376864b3f79917a82fc6482592cc2db2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 93
 Drops on patterned surfaces Halim Kusumaatmaja Alexandre Dupuis Julia Yeomans
Drops on patterned surfaces Halim Kusumaatmaja Alexandre Dupuis Julia Yeomans
 Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
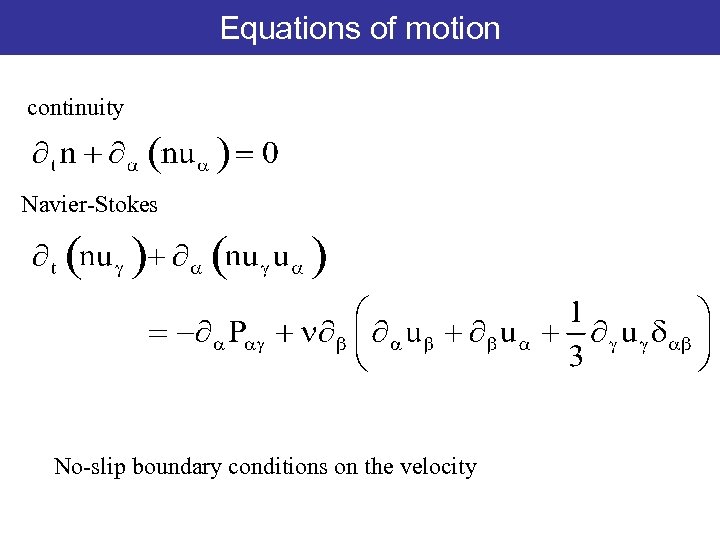 Equations Navier-Stokes equations of motion continuity Navier-Stokes No-slip boundary conditions on the velocity
Equations Navier-Stokes equations of motion continuity Navier-Stokes No-slip boundary conditions on the velocity
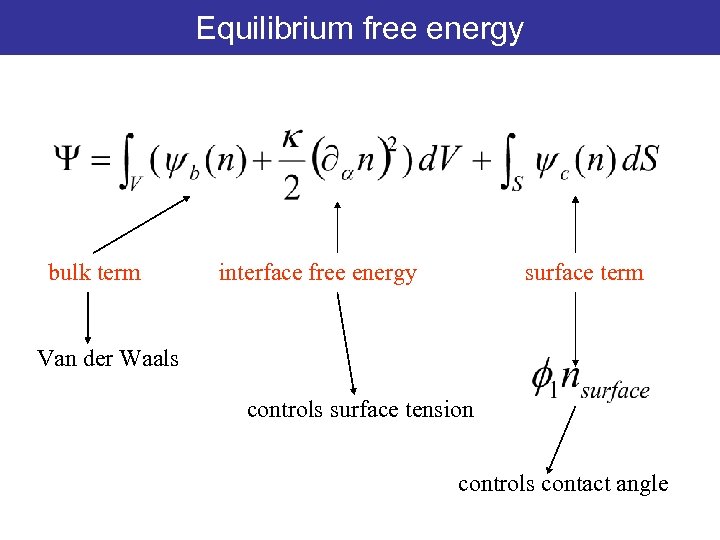 Equilibrium free energy bulk term interface free energy surface term Van der Waals controls surface tension controls contact angle
Equilibrium free energy bulk term interface free energy surface term Van der Waals controls surface tension controls contact angle
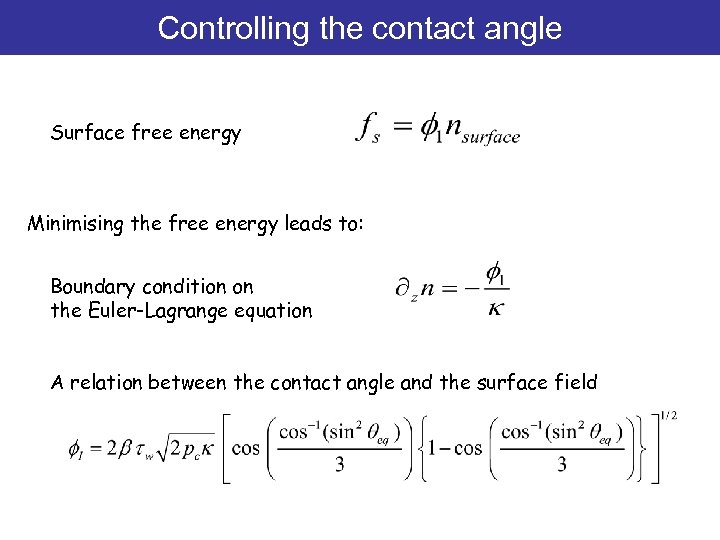
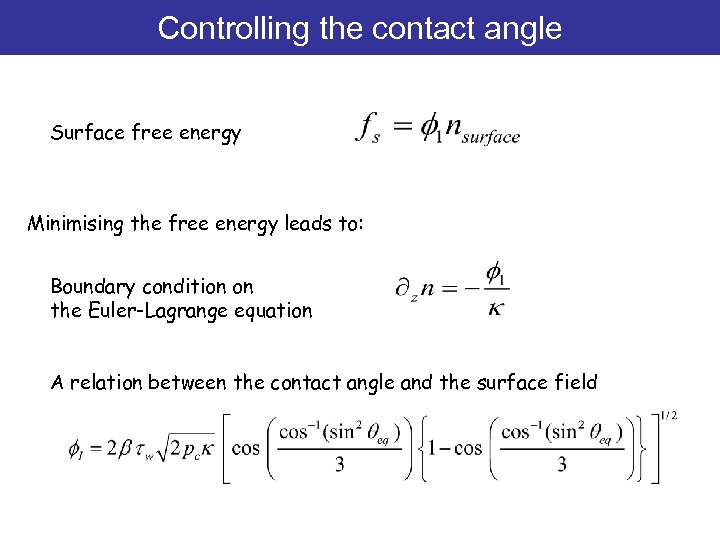 Controlling the contact angle Surface free energy Minimising the free energy leads to: Boundary condition on the Euler-Lagrange equation A relation between the contact angle and the surface field
Controlling the contact angle Surface free energy Minimising the free energy leads to: Boundary condition on the Euler-Lagrange equation A relation between the contact angle and the surface field
 Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
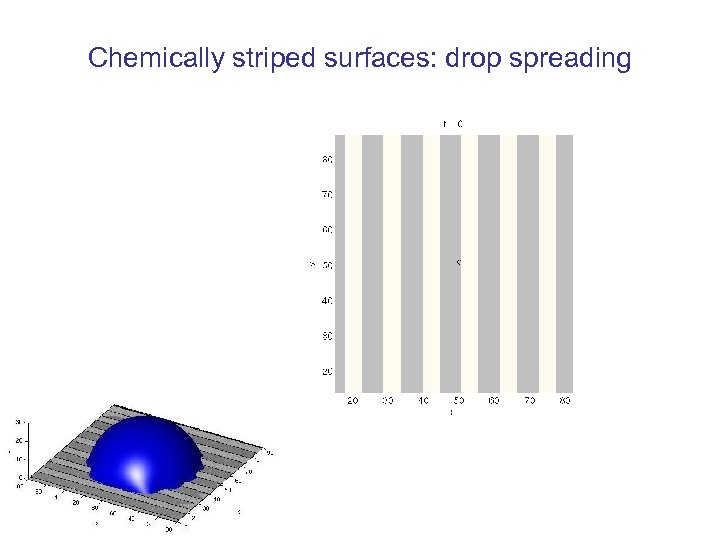 Chemically striped surfaces: drop spreading
Chemically striped surfaces: drop spreading
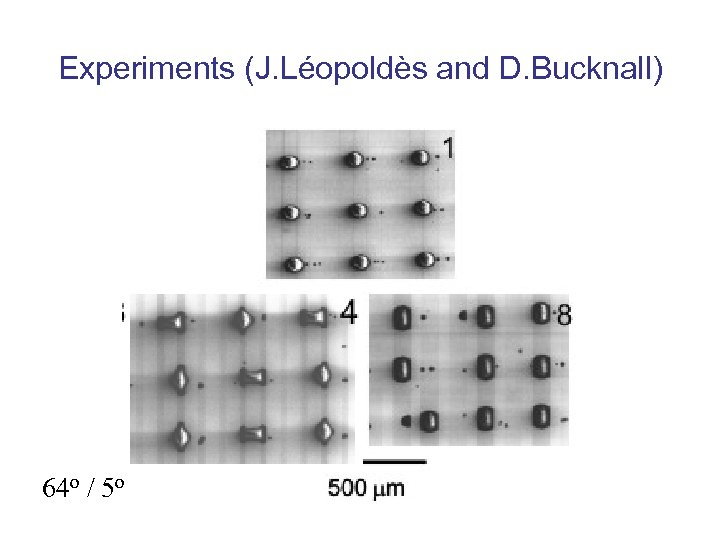 Experiments (J. Léopoldès and D. Bucknall) 64 o / 5 o
Experiments (J. Léopoldès and D. Bucknall) 64 o / 5 o
