c5748fa019c077d6fb989f1237899fd8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 88
 Doctors’ Health Services Around the World 10 th July 2004 Dr Julie Sladden MBBS(Hons), BMed. Sci
Doctors’ Health Services Around the World 10 th July 2004 Dr Julie Sladden MBBS(Hons), BMed. Sci






 Why Doctors’ Health Services? UK • Common mental disorder 28% • Depression (major) 10% • Newcastle junior doctors: -60% exceed safe limits of alcohol intake -36% males, 20% females use cannabis -13% males, 10% females other illicit drugs • Estimated 1: 15 doctors dependent on drugs.
Why Doctors’ Health Services? UK • Common mental disorder 28% • Depression (major) 10% • Newcastle junior doctors: -60% exceed safe limits of alcohol intake -36% males, 20% females use cannabis -13% males, 10% females other illicit drugs • Estimated 1: 15 doctors dependent on drugs.
 Why Doctors Health Services? Australia • 30% of GPs had mild psychiatric symptoms. • 13% severe psychiatric symptoms. • Suicide rate for female doctors x 6 general female population
Why Doctors Health Services? Australia • 30% of GPs had mild psychiatric symptoms. • 13% severe psychiatric symptoms. • Suicide rate for female doctors x 6 general female population
 Why Doctors’ Health Services? Canada • “One in 10 physicians will become dependent on psychoactive drugs or alcohol sufficient to impair their practice at some time during their careers. ” • “One in every 100 physicians will become a narcotics addict at some time during their career” Saskatchewan Physicians at Risk Committee, Canada
Why Doctors’ Health Services? Canada • “One in 10 physicians will become dependent on psychoactive drugs or alcohol sufficient to impair their practice at some time during their careers. ” • “One in every 100 physicians will become a narcotics addict at some time during their career” Saskatchewan Physicians at Risk Committee, Canada
 CMA 2003 Physician Resource Questionnaire: • 46% of respondents (n = 2, 251) reported symptoms suggesting advanced stages of burnout. Canadian Physician Health Program
CMA 2003 Physician Resource Questionnaire: • 46% of respondents (n = 2, 251) reported symptoms suggesting advanced stages of burnout. Canadian Physician Health Program
 Why doctors’ health services? -a unique group • • Often don’t have own physician ‘Corridor consultations’ Self prescribe Denial Access Trust and confidentiality Stigma, guilt, shame and remorse BUT highly motivated to recover!
Why doctors’ health services? -a unique group • • Often don’t have own physician ‘Corridor consultations’ Self prescribe Denial Access Trust and confidentiality Stigma, guilt, shame and remorse BUT highly motivated to recover!
 UK Doctors’ Health Services
UK Doctors’ Health Services
 Voluntary National Services 2004 • • • • Association of Anaesthetists' Sick Doctor Scheme BMA counselling service BMA Doctors for Doctors service British Doctors' and Dentists' Group British International Doctors’ Association British Medical Journal Careers websites Clinicians' Health Intervention Treatment & Support Doctors’ Support Network and Support. Line National Counselling Service for Sick Doctors Royal College of Surgeons’ CSAS (pilot) Royal College of O&G mentoring scheme Royal Medical Benevolent Fund Sick Doctors’ Trust
Voluntary National Services 2004 • • • • Association of Anaesthetists' Sick Doctor Scheme BMA counselling service BMA Doctors for Doctors service British Doctors' and Dentists' Group British International Doctors’ Association British Medical Journal Careers websites Clinicians' Health Intervention Treatment & Support Doctors’ Support Network and Support. Line National Counselling Service for Sick Doctors Royal College of Surgeons’ CSAS (pilot) Royal College of O&G mentoring scheme Royal Medical Benevolent Fund Sick Doctors’ Trust
 UK - Local Services • Local Medical Council • Occupational Health Services • Postgraduate deanery • Local Support Services
UK - Local Services • Local Medical Council • Occupational Health Services • Postgraduate deanery • Local Support Services
 UK - History • 1970 s - Sick Doctors Scheme of the Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland • 1980 - General Medical Council Health Procedures
UK - History • 1970 s - Sick Doctors Scheme of the Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland • 1980 - General Medical Council Health Procedures
 GMC Health Procedures • Four main stages: -preliminary consideration of the evidence -medical examination of the sick doctor -medical supervision and rehabilitation -the Health Committee
GMC Health Procedures • Four main stages: -preliminary consideration of the evidence -medical examination of the sick doctor -medical supervision and rehabilitation -the Health Committee
 UK - History • 1985 - National Counselling Service for Sick Doctors - (NCSSD) • 1995 - Sick Doctors’ Trust • 1996 - BMA Counselling Service • 1997 - Doctors Support Network • 2001 - BMA Chronic Illness Matching • 2003 - BMA Doctors for Doctors Service • 2003 - Clinician’s Health, Intervention, Treatment and Support - (CHITS)
UK - History • 1985 - National Counselling Service for Sick Doctors - (NCSSD) • 1995 - Sick Doctors’ Trust • 1996 - BMA Counselling Service • 1997 - Doctors Support Network • 2001 - BMA Chronic Illness Matching • 2003 - BMA Doctors for Doctors Service • 2003 - Clinician’s Health, Intervention, Treatment and Support - (CHITS)
 NCSSD National Counselling Service for Sick Doctors • Independent organisation • Confidential, 24/7 telephone access to professional contact point. • Panel of medical advisers from all specialties, distributed throughout UK
NCSSD National Counselling Service for Sick Doctors • Independent organisation • Confidential, 24/7 telephone access to professional contact point. • Panel of medical advisers from all specialties, distributed throughout UK
 NCSSD ‘To assist doctors access appropriate health care’ • Callers (sick doctor or colleague) given name and number of an adviser. • Confidential help and advice within defined ethical framework • Onward referral if indicated.
