0afe8efd26f75a4553e373ce41180460.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Dr. Serge S. AZAROV 2004 i. Law-2004 2005 Tallinn
Dr. Serge S. AZAROV 2004 i. Law-2004 2005 Tallinn
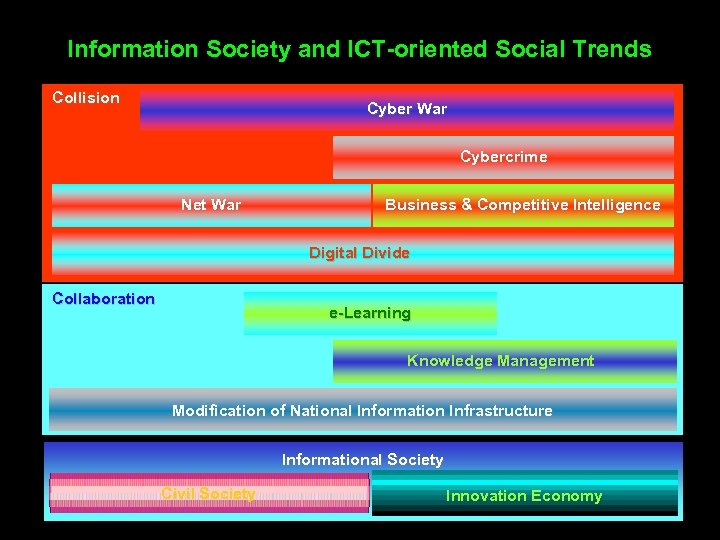 Information Society and ICT-oriented Social Trends Collision Cyber War Cybercrime Net War Business & Competitive Intelligence Digital Divide Collaboration e-Learning Knowledge Management Modification of National Information Infrastructure Informational Society Civil Society Innovation Economy
Information Society and ICT-oriented Social Trends Collision Cyber War Cybercrime Net War Business & Competitive Intelligence Digital Divide Collaboration e-Learning Knowledge Management Modification of National Information Infrastructure Informational Society Civil Society Innovation Economy
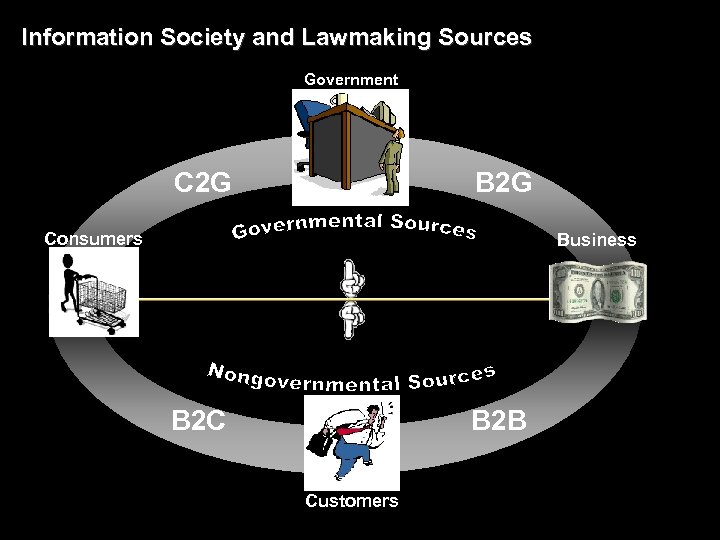 Information Society and Lawmaking Sources Government C 2 G B 2 G Consumers Business B 2 C B 2 B Customers
Information Society and Lawmaking Sources Government C 2 G B 2 G Consumers Business B 2 C B 2 B Customers
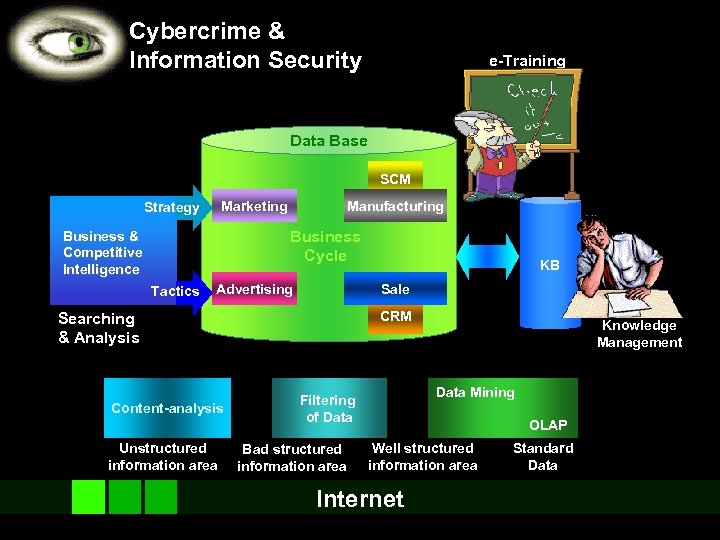 Cybercrime & Information Security e-Training Data Base SCM Marketing Strategy Manufacturing Business Cycle Business & Competitive Intelligence Tactics Advertising Sale CRM Searching & Analysis Content-analysis Unstructured information area KB Data Mining Filtering of Data Bad structured information area Knowledge Management OLAP Well structured information area Internet Standard Data
Cybercrime & Information Security e-Training Data Base SCM Marketing Strategy Manufacturing Business Cycle Business & Competitive Intelligence Tactics Advertising Sale CRM Searching & Analysis Content-analysis Unstructured information area KB Data Mining Filtering of Data Bad structured information area Knowledge Management OLAP Well structured information area Internet Standard Data
