4ef38115baceb35ee04fd7e7967f57c2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 DOI System: overview Norman Paskin International DOI Foundation
DOI System: overview Norman Paskin International DOI Foundation
 Introduction • Overview: 5 minute animation then: • More information on key points • Q and A
Introduction • Overview: 5 minute animation then: • More information on key points • Q and A
 Who? • DOI = Digital Object Identifier (system) ® • International DOI Foundation (“IDF”) – Common operations and governing organisation: www. doi. org • RAs = DOI Registration Agencies – members of IDF offering the DOI system – to customers who wish to assign DOIs – to offer a DOI-based service to users
Who? • DOI = Digital Object Identifier (system) ® • International DOI Foundation (“IDF”) – Common operations and governing organisation: www. doi. org • RAs = DOI Registration Agencies – members of IDF offering the DOI system – to customers who wish to assign DOIs – to offer a DOI-based service to users
 Status • • • Foundation launched to develop system in 1998. An ISO standard: ISO 26324 Currently used by c. 11, 000 naming authorities (assigners) e. g. 3, 000 STM publishers, science data sets, entertainment industry, EU documents, etc. 87 million DOIs assigned to date Via 9+ RAs (international) DOI services provided by RAs: build on DOI system Initial applications mainly are simple redirection to a URL. More sophisticated functionality available e. g. multiple resolution
Status • • • Foundation launched to develop system in 1998. An ISO standard: ISO 26324 Currently used by c. 11, 000 naming authorities (assigners) e. g. 3, 000 STM publishers, science data sets, entertainment industry, EU documents, etc. 87 million DOIs assigned to date Via 9+ RAs (international) DOI services provided by RAs: build on DOI system Initial applications mainly are simple redirection to a URL. More sophisticated functionality available e. g. multiple resolution
 Scope • • Digital Identifier of an Object = any entity (thing: physical, digital, or abstract) Resources, parties, licences, etc. Initial focus was documents/media e. g. articles, data sets. Now also moving into parties and licences. Extending to other sectors Digital Identifier = network actionable identifier (“click on it and do something”) • Extensible by design: not intended as a publishing-only solution (digital convergence) • Work with existing tools and data • International: RAs worldwide.
Scope • • Digital Identifier of an Object = any entity (thing: physical, digital, or abstract) Resources, parties, licences, etc. Initial focus was documents/media e. g. articles, data sets. Now also moving into parties and licences. Extending to other sectors Digital Identifier = network actionable identifier (“click on it and do something”) • Extensible by design: not intended as a publishing-only solution (digital convergence) • Work with existing tools and data • International: RAs worldwide.
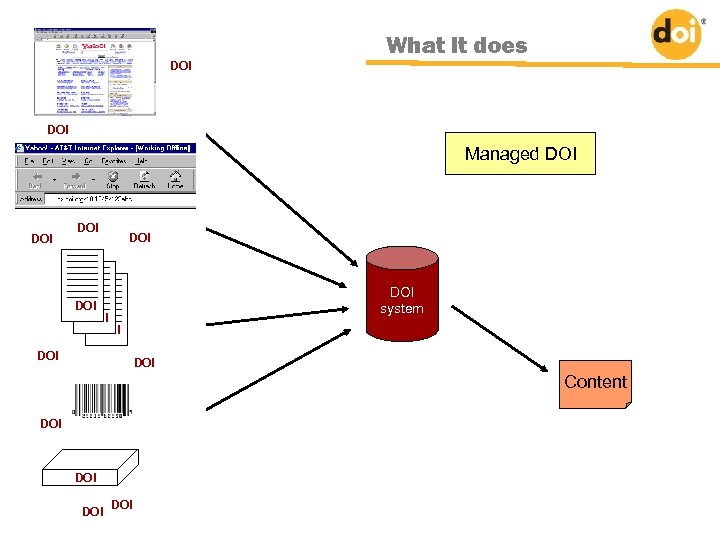 URL DOI What it does URL DOI Managed DOI URL DOI Content DOI URL DOI directory system DOI URL DOI Content DOI URL URLDOI URL
URL DOI What it does URL DOI Managed DOI URL DOI Content DOI URL DOI directory system DOI URL DOI Content DOI URL URLDOI URL
