bfdd62d07859517316ebcd174b420315.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 123

Doing Business in Spain Montreal, 22 nd May 2008

Invest in Spain: Economy, Business and Advantages for Canadian companies May, 2008 Marian Scheifler Phd. Chief Operations Manager

1. Political Structure. 2. Spain in Figures (I-II). 3. Canada-Spain: Some things we share. 4. Main Agreements Spain-Canada. 5. Main Reasons to Invest in Spain (I-III). 6. About INTERES.

1. POLITICAL STRUCTURE POLITICAL FRAMEWORK Political organization Parliamentary Monarchy. Head of State King Juan Carlos I. President of government José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero, since 11 April 2008 (2 nd mandate). Parliamentary representation Congress of Deputies (350 members) and Senate (264 members). Governing party Partido Socialista Obrero Español (PSOE). Territorial Organization The State is organized in municipalities, provinces and Autonomous Communities. European Union Member since 1986 and founding member of the European Monetary Union (January 1999). International organizations UN, OECD, OAS, World Bank, IMF, IDB, WTO, NATO, OSCE.
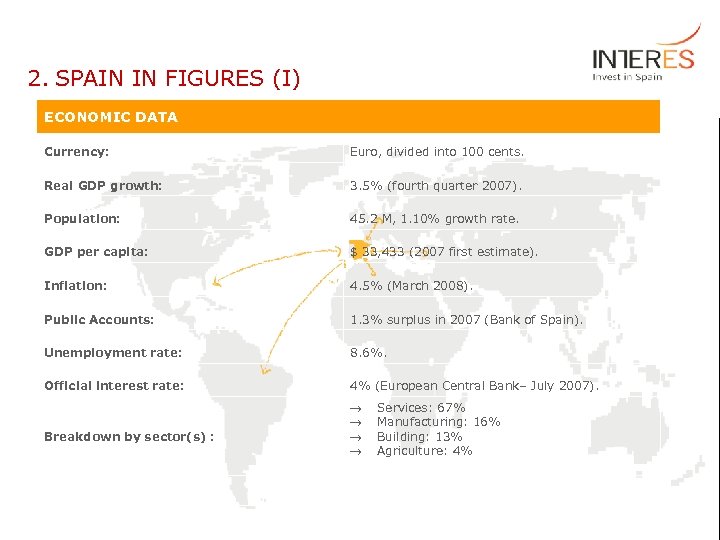
2. SPAIN IN FIGURES (I) ECONOMIC DATA Currency: Euro, divided into 100 cents. Real GDP growth: 3. 5% (fourth quarter 2007). Population: 45. 2 M, 1. 10% growth rate. GDP per capita: $ 33, 433 (2007 first estimate). Inflation: 4. 5% (March 2008). Public Accounts: 1. 3% surplus in 2007 (Bank of Spain). Unemployment rate: 8. 6%. Official interest rate: 4% (European Central Bank– July 2007). Breakdown by sector(s) : ® ® Services: 67% Manufacturing: 16% Building: 13% Agriculture: 4%

2. SPAIN IN FIGURES (II) 1. The world’s 8 th largest economy (market exchange rate); 11 th (purchasing power parity). (IMF-2008) 2. The 3 rd largest investor in the world and the 2 nd largest in Latin America. (World Investment Report 2007 (UNCTAD) 3. The 8 th largest FDI stock worldwide (6 th in the EU). (World Investment Report 2007 (UNCTAD) 4. The 10 th best place to live and the preferred work destination for Europeans. Worldwide Quality-of-life Index, Economist Intelligence Unit 5. The world’s 2 nd tourist destination. (Tourism Organization (WTO))

3. CANADA – SPAIN: SOME THINGS WE SHARE ü Multilingual and multicultural societies. ü Highly decentralized administrations: important role played by Provinces and Autonomous Communities. ü Economic performance. ü Great potential to strengthen trade and investment ties: current trade and investment flows belie the similarities in economic performance and complementarities in our economies.

CANADIAN COMPANIES IN SPAIN

4. MAIN AGREEMENTS SPAIN - CANADA § S&T: (Science and Technology) ü Spain’s R&D Plan for 2008 -2011 identifies Canada as one of the three non-EU strategic countries for cooperation. ü Canadeka: Bilateral program for technological cooperaton, CDTI – NRC. Support to joint projects of Spanish-Canadian companies. ü CSIC-NRC: Development of research and innovation projects. ü Genoma España – Genome Canada: Joint research projects. § CESCE-EDC: Reinsurance agreement for joint operations of Canadian and Spanish companies. § Double taxation: Agreement to avoid double taxation on income and capital.

5. MAIN REASONS TO INVEST IN SPAIN (I) § Geostrategic location: ü Privileged position for southern Europe's key markets, Latin America and North Africa. § Potential access to over 1. 2 billion consumers: ü 45 million consumers in Spain. ü 443 million consumers in Europe. ü Entry point for non-EU Mediterranean countries with 264 million consumers. (privileged relations with Morocco and Algeria). ü Hub for South and Central America, with 560 million consumers. ü Financial protocols with North Africa and Latin America.

5. MAIN REASONS TO INVEST IN SPAIN (I) § Ultra Modern Transport Infrastructure ü 47 airports. ü 53 ports on both the Atlantic and the Mediterranean coasts. ü 3 rd largest EU highway network. ü Ambitious plans for high speed trains (Spain will be the world leader with 2, 230 km in 2010). ü State-of-the-Art metro system in major cities.
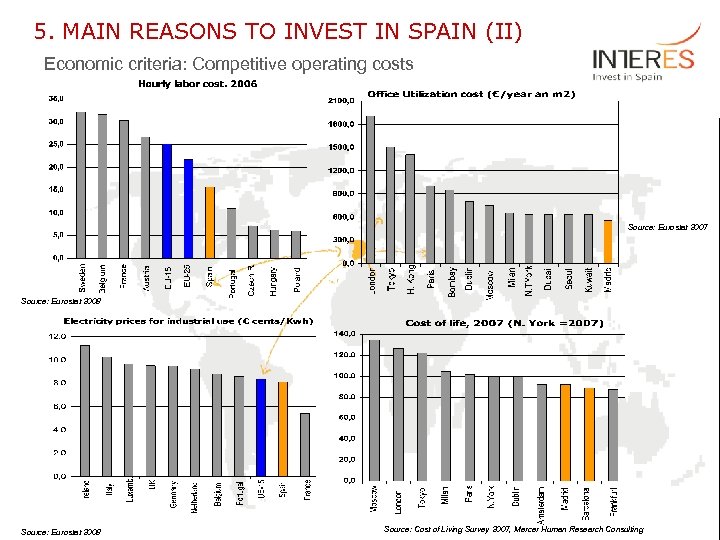
5. MAIN REASONS TO INVEST IN SPAIN (II) Economic criteria: Competitive operating costs Source: Eurostat 2007 Source: Eurostat 2008 Source: Cost of Living Survey 2007, Mercer Human Research Consulting
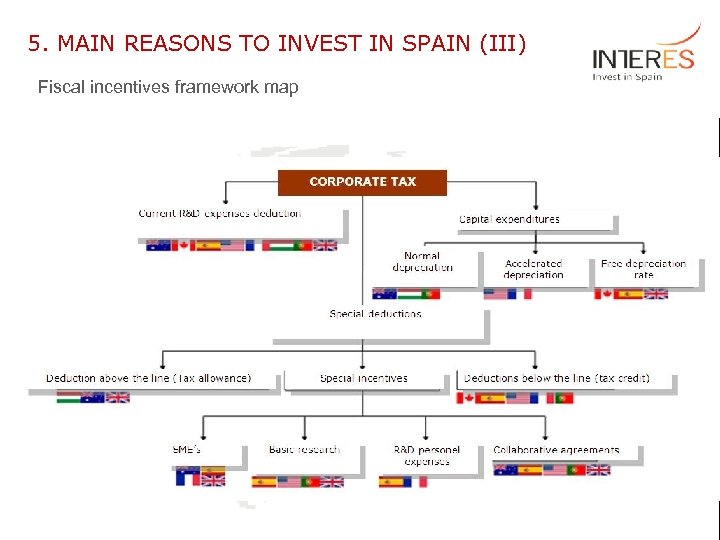
5. MAIN REASONS TO INVEST IN SPAIN (III) Fiscal incentives framework map