NCSSD ‘To assist doctors access appropriate health care’ • Callers (sick doctor or colleague) given name and number of an adviser. • Confidential help and advice within defined ethical framework • Onward referral if indicated.
 NCSSD • No. of calls to contact point now c. 200 per year (peak of 400 in 1994) • Yr 2000 – 65% male callers – Over 30% by or about career grades – Single contact with adviser in 46% – In 60% adviser reports +ve outcome
NCSSD • No. of calls to contact point now c. 200 per year (peak of 400 in 1994) • Yr 2000 – 65% male callers – Over 30% by or about career grades – Single contact with adviser in 46% – In 60% adviser reports +ve outcome
 Sick Doctors’ Trust • Addicted Physicians Program - est. 1995 • Self-help organisation for addicted physicians. • Provides early intervention and treatment • Protects patients whilst offering hope, recovery and rehabilitation to impaired colleagues.
Sick Doctors’ Trust • Addicted Physicians Program - est. 1995 • Self-help organisation for addicted physicians. • Provides early intervention and treatment • Protects patients whilst offering hope, recovery and rehabilitation to impaired colleagues.
 Birdsgrove House, Derbyshire
Birdsgrove House, Derbyshire
 Sick Doctors’ Trust • Treatment Centre for Health Professionals -Birdsgrove House • 12 -step program consisting of re-education, counselling, group work, AA/NA attendance • Practical help with lifestyle and livelihood • Family support • Follow-up support groups
Sick Doctors’ Trust • Treatment Centre for Health Professionals -Birdsgrove House • 12 -step program consisting of re-education, counselling, group work, AA/NA attendance • Practical help with lifestyle and livelihood • Family support • Follow-up support groups
 Sick Doctors’ Trust • 290 doctors treated so far • 46% family practitioners, 25% psychiatrists, 25% anaesthetists, 4% other hospital drs. • 86% sober after 2 years • 96% return to medical employment • Relapse rate of 4% for 5 -year follow-up for those who attend centre. • Special referee status
Sick Doctors’ Trust • 290 doctors treated so far • 46% family practitioners, 25% psychiatrists, 25% anaesthetists, 4% other hospital drs. • 86% sober after 2 years • 96% return to medical employment • Relapse rate of 4% for 5 -year follow-up for those who attend centre. • Special referee status

 Doctors Support Network • Self-help group for doctors with mental health problems • Peer support network • Meetings, newsletter and email forum • Website - www. dsn. org. uk
Doctors Support Network • Self-help group for doctors with mental health problems • Peer support network • Meetings, newsletter and email forum • Website - www. dsn. org. uk
 Doctors’ Support Network • • Doctors’ Support Line Confidential and anonymous service 36 hours/week (most evenings) Staffed by volunteer doctors trained in active listening skills • Topics covered include mental and physical health problems, personal issues, work issues, bullying and discrimination.
Doctors’ Support Network • • Doctors’ Support Line Confidential and anonymous service 36 hours/week (most evenings) Staffed by volunteer doctors trained in active listening skills • Topics covered include mental and physical health problems, personal issues, work issues, bullying and discrimination.
