3a0c215415c2f40a749beae58fdf455f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

DOING BUSINESS WITH THE UNITED NATIONS (UN) Presented by Niels Ramm (UNGM) and Susan Struck (HLCM PN) Athens, November 2008

How to do Business with the United Nations (UN) Overview of the United Nations UN Procurement Statistics How to Identify Business Opportunities General UN Procurement Procedures Global Compact & Ethics

Overview
Overview § The United Nations is made up of a variety of organizational entities (agencies, organizations, commissions, programmes, funds, etc). § Each entity has a distinct and separate mandate (covering the political, economic, social, scientific and technical fields).
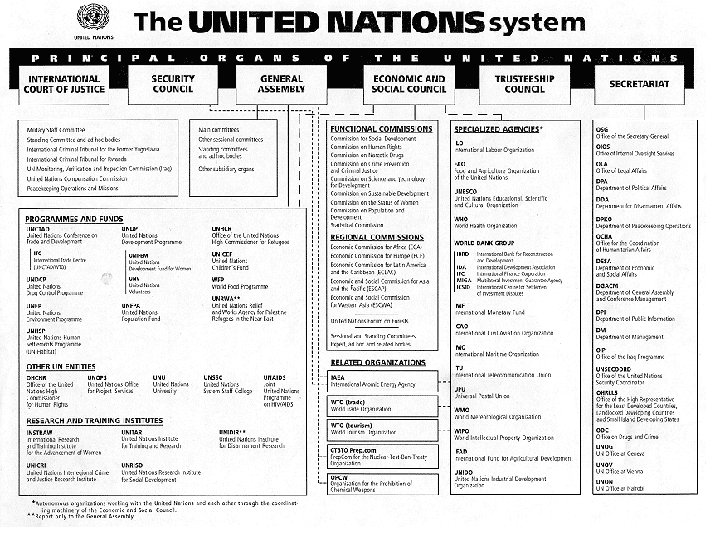
…………. ….
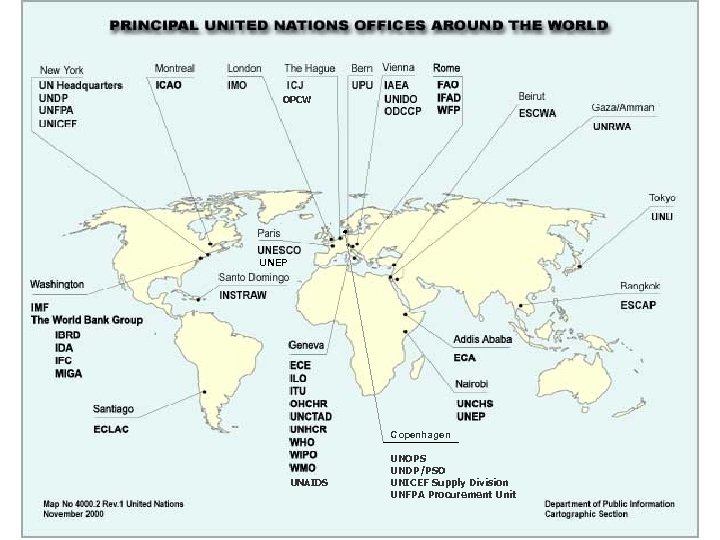
Le Nazioni Unite nel mondo OPCW UNEP Copenhagen UNAIDS UNOPS UNDP/PSO UNICEF Supply Division UNFPA Procurement Unit

Overview EACH ORGANISATION. . . • has its own special requirements for goods and services • may conduct its own procurement activities • follows, in general, common principles for procurement rules and regulations • constitutes a separate and distinct customer/partner