6. About INTERES Invest in Spain is the leading government organization that supports foreign companies seeking to set up or expand their business in Spain. We provide comprehensive, efficient and confidential consultation at no cost during all stages of the investment process. THE ONE-STOP SHOP FOR INVESTORS IN SPAIN.
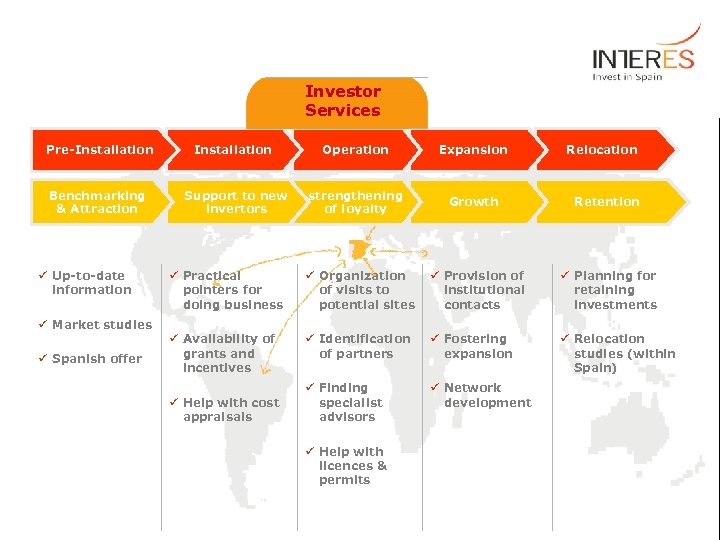
Investor Services Pre-Installation Operation Expansion Benchmarking & Attraction Support to new invertors strengthening of loyalty Growth ü Up-to-date information ü Market studies ü Spanish offer Relocation Retention ü Practical pointers for doing business ü Organization of visits to potential sites ü Provision of institutional contacts ü Planning for retaining investments ü Availability of grants and incentives ü Identification of partners ü Fostering expansion ü Relocation studies (within Spain) ü Finding specialist advisors ü Network development ü Help with cost appraisals ü Help with licences & permits


Thank you very much!

Doing Business in Spain Montreal, 22 nd May 2008

What makes Spain a winning location for the Life Sciences & Biotech industry? Ana Arias Biotech & Life Sciences Investor Services Manager

INDEX 1. Why Spain? 2. Why biotechnology? 3. Why you can bet on Spanish biotech 4. A piece of history 5. Business opportunities

Why Spain? v Highly qualified and competitive human resources v Quality and standard of living v Geo-strategic location v Cultural and educational levels v Weather v Natural resources v Logistics. . . Spain has solid scientific and technological capabilities that have enabled a competitive bio industry to emerge
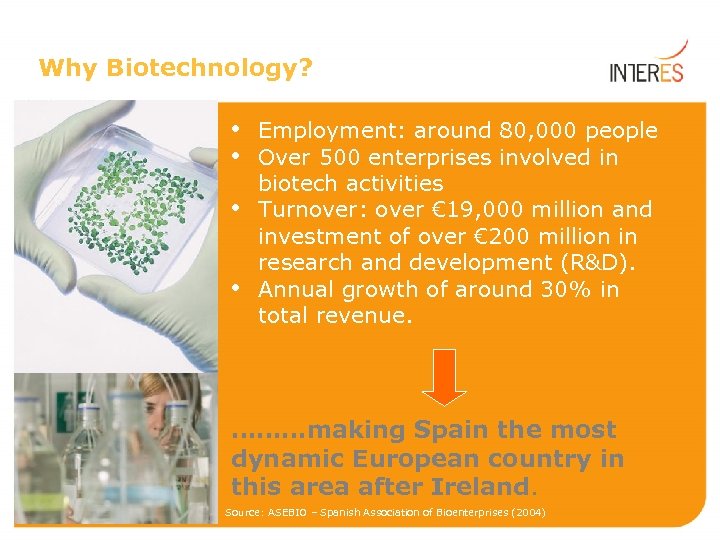
Why Biotechnology? • • Employment: around 80, 000 people Over 500 enterprises involved in biotech activities Turnover: over € 19, 000 million and investment of over € 200 million in research and development (R&D). Annual growth of around 30% in total revenue. ………making Spain the most dynamic European country in this area after Ireland. Source: ASEBIO – Spanish Association of Bioenterprises (2004)

Why Biotechnology? (cont. ) • Bio-economy heads Spain’s strategic agenda. • The Spanish pharmaceutical market is the fifth largest in the EU-15 and the seventh in the world. • Favourable financial environment: increase in the volume of venture capital operations in biotechnology. • New venture capital funds specialized in biotechnology and national networks of business angels are being created

Why you can bet on Spanish biotech I. Solid Science -Good scientific output Groups and Centers of Excellence -R&D Integrated System Efficient Work. Flow Excellent conditions for Translational Research Modern Science Parks and state of the art facilities Good partnership opportunities -“Value for Science” Every euro in the lab is put to good use II. Great potential -Huge body of knowledge yet to be exploited -Human Capital, very well trained

Why you can bet on Spanish biotech(cont. ) III. Emerging bio-economy -Increasing support from Governments for R&D and bio-enterprise creation -Competition among local Governments for talent and capital -Good balance between being competitive on cost and competitive in differentiation IV. Good personal attitudes -Creativity -Sense of community and focus on colective objectives and challenges -Positive spirit and commitment

Why you can bet on Spanish biotech(cont. ) A. Solid Science: Scientific and Technological Facilities and Capabilities The Genomics, Proteomics and Bioinformatics platforms boost the national participation in biotechnological advances: -National DNA Bank -Spanish National Genotyping Centre -National Proteomics Institute Proteo. Red -National Bioinformatics Institute INB A new framework for co-operative biomedical research is being created: -The Biomedical Research Thematic Networks (RETICs) -The Biomedical Research Centers Network (CIBER)
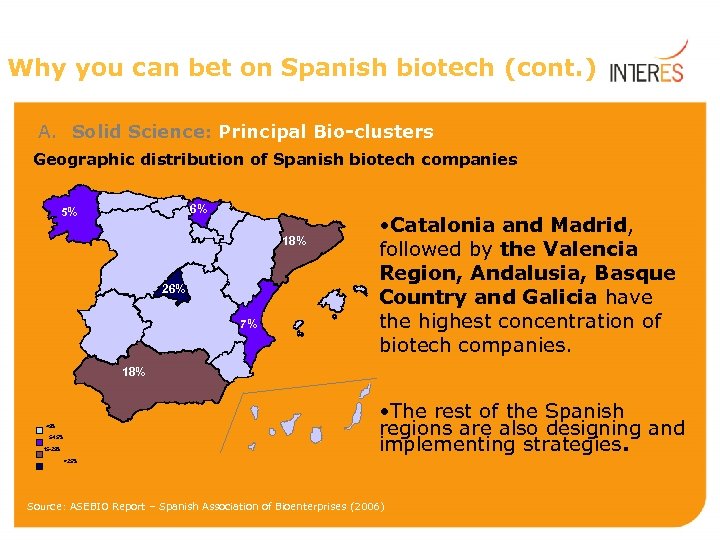
Why you can bet on Spanish biotech (cont. ) A. Solid Science: Principal Bio-clusters Geographic distribution of Spanish biotech companies 6% 5% 18% 26% 7% • Catalonia and Madrid, followed by the Valencia Region, Andalusia, Basque Country and Galicia have the highest concentration of biotech companies. 18% • The rest of the Spanish regions are also designing and implementing strategies. <5% 5 -15% 15 -25% >25% Source: ASEBIO Report – Spanish Association of Bioenterprises (2006)

Why you can bet on Spanish biotech (cont. ) B. Great potential to unlock: Workforce § 7, 000 researchers in biotechnology and biomedicine: 11 th position in the world. § 4 th position in Europe in scientific output in biotechnology. § 1995 -2003: number of scientific research papers published in Spain grew by over 12%. § 66% of biotechnology researchers working within the public Spanish R&D System were cited by U. S. patents.

