826931c754798c8244b6b9ec0b3ce5cd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 DR SUJATA PROFESSOR DEPT. OF ANAESTHESIOLOGY &CRITICAL CARE UCMS & GTB HOSPITAL
DR SUJATA PROFESSOR DEPT. OF ANAESTHESIOLOGY &CRITICAL CARE UCMS & GTB HOSPITAL
 CPBR/ CPCR Ø CPR Ø Cardiopulmonary brain resuscitation - CPBR Ø Cardiopulmonary cerebral resuscitation. CPCR
CPBR/ CPCR Ø CPR Ø Cardiopulmonary brain resuscitation - CPBR Ø Cardiopulmonary cerebral resuscitation. CPCR
 Goal ØSupport & restore effective oxygenation, ventilation and circulation with return of intact neurological function. Intermediate Goal: Return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC)
Goal ØSupport & restore effective oxygenation, ventilation and circulation with return of intact neurological function. Intermediate Goal: Return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC)
 Approach Ø BLS ( Basic Life Support) Primary survey. Ø ACLS (Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support) Secondary survey
Approach Ø BLS ( Basic Life Support) Primary survey. Ø ACLS (Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support) Secondary survey
 Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation A - Airway B - Breathing C - Circulation D- Defibrillation
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation A - Airway B - Breathing C - Circulation D- Defibrillation
 Does BLS work? BLS- maximum attention of public. MMajority(70 -80%) of cardiac arrests Out-of-Hospital. Pre-hospital care –key factor
Does BLS work? BLS- maximum attention of public. MMajority(70 -80%) of cardiac arrests Out-of-Hospital. Pre-hospital care –key factor
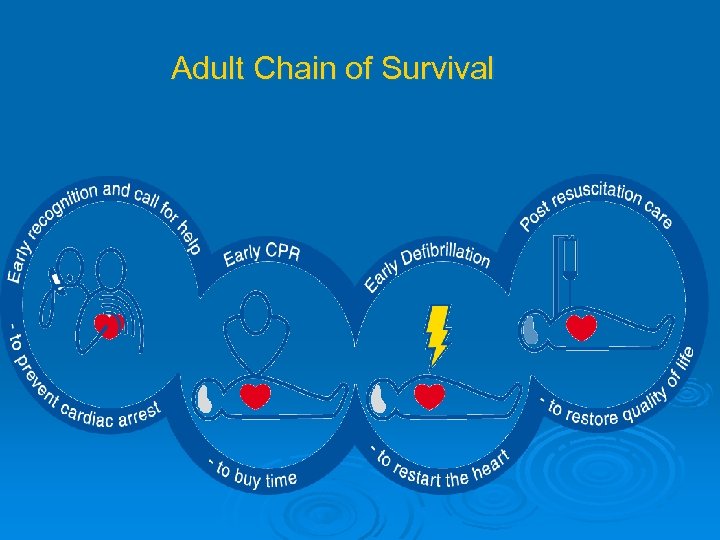 Adult Chain of Survival
Adult Chain of Survival
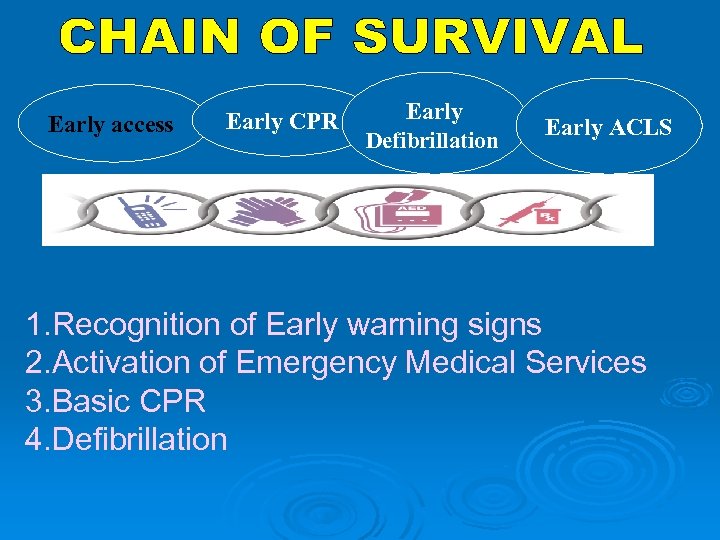 Early access Early CPR Early Defibrillation Early ACLS 1. Recognition of Early warning signs 2. Activation of Emergency Medical Services 3. Basic CPR 4. Defibrillation
Early access Early CPR Early Defibrillation Early ACLS 1. Recognition of Early warning signs 2. Activation of Emergency Medical Services 3. Basic CPR 4. Defibrillation
 Before BLS Primary Survey Ø Ø Ø Scene safety Check responsiveness Activate EMS and get AED Assess & Perform appropriate action. Performance of the action improves chances of survival and better neurological outcome
Before BLS Primary Survey Ø Ø Ø Scene safety Check responsiveness Activate EMS and get AED Assess & Perform appropriate action. Performance of the action improves chances of survival and better neurological outcome
 Before BLS Primary Survey Assess Scene safety Action For you and victim Check responsiveness Tap/ shake and shout “Are you all right? ” Activate emergency response system and get AED Alone- shout for help. Activate emergency 102/ 1099 Get AED…if available Return to victim ……start CPR
Before BLS Primary Survey Assess Scene safety Action For you and victim Check responsiveness Tap/ shake and shout “Are you all right? ” Activate emergency response system and get AED Alone- shout for help. Activate emergency 102/ 1099 Get AED…if available Return to victim ……start CPR
 BLS Primary survey Ø Support/ restore effective oxygenation, ventilation and circulation until ROSC or ACLS team takes over. Ø No advanced interventions- airway tech. / drugs (use universal precautions) Ø Early CPR and early defibrillation
BLS Primary survey Ø Support/ restore effective oxygenation, ventilation and circulation until ROSC or ACLS team takes over. Ø No advanced interventions- airway tech. / drugs (use universal precautions) Ø Early CPR and early defibrillation
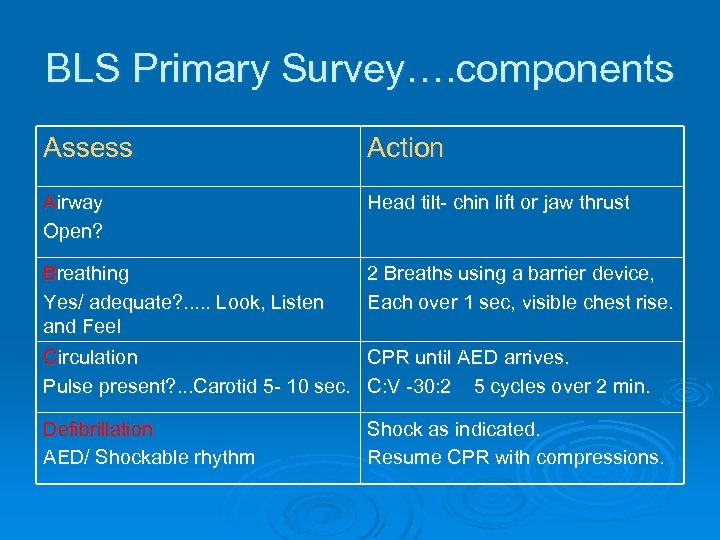 BLS Primary Survey…. components Assess Action Airway Open? Head tilt- chin lift or jaw thrust Breathing Yes/ adequate? . . . Look, Listen and Feel 2 Breaths using a barrier device, Each over 1 sec, visible chest rise. Circulation CPR until AED arrives. Pulse present? . . . Carotid 5 - 10 sec. C: V -30: 2 5 cycles over 2 min. Defibrillation AED/ Shockable rhythm Shock as indicated. Resume CPR with compressions.