Statistics (UN Procurement System)
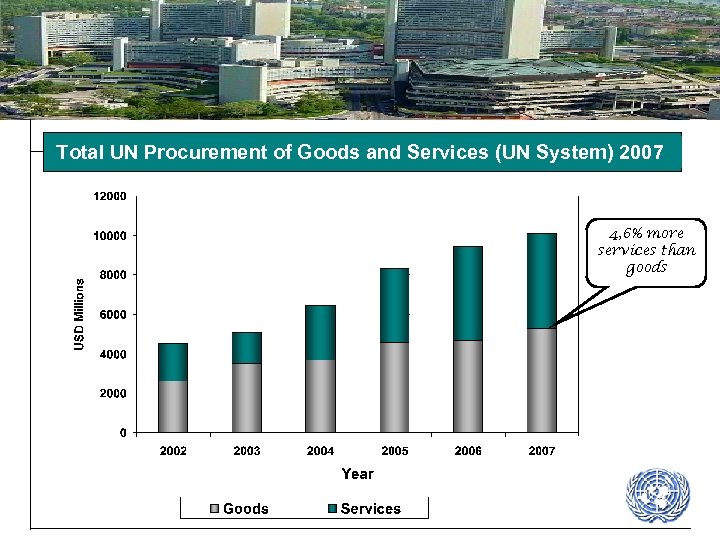
Total UN Procurement of Goods and Services (UN System) 2007 4, 6% more services than goods
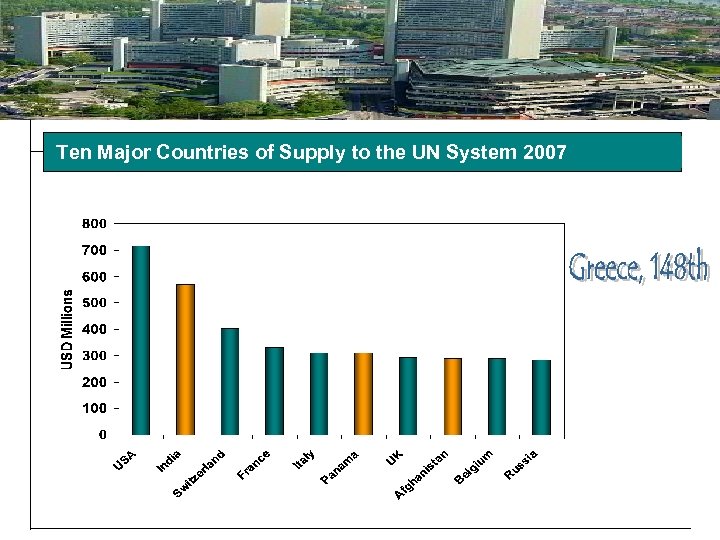
Ten Major Countries of Supply to the UN System 2007

Major Items procured by the UN System Goods Services • Food • Security Services • Pharmaceutical Supplies • Outsourced Personnel Services • Vehicles • Engineering Services • Computers and Software • Construction • Shelter and Housing • Corporate Services • Telecommunications Equipment • Freight Services • Laboratory Equipment • Printing Services and Equipment Rental • Building Materials • Consultancy Services • Telecommunication Services

Volume of Procurement in 2007 of the 15 Principal Agencies 1. UNDP 2424 9. IAEA 131 2. UN Sec 1904 10. UNHCR 128 3. WFP 1808 11. UNDP/IAPSO 106 4. UNOPS 659 12. FAO 85 5. PAHO 294 13. ILO 70 6. UNESCO 231 14. UNOG 69 7. UNFPA 224 15. UNIDO 55 8. UNRWA 180
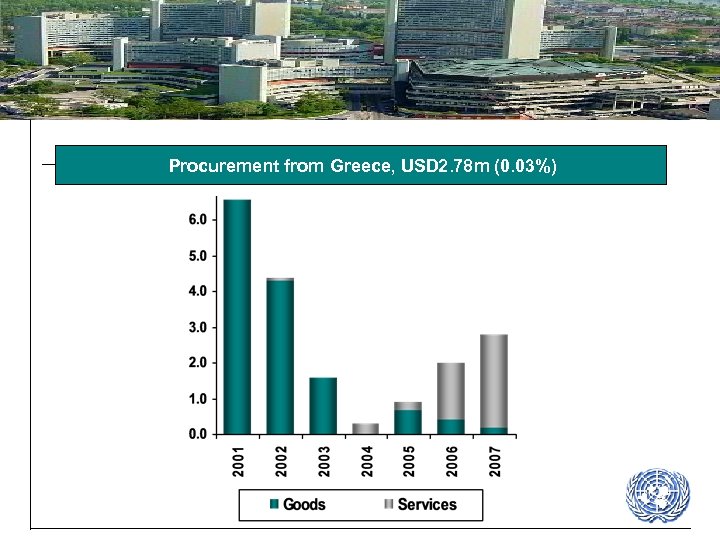
Procurement from Greece, USD 2. 78 m (0. 03%)
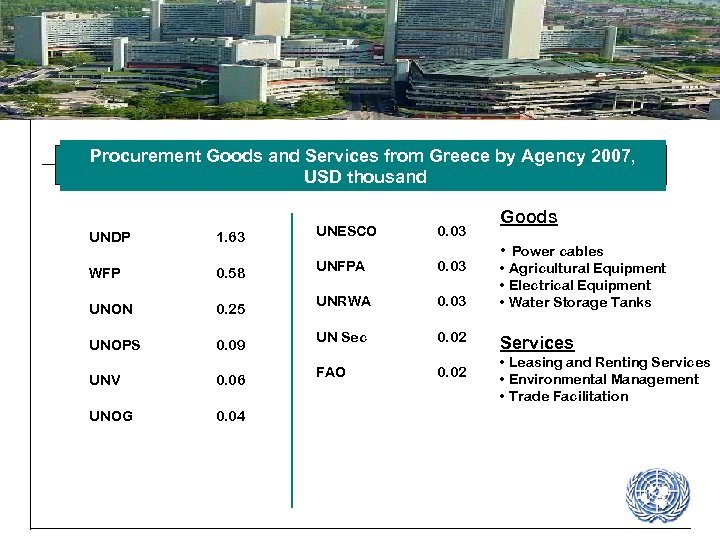
Procurement Goods and Services from Greece by Agency 2007, USD thousand UNDP 1. 63 UNESCO WFP 0. 58 UNFPA 0. 03 UNON 0. 25 UNRWA 0. 03 UNOPS 0. 09 UN Sec 0. 02 FAO 0. 02 UNV 0. 06 UNOG 0. 04 0. 03 Goods • Power cables • Agricultural Equipment • Electrical Equipment • Water Storage Tanks Services • Leasing and Renting Services • Environmental Management • Trade Facilitation