Why you can bet on Spanish biotech (cont. ) C. Emerging bio-economy: Legal framework § The new Spanish Law on Biomedical Research: creation of a National Biobank Register § Favourable legal framework: Cultivation of Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) and a unique Traceability and Labelling Law § Full Tax exemption on biofuels until Dec 2012. § Other Spanish instruments and laws.

Why you can bet on Spanish biotech (cont. ) C. Emerging bio-economy: Government support § The Ingenio 2010 Programme: to meet the Research, Development and Innovation convergence objectives of the Lisbon Strategy. § Sustained annual growth rates of the government’s budgets in recent years. § The Spanish Tax System is one of the most advanced in the world, especially in the Research, Development and Innovation field. § The adoption of the Young Innovative Company Status will no doubt help biotechnology firms.

A piece of history • 2001: The Spanish National Cancer Centre (CNIO) launches its first Oncochip. • 2002: Abengoa signs a $35. 5 M R&D project with the U. S Department of Energy (DOE). • 2003: Serono concentrates global production of its growth hormone in Spain. • 2005: Genetrix receives the first Orphan Status designation by the EMEA in Europe for a medicinal product based on the use of stem cells of adult origin. • 2005: GSK opens its Molecular Screening and Tropical diseases research facilities in Spain. • 2005: Natraceutical buys Braes Group (€ 80 M). In 2006 it acquires Forté Pharma (€ 82 M). • 2006: Spain continues to be the European leader in the cultivation of genetically modified crop varieties with a total of 53, 667 hectares under cultivation. • 2007: The EMEA approves Zeltia's drug Yondelis for the treatment of soft tissue sarcomas. • 2008: The OMS designated the ONT (Organización Nacional de Transplantes) as a WHO Collaborating Center on Donation and Transplants

Business Opportunities

BIO Business Opportunities Spain offers specific opportunities in…………. v Biochips: towards a personalized medicine v Food quality and security v Private Equity v Functional foods v Organic farming
BIO Business Opportunities (cont) Spain offers specific opportunities in…………. v Nanobiotechnology v Generic drugs v Gene silencing v Production of therapeutic proteins using non-genetically modified plants v Algae active ingredients
BIO Business Opportunities (cont. ) Spain offers specific opportunities in…………. v Production of enzymes with industrial applications in transgenic plants. v Drug development from target’s structural determination. v Pharmacogenetics: Genetic biomarkers. v Molecular diagnosis. DNA and protein arrays. v Bioinformatics.

Leading pharmaceutical & biotech multinationals are already successfully located in Spain

BIOSPAIN 2008 is the International Meeting on Biotechnology to be held in Granada from the 17 th to the 19 th of September 2008. Five events in one: v. BIOTEC 2008 " - Scientific Congress v. Plenary Sessions: "Towards a Sustainable Bioeconomy“ v. Investment Forum v. Partnering v. Trade Fair and Bio-Regions Hall

Thank you very much See you at BIOSPAIN’ 08! www. biospain 2008. org For further information please contact: Ana Arias Life Sciences & Biotech Investor Services Manager Email: aarias@interes. org

Doing Business in Spain Montreal, 22 nd May 2008

SPAIN: Business opportunities in Aeronautics Vanessa Guerrero, Investor Services Manager INTERES Invest in Spain May, 22 th 2008 MONTREAL

Why Spain
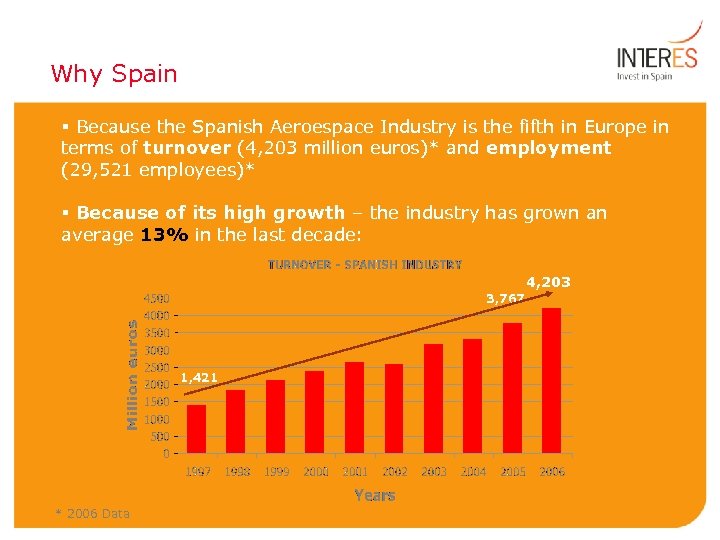
Why Spain § Because the Spanish Aeroespace Industry is the fifth in Europe in terms of turnover (4, 203 million euros)* and employment (29, 521 employees)* § Because of its high growth – the industry has grown an average 13% in the last decade: 4, 203 3, 767 1, 421 * 2006 Data
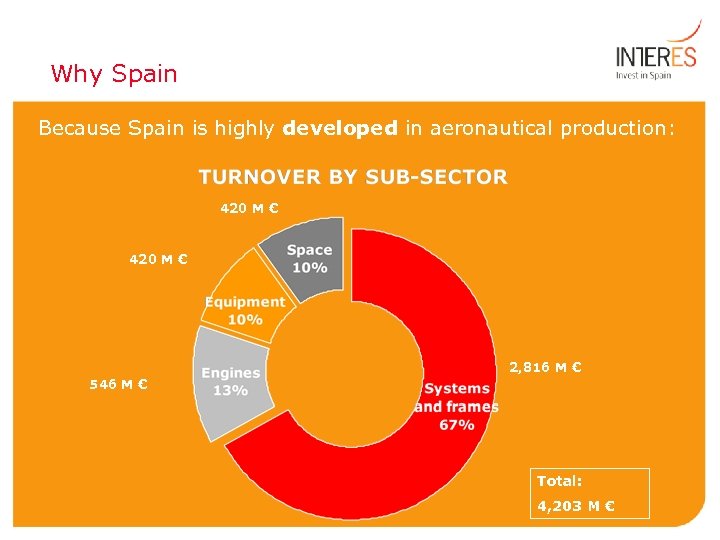
Why Spain Because Spain is highly developed in aeronautical production: 420 M € 2, 816 M € 546 M € Total: 4, 203 M €

