d37868d0b0e34327eadcf37574dabd9c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 e 2 EKey Resource Group Name: SEC WG Source: Qualcomm Inc. , Wolfgang Granzow & Phil Hawkes Meeting Date: SEC#20. 3, 2015 -12 -17 Agenda Item: End-to-End Security and Group Authentication
e 2 EKey Resource Group Name: SEC WG Source: Qualcomm Inc. , Wolfgang Granzow & Phil Hawkes Meeting Date: SEC#20. 3, 2015 -12 -17 Agenda Item: End-to-End Security and Group Authentication
 Background • For End-to-End security, we would like to be able to use certificates – E 2 E attribute security (e. g. AE-to-AE, signing tokens) – E 2 E message security (Originator-to-CSE) • Object security protocols – Java. Script Object Signing and Encryption (JOSE) IETF WG: • JSON Web Signature (JWS), JSON Web encryption (JWE) – XML Encryption and XML Signature. • These protocols support multiple target end-points – Applicable to some E 2 E Attribute security scenarios – Not applicable in E 2 E Message security (always 1 source & 1 target) • However, in many cases (including all E 2 E message security scenarios), there is 1 source and 1 target – This contribution targets only these use cases 2
Background • For End-to-End security, we would like to be able to use certificates – E 2 E attribute security (e. g. AE-to-AE, signing tokens) – E 2 E message security (Originator-to-CSE) • Object security protocols – Java. Script Object Signing and Encryption (JOSE) IETF WG: • JSON Web Signature (JWS), JSON Web encryption (JWE) – XML Encryption and XML Signature. • These protocols support multiple target end-points – Applicable to some E 2 E Attribute security scenarios – Not applicable in E 2 E Message security (always 1 source & 1 target) • However, in many cases (including all E 2 E message security scenarios), there is 1 source and 1 target – This contribution targets only these use cases 2
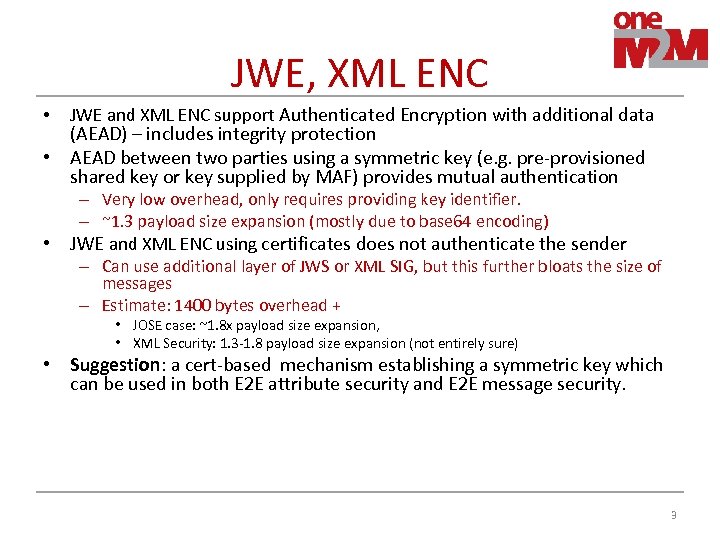 JWE, XML ENC • JWE and XML ENC support Authenticated Encryption with additional data • – Very low overhead, only requires providing key identifier. – ~1. 3 payload size expansion (mostly due to base 64 encoding) JWE and XML ENC using certificates does not authenticate the sender – Can use additional layer of JWS or XML SIG, but this further bloats the size of messages – Estimate: 1400 bytes overhead + (AEAD) – includes integrity protection • AEAD between two parties using a symmetric key (e. g. pre-provisioned shared key or key supplied by MAF) provides mutual authentication • JOSE case: ~1. 8 x payload size expansion, • XML Security: 1. 3 -1. 8 payload size expansion (not entirely sure) • Suggestion: a cert-based mechanism establishing a symmetric key which can be used in both E 2 E attribute security and E 2 E message security. 3
