4abf4867306d16d3daed95b118532fc0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 “Don’t make me read, make me understand “ www. makemegenius. com– Full of ingredients to make your child a genius. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
“Don’t make me read, make me understand “ www. makemegenius. com– Full of ingredients to make your child a genius. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 Electricity A. Electric Charge 1. Static electricity is the accumulation of excess electric charges on an object. a. More e¯ = negative charge b. More protons = + charge 2. Charge is conserved (e¯ move from one object to another). Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
Electricity A. Electric Charge 1. Static electricity is the accumulation of excess electric charges on an object. a. More e¯ = negative charge b. More protons = + charge 2. Charge is conserved (e¯ move from one object to another). Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
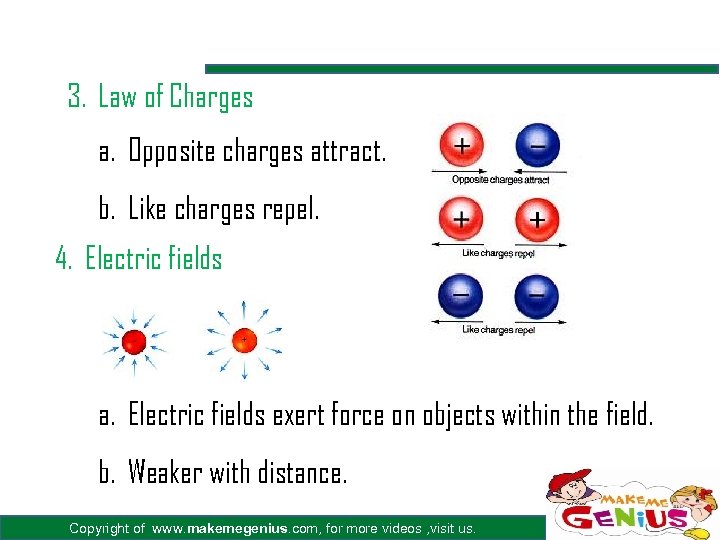 3. Law of Charges a. Opposite charges attract. b. Like charges repel. 4. Electric fields a. Electric fields exert force on objects within the field. b. Weaker with distance. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
3. Law of Charges a. Opposite charges attract. b. Like charges repel. 4. Electric fields a. Electric fields exert force on objects within the field. b. Weaker with distance. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 5. Transferring electric charge a. Conductors: e¯ move easily. b. Insulators: hold e¯ tightly. c. Contact charging is done when two materials are rubbed together (best with insulators). d. Charging by induction is done when one charged object induces a charge on another. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