Why Spain § Because Aeronautics companies based in Spain are leaders in: v Composite Aerostructures (especially, carbon fiber reinforced plastics) v Low pressure turbine engines v Air Traffic Management systems 3 out of 5 flights in the world use Spanish software for landing
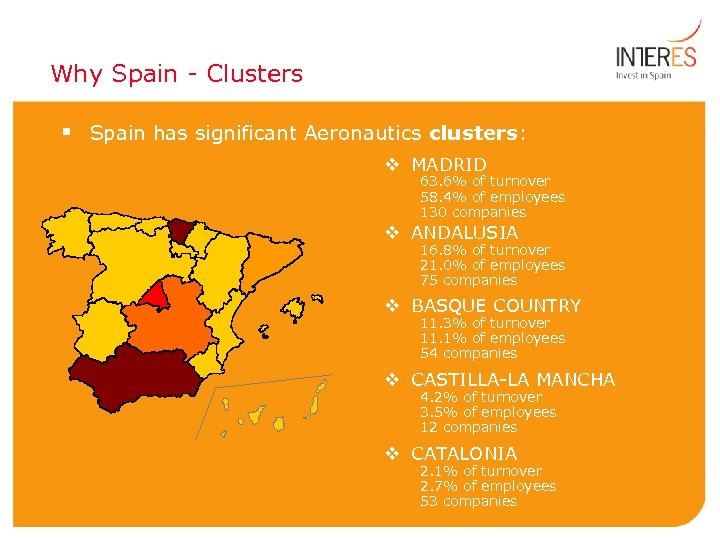
Why Spain - Clusters § Spain has significant Aeronautics clusters: v MADRID 63. 6% of turnover 58. 4% of employees 130 companies v ANDALUSIA 16. 8% of turnover 21. 0% of employees 75 companies v BASQUE COUNTRY 11. 3% of turnover 11. 1% of employees 54 companies v CASTILLA-LA MANCHA 4. 2% of turnover 3. 5% of employees 12 companies v CATALONIA 2. 1% of turnover 2. 7% of employees 53 companies

Why Spain – R&D § Because Aeronautics in Spain is a very innovative industry: v Investment: 575 M. € in 2006 (+26% from 2005) v 48% by companies v 13. 7% of turnover v 15% of turnover in the case of systems and frames v High quality public R&D Centers: Public Research Organization specialized in aerospace research and technology development FIDAMC : Research, Development and Applications of Composites Other important centers:

Why Spain – R&D § Both AIRBUS and BOEING have developed important R&D Centers in Spain: v Boeing Research and Technology Europe (Madrid) • First Boeing R&D center outside the USA • Main areas: safety, ATM and environmental technologies • April ’ 08: first flight of an airplane powered by hydrogen fuel cells According to Boeing: “The reason for choosing Spain was the outstanding role of the country in the EU and as a reference point with the Latin American countries. It also shows the relevant position that the Spanish Aerospace industry has acquired in the last few years and the capabilities of the country in environmental and ATM technologies” Source: www. boeing. es

Why Spain – R&D § Both AIRBUS and BOEING have developed important R&D Centers in Spain: v Airbus Advanced Composites Center ü Specialised in large curvature panels from carbon fiber reinforced plastic v Center of excellence for horizontal tail planes for all Airbus Aircraft worldwide v Airbus Spain: leader worldwide in composite material structures: first company in using carbon fiber for fuselage sections in commercial aircrafts over 100 seats
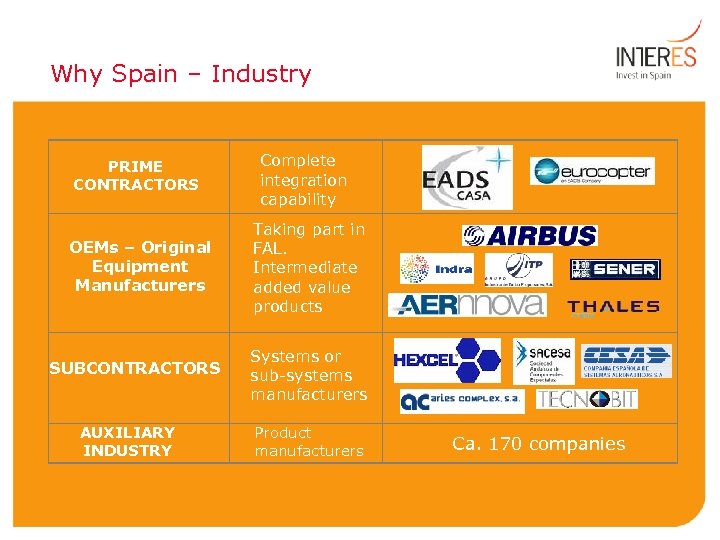
Why Spain – Industry PRIME CONTRACTORS OEMs – Original Equipment Manufacturers SUBCONTRACTORS AUXILIARY INDUSTRY Complete integration capability ) Taking part in FAL. Intermediate added value products Systems or sub-systems manufacturers Product manufacturers Ca. 170 companies

Why Spain – Industry § Growing importance of Spain in international programs: AIRBUS ü Spanish participation share: - Civil programs: ü 4. 2% in the first programs (manufacture) ü 10. 8% in A 380 (also design, development and certification); mostly in Madrid - Military programs: 15% in A 400 M (including the Final Assembly Line, and simulation and training center, in Seville, Andalusia) EADS ü Eurofighter Typhoon: 14% (in Madrid, major components: right wing and leading edge slats) ü Eurocopter: Brand-new plant in Albacete (Castilla-La Mancha), FAL and delivery center for NH-90, Tiger and EC-35
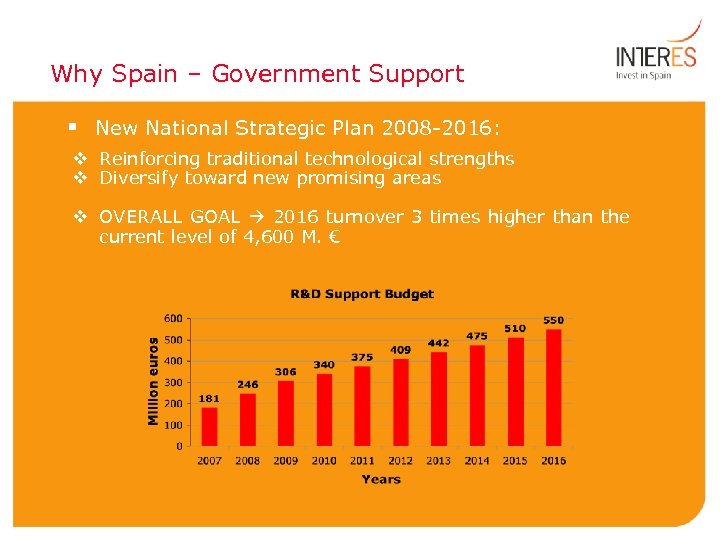
Why Spain – Government Support § New National Strategic Plan 2008 -2016: v Reinforcing traditional technological strengths v Diversify toward new promising areas v OVERALL GOAL 2016 turnover 3 times higher than the current level of 4, 600 M. €

Business Opportunities

Business Opportunities ü Navigation and avionic systems ü General aviation. Very Light Jets ü Helicopters ü Engines and propulsion engineering ü Training centers for professional pilots for air transport ü MRO (Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul) centers for transport aircrafts ü MRO centers for aircrafts designed for general and business aviation, schools and aerial works ü Simulators for aviation, based on lowcost technologies ü Manufacturing of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for civil uses

Flight Simulators § Used by both civil and military aviation for training, engineering, design, research, etc. v Development of Spanish Aeronautics and ITC industries v Spanish companies are mainly focused on the military market v Airlines outsourcing training activities v Growth in business aviation and low-cost carriers v Increase in flight training centers

Helicopters § Third Eurocopter FAL established in Spain § Opportunities v Services to ECE Helicopter FAL ü Engineering services ü Electronics and systems ü Tooling v Helicopter maintenance v Sections manufacturing § Top Reasons v Total market: 53. 6 Million € v Business size will increase: ECE – Participation in all future development v Presence of technological centers and parks * Source: Own estimations, 50% outsourcing assumed

