26a9b6b815dd5d4e01bda241a5bb82eb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 10
 DS 3 T 2: Data Handling, Control and Distributed Computing Kjeld v. d. Schaaf 4 September 2006 DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
DS 3 T 2: Data Handling, Control and Distributed Computing Kjeld v. d. Schaaf 4 September 2006 DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
 DS 3 T 2 progress report • Data Handling, Control and Distributed Computing …study the optimal signal handling and data processing issues …will address the optimal distribution of processing tasks and the most cost-effective technology for delivering it …bring in the LOFAR system design knowledge and experience • Objectives – System level architectural design of data processing – Technology exploration…and technology road mapping on processing resources – Software modelling and architectural design DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
DS 3 T 2 progress report • Data Handling, Control and Distributed Computing …study the optimal signal handling and data processing issues …will address the optimal distribution of processing tasks and the most cost-effective technology for delivering it …bring in the LOFAR system design knowledge and experience • Objectives – System level architectural design of data processing – Technology exploration…and technology road mapping on processing resources – Software modelling and architectural design DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
 Progress so far • Chip technology – Scope: signal processing (station) and data processing (central/correlator) – Analysed and modelled processing tasks in SKA telescope; formulated key performance indicators and design drivers – Considering custom full ASIC, based on existing IP blocks and system components – Evaluate performance of current high-end chips and extensions – Presented first results at future correlator workshop – Research collaboration with IBM: learn the real design issues DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
Progress so far • Chip technology – Scope: signal processing (station) and data processing (central/correlator) – Analysed and modelled processing tasks in SKA telescope; formulated key performance indicators and design drivers – Considering custom full ASIC, based on existing IP blocks and system components – Evaluate performance of current high-end chips and extensions – Presented first results at future correlator workshop – Research collaboration with IBM: learn the real design issues DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
