a050fb04220c7b21a1f666f768a66622.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 Drain Current Digitizer Chip (DCD) Status and Future Plans ASICs
Drain Current Digitizer Chip (DCD) Status and Future Plans ASICs
 DCDBv 1 Measurements § § § DCDBv 1 has been tested with and without sensor The chip is working well There are two smaller problems: A) Noise problem: At the designed full clock frequency, 350 MHz, that corresponds to 20 s frame readout time - the electronics noise is higher than expected. Noise is 150 n. A, that corresponds to ~ 300 ENC in DEPFET (gq=500 p. A/e) and SNR of 13 (assumption 4000 e signal). § The noise at a lower clock frequency – e. g. 200 MHz (32 s frame readout time) is as expected – 35 n. A (~70 ENC). SNR would be 53. § B) Yield problem: § There are too many non functional ADC channels on the chip, typically 6 out of 256. ASICs 2
DCDBv 1 Measurements § § § DCDBv 1 has been tested with and without sensor The chip is working well There are two smaller problems: A) Noise problem: At the designed full clock frequency, 350 MHz, that corresponds to 20 s frame readout time - the electronics noise is higher than expected. Noise is 150 n. A, that corresponds to ~ 300 ENC in DEPFET (gq=500 p. A/e) and SNR of 13 (assumption 4000 e signal). § The noise at a lower clock frequency – e. g. 200 MHz (32 s frame readout time) is as expected – 35 n. A (~70 ENC). SNR would be 53. § B) Yield problem: § There are too many non functional ADC channels on the chip, typically 6 out of 256. ASICs 2
 DCDBv 1 Measurements § Both problems have been extensively studied. § The noise problem is most probable related to one wrongly dimensioned component on the chip – the bias diode. This component generates the bias voltage for certain logic delay elements. The delay time is too long, which leads to malfunction of ADCs at higher clock rate. The result is excessive noise. § In order to examine the yield problem we tried to localize the damage in the non working channels. We have found out that the long digital lines (5 mm long and 0. 3 m wide) that connect the analog ADC part and digital data processor (see page 4) are broken. The layout of these lines is not optimal. Each of them has at least 5 single-“via” connections between layers and no ESD protecting devices (antenna diodes) that should protect the digital gates lines are connected to. This can lead to the damage of a few per cent of ~1000 lines on the chip. (2 per ADC, 512 ADCs on the chip). ASICs 3
DCDBv 1 Measurements § Both problems have been extensively studied. § The noise problem is most probable related to one wrongly dimensioned component on the chip – the bias diode. This component generates the bias voltage for certain logic delay elements. The delay time is too long, which leads to malfunction of ADCs at higher clock rate. The result is excessive noise. § In order to examine the yield problem we tried to localize the damage in the non working channels. We have found out that the long digital lines (5 mm long and 0. 3 m wide) that connect the analog ADC part and digital data processor (see page 4) are broken. The layout of these lines is not optimal. Each of them has at least 5 single-“via” connections between layers and no ESD protecting devices (antenna diodes) that should protect the digital gates lines are connected to. This can lead to the damage of a few per cent of ~1000 lines on the chip. (2 per ADC, 512 ADCs on the chip). ASICs 3
 DCD test chip and DCDBv 2 § In order to test the assumed cause of the noise problem we have designed and submitted a test chip with adjusted bias diode. § The remaining circuits are identical as on the big DCD, just the size of the chip is smaller. The test chip contains two out of 16 channel columns (full size DCD). (Layouts of both chips are shown in page 4. ) The test chip works excellent even at the clock frequency that is higher than the designed one. At the clock frequency of 400 MHz (~ 16 s frame readout time) we measure electronic noise between 30 n. A and 52 n. A, depending of the adjusted gain of the input amplifier. (Higher gain leads to lower noise, but also to a reduced dynamic range. ) SNR of DEPFET would be from 38 up to 66. The success of the test chip is a good sign that we have localized the source of the speed problem. § We have submitted a new version of the DCD chip – DCDBv 2 this March. § The chip has the adjusted bias diode and the improved layout of the long digital lines for better yield. We are quite confident that the new chip will work as good as the test chip and have much lass non working channels than DCDBv 1. § We expect the first measurements on DCDBv 2 in October. ASICs 4
