d2a383a90be2c6e4a7f79b95b3c35d29.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 DSS: Decision Support Systems and AI: Artificial Intelligence In Business
DSS: Decision Support Systems and AI: Artificial Intelligence In Business
 AI in Business Some Commercial Applications • Decision Support • Expert Systems • Information Retrieval • Virtual Reality • Robotics I’m ready to do some business
AI in Business Some Commercial Applications • Decision Support • Expert Systems • Information Retrieval • Virtual Reality • Robotics I’m ready to do some business
 Overview of AI • Goal of AI – develop computer systems that exhibit intelligence or simulate the ability to think • AI pioneered by Computer Science • But, AI involves a combination of – Computer Science, Biology, Psychology, Linguistics, Mathematics, Engineering
Overview of AI • Goal of AI – develop computer systems that exhibit intelligence or simulate the ability to think • AI pioneered by Computer Science • But, AI involves a combination of – Computer Science, Biology, Psychology, Linguistics, Mathematics, Engineering
 What really is Intelligence? • Specifically, what are the signs of Intelligent Behavior? • Think about it for a while
What really is Intelligence? • Specifically, what are the signs of Intelligent Behavior? • Think about it for a while
 Which of the following is the best example of intelligent behavior? 1. Ability to add numbers 2. Ability to see and recognize objects 3. Ability to adapt to surroundings 4. Ability to learn for mistakes 10
Which of the following is the best example of intelligent behavior? 1. Ability to add numbers 2. Ability to see and recognize objects 3. Ability to adapt to surroundings 4. Ability to learn for mistakes 10
 What really is Intelligence? • You are about to start an online chat (IM) with two entities: – One entity is a human – The other is a computer • After hours of conversation, you can not tell which entity is a computer. • Does this mean the computer is Intelligent?
What really is Intelligence? • You are about to start an online chat (IM) with two entities: – One entity is a human – The other is a computer • After hours of conversation, you can not tell which entity is a computer. • Does this mean the computer is Intelligent?
 Intelligent Behavior • What are some of the signs, attributes, or characteristics of Intelligent Behavior
Intelligent Behavior • What are some of the signs, attributes, or characteristics of Intelligent Behavior
 Characteristics of Intelligent Behavior 1. Learn from experience & apply the knowledge Computer can automatically improve performance based on Experience Machine Learning Computational Learning
Characteristics of Intelligent Behavior 1. Learn from experience & apply the knowledge Computer can automatically improve performance based on Experience Machine Learning Computational Learning
 Characteristics of Intelligent Behavior 2. Handle complex situations Computer Systems can often handle complexity better than humans Consider a process control system that must simultaneous track 100 different system variables.
Characteristics of Intelligent Behavior 2. Handle complex situations Computer Systems can often handle complexity better than humans Consider a process control system that must simultaneous track 100 different system variables.
 Characteristics of Intelligent Behavior 3. Solve problems when important information is missing Computer Systems can find patterns and deal with all sorts of missing information
Characteristics of Intelligent Behavior 3. Solve problems when important information is missing Computer Systems can find patterns and deal with all sorts of missing information
 Characteristics of Intelligent Behavior 4. React quickly & correctly to new situations; Acquire & Apply Knowledge Here is where computers start to fail. Adapting to completely new situations is a problem for computer systems. Its very difficult to design a computer system that can combine, connect, and acquire knowledge to solve completely new problems
Characteristics of Intelligent Behavior 4. React quickly & correctly to new situations; Acquire & Apply Knowledge Here is where computers start to fail. Adapting to completely new situations is a problem for computer systems. Its very difficult to design a computer system that can combine, connect, and acquire knowledge to solve completely new problems
 Characteristics of Intelligent Behavior 5. 6. 7. 8. Determine what is important. Exhibit creativity and imagination Process visual information efficiently Use reason to solve problems These are some other Characteristics that humans possess. Computer systems have a lot of catching up to do.
Characteristics of Intelligent Behavior 5. 6. 7. 8. Determine what is important. Exhibit creativity and imagination Process visual information efficiently Use reason to solve problems These are some other Characteristics that humans possess. Computer systems have a lot of catching up to do.
 Which of the following do computer need to catch up on? 1. Determine what is important. 2. Exhibit creativity and imagination 3. Process visual information efficiently 4. Use reason to solve problems 10
Which of the following do computer need to catch up on? 1. Determine what is important. 2. Exhibit creativity and imagination 3. Process visual information efficiently 4. Use reason to solve problems 10
 AI in Business • AI continues to improve and evolve. • Scientists and Engineers are pushing the envelope of what is possible. • In Business, there is a better understanding of the capabilities of Intelligent Computer Systems • It is important to know which types of problems are suited for humans, and which are suited for Computers.