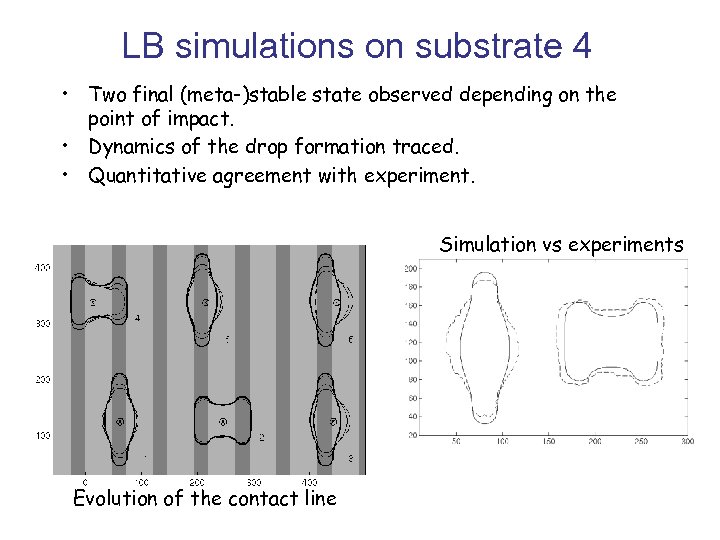 LB simulations on substrate 4 • Two final (meta-)stable state observed depending on the point of impact. • Dynamics of the drop formation traced. • Quantitative agreement with experiment. Simulation vs experiments Evolution of the contact line
LB simulations on substrate 4 • Two final (meta-)stable state observed depending on the point of impact. • Dynamics of the drop formation traced. • Quantitative agreement with experiment. Simulation vs experiments Evolution of the contact line
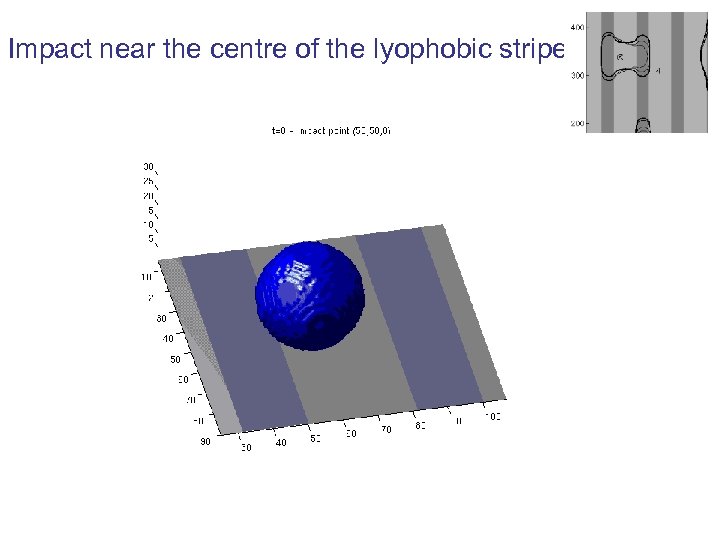 Impact near the centre of the lyophobic stripe
Impact near the centre of the lyophobic stripe
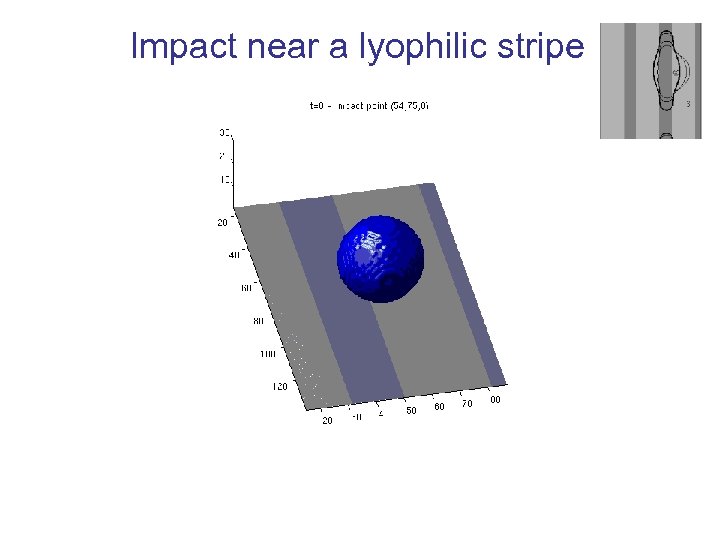 Impact near a lyophilic stripe
Impact near a lyophilic stripe
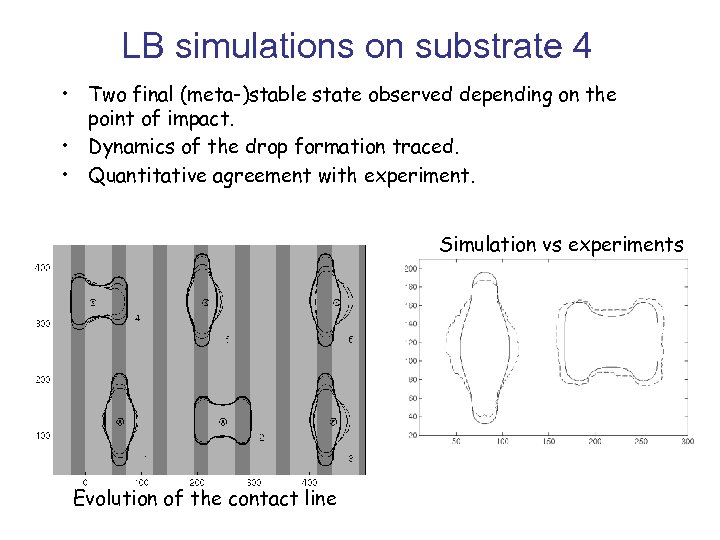 LB simulations on substrate 4 • Two final (meta-)stable state observed depending on the point of impact. • Dynamics of the drop formation traced. • Quantitative agreement with experiment. Simulation vs experiments Evolution of the contact line
LB simulations on substrate 4 • Two final (meta-)stable state observed depending on the point of impact. • Dynamics of the drop formation traced. • Quantitative agreement with experiment. Simulation vs experiments Evolution of the contact line
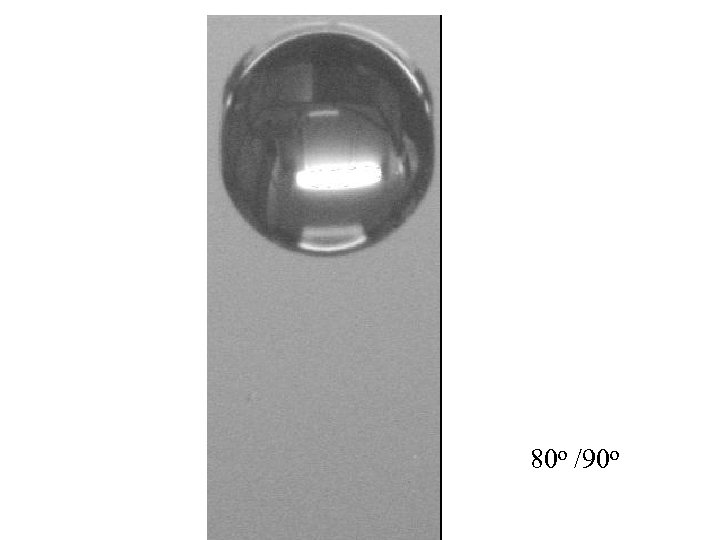 80 o /90 o
80 o /90 o
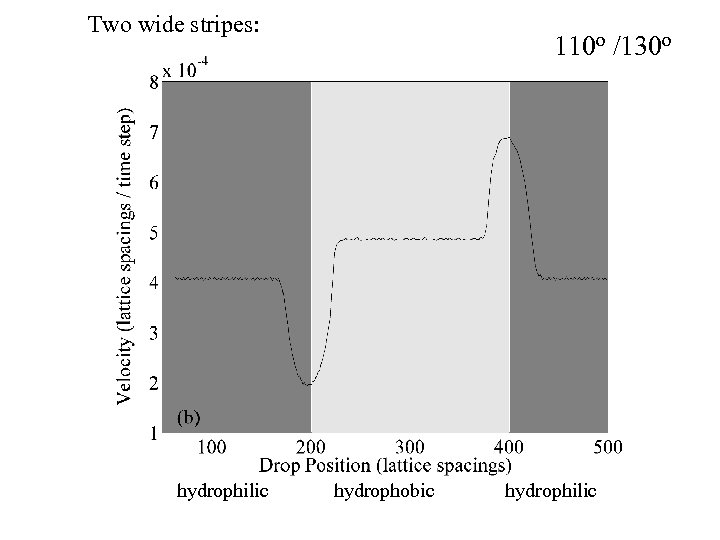 Two wide stripes: 110 o /130 o hydrophilic hydrophobic hydrophilic
Two wide stripes: 110 o /130 o hydrophilic hydrophobic hydrophilic
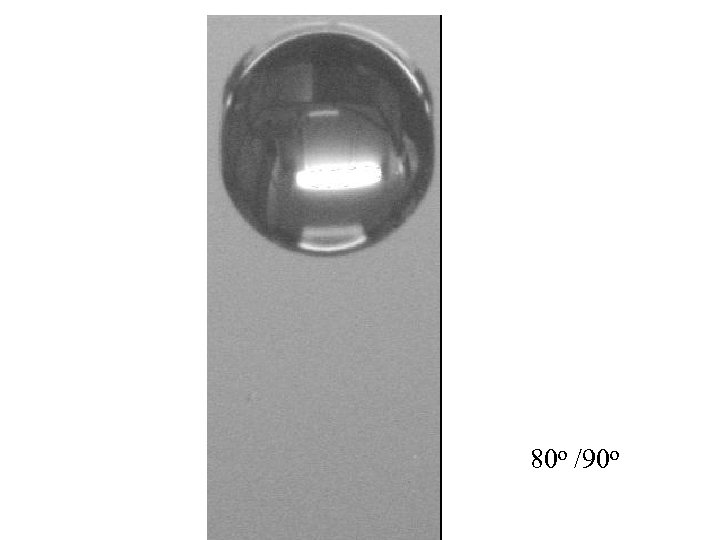 80 o /90 o
80 o /90 o
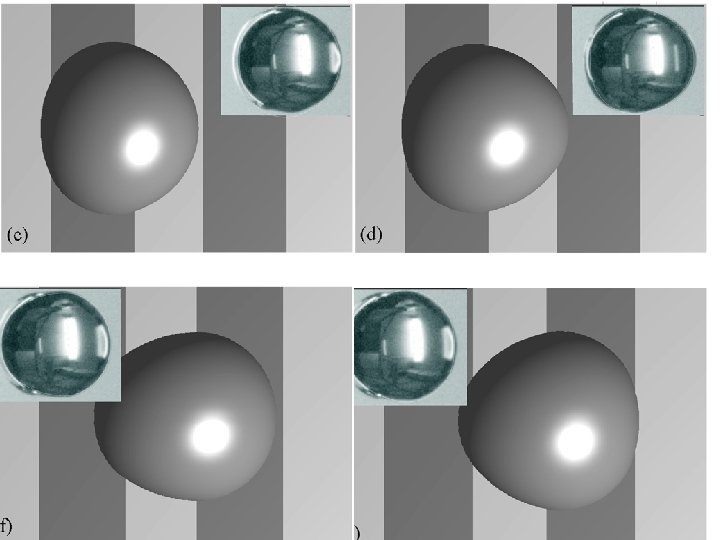
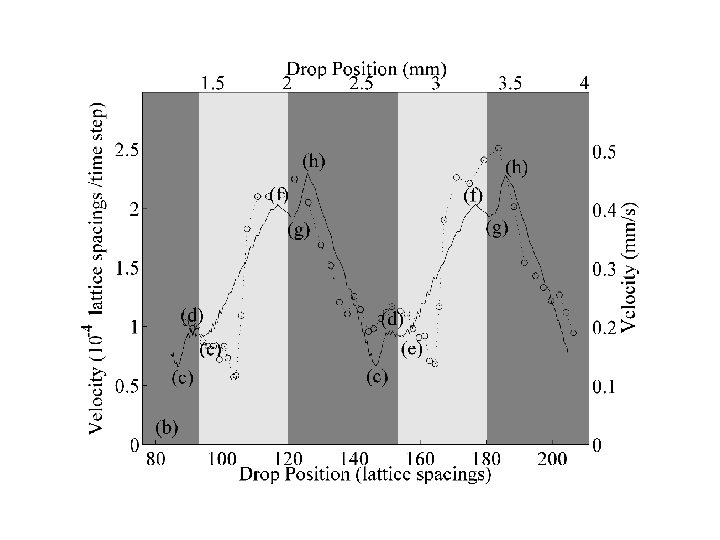
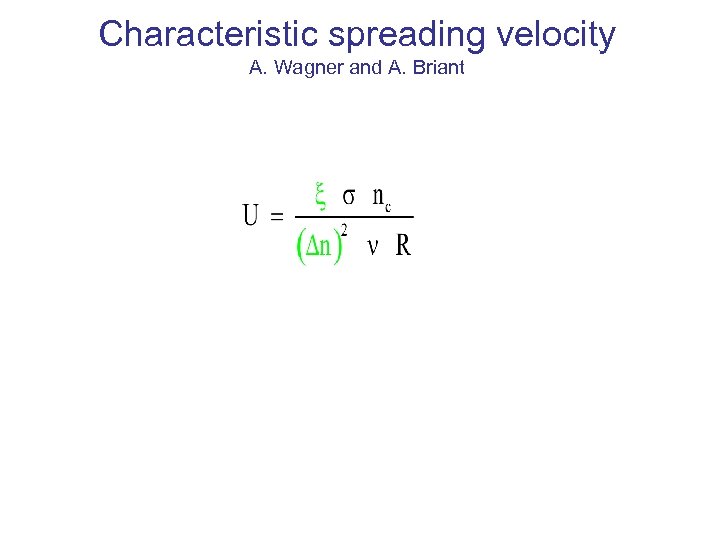 Characteristic spreading velocity A. Wagner and A. Briant
Characteristic spreading velocity A. Wagner and A. Briant
 Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
 Hysteresis
Hysteresis
 Hysteresis
Hysteresis
 Hysteresis
Hysteresis
 Hysteresis
Hysteresis
 Hysteresis
Hysteresis
 Hysteresis
Hysteresis
 Hysteresis
Hysteresis
 Hysteresis
Hysteresis
 Hysteresis
Hysteresis
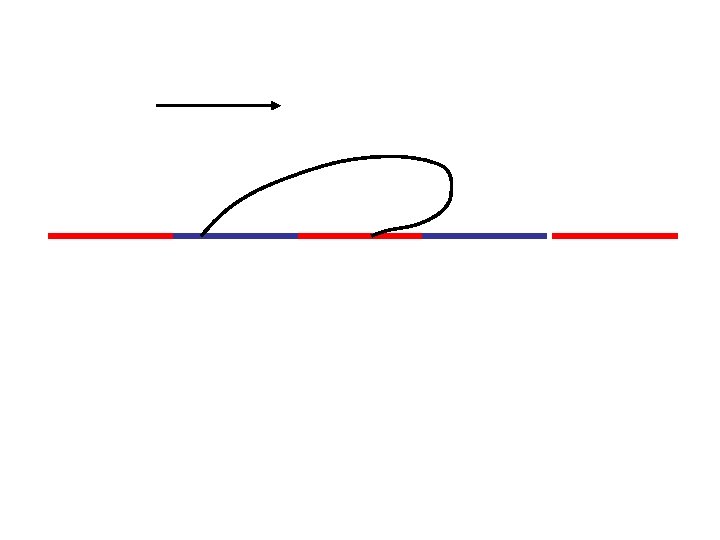
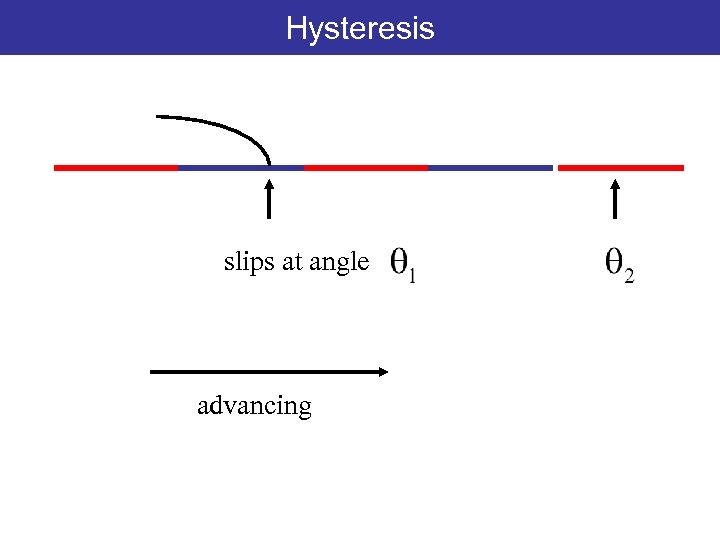 Hysteresis slips at angle advancing
Hysteresis slips at angle advancing
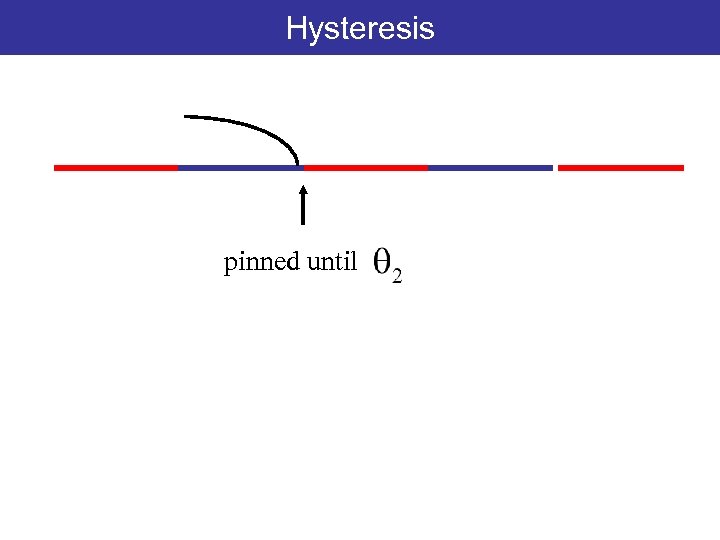 Hysteresis pinned until
Hysteresis pinned until
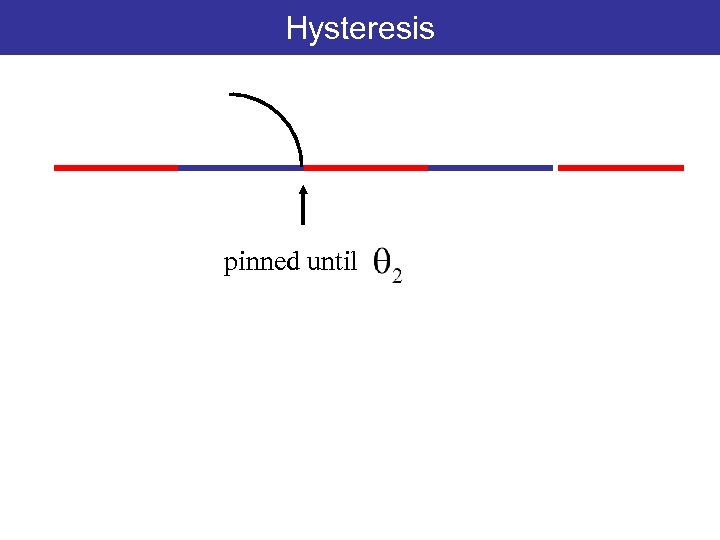 Hysteresis pinned until
Hysteresis pinned until
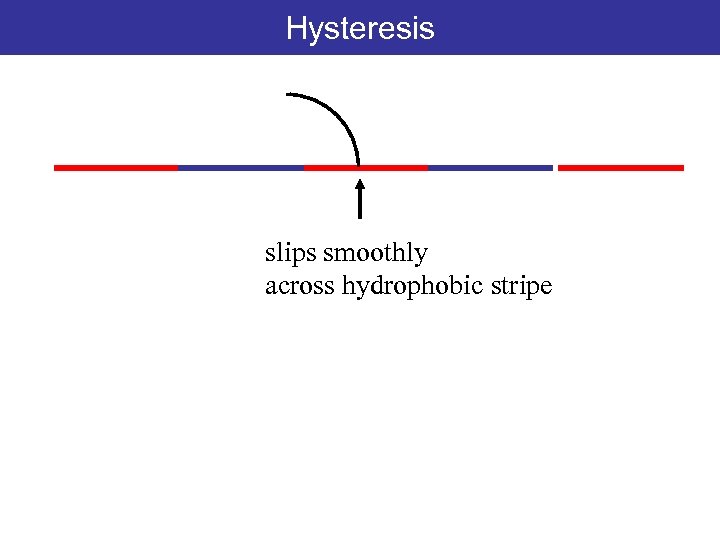 Hysteresis slips smoothly across hydrophobic stripe
Hysteresis slips smoothly across hydrophobic stripe
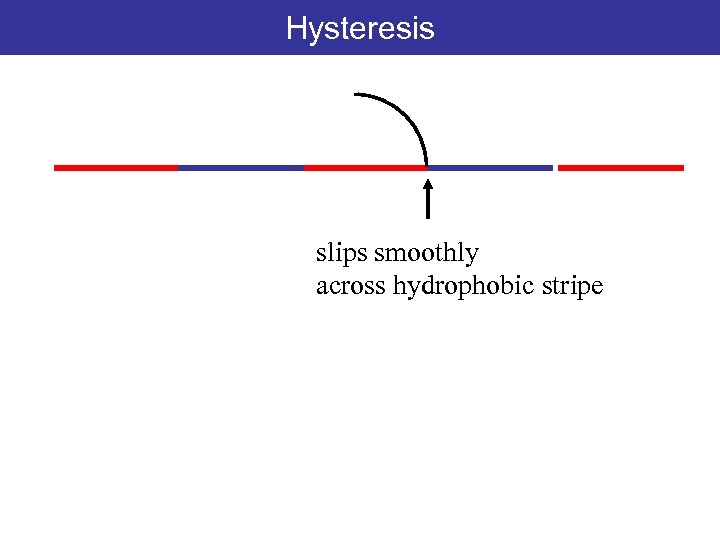 Hysteresis slips smoothly across hydrophobic stripe
Hysteresis slips smoothly across hydrophobic stripe
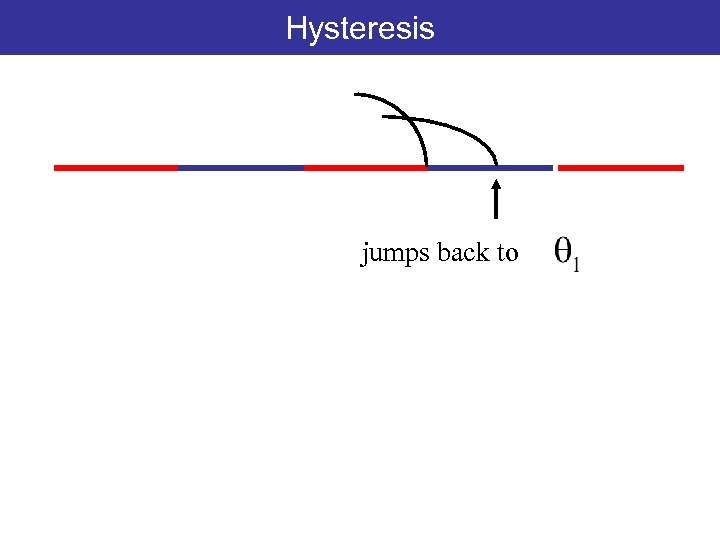 Hysteresis jumps back to
Hysteresis jumps back to
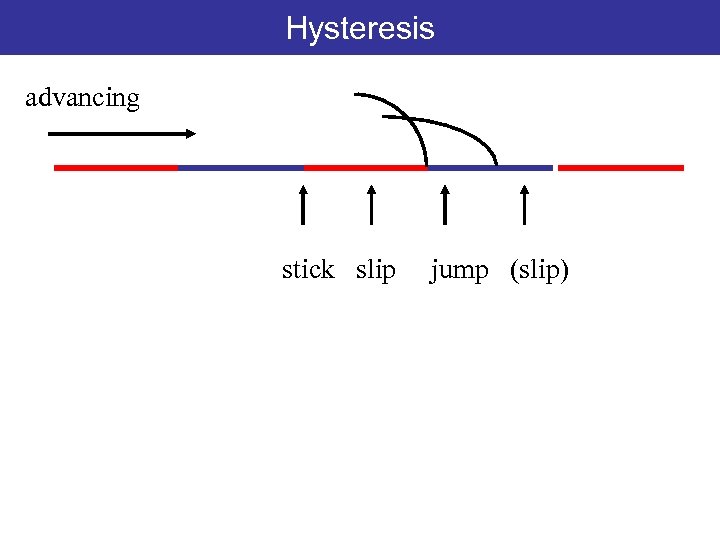 Hysteresis advancing stick slip jump (slip)
Hysteresis advancing stick slip jump (slip)
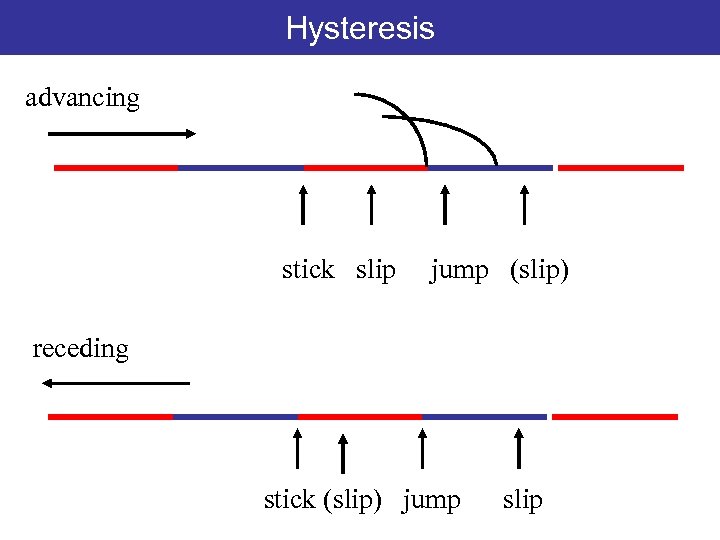 Hysteresis advancing stick slip jump (slip) receding stick (slip) jump slip
Hysteresis advancing stick slip jump (slip) receding stick (slip) jump slip
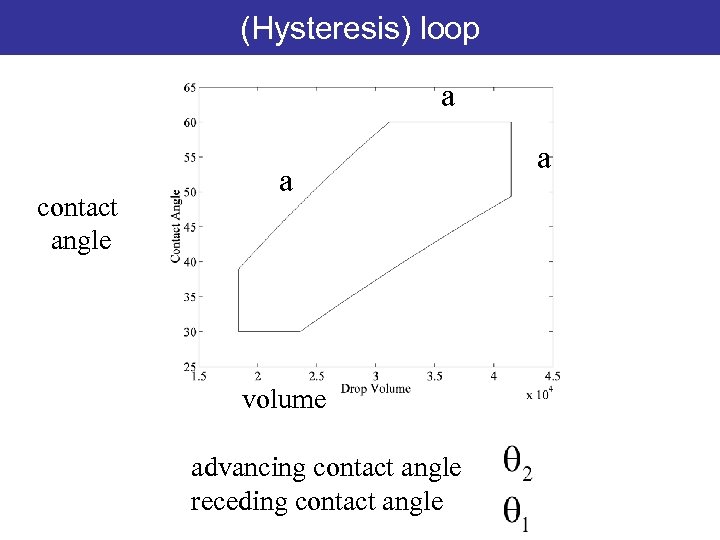 (Hysteresis) loop a contact angle a volume advancing contact angle receding contact angle a
(Hysteresis) loop a contact angle a volume advancing contact angle receding contact angle a
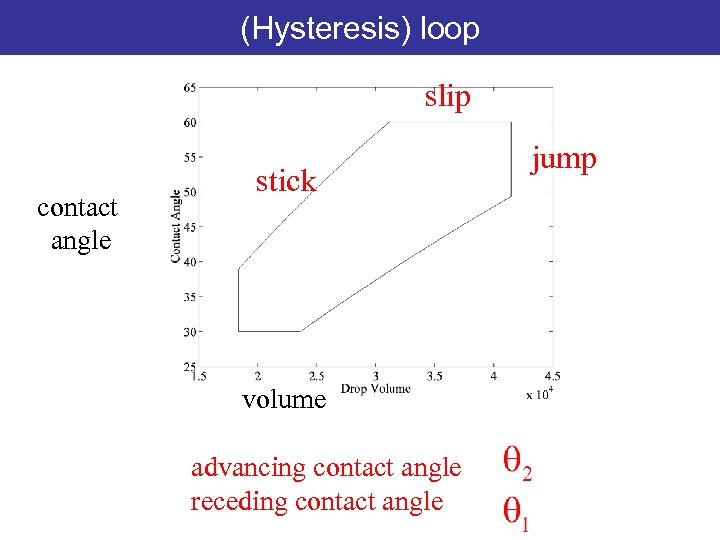 (Hysteresis) loop slip contact angle stick volume advancing contact angle receding contact angle jump
(Hysteresis) loop slip contact angle stick volume advancing contact angle receding contact angle jump
