b57f562cbe5db0fec07288ba4aaac780.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 8
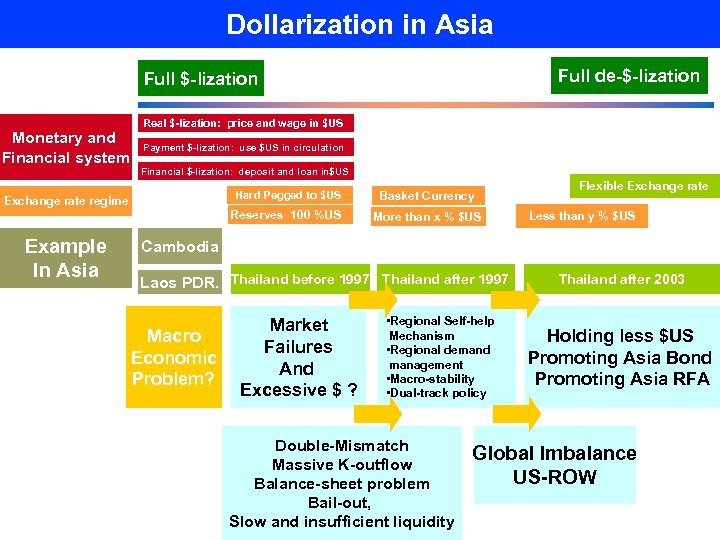 Dollarization in Asia Full de-$-lization Full $-lization Monetary and Financial system Real $-lization: price and wage in $US Payment $-lization: use $US in circulation Financial $-lization: deposit and loan in$US Hard Pegged to $US Exchange rate regime Reserves 100 %US Example In Asia Basket Currency More than x % $US Flexible Exchange rate Less than y % $US Cambodia Laos PDR. Thailand before 1997 Thailand after 1997 Macro Economic Problem? Market Failures And Excessive $ ? • Regional Self-help Mechanism • Regional demand management • Macro-stability • Dual-track policy Double-Mismatch Massive K-outflow Balance-sheet problem Bail-out, Slow and insufficient liquidity Thailand after 2003 Holding less $US Promoting Asia Bond Promoting Asia RFA Global Imbalance US-ROW
Dollarization in Asia Full de-$-lization Full $-lization Monetary and Financial system Real $-lization: price and wage in $US Payment $-lization: use $US in circulation Financial $-lization: deposit and loan in$US Hard Pegged to $US Exchange rate regime Reserves 100 %US Example In Asia Basket Currency More than x % $US Flexible Exchange rate Less than y % $US Cambodia Laos PDR. Thailand before 1997 Thailand after 1997 Macro Economic Problem? Market Failures And Excessive $ ? • Regional Self-help Mechanism • Regional demand management • Macro-stability • Dual-track policy Double-Mismatch Massive K-outflow Balance-sheet problem Bail-out, Slow and insufficient liquidity Thailand after 2003 Holding less $US Promoting Asia Bond Promoting Asia RFA Global Imbalance US-ROW