BLS Primary Survey…. components Assess Action Airway Open? Head tilt- chin lift or jaw thrust Breathing Yes/ adequate? . . . Look, Listen and Feel 2 Breaths using a barrier device, Each over 1 sec, visible chest rise. Circulation CPR until AED arrives. Pulse present? . . . Carotid 5 - 10 sec. C: V -30: 2 5 cycles over 2 min. Defibrillation AED/ Shockable rhythm Shock as indicated. Resume CPR with compressions.
 Basic airway skills Ø Head tilt- chin lift Ø Jaw thrust without head extension (? Cx spine trauma) Ø Mouth- to- mouth ventilation Ø Mouth- to- nose ventilation Ø Mouth- to- barrier device (pocket mask) Ø Bag-mask ventilation
Basic airway skills Ø Head tilt- chin lift Ø Jaw thrust without head extension (? Cx spine trauma) Ø Mouth- to- mouth ventilation Ø Mouth- to- nose ventilation Ø Mouth- to- barrier device (pocket mask) Ø Bag-mask ventilation
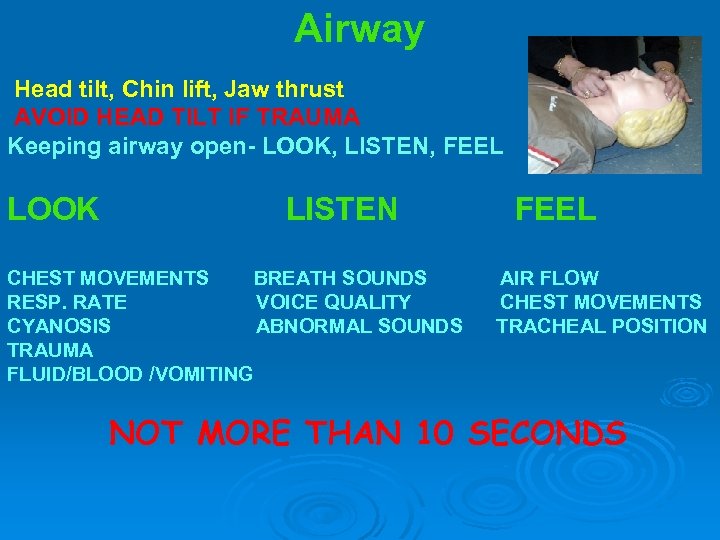 Airway Head tilt, Chin lift, Jaw thrust AVOID HEAD TILT IF TRAUMA Keeping airway open- LOOK, LISTEN, FEEL LOOK LISTEN CHEST MOVEMENTS BREATH SOUNDS RESP. RATE VOICE QUALITY CYANOSIS ABNORMAL SOUNDS TRAUMA FLUID/BLOOD /VOMITING FEEL AIR FLOW CHEST MOVEMENTS TRACHEAL POSITION NOT MORE THAN 10 SECONDS
Airway Head tilt, Chin lift, Jaw thrust AVOID HEAD TILT IF TRAUMA Keeping airway open- LOOK, LISTEN, FEEL LOOK LISTEN CHEST MOVEMENTS BREATH SOUNDS RESP. RATE VOICE QUALITY CYANOSIS ABNORMAL SOUNDS TRAUMA FLUID/BLOOD /VOMITING FEEL AIR FLOW CHEST MOVEMENTS TRACHEAL POSITION NOT MORE THAN 10 SECONDS
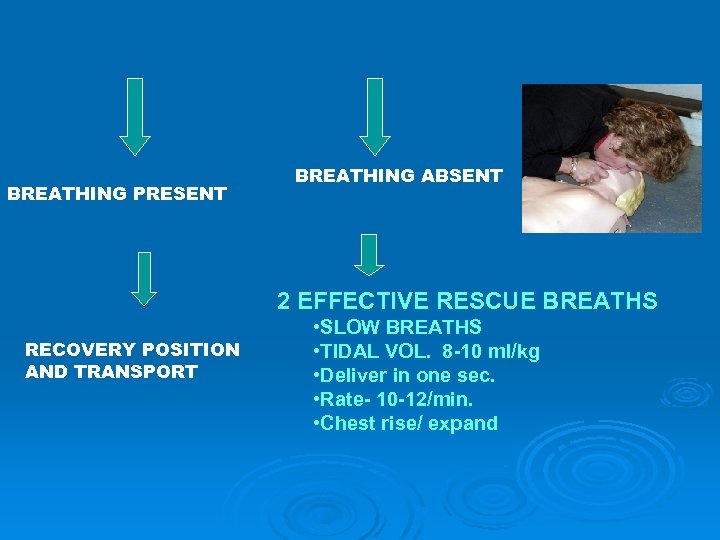 BREATHING PRESENT BREATHING ABSENT 2 EFFECTIVE RESCUE BREATHS RECOVERY POSITION AND TRANSPORT • SLOW BREATHS • TIDAL VOL. 8 -10 ml/kg • Deliver in one sec. • Rate- 10 -12/min. • Chest rise/ expand
BREATHING PRESENT BREATHING ABSENT 2 EFFECTIVE RESCUE BREATHS RECOVERY POSITION AND TRANSPORT • SLOW BREATHS • TIDAL VOL. 8 -10 ml/kg • Deliver in one sec. • Rate- 10 -12/min. • Chest rise/ expand
 Assessing the victim • • • • 1 -- Make sure the victim, any bystanders, and you are safe. 2 -- Check the victim for a response. Shake shoulders gently Ask “Are you all right If he responds Leave as you find him. Find out what is wrong. Reassess regularly If he does not respond: Activate Code Blue and get AED 4 --Keeping the airway open, look, listen, and feel for normal breathing. OPEN AIRWAY Look, listen and feel for NORMAL breathing Do not confuse agonal breathing with NORMAL breathing