5. Transferring electric charge a. Conductors: e¯ move easily. b. Insulators: hold e¯ tightly. c. Contact charging is done when two materials are rubbed together (best with insulators). d. Charging by induction is done when one charged object induces a charge on another. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 6. Lightning a. Large static discharge between the earth and clouds. b. Lightning was found to be static electricity by Ben Franklin. 7. Grounding a. Conductive path to Earth. b. Lightning rods & plumbing. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
6. Lightning a. Large static discharge between the earth and clouds. b. Lightning was found to be static electricity by Ben Franklin. 7. Grounding a. Conductive path to Earth. b. Lightning rods & plumbing. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
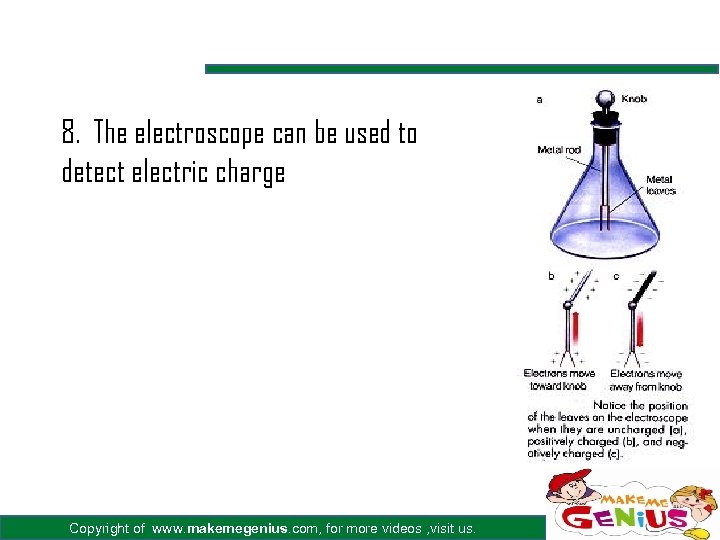 8. The electroscope can be used to detect electric charge Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
8. The electroscope can be used to detect electric charge Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 B. Electric Current 1. The reason electric charge flows from one place to another is voltage. HIGH LOW a. Voltage is the difference in electrical potential between two places where e¯ are flowing. b. Voltage is the “push” that makes electric charges move. c. Measured in volts (V). Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
B. Electric Current 1. The reason electric charge flows from one place to another is voltage. HIGH LOW a. Voltage is the difference in electrical potential between two places where e¯ are flowing. b. Voltage is the “push” that makes electric charges move. c. Measured in volts (V). Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 2. The flow of electric charge is called current. a. Current is measured in amperes, or amps (A). b. Voltage causes current. 3. The amount of electric charge is measured in coulombs. a. 1 coulomb is the charge carried by 6. 24 x 10^18 e¯. b. 1 amp is 1 coulomb per sec. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