 What it does • provides a resolvable, persistent, interoperable link: • resolvable – standard identifier syntax + network resolution mechanism (Handle System) • persistent – through: – technical infrastructure (registry database, proxy support, etc) – social infrastructure (obligations by Registration Agencies) • interoperable - through a data model (semantic interoperability)
What it does • provides a resolvable, persistent, interoperable link: • resolvable – standard identifier syntax + network resolution mechanism (Handle System) • persistent – through: – technical infrastructure (registry database, proxy support, etc) – social infrastructure (obligations by Registration Agencies) • interoperable - through a data model (semantic interoperability)
 Governance • • International DOI Foundation Provides common infrastructure – – • Deals with common issues – – • • Technical: resolution, data model Social: e. g. obligations for persistence, back-up, in event of failure, etc. Standardisation, liaisons, etc. Outreach to new communities “Not for profit” membership federation Registration Agencies are biggest part of membership Elected Board, working groups, meetings No full time staff (outsourced)
Governance • • International DOI Foundation Provides common infrastructure – – • Deals with common issues – – • • Technical: resolution, data model Social: e. g. obligations for persistence, back-up, in event of failure, etc. Standardisation, liaisons, etc. Outreach to new communities “Not for profit” membership federation Registration Agencies are biggest part of membership Elected Board, working groups, meetings No full time staff (outsourced)
 RAs and the DOI business model • • RAs are autonomous and independent of each other RAs business model with their customers is decided by the RA RAs obligation to IDF is a licence/operating agreement All RAs share costs of common infrastructure (IDF) All RAs implement standard DOI system RAs can add their own services on top RAs may choose to put DOIs “under the hood” or make a clear link Some RAs are commercial; most are themselves member communities (e. g. Cross. Ref, EIDR, Data. Cite)
RAs and the DOI business model • • RAs are autonomous and independent of each other RAs business model with their customers is decided by the RA RAs obligation to IDF is a licence/operating agreement All RAs share costs of common infrastructure (IDF) All RAs implement standard DOI system RAs can add their own services on top RAs may choose to put DOIs “under the hood” or make a clear link Some RAs are commercial; most are themselves member communities (e. g. Cross. Ref, EIDR, Data. Cite)
 Technical infrastructure • • • Handle system: persistent identification in digital networks Data model: principles for interoperability of data in ecommerce systems Both used elsewhere: aim was to not re-invent the wheel Handle: www. handle. net Data Model: indecs. Linked Content Coalition
Technical infrastructure • • • Handle system: persistent identification in digital networks Data model: principles for interoperability of data in ecommerce systems Both used elsewhere: aim was to not re-invent the wheel Handle: www. handle. net Data Model: indecs. Linked Content Coalition
