENCES Slurred speech Drowsiness Vomiting Diarrhea Upset stomach Headaches Breathing difficulties Distorted vision and hearing Impaired judgment/ lowered inhibitions Decreased perception and coordination Unconsciousness Anemia (loss of red blood cells) Coma Blackouts (memory lapses, where the drinker cannot remember events that occurred while under the influence)
 LONG TERM CONSEQUENCES High blood pressure, stroke, and other heart-related diseases Liver disease (Cirrhosis) Nerve damage Sexual problems Permanent damage to the brain Vitamin B 1 deficiency, which can lead to a disorder characterized by amnesia, apathy and disorientation Ulcers Gastritis (inflammation of stomach walls) Malnutrition Cancer of the mouth and throat Unintentional injuries such as car crash, falls, burns, drowning Intentional injuries such as firearm injuries, sexual assault, domestic violence Increased on-the-job injuries and loss of productivity Increased family problems, broken relationships
LONG TERM CONSEQUENCES High blood pressure, stroke, and other heart-related diseases Liver disease (Cirrhosis) Nerve damage Sexual problems Permanent damage to the brain Vitamin B 1 deficiency, which can lead to a disorder characterized by amnesia, apathy and disorientation Ulcers Gastritis (inflammation of stomach walls) Malnutrition Cancer of the mouth and throat Unintentional injuries such as car crash, falls, burns, drowning Intentional injuries such as firearm injuries, sexual assault, domestic violence Increased on-the-job injuries and loss of productivity Increased family problems, broken relationships
 MIXING ALCOHOL AND DRUGS
MIXING ALCOHOL AND DRUGS
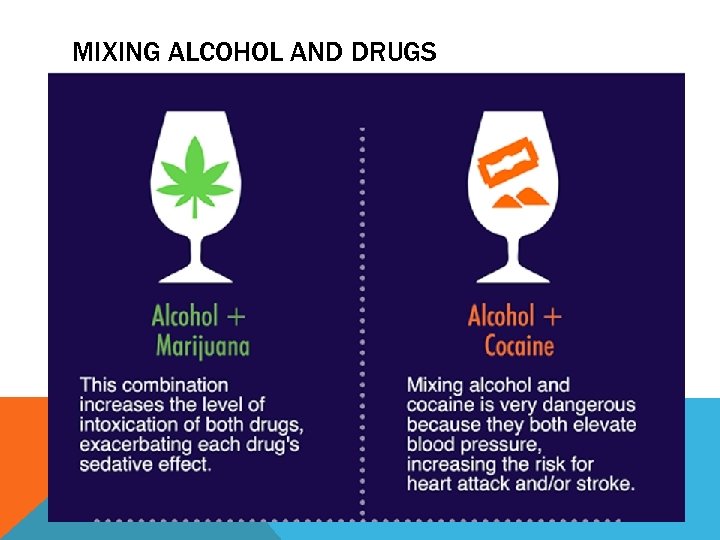 MIXING ALCOHOL AND DRUGS
MIXING ALCOHOL AND DRUGS
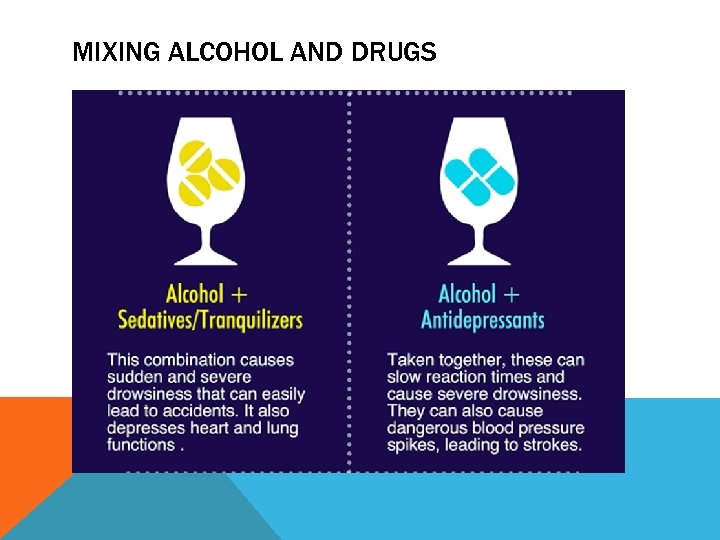 MIXING ALCOHOL AND DRUGS
MIXING ALCOHOL AND DRUGS

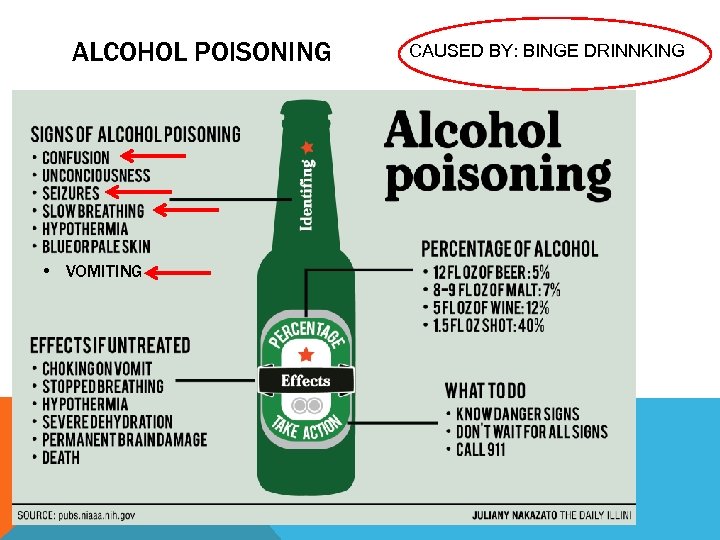 ALCOHOL POISONING • VOMITING CAUSED BY: BINGE DRINNKING
ALCOHOL POISONING • VOMITING CAUSED BY: BINGE DRINNKING

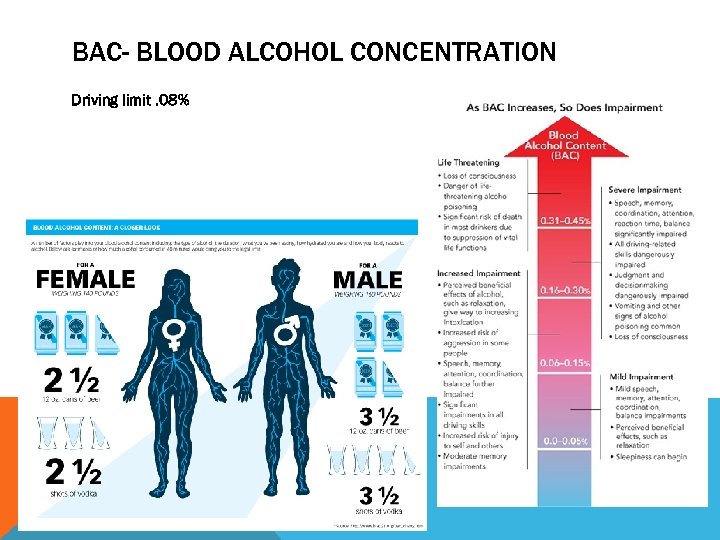 BAC- BLOOD ALCOHOL CONCENTRATION Driving limit. 08%
BAC- BLOOD ALCOHOL CONCENTRATION Driving limit. 08%
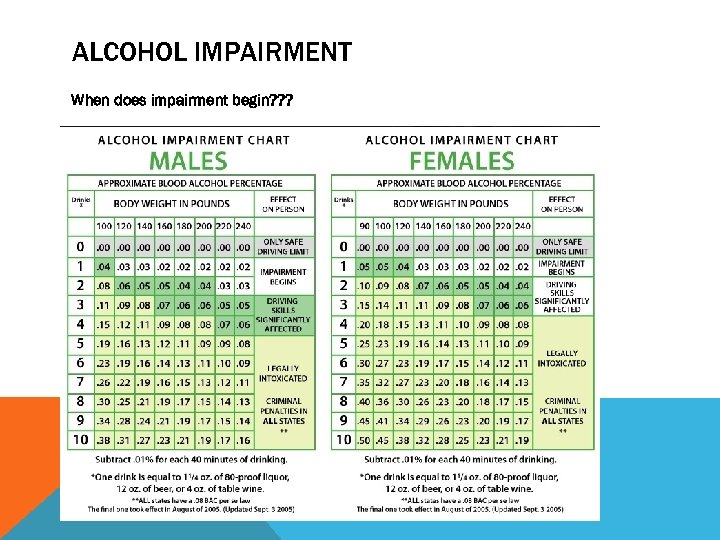 ALCOHOL IMPAIRMENT When does impairment begin? ? ?
