d119adf197b7ebbc4b535aadb8b09d94.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

 Dr Venkatagiri K. M, M. D. PGDMLE, PGDHHM, PGCHFWM Consultant: Anaesthesia, Govt. Gen. Hosp. , Kasaragod Vice President, ISA Kerala. President, ISA Kasaragod City Branch
Dr Venkatagiri K. M, M. D. PGDMLE, PGDHHM, PGCHFWM Consultant: Anaesthesia, Govt. Gen. Hosp. , Kasaragod Vice President, ISA Kerala. President, ISA Kasaragod City Branch
 MEDICAL RECORD l Clinical, Scientific, Administrative & Legal document relating to patient care on which is recorded sufficient data written in sequence of events to justify the diagnosis and warrant the treatment & end results (Mc Gibony)
MEDICAL RECORD l Clinical, Scientific, Administrative & Legal document relating to patient care on which is recorded sufficient data written in sequence of events to justify the diagnosis and warrant the treatment & end results (Mc Gibony)
 HISTORY OF MEDICAL RECORDS • 2500 B. C. : Surgical Notes on Walls of Paleolithic caverns of Spain • 3000 B. C. : Sx Records in Egypt • 460 B. C. : Hippocrates Case reports of Patients in Greek • 160 A. D. Galen: Bedside records for Teaching • 865 – 925 Rhases : Medical records
HISTORY OF MEDICAL RECORDS • 2500 B. C. : Surgical Notes on Walls of Paleolithic caverns of Spain • 3000 B. C. : Sx Records in Egypt • 460 B. C. : Hippocrates Case reports of Patients in Greek • 160 A. D. Galen: Bedside records for Teaching • 865 – 925 Rhases : Medical records
 Contd. • 1137 St. Barthalomew’s Hosp. London • 1667 1 st MRD at St. Barthalomew’s Hosp. London • 1752 Pennsylvania Hosp. in US Pt. Regstr • 1859 Massachusetts Gen. Hosp. , Boston Medical Record Library • 1894 – 1 st Anaesthesia Record • Dr. Franklin H. Martin & Dr. Malcolm H. Machan of ACS Improv in Qlt &Qnt of MR
Contd. • 1137 St. Barthalomew’s Hosp. London • 1667 1 st MRD at St. Barthalomew’s Hosp. London • 1752 Pennsylvania Hosp. in US Pt. Regstr • 1859 Massachusetts Gen. Hosp. , Boston Medical Record Library • 1894 – 1 st Anaesthesia Record • Dr. Franklin H. Martin & Dr. Malcolm H. Machan of ACS Improv in Qlt &Qnt of MR
 Medical Records in India • 1946 Bhore Committee • 1962 Mudaliar Committee • 1959 – 1961 Dr. M. C. Gibony Director of Hosp. Admin. Prgm. , Pittsburg Uni. Consultant to Go. I, Mo. H. Orientn prgm. for Principals/ Deans & Spdt. of MC • Jain Committee & Rao Committee • MRD trng. JIPMER & CMC 1962, Tvm MCH 1964