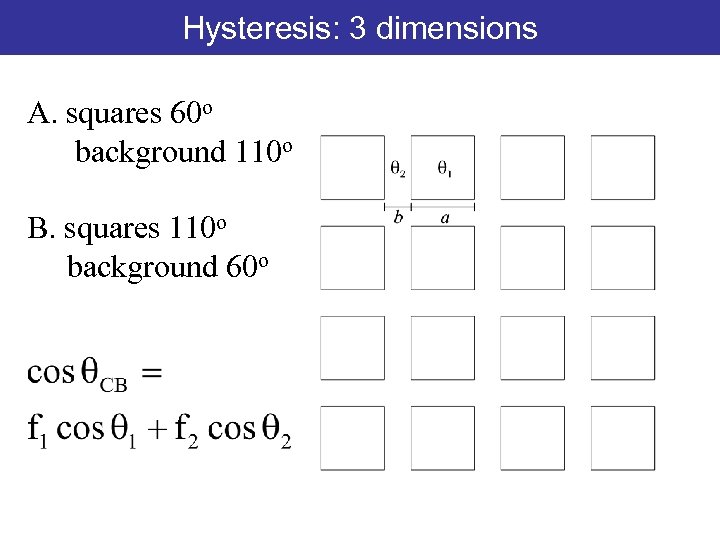 Hysteresis: 3 dimensions A. squares 60 o background 110 o B. squares 110 o background 60 o
Hysteresis: 3 dimensions A. squares 60 o background 110 o B. squares 110 o background 60 o
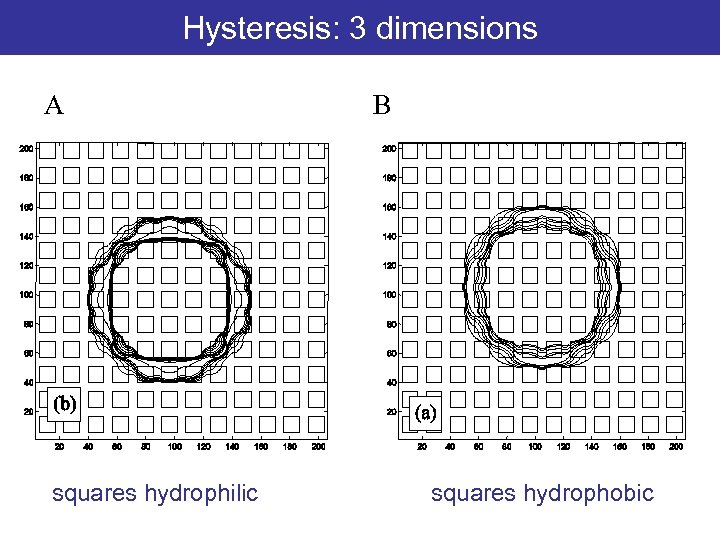 Hysteresis: 3 dimensions A squares hydrophilic B squares hydrophobic
Hysteresis: 3 dimensions A squares hydrophilic B squares hydrophobic
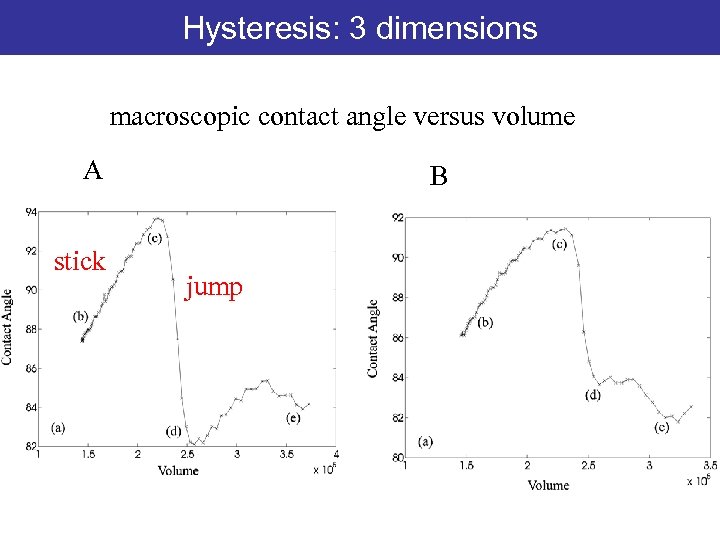 Hysteresis: 3 dimensions macroscopic contact angle versus volume A stick B jump
Hysteresis: 3 dimensions macroscopic contact angle versus volume A stick B jump
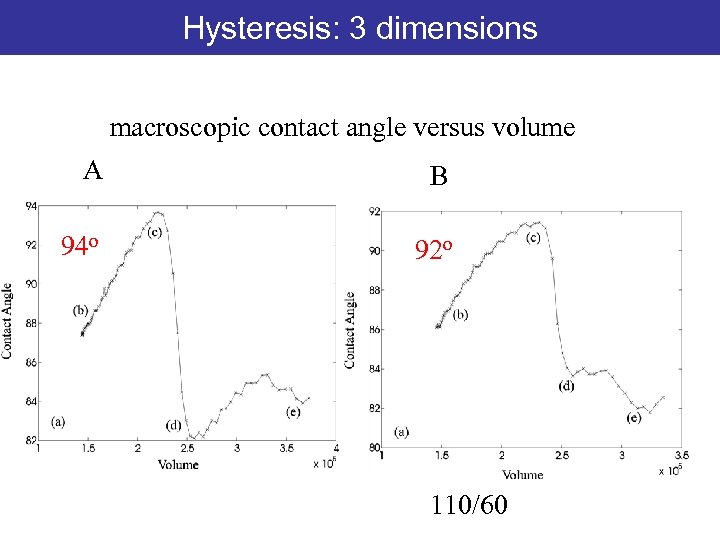 Hysteresis: 3 dimensions macroscopic contact angle versus volume A B 94 o 92 o 110/60
Hysteresis: 3 dimensions macroscopic contact angle versus volume A B 94 o 92 o 110/60
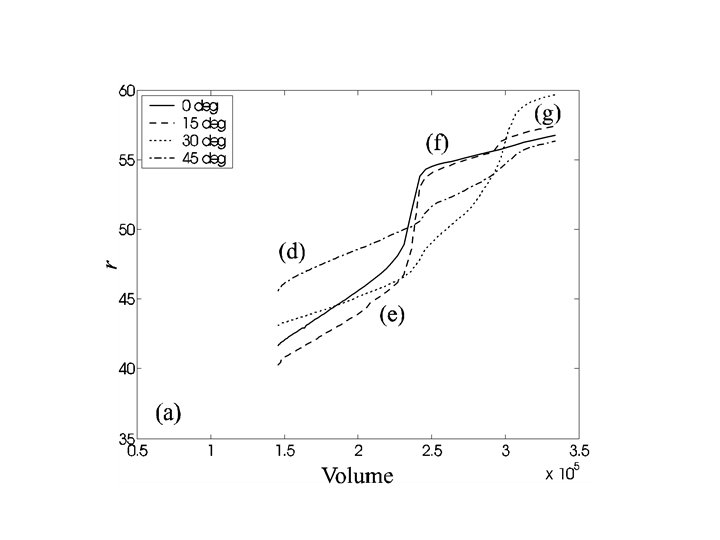
 Hysteresis on chemically patterned surfaces 1. Slip, stick, jump behaviour, but jumps at different volumes in different directions (but can be correlated) 2. Contact angle hysteresis different in different directions 3. Advancing angle (92 o) bounded by qmax (110 o) Receding angle (80 o) bounded by qmin (60 o) 4. Free energy balance between surface / drop interactions and interface distortions determines the hysteresis
Hysteresis on chemically patterned surfaces 1. Slip, stick, jump behaviour, but jumps at different volumes in different directions (but can be correlated) 2. Contact angle hysteresis different in different directions 3. Advancing angle (92 o) bounded by qmax (110 o) Receding angle (80 o) bounded by qmin (60 o) 4. Free energy balance between surface / drop interactions and interface distortions determines the hysteresis
 Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
 Superhydrophobic surfaces