ALCOHOL IMPAIRMENT When does impairment begin? ? ?
 DRINKING AND DRIVING Drinking alcohol slows your reflexes and Impairs coordination Injury Legal Consequences Death
DRINKING AND DRIVING Drinking alcohol slows your reflexes and Impairs coordination Injury Legal Consequences Death
 DUI $$$$ §Insurance Rates §DUI courses §Court fees §Property damage
DUI $$$$ §Insurance Rates §DUI courses §Court fees §Property damage
 DRINKING AND PREGNANCY
DRINKING AND PREGNANCY
 N O L SSC C O E T O B A 5
N O L SSC C O E T O B A 5
 TOBACCO PRODUCTS What do each of the pictures represent?
TOBACCO PRODUCTS What do each of the pictures represent?
 TOBACCO PRODUCTS
TOBACCO PRODUCTS
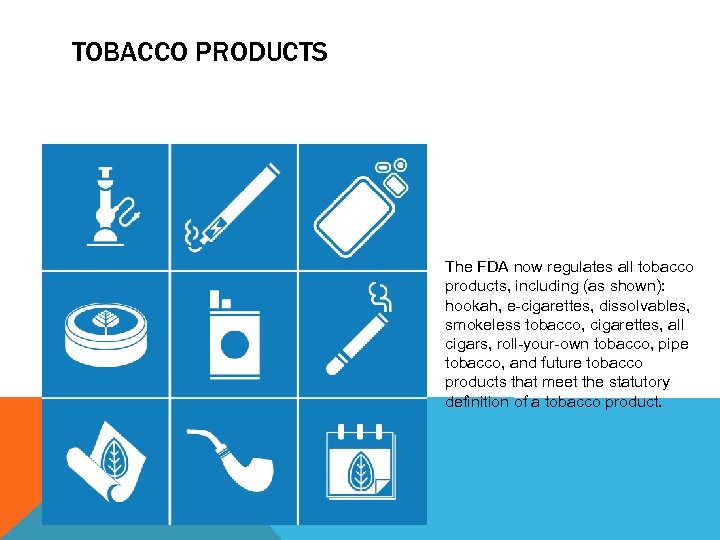 TOBACCO PRODUCTS The FDA now regulates all tobacco products, including (as shown): hookah, e-cigarettes, dissolvables, smokeless tobacco, cigarettes, all cigars, roll-your-own tobacco, pipe tobacco, and future tobacco products that meet the statutory definition of a tobacco product.
TOBACCO PRODUCTS The FDA now regulates all tobacco products, including (as shown): hookah, e-cigarettes, dissolvables, smokeless tobacco, cigarettes, all cigars, roll-your-own tobacco, pipe tobacco, and future tobacco products that meet the statutory definition of a tobacco product.
 TOBACCO PRODUCTS/SMOKE CONTAINS Carcinogens: cancer-causing substances. Tar: a thick, sticky, dark fluid produced when tobacco burns. Carbon Monoxide: another compound found in cigarette smoke, is a colorless, odorless, and poisonous gas. Nicotine: the addictive drug found in tobacco leaves. Nicotine is a Stimulant.
TOBACCO PRODUCTS/SMOKE CONTAINS Carcinogens: cancer-causing substances. Tar: a thick, sticky, dark fluid produced when tobacco burns. Carbon Monoxide: another compound found in cigarette smoke, is a colorless, odorless, and poisonous gas. Nicotine: the addictive drug found in tobacco leaves. Nicotine is a Stimulant.
