4ce483c8ef364fa7c3a2cf3b14be0001.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Donegal County Councils ‘Experience of Developing a Poverty Profile’ 15 th /16 th May 2006 By Ms Valerie Bryce Community Development Worker Community Culture and Enterprise 1
Donegal County Councils ‘Experience of Developing a Poverty Profile’ 15 th /16 th May 2006 By Ms Valerie Bryce Community Development Worker Community Culture and Enterprise 1
 Outline of Presentation 1. Background 2. What is a Local Anti Poverty Profile? 3. The Process to Building up a Poverty Profile in County Donegal 4. Steps involved in carrying out a Poverty Profile 5. Poverty in County Donegal 6. Difficulties and Challenges 7. Uses and Applications 2
Outline of Presentation 1. Background 2. What is a Local Anti Poverty Profile? 3. The Process to Building up a Poverty Profile in County Donegal 4. Steps involved in carrying out a Poverty Profile 5. Poverty in County Donegal 6. Difficulties and Challenges 7. Uses and Applications 2
 1. Background 3
1. Background 3
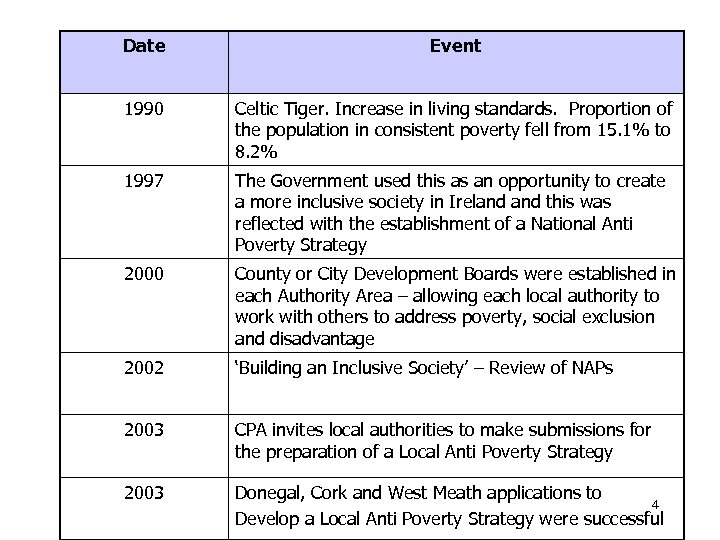 Date Event 1990 Celtic Tiger. Increase in living standards. Proportion of the population in consistent poverty fell from 15. 1% to 8. 2% 1997 The Government used this as an opportunity to create a more inclusive society in Ireland this was reflected with the establishment of a National Anti Poverty Strategy 2000 County or City Development Boards were established in each Authority Area – allowing each local authority to work with others to address poverty, social exclusion and disadvantage 2002 ‘Building an Inclusive Society’ – Review of NAPs 2003 CPA invites local authorities to make submissions for the preparation of a Local Anti Poverty Strategy 2003 Donegal, Cork and West Meath applications to 4 Develop a Local Anti Poverty Strategy were successful
Date Event 1990 Celtic Tiger. Increase in living standards. Proportion of the population in consistent poverty fell from 15. 1% to 8. 2% 1997 The Government used this as an opportunity to create a more inclusive society in Ireland this was reflected with the establishment of a National Anti Poverty Strategy 2000 County or City Development Boards were established in each Authority Area – allowing each local authority to work with others to address poverty, social exclusion and disadvantage 2002 ‘Building an Inclusive Society’ – Review of NAPs 2003 CPA invites local authorities to make submissions for the preparation of a Local Anti Poverty Strategy 2003 Donegal, Cork and West Meath applications to 4 Develop a Local Anti Poverty Strategy were successful
 What is Poverty? ‘People are living in poverty, if their income and resources (material, cultural and social) are so inadequate as to preclude them from having a standard of living, which is regarded as acceptable by Irish Society generally. As a result of inadequate income and resources people may be excluded and marginalised from participating in activities, which are considered the norm for other people in society’ 5