2. The flow of electric charge is called current. a. Current is measured in amperes, or amps (A). b. Voltage causes current. 3. The amount of electric charge is measured in coulombs. a. 1 coulomb is the charge carried by 6. 24 x 10^18 e¯. b. 1 amp is 1 coulomb per sec. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
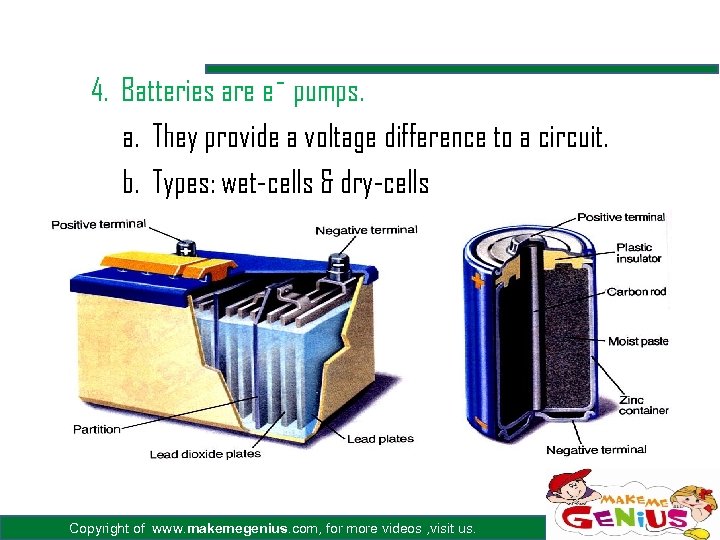 4. Batteries are e¯ pumps. a. They provide a voltage difference to a circuit. b. Types: wet-cells & dry-cells Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
4. Batteries are e¯ pumps. a. They provide a voltage difference to a circuit. b. Types: wet-cells & dry-cells Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 5. Resistance a. Opposition to the flow of e¯. b. It changes electrical energy into thermal energy and/or light. c. Measured in ohms. d. Conductors have less resistance than insulators. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
5. Resistance a. Opposition to the flow of e¯. b. It changes electrical energy into thermal energy and/or light. c. Measured in ohms. d. Conductors have less resistance than insulators. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
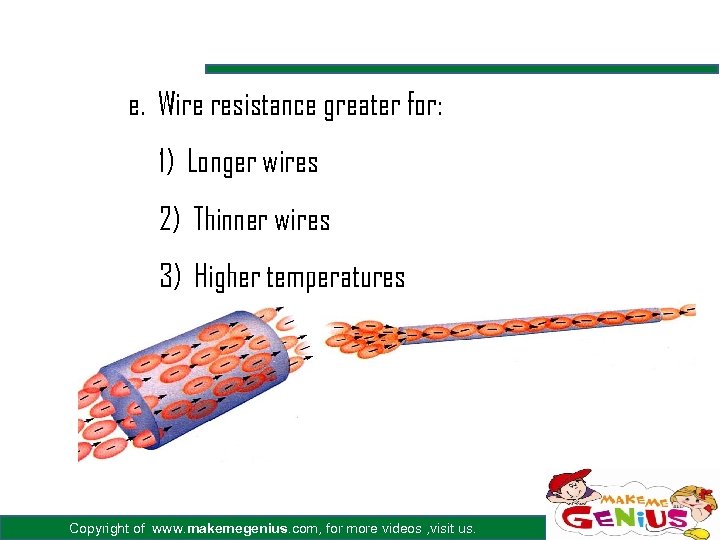 e. Wire resistance greater for: 1) Longer wires 2) Thinner wires 3) Higher temperatures Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
e. Wire resistance greater for: 1) Longer wires 2) Thinner wires 3) Higher temperatures Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
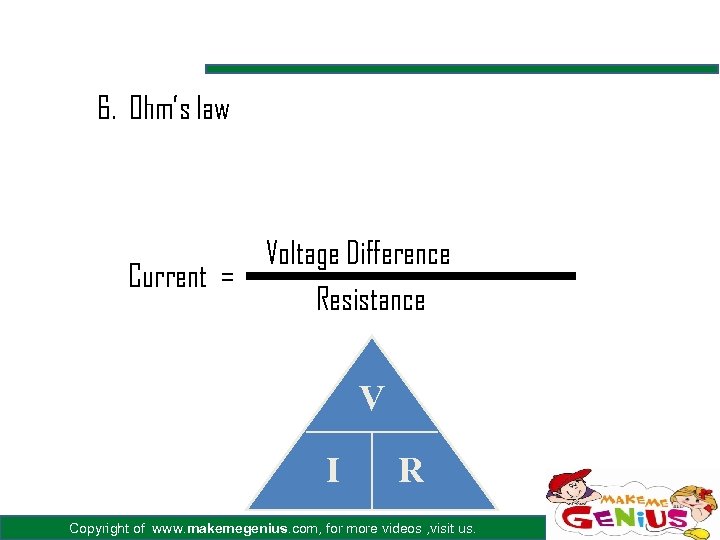 6. Ohm’s law Voltage Difference Current = Resistance V I R Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
6. Ohm’s law Voltage Difference Current = Resistance V I R Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
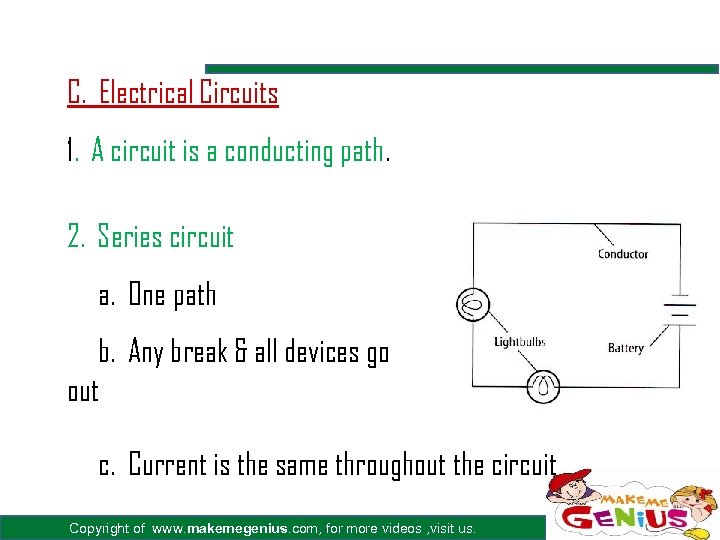 C. Electrical Circuits 1. A circuit is a conducting path. 2. Series circuit a. One path b. Any break & all devices go out c. Current is the same throughout the circuit Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