DCD test chip and DCDBv 2 § In order to test the assumed cause of the noise problem we have designed and submitted a test chip with adjusted bias diode. § The remaining circuits are identical as on the big DCD, just the size of the chip is smaller. The test chip contains two out of 16 channel columns (full size DCD). (Layouts of both chips are shown in page 4. ) The test chip works excellent even at the clock frequency that is higher than the designed one. At the clock frequency of 400 MHz (~ 16 s frame readout time) we measure electronic noise between 30 n. A and 52 n. A, depending of the adjusted gain of the input amplifier. (Higher gain leads to lower noise, but also to a reduced dynamic range. ) SNR of DEPFET would be from 38 up to 66. The success of the test chip is a good sign that we have localized the source of the speed problem. § We have submitted a new version of the DCD chip – DCDBv 2 this March. § The chip has the adjusted bias diode and the improved layout of the long digital lines for better yield. We are quite confident that the new chip will work as good as the test chip and have much lass non working channels than DCDBv 1. § We expect the first measurements on DCDBv 2 in October. ASICs 4
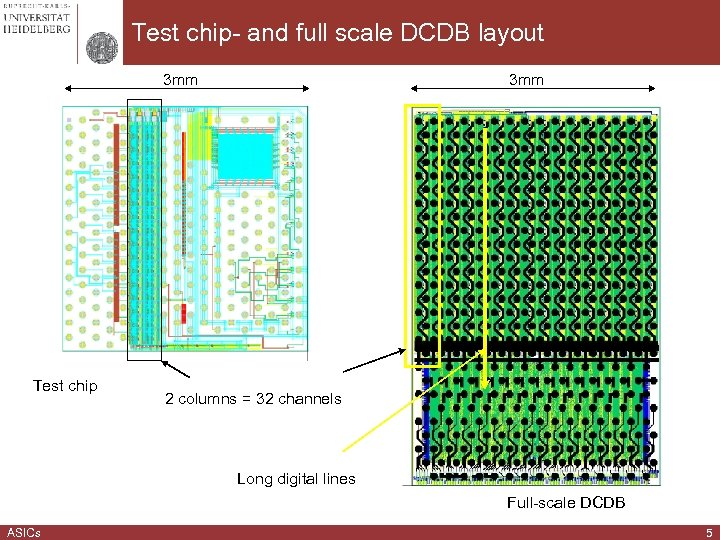 Test chip- and full scale DCDB layout 3 mm Test chip 3 mm 2 columns = 32 channels Long digital lines Full-scale DCDB ASICs 5
Test chip- and full scale DCDB layout 3 mm Test chip 3 mm 2 columns = 32 channels Long digital lines Full-scale DCDB ASICs 5
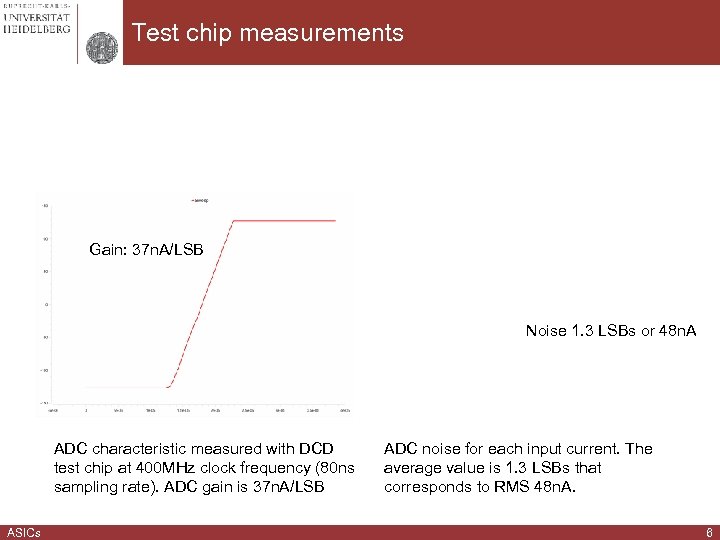 Test chip measurements Gain: 37 n. A/LSB Noise 1. 3 LSBs or 48 n. A ADC characteristic measured with DCD test chip at 400 MHz clock frequency (80 ns sampling rate). ADC gain is 37 n. A/LSB ASICs ADC noise for each input current. The average value is 1. 3 LSBs that corresponds to RMS 48 n. A. 6
Test chip measurements Gain: 37 n. A/LSB Noise 1. 3 LSBs or 48 n. A ADC characteristic measured with DCD test chip at 400 MHz clock frequency (80 ns sampling rate). ADC gain is 37 n. A/LSB ASICs ADC noise for each input current. The average value is 1. 3 LSBs that corresponds to RMS 48 n. A. 6
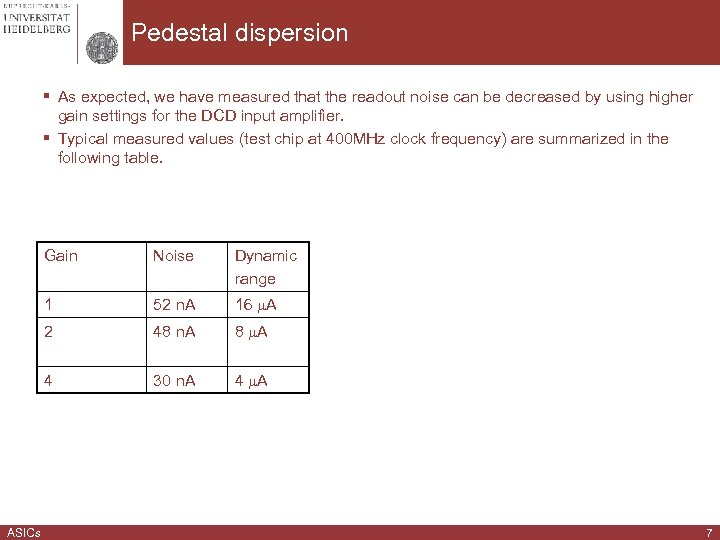 Pedestal dispersion § As expected, we have measured that the readout noise can be decreased by using higher gain settings for the DCD input amplifier. § Typical measured values (test chip at 400 MHz clock frequency) are summarized in the following table. Gain Dynamic range 1 52 n. A 16 A 2 48 n. A 8 A 4 ASICs Noise 30 n. A 4 A 7
Pedestal dispersion § As expected, we have measured that the readout noise can be decreased by using higher gain settings for the DCD input amplifier. § Typical measured values (test chip at 400 MHz clock frequency) are summarized in the following table. Gain Dynamic range 1 52 n. A 16 A 2 48 n. A 8 A 4 ASICs Noise 30 n. A 4 A 7
 Pedestal dispersion § Unfortunately, a higher gain setting leads not only to a better noise than also to a reduced dynamic range § The required dynamic range must cover the DEPFET pedestal current dispersion and leave some room for signal. § There are hints that DEPFET pedestal dispersion after irradiation can be as large as 150 A! § Clearly, auxiliary circuits are needed to extend the dynamic range of the ADC. § The present strategy is to use an extra 2 -bit DAC. This can typically reduce pedestal dispersion by factor of ~ 4. Our ADC must able to cope with the remaining pedestal dispersion and the signal § This would require a gain setting of ~ 0. 3. The price of such a low gain would be excessive input referred noise. § We have designed a circuit that can automatically compensate for the radiation induced part of the pedestal dispersion in very high range. The circuit will allow us to keep high gain settings for DCD amplifier even after many months of irradiation and keep the noise low. § The circuit have been implemented as an extra feature in the new DCDBv 2. ASICs 8
