8d0d8f2f9aafca08e8a772b68ae6b290.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Dr. Alex Thiermann President, Terrestrial Animal Health Code Commission World Organisation for Animal Health The role of the OIE in a safe and fair trade WTO Public Forum 2006 Geneva, CH, September 2006 1
Dr. Alex Thiermann President, Terrestrial Animal Health Code Commission World Organisation for Animal Health The role of the OIE in a safe and fair trade WTO Public Forum 2006 Geneva, CH, September 2006 1
 • an intergovernmental organisation • founded in 1924 by 28 countries • predates the U. N. World Organisation for Animal Health Organisation mondiale de la santé animale Organizacion Mundial de Sanidad Animal Common name adopted by the International Committee on May 2003 2
• an intergovernmental organisation • founded in 1924 by 28 countries • predates the U. N. World Organisation for Animal Health Organisation mondiale de la santé animale Organizacion Mundial de Sanidad Animal Common name adopted by the International Committee on May 2003 2
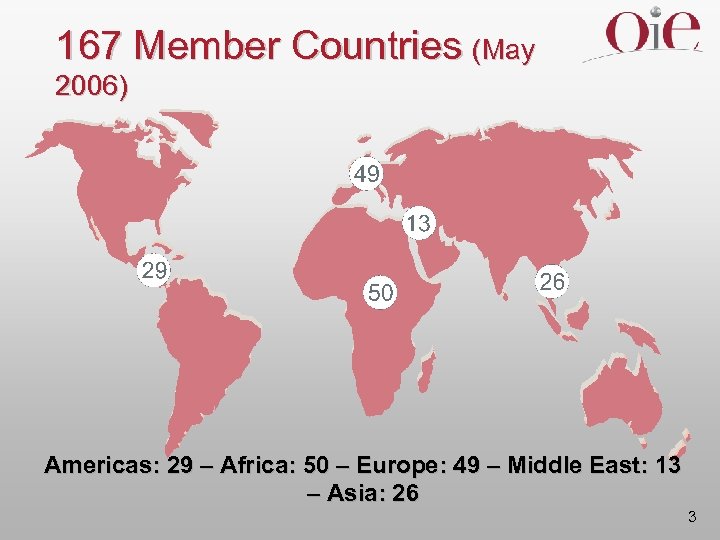 167 Member Countries (May 2006) Americas: 29 – Africa: 50 – Europe: 49 – Middle East: 13 – Asia: 26 3
167 Member Countries (May 2006) Americas: 29 – Africa: 50 – Europe: 49 – Middle East: 13 – Asia: 26 3
 Why an SPS Agreement? Removal of non-tariff barriers to trade GATT article XX(b) Øneed for clearer rules Concentrate on health measures ØProvide rights and obligations 4
Why an SPS Agreement? Removal of non-tariff barriers to trade GATT article XX(b) Øneed for clearer rules Concentrate on health measures ØProvide rights and obligations 4
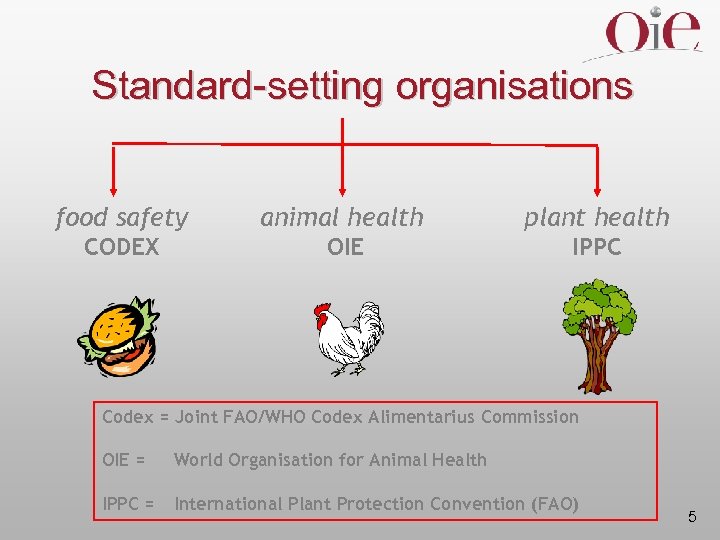 Standard-setting organisations food safety animal health plant health CODEX OIE IPPC Codex = Joint FAO/WHO Codex Alimentarius Commission OIE = World Organisation for Animal Health IPPC = International Plant Protection Convention (FAO) 5
Standard-setting organisations food safety animal health plant health CODEX OIE IPPC Codex = Joint FAO/WHO Codex Alimentarius Commission OIE = World Organisation for Animal Health IPPC = International Plant Protection Convention (FAO) 5
 OIE Objectives 1. To ensure accurate collection and transparency in reporting the animal health situation throughout the world. 2. Under the WTO-SPS Agreement mandate, establish standards on animal health and zoonoses for international trade in animals and animal products. 3. To collect, analyse and disseminate scientific veterinary information. 4. To provide technical expertise and encourage international solidarity in the control and eradication of animal diseases. 5. To improve the competencies and legal framework of Veterinary Services. 6. To develop guiding principles and specific recommendations for animal welfare 6
OIE Objectives 1. To ensure accurate collection and transparency in reporting the animal health situation throughout the world. 2. Under the WTO-SPS Agreement mandate, establish standards on animal health and zoonoses for international trade in animals and animal products. 3. To collect, analyse and disseminate scientific veterinary information. 4. To provide technical expertise and encourage international solidarity in the control and eradication of animal diseases. 5. To improve the competencies and legal framework of Veterinary Services. 6. To develop guiding principles and specific recommendations for animal welfare 6
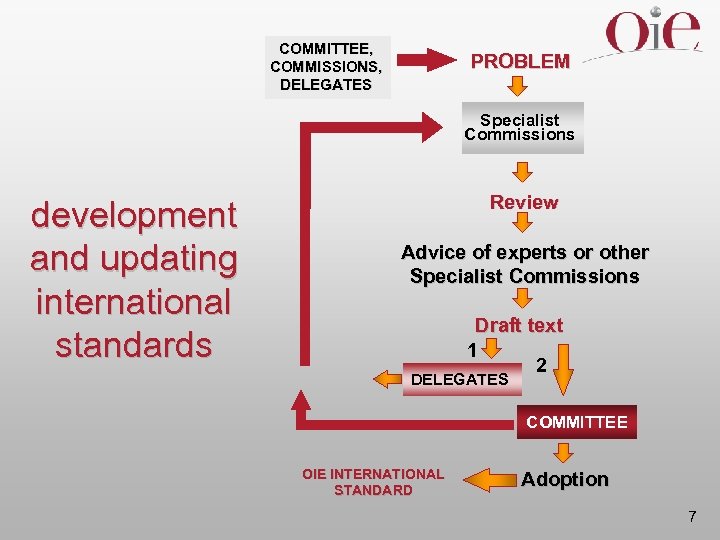 COMMITTEE, COMMISSIONS, DELEGATES PROBLEM Specialist Commissions development and updating international standards Review Advice of experts or other Specialist Commissions Draft text 1 2 DELEGATES COMMITTEE OIE INTERNATIONAL STANDARD Adoption 7