C. Electrical Circuits 1. A circuit is a conducting path. 2. Series circuit a. One path b. Any break & all devices go out c. Current is the same throughout the circuit Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
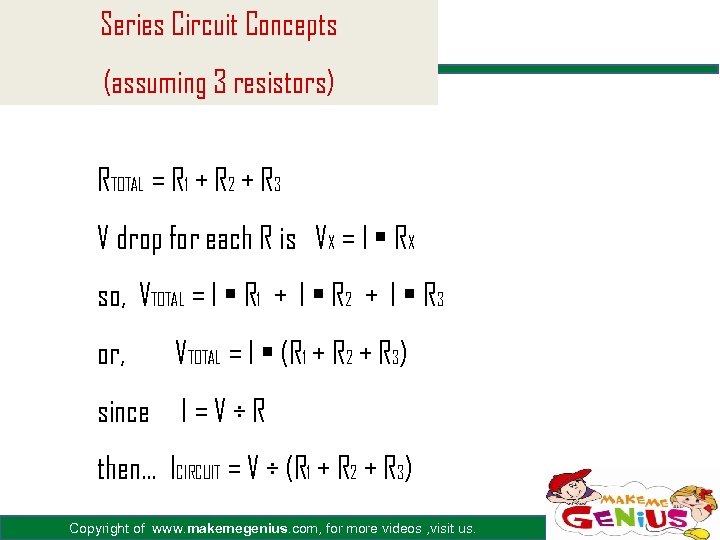 Series Circuit Concepts (assuming 3 resistors) RTOTAL = R 1 + R 2 + R 3 V drop for each R is VX = I • RX so, VTOTAL = I • R 1 + I • R 2 + I • R 3 or, VTOTAL = I • (R 1 + R 2 + R 3) since I = V ÷ R then… ICIRCUIT = V ÷ (R 1 + R 2 + R 3) Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
Series Circuit Concepts (assuming 3 resistors) RTOTAL = R 1 + R 2 + R 3 V drop for each R is VX = I • RX so, VTOTAL = I • R 1 + I • R 2 + I • R 3 or, VTOTAL = I • (R 1 + R 2 + R 3) since I = V ÷ R then… ICIRCUIT = V ÷ (R 1 + R 2 + R 3) Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
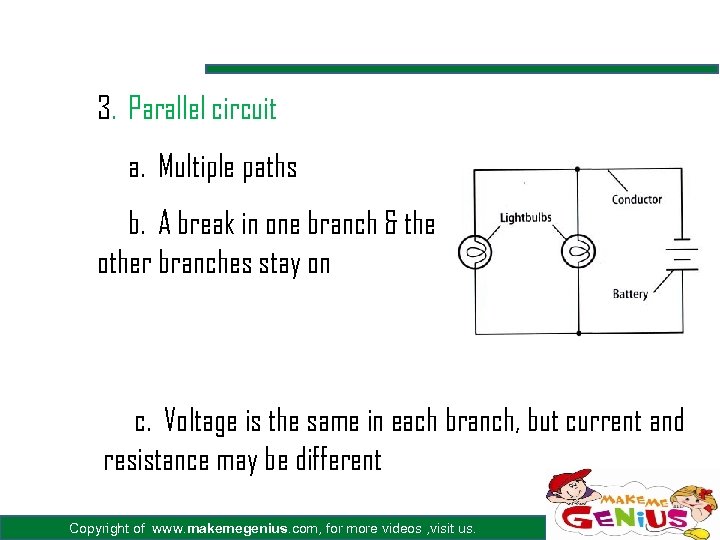 3. Parallel circuit a. Multiple paths b. A break in one branch & the other branches stay on c. Voltage is the same in each branch, but current and resistance may be different Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
3. Parallel circuit a. Multiple paths b. A break in one branch & the other branches stay on c. Voltage is the same in each branch, but current and resistance may be different Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
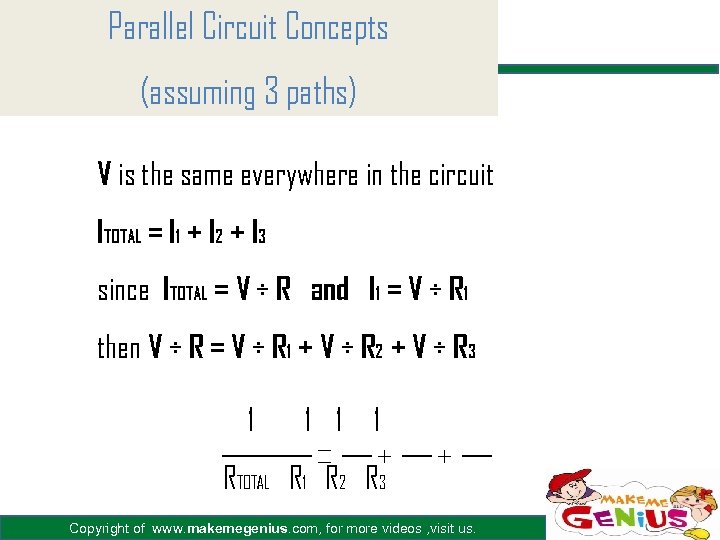 Parallel Circuit Concepts (assuming 3 paths) V is the same everywhere in the circuit ITOTAL = I 1 + I 2 + I 3 since ITOTAL = V ÷ R and I 1 = V ÷ R 1 then V ÷ R = V ÷ R 1 + V ÷ R 2 + V ÷ R 3 1 1 RTOTAL R 1 R 2 R 3 Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
Parallel Circuit Concepts (assuming 3 paths) V is the same everywhere in the circuit ITOTAL = I 1 + I 2 + I 3 since ITOTAL = V ÷ R and I 1 = V ÷ R 1 then V ÷ R = V ÷ R 1 + V ÷ R 2 + V ÷ R 3 1 1 RTOTAL R 1 R 2 R 3 Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 Comparison of series and parallel circuits The same voltage battery Notice the brightness of the bulbs Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