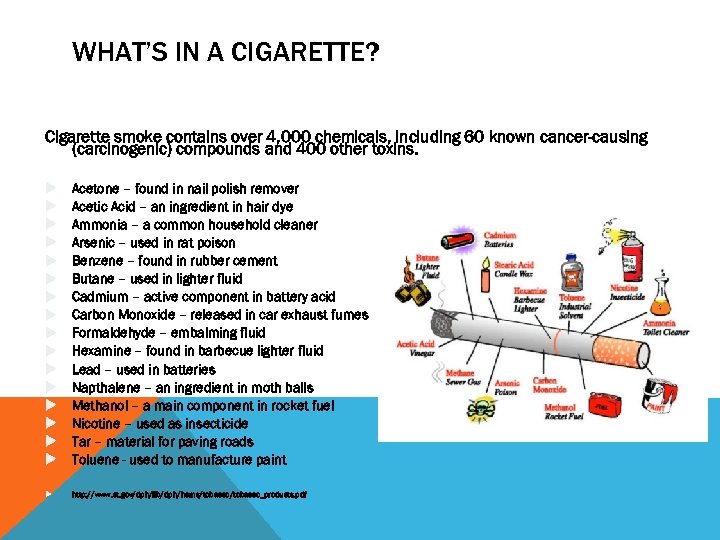 WHAT’S IN A CIGARETTE? Cigarette smoke contains over 4, 000 chemicals, including 60 known cancer-causing (carcinogenic) compounds and 400 other toxins. Acetone – found in nail polish remover Acetic Acid – an ingredient in hair dye Ammonia – a common household cleaner Arsenic – used in rat poison Benzene – found in rubber cement Butane – used in lighter fluid Cadmium – active component in battery acid Carbon Monoxide – released in car exhaust fumes Formaldehyde – embalming fluid Hexamine – found in barbecue lighter fluid Lead – used in batteries Napthalene – an ingredient in moth balls Methanol – a main component in rocket fuel Nicotine – used as insecticide Tar – material for paving roads Toluene - used to manufacture paint http: //www. ct. gov/dph/lib/dph/hems/tobacco_products. pdf
WHAT’S IN A CIGARETTE? Cigarette smoke contains over 4, 000 chemicals, including 60 known cancer-causing (carcinogenic) compounds and 400 other toxins. Acetone – found in nail polish remover Acetic Acid – an ingredient in hair dye Ammonia – a common household cleaner Arsenic – used in rat poison Benzene – found in rubber cement Butane – used in lighter fluid Cadmium – active component in battery acid Carbon Monoxide – released in car exhaust fumes Formaldehyde – embalming fluid Hexamine – found in barbecue lighter fluid Lead – used in batteries Napthalene – an ingredient in moth balls Methanol – a main component in rocket fuel Nicotine – used as insecticide Tar – material for paving roads Toluene - used to manufacture paint http: //www. ct. gov/dph/lib/dph/hems/tobacco_products. pdf
 WHO SMOKES? Each day, more than 3, 200 people under 18 smoke their first cigarette, and approximately 2, 100 youth and young adults become daily smokers. 9 out of 10 smokers start before the age of 18, and 98% start smoking by age 26. 1 in 5 adults and teenagers smoke. In 2011, an estimated 19% of U. S. adults were cigarette smokers. Approximately 18% of high school students smoke cigarettes. In 2011, nearly 18% of high school boys were current cigar users. From 1964 to 2014, the proportion of adult smokers declined from 42. 0% to 18. 0%.
WHO SMOKES? Each day, more than 3, 200 people under 18 smoke their first cigarette, and approximately 2, 100 youth and young adults become daily smokers. 9 out of 10 smokers start before the age of 18, and 98% start smoking by age 26. 1 in 5 adults and teenagers smoke. In 2011, an estimated 19% of U. S. adults were cigarette smokers. Approximately 18% of high school students smoke cigarettes. In 2011, nearly 18% of high school boys were current cigar users. From 1964 to 2014, the proportion of adult smokers declined from 42. 0% to 18. 0%.
 THINK QUESTION Knowing that all of these chemicals are in tobacco products, why do people start and continue to use tobacco products?
THINK QUESTION Knowing that all of these chemicals are in tobacco products, why do people start and continue to use tobacco products?