COMMITTEE, COMMISSIONS, DELEGATES PROBLEM Specialist Commissions development and updating international standards Review Advice of experts or other Specialist Commissions Draft text 1 2 DELEGATES COMMITTEE OIE INTERNATIONAL STANDARD Adoption 7
 Direct costs of participation delegates from 145/167 OIE Member Countries attended 2006 General Session Øregistration fees waived and daily expenses paid experts participating in OIE Specialist Commissions, working groups and expert groups have their fares and expenses paid EC has made available 100, 000 Euros to assist participation of experts from developing countries in standards development 8
Direct costs of participation delegates from 145/167 OIE Member Countries attended 2006 General Session Øregistration fees waived and daily expenses paid experts participating in OIE Specialist Commissions, working groups and expert groups have their fares and expenses paid EC has made available 100, 000 Euros to assist participation of experts from developing countries in standards development 8
 Terrestrial Animal Health Code Provides detailed recommendations of sanitary measures to be used by Chief Veterinary Officers of Member Countries in establishing regulations applying to the safe trade of animals and animal products, while avoiding unjustified restrictions Contains recommendations covering ruminants, swine, equidae, rabbits, bees, poultry, dogs and cats In five languages: English, French, Spanish and Russian (Arabic version recently released) 9
Terrestrial Animal Health Code Provides detailed recommendations of sanitary measures to be used by Chief Veterinary Officers of Member Countries in establishing regulations applying to the safe trade of animals and animal products, while avoiding unjustified restrictions Contains recommendations covering ruminants, swine, equidae, rabbits, bees, poultry, dogs and cats In five languages: English, French, Spanish and Russian (Arabic version recently released) 9
 Evolution of OIE standards Need to go from freedom status to risk-based Emphasis on safety of the commodity Essential role of epidemiological surveillance Strength of laboratory network Close link of surveillance to risk assessment Maximize stakeholder participation 10
Evolution of OIE standards Need to go from freedom status to risk-based Emphasis on safety of the commodity Essential role of epidemiological surveillance Strength of laboratory network Close link of surveillance to risk assessment Maximize stakeholder participation 10
 Zoning and Compartmentalization Regionalization: geographical ‘zoning’ Compartmentalization: ‘zoning’ on the basis of biosecurity in animal production systems Role of wildlife in zoning and regionalization Role of private and public sector 11
Zoning and Compartmentalization Regionalization: geographical ‘zoning’ Compartmentalization: ‘zoning’ on the basis of biosecurity in animal production systems Role of wildlife in zoning and regionalization Role of private and public sector 11
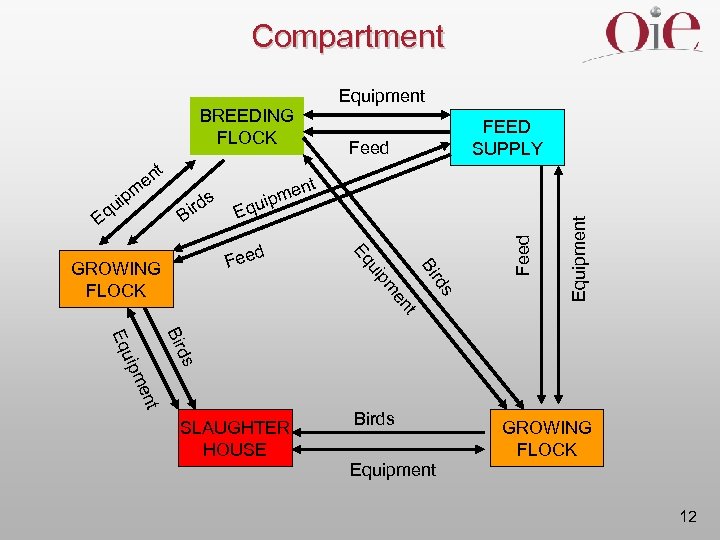 Compartment Equipment t ipm u Eq r Bi ds t men quip E s t en pm ui rd Bi Eq d Fee GROWING FLOCK Feed en FEED SUPPLY Equipment BREEDING FLOCK ds Bir uip Eq nt me SLAUGHTER HOUSE Birds GROWING FLOCK Equipment 12
Compartment Equipment t ipm u Eq r Bi ds t men quip E s t en pm ui rd Bi Eq d Fee GROWING FLOCK Feed en FEED SUPPLY Equipment BREEDING FLOCK ds Bir uip Eq nt me SLAUGHTER HOUSE Birds GROWING FLOCK Equipment 12