How to Identify Business Opportunities

Are you ready to supply to the UN (1/2)? § Market knowledge ― UN structure, procedure and value § Export experience / references ― Global and/or local operation § Languages ― Employees, documents § Competitive prices – Quality ― International competition – best value

Are you ready to supply to the UN (2/2)? § Networks / partner ― Country knowledge, after-sales services § Capacities ― Finance, personnel § Flexibility and accuracy ― Operational tempo § Persistence, endurance, patience

Web-Based Information Towards one single commercial and procurement portal: UN Global Market Place (UNGM) Additional information: www. ungm. org § The Annual Statistical Report § § The General Business Guide (GBG) Practical Tips — Doing Business with the UN § Procurement notices § Value-Added Service: Receive relevant procurement notices directly in your Inbox, USD 250 annually

Business Information The Annual Statistical Report UN procurement by country – UN Agency procurement by country, commodity or service – Purchase orders and Contracts (over USD 30, 000) placed by agency, by country of vendor, value and description of goods or services – Top Ten items procured by Agency The General Business Guide – Lists all UN Organizations, fields of activity, contact persons, procurement activities and requirements and registration procedures Available from www. ungm. org Both publications are updated on an annual basis

Step-by-Step Towards Success § Extensive market research ― Planning acquisition, contract award, UN information § Identification of relevant UN Organization ― Match capacity and requirements § Registration — United Nations Global Marketplace ― Mandatory for majority of UN agencies § Thorough information about procurement ― Principles, procedures § Obtain systematic / regular information about current procurement activities / opportunities ― Keep yourself up-to-date

UN Procurement Procedures

Common Guidelines for UN Procurement system Procurement activities of the UN system are based on the following principles: • • Advancing the interests of the organisation Obtaining value for money Ensuring probity through inter alia, fairness, integrity, transparency and effective competition Accountability for outcomes These Common Guidelines cover procurement stages from sourcing to execution of a procurement contract

How are vendors shortlist compiled? (Sourcing) § Competitive suppliers of previous procurement ― Past performance § Suppliers of the required goods or services, found on the UN Global Marketplace ― Codification § Through calls for Expression of Interest (EOI) ― Notices § Search of World Wide Web § Trade Missions, Chambers of Commerce § Exchange with other UN Agencies

Supplier Criteria § § Minimum of 3 years experience in relevant business line Export Experience (where applicable) Certified financial reports for the past 3 years (Annual turnover + annual profit + company’s own capital) References, 3 recent contracts, goods/services supplied, dates and client details Quality Certification § § General Terms and Conditions Supplier Code of Conduct §

How is the procurement method decided? § the value of the procurement § the nature of the goods and services to be procured § critical dates for delivery

Thresholds/Award for types of solicitation Up to 30, 000 USD ** - Informal, simplified acquisition procedure - Requests for Quotation (RFQ) - Lowest priced, technically acceptable bidder or best value bidder (evaluated). • Above 30, 000 USD** - Invitation to Bid (ITB) and Request for Proposal (RFP) - Open and formal: advertised (on the web) generally larger shortlist (minimum 6 potential bidders, 3 to comply) - Public bid opening - Review and Recommendation by Contract Committees ** Thresholds vary

Types of Solicitation § Expression of Interest (EOI) Written communication by a supplier to provide information about its products, resources, qualifications and experience § Request for Quotation (RFQ) Less formal solicitation, lower value, standard specifications, readily available on the market § Invitation to Bid (ITB) Formal solicitation, lowest evaluated price, compliant and technically compliant § Request for Proposal (RFP) Formal solicitation, requirements possibly met in a variety of ways, overall best solution will win the award (Combining technical solution and price considerations) -- not necessarily the lowest price

Types of Solicitation § Long Term Agreement (LTA)/Frame Agreement A long-term agreement based on ITB or RFP process 2 -4 years period Potentially more than one LTA for same goods/service Advantage: Shortens delivery time by shortening process § Direct Contracting Exception to the rule In case of extreme emergency Sole source If competitive bidding process has failed for valid reason Very stringent controls and has to be well justified

Common General Terms & Conditions § Cover both the procurement of goods and the contracting of services. § Most provisions are common within the UN procurement system, however some provisions may vary depending on individual agency requirements. § Familiarise yourself with the UN Terms & Conditions (UNGCC).