What is Poverty? ‘People are living in poverty, if their income and resources (material, cultural and social) are so inadequate as to preclude them from having a standard of living, which is regarded as acceptable by Irish Society generally. As a result of inadequate income and resources people may be excluded and marginalised from participating in activities, which are considered the norm for other people in society’ 5
 2. What is a Local Anti Poverty Profile? 6
2. What is a Local Anti Poverty Profile? 6
 2. What is a Local Anti Poverty Profile? A Local Poverty Profile involves systematically identifying gathering and mapping information on social and economic need in your area, it should clearly identify the areas and communities that experience the highest levels of disadvantage and the nature of that disadvantage. 7
2. What is a Local Anti Poverty Profile? A Local Poverty Profile involves systematically identifying gathering and mapping information on social and economic need in your area, it should clearly identify the areas and communities that experience the highest levels of disadvantage and the nature of that disadvantage. 7
 3. The Process 8
3. The Process 8
 The Process q Cross Directorate Internal Working Group established in Donegal County Council q CPA Consultant assigned to work with DCC on the development of all stages of the Local Anti Poverty Strategy including the development of the Local Poverty Profile q Research undertaken by Research and Policy Unit in Donegal County Council - but under taken by Social Inclusion Units in both West Meath and Cork County Councils 9
The Process q Cross Directorate Internal Working Group established in Donegal County Council q CPA Consultant assigned to work with DCC on the development of all stages of the Local Anti Poverty Strategy including the development of the Local Poverty Profile q Research undertaken by Research and Policy Unit in Donegal County Council - but under taken by Social Inclusion Units in both West Meath and Cork County Councils 9
 The Process q Learning from Experience of other local authorities that had compiled poverty profiles q Indicators identified by q CPA - National Poverty Indicators q Internal Cross Directorate Working Group q Research and Policy Unit q Data Gathered and Analysed by Research and Policy q Drafts presented to Internal Cross Directorate Working Group, who made the final sign off q 10 Copies of final draft sent to SIM and CDB for Information Purposes
The Process q Learning from Experience of other local authorities that had compiled poverty profiles q Indicators identified by q CPA - National Poverty Indicators q Internal Cross Directorate Working Group q Research and Policy Unit q Data Gathered and Analysed by Research and Policy q Drafts presented to Internal Cross Directorate Working Group, who made the final sign off q 10 Copies of final draft sent to SIM and CDB for Information Purposes
 4. Steps in Developing a Local Poverty Profile 11
