d8c9ab32b919cfb71e803a47e5516add.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

E-Books and Libraries Marie Harms State Library of Iowa Webinar 4/6/2011

Overview E-book basics Modes of delivery E-books in your library

Why are E-books suddenly so hot? Overdrive as a major player for Iowa Rise of the e-book readers Price drop of readers Invention of EPUB Many publishers getting in on the action

On a Personal Level…

An electronic book (also ebook, digital book) is a text and imagebased publication in digital form produced on, published by, and readable on computers or other digital devices -Wikipedia What is an E-book?

Who wants it? I am a traveler I am a student I am a professional I have a physical disability I am impatient!

Who uses e -books?

Where do I get it?

How do I get it? Free Buy it Apps Check it out from a library

How do I read it?

What can I do with it? Change font size Bookmark sections Add notes Text-to-speech Save passages Look up references on Websites Full color
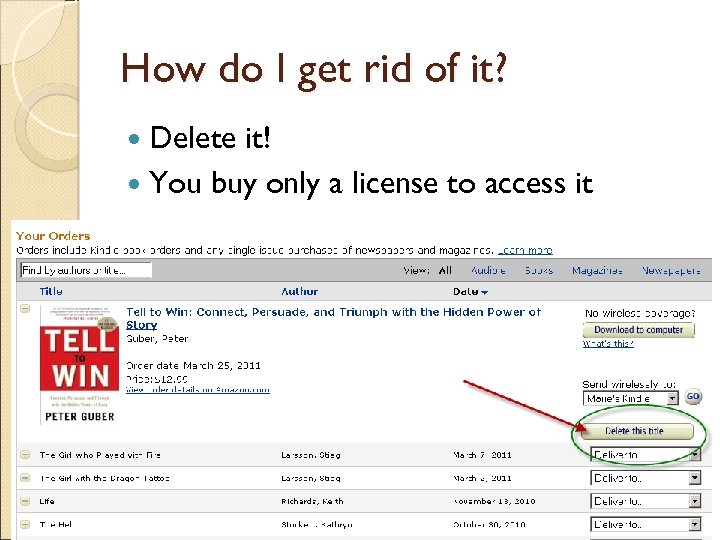
How do I get rid of it? Delete it! You buy only a license to access it
Library E-books vs. Consumer Ebooks Consumer E-books ◦ consumer buys the book and has it forever or for a specified time ◦ consumers buy title by title and pay more ◦ consumer E-books tend to be fiction

Library E-books vs. Consumer E-books Library E-books ◦ library buys the book, patron checks it out for a specified time (requires authentication) ◦ libraries buy package deals & get better prices ◦ library E-books tend to be more non-fiction and self-help

Types of E-Books

Why Offer E-books at the Library? Budget cuts vs. new technologies True cost savings for libraries Time savings Space savings Patron demand Easy access to obscure books Reach new people in the community Can increase support for the library Available 24/7 when the library isn’t open

Collection Development Policy From the Free Library of Philadelphia Electronic Resources Electronic materials play an increasingly important role in the Library’s collections and are selected in accordance with this Materials Selection Policy. These materials include, but are not limited to, databases, internet based tools, downloadable and e -books, and downloadable and streaming music and video. In addition to standard criteria used in selecting other formats, special selection criteria include ability to offer to remote users, availability of content in other formats, compatibility with existing technical set-ups, vendor usage statistics, and cost.

Where to get E-books

Issues to Consider Collection strengths Costs Leasing option available? Purchasing option available? Are the books downloadable? User accounts required? Are MARC records provided? Interface, technical problems, etc.

Costs—Pricing can depend on: ◦ # of cardholders ◦ jurisdiction population ◦ # of branches

Perpetual Ownership Model Buy the E-book, you have it forever You own the book More expensive, title may become outdated/superseded

Subscription Model Subscribe to the book, as you do to e- databases Cheaper, superseded titles replaced for free No permanence to the book

Modes of delivery Reading online Downloading for offline or portable use

Reading Online Does not require a special software reader Does require that you are online Most in-library use is reading online Good for quick accesses, not sustained reading

Downloading Requires a free software reader (Adobe, Microsoft, Media Console etc. ) Can display book on different devices Download takes some time Automatic expiration of book at end of checkout period

Device-Dependent Books Publishers started in the E-book market this way—bad decision. Examples from the past ◦ Rocket e. Book ◦ Soft Book Reader

But then came EPUB - electronic publication is a free and open e-book standard by the International Digital Publishing Forum (IDPF) Official standard of IDPF in September 2007 Designed for reflowable content, text display can be optimized for the particular display device used by the reader of the EPUB-formatted book

Device-Independent Books You can read the book on whatever you have: ◦ desktop or laptop computer ◦ PDA ◦ i. Pad ◦ i. Phone, or Smartphone ◦ i. Pod or other MP 3 player ◦ Blio

Digital Rights Management (DRM) Limits access, functionality & use of e- books DRM was created to placate publishers Harper Collins is using DRM to limit number of times an e-book can circulate

Common problems with DRM & Ebooks Requires lengthy installation of new software Requires new accounts & password to be created Can disallow copying & pasting of text of Ebook Auto expiration sometimes malfunctions

Budgeting for Ebooks Where should the money come from? ◦ standing order budget (just like regular books) ◦ e-resources budget How much do Ebooks cost as compared to print books? ◦ less than print books, depending on your subscription prices and averted space, processing, and circulation staff costs How much of your budget should be spent on Ebooks? ◦ it depends on you and your library

E-books in Libraries Still represents a small percentage of circ Demand will continue to grow

Imagine the future What percentage of your collection do you think will be in e-books 10 years from now? What will the physical space of your library look like as you move to e-books?

Imagine the future Imagine the Future What percentage of your collection do you think will be in e-books 10 years from now? What will the physical space of your library look like as you move to ebooks?

The End Thanks for attending! You will receive the link to the recording You will receive a link to the evaluation Please complete the evaluation for 1 hour CE credit
d8c9ab32b919cfb71e803a47e5516add.ppt