Thank you very much

Doing Business in Spain Montreal, 22 nd May 2008

“DOING BUSINESS IN SPAIN” LEGAL ENVIRONMENT Best Practices Alberto Echarri Partner - Head of M&A Gómez-Acebo & Pombo Abogados Toronto, Ottawa, Montreal May 2008

INVEST IN SPAIN: FACTS & FIGURES n n Spain is the world’s 8 th largest economy, with sustained growth above the EU average. It is the country with the fastest rate of job creation in the OECD. Spain is the 8 th largest FDI recipient in the world and the 3 rd largest investor in the world. Spain has a privileged geo-strategic position: access to 1, 300 million consumers in the world. It is an international business hub. 440 million people in the world speak Spanish. 59

INVEST IN SPAIN: FACTS & FIGURES What foreign investors value most of Spain is: 1. 2. 3. Cost of investment Local human resources Geographical & Financial Environment Generous incentives for R&D. Access to the EU and Latin America. 60

INVEST IN SPAIN: FACTS & FIGURES More than 11, 000 foreign companies & 54 international banks are located in Spain has modern infrastructures and excellent business opportunities, namely in ICT, Biotechnology, Renewable Energy, Environment & Water Treatment. Quality of life: Spain is the first choice for European executives faced with relocation, according to Financial Times. It is the world’s 2 nd tourist destination and is known for its passion for work, arts, sports, and life. 61

PRIORITY SECTORS: ICT Spain has one of the most burgeoning ICT (Information & Communications Technologies) markets in Europe, with a turnover of 87+ billion €. 40% of private R&D investment in Spain is devoted to this sector. Spain offers tax advantages / cost relief for companies. The Spanish telecom network is completely digital and has over 1, 400, 000 km of transmission networks. Mobile phone penetration exceeds 105%. Growth in broadband connection was more than 45% in 2005, with 4. 5 million users. 16% of employees in this sector are devoted to R&D. 62

PRIORITY SECTORS: RENEWABLE ENERGIES 3 main renewable energy resources: 1. Solar 2. Wind 3. Co-generation Spain is one of the most attractive countries in the world for renewable energy projects: Spain is the 3 rd country in the world in wind energy. Spain has 13% market share in this sector. According to Greenpeace, if Spain exploited its natural energy resources, it would have 50 times more energy than necessary by 2050. Spain possesses insulation towers for solar energy: Companies will invest over 1 billion $ in solar parks over the next few years. 63

PRORITY SECTORS: BIOTECH, PHARMA, HEALTH The biotech sector has expanded over 300% in the last 4 years. Spain is the 4 th country in the EU for biotechnology scientific production. Spain has 60 scientific & technological parks within the biotech industry, with 150 companies fully dedicated to biotech whose revenues total 420 million €. The number of biotech companies has multiplied by 3 in the last 5 years, such that over 14, 500 professionals & 425 research units are involved in biotech projects in Spain, producing over 4% of the world’s publications in this field. Spain’s government wants R&D in this sector to reach 2% of GDP by 2010. As such, many new start-ups are funded by the government. Spain collaborates with over 200 centers in the development of almost 128 clinical studies of the highest quality. 64

PRIORITY SECTORS: ENVIRONMENT Spain is the world’s leader in water treatment and desalination using reverse osmosis technology. There are over 900 desalination plants in Spain. 1. 5 million m 3 of desalinated water is produced per day. The economy is looking for a new impulse in recycling. There are 814 Spanish companies authorized to work as used-vehicle treatment centers. Cars & motors are increasingly environmentally friendly. 4 million tons of recycled waste was produced from 20002004. 250, 000 tons of tires are recycled per year. 65

PRIORITY SECTORS: ENVIRONMENT According to European regulations, Spain and the rest of the EU countries must reuse and recover 95% of materials used in vehicle production by 2015. Recycling culture also affects home appliances, such that they are dismantled rather than buried in landfills. Spain aims to manage 160, 000 tons of this waste using environmentally-friendly methods. Currently, 100, 000+ tons are treated. The number of home appliances recovered grows by 10% every year. Spain is working to recover and transform sludge from construction material extraction processes and agricultural waste plastic. 66

MOST DYNAMIC SECTORS 1. Private equity – Declining Energy – Power companies: ENDESA/IBERDROLA – Renewable Energies Air transport – IBERIA – SPANAIR Hospitality Chemical sector Environment Real estate 67

THE LEGAL ENVIRONMENT Sophisticated legal system – Meets EU/US/CAN standards – Principles equivalent to Common Law Common legislation throughout the country – Civil law exceptions: inheritance / family law – Specific sector regulations: • Generally central regulations • Regional legislation for delegated matters – Transportation – Hospitality sector – Environment – Water treatment – Tax in Basque Country, Navarra and Canary Is. Municipal regulations 68

THE LEGAL ENVIRONMENT Friendly and open environment – Contract law principle of freedom of will of the parties – Contractual restraints limited by: • EU competition regulations / vertical restraints • Employment law – Freedom of investment / disinvestment – Freedom of establishment in the EU – Foreign investment deregulation 69

ESTABLISHING A BUSINESS Incorporation formalities – – – Standard documentation Notarized incorporation: 10 days 15 -30 days for registration of company Companies may operate from day 1 SS and TAX registration: day 2 No registration of agreements except – Effects vis-à-vis third parties • Corporate documents • Real Estate deals • Guarantees 70

HOME COUNTRY AGREEMENTS Generally adjustable to local requirements – Commercial agreements – Acquisition agreements Choice of law Choice of forum Choice of language Arbitration 71
MOST COMMON VEHICLES Common distribution agreements – Agency – Distribution / Licensing / Concession – Franchising Joint ventures Direct acquisition of – Shares – Assets – Securities 72

AGENCY AGREEMENTS Free will of the parties Contractual restraints – In-term – Post-term Public order rules / Agency Act – Goodwill indemnity payment – Spanish law – Spanish forum 73
DISTRIBUTION AGREEMENTS COMMERCIAL DISTRIBUTION – Exclusive / Non-exclusive – Contractual restraints – Limited non-compete clauses • EU Regulations on concessionaires LICENSING/TECHNOLOGY TRANSFER – Know-How, Technical Assistance, IP – EU BER on licensing agreements FRANCHISING – Represents almost 8% of retail trade – Governed by agreement – Pre-contractual information required – BE Regulation for anti-compete clauses 74
JOINT VENTURES (I) Common SPVs – Limited liability company (SA / SL) – UTE – EIG Legal Structure/Documentation – Corporate SPV – By-laws of SPV – Shareholders´ Agreement – Business Plan 75

JOINT VENTURES (II) Corporate governance rules Non-compete clauses Territorial scope Veto rights Investment restraints Financial provisions Step-out clauses – Russian Roulette – Put and call options 76

ACQUISITION (I) Standard international practices Players LOI Offer letter and exclusivity period NDA DD Review – Legal – Tax & Finance Acquisition agreement Agreements with managers and directors Non-compete covenants 77

ACQUISITION (II) Price – Price retention – Escrow / bank guarantees Reps. & Warranties – Standard Common Law provisions – Time limitations – Caps – Labour contingencies Conditions precedent (antitrust) Interim period clauses (MAE, BAU) 78

ACQUISITION (III) Public companies – 30% threshhold – Reporting obligations Financing – Acquisition finance • Financial assistance prohibited • Guarantees – Project finance • Project guarantees – Shareholder loans: subordinated/Equity – Capital contributions 79

REAL ESTATE DEALS Corporate acquisition Assets Due diligence – Land Registry searches – Zoning certificates – Leased property Purchase agreement – Notarized deed Complex acquisitions – Shopping malls – Sites under construction 80

GUIDE FOREIGN INVESTORS Friendly legal environment – Sophisticated legal advisors – Reliable judiciary – Arbitration Standardized practices – Adjustment of home agreements – Choice of law and forum. English language Exchange control de-regulation Tax-efficient SPVs/Spanish Holdcos Standard business and financial practices Minor business culture differences 81

Doing Business in Spain Montreal, 22 nd May 2008

Title Case study of a biotechnology startup in Spain

The path to Spain Alec Mian Canada B. Sc. Mc. Gill University, Montreal. UK Ph. D. University of Cambridge, UK USA Harvard Medical School, Boston. Co-founded Gamera Biosciences (Cambridge, MA). Sold to Tecan Holding (SWX: TECN) in 2000 Spain 3 year sabbatical, co-founded a design company La Evolucion, SL. Currently on Board of Directors of Santa & Cole, SA. (Design) Started Genmedica Therapeutics, SL.

