99b7e975cae5657a45e70d7ae47b1cc5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
 Dynamic Proxies in Java And so on into winter Till even I have ceased To come as a foot printer, And only some slight beast So mousy or foxy Shall print there as my proxy. Robert Frost “Closed for Good” Joe Dane jdane@hawaii. edu April 28, 2004 (1)
Dynamic Proxies in Java And so on into winter Till even I have ceased To come as a foot printer, And only some slight beast So mousy or foxy Shall print there as my proxy. Robert Frost “Closed for Good” Joe Dane jdane@hawaii. edu April 28, 2004 (1)
 What’s a Proxy? “The agency for another who acts through the agent; authority to act for another” (Webster) “Provide a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it” (Go. F) Types of proxies mentioned: • remote • “virtual” (e. g. loading on demand) • protection • “smart references” -e. g. ref counting, locking, etc. (2)
What’s a Proxy? “The agency for another who acts through the agent; authority to act for another” (Webster) “Provide a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it” (Go. F) Types of proxies mentioned: • remote • “virtual” (e. g. loading on demand) • protection • “smart references” -e. g. ref counting, locking, etc. (2)
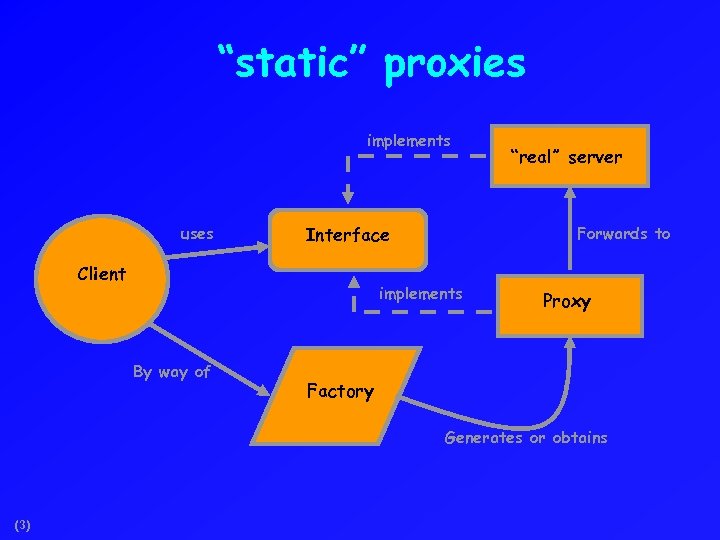 “static” proxies implements uses Interface Client Forwards to implements By way of “real” server Proxy Factory Generates or obtains (3)
“static” proxies implements uses Interface Client Forwards to implements By way of “real” server Proxy Factory Generates or obtains (3)
 General Proxy comments Using static proxies means tracking changes in interfaces, writing dummy methodsm recompiling. Also implies that we can’t use a framework that doesn’t know about our interfaces. Can’t use a Constructor • Go. F doesn’t mention this • Must use a factory or registry (4)
General Proxy comments Using static proxies means tracking changes in interfaces, writing dummy methodsm recompiling. Also implies that we can’t use a framework that doesn’t know about our interfaces. Can’t use a Constructor • Go. F doesn’t mention this • Must use a factory or registry (4)
 Dynamic What? “Proxy”, because we create an object to “stand in” for another object “Dynamic” because the object is defined at runtime. • Means we must have JVM support. Bottom line: at runtime, create objects which wrap other objects (services) and add functionality. (5)
Dynamic What? “Proxy”, because we create an object to “stand in” for another object “Dynamic” because the object is defined at runtime. • Means we must have JVM support. Bottom line: at runtime, create objects which wrap other objects (services) and add functionality. (5)
 Why proxies? Enhance services w/o changing either clients or servers • If you need to look at the method, you probably don’t want a D. P. Explicit control over method invocation. No need to explicitly implement all methods in an interface. You’re probably already using them. • App servers, Axis, hibernate (6)
Why proxies? Enhance services w/o changing either clients or servers • If you need to look at the method, you probably don’t want a D. P. Explicit control over method invocation. No need to explicitly implement all methods in an interface. You’re probably already using them. • App servers, Axis, hibernate (6)
 Some Examples Logging, failover “Memoization” XML data binding Enforce security restrictions Transaction management (7)