4. Steps in Developing a Local Poverty Profile 11
 3. Steps in developing a Local Poverty Profile I. Selection of Themes II. Selection of Indicators III. Data Identification & Collection IV. Basic Data Analysis V. Mapping (using GIS) VI. Presentation & Review 12
3. Steps in developing a Local Poverty Profile I. Selection of Themes II. Selection of Indicators III. Data Identification & Collection IV. Basic Data Analysis V. Mapping (using GIS) VI. Presentation & Review 12
 I. Selection of Themes – Poverty and people – Welfare Dependency and Employment – Housing – Health and Poverty – Educational Disadvantage – Quality of Life – Physical Environment – Infrastructure and Accessibility – Local Specific Aspects 13
I. Selection of Themes – Poverty and people – Welfare Dependency and Employment – Housing – Health and Poverty – Educational Disadvantage – Quality of Life – Physical Environment – Infrastructure and Accessibility – Local Specific Aspects 13
 II. Selection of Indicators Source – Indicators identified under the 7 themes of NAPs – Indicators and data relating to poverty and social exclusion collected from national and international publications like the CSO, DSCFA, International Labour Office etc. – Indicators held by the different Local Authority Directorates on housing, roads, cultural services etc 14
II. Selection of Indicators Source – Indicators identified under the 7 themes of NAPs – Indicators and data relating to poverty and social exclusion collected from national and international publications like the CSO, DSCFA, International Labour Office etc. – Indicators held by the different Local Authority Directorates on housing, roads, cultural services etc 14
 III. Identifying and Gathering Data Finding the most appropriate data is one of the key tasks in building up a Local Poverty Profile this was done: • Though Desk Research by the Research and Policy Unit under the direction of the Strategic Policy Manager to identify relevant local, national and international publications and datasets • In the Internal Cross Directorate Working Group to identify appropriate indicators • Through Consultations with each Directorate of Donegal County Council to identify data or datasets held within each directorate of the council 15
III. Identifying and Gathering Data Finding the most appropriate data is one of the key tasks in building up a Local Poverty Profile this was done: • Though Desk Research by the Research and Policy Unit under the direction of the Strategic Policy Manager to identify relevant local, national and international publications and datasets • In the Internal Cross Directorate Working Group to identify appropriate indicators • Through Consultations with each Directorate of Donegal County Council to identify data or datasets held within each directorate of the council 15