Pedestal dispersion § Unfortunately, a higher gain setting leads not only to a better noise than also to a reduced dynamic range § The required dynamic range must cover the DEPFET pedestal current dispersion and leave some room for signal. § There are hints that DEPFET pedestal dispersion after irradiation can be as large as 150 A! § Clearly, auxiliary circuits are needed to extend the dynamic range of the ADC. § The present strategy is to use an extra 2 -bit DAC. This can typically reduce pedestal dispersion by factor of ~ 4. Our ADC must able to cope with the remaining pedestal dispersion and the signal § This would require a gain setting of ~ 0. 3. The price of such a low gain would be excessive input referred noise. § We have designed a circuit that can automatically compensate for the radiation induced part of the pedestal dispersion in very high range. The circuit will allow us to keep high gain settings for DCD amplifier even after many months of irradiation and keep the noise low. § The circuit have been implemented as an extra feature in the new DCDBv 2. ASICs 8
 SWITCHER Chip ASICs
SWITCHER Chip ASICs
 SWITCHER Status § The preset version of SWITCHER chip has been tested on a dedicated PCB and used to build DEPFET modules § The stand alone chip works excellent. However, only one was tested so far. § Some of the chips that were mounted onto the DEPFET hybrids was broken after assembly. § The mounting yield issue is still under investigation. § Currently a diploma student in Heidelberg is developing a probe station based test setup for SWITCHER and DCD. § The test setup will allow us to test SWITCHERs and DCDs before they are mounted. ASICs 10
SWITCHER Status § The preset version of SWITCHER chip has been tested on a dedicated PCB and used to build DEPFET modules § The stand alone chip works excellent. However, only one was tested so far. § Some of the chips that were mounted onto the DEPFET hybrids was broken after assembly. § The mounting yield issue is still under investigation. § Currently a diploma student in Heidelberg is developing a probe station based test setup for SWITCHER and DCD. § The test setup will allow us to test SWITCHERs and DCDs before they are mounted. ASICs 10
 SWITCHER Plans § Presently a student in Heidelberg is working within her practice semester on the translation of the SWITCHER circuits and layouts to the newer technology - AMS HV 0. 18 m. § A SWITCHER in 0. 18 m would have certain advantages, such as: § Smaller chip width (the present chip extends over the active DEPFET area) § Better radiation hardness -> no need for the use of non-standard annular transistors -> standard logic cells / HV transistors can be used -> safer and easier design § Digital supply voltage compatible to the one of DCD and DHP, less power lines on DEPFET module, no level shifter, simpler design § Less (digital) power consumption, faster switching § Possibility to buy the chip with solder bumps ASICs 11
SWITCHER Plans § Presently a student in Heidelberg is working within her practice semester on the translation of the SWITCHER circuits and layouts to the newer technology - AMS HV 0. 18 m. § A SWITCHER in 0. 18 m would have certain advantages, such as: § Smaller chip width (the present chip extends over the active DEPFET area) § Better radiation hardness -> no need for the use of non-standard annular transistors -> standard logic cells / HV transistors can be used -> safer and easier design § Digital supply voltage compatible to the one of DCD and DHP, less power lines on DEPFET module, no level shifter, simpler design § Less (digital) power consumption, faster switching § Possibility to buy the chip with solder bumps ASICs 11