 Influences on standards pressure from exporting countries for less restrictions pressure from importing countries for maximum protection consumer and NGO reactions pressure from developing countries for assistance in participating in the process 13
Influences on standards pressure from exporting countries for less restrictions pressure from importing countries for maximum protection consumer and NGO reactions pressure from developing countries for assistance in participating in the process 13
 Importance of adherence to OIE standards Safe trade, based on scientific risk analysis Commodity specific risk mitigation measures Provides credibility to the Veterinary Services Consistency of message to consumers Demonstrate ability to detect emerging diseases 14
Importance of adherence to OIE standards Safe trade, based on scientific risk analysis Commodity specific risk mitigation measures Provides credibility to the Veterinary Services Consistency of message to consumers Demonstrate ability to detect emerging diseases 14
 International standards, conclusions National authorities and their stakeholders must become more involved in the OIE standard setting process Authorities must implement the adopted OIE standards in their national regulations Often national industry interests and short sighted politics interfere in the implementation of science based regulations Global organizations and corporations can play a key role in the implementation of standards at national levels, as well as in the harmonization of animal health and safety of food rules 15
International standards, conclusions National authorities and their stakeholders must become more involved in the OIE standard setting process Authorities must implement the adopted OIE standards in their national regulations Often national industry interests and short sighted politics interfere in the implementation of science based regulations Global organizations and corporations can play a key role in the implementation of standards at national levels, as well as in the harmonization of animal health and safety of food rules 15
 Animal Welfare, current reality Globalization is becoming a force that is revolutionizing international trade The WTO recognizes the OIE as the standardsetting organization for animal health There is an important link between animal health and animal welfare However, there is no specific mention of animal welfare in the WTO agreements 16
Animal Welfare, current reality Globalization is becoming a force that is revolutionizing international trade The WTO recognizes the OIE as the standardsetting organization for animal health There is an important link between animal health and animal welfare However, there is no specific mention of animal welfare in the WTO agreements 16
 Animal Welfare guidelines Current guidelines: ØSea transport ØLand transport ØSlaughter ØKilling for disease control On-going work: ØFish transport and slaughter ØUrban dog control ØLaboratory animals 17
Animal Welfare guidelines Current guidelines: ØSea transport ØLand transport ØSlaughter ØKilling for disease control On-going work: ØFish transport and slaughter ØUrban dog control ØLaboratory animals 17
 Animal Welfare predictions! Animal welfare will increase in importance as a consumer demand therefore international trade Acceptance and enforcement of animal welfare guidelines in international trade will be slow Animal welfare guidelines will be slowly incorporated through positive labeling The welfare in traditional farming can easily become a competitive advantage to developing countries 18