Superhydrophobic surfaces
 Superhydrophobic surfaces
Superhydrophobic surfaces
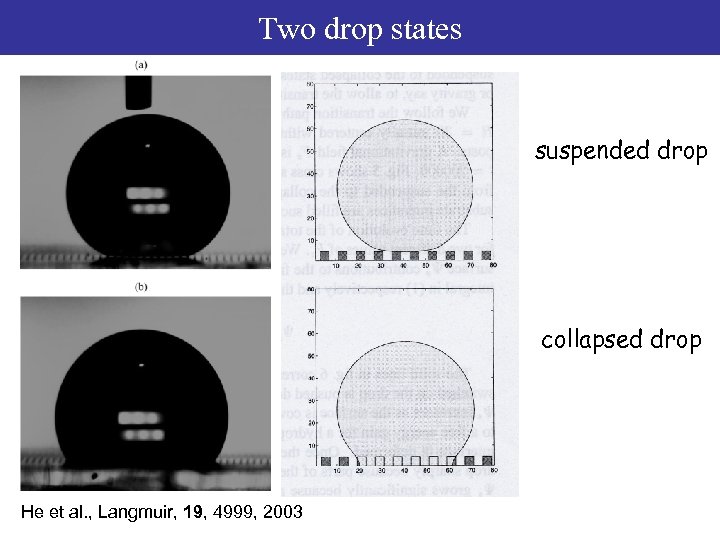 Two drop states suspended drop collapsed drop He et al. , Langmuir, 19, 4999, 2003
Two drop states suspended drop collapsed drop He et al. , Langmuir, 19, 4999, 2003
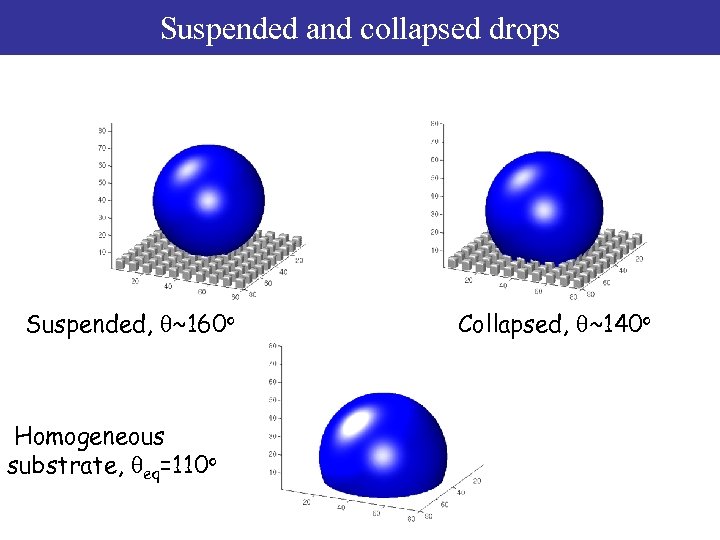 Suspended and collapsed drops Suspended, q~160 o Homogeneous substrate, qeq=110 o Collapsed, q~140 o
Suspended and collapsed drops Suspended, q~160 o Homogeneous substrate, qeq=110 o Collapsed, q~140 o
 Hysteresis: suspended state 180 o
Hysteresis: suspended state 180 o
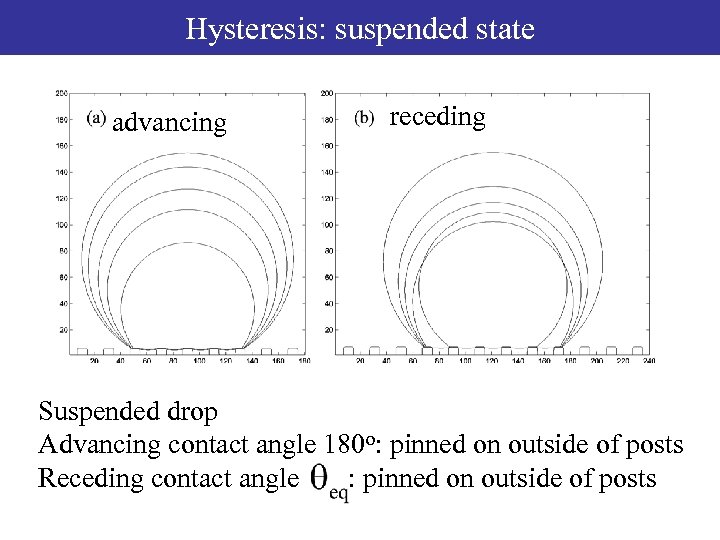 Hysteresis: suspended state advancing receding Suspended drop Advancing contact angle 180 o: pinned on outside of posts Receding contact angle : pinned on outside of posts
Hysteresis: suspended state advancing receding Suspended drop Advancing contact angle 180 o: pinned on outside of posts Receding contact angle : pinned on outside of posts
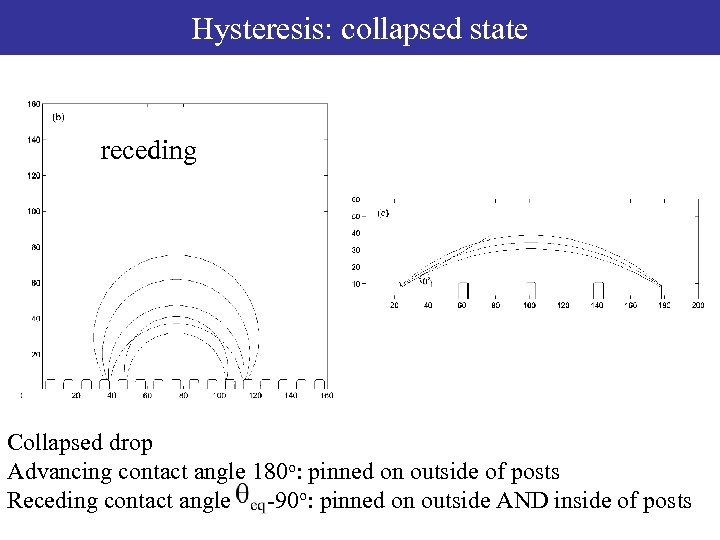 Hysteresis: collapsed state receding Collapsed drop Advancing contact angle 180 o: pinned on outside of posts Receding contact angle -90 o: pinned on outside AND inside of posts
Hysteresis: collapsed state receding Collapsed drop Advancing contact angle 180 o: pinned on outside of posts Receding contact angle -90 o: pinned on outside AND inside of posts
 Hysteresis: three dimensions 2 D Suspended drop: advancing angle 180 o receding angle qe Collapsed drop: advancing angle 180 o receding angle qe-90 o 3 D
Hysteresis: three dimensions 2 D Suspended drop: advancing angle 180 o receding angle qe Collapsed drop: advancing angle 180 o receding angle qe-90 o 3 D