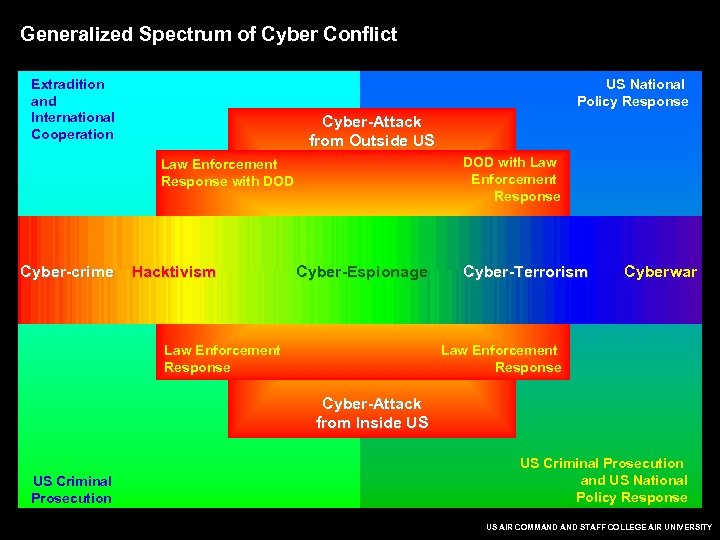 Generalized Spectrum of Cyber Conflict Extradition and International Cooperation US National Policy Response Cyber-Attack from Outside US DOD with Law Enforcement Response with DOD Cyber-crime Hacktivism Cyber-Espionage Law Enforcement Response Cyber-Terrorism Cyberwar Law Enforcement Response Cyber-Attack from Inside US US Criminal Prosecution and US National Policy Response US AIR COMMAND STAFF COLLEGE AIR UNIVERSITY
Generalized Spectrum of Cyber Conflict Extradition and International Cooperation US National Policy Response Cyber-Attack from Outside US DOD with Law Enforcement Response with DOD Cyber-crime Hacktivism Cyber-Espionage Law Enforcement Response Cyber-Terrorism Cyberwar Law Enforcement Response Cyber-Attack from Inside US US Criminal Prosecution and US National Policy Response US AIR COMMAND STAFF COLLEGE AIR UNIVERSITY
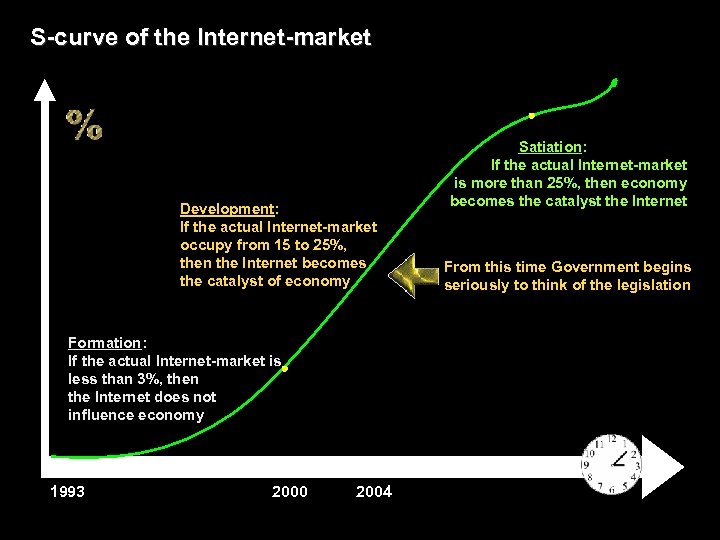 S-curve of the Internet-market Development: If the actual Internet-market occupy from 15 to 25%, then the Internet becomes the catalyst of economy Formation: If the actual Internet-market is less than 3%, then the Internet does not influence economy 1993 2000 2004 Satiation: If the actual Internet-market is more than 25%, then economy becomes the catalyst the Internet From this time Government begins seriously to think of the legislation