Assessing the victim • • • • 1 -- Make sure the victim, any bystanders, and you are safe. 2 -- Check the victim for a response. Shake shoulders gently Ask “Are you all right If he responds Leave as you find him. Find out what is wrong. Reassess regularly If he does not respond: Activate Code Blue and get AED 4 --Keeping the airway open, look, listen, and feel for normal breathing. OPEN AIRWAY Look, listen and feel for NORMAL breathing Do not confuse agonal breathing with NORMAL breathing
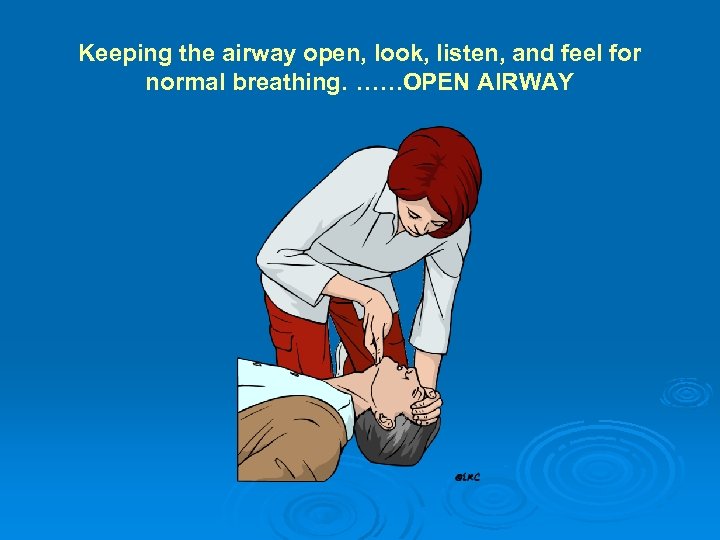 Keeping the airway open, look, listen, and feel for normal breathing. ……OPEN AIRWAY
Keeping the airway open, look, listen, and feel for normal breathing. ……OPEN AIRWAY
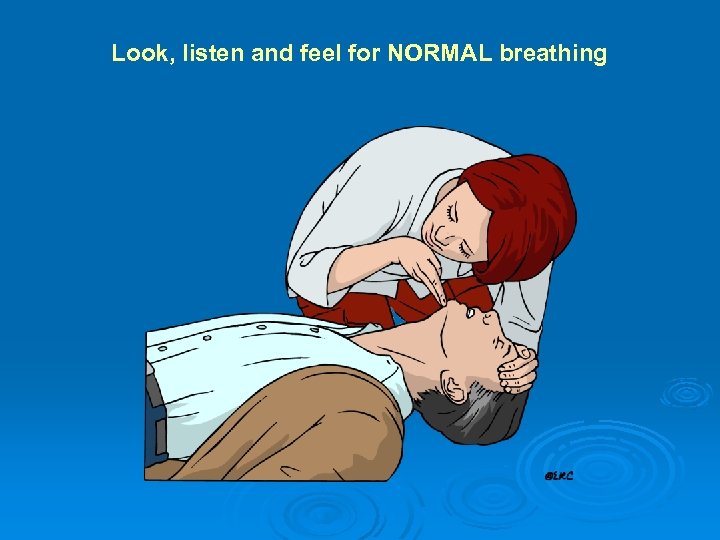 Look, listen and feel for NORMAL breathing
Look, listen and feel for NORMAL breathing
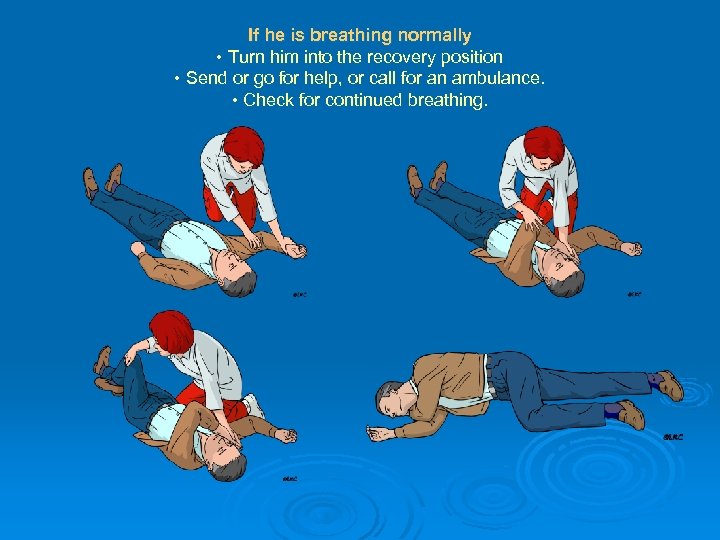 If he is breathing normally • Turn him into the recovery position • Send or go for help, or call for an ambulance. • Check for continued breathing.
If he is breathing normally • Turn him into the recovery position • Send or go for help, or call for an ambulance. • Check for continued breathing.
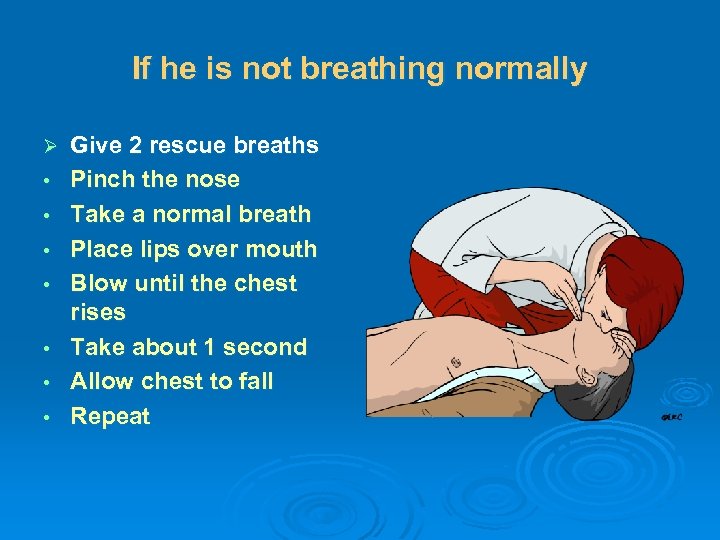 If he is not breathing normally Ø • • Give 2 rescue breaths Pinch the nose Take a normal breath Place lips over mouth Blow until the chest rises Take about 1 second Allow chest to fall Repeat
If he is not breathing normally Ø • • Give 2 rescue breaths Pinch the nose Take a normal breath Place lips over mouth Blow until the chest rises Take about 1 second Allow chest to fall Repeat
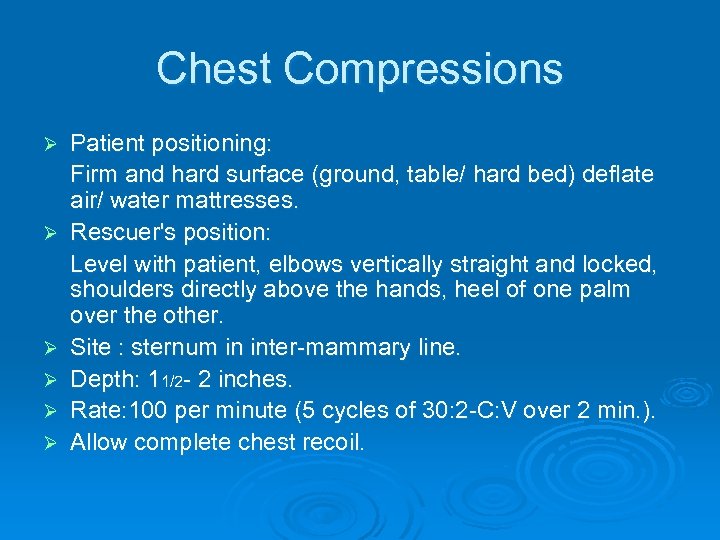 Chest Compressions Ø Ø Ø Patient positioning: Firm and hard surface (ground, table/ hard bed) deflate air/ water mattresses. Rescuer's position: Level with patient, elbows vertically straight and locked, shoulders directly above the hands, heel of one palm over the other. Site : sternum in inter-mammary line. Depth: 11/2 - 2 inches. Rate: 100 per minute (5 cycles of 30: 2 -C: V over 2 min. ). Allow complete chest recoil.