 SHORT-TERM EFFECTS OF TOBACCO USE Changes in brain chemistry Increased respiration and heart rate. Dulled taste buds and reduced appetite. Bad breath and smelly hair, clothes, and skin. Body craves more nicotine
SHORT-TERM EFFECTS OF TOBACCO USE Changes in brain chemistry Increased respiration and heart rate. Dulled taste buds and reduced appetite. Bad breath and smelly hair, clothes, and skin. Body craves more nicotine
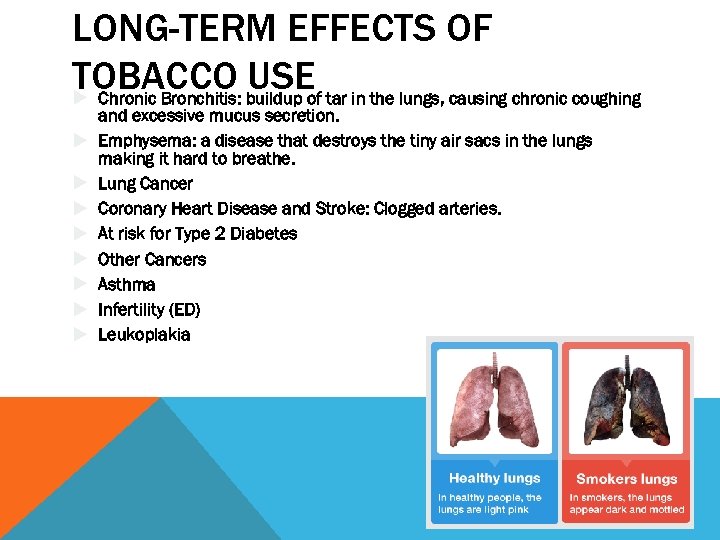 LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF TOBACCO buildup of tar in the lungs, causing chronic coughing USE Chronic Bronchitis: and excessive mucus secretion. Emphysema: a disease that destroys the tiny air sacs in the lungs making it hard to breathe. Lung Cancer Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke: Clogged arteries. At risk for Type 2 Diabetes Other Cancers Asthma Infertility (ED) Leukoplakia
LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF TOBACCO buildup of tar in the lungs, causing chronic coughing USE Chronic Bronchitis: and excessive mucus secretion. Emphysema: a disease that destroys the tiny air sacs in the lungs making it hard to breathe. Lung Cancer Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke: Clogged arteries. At risk for Type 2 Diabetes Other Cancers Asthma Infertility (ED) Leukoplakia
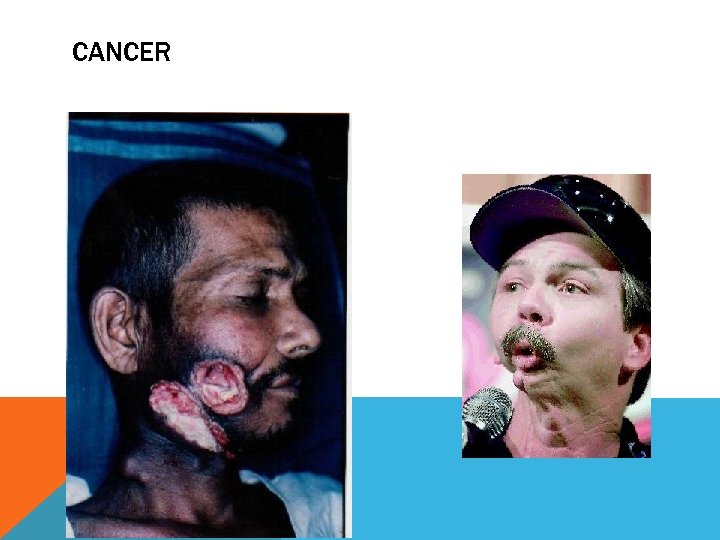 CANCER
CANCER
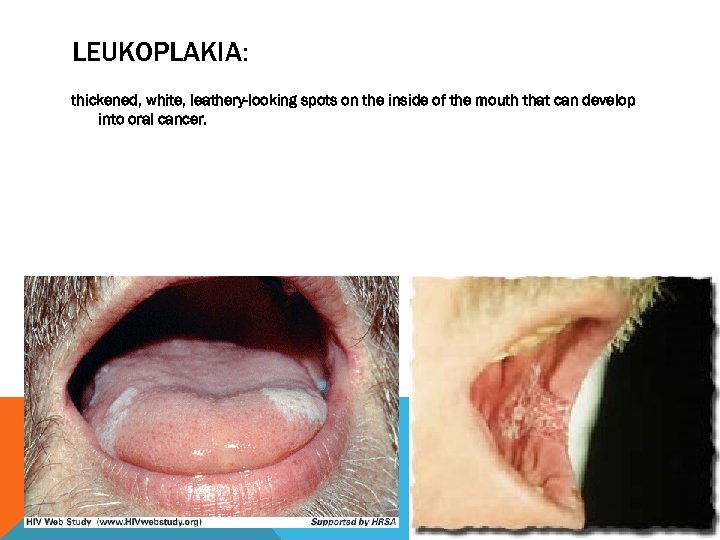 LEUKOPLAKIA: thickened, white, leathery-looking spots on the inside of the mouth that can develop into oral cancer.