 BMA Counselling Service - 1 • Established 1996: telephone service • Telephone counselling by qualified counsellors for doctors and their families Ave No. of Calls per month
BMA Counselling Service - 1 • Established 1996: telephone service • Telephone counselling by qualified counsellors for doctors and their families Ave No. of Calls per month
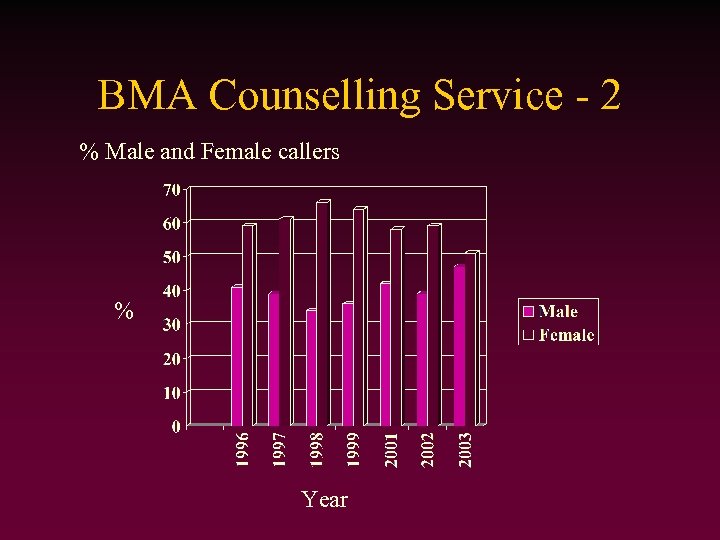 BMA Counselling Service - 2 % Male and Female callers % Year
BMA Counselling Service - 2 % Male and Female callers % Year
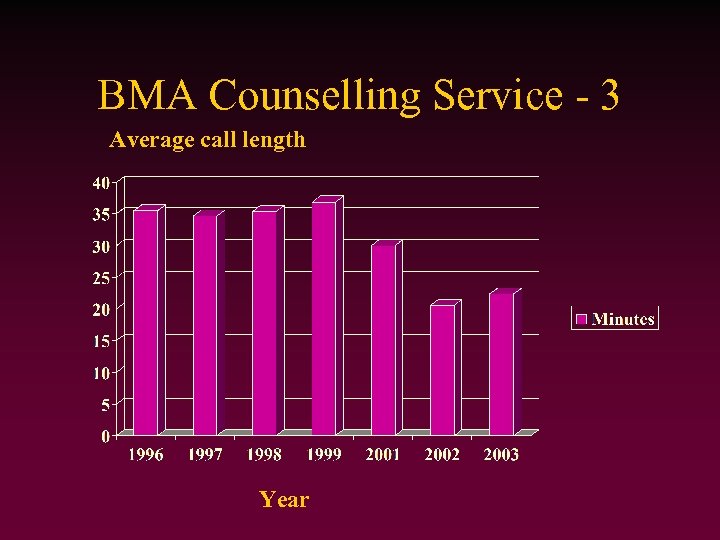 BMA Counselling Service - 3 Average call length Year
BMA Counselling Service - 3 Average call length Year
 BMA Counselling Service - 4 • Jan 2002 Calls: -161 calls in total -40 (25%) of these mental health related -18 (11%) marital or couple related -5 calls (3%) physical health and welfare -1 call alcohol related
BMA Counselling Service - 4 • Jan 2002 Calls: -161 calls in total -40 (25%) of these mental health related -18 (11%) marital or couple related -5 calls (3%) physical health and welfare -1 call alcohol related
 BMJ Careers - CHILL - 1 Chronic Illness Matching Scheme • • • Simple concept Peer support Web based International Doctors and medical students All illness and disabilities
BMJ Careers - CHILL - 1 Chronic Illness Matching Scheme • • • Simple concept Peer support Web based International Doctors and medical students All illness and disabilities
 BMJ Careers - CHILL - 2 • apply by completing electronic form • held in secure database • state preferences for matching (illness, specialty, grade, country) • when suitable match applies, each are sent the other’s e-mail address • manual matching, confidentiality assured
BMJ Careers - CHILL - 2 • apply by completing electronic form • held in secure database • state preferences for matching (illness, specialty, grade, country) • when suitable match applies, each are sent the other’s e-mail address • manual matching, confidentiality assured
 BMJ Careers - CHILL - 3 • 578 doctors and medical students on the scheme • 139 matches (i. e. 278 doctors matched) • No systematic feedback due to confidentiality • Anecdotal feedback all very positive Information from Dr Rhona Mac. Donald
BMJ Careers - CHILL - 3 • 578 doctors and medical students on the scheme • 139 matches (i. e. 278 doctors matched) • No systematic feedback due to confidentiality • Anecdotal feedback all very positive Information from Dr Rhona Mac. Donald
 Initiatives BMA Doctors for Doctors Unit • Help for doctors in employment difficulties especially in relation to mental health problems and abuse of alcohol and drugs • Sign-posting service for doctors/concerned colleagues to most appropriate area of help • Data and information collection about existing services/initiatives • Co-ordination and facilitation of existing services (neutral)