JWE, XML ENC • JWE and XML ENC support Authenticated Encryption with additional data • – Very low overhead, only requires providing key identifier. – ~1. 3 payload size expansion (mostly due to base 64 encoding) JWE and XML ENC using certificates does not authenticate the sender – Can use additional layer of JWS or XML SIG, but this further bloats the size of messages – Estimate: 1400 bytes overhead + (AEAD) – includes integrity protection • AEAD between two parties using a symmetric key (e. g. pre-provisioned shared key or key supplied by MAF) provides mutual authentication • JOSE case: ~1. 8 x payload size expansion, • XML Security: 1. 3 -1. 8 payload size expansion (not entirely sure) • Suggestion: a cert-based mechanism establishing a symmetric key which can be used in both E 2 E attribute security and E 2 E message security. 3
 Cert-based pairwise. E 2 EKey establishment • Options for establishing pairwise. E 2 EKey using certificates – Devise our own handshake using JWE/JWS or XML ENC/SIG • JWE/JWS and XML/ENC/SIG wasn’t really intended for this • We are 100% guaranteed to do something wrong – Use something we are familiar with • Certificate-based TLS handshake, from which pairwise. E 2 EKey is exported – pairwise. E 2 EPrimitive. Key and pairwise. E 2 EAttribute. Key are derived from pairwise. E 2 EKey • Challenge – How do we do a TLS handshake transported using one. M 2 M requests and responses? 4
Cert-based pairwise. E 2 EKey establishment • Options for establishing pairwise. E 2 EKey using certificates – Devise our own handshake using JWE/JWS or XML ENC/SIG • JWE/JWS and XML/ENC/SIG wasn’t really intended for this • We are 100% guaranteed to do something wrong – Use something we are familiar with • Certificate-based TLS handshake, from which pairwise. E 2 EKey is exported – pairwise. E 2 EPrimitive. Key and pairwise. E 2 EAttribute. Key are derived from pairwise. E 2 EKey • Challenge – How do we do a TLS handshake transported using one. M 2 M requests and responses? 4
 Proposal •
Proposal •