Chest Compressions Ø Ø Ø Patient positioning: Firm and hard surface (ground, table/ hard bed) deflate air/ water mattresses. Rescuer's position: Level with patient, elbows vertically straight and locked, shoulders directly above the hands, heel of one palm over the other. Site : sternum in inter-mammary line. Depth: 11/2 - 2 inches. Rate: 100 per minute (5 cycles of 30: 2 -C: V over 2 min. ). Allow complete chest recoil.
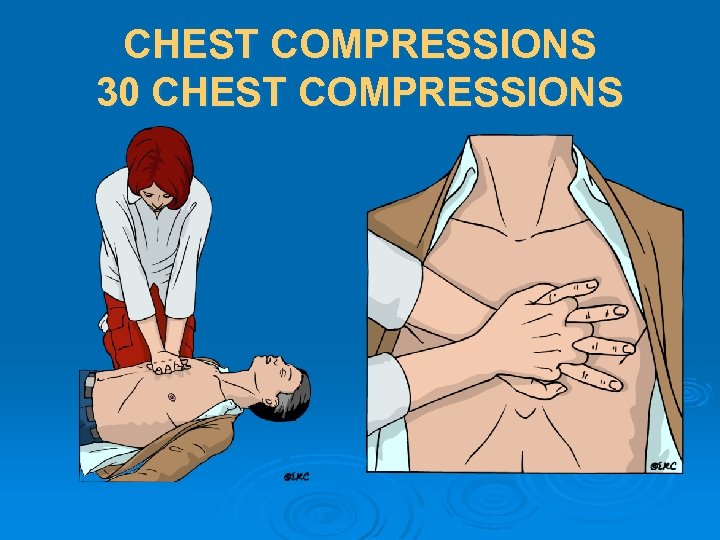 CHEST COMPRESSIONS 30 CHEST COMPRESSIONS
CHEST COMPRESSIONS 30 CHEST COMPRESSIONS
 Hands off- time Less than 10 sec. Ø Specific interventions: defibrillation, advanced airway, moving the patient. Ø Avoid : Ø Prolonged rhythm analysis Ø Frequent pulse checks Ø Too long breaths Ø Unnecessary moving the pt.
Hands off- time Less than 10 sec. Ø Specific interventions: defibrillation, advanced airway, moving the patient. Ø Avoid : Ø Prolonged rhythm analysis Ø Frequent pulse checks Ø Too long breaths Ø Unnecessary moving the pt.
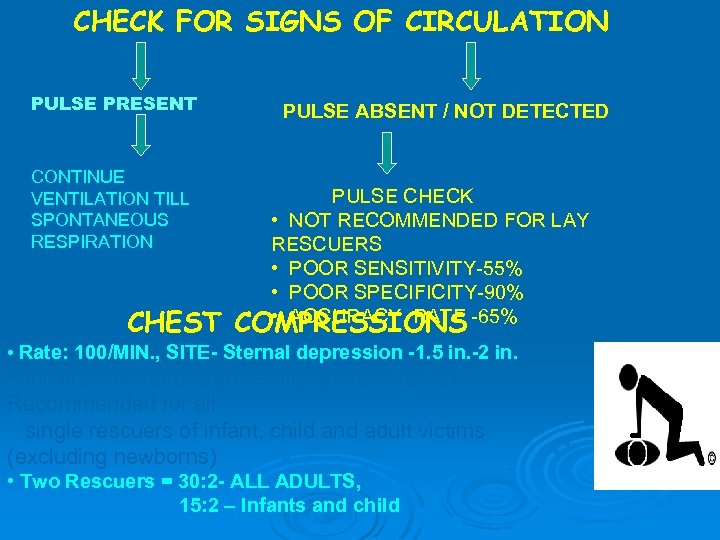 CHECK FOR SIGNS OF CIRCULATION PULSE PRESENT CONTINUE VENTILATION TILL SPONTANEOUS RESPIRATION CHEST PULSE ABSENT / NOT DETECTED PULSE CHECK • NOT RECOMMENDED FOR LAY RESCUERS • POOR SENSITIVITY-55% • POOR SPECIFICITY-90% • ACCURACY RATE COMPRESSIONS -65% • Rate: 100/MIN. , SITE- Sternal depression -1. 5 in. -2 in. • Universal compression-ventilation ratio (30: 2) Recommended for all single rescuers of infant, child and adult victims (excluding newborns) • Two Rescuers = 30: 2 - ALL ADULTS, 15: 2 – Infants and child
CHECK FOR SIGNS OF CIRCULATION PULSE PRESENT CONTINUE VENTILATION TILL SPONTANEOUS RESPIRATION CHEST PULSE ABSENT / NOT DETECTED PULSE CHECK • NOT RECOMMENDED FOR LAY RESCUERS • POOR SENSITIVITY-55% • POOR SPECIFICITY-90% • ACCURACY RATE COMPRESSIONS -65% • Rate: 100/MIN. , SITE- Sternal depression -1. 5 in. -2 in. • Universal compression-ventilation ratio (30: 2) Recommended for all single rescuers of infant, child and adult victims (excluding newborns) • Two Rescuers = 30: 2 - ALL ADULTS, 15: 2 – Infants and child
 Defibrillation Ø AED: Follow the prompts. Ø Manual defibrillator: Analyse rhythm, shockable- decide shock (Monophasic 360 J, Biphasic 120 -200 J ), apply gel, charge, clear the patient, no inflammables (incl. oxygen), deliver shock…. . Resume CPR immediately.
Defibrillation Ø AED: Follow the prompts. Ø Manual defibrillator: Analyse rhythm, shockable- decide shock (Monophasic 360 J, Biphasic 120 -200 J ), apply gel, charge, clear the patient, no inflammables (incl. oxygen), deliver shock…. . Resume CPR immediately.