S-curve of the Internet-market Development: If the actual Internet-market occupy from 15 to 25%, then the Internet becomes the catalyst of economy Formation: If the actual Internet-market is less than 3%, then the Internet does not influence economy 1993 2000 2004 Satiation: If the actual Internet-market is more than 25%, then economy becomes the catalyst the Internet From this time Government begins seriously to think of the legislation
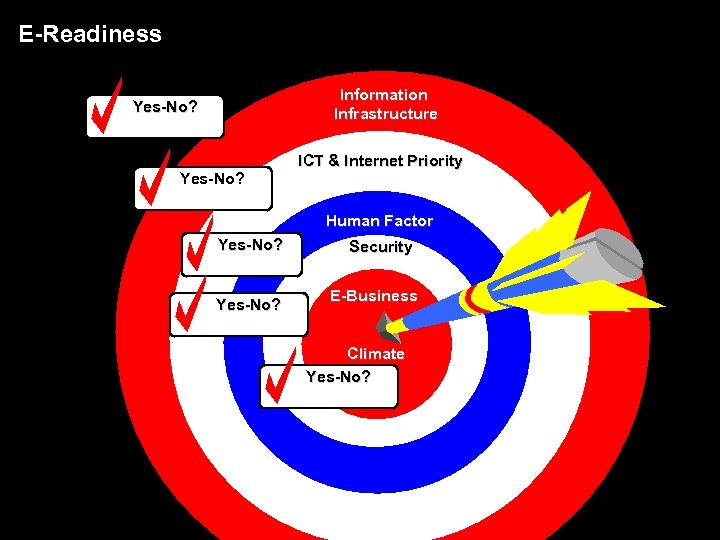 E-Readiness Information Infrastructure Yes-No? ICT & Internet Priority Human Factor Yes-No? Security E-Business Climate Yes-No?
E-Readiness Information Infrastructure Yes-No? ICT & Internet Priority Human Factor Yes-No? Security E-Business Climate Yes-No?
 i. Law-Readiness • The demands of private sector development as the guarantor of growth on new markets for goods and services comes into conflict with national taxation systems. • "Investing for the Future" via substantially expanded education spending by the state requires money that the state does not have under the present conditions of economic crisis. • The "Human Factor" clashes development of the regions. with uneven economic • Harmonization of national legal systems may contradict traditional notions of sovereignty and security.
i. Law-Readiness • The demands of private sector development as the guarantor of growth on new markets for goods and services comes into conflict with national taxation systems. • "Investing for the Future" via substantially expanded education spending by the state requires money that the state does not have under the present conditions of economic crisis. • The "Human Factor" clashes development of the regions. with uneven economic • Harmonization of national legal systems may contradict traditional notions of sovereignty and security.