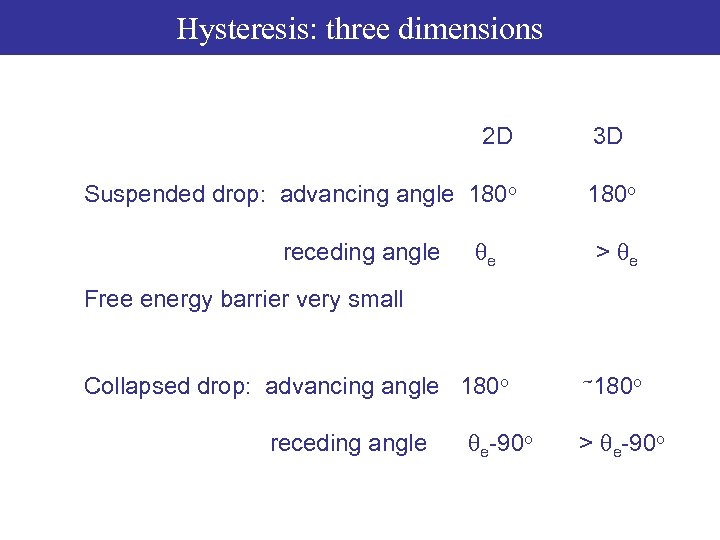 Hysteresis: three dimensions 2 D Suspended drop: advancing angle 180 o receding angle qe 3 D 180 o > qe Free energy barrier very small Collapsed drop: advancing angle 180 o receding angle qe-90 o ~180 o > qe-90 o
Hysteresis: three dimensions 2 D Suspended drop: advancing angle 180 o receding angle qe 3 D 180 o > qe Free energy barrier very small Collapsed drop: advancing angle 180 o receding angle qe-90 o ~180 o > qe-90 o
 Hysteresis on superhydrophobic surfaces 1. Advancing contact angles are close to 180 o 2. Hysteresis smaller for suspended than collapsed drop High receding contact angle -- weak adhesion Small contact angle hysteresis – slides easily? ? 3. Free energy balance between drop -- surface interactions and interface distortion determines the hysteresis ? ? Forced hysteresis ? ? Changing relative length scales ? ? Relation between hysteresis and easy run off
Hysteresis on superhydrophobic surfaces 1. Advancing contact angles are close to 180 o 2. Hysteresis smaller for suspended than collapsed drop High receding contact angle -- weak adhesion Small contact angle hysteresis – slides easily? ? 3. Free energy balance between drop -- surface interactions and interface distortion determines the hysteresis ? ? Forced hysteresis ? ? Changing relative length scales ? ? Relation between hysteresis and easy run off
 Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
 Drop collapse: Mathilde Reyssat and David Quere 200 m
Drop collapse: Mathilde Reyssat and David Quere 200 m
 Drop collapse: simulations
Drop collapse: simulations
 1. Curvature driven collapse : short posts 2. Free energy driven collapse : long posts
1. Curvature driven collapse : short posts 2. Free energy driven collapse : long posts
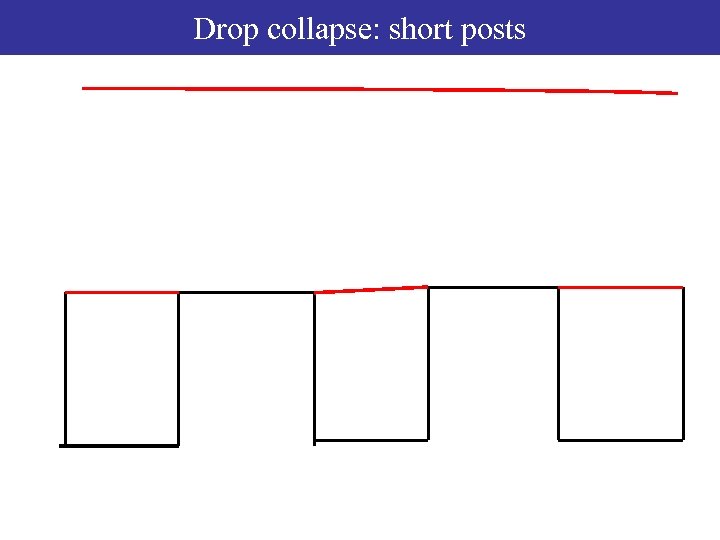 Drop collapse: short posts