 TLS Messages (Background) Messages TLS Handshake parameters (success case) Description 1 Client. Hello List of supported ciphersuites, random value 2 Server. Hello Selected ciphersuite, random value Certificate Terminating End-Point’s Certificate Server. Key. Exchange Key exchange parameters generated by the Terminating End -Point. Dependent on selected ciphersuite Certificate. Request the Initiating End-Point to authenticate itself with a certificate Server. Hello. Done End of message Certificate Initiating End-Point’s Certificate Client. Key. Exchange Key exchange parameters generated by the Terminating End -Point. Dependent on selected ciphersuite Certificate. Verify Signature by Initiating End-Point (Change. Cipher. Spec*) Signal to start using new keys Finished MIC on handshake messages using session secrets 3 4 * Not really part of the handshake protocol. Investigating if this is needed 6
TLS Messages (Background) Messages TLS Handshake parameters (success case) Description 1 Client. Hello List of supported ciphersuites, random value 2 Server. Hello Selected ciphersuite, random value Certificate Terminating End-Point’s Certificate Server. Key. Exchange Key exchange parameters generated by the Terminating End -Point. Dependent on selected ciphersuite Certificate. Request the Initiating End-Point to authenticate itself with a certificate Server. Hello. Done End of message Certificate Initiating End-Point’s Certificate Client. Key. Exchange Key exchange parameters generated by the Terminating End -Point. Dependent on selected ciphersuite Certificate. Verify Signature by Initiating End-Point (Change. Cipher. Spec*) Signal to start using new keys Finished MIC on handshake messages using session secrets 3 4 * Not really part of the handshake protocol. Investigating if this is needed 6
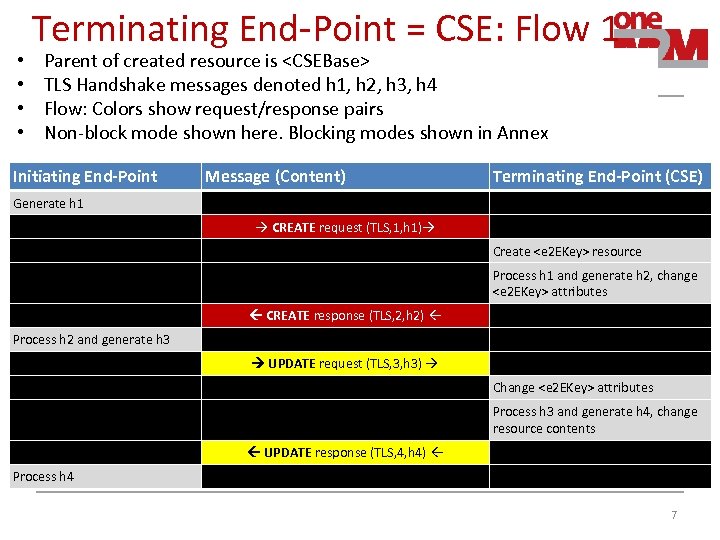 • • Terminating End-Point = CSE: Flow 1 Parent of created resource is
• • Terminating End-Point = CSE: Flow 1 Parent of created resource is
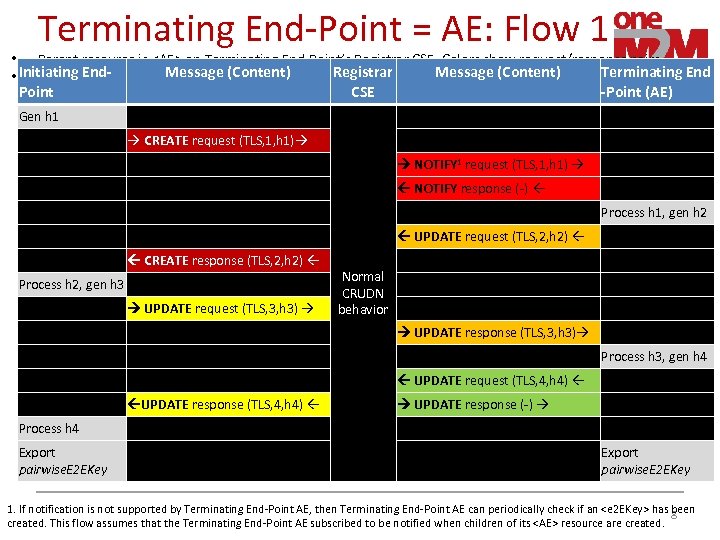 Terminating End-Point = AE: Flow 1 • Parent resource is
Terminating End-Point = AE: Flow 1 • Parent resource is
 Further comments • pairwise. E 2 EKey identifier options 1. 2. Identifier of the created resource Random identifier exported with pairwise. E 2 EKey • For ARC consideration: Behavior of CSE changes depending on whether the CSE is the Terminating end-point, or a registered AE is the Terminating end-point – Might make sense to have two distinct resource types for e 2 EKey functionality; • One resource type for when CSE is the Terminating end-point, and • One resource type for when a registered AE is the Terminating end-point. – This is an ARC specification detail – makes no difference to SEC specifications – For now assuming it is OK to have a single resource type