 Progress so far (2) • Chip technology and correlators; design approach – Special attention to the LOFAR correlator design – Software centric architecture • Very short development time (~5 man-year) • Short development period (~2 years) • Due to large knowledge and product buy-in – Compilers, debuggers – Communication library, control/timing protocols – Flexibility and extendibility – Presented at correlator workshop – Reference LOFAR documentation and papers – Approach to be included in software system design DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
Progress so far (2) • Chip technology and correlators; design approach – Special attention to the LOFAR correlator design – Software centric architecture • Very short development time (~5 man-year) • Short development period (~2 years) • Due to large knowledge and product buy-in – Compilers, debuggers – Communication library, control/timing protocols – Flexibility and extendibility – Presented at correlator workshop – Reference LOFAR documentation and papers – Approach to be included in software system design DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
 Progress so far (3) • Software architectural design – In context of SKA computing TF – Control system • Extensions of LOFAR and KAT, x. NTD designs • Scaling to many-elements stations (esp. AA and FPA); • Draft SKA memo – Multi-observations • Explicit observation controll components • Mapping onto instrument resources • Many contraints on automated scheduler – Analysed and algorithms identified – Proto types available in LOFAR project DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
Progress so far (3) • Software architectural design – In context of SKA computing TF – Control system • Extensions of LOFAR and KAT, x. NTD designs • Scaling to many-elements stations (esp. AA and FPA); • Draft SKA memo – Multi-observations • Explicit observation controll components • Mapping onto instrument resources • Many contraints on automated scheduler – Analysed and algorithms identified – Proto types available in LOFAR project DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
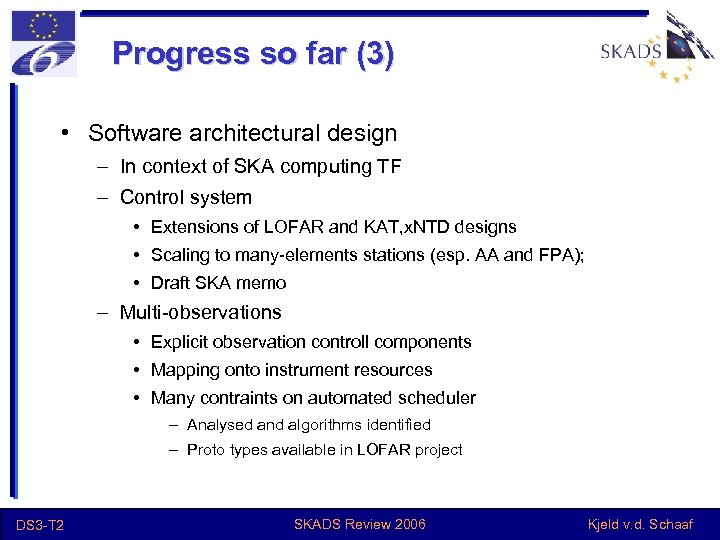
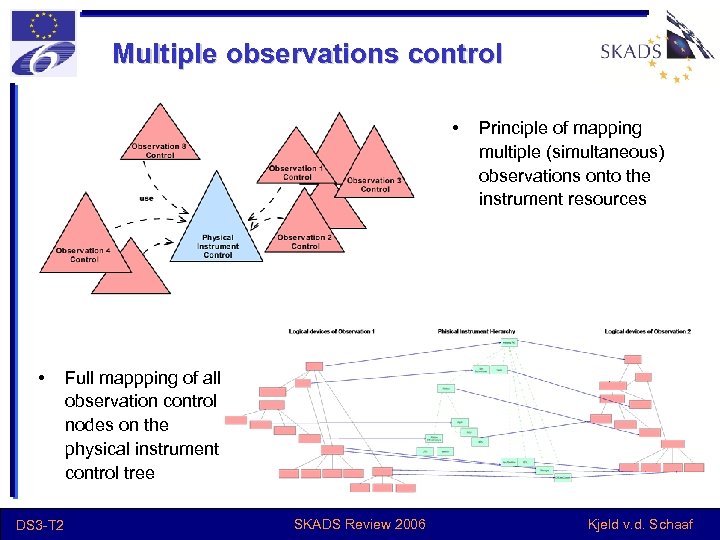 Multiple observations control • • DS 3 -T 2 Principle of mapping multiple (simultaneous) observations onto the instrument resources Full mappping of all observation control nodes on the physical instrument control tree SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