Some Examples Logging, failover “Memoization” XML data binding Enforce security restrictions Transaction management (7)
 Our model Services • Interfaces which define behaviors Servers • Programs which provide (implement) one or more services Clients • Obtain references to services (cf factory pattern) • No knowledge of server details • Services may be local or remote (8)
Our model Services • Interfaces which define behaviors Servers • Programs which provide (implement) one or more services Clients • Obtain references to services (cf factory pattern) • No knowledge of server details • Services may be local or remote (8)
 Digression: Reflection Basics java. lang. reflect package Classes which represent the basic units of Java. • Class, Method, Constructor • From a Class, we can get a Method. • From a Method, we can ‘invoke’ on an object and arguments. -object. methodname(arg 1, arg 2, …) -method. invoke(object, args[]) Syntax: Foo. class (9)
Digression: Reflection Basics java. lang. reflect package Classes which represent the basic units of Java. • Class, Method, Constructor • From a Class, we can get a Method. • From a Method, we can ‘invoke’ on an object and arguments. -object. methodname(arg 1, arg 2, …) -method. invoke(object, args[]) Syntax: Foo. class (9)
 Creating a proxy Things you need • A Class. Loader • An array of interfaces to implement • An Invocation. Handler What’s the Invocation. Handler? • Basically, a single method. Could do anything • Doesn’t usually implement any essential business logic • Dispatches to an underlying service, possibly after (or before) providing some additional service. • Note: underlying service may itself be a proxy! (10)
Creating a proxy Things you need • A Class. Loader • An array of interfaces to implement • An Invocation. Handler What’s the Invocation. Handler? • Basically, a single method. Could do anything • Doesn’t usually implement any essential business logic • Dispatches to an underlying service, possibly after (or before) providing some additional service. • Note: underlying service may itself be a proxy! (10)
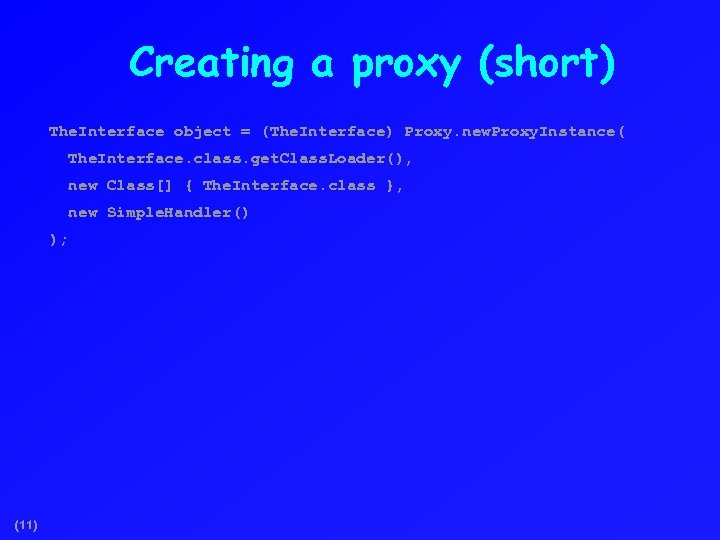 Creating a proxy (short) The. Interface object = (The. Interface) Proxy. new. Proxy. Instance( The. Interface. class. get. Class. Loader(), new Class[] { The. Interface. class }, new Simple. Handler() ); (11)
Creating a proxy (short) The. Interface object = (The. Interface) Proxy. new. Proxy. Instance( The. Interface. class. get. Class. Loader(), new Class[] { The. Interface. class }, new Simple. Handler() ); (11)
 Creating a proxy (long) try { Class proxy. Class = Proxy. get. Proxy. Class( The. Interface. class. get. Class. Loader(), new Class[] { The. Interface. class } ); Constructor constructor = proxy. Class. get. Constructor(new Class[] { Invocation. Handler. class }); Invocation. Handler handler = new Simple. Handler(); The. Interface object = (The. Interface) constructor. new. Instance(new Object[] { handler }); } catch (Exception e) { … } (12)
Creating a proxy (long) try { Class proxy. Class = Proxy. get. Proxy. Class( The. Interface. class. get. Class. Loader(), new Class[] { The. Interface. class } ); Constructor constructor = proxy. Class. get. Constructor(new Class[] { Invocation. Handler. class }); Invocation. Handler handler = new Simple. Handler(); The. Interface object = (The. Interface) constructor. new. Instance(new Object[] { handler }); } catch (Exception e) { … } (12)