Animal Welfare predictions! Animal welfare will increase in importance as a consumer demand therefore international trade Acceptance and enforcement of animal welfare guidelines in international trade will be slow Animal welfare guidelines will be slowly incorporated through positive labeling The welfare in traditional farming can easily become a competitive advantage to developing countries 18
 Emerging Zoonosis An emerging zoonosis is a zoonosis that is newly recognized or newly evolved, or that has occurred previously but shows an increase in incidence or expansion in a geographic, host, or vector range. Some of these diseases may further evolve and become effectively and essentially transmissible from human to human. 19
Emerging Zoonosis An emerging zoonosis is a zoonosis that is newly recognized or newly evolved, or that has occurred previously but shows an increase in incidence or expansion in a geographic, host, or vector range. Some of these diseases may further evolve and become effectively and essentially transmissible from human to human. 19
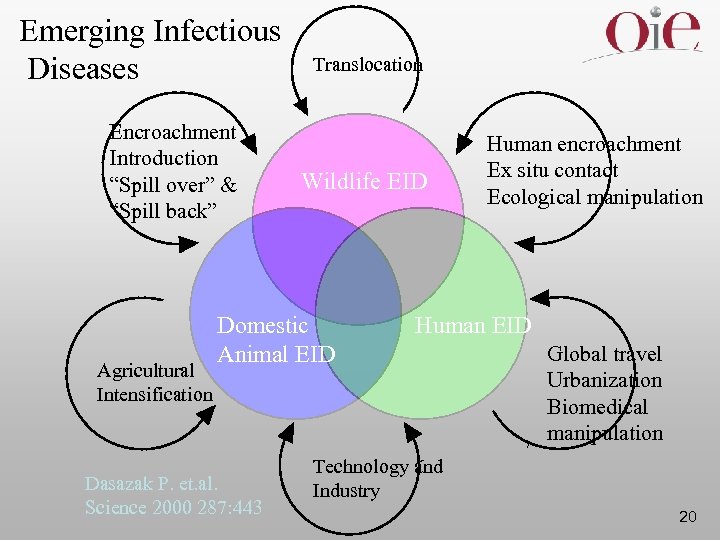 Emerging Infectious Diseases Encroachment Introduction “Spill over” & “Spill back” Agricultural Intensification Translocation Wildlife EID Domestic Animal EID Dasazak P. et. al. Science 2000 287: 443 Human encroachment Ex situ contact Ecological manipulation Human EID Global travel Urbanization Biomedical manipulation Technology and Industry 20
Emerging Infectious Diseases Encroachment Introduction “Spill over” & “Spill back” Agricultural Intensification Translocation Wildlife EID Domestic Animal EID Dasazak P. et. al. Science 2000 287: 443 Human encroachment Ex situ contact Ecological manipulation Human EID Global travel Urbanization Biomedical manipulation Technology and Industry 20
 Specific Challenges for Emerging and Re-Emerging Zoonoses Improving the global capacity for response Improving early warning and surveillance systems using innovative technologies Improving disease reporting Improving diagnostics 21
Specific Challenges for Emerging and Re-Emerging Zoonoses Improving the global capacity for response Improving early warning and surveillance systems using innovative technologies Improving disease reporting Improving diagnostics 21
 Conclusions The era of emerging zoonoses will continue and expand. The factors and driving forces producing this era show no sign of abatement. Local emerging diseases quickly become global. The significance and implications of emerging zoonoses are rapidly increasing in scope, scale, and importance. The convergence of human and animal health offers both important challenges and opportunities. 22
Conclusions The era of emerging zoonoses will continue and expand. The factors and driving forces producing this era show no sign of abatement. Local emerging diseases quickly become global. The significance and implications of emerging zoonoses are rapidly increasing in scope, scale, and importance. The convergence of human and animal health offers both important challenges and opportunities. 22
 Strengthening veterinary services OIE considers Veterinary Services to be a Global Public Good their coming into line with international standards is a public investment priority Østructure, organisation, resources, capacities, role of the private sector and para-professionals 2001 World Bank/OIE MOU supports this view 23