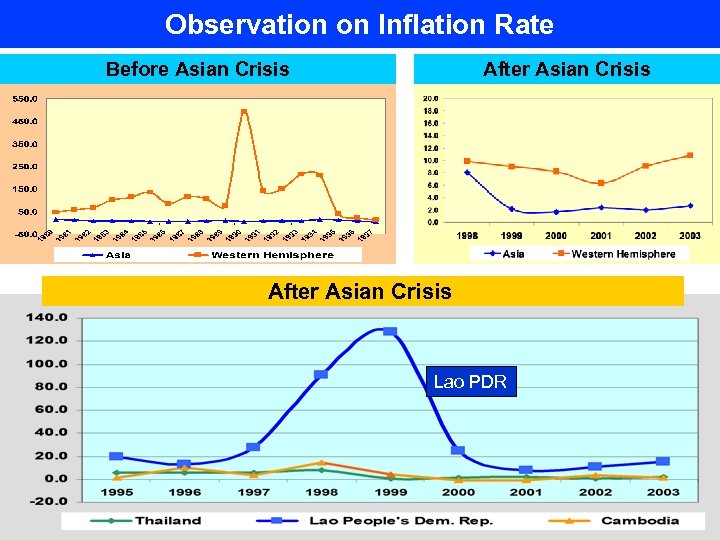 Observation on Inflation Rate Before Asian Crisis After Asian Crisis Lao PDR
Observation on Inflation Rate Before Asian Crisis After Asian Crisis Lao PDR
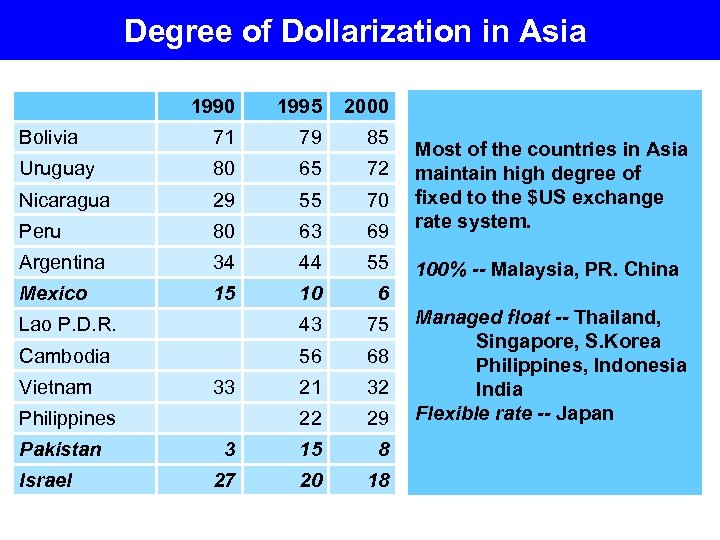 Degree of Dollarization in Asia 1990 1995 2000 Bolivia 71 79 85 Uruguay 80 65 72 Nicaragua 29 55 70 Peru 80 63 69 Most of the countries in Asia maintain high degree of fixed to the $US exchange rate system. Argentina 34 44 55 100% -- Malaysia, PR. China Mexico 15 10 6 Lao P. D. R. 43 75 Cambodia 56 68 21 32 22 29 3 15 8 27 20 18 Vietnam 33 Philippines Pakistan Israel Managed float -- Thailand, Singapore, S. Korea Philippines, Indonesia India Flexible rate -- Japan
Degree of Dollarization in Asia 1990 1995 2000 Bolivia 71 79 85 Uruguay 80 65 72 Nicaragua 29 55 70 Peru 80 63 69 Most of the countries in Asia maintain high degree of fixed to the $US exchange rate system. Argentina 34 44 55 100% -- Malaysia, PR. China Mexico 15 10 6 Lao P. D. R. 43 75 Cambodia 56 68 21 32 22 29 3 15 8 27 20 18 Vietnam 33 Philippines Pakistan Israel Managed float -- Thailand, Singapore, S. Korea Philippines, Indonesia India Flexible rate -- Japan
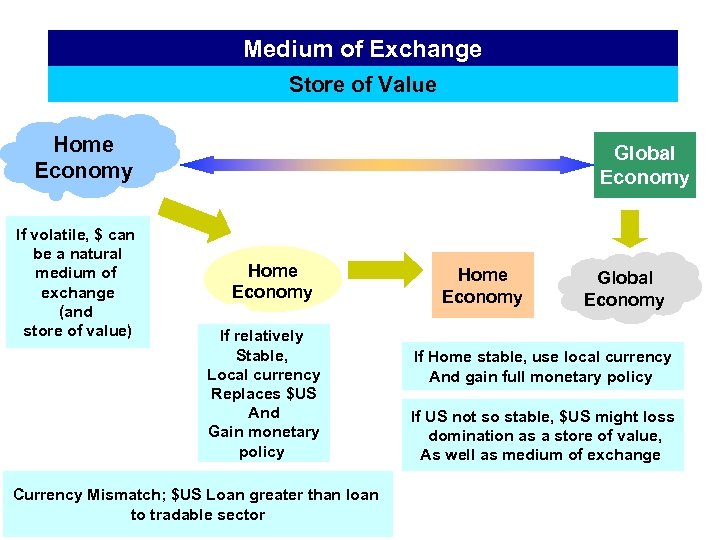 Medium of Exchange Store of Value Home Economy If volatile, $ can be a natural medium of exchange (and store of value) Global Economy Home Economy If relatively Stable, Local currency Replaces $US And Gain monetary policy Currency Mismatch; $US Loan greater than loan to tradable sector Home Economy Global Economy If Home stable, use local currency And gain full monetary policy If US not so stable, $US might loss domination as a store of value, As well as medium of exchange