Company goals and strategy Goal • Create a focused portfolio of drug candidates for diabetes • Financable, milestone driven development path (seed, Series A, B and C…) • Product partnering opportunities with large pharma in 2009/2010 • Exit by trade sale or IPO (2011) Strategy • Focus on an emerging, protectable area within diabetes • Leverage local resources to get started • Attract international resources to accelerate growth and value

History 2005 • Incorporated • Licensing with University of Barcelona - first drug candidate (GMC-1) 2006 • GMC-1: research and additional patents filed • GMC-2: drug candidates researched and patents filed • Initiated formation of Board of Directors (BOD) and Scientific Advisory Board (SAB) 2007 • Largest first round biotechnology financing in Spain (Spanish VC’s: BCN-Empren, Innova 31, Unirisco; Public: ENISA, CIDEM, Torres Quevedo) • GMC-3 research and patents filed • Initial development team hired. CRO’s work initiated 2008 • Cellular and animal based development of drug candidates , additional patents filed • More hiring.
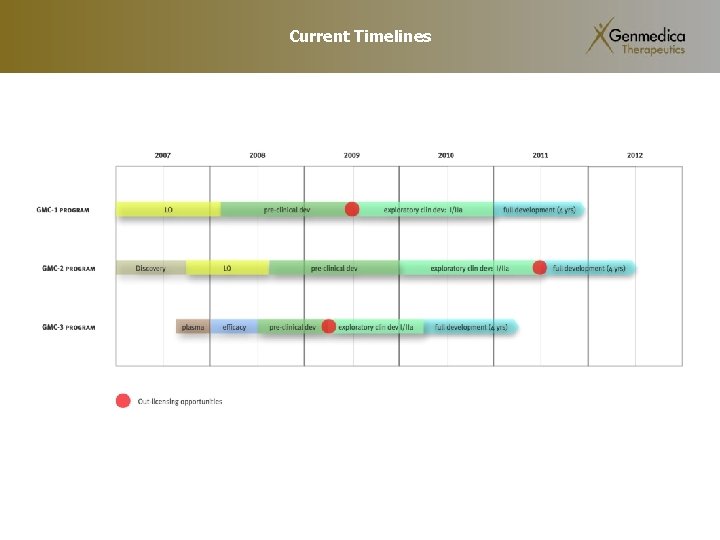
Current Timelines
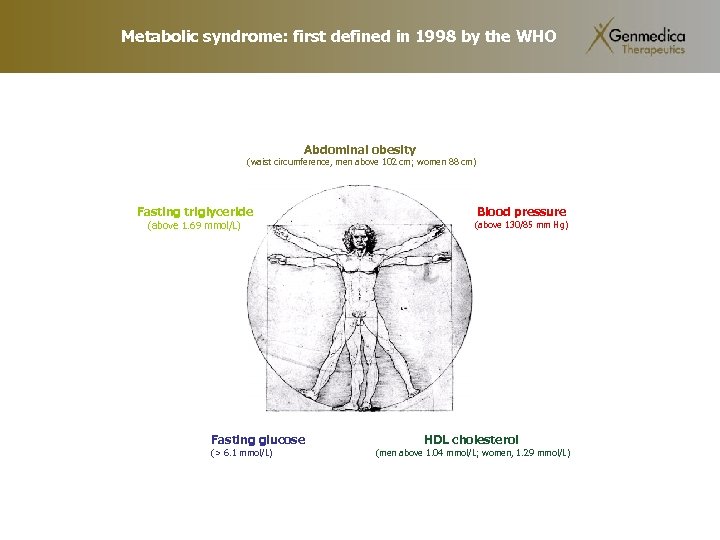
Metabolic syndrome: first defined in 1998 by the WHO Abdominal obesity (waist circumference, men above 102 cm; women 88 cm) Fasting triglyceride (above 1. 69 mmol/L) Fasting glucose (> 6. 1 mmol/L) Blood pressure (above 130/85 mm Hg) HDL cholesterol (men above 1. 04 mmol/L; women, 1. 29 mmol/L)
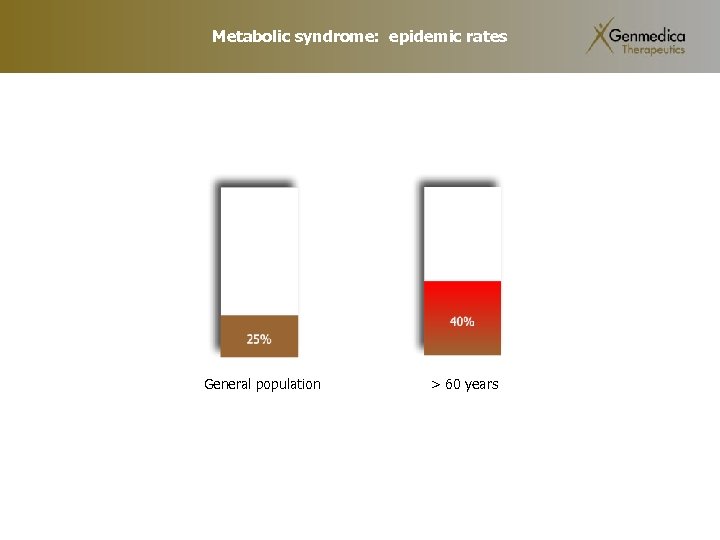
Metabolic syndrome: epidemic rates General population > 60 years
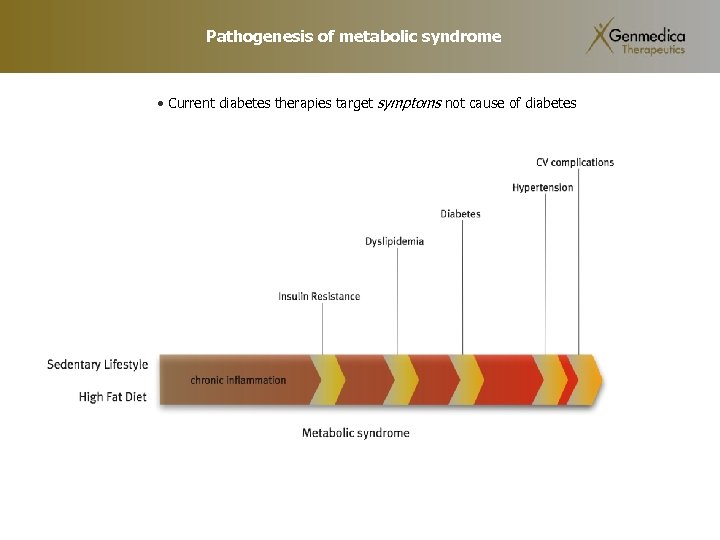
Pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome • Current diabetes therapies target symptoms not cause of diabetes
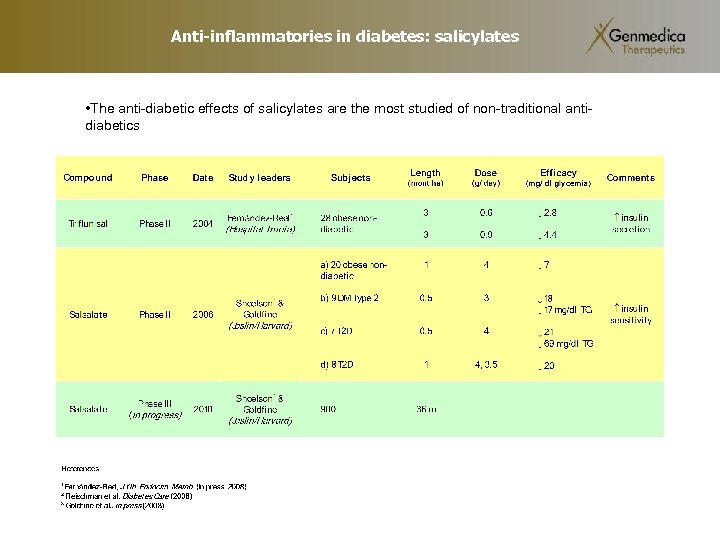
Anti-inflammatories in diabetes: salicylates • The anti-diabetic effects of salicylates are the most studied of non-traditional antidiabetics