Drop collapse: short posts
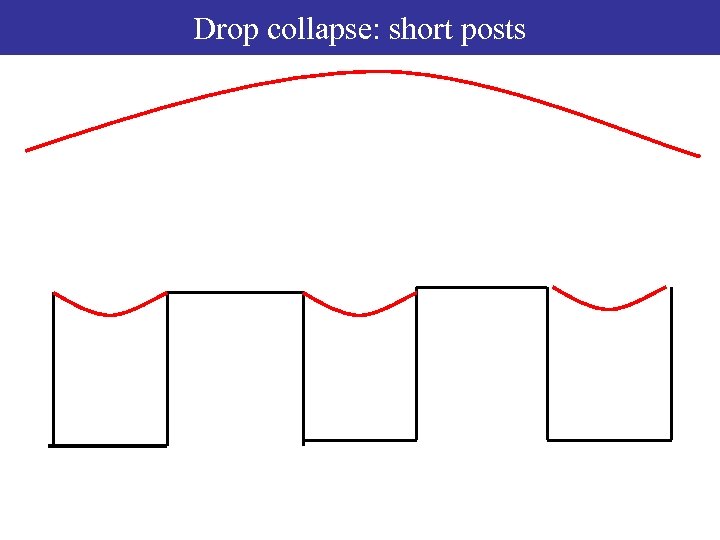 Drop collapse: short posts
Drop collapse: short posts
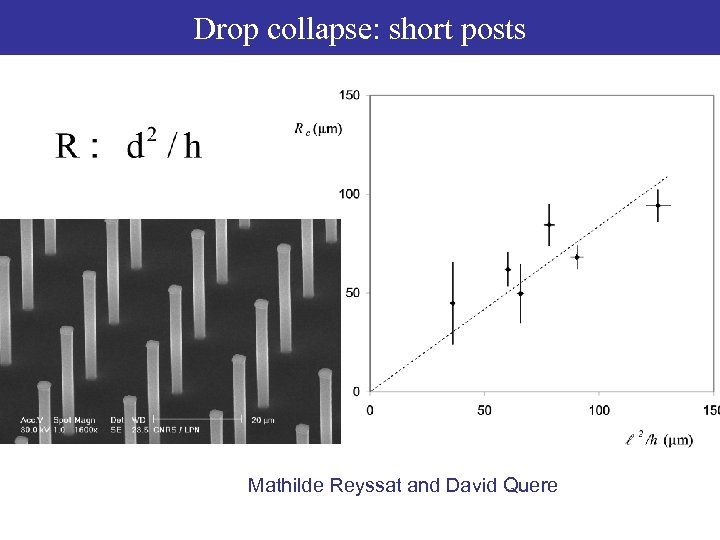 Drop collapse: short posts Drop collapse: simulations Mathilde Reyssat and David Quere
Drop collapse: short posts Drop collapse: simulations Mathilde Reyssat and David Quere
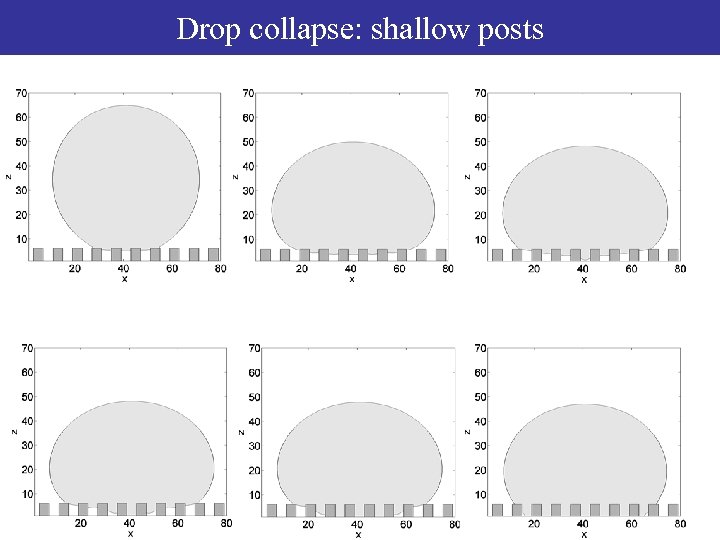 Drop collapse: shallow posts
Drop collapse: shallow posts
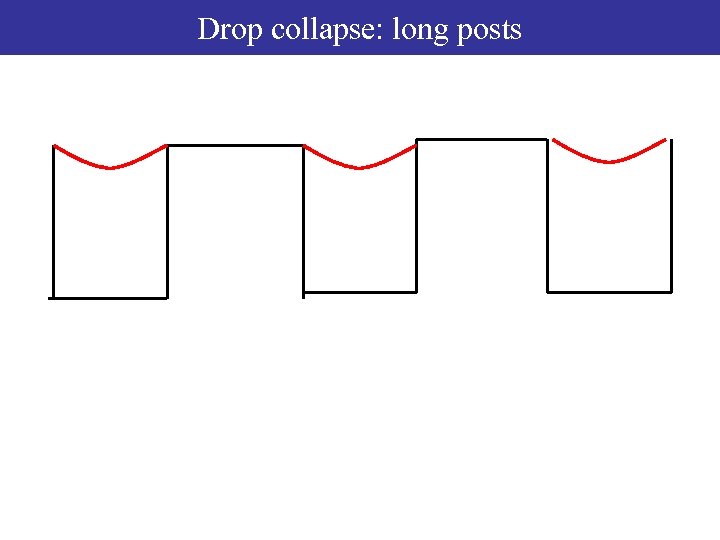 Drop collapse: long posts
Drop collapse: long posts
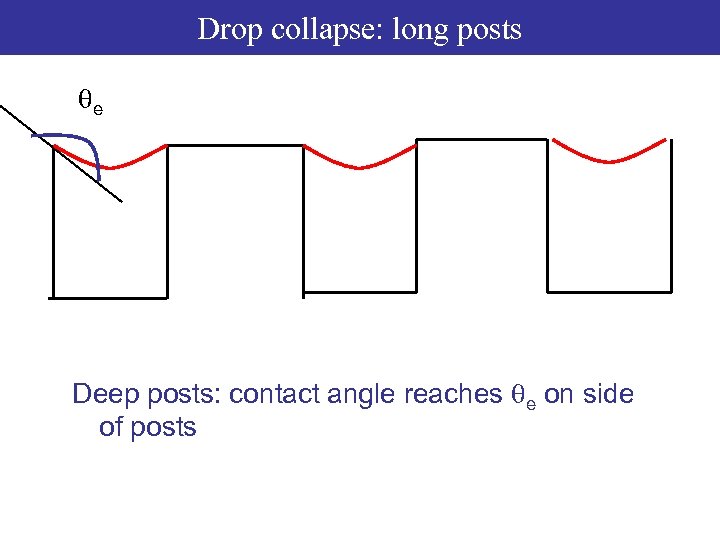 Drop collapse: long posts qe Deep posts: contact angle reaches qe on side of posts
Drop collapse: long posts qe Deep posts: contact angle reaches qe on side of posts
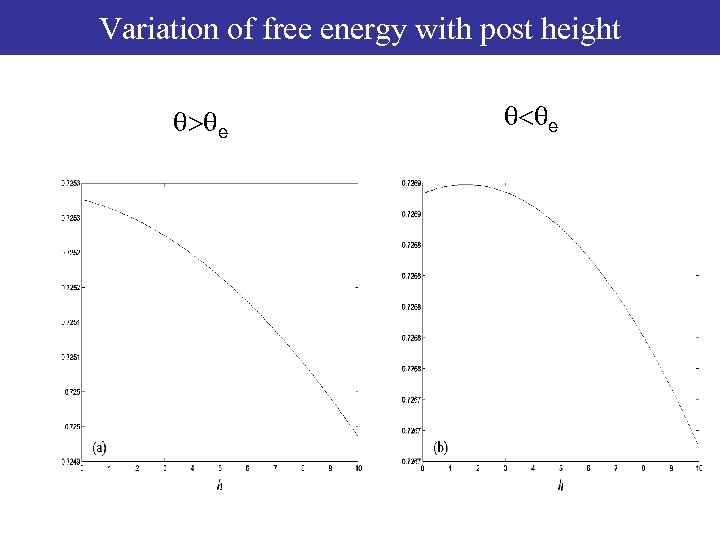 Variation of free energy with post height q>qe q
Variation of free energy with post height q>qe q
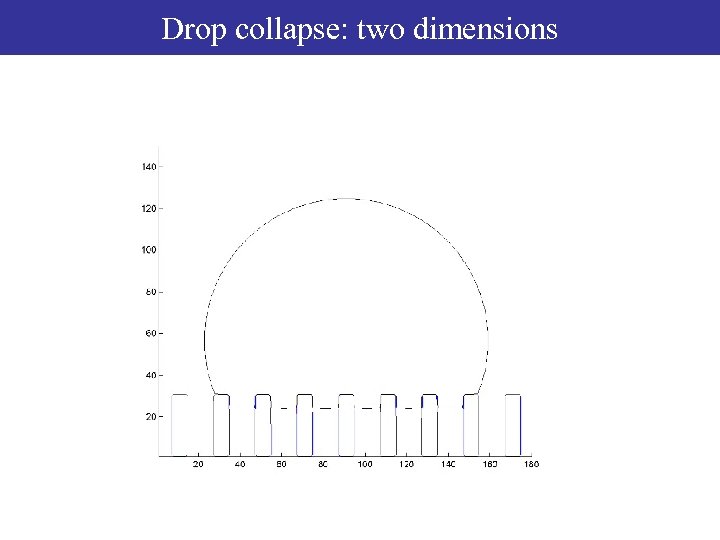 Drop collapse: two dimensions
Drop collapse: two dimensions
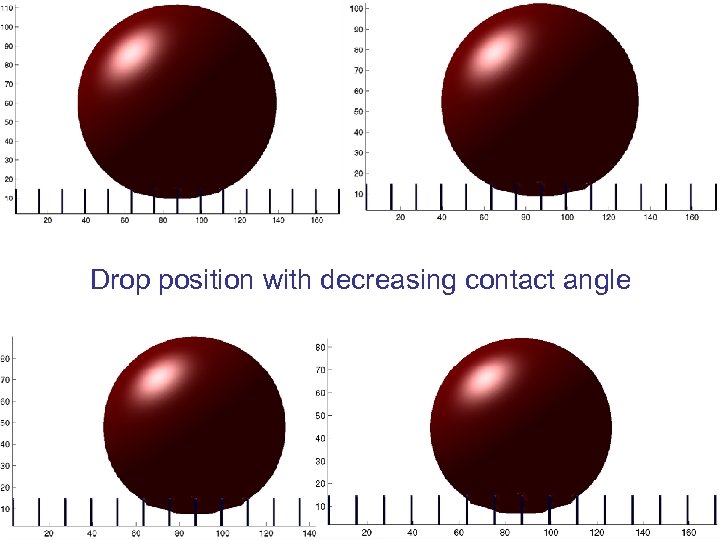 Drop position with decreasing contact angle
Drop position with decreasing contact angle
 Collapse on superhydrophobic surfaces Shallow posts: curvature driven collapse Deep posts: 2 dimensions – free energy driven collapse Deep posts: 3 dimensions – is collapse possible ? ?
Collapse on superhydrophobic surfaces Shallow posts: curvature driven collapse Deep posts: 2 dimensions – free energy driven collapse Deep posts: 3 dimensions – is collapse possible ? ?
 Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
 With thanks to Alexandre Dupuis Halim Kusumaatmaja
With thanks to Alexandre Dupuis Halim Kusumaatmaja
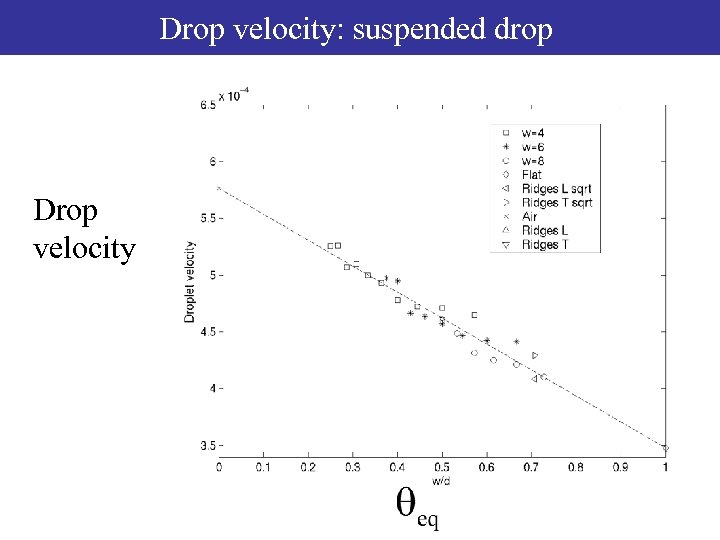 Drop velocity: suspended drop Droplet velocity Drop velocity