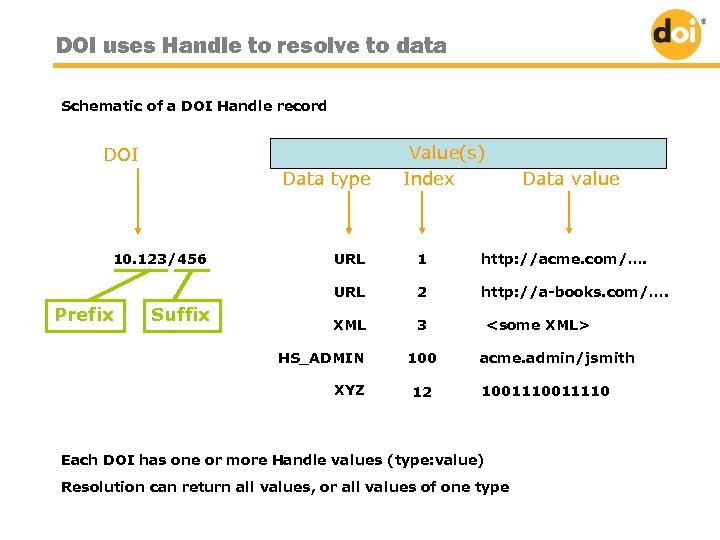 DOI uses Handle to resolve to data Schematic of a DOI Handle record DOI Data type 10. 123/456 Value(s) Index Data value Suffix 1 http: //acme. com/…. URL Prefix URL 2 http: //a-books. com/…. XML 3 HS_ADMIN XYZ 100 12
DOI uses Handle to resolve to data Schematic of a DOI Handle record DOI Data type 10. 123/456 Value(s) Index Data value Suffix 1 http: //acme. com/…. URL Prefix URL 2 http: //a-books. com/…. XML 3 HS_ADMIN XYZ 100 12
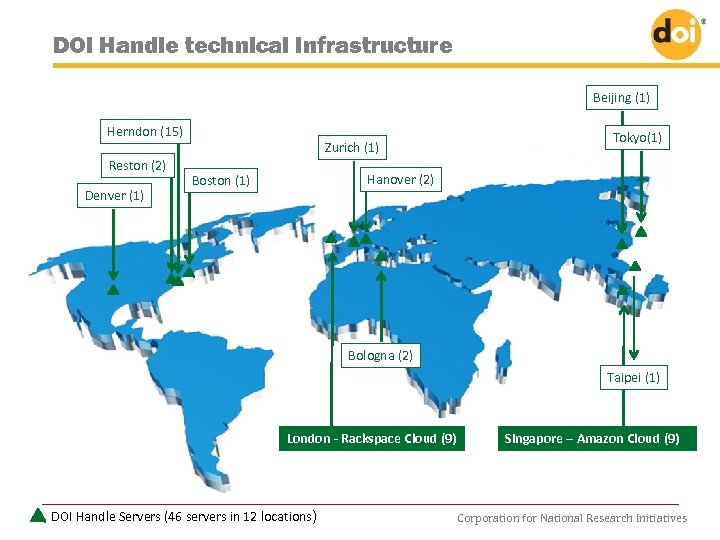 DOI Handle technical infrastructure Beijing (1) Herndon (15) Reston (2) Denver (1) Zurich (1) Tokyo(1) Hanover (2) Boston (1) Bologna (2) Taipei (1) London - Rackspace Cloud (9) DOI Handle Servers (46 servers in 12 locations) Singapore – Amazon Cloud (9) Corporation for National Research Initiatives
DOI Handle technical infrastructure Beijing (1) Herndon (15) Reston (2) Denver (1) Zurich (1) Tokyo(1) Hanover (2) Boston (1) Bologna (2) Taipei (1) London - Rackspace Cloud (9) DOI Handle Servers (46 servers in 12 locations) Singapore – Amazon Cloud (9) Corporation for National Research Initiatives
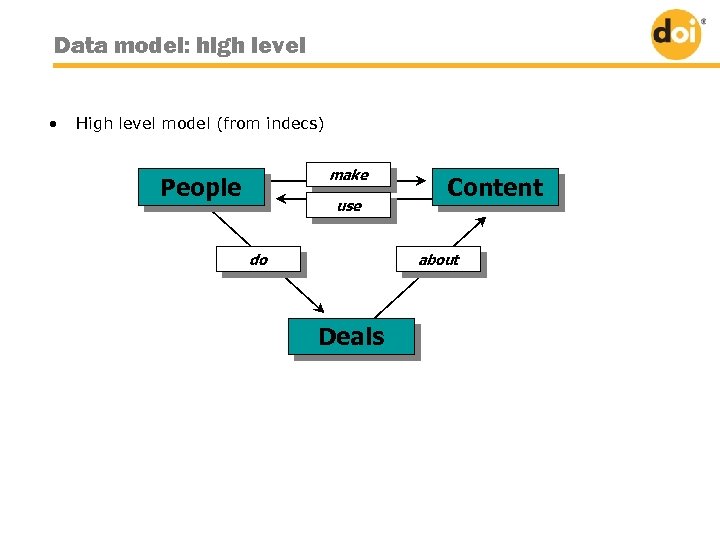 Data model: high level • High level model (from indecs) make People use do Content about Deals
Data model: high level • High level model (from indecs) make People use do Content about Deals
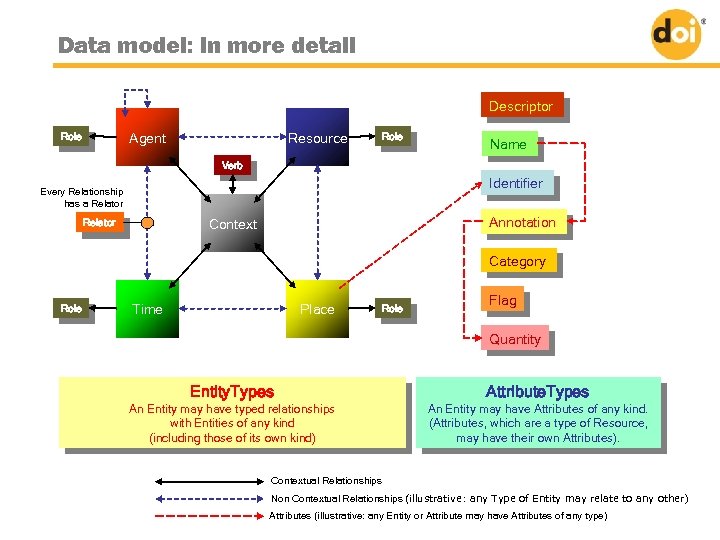 Figure 1 COA Meta. Model Data model: in more detail Overview Descriptor Role Agent Resource Role Verb Identifier Every Relationship has a Relator Annotation Context Relator Name Category Role Time Place Role Flag Quantity Entity. Types An Entity may have typed relationships with Entities of any kind (including those of its own kind) Attribute. Types An Entity may have Attributes of any kind. (Attributes, which are aa type of Resource, (Attributes, which are type of Resource, may have their own Attributes). Contextual Relationships Non Contextual Relationships (illustrative: any Type of Entity may relate to any other) Attributes (illustrative: any Entity or Attribute may have Attributes of any type)
Figure 1 COA Meta. Model Data model: in more detail Overview Descriptor Role Agent Resource Role Verb Identifier Every Relationship has a Relator Annotation Context Relator Name Category Role Time Place Role Flag Quantity Entity. Types An Entity may have typed relationships with Entities of any kind (including those of its own kind) Attribute. Types An Entity may have Attributes of any kind. (Attributes, which are aa type of Resource, (Attributes, which are type of Resource, may have their own Attributes). Contextual Relationships Non Contextual Relationships (illustrative: any Type of Entity may relate to any other) Attributes (illustrative: any Entity or Attribute may have Attributes of any type)
 Data Model – end result • Each DOI has some basic metadata – • Metadata is held and managed by the RA – • Common model for DOI System More metadata can be added – – • • • All DOIs have this “kernel” Appropriate to an RA or DOI service Some groups of DOIs will have the same metadata terms Extensible to any level needed Can use existing metadata and map it to DOIs with the same service or same metadata can be grouped and managed as a class
