Appendix.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

Dr A. Badrek-Amoudi ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures FRCS

• A 15 year old girl presents with a right lower abdominal pain. • A 6 year old boy with a history of sore throat presents with lower abdominal pain • A 45 year old man presents with a sudden onset of epigastric pain localised to RIF 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. How do you diagnose appendicitis. What are the classical and atypical features of appendicitis Are investigations always needed and what is their role How do you prepare your patient prior to surgery What are the surgical approaches How do you care for your patient after surgery ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix Introduction 1889 Mac Burney described location, the clinical features of appendicitis and the importance of operative intervention and muscle-splitting incision. ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

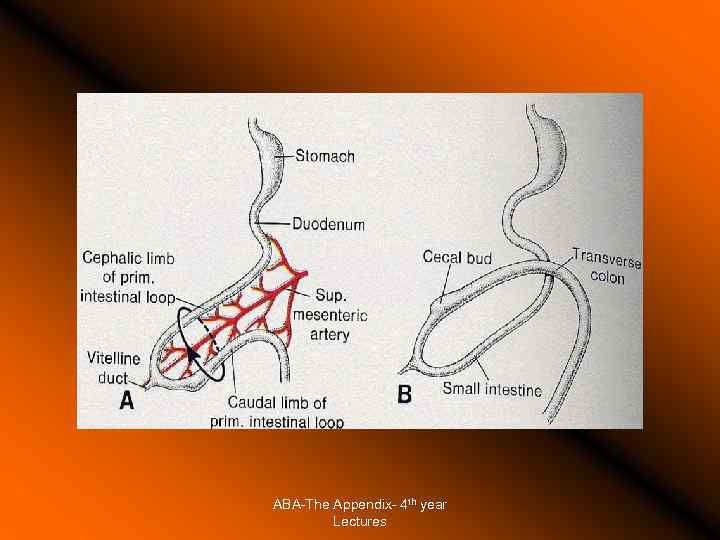
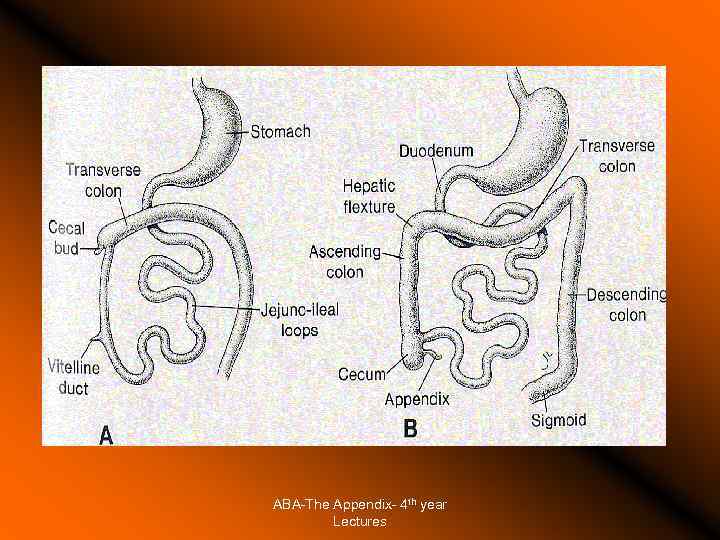
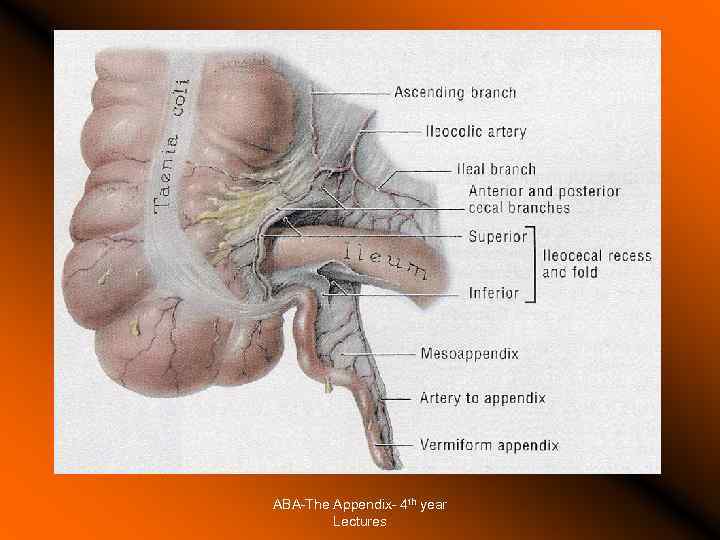
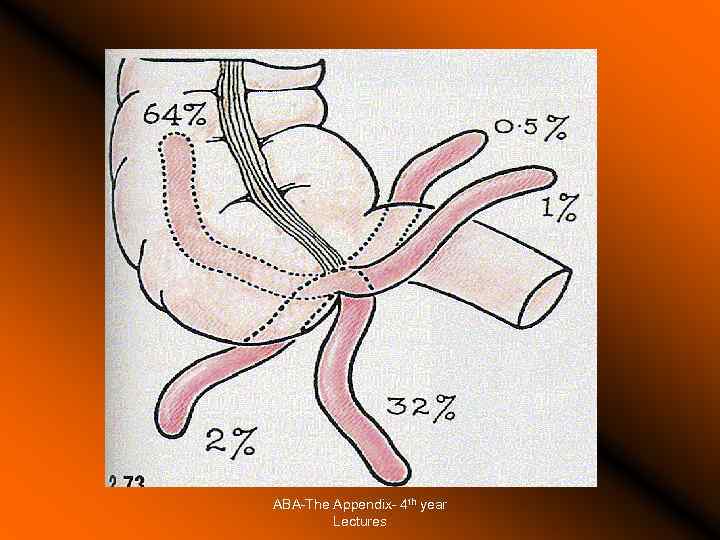
The Appendix Surgical Anatomy Surface anatomy Development: diverticulum of ceacum appearing in the 8 th week of life Positions: constant base, tip varies (retroceacal, pelvic, subcaecal, preileal, pericolic) Blood supply Location during surgery Surrounding anatomical structures Part of the gut lymphoid tissue. ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix Acute Appendicitis Epidemiology Most common surgical emergency. Slightly more common in men. Incidence are falling from 100 to 50 in 100 000 (1975 -1991). 1 in 6 of the population will have an appendectomy. In Saudi Arabia incidence are comparable to western figures ? More common in European societies (Diet). ? Relation to class status. Age > 2 yrs, (associated with lymphoid development). Up to 16% of appendicectomies are normal 75% are in women ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