Comparison of series and parallel circuits The same voltage battery Notice the brightness of the bulbs Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 4. Household circuits a. Mostly parallel. b. 120 V in the U. S. c. More devices plugged in a circuit mean more current. d. More current means more heat in the wiring. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
4. Household circuits a. Mostly parallel. b. 120 V in the U. S. c. More devices plugged in a circuit mean more current. d. More current means more heat in the wiring. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
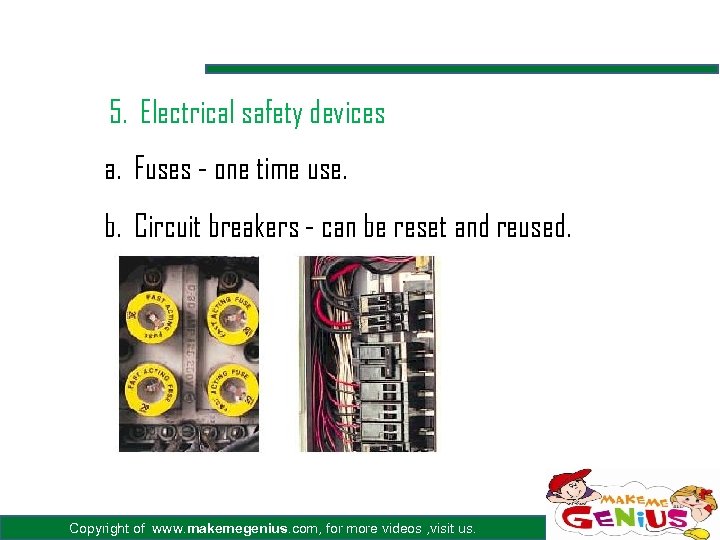 5. Electrical safety devices a. Fuses - one time use. b. Circuit breakers - can be reset and reused. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
5. Electrical safety devices a. Fuses - one time use. b. Circuit breakers - can be reset and reused. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 D. Electric Power and Energy 1. Electrical power is the rate at which electricity is converted into another form of energy. a. Power = current x voltage b. Unit is the watt or kilowatt. 2. Electrical energy a. Energy = power x time b. Unit is the kilowatt-hour. (1000 watts for 1 hour) c. This is what we buy from the electric company. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
D. Electric Power and Energy 1. Electrical power is the rate at which electricity is converted into another form of energy. a. Power = current x voltage b. Unit is the watt or kilowatt. 2. Electrical energy a. Energy = power x time b. Unit is the kilowatt-hour. (1000 watts for 1 hour) c. This is what we buy from the electric company. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