 IV Data Analysis Headline indicators were presented to – Determine the extent of poverty within County Donegal across a number of thematic areas – Allow for relative poverty comparisons between the Headline Poverty Indicators in County Donegal and State – Determine the extent of deprivation across the 149 different Electoral Divisions (149) within County Donegal (I. e. by mapping the Trutz Haase Deprivation Index) – Examine poverty over a time series ie 1991 – 1996 and 1996 – 2002 in 16 an effort to determine if the situation is deteriorating of improving
IV Data Analysis Headline indicators were presented to – Determine the extent of poverty within County Donegal across a number of thematic areas – Allow for relative poverty comparisons between the Headline Poverty Indicators in County Donegal and State – Determine the extent of deprivation across the 149 different Electoral Divisions (149) within County Donegal (I. e. by mapping the Trutz Haase Deprivation Index) – Examine poverty over a time series ie 1991 – 1996 and 1996 – 2002 in 16 an effort to determine if the situation is deteriorating of improving
 5. Poverty in County Donegal 17
5. Poverty in County Donegal 17
 I. A comparion of deprivation scores between the State, Border, County and Sub. County Level 18
I. A comparion of deprivation scores between the State, Border, County and Sub. County Level 18
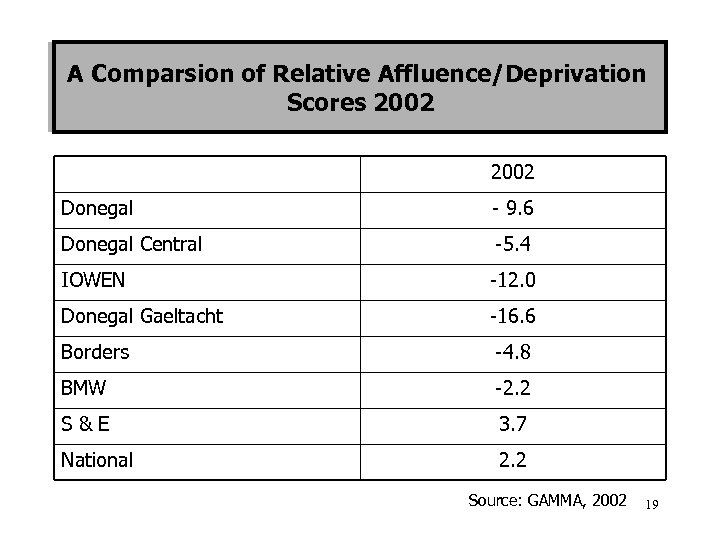 A Comparsion of Relative Affluence/Deprivation Scores 2002 Donegal - 9. 6 Donegal Central -5. 4 IOWEN -12. 0 Donegal Gaeltacht -16. 6 Borders -4. 8 BMW -2. 2 S&E 3. 7 National 2. 2 Source: GAMMA, 2002 19
A Comparsion of Relative Affluence/Deprivation Scores 2002 Donegal - 9. 6 Donegal Central -5. 4 IOWEN -12. 0 Donegal Gaeltacht -16. 6 Borders -4. 8 BMW -2. 2 S&E 3. 7 National 2. 2 Source: GAMMA, 2002 19
 I. Deprivation Scores at sub county level 20
I. Deprivation Scores at sub county level 20
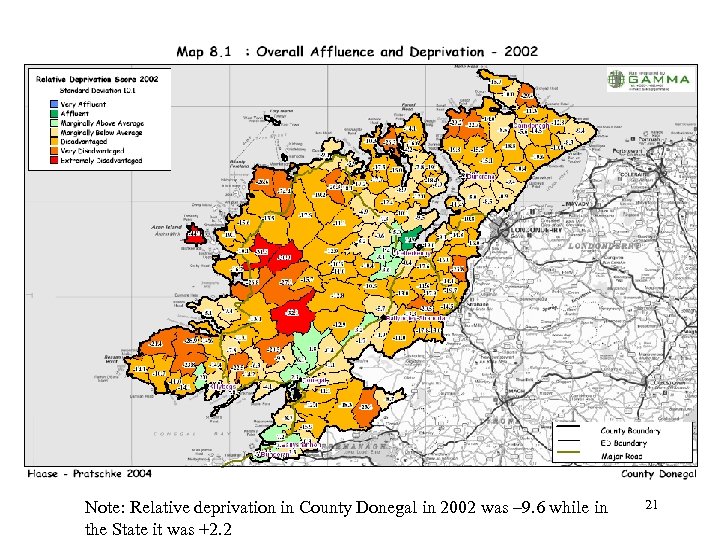 Note: Relative deprivation in County Donegal in 2002 was – 9. 6 while in the State it was +2. 2 21
Note: Relative deprivation in County Donegal in 2002 was – 9. 6 while in the State it was +2. 2 21
 II. A comparsion of headline indicators between County Donegal and the State 22
II. A comparsion of headline indicators between County Donegal and the State 22
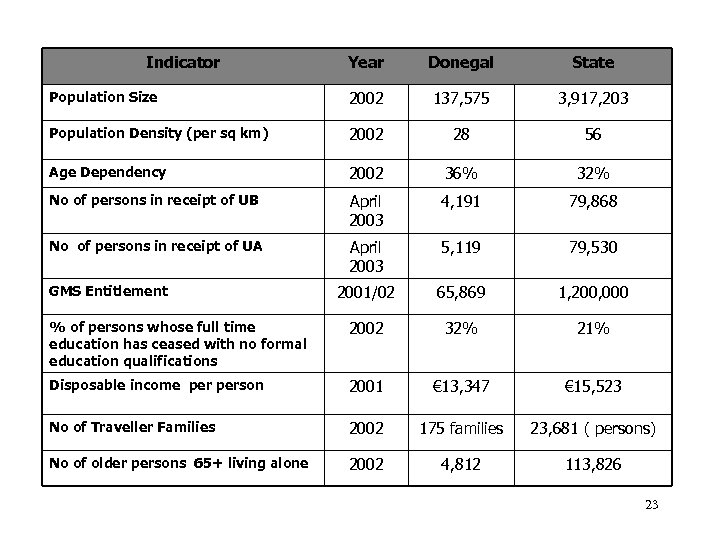 Indicator Year Donegal State Population Size 2002 137, 575 3, 917, 203 Population Density (per sq km) 2002 28 56 Age Dependency 2002 36% 32% No of persons in receipt of UB April 2003 4, 191 79, 868 No of persons in receipt of UA April 2003 5, 119 79, 530 2001/02 65, 869 1, 200, 000 % of persons whose full time education has ceased with no formal education qualifications 2002 32% 21% Disposable income person 2001 € 13, 347 € 15, 523 No of Traveller Families 2002 175 families 23, 681 ( persons) No of older persons 65+ living alone 2002 4, 812 113, 826 GMS Entitlement 23