The Appendix Acute Appendicitis Pathology I Luminal obstruction. • • • Lymphoid hyperplasia 60% Faecolith 35%. Inspissated barium. Fruit seeds. }<4% Worms. < 1% Extra-luminal obstruction eg Ca Cecum Raised intra-luminal pressure • Mucus accumulation • Multiplication of bacteria. ( E. Coli, Bacteroids, peptostreptococcus, Psuedomonas) • Venous and lymphoid congestion and. ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix Acute Appendicitis Pathology II Impaired arterial flow, thrombosis and gangrene. Perforation may occur through devitalized tissue. Histological terms used: Catarrhal appendicitis Suppurative ; ; ; Necrotic ; ; ; Gangrenous ; ; ; Perforated ; ; ; Appendicular mass The risk of perforation is not inevitable. ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis Clinical Features I Full History Duration, severity, onset, System review. and examination: General, throat, chest…. . etc Only 55% have classical features. Atypical 45% History 24 -36 hours Abdominal pain: (diffuse and periumbilical, localizing to the RIF) Anorexia (almost always). Vomiting (75%). Low grade fever. • If >38 suspect perforation Tenderness, guarding and rebound: Be gentle Rovsing’s, psoas, obturator signs: unreliable and late ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis Clinical Features II Tender Appendicular mass Atypical: • (loin, high RUQ, deep pelvic) • Diarrhea ( not always gastroenteritis) • Urinary frequency The Extremes of Age: • Children < 5 rapid progression • Pain in the elderly is less intense ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

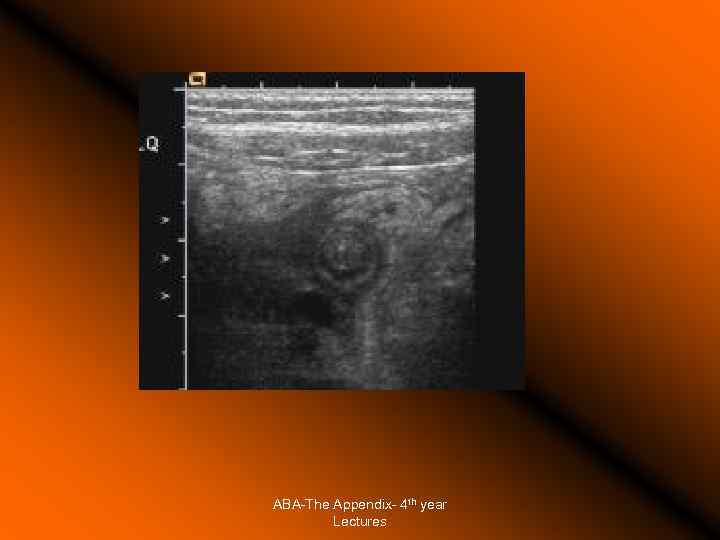
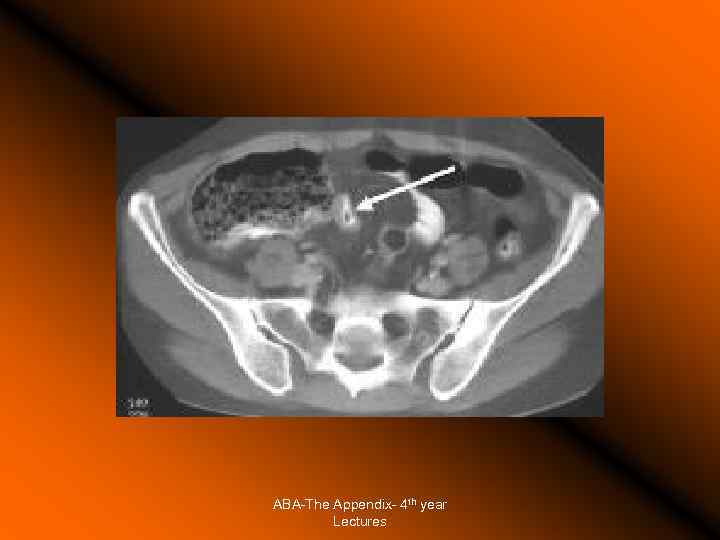