AI in Business • AI continues to improve and evolve. • Scientists and Engineers are pushing the envelope of what is possible. • In Business, there is a better understanding of the capabilities of Intelligent Computer Systems • It is important to know which types of problems are suited for humans, and which are suited for Computers.
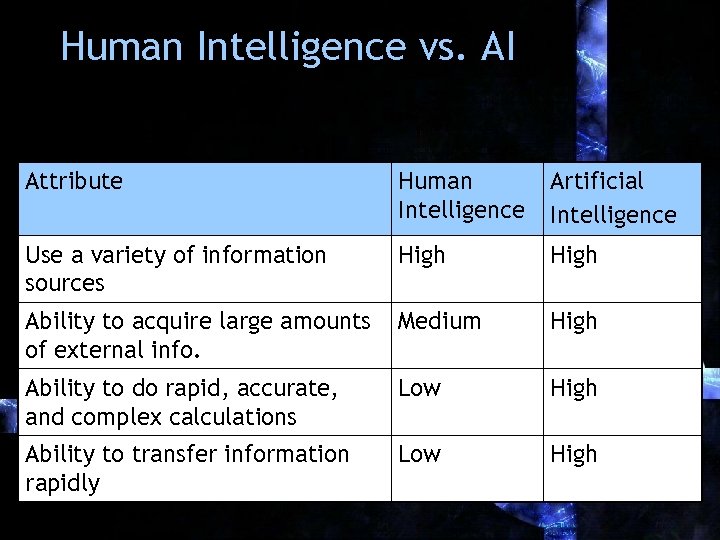 Human Intelligence vs. AI Attribute Human Intelligence Artificial Intelligence Use a variety of information sources High Ability to acquire large amounts of external info. Medium High Ability to do rapid, accurate, and complex calculations Low High Ability to transfer information rapidly Low High
Human Intelligence vs. AI Attribute Human Intelligence Artificial Intelligence Use a variety of information sources High Ability to acquire large amounts of external info. Medium High Ability to do rapid, accurate, and complex calculations Low High Ability to transfer information rapidly Low High
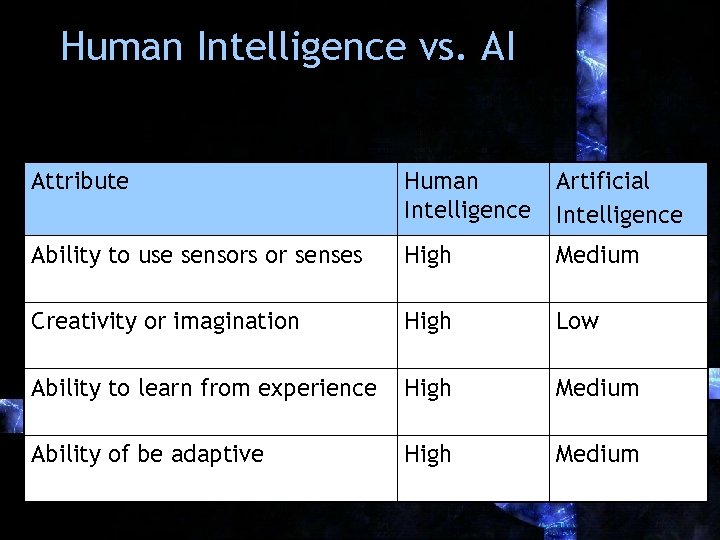 Human Intelligence vs. AI Attribute Human Intelligence Artificial Intelligence Ability to use sensors or senses High Medium Creativity or imagination High Low Ability to learn from experience High Medium Ability of be adaptive High Medium
Human Intelligence vs. AI Attribute Human Intelligence Artificial Intelligence Ability to use sensors or senses High Medium Creativity or imagination High Low Ability to learn from experience High Medium Ability of be adaptive High Medium
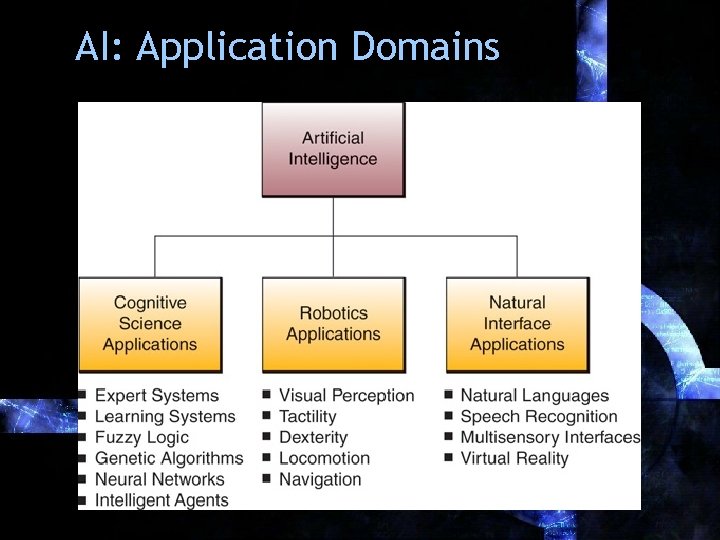 AI: Application Domains
AI: Application Domains
 AI: Commercial Domains • Decision Support – Integrating the advantages of AI with Human Intelligence. – More intelligent Interfaces – More intelligent processing for massive data
AI: Commercial Domains • Decision Support – Integrating the advantages of AI with Human Intelligence. – More intelligent Interfaces – More intelligent processing for massive data
 AI: Commercial Domains • Information Retrieval – Automatic simplification for massive data – Natural language technology: computer can speak our language.
