d93f63978bc6ea8084d219aaf81522fb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 137

Drugs Of Abuse Core Rounds, Feb 6, 2003 A. F. Chad, MD, CCFP M. Yarema, MD, FRCP


Case #1 • 24 yo M • Car chase -> Pulled over • • • by Crockett & Tubbs “I’m F__kin’ High!!” “I took a bunch of blow!!!” Agitated, sweating, , aggressive, h/a & cp Cuffed -> collapse -> no pulse EMS -> CPR, tubed, pulse, Tx to Hospital Now What?
Case #2 • 19 yo M • Out “dancing and • • Partying” Glow sticks & Soother & bottled water Euphoric, sl agitation Tachy, mydriatic, hyperthermic, brown urine What now?

Case # 3 • 21 yo “Hot Chick” • “Girls Night Out” • Dude with earrings, • • sideburns, soul patch & silver sequined cowboy hat buys her a drink She feels “off” Sluggish -> LOC Friends freak-> Sonny & Rico (who happened to be there undercover) escort to FHH What now?

Case # 4 • Same creepy dude looking • • • for love (after getting shut down by “Hot Chick”) Buys drink for previous 21 yo “Hot Chick’s” “Sweet looking friend” Drink tastes fine She becomes sleepy, “out of it”, separated from friends Wakes up in strange apt. No memories of night out What’s up?

Case # 5 • 32 yo Cletus from • • • Spokane EMS called re explosion inside trailer He comes out agitated, aggressive, wielding axe “detained” by our Miami Vice heroes and escorted to FHH Tachy, HTN, psychotic What’s up?
Case # 6 • 18 yo F • Dancing all night • Ate some powder given by a Kellogg’s rep • Feels like she’s floating • Nystagmus, “out of it” • What’s up?

Outline • Cocaine • History, pharmacology, presentation, complications, treatment • MDMA • History, pharmacology, presentation, complications, treatment • GHB • History, pharmacology, presentation, complications, treatment • Methamphetamine • History, pharmacology, presentation, complications, treatment • Ketamine • History, pharmacology, presentation, complications, treatment • Flunitrazepam • History, pharmacology, presentation, complications, treatment

USA Controlled Substances Act 1984

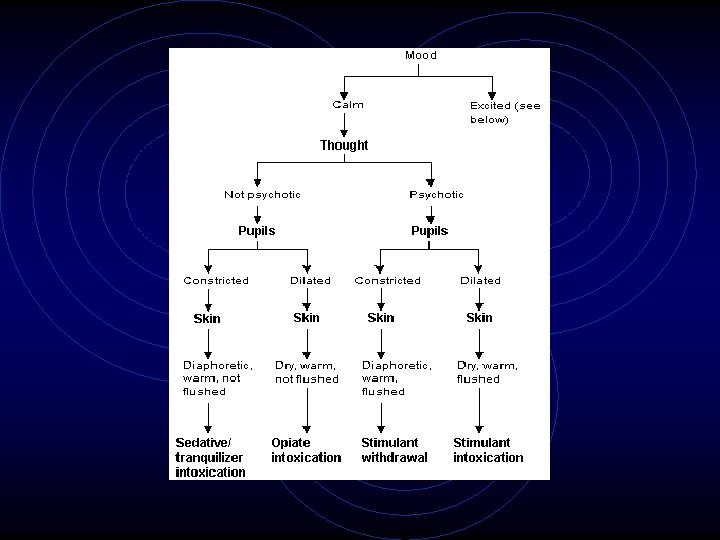
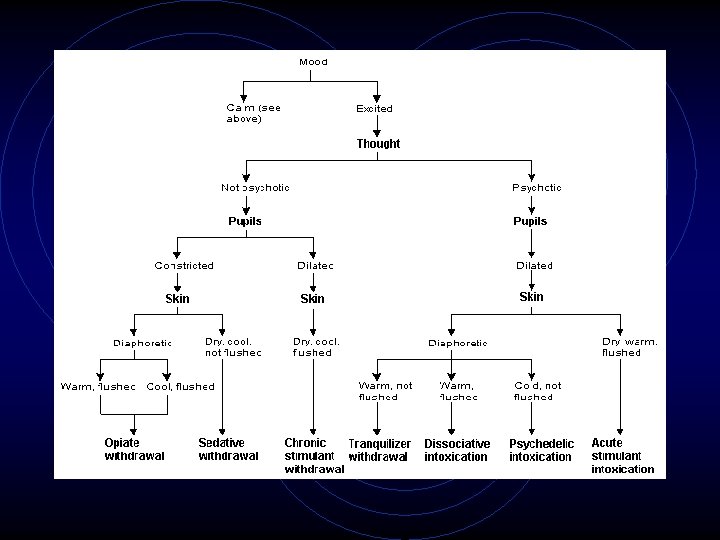
A couple general approach slides

COCAINE Blow


Cocaine • • • From Coca Leaves Use noted from 2000 B. C. 1859 Spanish MD’s use as Rx 1863 French wine with 6 mg cocaine sold 1884 William Stewart Halsted does 1 st Cocaine nerve block • Halsted: 1 st cocaine impaired MD on record • 1893 cocaine related deaths noted • 1914 Harrison Narcotics Act bans non-Rx cocaine