Medical Records in India • 1946 Bhore Committee • 1962 Mudaliar Committee • 1959 – 1961 Dr. M. C. Gibony Director of Hosp. Admin. Prgm. , Pittsburg Uni. Consultant to Go. I, Mo. H. Orientn prgm. for Principals/ Deans & Spdt. of MC • Jain Committee & Rao Committee • MRD trng. JIPMER & CMC 1962, Tvm MCH 1964
 ANAESTHESIA RECORD • • • Part of Medical Record Manual or Computer based Started from time immemorial Duty & responsibility of Anaesthesiologist Legible, comprehensive, accurate & detailed • Pre op – intra op – post op • Describes events in a time scale
ANAESTHESIA RECORD • • • Part of Medical Record Manual or Computer based Started from time immemorial Duty & responsibility of Anaesthesiologist Legible, comprehensive, accurate & detailed • Pre op – intra op – post op • Describes events in a time scale
 Need For Maintenance of Record • Part of Life. • Anaesthesia – Critical period – Dynamic process. Game of “passing the buck”. • Conduct of Anaesthesia • Patient & Anaesthesiologist safety • Future conduct of Anaesthesia
Need For Maintenance of Record • Part of Life. • Anaesthesia – Critical period – Dynamic process. Game of “passing the buck”. • Conduct of Anaesthesia • Patient & Anaesthesiologist safety • Future conduct of Anaesthesia
 Contd. Research & Study q Statistics q Medico legal q Courts take serious note of poor record q Require by law q If you did it, you must record it q Not recorded – not done q
Contd. Research & Study q Statistics q Medico legal q Courts take serious note of poor record q Require by law q If you did it, you must record it q Not recorded – not done q
 Types of Anaesthesia Record • Manual • Computer based connected to HIMS • AAR- Automated Anaesthesia Record • AIMS- Anaesthetic Information Management System • EAR- Electronic Anaesthesia Record • CPRA- Computer Based Patient Record for Anaesthesia Pre op to post op period
Types of Anaesthesia Record • Manual • Computer based connected to HIMS • AAR- Automated Anaesthesia Record • AIMS- Anaesthetic Information Management System • EAR- Electronic Anaesthesia Record • CPRA- Computer Based Patient Record for Anaesthesia Pre op to post op period
 Manual Anaesthesia Record • • Leaves to Paper Observe, watch and write Record as soon as you do Delay will dilute / miss / forget crucial points – credibility lost • Adjust for convenience • Smoothening / Normalize • Spoilation
