(ISW) Case 4 - копия.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 27

Done by: Sandibaeva Anel Zhuraeva Guncha

Current ratio – is a liquidity ratio that measures a company's ability to pay shortterm obligations (debt and payables) with its short-term assets (cash, inventory, receivables). The higher the current ratio, the more capable the company is of paying its obligations. A ratio under 1 suggests that the company would be unable to pay off its obligations if they came due at that point.

Current ratio = Total current assets / Total current liabilities 2009 year 4 510 / 4 730 =0, 953488372 2011 year 15 910 / 15 131 1 =05148371

A stringent indicator that determines whether a firm has enough short-term assets to cover its immediate liabilities without selling inventory. The acid-test ratio is far more strenuous than the working capital ratio, primarily because the working capital ratio allows for the inclusion of inventory assets.

2009 year 4 510 - 4 500 / 4 730 0, 002 2011 year 15 910 - 15 400 / 15 131 0, 695 In 2009 most of the current assets consisted form inventories, in 2011 it now only consists from inventories by 30, 5%

A measure of a company's financial leverage calculated by dividing its total liabilities by stockholders' equity. It indicates what proportion of equity and debt the company is using to finance its assets.

2009 year 6 270 / 1 540 4, 071428571 2011 year 17 190 / 2 059 8, 34871297 Most of activities of the company is financed by the debt, this is not a good condition, especially that it was doubled.

Total debt to total assets is a leverage ratio that defines the total amount of debt relative to assets. This enables comparisons of leverage to be made across different companies. The higher the ratio, the higher the degree of leverage, and consequently, financial risk. This is a broad ratio that includes long-term and short-term debt (borrowings maturing within one year), as well as all assets – tangible and intangible.

2009 year 1 = 6 270 / 6 270 2011 year 1 = 17 190 / 17 190 All of the assets were bought on credit in both 2009 and 2011 years.

Capitalization = (Total liabilities - Total current liabilities) / ((Total liabilities - Total current liabilities)+ Shareholder's equity ) 2009 year 0, 5 = (6 270 - 4 730) / ((6 270 - 4 730)+ 1 540 2011 year 0, 5 = (17 190 - 15 131) / ((17 190 15 131) + 2 059 Half of the long-term financing of the firm are covered with long-term debts

A ratio used to determine how easily a company can pay interest on outstanding debt. The interest coverage ratio is calculated by dividing a company's earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) of one period by the company's interest expenses of the same period:
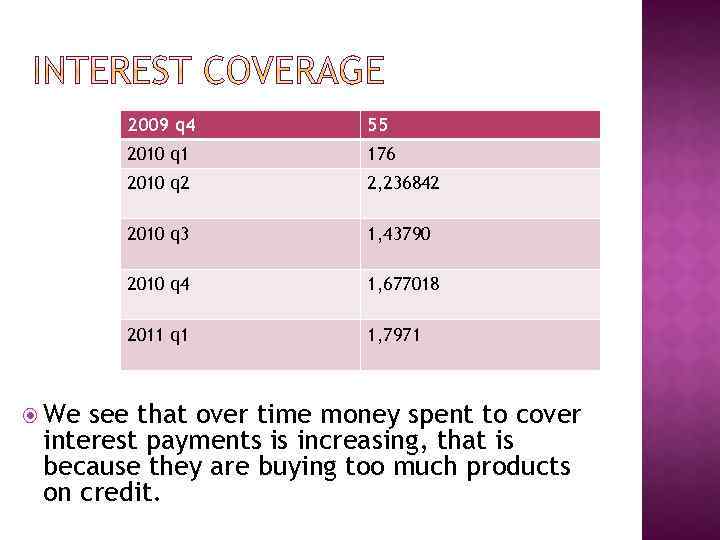
2009 q 4 2010 q 1 176 2010 q 2 2, 236842 2010 q 3 1, 43790 2010 q 4 1, 677018 2011 q 1 We 55 1, 7971 see that over time money spent to cover interest payments is increasing, that is because they are buying too much products on credit.

An accounting measure used to quantify a firm's effectiveness in extending credit as well as collecting debts. The receivables turnover ratio is an activity ratio, measuring how efficiently a firm uses its assets. Receivable turnover = Revenues / Receivables

2011 year q = 1 0, 52380952 5 500 / 10 500 In 2011 receivable turnover was equal to an almost 2 years.

The approximate amount of time that it takes for a business to receive payments owed, in terms of receivables, from its customers and clients.

Avg. collection period = 365 / Receivable turnover 2011 year q 1 696, 818 = 365/ 0, 52380952 696 days is needed average to collect profit from buyers.

This ratio is more useful for growth companies to check if in fact they are growing revenue in proportion to assets. Asset turnover measures a firm's efficiency at using its assets in generating sales or revenue - the higher the number the better. It also indicates pricing strategy: companies with low profit margins tend to have high asset turnover, while those with high profit margins have low asset turnover.

Total asset turnover = Revenues / Total assets 0, 31995346 5 500 / 17 190 31% of assets utilized is returned back as a revenue.