Medium of Exchange Store of Value Home Economy If volatile, $ can be a natural medium of exchange (and store of value) Global Economy Home Economy If relatively Stable, Local currency Replaces $US And Gain monetary policy Currency Mismatch; $US Loan greater than loan to tradable sector Home Economy Global Economy If Home stable, use local currency And gain full monetary policy If US not so stable, $US might loss domination as a store of value, As well as medium of exchange
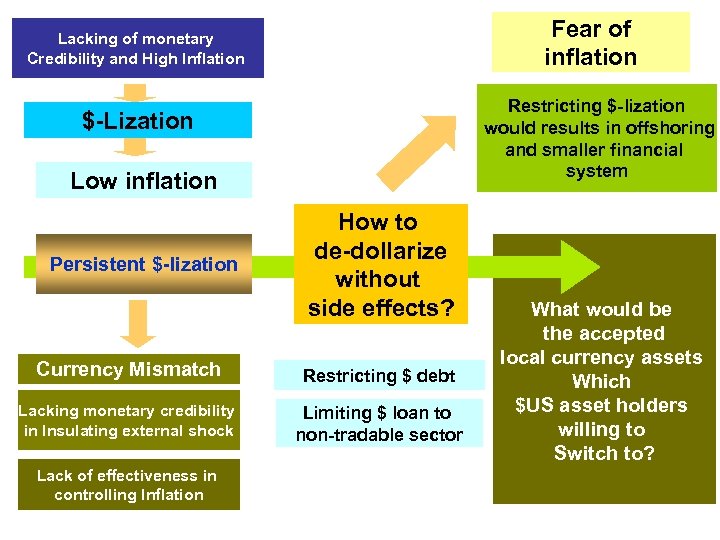 Fear of inflation Lacking of monetary Credibility and High Inflation Restricting $-lization would results in offshoring and smaller financial system $-Lization Low inflation Persistent $-lization How to de-dollarize without side effects? Currency Mismatch Restricting $ debt Lacking monetary credibility in Insulating external shock Limiting $ loan to non-tradable sector Lack of effectiveness in controlling Inflation What would be the accepted local currency assets Which $US asset holders willing to Switch to?
Fear of inflation Lacking of monetary Credibility and High Inflation Restricting $-lization would results in offshoring and smaller financial system $-Lization Low inflation Persistent $-lization How to de-dollarize without side effects? Currency Mismatch Restricting $ debt Lacking monetary credibility in Insulating external shock Limiting $ loan to non-tradable sector Lack of effectiveness in controlling Inflation What would be the accepted local currency assets Which $US asset holders willing to Switch to?