Further comments • pairwise. E 2 EKey identifier options 1. 2. Identifier of the created resource Random identifier exported with pairwise. E 2 EKey • For ARC consideration: Behavior of CSE changes depending on whether the CSE is the Terminating end-point, or a registered AE is the Terminating end-point – Might make sense to have two distinct resource types for e 2 EKey functionality; • One resource type for when CSE is the Terminating end-point, and • One resource type for when a registered AE is the Terminating end-point. – This is an ARC specification detail – makes no difference to SEC specifications – For now assuming it is OK to have a single resource type
 ARC Impact: TS-0001 • Update to existing text – Table 9. 6. 1. 1 -1 Resource Types – Clause 9. 6. 3 Resource Type CSEBase • Add an attribute to
ARC Impact: TS-0001 • Update to existing text – Table 9. 6. 1. 1 -1 Resource Types – Clause 9. 6. 3 Resource Type CSEBase • Add an attribute to
 SEC Impact TS-0003 • Stage 2 – Specify sequence of TLS handshake messages exchanged and processing at end-points. • Stage 3 – TLS ciphersuites – Certificate profiles – Details for exporting pairwise. E 2 EKey • Suggested Authors – Qualcomm 11
SEC Impact TS-0003 • Stage 2 – Specify sequence of TLS handshake messages exchanged and processing at end-points. • Stage 3 – TLS ciphersuites – Certificate profiles – Details for exporting pairwise. E 2 EKey • Suggested Authors – Qualcomm 11
 Annex: Some Non-Blocking
Annex: Some Non-Blocking
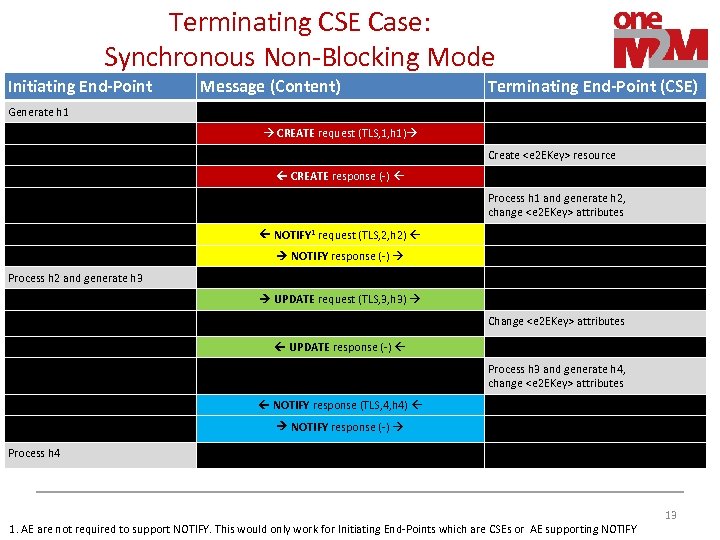 Terminating CSE Case: Synchronous Non-Blocking Mode Initiating End-Point Message (Content) Generate h 1 Parent of created resource is
Terminating CSE Case: Synchronous Non-Blocking Mode Initiating End-Point Message (Content) Generate h 1 Parent of created resource is
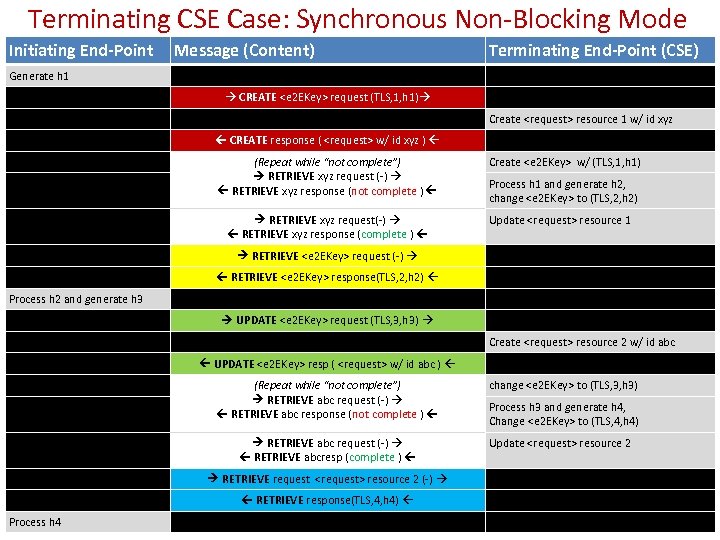 Terminating CSE Case: Synchronous Non-Blocking Mode Initiating End-Point Message (Content) Terminating End-Point (CSE) Generate h 1 • • • CREATE
Terminating CSE Case: Synchronous Non-Blocking Mode Initiating End-Point Message (Content) Terminating End-Point (CSE) Generate h 1 • • • CREATE
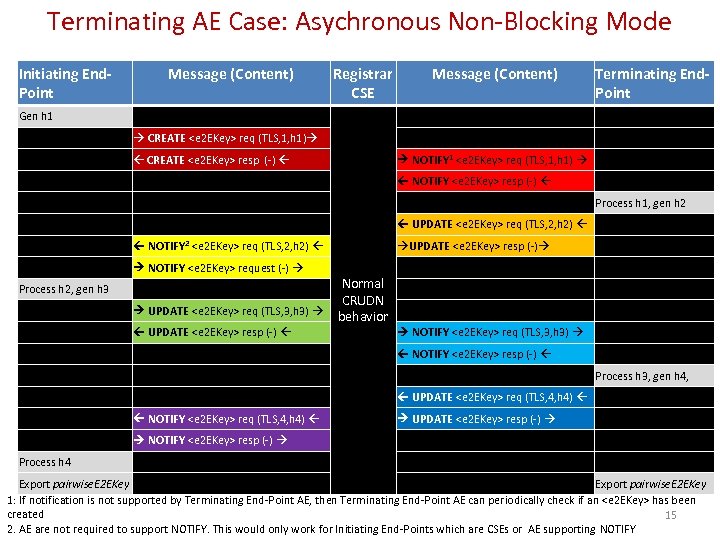 Terminating AE Case: Asychronous Non-Blocking Mode Initiating End. Point Message (Content) Registrar CSE Message (Content) Terminating End. Point Gen h 1 CREATE
Terminating AE Case: Asychronous Non-Blocking Mode Initiating End. Point Message (Content) Registrar CSE Message (Content) Terminating End. Point Gen h 1 CREATE