Cocaine in the USA (New Springsteen hit? ) • 2000: 926, 000 new users • average of 1 st time users: 20 years • 27. 8 million (12. %) Americans ages 12 or older tried cocaine at least once • 4. 2 million (1. 9%) used cocaine in the past year • 1. 7 million (0. 7%) used cocaine w/i the month • peak use in 1985: 5. 7 million Americans ( 3% of the population)

Rock, Blow, Snow • benzoylmethylecgonine • leaves of Erythroxylon coca: shrub indigenous to Peru, Bolivia, Mexico, West Indies and Indonesia • crystalline alkaloid: C 17 H 21 NO 4 • Commonly in cocaine HCl form • Ester-type local anaesthetic

Jimmy Crack Pipe & He Don’t Care • Remove HCl via ether extraction = crack • Frees the basic cocaine molecule = “free basing” • Crack -> cracking sound when smoked • Vaporizes @ 98 degs C -> no ruining • Allows for smoking a bowl

Cocaine Pharmacology • 1 st - blocks norepinephrine uptake • 2 nd - causes norepinephrine release • 3 rd - moderate release and reuptake blockade of dopamine & serotonin • Has Na+ & K+ channel blockade effects

Cocaine Pharmacology • Fat soluble -> easily crosses BBB • Stimulates CNS esp in Limbic area with dopamine -> “high as a frikkin’ kite” • metabolized by hepatic esterases and plasma pseudocholinesterase • benzoylecgonine & ecgonine methylester are active metabolites

Cocaine: How Can You do it? • ALL mucous membranes • IV (100% bioavailability) • Eaten (20 -30% bioavailability) • • • poor absorption in stomach, good in duodenum Smoked (crack) (20 -30% bioavailability) 1 inch line = 25 -100 mg coke Spoon = 5 -25 mg coke LD 50 = 1 gm (po)


When am I gonna Get High? • Inhalation • 7 s onset, 1 -5 min peak, 20 min duration, 40 -60 min half-life • IV • 15 s onset, 3 -5 min peak, 20 -30 min duration, 40 -60 min half-life • Nasal • 3 min onset, 15 min peak, 45 -90 min duration, 60 -90 min half-life • Oral • 10 min onset, 60 min peak, 60 min duration, 60 -90 min half- life

When Coke Alone Ain’t Enough • Et. OH: Metabolite • Ethylbenzoylecgonine (cocaethylene) Increases T 1/2 and Lowers LD 50 • Nicotine • increases sympathetic response • Heroin • speedball = IV/smoke heroin, then smoke crack, moderates withdrawal -> higher doses

3 Phases of Toxicity • Phase I - Early stimulation • CNS: Mydriasis, headache, bruxism, nausea, • • vomiting, vertigo, nonintentional tremor , tics, preconvulsive movements, pseudohallucinations CVS - HTN / Hypo. TN, tachy / brady, pallor Respiratory - Increased rate & Vt Temperature - Elevated Behavioral - Euphoria, elation garrulous talk, agitation, apprehension, excitation, restlessness, verbalization of impending doom, emotional instability

3 Phases of Toxicity • Phase II - Advanced stimulation • CNS: Malignant encephalopathy, seizures and status, decreased responsiveness, increased DTR, incontinence • CVS: HTN, tachy; ventricular dysrhythmias, weak, rapid, irregular pulse and hypotension; peripheral cyanosis • Respiratory: Tachypnea, dyspnea, gasping, irregular breathing • Temperature: Severe hyperthermia

3 Phases of Toxicity • Phase III - Depression and premorbid state • CNS: Coma, areflexia, pupils fixed and dilated, flaccid paralysis, and loss of vital support functions • CVS: Circulatory failure, cardiac arrest (ventricular fibrillation or asystole) • Respiratory: Respiratory failure, gross pulmonary edema, cyanosis, agonal respirations,

Cocaine: Not so safe • • • CVS CNS Respiratory Packers / Stuffers Other

Cocaine Dysrhythmias • ST, SVT, A. Flutter, A. Fib, VT, V. Fib, • • AVB, Asystole, long QT ->Td. P Like a type 1 A Na+ blocker (procainamide, quinidine) Direct SNS overload? Cardiotoxic -> arrythmogenic foci Accelerated atherosclerosis

Rx Cocaine Dysrhythmias • Depends on Rhythm • NO B-blocker, procainamide, quinidine • Na. HCO 3 may be of help • Beckman KJ, Parker RB, Hariman RJ, et al. Hemodynamic and electrophysiological actions of cocaine: Effects of sodium bicarbonate as an antidote in dogs. Circulation 1993; 83: 1799 -1807. • Benzos if 2 nd to increased catacholamines • Lidocaine is safe if indicated • Shih RD, Hollander JE, Burstein JL, et al. Clinical safety of lidocaine in patients with cocaineassociated myocardial infarction. Ann Emerg Med
Coke: close to the Heart • Vasoconstriction, plt clumping, thrombi • Higher O 2 demand • Direct myocardial toxicity • Goldfrank LR, Hoffman RS. The cardiovascular effects of cocaine. Ann Emerg Med 1991; 20: 165 -175. • Accelerated atherogenesis • Minor RL Jr, Scott BD, Brown DD, et al. Cocaineinduced MI in patients with normal coronary arteries. Ann Intern Med 1991; 115: 797 -806.