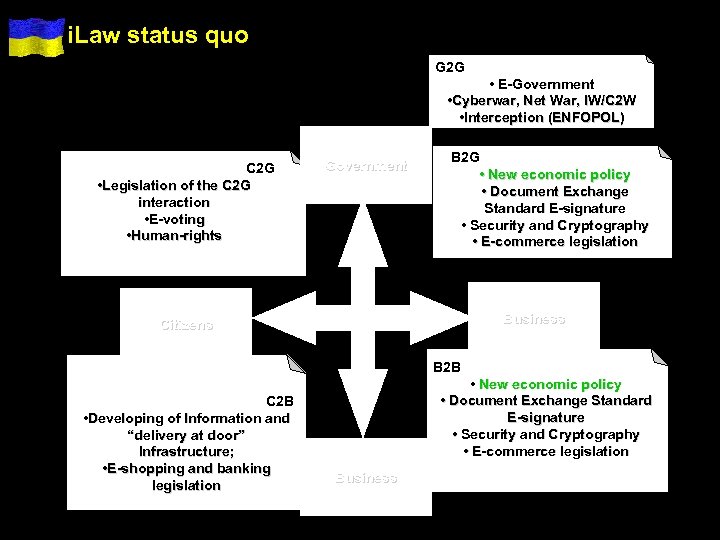 i. Law status quo G 2 G • E-Government • Cyberwar, Net War, IW/C 2 W • Interception (ENFOPOL) C 2 G • Legislation of the C 2 G interaction • E-voting • Human-rights Government B 2 G • New economic policy • Document Exchange Standard E-signature • Security and Cryptography • E-commerce legislation Business Citizens B 2 B C 2 B • Developing of Information and “delivery at door” Infrastructure; • E-shopping and banking legislation • New economic policy • Document Exchange Standard E-signature • Security and Cryptography • E-commerce legislation Business
i. Law status quo G 2 G • E-Government • Cyberwar, Net War, IW/C 2 W • Interception (ENFOPOL) C 2 G • Legislation of the C 2 G interaction • E-voting • Human-rights Government B 2 G • New economic policy • Document Exchange Standard E-signature • Security and Cryptography • E-commerce legislation Business Citizens B 2 B C 2 B • Developing of Information and “delivery at door” Infrastructure; • E-shopping and banking legislation • New economic policy • Document Exchange Standard E-signature • Security and Cryptography • E-commerce legislation Business
 i. Law Development: Ukrainian Ways 1. Main principles of cyberspace regulation 2. Customs and Taxation, Cross border Transactions 3. Electronic Payment Systems 4. Uniform Commercial (for Commerce Conducted on the Internet) 5. Information Code 6. Intellectual Property Protection (Copyrights, Patents, Trademarks) 7. Privacy 8. Information Security 9. Telecommunications Infrastructure 10. Content 11. Technical Standards 12. Universal Service 13. Labor 14. Governmental Approaches
i. Law Development: Ukrainian Ways 1. Main principles of cyberspace regulation 2. Customs and Taxation, Cross border Transactions 3. Electronic Payment Systems 4. Uniform Commercial (for Commerce Conducted on the Internet) 5. Information Code 6. Intellectual Property Protection (Copyrights, Patents, Trademarks) 7. Privacy 8. Information Security 9. Telecommunications Infrastructure 10. Content 11. Technical Standards 12. Universal Service 13. Labor 14. Governmental Approaches
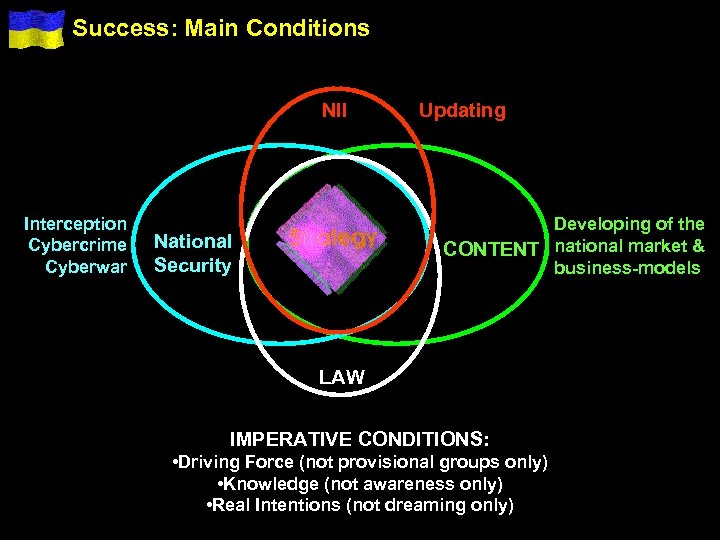 Success: Main Conditions NII Interception Cybercrime Cyberwar Updating Developing of the CONTENT national market & business-models National Security LAW IMPERATIVE CONDITIONS: • Driving Force (not provisional groups only) • Knowledge (not awareness only) • Real Intentions (not dreaming only)
Success: Main Conditions NII Interception Cybercrime Cyberwar Updating Developing of the CONTENT national market & business-models National Security LAW IMPERATIVE CONDITIONS: • Driving Force (not provisional groups only) • Knowledge (not awareness only) • Real Intentions (not dreaming only)
 Contacts (380 + 44) 205 -44 -55 azarov@lucky. net
Contacts (380 + 44) 205 -44 -55 azarov@lucky. net