“ The Global Compact

The UN Global Compact — Ten Principles Business should: 1. Support and respect the protection of internationally proclaimed human rights (policies, basic working conditions, right to health/privacy, workplace health and safety) 2. Make sure that they are not complicit in human rights abuses (know who your partners are, policies apply to subsidiaries) 3. Business should uphold the freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining (allow workers to form trade unions) 4. The elimination of all forms of forced and compulsory labor (treat migrant workers fairly, have contracts for all workers) 5. The effective abolition of child labor (age verification, programs for children of workers) 6. The elimination of discrimination in respect of employment and occupation (policies, zero tolerance) 7. Business should support a precautionary approach to environmental challenges (policies) 8. Undertake initiatives to promote greater environmental responsibility (reduce energy consumption) 9. Encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies 10. Business should work against all forms of corruption, including extortion and bribery (zero tolerance, anti -corruption policy, political donations are published) www. unglobalcompact. org
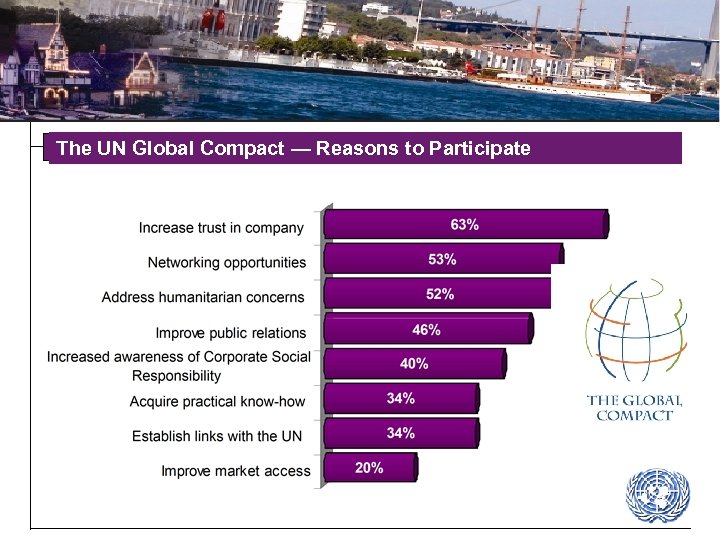
The UN Global Compact — Reasons to Participate

Ethics in General ¬ We continue to strive for Integrity, Fairness and Transparency ¬ Financial, personal or professional interest with suppliers must be declared and precludes any participation in the procurement process ¬ Zero tolerance. . . ¬ Disputes? Contact Head of Procurement at Organization
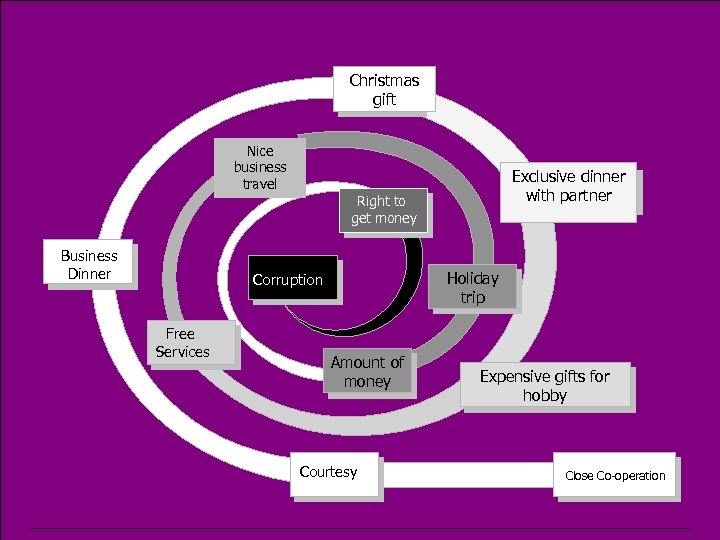
Christmas gift Nice business travel Business Dinner Right to get money Holiday trip Corruption Free Services Exclusive dinner with partner Amount of money Courtesy Expensive gifts for hobby Close Co-operation

Thank you & good luck!
3a0c215415c2f40a749beae58fdf455f.ppt