Drop velocity: suspended drop Droplet velocity Drop velocity
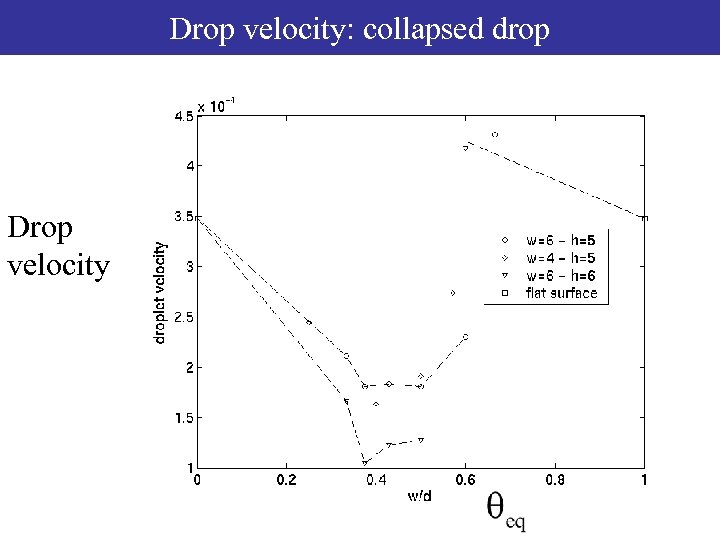 Drop velocity: collapsed drop Dynamics of collapsed droplets Drop velocity
Drop velocity: collapsed drop Dynamics of collapsed droplets Drop velocity
 Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
Summary The model Chemically patterned surfaces Spreading on stripes Hysteresis Superhydrophobic surfaces Introduction Hysteresis Transitions between states Dynamics
 With thanks to Alexandre Dupuis Halim Kusumaatmaja
With thanks to Alexandre Dupuis Halim Kusumaatmaja



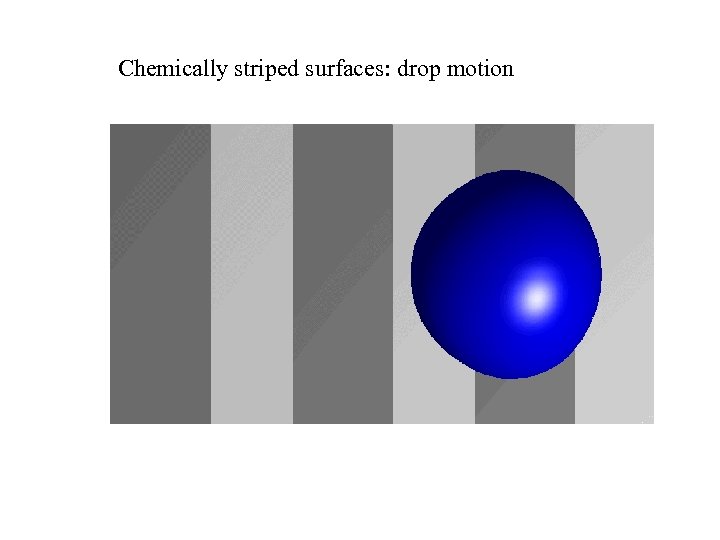 Chemically striped surfaces: drop motion
Chemically striped surfaces: drop motion
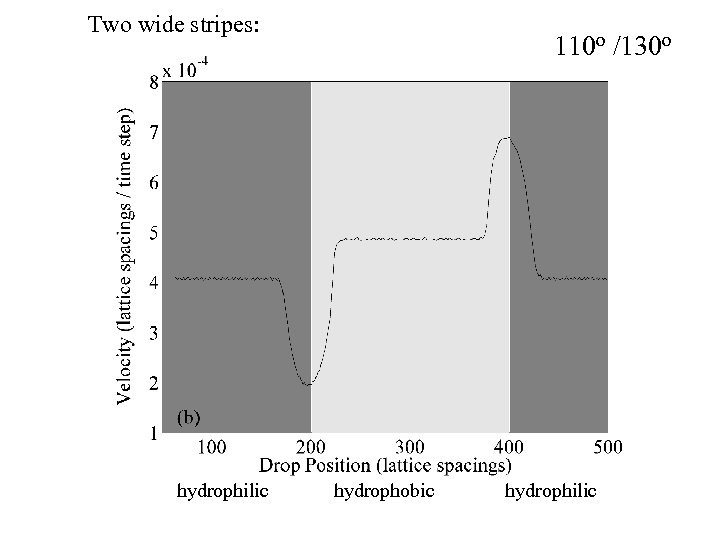 Two wide stripes: 110 o /130 o hydrophilic hydrophobic hydrophilic
Two wide stripes: 110 o /130 o hydrophilic hydrophobic hydrophilic
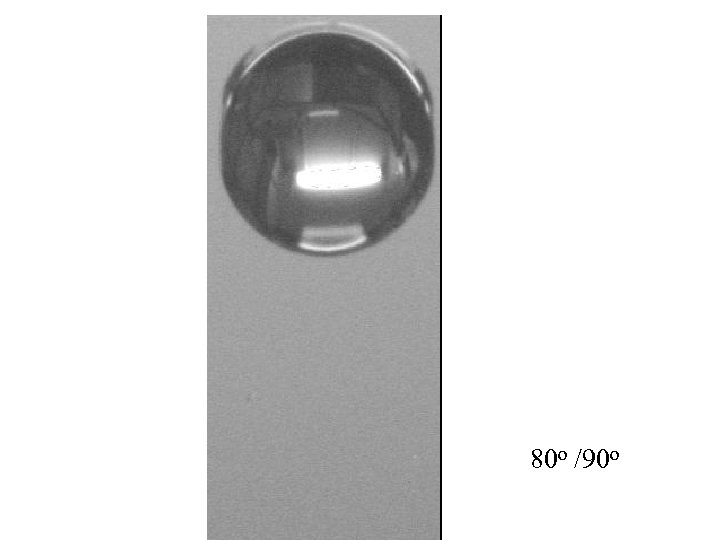 80 o /90 o
80 o /90 o
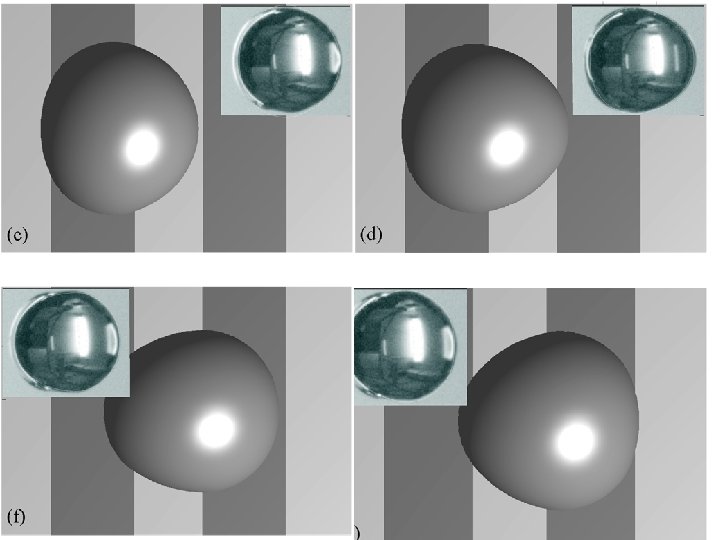
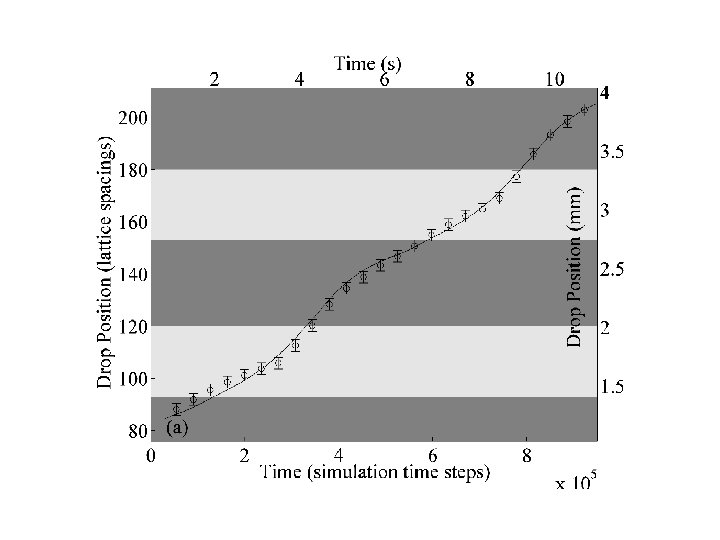
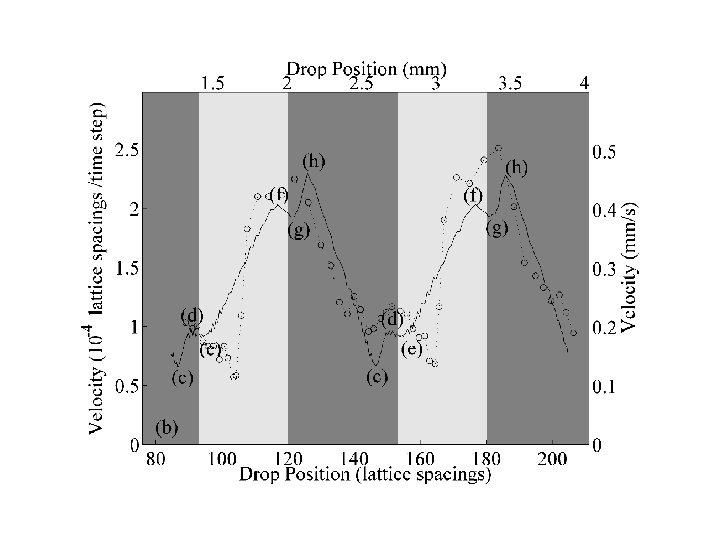
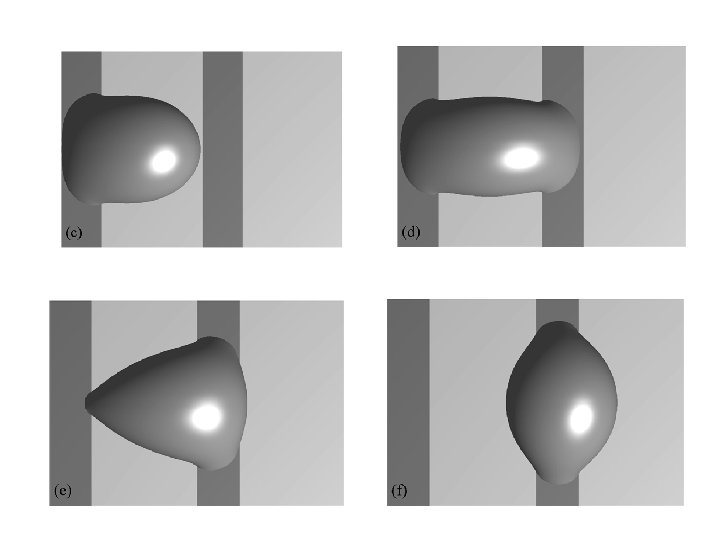
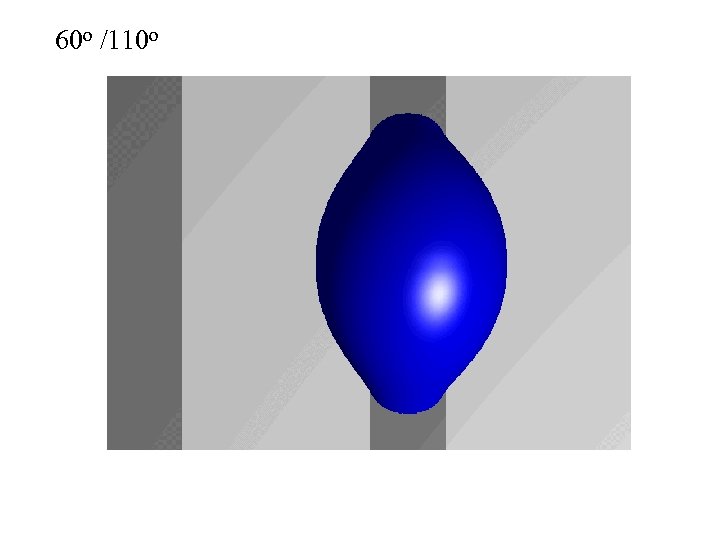 60 o /110 o
60 o /110 o
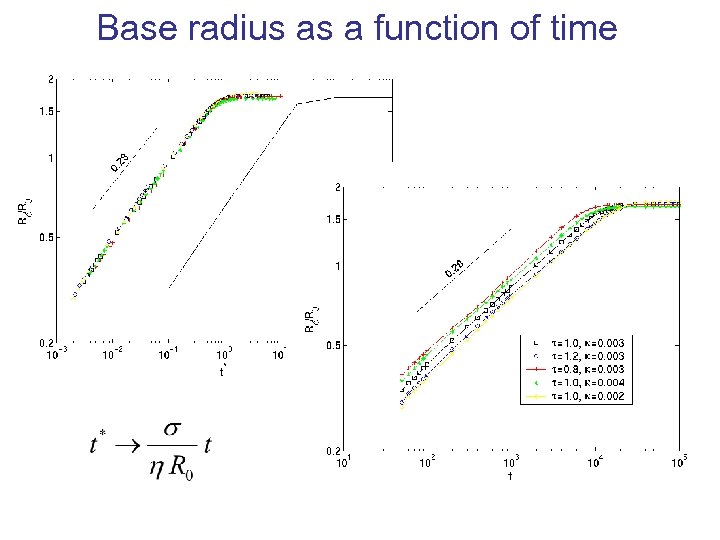 Base radius as a function of time
Base radius as a function of time
 Controlling the contact angle Surface free energy Minimising the free energy leads to: Boundary condition on the Euler-Lagrange equation A relation between the contact angle and the surface field
Controlling the contact angle Surface free energy Minimising the free energy leads to: Boundary condition on the Euler-Lagrange equation A relation between the contact angle and the surface field
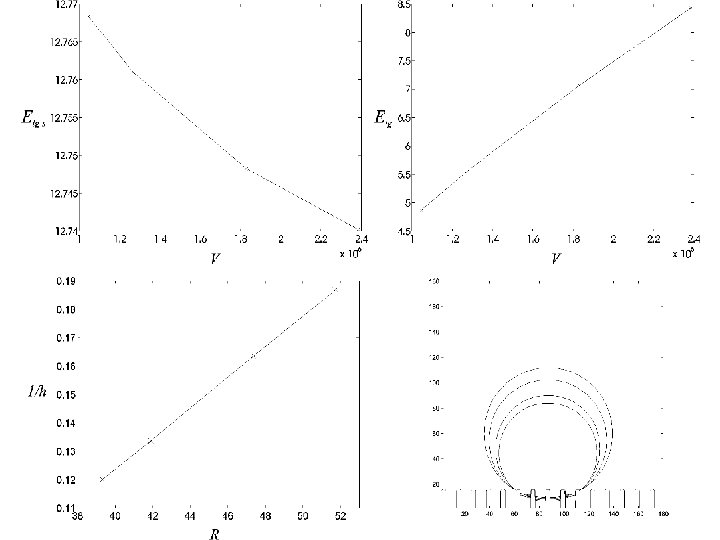
 Mathilde Callies and David Quere 2006
Mathilde Callies and David Quere 2006