Multiple observations control • • DS 3 -T 2 Principle of mapping multiple (simultaneous) observations onto the instrument resources Full mappping of all observation control nodes on the physical instrument control tree SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
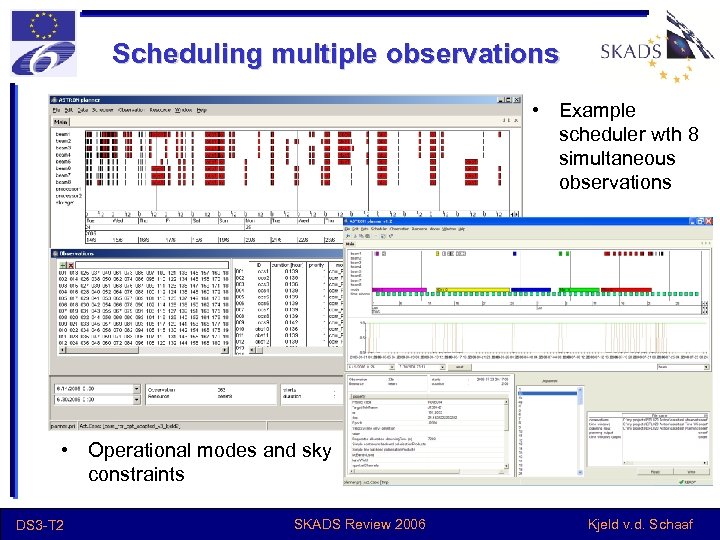 Scheduling multiple observations • Example scheduler wth 8 simultaneous observations • Operational modes and sky constraints DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
Scheduling multiple observations • Example scheduler wth 8 simultaneous observations • Operational modes and sky constraints DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
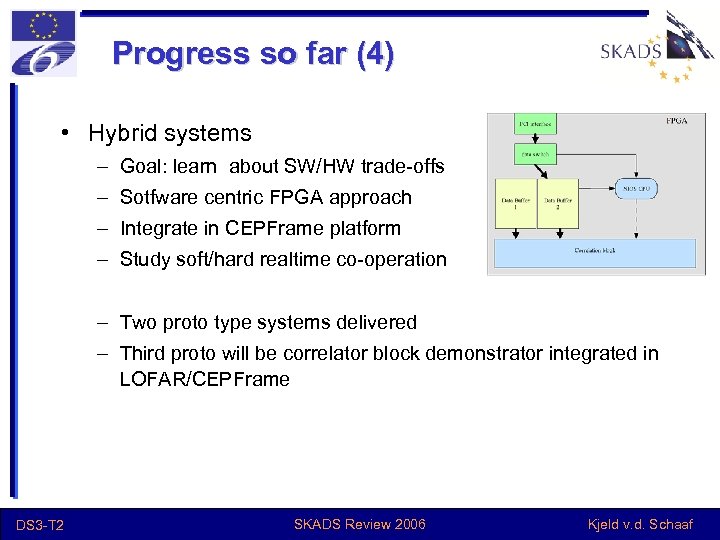 Progress so far (4) • Hybrid systems – Goal: learn about SW/HW trade-offs – Sotfware centric FPGA approach – Integrate in CEPFrame platform – Study soft/hard realtime co-operation – Two proto type systems delivered – Third proto will be correlator block demonstrator integrated in LOFAR/CEPFrame DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
Progress so far (4) • Hybrid systems – Goal: learn about SW/HW trade-offs – Sotfware centric FPGA approach – Integrate in CEPFrame platform – Study soft/hard realtime co-operation – Two proto type systems delivered – Third proto will be correlator block demonstrator integrated in LOFAR/CEPFrame DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
 Next steps • Experience input from LOFAR project ongoing • Major activities next year: – Reference architectural models (system and software) – Software cost models – Next generation chip technology and industry link • Deliverables: evaluation reports, reference designs, whitepaper input DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
Next steps • Experience input from LOFAR project ongoing • Major activities next year: – Reference architectural models (system and software) – Software cost models – Next generation chip technology and industry link • Deliverables: evaluation reports, reference designs, whitepaper input DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
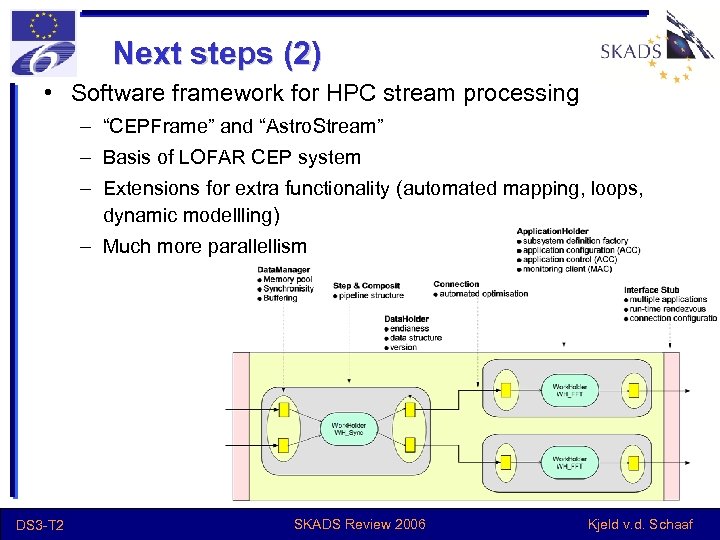 Next steps (2) • Software framework for HPC stream processing – “CEPFrame” and “Astro. Stream” – Basis of LOFAR CEP system – Extensions for extra functionality (automated mapping, loops, dynamic modellling) – Much more parallellism DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf
Next steps (2) • Software framework for HPC stream processing – “CEPFrame” and “Astro. Stream” – Basis of LOFAR CEP system – Extensions for extra functionality (automated mapping, loops, dynamic modellling) – Much more parallellism DS 3 -T 2 SKADS Review 2006 Kjeld v. d. Schaaf