 AED
AED
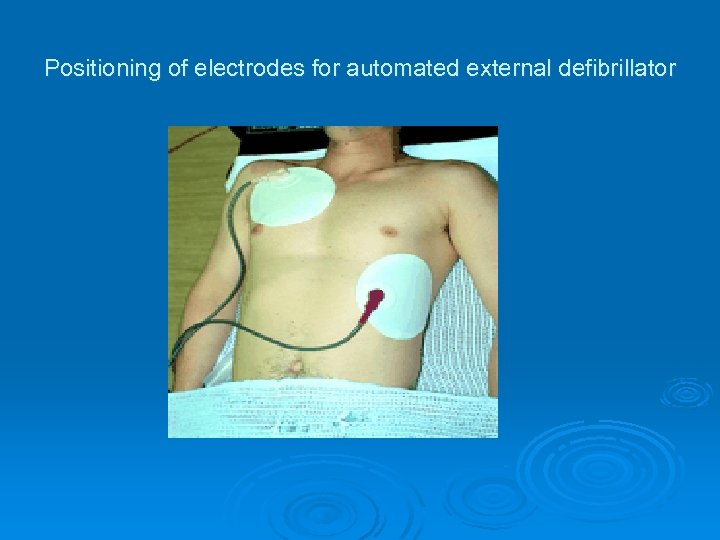 Positioning of electrodes for automated external defibrillator
Positioning of electrodes for automated external defibrillator
 DEFIBRILLATION ATTACH PADS TO VICTIM’S BARE CHEST
DEFIBRILLATION ATTACH PADS TO VICTIM’S BARE CHEST
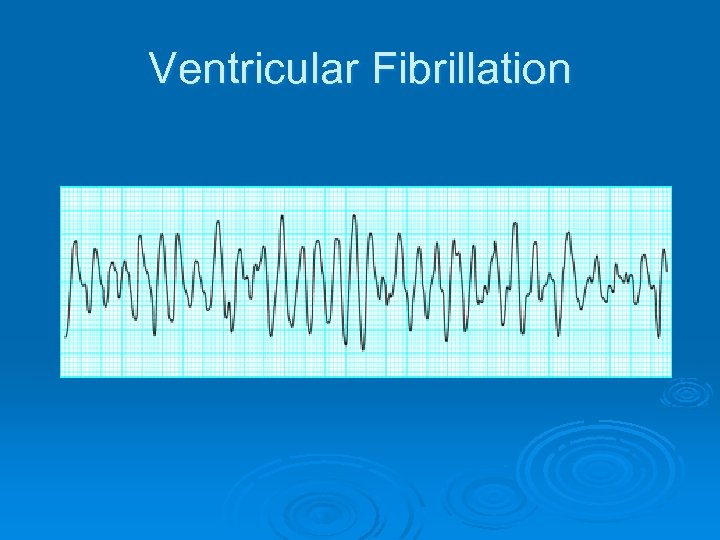 Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular Fibrillation
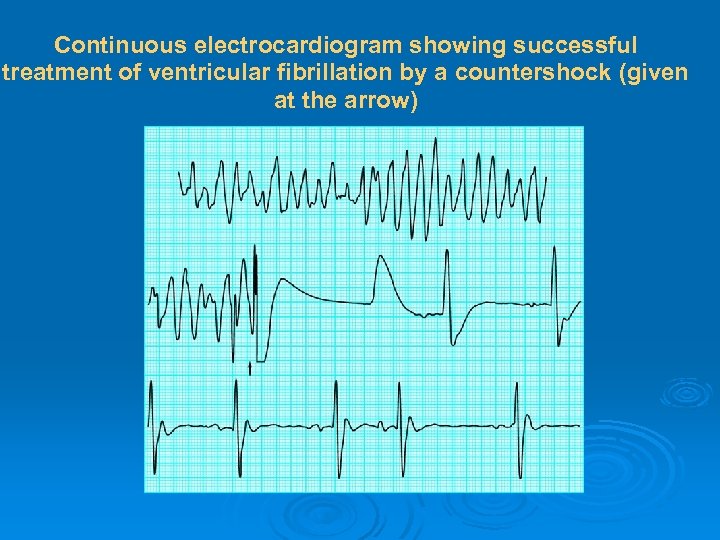 Continuous electrocardiogram showing successful treatment of ventricular fibrillation by a countershock (given at the arrow)
Continuous electrocardiogram showing successful treatment of ventricular fibrillation by a countershock (given at the arrow)
 ANALYSING RHYTHM DO NOT TOUCH VICTIM SHOCK INDICATED Stand clear Speak Aloud- “I Clear. . . You Clear. . . . All Clear!” Deliver shock IF VICTIM STARTS TO BREATHE NORMALLY PLACE IN RECOVERY POSITION
ANALYSING RHYTHM DO NOT TOUCH VICTIM SHOCK INDICATED Stand clear Speak Aloud- “I Clear. . . You Clear. . . . All Clear!” Deliver shock IF VICTIM STARTS TO BREATHE NORMALLY PLACE IN RECOVERY POSITION
 ACLS Secondary survey Advanced, invasive assessment and management techniques required. Basic airway adjuncts: OPA, NPA Advanced Airway interventions: Combitube, LMA, Endotracheal intubation. Advanced circulatory interventions: Drugs to control heart rhythm and blood pressure.
ACLS Secondary survey Advanced, invasive assessment and management techniques required. Basic airway adjuncts: OPA, NPA Advanced Airway interventions: Combitube, LMA, Endotracheal intubation. Advanced circulatory interventions: Drugs to control heart rhythm and blood pressure.