A financial metric used to assess a firm's financial health by revealing the proportion of money left over from revenues after accounting for the cost of goods sold. Gross profit margin serves as the source for paying additional expenses and future savings.
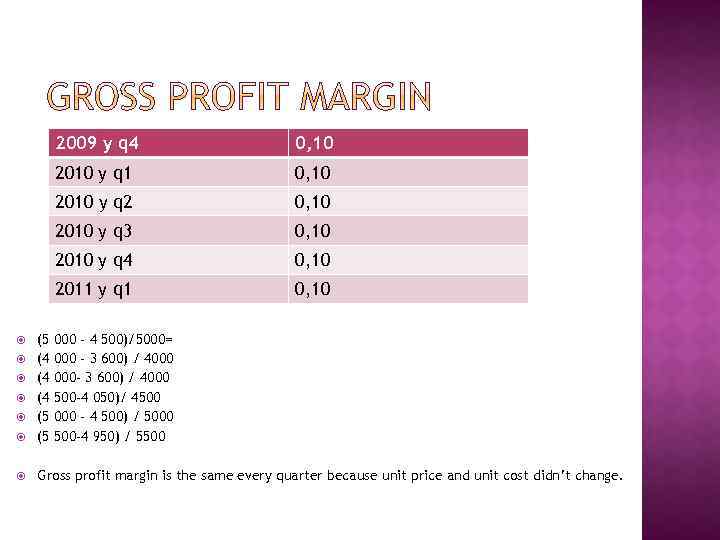
2009 y q 4 0, 10 2010 y q 1 0, 10 2010 y q 2 0, 10 2010 y q 3 0, 10 2010 y q 4 0, 10 2011 y q 1 0, 10 (5 (4 (4 (4 (5 (5 Gross profit margin is the same every quarter because unit price and unit cost didn’t change. 000 - 4 500)/5000= 000 - 3 600) / 4000 000 - 3 600) / 4000 500 -4 050)/ 4500 000 - 4 500) / 5000 500 -4 950) / 5500

A ratio of profitability calculated as net income divided by revenues, or net profits divided by sales. It measures how much out of every dollar of sales a company actually keeps in earnings. Profit margin is very useful when comparing companies in similar industries. A higher profit margin indicates a more profitable company that has better control over its costs compared to its competitors.
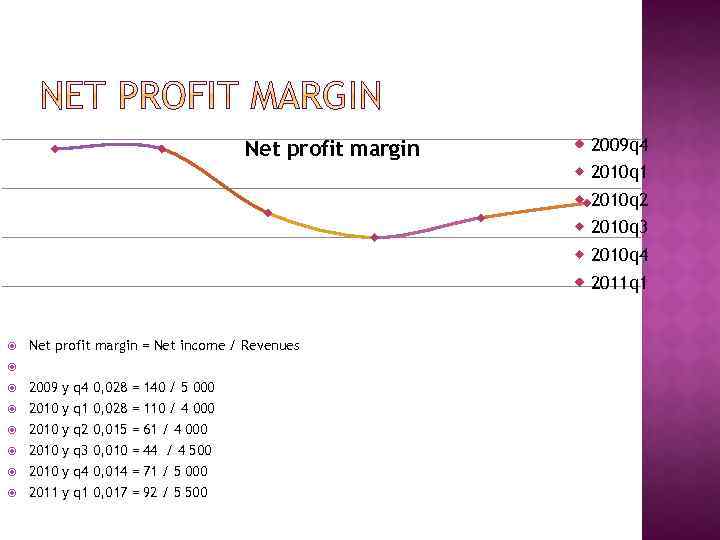
Net profit margin 2009 q 4 2010 q 1 2010 q 2 2010 q 3 2010 q 4 2011 q 1 Net profit margin = Net income / Revenues 2009 y q 4 0, 028 = 140 / 5 000 2010 y q 1 0, 028 = 110 / 4 000 2010 y q 2 0, 015 = 61 / 4 000 2010 y q 3 0, 010 = 44 / 4 500 2010 y q 4 0, 014 = 71 / 5 000 2011 y q 1 0, 017 = 92 / 5 500

A performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or to compare the efficiency of a number of different investments. To calculate ROI, the benefit (return) of an investment is divided by the cost of the investment; the result is expressed as a percentage or a ratio.

Return on investment = Net income / Total assets 2011 92 / 17 190= 1 0, 005369 From 100$ of assets firm has 0, 5$ of net income, which is too low, , most of income is deducted as interest charges.

The amount of net income returned as a percentage of shareholders equity. Return on equity measures a corporation's profitability by revealing how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested.

Return on equity = Net income / Shareholder's equity 92 / 2 0592011 y q 1 0, 04483 Shareholders income. have about 0, 4% from net

As a result of the analysis, we defined that the company is in an adverse stage for development. It is too much borrowed funds which don't cover percentage payments. During that there can be heavy losses of the company. Commodity turnover of the company doesn't meet a loan though the profit increases, the quantity of profit on the sold cars increases. There is no guaranteeing that the company will cope with obligations in short terms.
(ISW) Case 4 - копия.pptx