Manual Anaesthesia Record • • Leaves to Paper Observe, watch and write Record as soon as you do Delay will dilute / miss / forget crucial points – credibility lost • Adjust for convenience • Smoothening / Normalize • Spoilation
 Contd. Consumes 15% - 20% of time n Continuous watching / observing n n Patient & Monitors Record every drug / fluid & event n Record vitals every 5 min. – 15 min. n Cumbersome but write legibly n May not get time n Patient care more important n
Contd. Consumes 15% - 20% of time n Continuous watching / observing n n Patient & Monitors Record every drug / fluid & event n Record vitals every 5 min. – 15 min. n Cumbersome but write legibly n May not get time n Patient care more important n
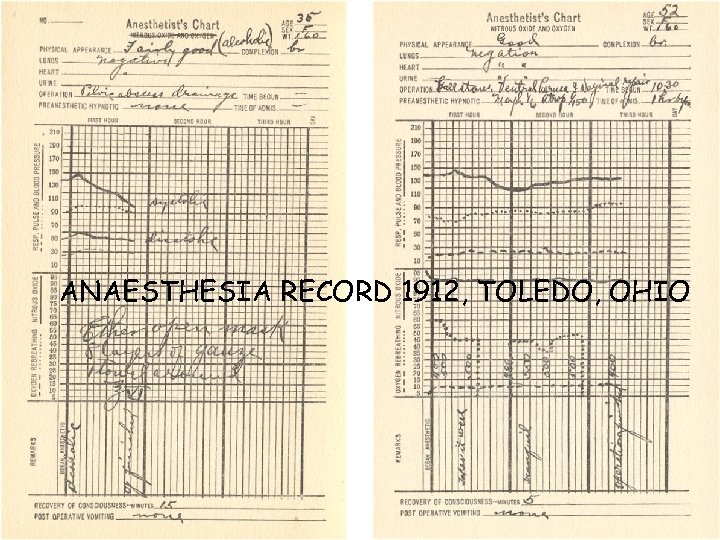 ANAESTHESIA RECORD 1912, TOLEDO, OHIO
ANAESTHESIA RECORD 1912, TOLEDO, OHIO
 AUDIT OF ANAESTHESIA RECORD 25% NO RECORD n 45% INCOMPLETE OR ILLEGIBLE IN ALL OR SOME RESPECT n 30% COMPLETE & LEGIBLE n n= 100%
AUDIT OF ANAESTHESIA RECORD 25% NO RECORD n 45% INCOMPLETE OR ILLEGIBLE IN ALL OR SOME RESPECT n 30% COMPLETE & LEGIBLE n n= 100%

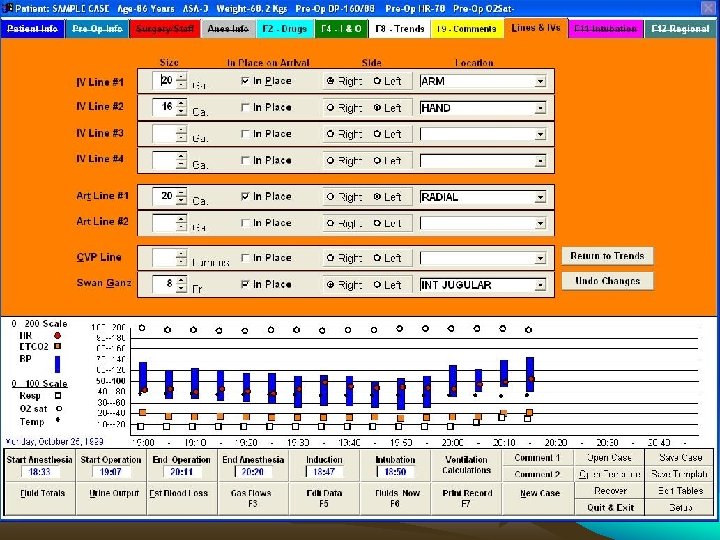
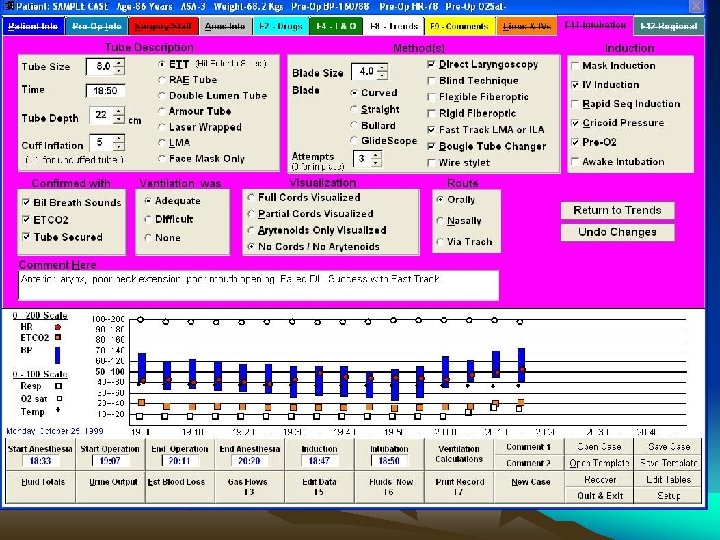
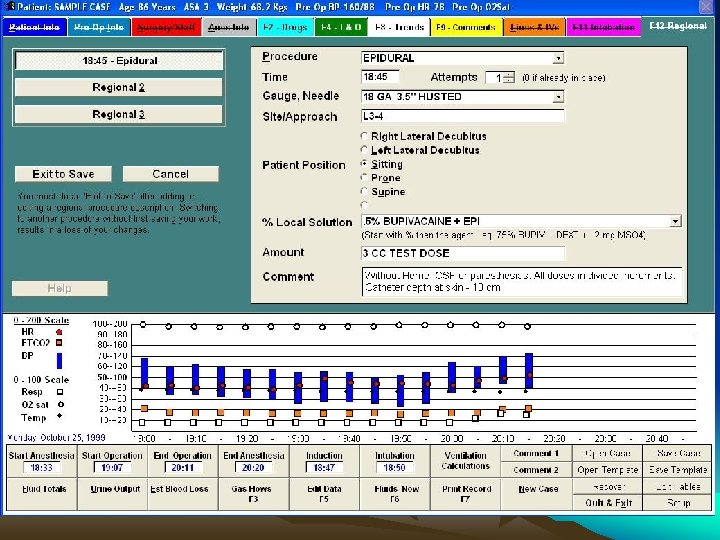
 Computer Based Anae. Record • • Robust real time second to second Paperless Hospitals Advanced countries Saves time Full details from Pre Op to Post Op Online entries of drugs Automated recording of monitor data
Computer Based Anae. Record • • Robust real time second to second Paperless Hospitals Advanced countries Saves time Full details from Pre Op to Post Op Online entries of drugs Automated recording of monitor data
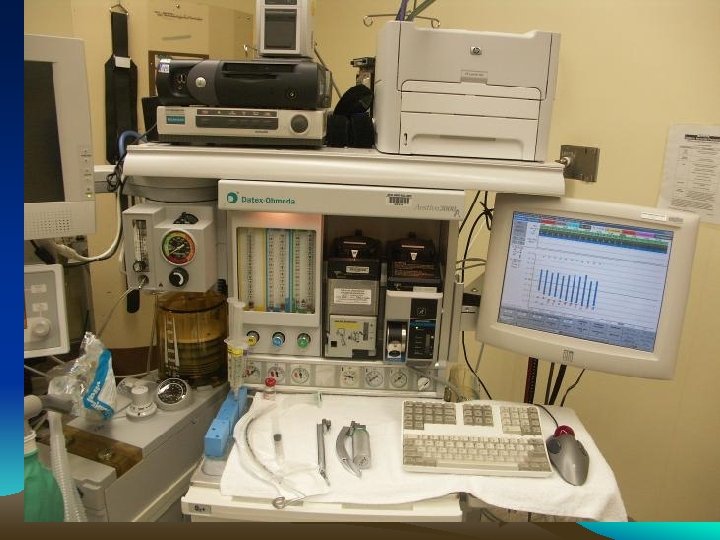

 • • Contd. More accurate More details & more reliable Easily retrievable Connected to HIMS Get access any where for any one Cannot change / alter entries Cannot normalize / smoothen BUT Spoilation: Intentional distruction / mutilation/ concedment / alteration of evidence
• • Contd. More accurate More details & more reliable Easily retrievable Connected to HIMS Get access any where for any one Cannot change / alter entries Cannot normalize / smoothen BUT Spoilation: Intentional distruction / mutilation/ concedment / alteration of evidence
 Contd. • AIMS Handles Record of All Patients. • It can be used in ICU, PICU, Trauma Care Centres, Labour Room, Etc. • One can monitor many Smooth transition to • Recovery room • Post op room • Ward • Needs knowledge of computer • Cumbersome clumsy keys High Cost of Hardware, Software.