Coke Chest Pain • • • Most common complaint post coke use 6% will have MI (rookies or crack heads) Often classic sounding cp ECG non-diagnostic in 60% CK-MB and TNT NOT increased by coke alone (cardiac event) • CK increased (rhabdo)

Coke & CP • Need observation x 12 hours (consensus) • 33% develop bad stuff • Serial ECG & enzymes • 0. 2% problems post 12 hours • Hollander JE. The management of cocaineassociated myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 1267 -1272.

Coke & CP • • Is 6 hours good enough? 197 pts Check enzymes 0, 3, 6 hrs If all N + no ECG changes -> OK • Kushman SO, Storrow AB, Liu T et al. Cocaine- associated chest pain in a chest pain center. Am J Cardiol 2000; 85: 394 -396.



MI with your Coke? • Same Rx as normal but NO B-blockers!!!! • phentolamine or verapamil? • Hollander JE, Carter WA, Hoffman RS. Use of phentolamine for cocaine-induced myocardial ischemia. N Engl J Med 1992; 327: 361. • Benzos as good as NTG as good as both • Weber JE, Chudnofsky CR, Boczar M, et al. Cocaineassociated chest pain: How common is MI? Acad Emerg Med 2000; 7: 873 -885.

Thrombolysis & Coke? • Crap? • Hollander JE, Burstein JL, Hoffman RS, et al. Cocaineassociated MI: Clinical safety of thrombolytic therapy. Cocaine Associated Myocardial Infarction (CAMI) Study Group. Chest 1995; 107: 1237 -1241. • Good? • Mueller PD, Benowitz NL, Olson KR. Cocaine. Emerg Med Clin North Am 1990; 8: 481 -493. • Be REALLY Careful? • Hollander JE, Wilson LD, Leo PJ, et al. Complications from the use of thrombolytic agents in patients with cocaine associated chest pain. J Emerg Med 1996; 14: 731 -736.

Well, we have Angio in Calgary • Case reports suggest ok • Shah DM, Dy TC, Szto GY, et al. PTCA and stenting for cocaine-induced AMI: A case report and review. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2000; 49: 447 -451.

Coke Shake • • • Seizures in 2 -10% Stoke not uncommon Need CT BENZOS!!!! Phenobarb GA

Strokey Cokey • • • Most common cause of stroke in young 60% users get h/a post use Stroked pts usually h/a 3 -6 hours post Can cause SAH, ischemia, ICH, vasculitis NEED CT +/- LP if concerned

Crack Lung • Distinct entity 1 -12 hours post smoking • fever, dyspnea, hemoptysis, hypoxia, chest pain, infiltrates, respiratory failure • Rx steroids (eosinophils on Bx) • Other Resp Problems • Upper airway burn, epiglotitis, asthma, pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, noncardiogenic pulmonary edema, pulmonary hemorrhage/infarction

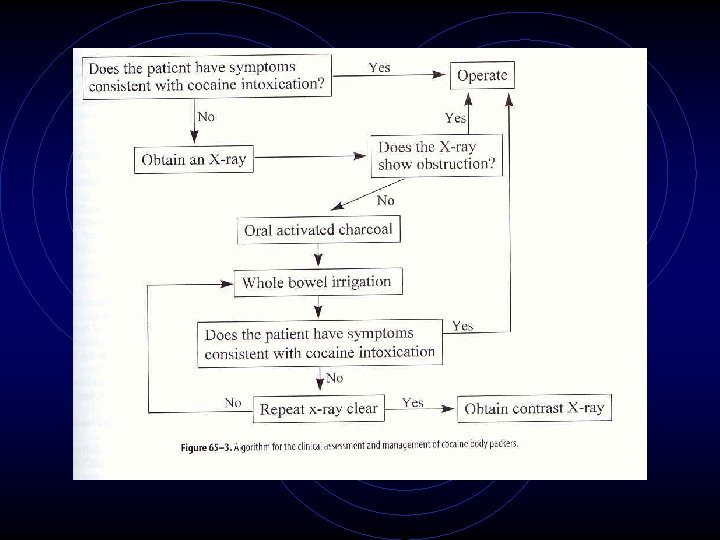
Snow Stuffers • • Hiding it from Crockett & Tubbs Quickly ingested, not prepared Toxicity!!! AC + whole bowel irrigation

Put it in my Crack Pack • • • Packers = well prepared packets of drug Large amounts Bowel obst, sudden death (bag bursts) + tox screen (95% sensitive) Xray, contrast, CT NO SCOPE!!! AC -> polyethylene glycol -> clear fluid Admit until all packets out Surgery if concerns