Strengthening veterinary services OIE considers Veterinary Services to be a Global Public Good their coming into line with international standards is a public investment priority Østructure, organisation, resources, capacities, role of the private sector and para-professionals 2001 World Bank/OIE MOU supports this view 23
 STDF global programme in capacity building and technical assistance for developing countries strategic aim is to assist countries to enhance their expertise and capacity to analyse and implement international SPS standards Øimproving their human, animal and plant health situations Øimproving ability to gain and maintain markets direct response to the demand to tailor technical assistance to countries’ needs Ønot to merely provide 'generic' assistance 24
STDF global programme in capacity building and technical assistance for developing countries strategic aim is to assist countries to enhance their expertise and capacity to analyse and implement international SPS standards Øimproving their human, animal and plant health situations Øimproving ability to gain and maintain markets direct response to the demand to tailor technical assistance to countries’ needs Ønot to merely provide 'generic' assistance 24
 STDF 3 OIE STDF projects to date ØTrain the trainers ØTool for evaluation of veterinary services ØStrengthening veterinary services in Africa (ALive) 25
STDF 3 OIE STDF projects to date ØTrain the trainers ØTool for evaluation of veterinary services ØStrengthening veterinary services in Africa (ALive) 25
 Train the trainers to train a cadre of professionals capable of providing continuing training to private and public sectors Øadapted to the conditions, cultures and languages of each region Øfor enhanced implementation of the SPS Agreement 26
Train the trainers to train a cadre of professionals capable of providing continuing training to private and public sectors Øadapted to the conditions, cultures and languages of each region Øfor enhanced implementation of the SPS Agreement 26
 Train the trainers training covers: ØSPS Agreement including dispute settlement mechanisms, and the roles of the 3 sisters ØOIE standards, and its standard setting and implementation process ØOIE animal health information system Øanimal production food safety and collaboration with Codex Øanimal health risk analysis with practical examples tailored to the region Øevaluation of veterinary services 27
Train the trainers training covers: ØSPS Agreement including dispute settlement mechanisms, and the roles of the 3 sisters ØOIE standards, and its standard setting and implementation process ØOIE animal health information system Øanimal production food safety and collaboration with Codex Øanimal health risk analysis with practical examples tailored to the region Øevaluation of veterinary services 27
 Train the trainers training will be adapted to animal health issues of greatest interest in each region initially, workshops will be attached to ‘traditional’ WTO SPS workshops aim to attract and prepare experts who are assigned at the national level to promote activities within OIE’s mandate pilot workshops have developed training DVD to be used as base material (Bamako, Bangkok, Cairo, Vienna, Colombia) 28
Train the trainers training will be adapted to animal health issues of greatest interest in each region initially, workshops will be attached to ‘traditional’ WTO SPS workshops aim to attract and prepare experts who are assigned at the national level to promote activities within OIE’s mandate pilot workshops have developed training DVD to be used as base material (Bamako, Bangkok, Cairo, Vienna, Colombia) 28