Contd. • AIMS Handles Record of All Patients. • It can be used in ICU, PICU, Trauma Care Centres, Labour Room, Etc. • One can monitor many Smooth transition to • Recovery room • Post op room • Ward • Needs knowledge of computer • Cumbersome clumsy keys High Cost of Hardware, Software.
 Recent trends • AARK used in more hospitals • Connected to master server • Real time transmission
Recent trends • AARK used in more hospitals • Connected to master server • Real time transmission
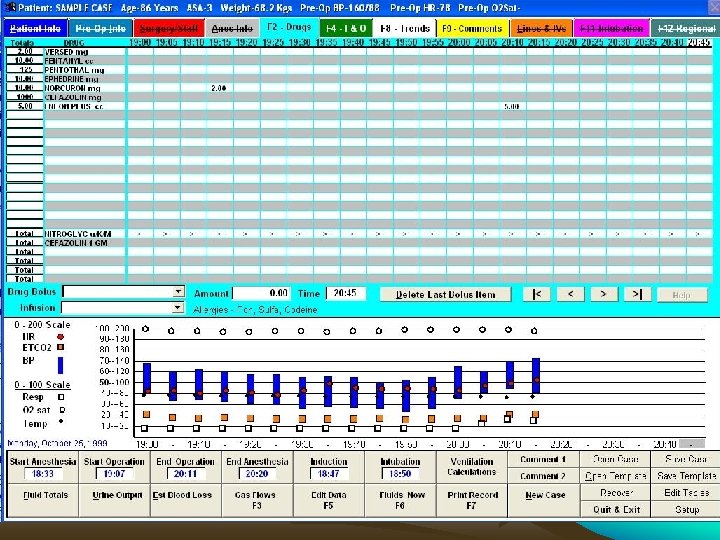
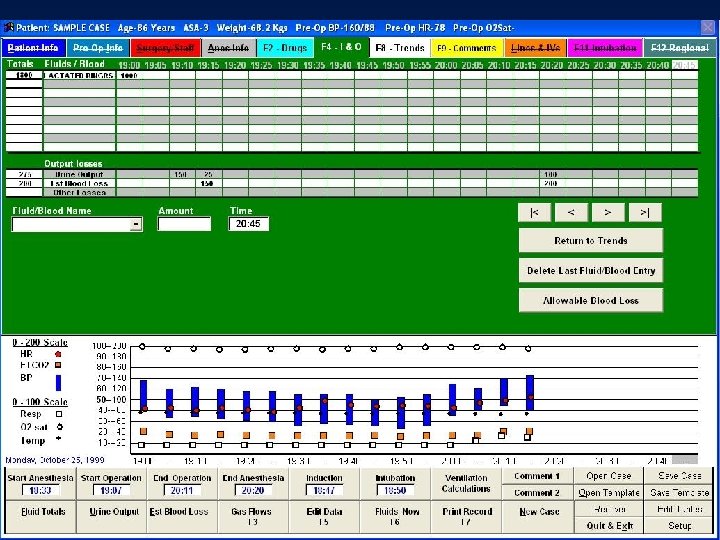
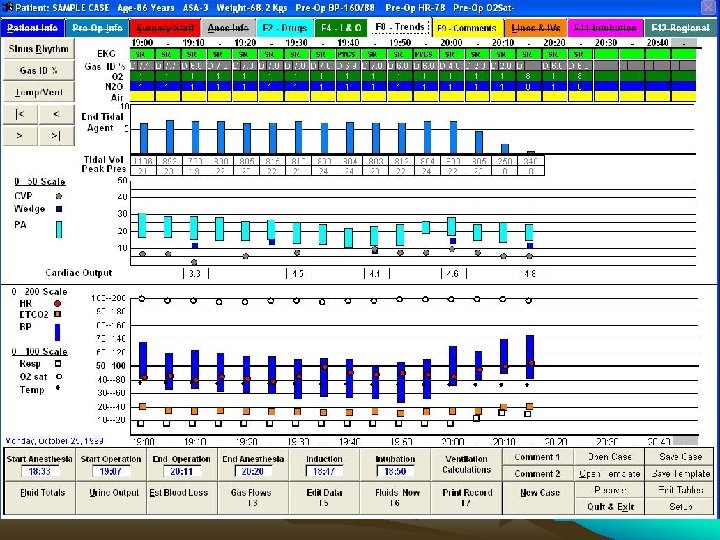
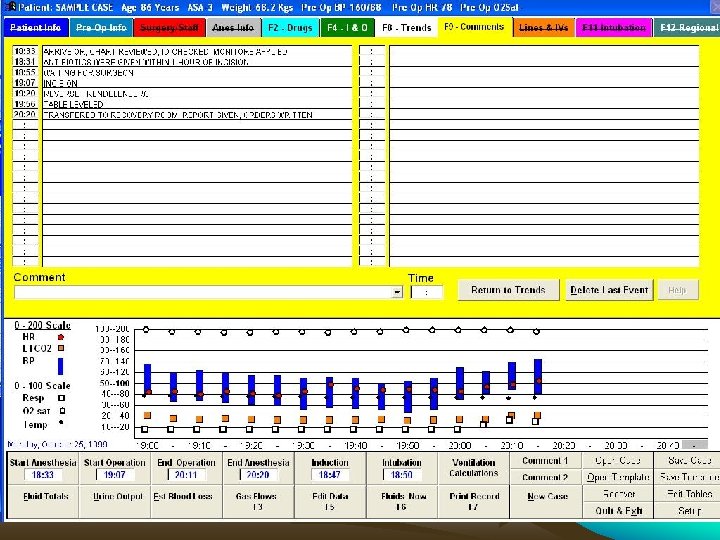
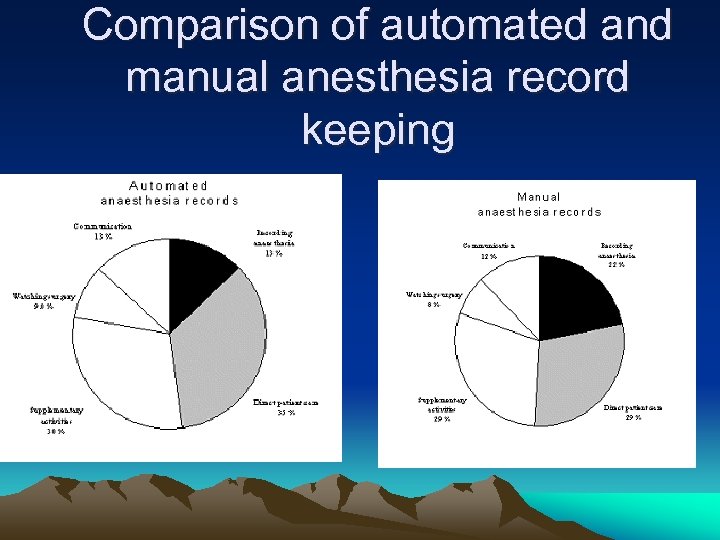 Comparison of automated and manual anesthesia record keeping
Comparison of automated and manual anesthesia record keeping
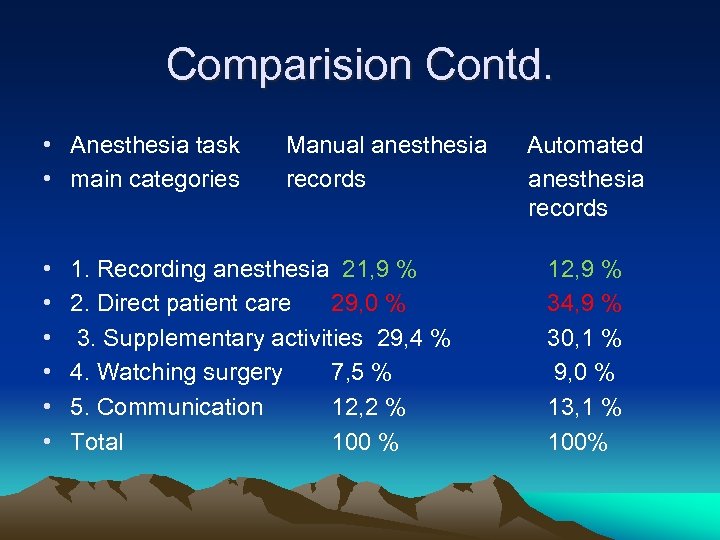 Comparision Contd. • Anesthesia task • main categories • • • Manual anesthesia records 1. Recording anesthesia 21, 9 % 2. Direct patient care 29, 0 % 3. Supplementary activities 29, 4 % 4. Watching surgery 7, 5 % 5. Communication 12, 2 % Total 100 % Automated anesthesia records 12, 9 % 34, 9 % 30, 1 % 9, 0 % 13, 1 % 100%
Comparision Contd. • Anesthesia task • main categories • • • Manual anesthesia records 1. Recording anesthesia 21, 9 % 2. Direct patient care 29, 0 % 3. Supplementary activities 29, 4 % 4. Watching surgery 7, 5 % 5. Communication 12, 2 % Total 100 % Automated anesthesia records 12, 9 % 34, 9 % 30, 1 % 9, 0 % 13, 1 % 100%