Company architecture • Leveraging local and international resources
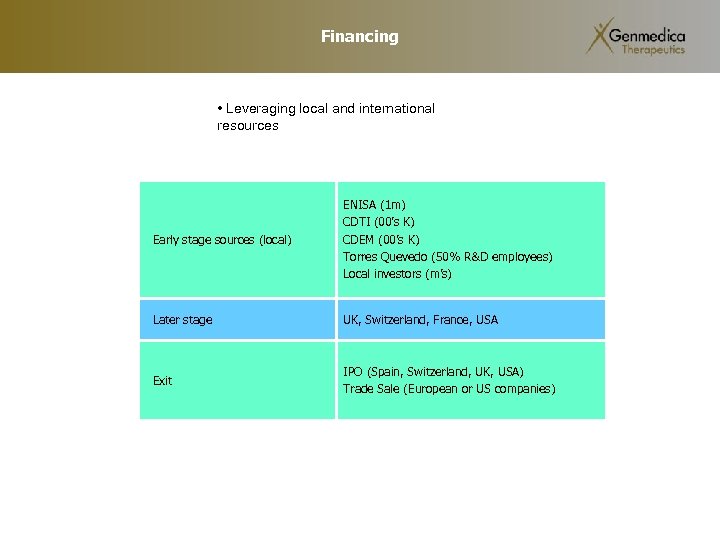
Financing • Leveraging local and international resources Early stage sources (local) ENISA (1 m) CDTI (00’s K) CDEM (00’s K) Torres Quevedo (50% R&D employees) Local investors (m’s) Later stage UK, Switzerland, France, USA Exit IPO (Spain, Switzerland, UK, USA) Trade Sale (European or US companies)
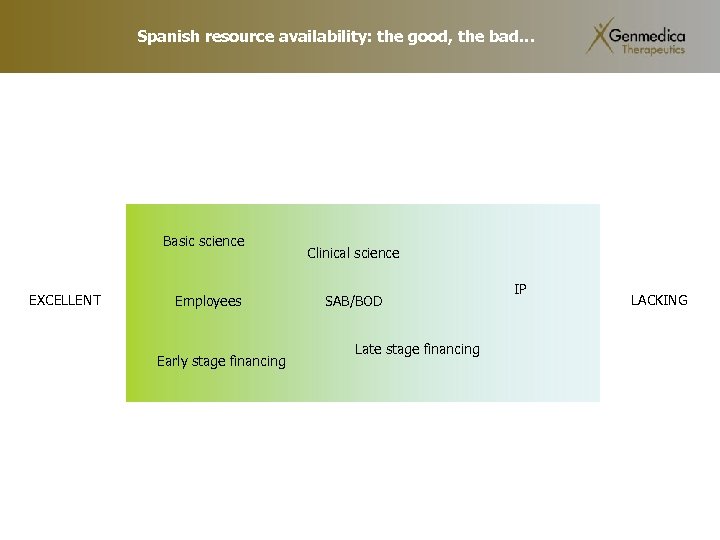
Spanish resource availability: the good, the bad… Basic science EXCELLENT Employees Early stage financing Clinical science SAB/BOD Late stage financing IP LACKING

Next steps for Genmedica • • • Continue to fund early development in Spain Continue to build team in Spain, continue work with international CRO’s (France, India) API chemistry will be done in Spain Clinical studies in Germany or UK Next financing round probably European Union or US-based

Doing Business in Spain Montreal, 22 nd May 2008

CAE Corporate Overview May 2008

Agenda Ø Corporate Overview Ø Market leader in Civil and Military simulation equipment Ø Civil Training and Services Ø OEM Relationships Ø Global Academy & Ab-Initio Training CAE Inc. Confidential and/or Proprietary Information

Overview of CAE Inc. One of Canada’s Largest Aerospace Companies Ø Founded in 1947 in Montreal Ø Civil 5, 000 employees worldwide • More than 3, 000 in Canada • More than 1, 000 in USA • More than 1, 000 in the rest of the world Ø Annual revenues of more than C$1. 2 billion Ø Over 90% of revenues from global exports and international activities in 50 countries Ø Operations and training facilities in 19 countries on 5 continents Ø Train over 50, 000 pilots/year CAE Inc. Confidential and/or Proprietary Information Military
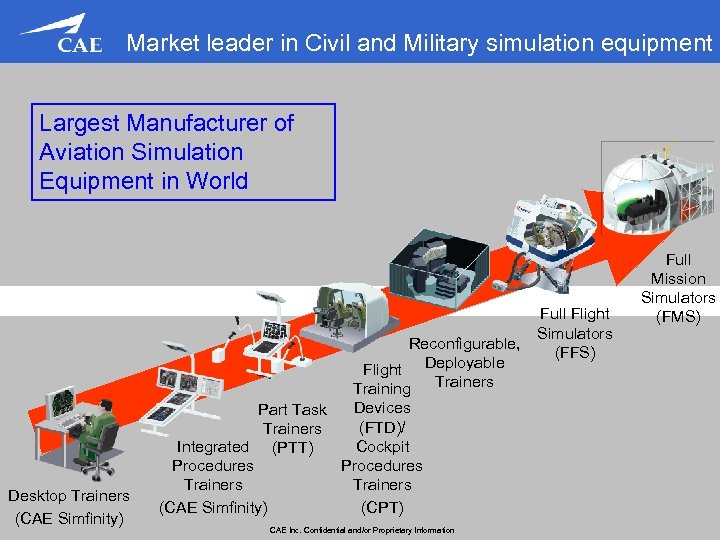
Market leader in Civil and Military simulation equipment Largest Manufacturer of Aviation Simulation Equipment in World Full Flight Simulators Reconfigurable, (FFS) Deployable Flight Training Trainers Desktop Trainers (CAE Simfinity) Part Task Devices (FTD)/ Trainers Integrated (PTT) Cockpit Procedures Trainers (CAE Simfinity) (CPT) CAE Inc. Confidential and/or Proprietary Information Full Mission Simulators (FMS)