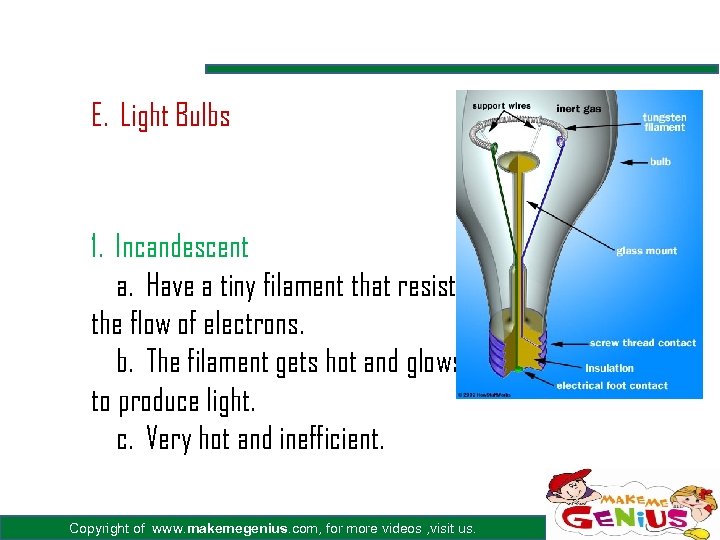 E. Light Bulbs 1. Incandescent a. Have a tiny filament that resists the flow of electrons. b. The filament gets hot and glows to produce light. c. Very hot and inefficient. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
E. Light Bulbs 1. Incandescent a. Have a tiny filament that resists the flow of electrons. b. The filament gets hot and glows to produce light. c. Very hot and inefficient. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
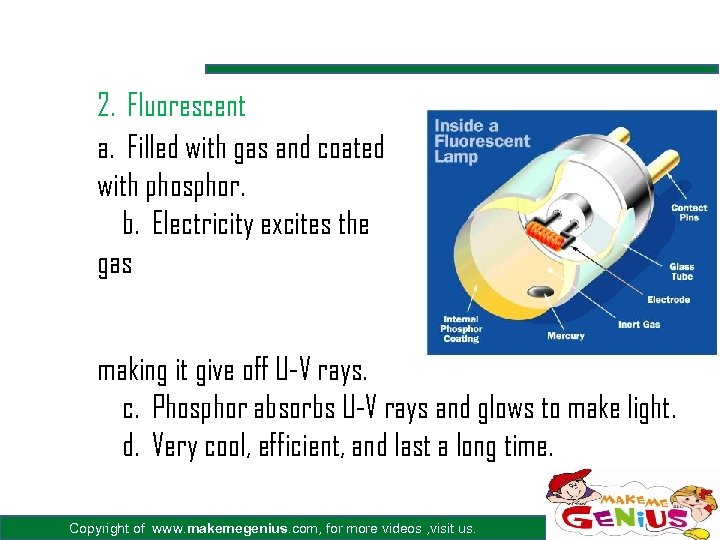 2. Fluorescent a. Filled with gas and coated with phosphor. b. Electricity excites the gas making it give off U-V rays. c. Phosphor absorbs U-V rays and glows to make light. d. Very cool, efficient, and last a long time. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
2. Fluorescent a. Filled with gas and coated with phosphor. b. Electricity excites the gas making it give off U-V rays. c. Phosphor absorbs U-V rays and glows to make light. d. Very cool, efficient, and last a long time. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 Thanks Submitted by Deepanka Mishra DAV Public School Chandigarh Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
Thanks Submitted by Deepanka Mishra DAV Public School Chandigarh Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 If you also want to share your own or your kid’s presentation(ppt) please send it on info@makemegenius. com Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
If you also want to share your own or your kid’s presentation(ppt) please send it on info@makemegenius. com Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
 “Don’t make me read, make me understand “ www. makemegenius. com– Full of ingredients to make your child a genius. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.
“Don’t make me read, make me understand “ www. makemegenius. com– Full of ingredients to make your child a genius. Copyright of www. makemegenius. com, for more videos , visit us.