Indicator Year Donegal State Population Size 2002 137, 575 3, 917, 203 Population Density (per sq km) 2002 28 56 Age Dependency 2002 36% 32% No of persons in receipt of UB April 2003 4, 191 79, 868 No of persons in receipt of UA April 2003 5, 119 79, 530 2001/02 65, 869 1, 200, 000 % of persons whose full time education has ceased with no formal education qualifications 2002 32% 21% Disposable income person 2001 € 13, 347 € 15, 523 No of Traveller Families 2002 175 families 23, 681 ( persons) No of older persons 65+ living alone 2002 4, 812 113, 826 GMS Entitlement 23
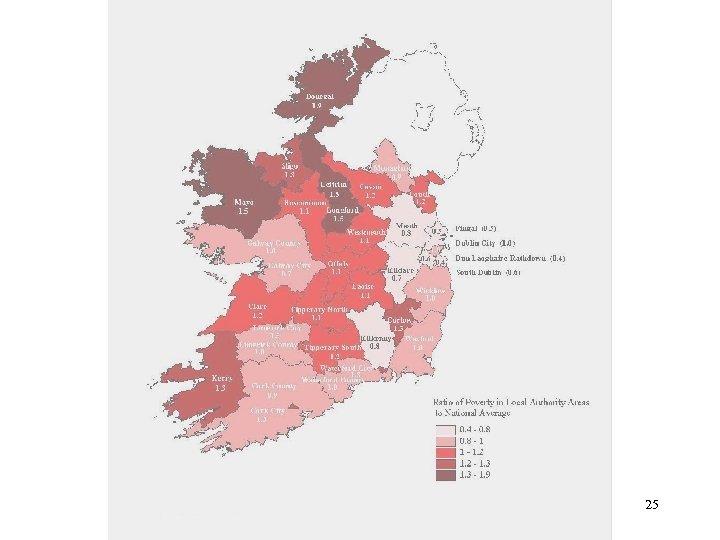
 III. A comparsion of poverty levels across counties in Ireland 24
III. A comparsion of poverty levels across counties in Ireland 24
 25
25
 IV. Lower Social Classes in County Donegal vis-à -vis the State 1986, 1991, 1996, 2002 26
IV. Lower Social Classes in County Donegal vis-à -vis the State 1986, 1991, 1996, 2002 26
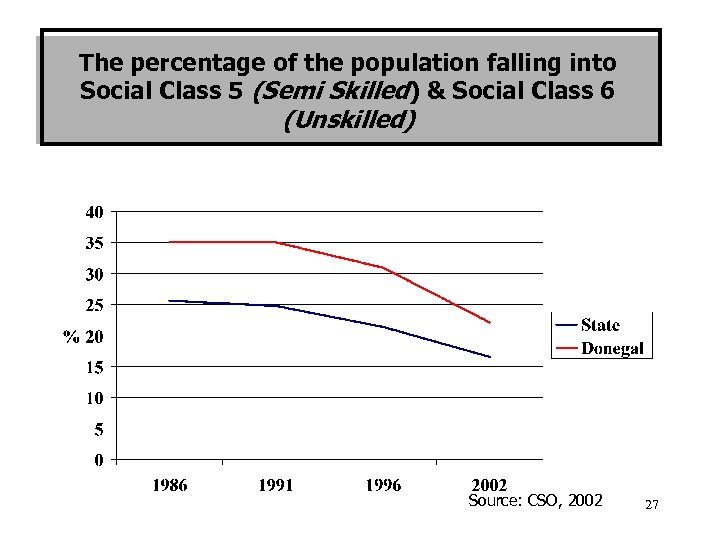 The percentage of the population falling into Social Class 5 (Semi Skilled) & Social Class 6 (Unskilled) Source: CSO, 2002 27
The percentage of the population falling into Social Class 5 (Semi Skilled) & Social Class 6 (Unskilled) Source: CSO, 2002 27
 6. Difficulties and Challenges 28
6. Difficulties and Challenges 28
 6. Difficulties and Challenges q Lack of a dedicated Social Inclusion Unit in County Donegal Unlike Cork and Westmeath Local Authorities Donegal was capturing data for the first time and not building on the work already done q Difficulties in Dis-aggregation of Statistical Information to County Level In some cases the only available data is at national or regional level for example Health Board Data q Timeliness of Data There was a reliance on the 1996 or 2002 data, which was only coming on stream when the profile was being 29 developed
6. Difficulties and Challenges q Lack of a dedicated Social Inclusion Unit in County Donegal Unlike Cork and Westmeath Local Authorities Donegal was capturing data for the first time and not building on the work already done q Difficulties in Dis-aggregation of Statistical Information to County Level In some cases the only available data is at national or regional level for example Health Board Data q Timeliness of Data There was a reliance on the 1996 or 2002 data, which was only coming on stream when the profile was being 29 developed
 6. Difficulties and Challenges q Lack of information in some areas on specific circumstances of target groups Early school leavers Literacy Levels q Inability to attain specific indicators – the number of older people without access to a telephone – The number of lone parents or older people who rely solely on state benefits for their income q No Primary Research It was not within the scope of the poverty profiles to undertake additional primary research to gather information. Therefore, the poverty profiles are based soely on secondary sources and from existing statistical resources of agencies currently working 30 within the field
