6b98ade0baaebedd3dd0b0d96e34a990.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

E-Business Security 1 Alter – Information Systems 4 th ed. © 2002 Prentice Hall

Threat of Accidents and Malfunctions n n n n 2 Operator error Hardware malfunction Software bugs Data errors Accidental disclosure of information Damage to physical facilities Inadequate system performance Liability for system failure

Threat of Computer Crime: Theft n n n 3 Theft of software and equipment Unauthorized use of access codes and financial passwords Theft by entering fraudulent transaction data Theft by stealing or modifying data Internet hoaxes for illegal gain Theft by modifying software

Threat of Computer Crime: Sabotage and Vandalism n Trap door n n Trojan horse n 4 A set of instructions that permits a user to bypass the computer system’s security measures A program that appears to be valid but contains hidden instructions that can cause damage

Threat of Computer Crime: Sabotage and Vandalism (cont. ) n Logic bomb n n Virus n n A special type of Trojan horse that can replicate itself and spread Denial of service attack n 5 A type of Trojan horse set to activate when a particular condition occurs Sabotaging a Web site by flooding it with incoming messages

Factors that Increase the Risks n n n 6 The nature of complex systems Human limitations Pressures in the business environment

Methods for Minimizing Risks n Controlling system development and modifications n n Providing security training n 7 Software change control systems Physical access controls

Controlling Access to Data, Computers, and Networks n n n Guidelines for manual data handling Access privileges Access control based on what you know n n 8 Password schemes Access control based on what you have Access control based on where you are Access control based on who you are

n Controlling incoming data flowing through networks and other media Commercially available virus protection products n Firewall software that inspects each incoming data packet, and decides whether it is acceptable based on its IP address n 9
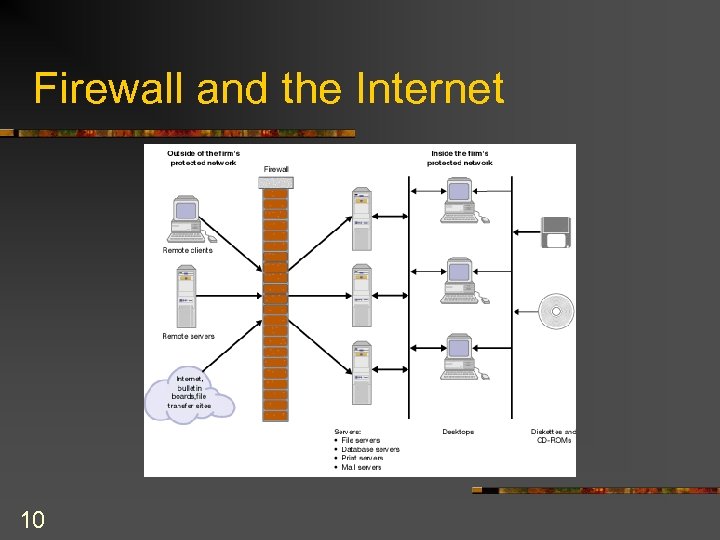
Firewall and the Internet 10

Making the Data Meaningless to Unauthorized Users n Public key encryption – encryption method based on two related keys, a public key and a private (secret) key n n 11 Also used to transmit the secret key used by the Data Encryption Standard (DES) Digital signatures – use public key encryption to authenticate the sender of a message and the message content
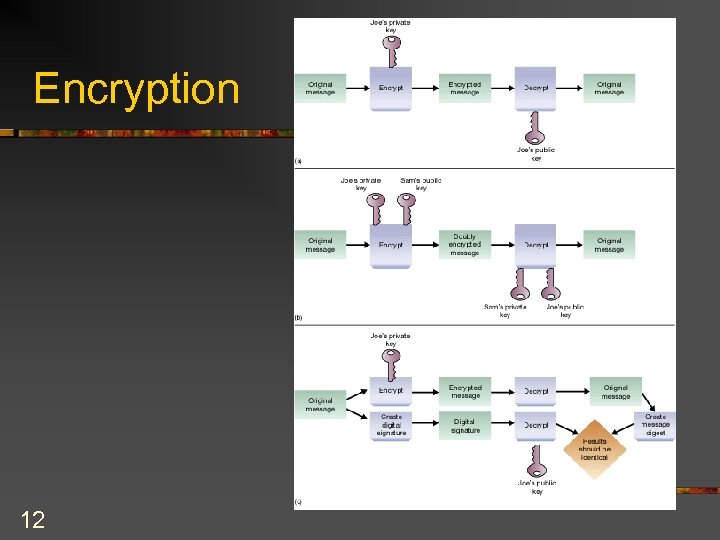
Encryption 12

Controlling Traditional Transaction Processing n n 13 Data preparation and authorization Data validation Error correction Backup and recovery

Maintaining Security in Web. Based Transactions n Public key infrastructure (PKI) n Certification authority (CA) – a company that issues digital certificates n 14 Computer-based records that identify the CA, identify the sender that is being verified, contain the sender’s public key, an is digitally signed by the CA

Transaction Privacy, Authentication, Integrity, and Nonrepudiation n Web transactions are encrypted using the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol n Encrypts the transmission using a temporary key generated automatically based on session information n Transaction authentication – n Transaction integrity – n Nonrepudiation – the process of verifying the identity of the participants in a transaction ensuring that information is not changed after the transaction is completed the transaction occurred 15 ensuring that neither party can deny that

Difficulties With Security Methods for Web Transactions n Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) method: n n n 16 Proposed by a consortium of credit card companies More secure than SSL Costly, and very slow adoption rate

Motivating Efficient and Effective Operation n Monitoring information system usage n n Charging users to encourage efficiency n 17 Business process performance Information system performance Unusual activity Chargeback systems try to motivate efficient usage by assigning the cost of information systems to the user departments

Auditing the Information System n n 18 Auditing ensures that financial operations are neither misrepresented nor threatened due to defective procedures or accounting systems Auditing around the computer vs. auditing through the computer

Preparing for Disasters n Disaster plan – a plan of action to recover from occurrences that shut down or harm major information systems 19
6b98ade0baaebedd3dd0b0d96e34a990.ppt