 Future • Bar Coded ETTs. • Bar Coded pre filled Syringes for different Medicines. • Bar Coded I. V. Fluids. • Specially Created Key Board • Special Pencil • Touch Screen • Speech Recognising Computer
Future • Bar Coded ETTs. • Bar Coded pre filled Syringes for different Medicines. • Bar Coded I. V. Fluids. • Specially Created Key Board • Special Pencil • Touch Screen • Speech Recognising Computer
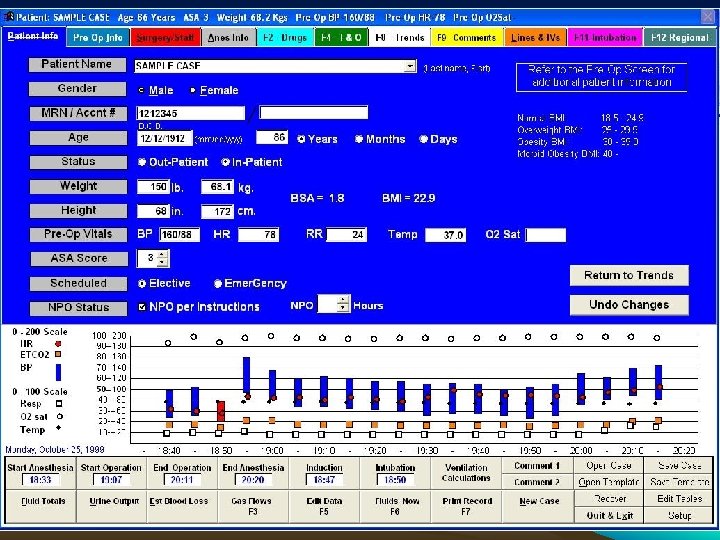
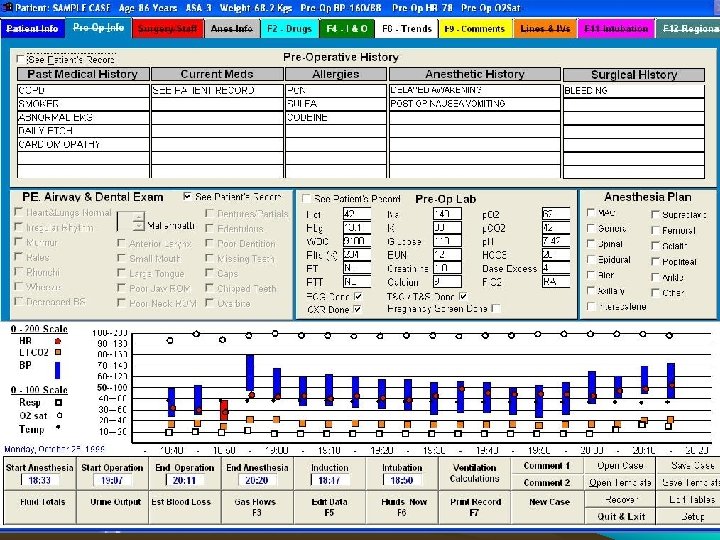
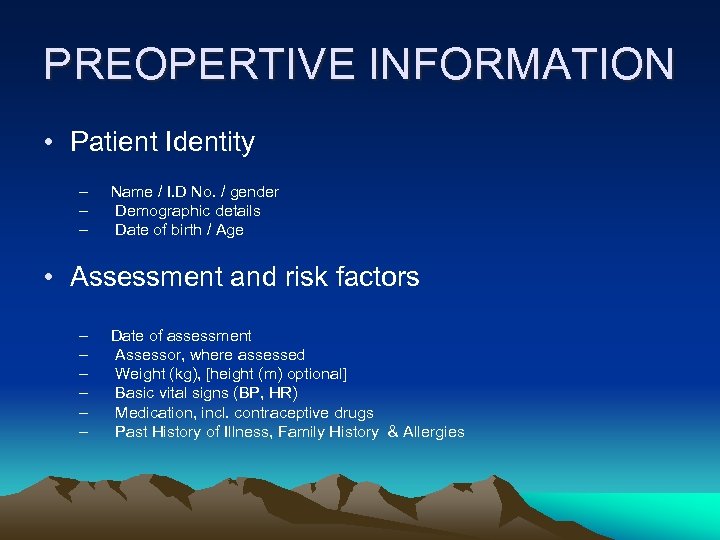 PREOPERTIVE INFORMATION • Patient Identity – – – Name / I. D No. / gender Demographic details Date of birth / Age • Assessment and risk factors – – – Date of assessment Assessor, where assessed Weight (kg), [height (m) optional] Basic vital signs (BP, HR) Medication, incl. contraceptive drugs Past History of Illness, Family History & Allergies
PREOPERTIVE INFORMATION • Patient Identity – – – Name / I. D No. / gender Demographic details Date of birth / Age • Assessment and risk factors – – – Date of assessment Assessor, where assessed Weight (kg), [height (m) optional] Basic vital signs (BP, HR) Medication, incl. contraceptive drugs Past History of Illness, Family History & Allergies
 Contd. – – – – Other problems Addiction (alcohol, tobacco, drugs) & Habits Experience of Previous Anaesthesia Nature of Surgery Examination of Patient Potential airway problems Prostheses, teeth, crown, contact lens – Examination of Patient – Investigations as per Protocol – Cardio Respiratory fitness • As per protocol & sos – Optimise the Condition – Categorise ASA risk grading