LEUKOPLAKIA: thickened, white, leathery-looking spots on the inside of the mouth that can develop into oral cancer.
 ETS- ENVIRONMENTAL TOBACCO SMOKE Secondhand smoke is also known as environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) or passive smoke. It is a mixture of 2 forms of smoke that come from burning tobacco: sidestream smoke (smoke that comes from the end of a lighted cigarette, pipe, or cigar) and mainstream smoke (smoke that is exhaled by a smoker). Even though we think of these as the same, they aren't. The sidestream smoke has higher concentrations of cancer-causing agents (carcinogens) than the mainstream smoke. And, it contains smaller particles than mainstream smoke, which make their way into the body's cells more easily
ETS- ENVIRONMENTAL TOBACCO SMOKE Secondhand smoke is also known as environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) or passive smoke. It is a mixture of 2 forms of smoke that come from burning tobacco: sidestream smoke (smoke that comes from the end of a lighted cigarette, pipe, or cigar) and mainstream smoke (smoke that is exhaled by a smoker). Even though we think of these as the same, they aren't. The sidestream smoke has higher concentrations of cancer-causing agents (carcinogens) than the mainstream smoke. And, it contains smaller particles than mainstream smoke, which make their way into the body's cells more easily
 ETS- ENVIRONMENTAL TOBACCO SMOKE More than 100, 000 of the smoking-caused deaths over the last 50 years were of babies who died from SIDS In babies aged 18 months and younger in the United States, secondhand smoke exposure is responsible for: 150, 000– 300, 000 new cases of bronchitis and pneumonia annually Approximately 7, 500– 15, 000 hospitalizations annually Babies who breathe secondhand smoke are sick more often with bronchitis, pneumonia, and ear infections. Each year, primarily because of exposure to secondhand smoke, an estimated 3, 000 nonsmoking Americans die of lung cancer
ETS- ENVIRONMENTAL TOBACCO SMOKE More than 100, 000 of the smoking-caused deaths over the last 50 years were of babies who died from SIDS In babies aged 18 months and younger in the United States, secondhand smoke exposure is responsible for: 150, 000– 300, 000 new cases of bronchitis and pneumonia annually Approximately 7, 500– 15, 000 hospitalizations annually Babies who breathe secondhand smoke are sick more often with bronchitis, pneumonia, and ear infections. Each year, primarily because of exposure to secondhand smoke, an estimated 3, 000 nonsmoking Americans die of lung cancer
 OTHER CONSEQUENCES Legal Consequences: pay a fine for providing tobacco to anyone under the age of 21. Social Consequences: being excluded by nonsmokers. Financial Consequences: using tobacco can become extremely expensive.
OTHER CONSEQUENCES Legal Consequences: pay a fine for providing tobacco to anyone under the age of 21. Social Consequences: being excluded by nonsmokers. Financial Consequences: using tobacco can become extremely expensive.
 THINK QUESTION How can you advocate for your health and the health of others around people who use tobacco smoke?
THINK QUESTION How can you advocate for your health and the health of others around people who use tobacco smoke?