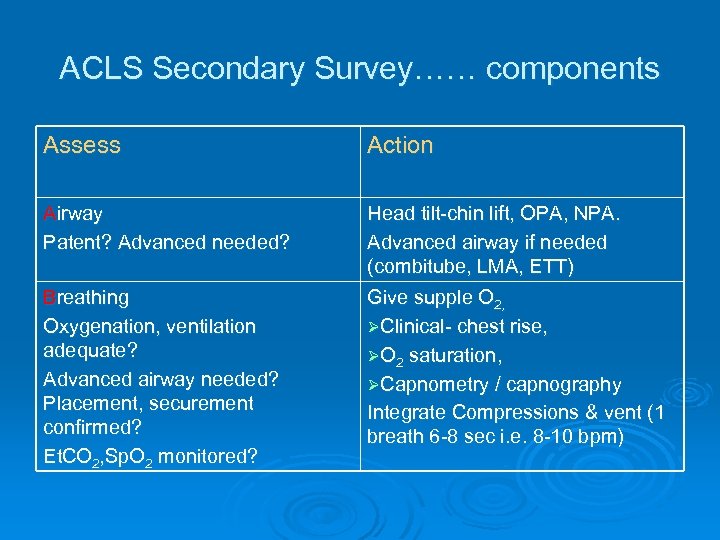 ACLS Secondary Survey…… components Assess Action Airway Patent? Advanced needed? Head tilt-chin lift, OPA, NPA. Advanced airway if needed (combitube, LMA, ETT) Breathing Oxygenation, ventilation adequate? Advanced airway needed? Placement, securement confirmed? Et. CO 2, Sp. O 2 monitored? Give supple O 2, ØClinical- chest rise, ØO 2 saturation, ØCapnometry / capnography Integrate Compressions & vent (1 breath 6 -8 sec i. e. 8 -10 bpm)
ACLS Secondary Survey…… components Assess Action Airway Patent? Advanced needed? Head tilt-chin lift, OPA, NPA. Advanced airway if needed (combitube, LMA, ETT) Breathing Oxygenation, ventilation adequate? Advanced airway needed? Placement, securement confirmed? Et. CO 2, Sp. O 2 monitored? Give supple O 2, ØClinical- chest rise, ØO 2 saturation, ØCapnometry / capnography Integrate Compressions & vent (1 breath 6 -8 sec i. e. 8 -10 bpm)
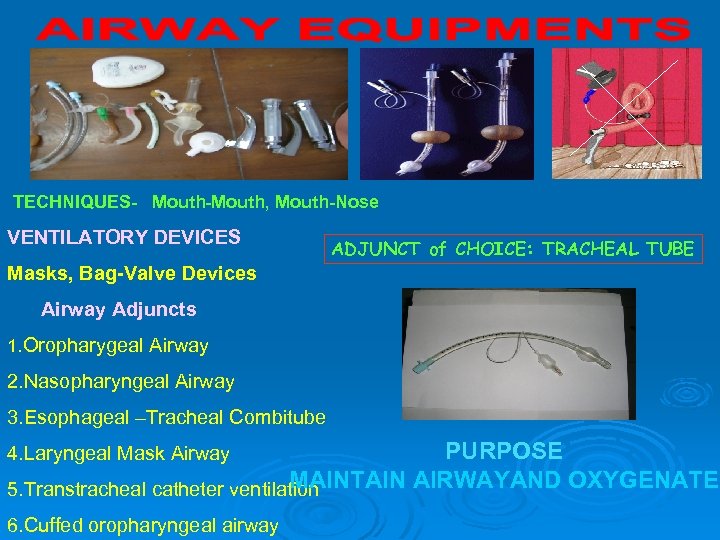 TECHNIQUES- Mouth-Mouth, Mouth-Nose VENTILATORY DEVICES ADJUNCT of CHOICE: TRACHEAL TUBE Masks, Bag-Valve Devices Airway Adjuncts 1. Oropharygeal Airway 2. Nasopharyngeal Airway 3. Esophageal –Tracheal Combitube PURPOSE MAINTAIN AIRWAYAND OXYGENATE 5. Transtracheal catheter ventilation 4. Laryngeal Mask Airway 6. Cuffed oropharyngeal airway
TECHNIQUES- Mouth-Mouth, Mouth-Nose VENTILATORY DEVICES ADJUNCT of CHOICE: TRACHEAL TUBE Masks, Bag-Valve Devices Airway Adjuncts 1. Oropharygeal Airway 2. Nasopharyngeal Airway 3. Esophageal –Tracheal Combitube PURPOSE MAINTAIN AIRWAYAND OXYGENATE 5. Transtracheal catheter ventilation 4. Laryngeal Mask Airway 6. Cuffed oropharyngeal airway
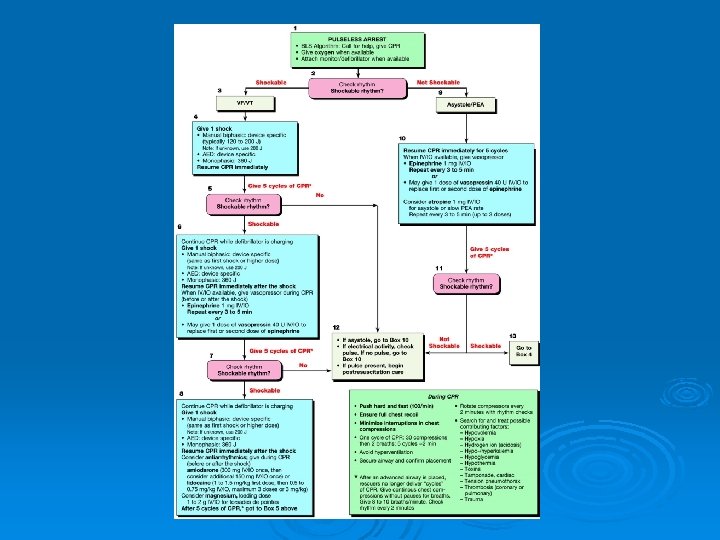
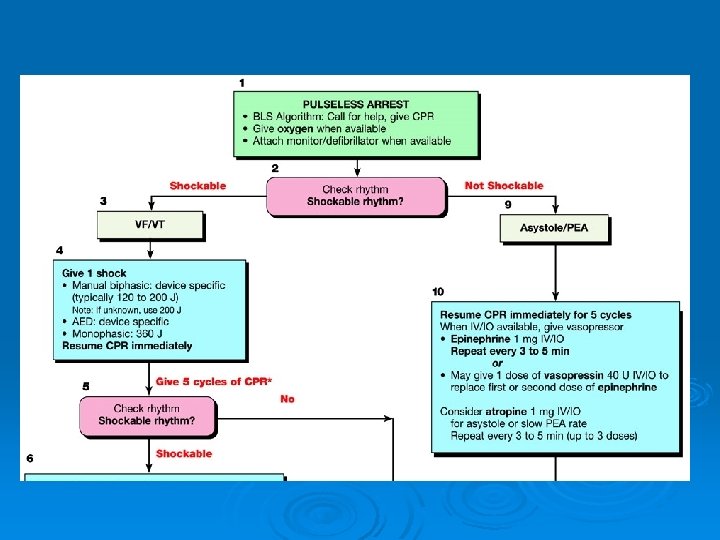
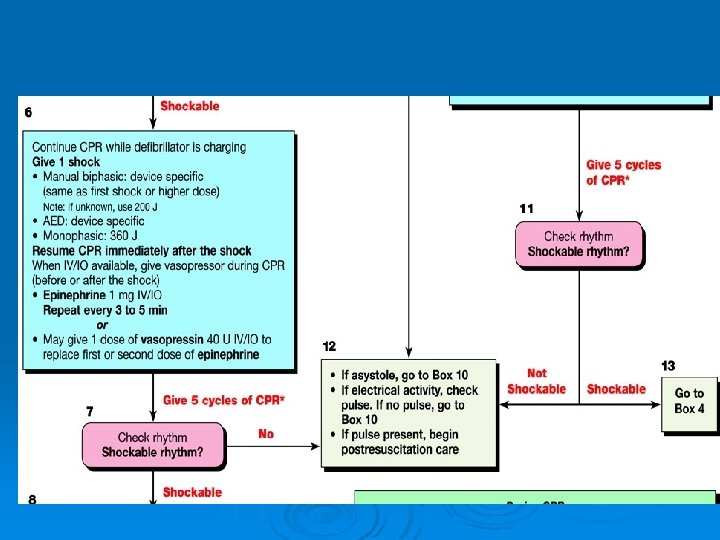
 ACLS Secondary Survey……. components Assess Action Circulation Initial/ current cardiac rhythm? Access for drugs/ fluids? Needs volume/ drugs Obtain IV/ IO access Attach ECG leads, monitor for rhythms (Cardiac arrest: VF, Pulseless VT, Asystole, PEA). Give IV/ IO fluids Appropriate drugs (Rhythm: Amiodarone, Lidocaine, Atropine, Magnesium; BP: Adrenaline, Vasopressin, Dopamine) Differential Diagnosis Reversible cause of arrest? Search for, find and treat the cause (H`s and T`s)
ACLS Secondary Survey……. components Assess Action Circulation Initial/ current cardiac rhythm? Access for drugs/ fluids? Needs volume/ drugs Obtain IV/ IO access Attach ECG leads, monitor for rhythms (Cardiac arrest: VF, Pulseless VT, Asystole, PEA). Give IV/ IO fluids Appropriate drugs (Rhythm: Amiodarone, Lidocaine, Atropine, Magnesium; BP: Adrenaline, Vasopressin, Dopamine) Differential Diagnosis Reversible cause of arrest? Search for, find and treat the cause (H`s and T`s)