Contd. – – – – Other problems Addiction (alcohol, tobacco, drugs) & Habits Experience of Previous Anaesthesia Nature of Surgery Examination of Patient Potential airway problems Prostheses, teeth, crown, contact lens – Examination of Patient – Investigations as per Protocol – Cardio Respiratory fitness • As per protocol & sos – Optimise the Condition – Categorise ASA risk grading
 Contd. – Informed Consent • • • Separate for Anaesthesia Individualise Highlight Specific Problems & discuss plans, pros & cons Speak to Patient's Relative ASA Grading +/- comment Signature / Witness – Plan for Anaesthesia Technique – Order Pre-medication • Urgency – Scheduled-listed on routine list – Urgent-resuscitated, not on a routine list – Emergency-not fully resuscitated
Contd. – Informed Consent • • • Separate for Anaesthesia Individualise Highlight Specific Problems & discuss plans, pros & cons Speak to Patient's Relative ASA Grading +/- comment Signature / Witness – Plan for Anaesthesia Technique – Order Pre-medication • Urgency – Scheduled-listed on routine list – Urgent-resuscitated, not on a routine list – Emergency-not fully resuscitated
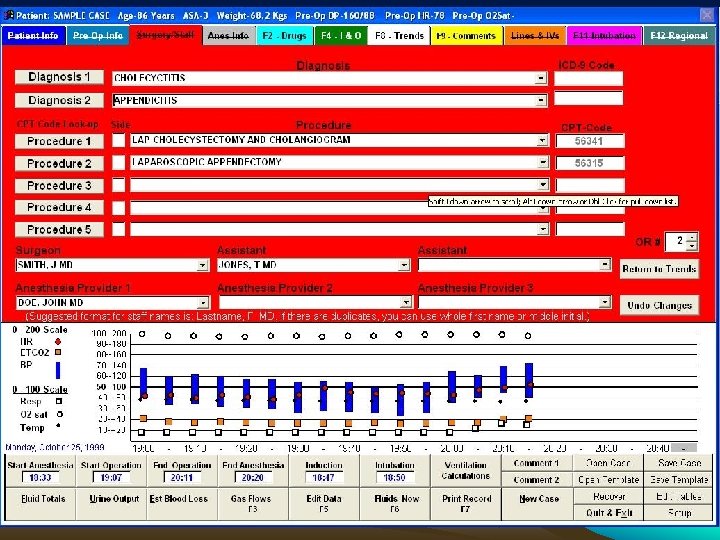
 In OT / Induction room • Checks – – Nil by mouth Consent Premedication, type and effect Drugs including blood & fluids, accessories like ETT, Ambu, Laryngoscope • Place and Time – Place – Date, start and end times • Personnel – – All anaesthetists named Operating surgeon Qualified assistant present Duty consultant informed