Data Model – end result • Each DOI has some basic metadata – • Metadata is held and managed by the RA – • Common model for DOI System More metadata can be added – – • • • All DOIs have this “kernel” Appropriate to an RA or DOI service Some groups of DOIs will have the same metadata terms Extensible to any level needed Can use existing metadata and map it to DOIs with the same service or same metadata can be grouped and managed as a class
 Social infrastructure • • • Shared development – e. g. APIs, etc Shared tools e. g. running mirror servers Obligations for persistence: – – • • To customers (within the RA) In event of failure, etc. (beyond the RA) Collaborate Enable shared DOI services where practical – A customer could use more than one DOI service
Social infrastructure • • • Shared development – e. g. APIs, etc Shared tools e. g. running mirror servers Obligations for persistence: – – • • To customers (within the RA) In event of failure, etc. (beyond the RA) Collaborate Enable shared DOI services where practical – A customer could use more than one DOI service
 Standardisation • • ISO 26324: 2012. Through TC 46/SC 9 (“Information and Documentation”) – same as ISBN etc. ISO standard contains basic specification DOI Handbook and procedures has more detail of implementation Other standards: URI (DOI via http proxy) URN
Standardisation • • ISO 26324: 2012. Through TC 46/SC 9 (“Information and Documentation”) – same as ISBN etc. ISO standard contains basic specification DOI Handbook and procedures has more detail of implementation Other standards: URI (DOI via http proxy) URN
 DOI and other identifier schemes • DOI has strong focus on interoperability and on working with existing and new schemes. Can take an existing identifier and make it a DOI: • – – • • Enables re-use of registries, metadata, etc. Must be certain that the existing ID and the DOI refer to the same thing (easiest in deal with an existing registry) Complicated in digital content: • – – • • Use the existing identifier in a DOI suffix; or Define “same as” identifier in the DOI metadata abstractions (e. g. current version or dated version; abstract work or specific edition; etc. ) Not always “same as” Community and proprietary issues See “Identifier Interoperability” fact sheet
DOI and other identifier schemes • DOI has strong focus on interoperability and on working with existing and new schemes. Can take an existing identifier and make it a DOI: • – – • • Enables re-use of registries, metadata, etc. Must be certain that the existing ID and the DOI refer to the same thing (easiest in deal with an existing registry) Complicated in digital content: • – – • • Use the existing identifier in a DOI suffix; or Define “same as” identifier in the DOI metadata abstractions (e. g. current version or dated version; abstract work or specific edition; etc. ) Not always “same as” Community and proprietary issues See “Identifier Interoperability” fact sheet
 Documentation • Website: www. doi. org • • • Quick summary: “Key facts on DOI system” factsheet Other Factsheets – more topics in detail: www. doi. org/factsheets. html • DOI Handbook
Documentation • Website: www. doi. org • • • Quick summary: “Key facts on DOI system” factsheet Other Factsheets – more topics in detail: www. doi. org/factsheets. html • DOI Handbook