 HOW TO AVOID TOBACCO USE…. . Choose friends who are tobacco free! Avoid situations where tobacco products may be used. Practice and use refusal skills (simple as “No thanks. ”)
HOW TO AVOID TOBACCO USE…. . Choose friends who are tobacco free! Avoid situations where tobacco products may be used. Practice and use refusal skills (simple as “No thanks. ”)
 NICOTINE WITHDRAWALS Nicotine Withdrawal: the process that occurs in the body when nicotine, an addictive drug, is no longer used. § intense cravings for nicotine, sweating, nausea, headaches, insomnia, anxiety, depression, mood swings Nicotine Substitute: a product that delivers small amounts of nicotine into the body to help wean smokers from addiciton. Gum, Lozenges
NICOTINE WITHDRAWALS Nicotine Withdrawal: the process that occurs in the body when nicotine, an addictive drug, is no longer used. § intense cravings for nicotine, sweating, nausea, headaches, insomnia, anxiety, depression, mood swings Nicotine Substitute: a product that delivers small amounts of nicotine into the body to help wean smokers from addiciton. Gum, Lozenges
 HOW TO QUIT……………. Prepare a date to quit. Get a support group. Know health-related services in the community. Use healthier alternatives (gum) Change daily routines that may cause tobacco use. Engage in physical activities.
HOW TO QUIT……………. Prepare a date to quit. Get a support group. Know health-related services in the community. Use healthier alternatives (gum) Change daily routines that may cause tobacco use. Engage in physical activities.
 SMOKING 30 PACKS https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=HD__r 66 s. Fjk
SMOKING 30 PACKS https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=HD__r 66 s. Fjk
 6 N TES O L S RET ES G A E -C I A N D V A P IN G
6 N TES O L S RET ES G A E -C I A N D V A P IN G
 WHAT DO WE KNOW ABOUT E-CIGARETTES AND VAPING E-cigarettes are now the most commonly used tobacco product among youth, surpassing conventional cigarettes in 2014. E-cigarette use is strongly associated with the use of other tobacco products among youth and young adults, including cigarettes and other burned tobacco products E-cigarettes are a rapidly emerging and diversified product class. These devices typically deliver nicotine, flavorings, and other additives to users via an inhaled aerosol. These devices are referred to by a variety of names, including “e-cigs, ” “e -hookahs, ” “mods, ” “vape pens, ” “vapes, ” and “tank systems. ” E-cigarettes are marketed by promoting flavors and using a wide variety of media channels and approaches that have been used in the past for marketing conventional tobacco products to youth and young adults. E-cigarette aerosol is not harmless. It can contain harmful and potentially harmful constituents including nicotine. Nicotine exposure during adolescence can cause addiction and can harm the developing adolescent brain. The use of products containing nicotine poses dangers to youth, pregnant women, and fetuses. The use of products containing nicotine in any form among youth, including in e-cigarettes, is unsafe. E-cigarette use among youth and young adults has become a public health concern. In 2014, current use of e-cigarettes by young adults 18 -24 years of age surpassed that of adults 25 years of age and older
WHAT DO WE KNOW ABOUT E-CIGARETTES AND VAPING E-cigarettes are now the most commonly used tobacco product among youth, surpassing conventional cigarettes in 2014. E-cigarette use is strongly associated with the use of other tobacco products among youth and young adults, including cigarettes and other burned tobacco products E-cigarettes are a rapidly emerging and diversified product class. These devices typically deliver nicotine, flavorings, and other additives to users via an inhaled aerosol. These devices are referred to by a variety of names, including “e-cigs, ” “e -hookahs, ” “mods, ” “vape pens, ” “vapes, ” and “tank systems. ” E-cigarettes are marketed by promoting flavors and using a wide variety of media channels and approaches that have been used in the past for marketing conventional tobacco products to youth and young adults. E-cigarette aerosol is not harmless. It can contain harmful and potentially harmful constituents including nicotine. Nicotine exposure during adolescence can cause addiction and can harm the developing adolescent brain. The use of products containing nicotine poses dangers to youth, pregnant women, and fetuses. The use of products containing nicotine in any form among youth, including in e-cigarettes, is unsafe. E-cigarette use among youth and young adults has become a public health concern. In 2014, current use of e-cigarettes by young adults 18 -24 years of age surpassed that of adults 25 years of age and older