In OT / Induction room • Checks – – Nil by mouth Consent Premedication, type and effect Drugs including blood & fluids, accessories like ETT, Ambu, Laryngoscope • Place and Time – Place – Date, start and end times • Personnel – – All anaesthetists named Operating surgeon Qualified assistant present Duty consultant informed
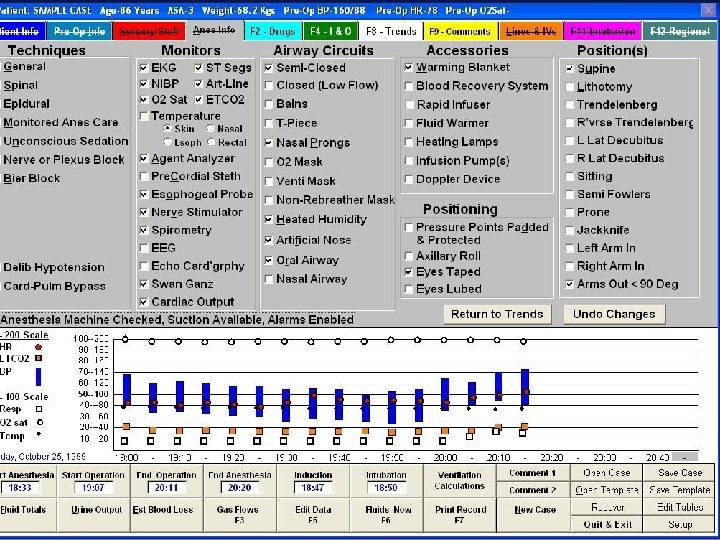
 In OT, before Sx Check • Check the Anaesthesia Machine, Gas Connections, Airway and breathing system, Monitors – Record their proper working. • Sx planned • Vital signs recording/charting • Drugs and Fluids • Blood / Blood product availability • Patient position and attachments • Selection of Vein for I. V. Line – Record.
In OT, before Sx Check • Check the Anaesthesia Machine, Gas Connections, Airway and breathing system, Monitors – Record their proper working. • Sx planned • Vital signs recording/charting • Drugs and Fluids • Blood / Blood product availability • Patient position and attachments • Selection of Vein for I. V. Line – Record.
 Intra Operative Record • Most Important & Most Difficult. • Record Position of Patient. • Record Vital Signs Every 5 Minutes. • Record Administration of Drugs. • I. V. Fluids, Blood & Blood products. • Record Batch No. Exp. Date & Manufacturer of all Drugs. • Mark Important Landmarks of Surgery
Intra Operative Record • Most Important & Most Difficult. • Record Position of Patient. • Record Vital Signs Every 5 Minutes. • Record Administration of Drugs. • I. V. Fluids, Blood & Blood products. • Record Batch No. Exp. Date & Manufacturer of all Drugs. • Mark Important Landmarks of Surgery
 Contd. • Difficult - To Administer Anaesthesia. Keep Watch on Patient. Prepare Drugs. Keep Record Simultaneously. • If Record Keeping Delayed -Facts Missed. -Credibility Diluted.