Other • Rhabdo • Normal Rx • Excited Delirium • Loss of pregnancy • Hyperthermia • Dopaminergic regulated

Pepsi vs Coke • • ABCD!!! Need monitors, IV’s, Tubes, O 2 Remove any residual cocaine from nasal use. Protect the patient from hypoglycemia, Rely on clinical findings re toxidrome Reassurance if the patient is oriented. Avoid physical or pharmacological restraints if possible. • Symptoms usually abate by 6 hours unless complications arise or coingested with longer acting agent (amphetamines)

Pepsi vs Coke • CBC, lytes, coags, glucose, U/A, CK, TNT, Bhcg, • • • ABG, creatinine, tox screen CXR ECG CT +/- LP Fancy tests NB: Urine screen for cocaine metabolites detects use within past 3 -4 days, sometimes as long as 3 weeks

Pepsi Drugs • BENZOS!!!! • As much as needed!!!! • Epi? • Still use in arrest • Lido? • Theoretically can worsen • B-Blockers? • BAD -> uncontrolled A stim • Even labetalol has 7: 1 beta: alpha effect ratio


Crank the Techno, Grab a Dasani, Soother & Glow Sticks Rave it Up!!!


MDMA 3, 4 Methylenedioxymethamphetamine Ecstasy E

E! Now • 1914 German Appetite Suppressant • • • “Who needs bratwurst when you are High? ” 1970’s adjunct to psychotherapy 1980’s big hit on the street 1985 DEA schedule 1 controlled substance 1990’s Rave culture’s drug of choice • Gross SR, Barrett SP, Shestowsky JS, Pihl RO. Ecstasy and drug consumption patterns: a Canadian rave population study. Can J Psychiatry 2002 Aug; 47(6): 546 -51

E Pharmacology • • • 3, 4 -methylenedioxy-methamphetamine Derivative of methamphetamine Has similarities to hallucinogen mescaline Similar to epinephrine and dopamine Not naturally occurring Amines (free bases or salts) Increased Norepinephrine release Blocks serotonin & dopamine reuptake Hepatic Metabolism • Cytochrome P 450 (CYP 2 D 6)

How can I score some E? • • • Check out a Rave Very high boiling point -> hard to inhale IV Snorting Orally most common • Onset 30 -60 mins • Peak levels = 2 hrs, T 1/2 = 8 -9 hrs • Tabs anywhere from 50 -150 mg • Birds, dolphins, pop culture

But I’m so Happy • Deaths not related to dose, rookies / chronic • Patel, Manish M, Bruemmer, Susan, Parramore, Constance S, Miller, Michael A. Pathology, Toxicology, Cause, and Manner of Death in MDMA-related Fatalities. Acad Emerg Med 2002 9: 533

Soothers & Glow Sticks • • General CVS Hyponatremia CNS Psych Hepatic Renal

I Love You Man! • Early (30 -60 mins): • anxiety, tachycardia, and elevated BP diaphoresis, bruxism, jaw clenching, paresthesias, dry mouth, increased psychomotor activity, blurred vision. • Peak (60 -90 mins): feelings of relaxation, euphoria, increased empathy and communication

I love you with all my Heart (what’s left of it) • • • Catacholamine & serotonin mediated Dysrhythmias HTN Hyperthermia Cardiotoxic

E is great, but I need to score me some 5 -HT • • Serotonin syndrome Massive 5 -HT release “vigorous” dancing, not enough H 20 hyperthermia, mental status changes, autonomic instability, altered muscle tone and/or rigidity, DIC, renal / hepatic failure

No Salt for me, the dancin’ fool • • • Hyponatremia Excess H 20 intake Excess sweating ADH release LOC, SZ, confusion

It’s all in your Head • • • SZ Stroke ICH SAH Retinal Hemorrhage

It’s all in your Mind • Long term psychiatric effects 2 nd to 5 -HT toxicity • Impairment of: Memory, executive fnc, anxiety / panic attacks, paranoia, severe depression • Harold Kalant. The pharmacology and toxicology of “ecstasy” (MDMA) and related drugs. CMAJ: Volume 165 • Number 7 • October 2, 2001

I’ll be Liver-ing it up • • Overwhelm enzymes? allergy? hyperpyrexia? Cytochrome P 450 • Metabolites interact with glutathione • ? Role for NAC?

I’ll be Liver-ing it up • Mild Hepatitis • Like viral hepatitis picture • jaundice, enlarged tender liver, increased bleeding tendency, raised liver enzyme levels, biopsy picture of acute hepatitis • Recovery over several wks to mos • Can have chronic attacks in chronic users

I’ll be Liver-ing it up • Severe Hepatitis • fulminant hepatic failure needing Transplant • Moderate severity • chronic fibrosis

I’m just kidney-ing • Rhabdomyalysis +/- ARF • direct toxicity, intense physical activity
E History • Central nervous system • Change in mental status, seizures, Anxiety, paranoia, Increased psychomotor activity, restlessness, Hyperthermia, hot flashes, Headache, Ataxia , Blurred vision, halos, Syncope • Cardiovascular • Palpitations, Chest pain • Gastrointestinal • Dry mouth, N&V, Abdo cramping, Anorexia • Skin • Diaphoresis, Piloerection • Urinary retention, Sexual dysfunction