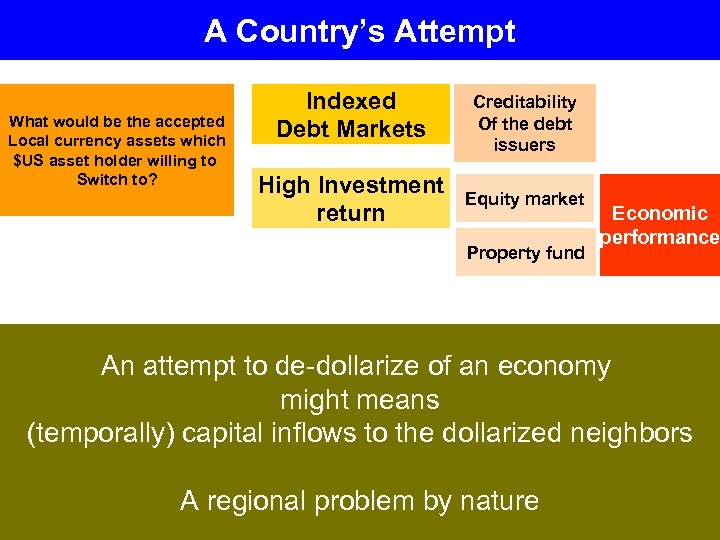 A Country’s Attempt What would be the accepted Local currency assets which $US asset holder willing to Switch to? Indexed Debt Markets Creditability Of the debt issuers High Investment return Equity market Property fund Economic performance An attempt to de-dollarize of an economy might means (temporally) capital inflows to the dollarized neighbors A regional problem by nature
A Country’s Attempt What would be the accepted Local currency assets which $US asset holder willing to Switch to? Indexed Debt Markets Creditability Of the debt issuers High Investment return Equity market Property fund Economic performance An attempt to de-dollarize of an economy might means (temporally) capital inflows to the dollarized neighbors A regional problem by nature
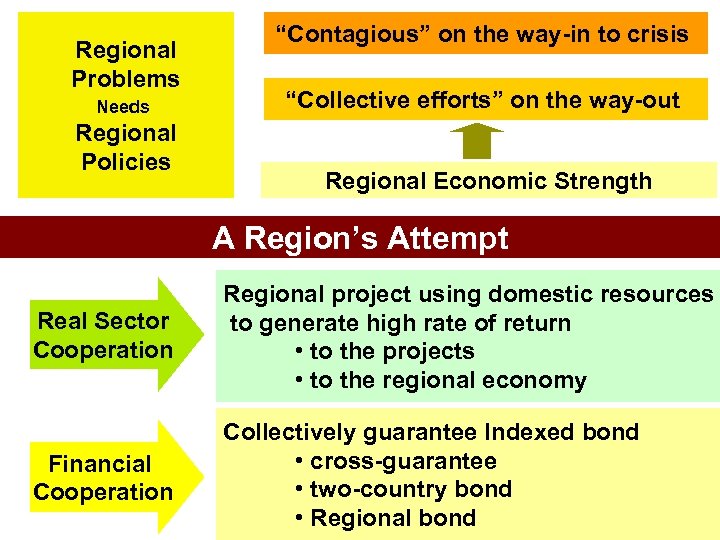 Regional Problems Needs Regional Policies “Contagious” on the way-in to crisis “Collective efforts” on the way-out Regional Economic Strength A Region’s Attempt Real Sector Cooperation Regional project using domestic resources to generate high rate of return • to the projects • to the regional economy Financial Cooperation Collectively guarantee Indexed bond • cross-guarantee • two-country bond • Regional bond
Regional Problems Needs Regional Policies “Contagious” on the way-in to crisis “Collective efforts” on the way-out Regional Economic Strength A Region’s Attempt Real Sector Cooperation Regional project using domestic resources to generate high rate of return • to the projects • to the regional economy Financial Cooperation Collectively guarantee Indexed bond • cross-guarantee • two-country bond • Regional bond
 A Region’s Attempt on Regional Financial Arrangement Economic Surveillance Remember the contagious effect (always) • Peer Review • Strong academic comments—IADB? Collectively we have sufficient reserves Resource Pooling Regional Bond Market (Mexico-Brazil-Venesuela-Chile-Agentina: 30 -25 -8 -8 -7 %) • Guarantee to re-lend capital in-flows from neighboring country • Swap arrangement (Government bond in local currency as collateral is preferable) Local-currency denominated bonds • Cross- investment by central banks (accepting as reserves) • Cross-investment by private investors
A Region’s Attempt on Regional Financial Arrangement Economic Surveillance Remember the contagious effect (always) • Peer Review • Strong academic comments—IADB? Collectively we have sufficient reserves Resource Pooling Regional Bond Market (Mexico-Brazil-Venesuela-Chile-Agentina: 30 -25 -8 -8 -7 %) • Guarantee to re-lend capital in-flows from neighboring country • Swap arrangement (Government bond in local currency as collateral is preferable) Local-currency denominated bonds • Cross- investment by central banks (accepting as reserves) • Cross-investment by private investors