The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis Investigations White cell count: high sensitivity 96%, low specificity Urine analysis Plain Xray, nonspecific Ultrasound highly sensitive (80 -90%), excludes other pathologies. Computer Tomography: More superior to USS in diagnostic accuracy. Barium enema: Good accuracy, but technically difficult and false positives are common. Laparoscopy Active observation Computer aided diagnosis. Peritoneal lavage ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis The Very Young Diagnosis may be more difficult to establish, WBC is likely to be normal (12% are normal). Children are more likely to progress to perforated appendix (? Under-developed Greater Omentum). ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis The Very Old Greater morbidity and mortality Less typical presentation Cancer may be a possibility as an underlying cause. Perforation of 50% and mortality of 20% has been reported ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis The Pregnant Implications: Clinical Findings, Lab Ix, Surgery 1: 2000 pregnancies. More common in the first two trimesters The appendix is pushed superiorly and laterally WBC > 15 Premature Labor 10 -15% with surgery Perforated appendix leads to fetal death in 20% Rapid diagnosis and treatment is advised. ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis In AIDS Patients Be aware of CMV or Kaposi sarcoma as the underlying cause WBC may not rise ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis The Management Preop: • IVI, • analgesia, • IV antibiotics Conventional appendicectomy Types of incisions Laparoscopic appendicectomy: (questions regarding pain, hospital stay, operation time, to daily activity, wound infection) ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
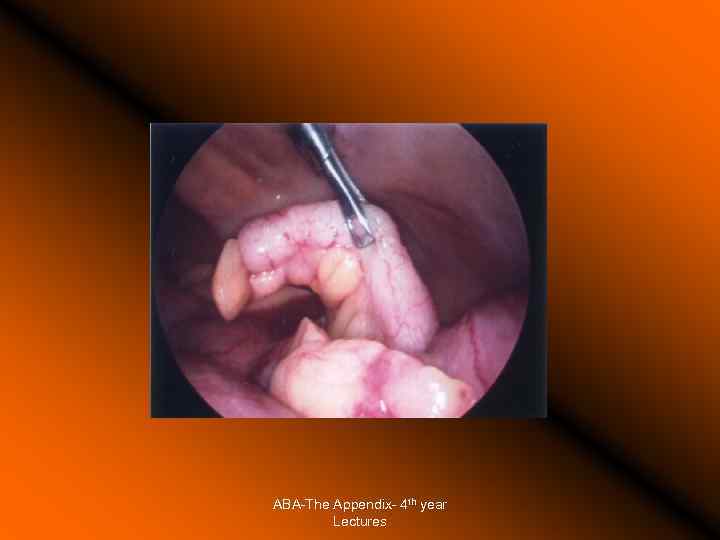
ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis Post-Operative 1. Check the vitals 2. Check the abdominal signs and bowel movement 3. Check the wound 4. Advise on mobilization 5. In OPD: 1. Check wound 2. Check the Histology ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis Prognosis Mortality: from 0. 2% to 1% Complications increase with perforation Morbidity: • • • Wound abscess, Wound infection (less with Mac. Burney’s incision), Wound dehiscence Intra-abdominal abscess, Faecal fistula, Intestinal obstruction, Adhesive band, inguinal hernia. Fertility ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
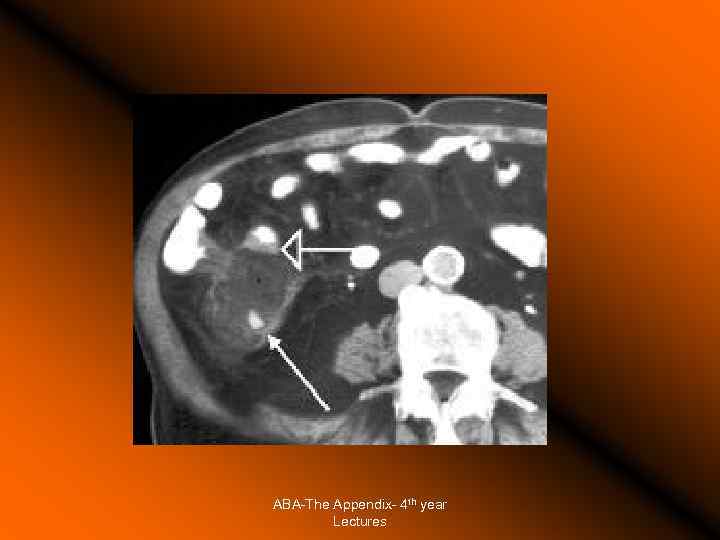
ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix - Acute Appendicitis Problems Mass palpable pre-operatively Appendix is normal at operation Tumor is found in appendix Prophylactic appendicectomy ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix – Chronic Appendicular Conditions Chronic Appendicitis A loose term referring to a multitude of conditions associated with RIF pain and in which pathology of the appendix has been found. ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
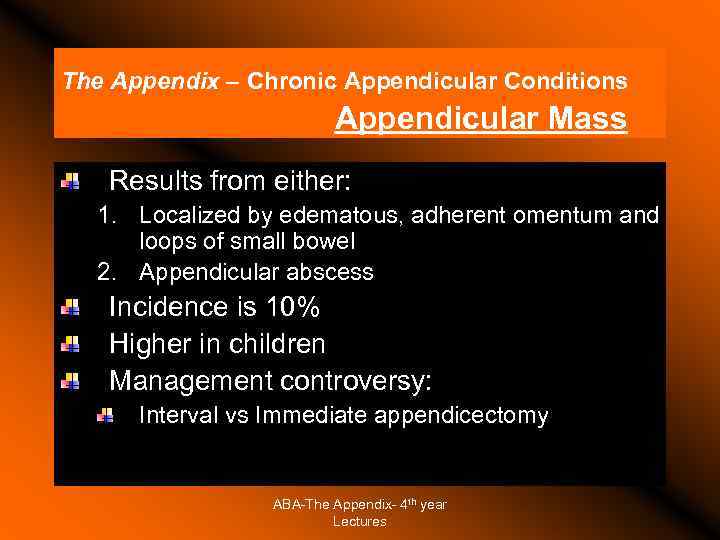
The Appendix – Chronic Appendicular Conditions Appendicular Mass Results from either: 1. Localized by edematous, adherent omentum and loops of small bowel 2. Appendicular abscess Incidence is 10% Higher in children Management controversy: Interval vs Immediate appendicectomy ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

The Appendix – Chronic Appendicular Conditions Tumors of The Appendix Carcinoid: • • Arise from Kluchitsky cells Mean age 20 -40 Yellow bulbar mass In F>M In third decade of life Usually lies near the tip In the absence of LN spread with <2 cm in diameter appendicectomy is sufficient. Otherwise a R hemicolectomy is necessary. Adenocarcinoma and Lymphoma. ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures

ABA-The Appendix- 4 th year Lectures
Appendix.ppt