6. Difficulties and Challenges q Lack of information in some areas on specific circumstances of target groups Early school leavers Literacy Levels q Inability to attain specific indicators – the number of older people without access to a telephone – The number of lone parents or older people who rely solely on state benefits for their income q No Primary Research It was not within the scope of the poverty profiles to undertake additional primary research to gather information. Therefore, the poverty profiles are based soely on secondary sources and from existing statistical resources of agencies currently working 30 within the field
 7. Uses and Applications 31
7. Uses and Applications 31
 Uses of a Profile q Identify key priority or focus areas for the Development of the Local Anti Poverty Strategy q Raising Awareness on Poverty Issues across Local Authority Directorates q Local Authority Service Planning -By identifying target groups where an integrated service approach is required towards tackling poverty and social exclusion 32
Uses of a Profile q Identify key priority or focus areas for the Development of the Local Anti Poverty Strategy q Raising Awareness on Poverty Issues across Local Authority Directorates q Local Authority Service Planning -By identifying target groups where an integrated service approach is required towards tackling poverty and social exclusion 32
 Uses of a Profile q Economic Taskforces - by identifying gaps in socio economic infrastructure and highlighting the requirements for investments to fill those gaps q External Dissemination – to ensure that appropriate national, regional, local funding and resources can be targeted to areas of greatest need q By Area Partnerships in service planning ie DLDC, IRDL, MFG 33
Uses of a Profile q Economic Taskforces - by identifying gaps in socio economic infrastructure and highlighting the requirements for investments to fill those gaps q External Dissemination – to ensure that appropriate national, regional, local funding and resources can be targeted to areas of greatest need q By Area Partnerships in service planning ie DLDC, IRDL, MFG 33
 Uses of a Profile q By Letterkenny Institute & other institutes to develop and devise educational initiatives to address gaps in service delivery q Establishing a baseline against which the progress made in alleviating poverty in the county & can be monitored on an ongoing basis q Used by SIM to identify a target group action plan 34
Uses of a Profile q By Letterkenny Institute & other institutes to develop and devise educational initiatives to address gaps in service delivery q Establishing a baseline against which the progress made in alleviating poverty in the county & can be monitored on an ongoing basis q Used by SIM to identify a target group action plan 34
 Outline of Presentation 1. What is a Local Anti Poverty Profile? 2. Steps involved 3. The Process to Building up a Poverty Profile 4. Poverty in County Donegal 5. Difficulties and Challenges 6. Uses and Applications 35
Outline of Presentation 1. What is a Local Anti Poverty Profile? 2. Steps involved 3. The Process to Building up a Poverty Profile 4. Poverty in County Donegal 5. Difficulties and Challenges 6. Uses and Applications 35