E Physical • HEENT • Mydriasis, Nystagmus , Decreased VA, Bruxism, • CNS • Hyperthermia, psychomotor agitation, Hypervigilance, Agitation, anxiety, Ataxia, Hallucinations, • Cardiovascular • Tachycardia, Dysrhythmias, Hypertensive crisis • Respiratory • Resp distress /failure, noncardiogenic pulmonary edema • Diaphoresis, Abdo cramping, Muscle spasm, Sexual dysfunction, Urinary retention

E Tests • • • CBC, lytes (Na) glucose coags LFT’s U/A, CK, creatinine, Bhcg tox screen ABG Fancy tests as indicated

Down from Ecstasy • • • ABCD!!! Need monitors, IV’s, Tubes, O 2 Protect the patient from hypoglycemia, Rely on clinical findings re toxidrome Reassurance if the patient is oriented. Avoid physical or pharmacological restraints if possible.

Down from Ecstasy • • Charcoal Urine output / Foley Benzos!!! Hyperthermia • Undress the patient. • Apply evaporative cooling with water and a fan. • ice packs to the groin and axilla. • Iced gastric lavage may be considered. • Control shivering with benzos • Antipyretics are not useful. • Dantrolene?

GHB (GAMMAHYDROXYBUTYRATE) • Easy Lay • fantasy

HISTORY • 1963 -73: studied as a potential anesthetic but abandoned when it was found to have no analgesic effects and cause seizures • 1980’s: sold as a dietary supplement that enhanced bodybuilding and hastened weight loss (unproven) • 1990’s: popular for its intoxicating, euphoric and sexuallyenhancing effects, and therefore as a date-rape drug

HISTORY • 1990: FDA declares that GHB is unsafe and illicit unless consumed under FDA-approved, MDsupervised protocols. OTC sales banned. • 1995: CNS GHB receptors discovered, solidifying GHB’s status as a neurotransmitter • 1997: FDA issues second warning against GHB

HISTORY • 1999: listed as schedule III under Controlled Drugs and Substances Act in Canada • prohibits possession, possession from trafficking, importation, exportation, possession for purposes of exportation and production of this drug and related products • legitimate distribution and possession under controlled conditions for medical or scientific purposes is allowed

HISTORY • March 13, 2000: classified as a Schedule 1 substance in the U. S. • definition of Schedule I: • the drug has a high potential for abuse • the drug has no currently accepted medical use in treatment in the United States • there is a lack of accepted safety for use of the drug under medical supervision

HISTORY • Schedule 1 (con’t) • illicit manufacture or trafficking of GHB can result in a sentence of up to 20 years in prison • if death occurs, a life sentence can be imposed • currently being studied for treatment of: • narcolepsy (GHB increases REM sleep efficiency) • opioid withdrawal • ethanol withdrawal

WHAT IS GHB? • naturally-occurring 4 carbon molecule • • (short chain fatty acid) formed from metabolism of GABA and GBL found in basal ganglia, kidney, heart, skeletal muscle, and brown fat rapidly absorbed by oral and IV routes small volume of distribution not bound to plasma proteins

WHAT IS GHB? • • exhibits clinical effect within 15 minutes elimination t 1/2 = 27 -35 minutes crosses BBB and placenta binding sites in cortex, midbrain, substantia nigra, basal ganglia, and hippocampus • mostly eliminated in expired air as CO 2, 25% eliminated in urine
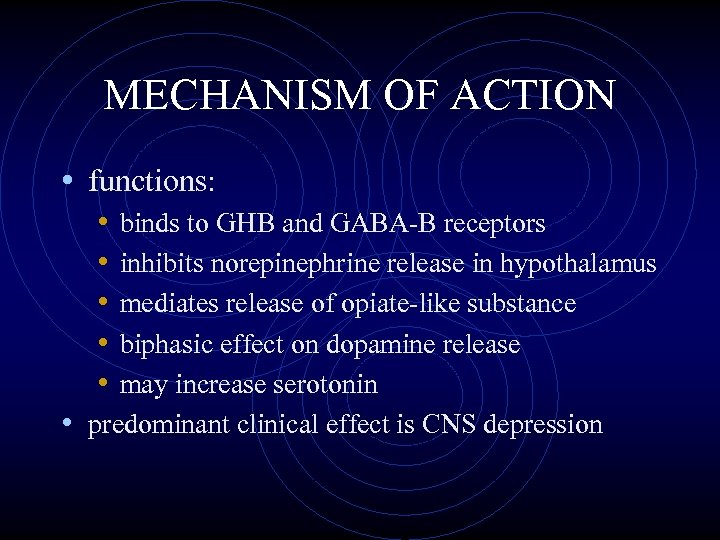
MECHANISM OF ACTION • functions: • • • binds to GHB and GABA-B receptors inhibits norepinephrine release in hypothalamus mediates release of opiate-like substance biphasic effect on dopamine release may increase serotonin • predominant clinical effect is CNS depression
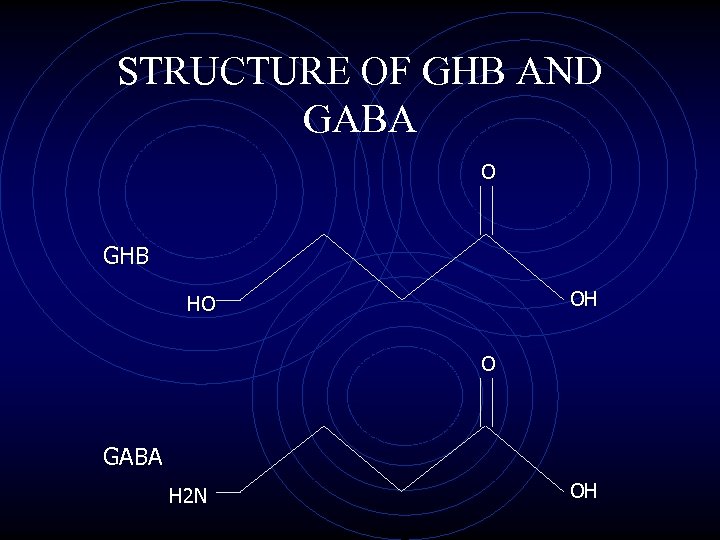
STRUCTURE OF GHB AND GABA O GHB OH HO O GABA H 2 N OH