 E CIGARETTES LINKED TO POPCORN LUNG https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=w. Llx. Kmcw. Xbc
E CIGARETTES LINKED TO POPCORN LUNG https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=w. Llx. Kmcw. Xbc
 7 N UG FR O L S DR ES G L IV IN E E
7 N UG FR O L S DR ES G L IV IN E E
 LIVING DRUG FREE NOTE SET UP Preventing Drug Use Assertive Communication Skills and Refusal Skills § Respond Rapidly § Saying “No” § Broken Record § Be Assertive Resources
LIVING DRUG FREE NOTE SET UP Preventing Drug Use Assertive Communication Skills and Refusal Skills § Respond Rapidly § Saying “No” § Broken Record § Be Assertive Resources
 WHAT YOU CAN DO REDUCE/PREVENT DRUG USE Self-Control Involvement with other activities Building resistance skills and assertive communication skills Build a healthy self-esteem healthy relationships/ positive influences Goals and plans
WHAT YOU CAN DO REDUCE/PREVENT DRUG USE Self-Control Involvement with other activities Building resistance skills and assertive communication skills Build a healthy self-esteem healthy relationships/ positive influences Goals and plans
 ASSERTIVE COMMUNICATION AND REFUSAL SKILLS Respond Rapidly: the faster you can say no to offers of drugs and alcohol, the less likely you are to give in. If you hesitate, it allows time to think of excuses to go along. Respond with a clear and firm “no” that does not leave the door open to future offers for alcohol or other drugs. Leave out any excuses or qualifiers – state “no” or “no, thank you” or “no, I don’t drink or drug. ” “No” can be followed by: Changing the subject “No thanks, but tell more about whats been going on in your life. ” Suggesting alternative activities “No thanks, but would you like to head over to Starbucks for coffee. ” Clearly requesting that the individual not offer alcohol and other drugs again “No thank you and I don’t want to be asked again. ” “No” (leave out the thank you if you have to repeat it a second time). “No (one more time) and I need to leave now. ” Broken Record: Continue to say no. You may feel uncomfortable at first, but reminding yourself that they are also trying to make you uncomfortable enough to drink or use, will be a helpful tool.
ASSERTIVE COMMUNICATION AND REFUSAL SKILLS Respond Rapidly: the faster you can say no to offers of drugs and alcohol, the less likely you are to give in. If you hesitate, it allows time to think of excuses to go along. Respond with a clear and firm “no” that does not leave the door open to future offers for alcohol or other drugs. Leave out any excuses or qualifiers – state “no” or “no, thank you” or “no, I don’t drink or drug. ” “No” can be followed by: Changing the subject “No thanks, but tell more about whats been going on in your life. ” Suggesting alternative activities “No thanks, but would you like to head over to Starbucks for coffee. ” Clearly requesting that the individual not offer alcohol and other drugs again “No thank you and I don’t want to be asked again. ” “No” (leave out the thank you if you have to repeat it a second time). “No (one more time) and I need to leave now. ” Broken Record: Continue to say no. You may feel uncomfortable at first, but reminding yourself that they are also trying to make you uncomfortable enough to drink or use, will be a helpful tool.
 ASSERTIVE COMMUNICATION AND REFUSAL SKILLS Be Assertive Pay attention to body language and non-verbal cues. Good eye contact – don’t take your eyes of of the other person’s eyes Standing squarely towards the other person Appear Confident Use a calm even voice tone and volume Keep your “body language” consistent with your statements Maintain a posture and attitude of equality Speak firmly, positively, & loud enough to be heard easily Use clear, concise speech Leave only after you have said no a second or third time If all else fails, leave the situation
ASSERTIVE COMMUNICATION AND REFUSAL SKILLS Be Assertive Pay attention to body language and non-verbal cues. Good eye contact – don’t take your eyes of of the other person’s eyes Standing squarely towards the other person Appear Confident Use a calm even voice tone and volume Keep your “body language” consistent with your statements Maintain a posture and attitude of equality Speak firmly, positively, & loud enough to be heard easily Use clear, concise speech Leave only after you have said no a second or third time If all else fails, leave the situation
 RESOURCES FOR DRUGS, TOBACCO AND ALCOHOL SAMHSA 1 -800 -662 -HELP http: //www. al-anon. alateen. org/ http: //wp. sbcounty. gov/dbh/ads/ CA smoker Hotline 1 -800 -NO-BUTTS
RESOURCES FOR DRUGS, TOBACCO AND ALCOHOL SAMHSA 1 -800 -662 -HELP http: //www. al-anon. alateen. org/ http: //wp. sbcounty. gov/dbh/ads/ CA smoker Hotline 1 -800 -NO-BUTTS