 Strengthening Vet Services in Africa ALive (African Livestock), a World Bank initiative focused on livestock in Africa, aims to map existing programs and fill gaps between them, and initiate others Øfocused on poverty reduction, economic growth, research, regional and international market access, and sustainable institutions including Veterinary Services reinforces OIE’s involvement in promoting animal health, both for poverty alleviation and for the safe conduct of international trade in animals and animal products 29
Strengthening Vet Services in Africa ALive (African Livestock), a World Bank initiative focused on livestock in Africa, aims to map existing programs and fill gaps between them, and initiate others Øfocused on poverty reduction, economic growth, research, regional and international market access, and sustainable institutions including Veterinary Services reinforces OIE’s involvement in promoting animal health, both for poverty alleviation and for the safe conduct of international trade in animals and animal products 29
 Strengthening Vet Services in Africa the livestock sector in developing countries requires greater financial and operational challenges than other agricultural sectors developed countries have a strong incentive to help control developing countries’ livestock diseases because of the likelihood of these diseases spreading internationally OIE is examining the use of ALive in all Regions facing similar concerns 30
Strengthening Vet Services in Africa the livestock sector in developing countries requires greater financial and operational challenges than other agricultural sectors developed countries have a strong incentive to help control developing countries’ livestock diseases because of the likelihood of these diseases spreading internationally OIE is examining the use of ALive in all Regions facing similar concerns 30
 Building a scientific community through twinning arrangements several twinning arrangements are in place between OIE reference laboratories role of the OIE as coordinator/catalyst in these arrangements Øselection of priorities Øselection of relevant laboratories Ømediator/facilitator in discussions Øevaluation of outputs use of funds Øexchange of scientists Øorganisation of workshops 31
Building a scientific community through twinning arrangements several twinning arrangements are in place between OIE reference laboratories role of the OIE as coordinator/catalyst in these arrangements Øselection of priorities Øselection of relevant laboratories Ømediator/facilitator in discussions Øevaluation of outputs use of funds Øexchange of scientists Øorganisation of workshops 31
 Regional Representations strengthening the OIE Regional Representations Ø implementation of capacity building programmes tailored to each Region Ø direct input into OIE Headquarters’ activities focuse on assisting new OIE Delegates 32
Regional Representations strengthening the OIE Regional Representations Ø implementation of capacity building programmes tailored to each Region Ø direct input into OIE Headquarters’ activities focuse on assisting new OIE Delegates 32
 World organisation for animal health Organisation mondiale de la santé animale Organizacion Mundial de Sanidad Animal 12 rue de Prony 75017 Paris, France Tel: + 33 (0)1 44 15 18 88 – Fax: + 33 (0)1 42 67 09 87 Email: oie@oie. int http: //www. oie. int 33
World organisation for animal health Organisation mondiale de la santé animale Organizacion Mundial de Sanidad Animal 12 rue de Prony 75017 Paris, France Tel: + 33 (0)1 44 15 18 88 – Fax: + 33 (0)1 42 67 09 87 Email: oie@oie. int http: //www. oie. int 33