A RECIPE FOR GHB • GHB’s ease of preparation has led to its easy accessibility • formed by ester hydrolysis of GBL in the presence of sodium or potassium hydroxide (e. g. add wood cleaner or paint remover to lye) • improper preparation can lead to caustic burns due to undissolved sodium hydroxide and citric acid • multiple internet sites provided simple instructions on how to make GHB in the kitchen (now outlawed)
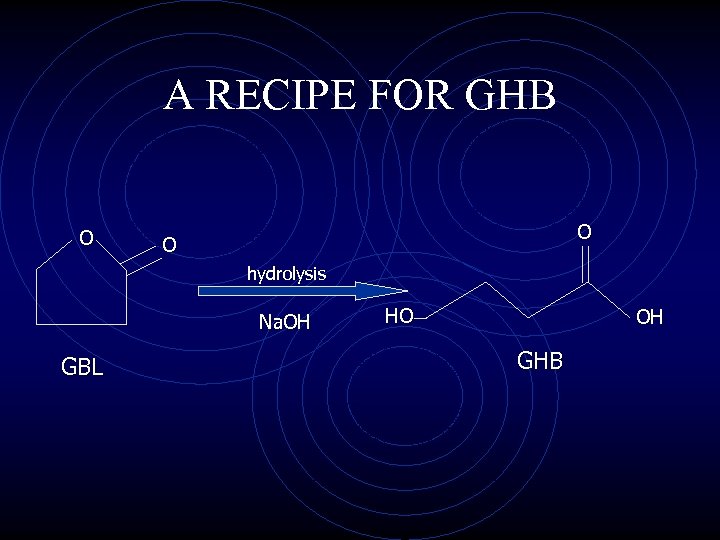
A RECIPE FOR GHB O O O hydrolysis Na. OH GBL HO OH GHB
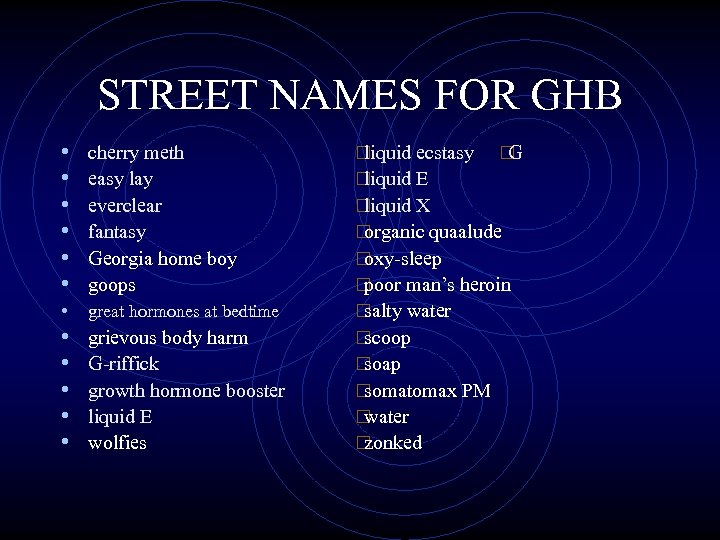
STREET NAMES FOR GHB • • • cherry meth easy lay everclear fantasy Georgia home boy goops • great hormones at bedtime • grievous body harm • G-riffick • growth hormone booster • liquid E • wolfies liquid ecstasy G liquid E liquid X organic quaalude oxy-sleep poor man’s heroin salty water scoop soap somatomax PM water zonked

COST FOR A “HIT” • GHB sold as a either a colorless, odorless liquid or a grainy, white or sandy-colored powder • dispensed in water-bottle cap doses (equivalent to hotel shampoo bottle or vial of Liquid Paper) • cost per capful ranges from $5 -10 U. S. and has the approximate equivalent intoxication of 26 oz. of hard liquor