AI: Commercial Domains • Information Retrieval – Automatic simplification for massive data – Natural language technology: computer can speak our language.
 AI: Commercial Domains • Virtual Reality – Better training environment from pilots to doctors • Robotics – Bringing the precision and speed of computers into the physical world – Goes beyond manufacturing and assembly lines; Baggage Inspection, Bomb Removal, Replacement Limbs.
AI: Commercial Domains • Virtual Reality – Better training environment from pilots to doctors • Robotics – Bringing the precision and speed of computers into the physical world – Goes beyond manufacturing and assembly lines; Baggage Inspection, Bomb Removal, Replacement Limbs.
 Expert Systems • The idea is to inject expert knowledge in to a computer system. • The primary purpose is to automate decision making. • The decision environments have structure • The alternatives and goals are often established in advance.
Expert Systems • The idea is to inject expert knowledge in to a computer system. • The primary purpose is to automate decision making. • The decision environments have structure • The alternatives and goals are often established in advance.
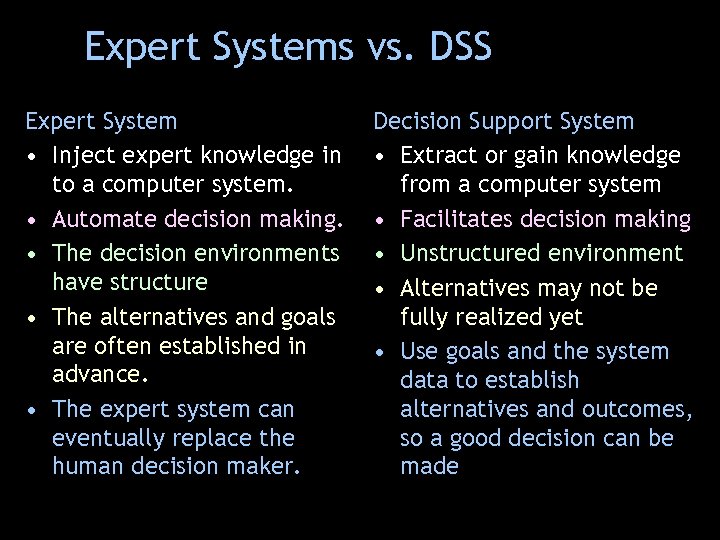 Expert Systems vs. DSS Expert System • Inject expert knowledge in to a computer system. • Automate decision making. • The decision environments have structure • The alternatives and goals are often established in advance. • The expert system can eventually replace the human decision maker. Decision Support System • Extract or gain knowledge from a computer system • Facilitates decision making • Unstructured environment • Alternatives may not be fully realized yet • Use goals and the system data to establish alternatives and outcomes, so a good decision can be made
Expert Systems vs. DSS Expert System • Inject expert knowledge in to a computer system. • Automate decision making. • The decision environments have structure • The alternatives and goals are often established in advance. • The expert system can eventually replace the human decision maker. Decision Support System • Extract or gain knowledge from a computer system • Facilitates decision making • Unstructured environment • Alternatives may not be fully realized yet • Use goals and the system data to establish alternatives and outcomes, so a good decision can be made