Contd. • Difficult - To Administer Anaesthesia. Keep Watch on Patient. Prepare Drugs. Keep Record Simultaneously. • If Record Keeping Delayed -Facts Missed. -Credibility Diluted.
 POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS • • Drugs, fluids and doses Analgesic techniques Special airway instructions, incl. oxygen Monitoring
POSTOPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS • • Drugs, fluids and doses Analgesic techniques Special airway instructions, incl. oxygen Monitoring
 Summary • • • Duty bound to care & record Pre op – intra op – post op Recording is mandatory Not recorded = not done Delay will miss & cost you & your pt. more Till AAR come do manual recording
Summary • • • Duty bound to care & record Pre op – intra op – post op Recording is mandatory Not recorded = not done Delay will miss & cost you & your pt. more Till AAR come do manual recording
 Carry home message • • Keeping records is must. If you did it, write it down. If you don’t write it down, it didn’t happen. Courts believe more in what you have written than what you Say. • Keep Records for all the Cases. • Only Detailed Record for case under consideration = “Fabrication of Evidence”.
Carry home message • • Keeping records is must. If you did it, write it down. If you don’t write it down, it didn’t happen. Courts believe more in what you have written than what you Say. • Keep Records for all the Cases. • Only Detailed Record for case under consideration = “Fabrication of Evidence”.