 Proxy Properties Can be cast to any interface used in creating the proxy class. instanceof works as expected Proxy. is. Proxy. Class() is true for the class Class name is undetermined, but will probably be something like Proxy$1. Method invocation is encoded and dispatched to the handler’s invoke method. Is Serializable • This is huge! • Implications for (13) RMI, JNDI, J 2 EE
Proxy Properties Can be cast to any interface used in creating the proxy class. instanceof works as expected Proxy. is. Proxy. Class() is true for the class Class name is undetermined, but will probably be something like Proxy$1. Method invocation is encoded and dispatched to the handler’s invoke method. Is Serializable • This is huge! • Implications for (13) RMI, JNDI, J 2 EE
 Simple proxy use Get proxy reference Client Factory Proxy handler (14) Service
Simple proxy use Get proxy reference Client Factory Proxy handler (14) Service
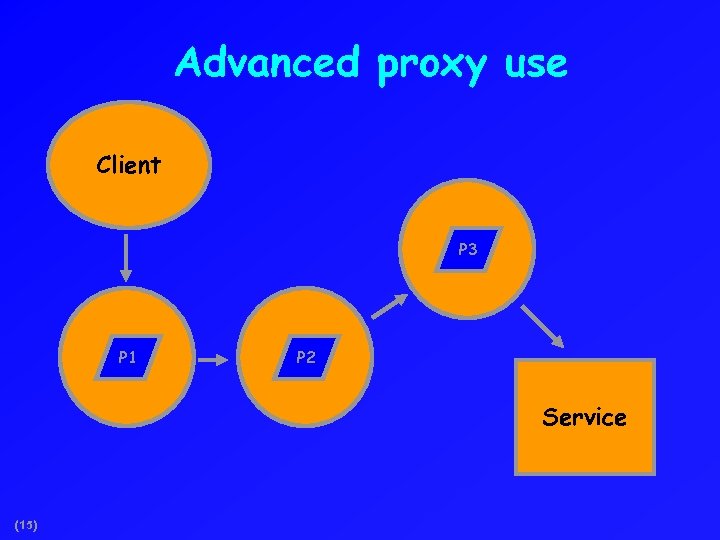 Advanced proxy use Client P 3 P 1 P 2 Service (15)
Advanced proxy use Client P 3 P 1 P 2 Service (15)
 Downsides Loss of static guarantees Can make code difficult to understand Can’t proxy classes, only interfaces Slow? Requires JDK 1. 3 All invocations go through the handler, even to. String, equals(), etc. , which were not in any interface. The creation syntax is ugly. (16)
Downsides Loss of static guarantees Can make code difficult to understand Can’t proxy classes, only interfaces Slow? Requires JDK 1. 3 All invocations go through the handler, even to. String, equals(), etc. , which were not in any interface. The creation syntax is ugly. (16)
 Upsides Proxy handlers don’t have to be updated when service interfaces change. SOC: We can add behavior w/o changing servers or clients. Serializable means we can store proxies anywhere we like. • c. f. App Servers: Web. Logic, JBOSS, etc. Slow? Not really. (17)
Upsides Proxy handlers don’t have to be updated when service interfaces change. SOC: We can add behavior w/o changing servers or clients. Serializable means we can store proxies anywhere we like. • c. f. App Servers: Web. Logic, JBOSS, etc. Slow? Not really. (17)
 Proxy examples Simple example Simple (but slightly more realistic) example Logging and profiling method calls A “memoizing” handler Load balancing and fail-over Some timing examples A “real world” example, time permitting (18)
Proxy examples Simple example Simple (but slightly more realistic) example Logging and profiling method calls A “memoizing” handler Load balancing and fail-over Some timing examples A “real world” example, time permitting (18)
 References java. lang. reflect API docs Sun’s web page describing dynamic proxies. Contains simple examples and one more complicated example. Good starting point. • http: //java. sun. com/j 2 ee/1. 3/docs/guide/reflection/proxy. html Post to RMI-USERS mailing list describing how to use dynamic proxies to eliminate the need for rmic. Mind bending, not for the faint hearted. • http: //swjscmail. java. sun. com/cgi-bin/wa? A 2=ind 0009&L=rmi-users&P=R 3631 Related projects: cglib, BCEL, Ao. P (19)
References java. lang. reflect API docs Sun’s web page describing dynamic proxies. Contains simple examples and one more complicated example. Good starting point. • http: //java. sun. com/j 2 ee/1. 3/docs/guide/reflection/proxy. html Post to RMI-USERS mailing list describing how to use dynamic proxies to eliminate the need for rmic. Mind bending, not for the faint hearted. • http: //swjscmail. java. sun. com/cgi-bin/wa? A 2=ind 0009&L=rmi-users&P=R 3631 Related projects: cglib, BCEL, Ao. P (19)