 What is the biggest difference between a Decision Support System and an MIS 1. DSS’s are interactive and ad hoc 2. DSS’s focus on transforming information into knowledge 3. MIS’s focus on transforming data into information 4. All of the above 10
What is the biggest difference between a Decision Support System and an MIS 1. DSS’s are interactive and ad hoc 2. DSS’s focus on transforming information into knowledge 3. MIS’s focus on transforming data into information 4. All of the above 10
 What is the biggest difference between an MIS and TPS 1. in a TPS there is no analysis 2. an MIS focuses on reports 3. an TPS focuses on updating a database 4. All of the above 10
What is the biggest difference between an MIS and TPS 1. in a TPS there is no analysis 2. an MIS focuses on reports 3. an TPS focuses on updating a database 4. All of the above 10
 How is the analysis different for a MIS vs. DSS 1. MIS: Analysis involves computing aggregates 2. MIS: Analysis involves creating useful charts and graphs 3. DSS: Connects information with decisions 10
How is the analysis different for a MIS vs. DSS 1. MIS: Analysis involves computing aggregates 2. MIS: Analysis involves creating useful charts and graphs 3. DSS: Connects information with decisions 10
 Some Interesting Applications of Expert Systems • Triage – Medical Diagnosis (Medical Expert System) – User enters symptoms – System makes diagnosis – Doctors collective expertise is captured in the system • Patriot Missile Guidance System – Radar identifies Scud missile – System steers Patriot missile to it intercepts Scud missile – Laws of physics, expert knowledge about missile trajectory is captured in the system • Financial Decision Making – Currency Trading
Some Interesting Applications of Expert Systems • Triage – Medical Diagnosis (Medical Expert System) – User enters symptoms – System makes diagnosis – Doctors collective expertise is captured in the system • Patriot Missile Guidance System – Radar identifies Scud missile – System steers Patriot missile to it intercepts Scud missile – Laws of physics, expert knowledge about missile trajectory is captured in the system • Financial Decision Making – Currency Trading