 Common Reversible Causes H`s T`s Hypovolemia Toxins Hypoxia Tamponade (cardiac) Hydrogen ion (Acidosis) Tension pneumothorax Hyper-/ Hypokalemia Thrombosis (coronary/ pulmonary) Trauma Hypoglycemia Hypothermia
Common Reversible Causes H`s T`s Hypovolemia Toxins Hypoxia Tamponade (cardiac) Hydrogen ion (Acidosis) Tension pneumothorax Hyper-/ Hypokalemia Thrombosis (coronary/ pulmonary) Trauma Hypoglycemia Hypothermia
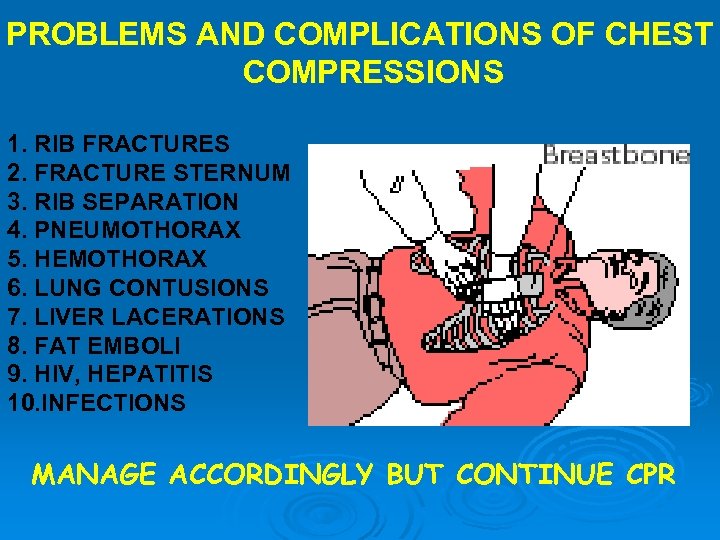 PROBLEMS AND COMPLICATIONS OF CHEST COMPRESSIONS 1. RIB FRACTURES 2. FRACTURE STERNUM 3. RIB SEPARATION 4. PNEUMOTHORAX 5. HEMOTHORAX 6. LUNG CONTUSIONS 7. LIVER LACERATIONS 8. FAT EMBOLI 9. HIV, HEPATITIS 10. INFECTIONS MANAGE ACCORDINGLY BUT CONTINUE CPR
PROBLEMS AND COMPLICATIONS OF CHEST COMPRESSIONS 1. RIB FRACTURES 2. FRACTURE STERNUM 3. RIB SEPARATION 4. PNEUMOTHORAX 5. HEMOTHORAX 6. LUNG CONTUSIONS 7. LIVER LACERATIONS 8. FAT EMBOLI 9. HIV, HEPATITIS 10. INFECTIONS MANAGE ACCORDINGLY BUT CONTINUE CPR
 EFFECTIVE CHEST COMPRESSION WITH MINIMAL HANDS OFF IS KEY FOR EFFECTIVE CPR
EFFECTIVE CHEST COMPRESSION WITH MINIMAL HANDS OFF IS KEY FOR EFFECTIVE CPR
 When to stop BLS Ø ROSC, Conscious pt. Ø ACLS team takes over Ø Rescuer tired
When to stop BLS Ø ROSC, Conscious pt. Ø ACLS team takes over Ø Rescuer tired
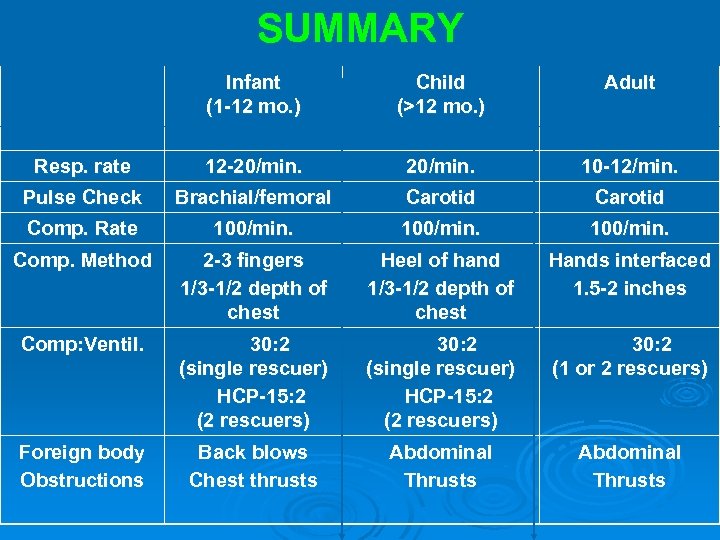 SUMMARY Infant (1 -12 mo. ) Child (>12 mo. ) Adult Resp. rate 12 -20/min. 10 -12/min. Pulse Check Brachial/femoral Carotid Comp. Rate 100/min. Comp. Method 2 -3 fingers 1/3 -1/2 depth of chest Heel of hand 1/3 -1/2 depth of chest Hands interfaced 1. 5 -2 inches Comp: Ventil. 30: 2 (single rescuer) HCP-15: 2 (2 rescuers) 30: 2 (1 or 2 rescuers) Foreign body Obstructions Back blows Chest thrusts Abdominal Thrusts
SUMMARY Infant (1 -12 mo. ) Child (>12 mo. ) Adult Resp. rate 12 -20/min. 10 -12/min. Pulse Check Brachial/femoral Carotid Comp. Rate 100/min. Comp. Method 2 -3 fingers 1/3 -1/2 depth of chest Heel of hand 1/3 -1/2 depth of chest Hands interfaced 1. 5 -2 inches Comp: Ventil. 30: 2 (single rescuer) HCP-15: 2 (2 rescuers) 30: 2 (1 or 2 rescuers) Foreign body Obstructions Back blows Chest thrusts Abdominal Thrusts
 DRUGS EPINEPHRINE 1. Peripheral vasoconstriction -adrenergic 2. Increase in Central aortic perfusion pressure 3. Decrease Threshold for Defibrillation 4. Fine VF to Coarse VF
DRUGS EPINEPHRINE 1. Peripheral vasoconstriction -adrenergic 2. Increase in Central aortic perfusion pressure 3. Decrease Threshold for Defibrillation 4. Fine VF to Coarse VF
 DRUGS For Rhythm • Amiodarone • Lidocaine • Atropine • Magnesium For Blood Pressure • Epinephrine • Vasopressin • DOPAMINE-2 -4 micro/kg/min. -DA rec 4 -10 micro/kg/min- Beta-rec. 10 -20 micro/kg/min- Alpha rec.