DOSE EQUIVALENTS • usually 1 -2 capfuls taken or poured into a drink • 1 vial or capful can contain 3 -10 doses with anywhere from 3 -20 g per dose • 1 tsp. ~ 2. 5 g • 4 tbsp. ~ 30 g

USES • as a CNS depressant, thereby inducing an intoxicated state • as a sedative to reduce the effects of stimulants (cocaine, amphetamine, and ephedrine) or hallucinogens • for prevention of withdrawal symptoms
CLINICAL FEATURES • H + N: • nystagmus • Resp: • bradypnea • apnea • CVS: • bradycardia • orthostatic hypotension • hypertension

CLINICAL FEATURES • GI: • nausea • vomiting • increased salivation • esophageal burns • GU: • incontinence • hematuria

CLINICAL FEATURES • MSK: • hypotonia • extrapyramidal symptoms • DERM: • profuse sweating

CLINICAL FEATURES • CNS: • altered LOC (confusion --> coma) • euphoria • delusions and hallucinations • headache • ataxia • seizures or seizure-like activity • agitation when stimulated • emergence phenomena

KEY CLINICAL FEATURES • extreme combativeness in the face of near or total respiratory failure (esp. when trying to intubate) • brief duration of coma (1 -2 hours) with rapid awakening • effects enhanced by co-ingestion of other CNS depressants

DOSE/EFFECT RELATIONSHIP

INVESTIGATIONS • mild hyperglycemia • hypernatremia if the sodium salt of GHB is used • ECG • U waves (with normal potassium) • 1 st degree AV block • A fib • RBBB • ventricular ectopy • wide QRS (inconsistently found)

INVESTIGATIONS • GHB detection • multiple assays described for detection (GC, MS) • qualitative spot urine test described but not commonly in use • undetectable in blood or urine after 8 hours postingestion in doses up to 4. 5 g • assays not available locally

MANAGEMENT • ABC’s and good supportive care (ventilation and oxygenation, fluids, sedation PRN) • GI decontamination if co-ingestants suspected • not expected to be of benefit in GHB,

REVERSAL AGENTS • naloxone • not useful • flumazenil • not useful • may interfere with use of benzos for sedation • physostigmine • limited effect • 2 case reports demonstrating improved LOC after physostigmine • neostigmine • limited effect

REVERSAL AGENTS • overall, these agents have limited use in management of GHB toxicity as most patients improve with good supportive care

SEQUELAE • symptoms last from 3 -6 hours if not intubated and ~ 6 hours if intubated • longer if mixed with other CNS depressants • emergence phenomena may occur once consciousness returns • myoclonus, altered mental status, combativeness, insomnia • can last for 3 -12 days • dizziness may last for up to 2 weeks

Flunitrazepam

Flunitrazepam: Rohypnol

History of Roofies • 1975 Used as anaesthetic & sleeping pill Latin America, Europe, Asia • 1995 changed to Sched 3 drug • 1996 Drug-Induced Rape Prevention and Punishment Act

Pharm Roof • Benzodiazepine • Benzo receptors in CNS enhance affinity of GABA receptors for GABA • Influx Cl -> hyperpolarization of cell membranes -> inhibits action potentials • Hepatic CP 450 metabolism • T 1/2 = 16 -35 hrs

Pharm Roof • Tablet form, can be crushed to powder • Tasteless, odourless, colourless • Hoffman-La. Roche now added a green colour to aid detection • PO, snorted, parenteral, crushed and slipped into drinks • Onset 30 mins, peak 2 hrs, lasts 8 hrs • 10 X more potent than Diazepam

On the Roof again • • • Amnesia Anxiolysis Sedation Hypnosis Anticonvulsant Muscle relaxation H/A Hypo. TN Resp depression

You won’t go on a date with me!? !? We’ll see about that…Wanna Drink? • Original date rape drug • Amnesia induced while under influence • "Some patients may have no recollection of any awakenings occurring in the 6 to 8 hours during which the drug exerts its action. "

What’s on the Roof? • • • Decreased LOC Resp depression Amnesia Hypotonia Hypo. TN Effects potentiated by Et. OH, other seds, hyps

Get off the roof • ABC’s • Supportive care • Consider sexual assault • rape kit, CPS, social work • Flumazenil • May not show up on benzo drug screen • May show up on specific urinalysis test up to 72 hrs post ingestion • Important in forensic cases

Methamphetamine Crystal Meth


Methamphetamine • • • Blue Mollies Chalk Crank Crystal Glass Go-Fast Ice LA Glass Meth • • • Methlies Quick Mexican Crack Quartz Shabu Sketch Speed Stove Top West Coast Yellow Bam

History of Meth • • • 1919 made by Japanese pharmacologist 1930 structure confirmed 1930’s Rx asthma & rhinitis 1937 reported meth = smarter, more alert WW 2 military kept “up” 1970 Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act: Sched 2 drug • 1991 Desert Storm troops felt “up” • 2000’s “War on Meth” all over USA (Midwest)