 Expert System Categories • Decision Making – buy/sell – risk/no risk – rain/ no rain • Trouble Shooting / Diagnosis • Selection/Classification – Tell me what you see, expert system figures out what it really is. . . • Process Monitoring and Control – Robot control, assemblyline control, missile control – Hello welcome to Dell; how can I help you? – Suddenly an idiot seems • Design/Configuration – Specify what you want, like an expert system figures out specifically how to do it.
Expert System Categories • Decision Making – buy/sell – risk/no risk – rain/ no rain • Trouble Shooting / Diagnosis • Selection/Classification – Tell me what you see, expert system figures out what it really is. . . • Process Monitoring and Control – Robot control, assemblyline control, missile control – Hello welcome to Dell; how can I help you? – Suddenly an idiot seems • Design/Configuration – Specify what you want, like an expert system figures out specifically how to do it.
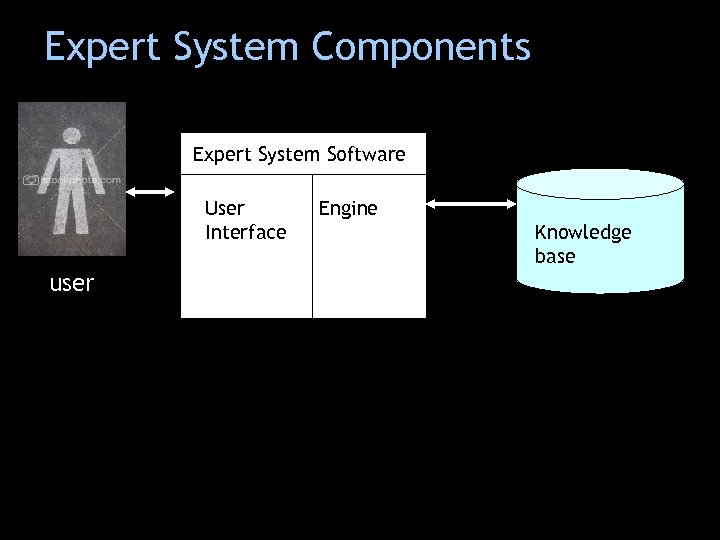 Expert System Components Expert System Software User Interface user Engine Knowledge base
Expert System Components Expert System Software User Interface user Engine Knowledge base
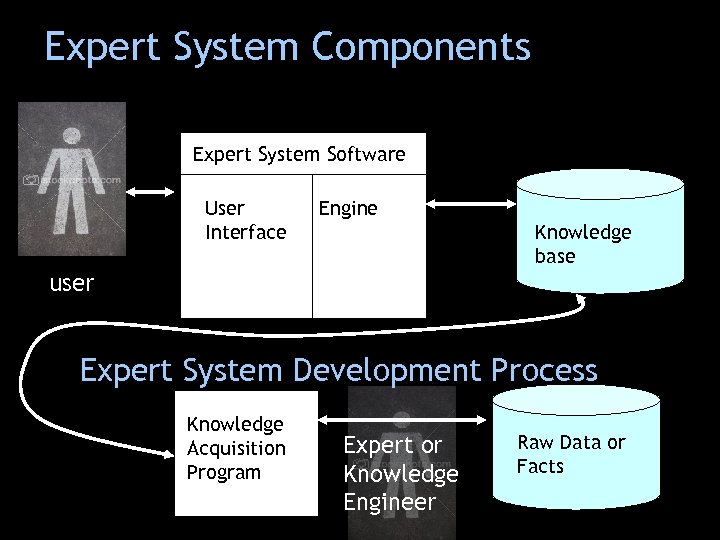 Expert System Components Expert System Software User Interface Engine Knowledge base user Expert System Development Process Knowledge Acquisition Program Expert or Knowledge Engineer Raw Data or Facts
Expert System Components Expert System Software User Interface Engine Knowledge base user Expert System Development Process Knowledge Acquisition Program Expert or Knowledge Engineer Raw Data or Facts
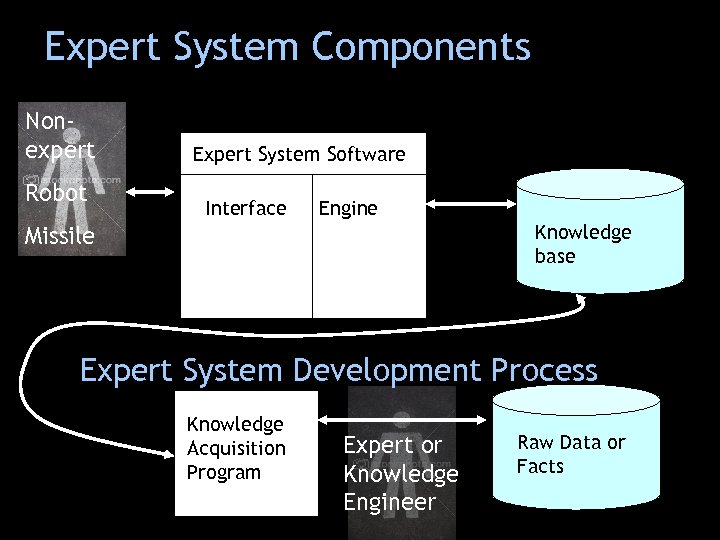 Expert System Components Nonexpert Robot Expert System Software Interface Engine Knowledge base Missile Expert System Development Process Knowledge Acquisition Program Expert or Knowledge Engineer Raw Data or Facts
Expert System Components Nonexpert Robot Expert System Software Interface Engine Knowledge base Missile Expert System Development Process Knowledge Acquisition Program Expert or Knowledge Engineer Raw Data or Facts
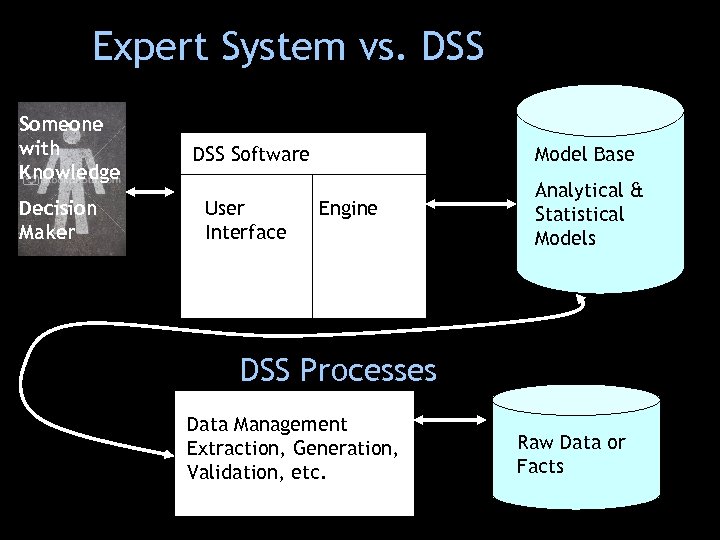 Expert System vs. DSS Someone with Knowledge Decision Maker DSS Software Model Base User Interface Analytical & Statistical Models Engine DSS Processes Data Management Extraction, Generation, Validation, etc. Raw Data or Facts
Expert System vs. DSS Someone with Knowledge Decision Maker DSS Software Model Base User Interface Analytical & Statistical Models Engine DSS Processes Data Management Extraction, Generation, Validation, etc. Raw Data or Facts