DRUGS For Rhythm • Amiodarone • Lidocaine • Atropine • Magnesium For Blood Pressure • Epinephrine • Vasopressin • DOPAMINE-2 -4 micro/kg/min. -DA rec 4 -10 micro/kg/min- Beta-rec. 10 -20 micro/kg/min- Alpha rec.
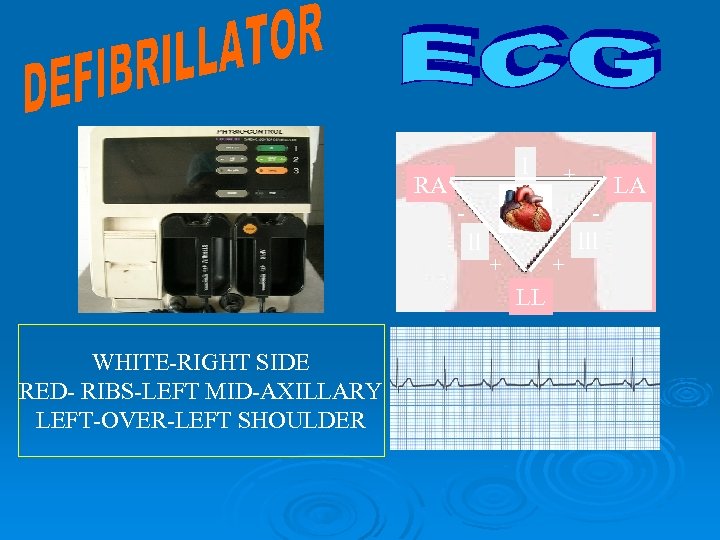 l - RA + ll + + LL WHITE-RIGHT SIDE RED- RIBS-LEFT MID-AXILLARY LEFT-OVER-LEFT SHOULDER LA lll
l - RA + ll + + LL WHITE-RIGHT SIDE RED- RIBS-LEFT MID-AXILLARY LEFT-OVER-LEFT SHOULDER LA lll
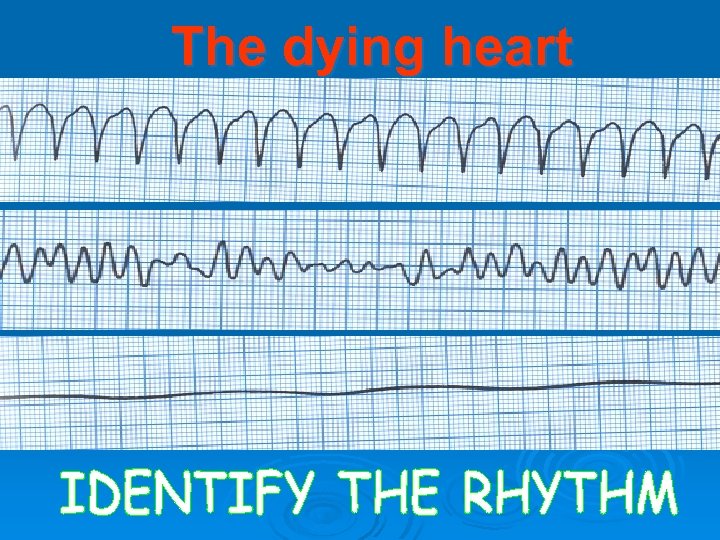 The dying heart
The dying heart
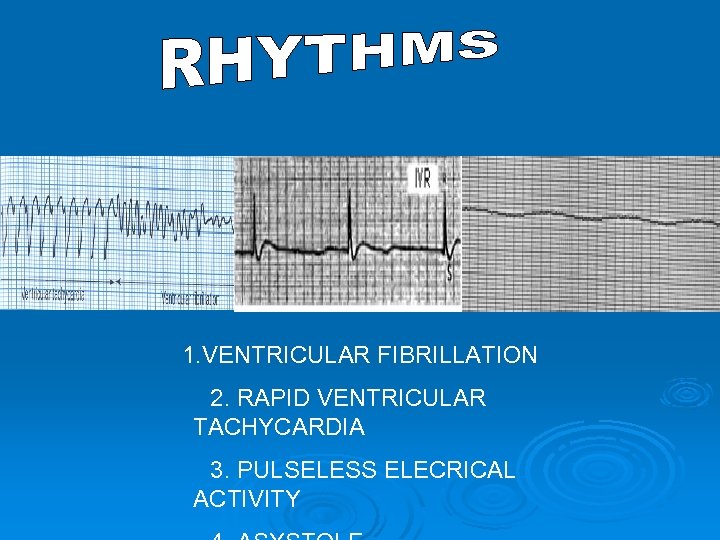 1. VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. RAPID VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA 3. PULSELESS ELECRICAL ACTIVITY
1. VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. RAPID VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA 3. PULSELESS ELECRICAL ACTIVITY
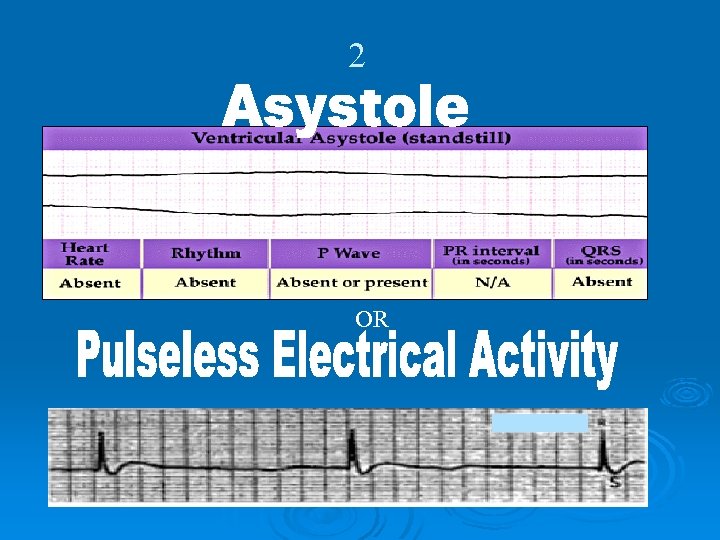 2 OR
2 OR