Meth for Dummies • Easy to make, lots of fun on web • Derivative of phenylethylamine • Ephedrine, chloroephedrine, or methylephedrine reduced by hydriodic acid & red phosphorus -> Meth • Lipid soluble pure base, volatile @ Room T • H 2 O soluble as HCl salt

Meth for Dummies • Blocks pre-synaptic uptake of norepinephrine & dopamine • Prevents catacholamine storage • Prevents cytoplasmic catacholamine destruction • T 1/2 = 10 -20 hrs

Meth for Dummies 2: ICE • Smoked form • Purify meth HCl via adding to H 2 O and heating to 80 -100 degs • Supersaturated sol’n -> cools -> ppt to ICE • Put on foil -> heat -> inhale -> high

I gonna get me my Meth fix! • ALL mucous membranes, oral, inhaled, • • snorted, smoked, IV, IM Peak 30 mins post IM / IV Peak 2 -3 hrs po CSF levels @ 80% of plasma Hepatic metabolism, urinary excretion • glucuronide and glycine addition


Meth Lab • From Rolling stone, paraphrased from a Midwest Detective: • “ 2 things you find at a meth lab: tonnes of porn and more guns than you can imagine. . . More often than not, the labs are full of booby traps”

Meth Lab • Can make Meth ANYWHERE • Contaminated “home brew” from impure ingredients • Lead, mercury, solvents, volatile meth often present • Need big-time WHIMS action + HAZMAT suits if going in

Meth • Similar presentation • ++++ longer T 1/2 • ? faster onset? • Easy to make vs Coke • Similar routes • Short acting • Quick onset • “Trip down South to warmer climes to visit gents in silk suits” • Haldol Rx of Choice, (benzos still good) • Benzos Rx of Choice

Haldol better than Benzos? • Better sedation and return of VSs in RCT • N=146 • Richards JR, Derlet RW, Duncan DR: Methamphetamine toxicity: treatment with a benzodiazepine versus a butyrophenone. Eur J Emerg Med 1997 Sep; 4(3): 130 -5


Ketamine • Special K, vitamin K, K, Super K, Ketaset, Jet, Super Acid, Green, Purple, Mauve, and Special LA Coke

Special K pharmacology • • 1960 - dissociative anaesthetic Parke-Davis 1970’s abuse begins 1980’s New Age Spiritualists adopt 2000 -> techno is king

K Pharm • Binds to PCP receptor in N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) channel • Non-competitive inhibitor of glutamate • Effects on other receptors • non-NMDA-glutamate, nicotinic & muscarinic, sigma, monoaminergic, opioid, Ca & Na channels • Stimulates NO release • Inhibits reuptake Norepinephrine, dopamine, 5 -HT
K Pharm • Hepatic CP 450 metabolism • Oral undergoes +++ 1 st pass • Norketamine is active metabolite • Urinary excretion • T 1/2 = 2 hrs • Dosing: 15 -300 mg • High therapeutic index • Difficult to OD

Is this Special K in a box? • IV • onset 1 min, lasts 30 mins • IM • Onset variable, lasts 30 mins • PO • Onset 30 mins, lasts 3 hrs • Snorted & Smoked • Onset 15 mins, lasts 1 hr • Liquid form heated and dried to powdered form

What’s so special about it? • • • Out of body, floating sensation Derealization Positive & Negative Sx of Schizophrenia Emotional w/d, psychomotor slowing Flashbacks & hallucinations Short & Long lasting memory lapses • Curran HV, Monaghan L. In and out of the K-hole: a comparison of the acute and residual effects of ketamine in frequent and infrequent ketamine users. Addiction. 2001 May; 96(5): 749 -60.

What’s so special about it? • CNS: • nystagmus, mydriasis, agitation, slurred speech, delirium, floating sensations, hypertonus, rigidity, anxiety, vivid dreams, hallucinations, seizures, bizarre facial expressions, loss of coordination, bizarre limb movements, dystonic reactions, persistent repetition of acts or words, shouting, • Rhabdomyalysis • CVS • palpitations, tachycardia, HTN, increased CO • Resp • respiratory depression, apnea, pulmonary edema,

K in the ED • Tests: • As indicated, CK • Can do ketamine level, but hard to get & why? • Rx: • Benzos, supportive, Rx rhabdo • ? Haldol • Giannini AJ, Underwood NA, Condon M. Acute ketamine intoxication treated by haloperidol: a preliminary study. Am J Ther. 2000 Nov; 7(6): 389 -91.

Although safe. . . • Breitmeier D, Passie T, Mansouri F, Albrecht K, Kleemann WJ. Autoerotic accident associated with self-applied ketamine. Int J Legal Med. 2002 Apr; 116(2): 113 -6

Shout Outs • Dr. Mark Yarema • Info, “borrowed slides” • Don “Sonny Crockett” Johnson & Philip Michael “Rico Tubbs” Thomas • For keepin’ it real • Need I say more?

Don’t Do Drugs!
d93f63978bc6ea8084d219aaf81522fb.ppt