Civil Training & Services Market presence MARKET LEADER IN PILOT TRAINING Ø 23 training centres across 5 continents Ø 110 full-flight simulators deployed Ø Serving approximately 3, 500 customers Ø Training and Services segments addressed • Commercial • Regional • Business • General aviation Global market reach across all market segments CAE Inc. Confidential and/or Proprietary Information
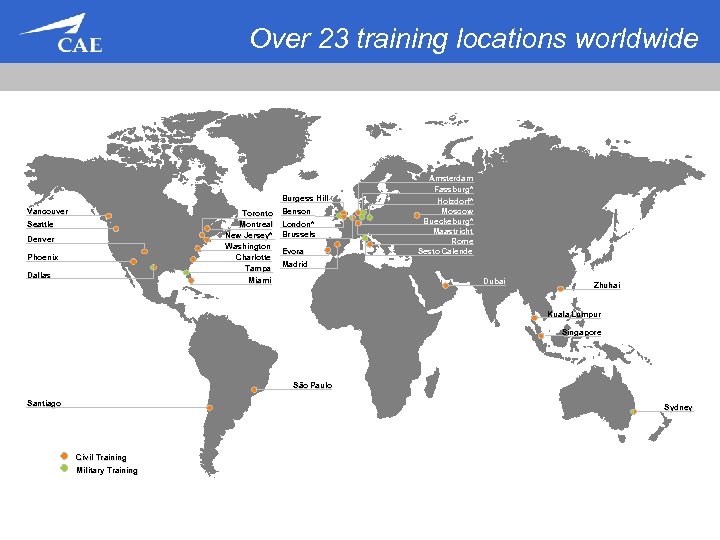
Over 23 training locations worldwide Burgess Hill Vancouver Toronto Montreal New Jersey* Washington Charlotte Tampa Miami Seattle Denver Phoenix Dallas Benson London* Brussels Evora Amsterdam Fassburg* Holzdorf* Moscow Bueckeburg* Maastricht Rome Sesto Calende Madrid Dubai Zhuhai Kuala Lumpur Singapore São Paulo Santiago Sydney Civil Training Military Training CAE Inc. Confidential and/or Proprietary Information

OEM Relationships CAE Airbus Embraer Dassault Bombardier Agusta Lockheed Martin CAE Delivers factory training for sever of world’s largest aircraft manufactures CAE Inc. Confidential and/or Proprietary Information
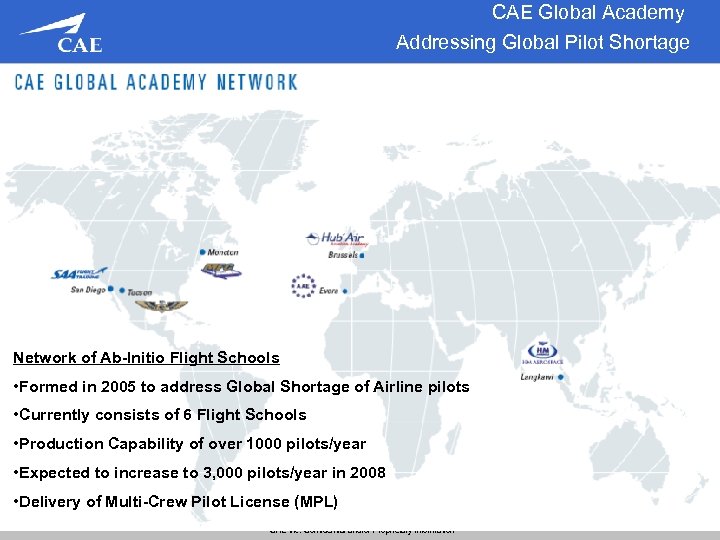
CAE Global Academy Addressing Global Pilot Shortage Network of Ab-Initio Flight Schools • Formed in 2005 to address Global Shortage of Airline pilots • Currently consists of 6 Flight Schools • Production Capability of over 1000 pilots/year • Expected to increase to 3, 000 pilots/year in 2008 • Delivery of Multi-Crew Pilot License (MPL) CAE Inc. Confidential and/or Proprietary Information

Thank You! CAE Inc. Confidential and/or Proprietary Information

Doing Business in Spain Montreal, 22 nd May 2008

International Technology Cooperation With Spain - CANADEKA Claude Morasse National Research Council Canada Director, IRAP Ontario May 20, 2008

National Research Council Canada Industrial Research Assistance Program NRC- IRAP

NRC - Industrial Research Assistance Program Our Mandate : Stimulate wealth creation in Canada through technological innovation. . Our Mission : Stimulate innovation in Canadian SMEs. Our strategic objective : Increase innovation capacity of Canadian SMEs.

NRC’s Industrial Research Assistance Program • In existence since 1947 • In Canada : – Invests over $100 M per year in contribution to SMEs ( less than 500 employees ) – Work with over 10, 000 SMEs / year and provide funding support to over 2, 500 projects / year

The Toolbox • Support to Firms for R&D • Financial Support for Firms’ Technology Development • Financial Support to Bring New Skills to Firms • Financial Support for Organizations Providing Innovation Assistance to SMES • Technology and Advisory Services • Networking and Linkages

Firms eligible to NRCIRAP financial support • For profit, incorporated commercial entity; • 500 employees or less; • Willingness and potential to improve their technological innovation capability; • Open to establishing a trusted relationship with NRC-IRAP; • With a coherent business plan demonstrating required skills in marketing, technology and management, as well as the appropriate financial capacity to undertake the project and exploit its results.

IRAP’s International Partnering Goals • Key to IRAP’s strategic planning is growing SMEs to a mid size and ready for international technology opportunities • We work in close collaboration with Canadian embassies and other federal government departments • IRAP has long supported SMEs to seek out international technology partners • Our support includes: – Information and competitive intelligence on international markets and technologies – Host foreign SMEs and missions that visit Canada – Funding to Canadian SMEs to carry out technology missions – Funding to support international R & D collaboration projects

International Partnering Approach • Across Canada, IRAP’s Industrial Technology Advisors monitor clients for international interests • This results in individual SMEs visiting research institutions and firms, or organized missions with several firms ( 5 -15 SMEs ) • Increasingly, our planning involves competitive intelligence and activities • Support follow-up activities by Canadian SMEs to pursue international collaborative projects • Seek to partner with organizations in other countries with similar mandates


CANADEKA NRC-IRAP’s ultimate goal is to encourage science and technology development and commercialization by SMEs and realizes that partnerships and agreements like the one held with Spain’s Centre for the Development of Industrial Technology (CDTI) will assist in achieving this goal.

CANADEKA • NRC-IRAP and CDTI are collaborating on a reciprocal basis to further each other’s support of SME growth, technology transfer and technology development for the purpose of generating economic benefits for both Canada and Spain. • This agreement allows for mutual collaboration between our countries, and is an opportunity to build greater partnerships between Canadian and Spanish companies as well as research institutions that continue to make headway in all areas of innovation.

CANADEKA - CRITERIA 1. Involve at least one qualified company from each country (Spain and Canada). 2. Be directed at developing a product, process or service having a wide market potential. 3. Have some identified expected benefit from pursuing the project on a cooperative basis. 4. Be directed towards the development or use of advanced technologies. 5. Aim to secure a significant technological advance with regards to the product, process or service concerned. 6. Clearly identify a commercial application to benefit mankind.

PROJECTS TO DATE • 7 to date in manufacturing engineering, ICT, bioenergy and biotechnology • 8 in development in bioenergy, ICT, and biotech

KEY CONTACTS In Canada In Spain National Coordinator George Ortega (204) 984 -4400 george. ortega@nrc-cnrc. gc. ca National Coordinator Ismael Rodrigo Barco Executive Coordinator Bill Dobson (416) 954 -8330 bill. dobson@nrc-cnrc. gc. ca Executive Coordinator Jose Manuel Leceta rodrigo_ismael@cdti. es jmlg@cdti. es



Doing Business in Spain Toronto, 20 th May 2008
bfdd62d07859517316ebcd174b420315.ppt