Initiatives BMA Doctors for Doctors Unit • Help for doctors in employment difficulties especially in relation to mental health problems and abuse of alcohol and drugs • Sign-posting service for doctors/concerned colleagues to most appropriate area of help • Data and information collection about existing services/initiatives • Co-ordination and facilitation of existing services (neutral)
 Initiatives - CHITS Clinicians Health, Intervention, Treatment and Support • Confederation committed to meeting needs of staff affected by alcohol or drug misuse • Advises on program development • Negotiates for financial assistance • Local network building • Education • Employment policies
Initiatives - CHITS Clinicians Health, Intervention, Treatment and Support • Confederation committed to meeting needs of staff affected by alcohol or drug misuse • Advises on program development • Negotiates for financial assistance • Local network building • Education • Employment policies
 Australian Doctors’ Health Services
Australian Doctors’ Health Services
 History • 1896 - Medical Benevolent Society - NSW • 1982 - Doctors’ Health Advisory Service • 1998 - AMA publish Position Statement on ‘The Health of Medical Practitioners’ • 1999 - 1 st National Conference on Doctors’ Health. • 2001/3 - Further Conferences
History • 1896 - Medical Benevolent Society - NSW • 1982 - Doctors’ Health Advisory Service • 1998 - AMA publish Position Statement on ‘The Health of Medical Practitioners’ • 1999 - 1 st National Conference on Doctors’ Health. • 2001/3 - Further Conferences
 Structure • National Database • State-based services (DHAS, MBA, other) • Regional programs (over 30) Local Support • Australian Medical Association (AMA) • Medical Board • Colleges
Structure • National Database • State-based services (DHAS, MBA, other) • Regional programs (over 30) Local Support • Australian Medical Association (AMA) • Medical Board • Colleges
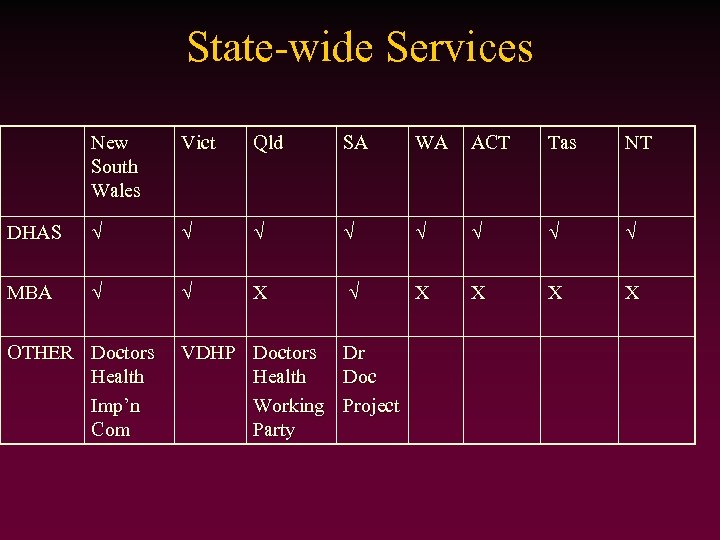 State-wide Services New South Wales Vict Qld SA WA ACT Tas NT DHAS MBA X X X OTHER Doctors Health Imp’n Com VDHP Doctors Health Working Party Dr Doc Project
State-wide Services New South Wales Vict Qld SA WA ACT Tas NT DHAS MBA X X X OTHER Doctors Health Imp’n Com VDHP Doctors Health Working Party Dr Doc Project
 DHAS - 1 • • Began in 1982 with AMA/MBA support Independent, confidential service Doctors, dentists, veterinarians, students 24 -hr help line Caller put in contact with panel member Advice given Referral if necessary
DHAS - 1 • • Began in 1982 with AMA/MBA support Independent, confidential service Doctors, dentists, veterinarians, students 24 -hr help line Caller put in contact with panel member Advice given Referral if necessary
 DHAS - 2 • ‘No problem is too serious or too trivial!’ • Problems: -alcoholism -physical illness -drug addiction -financial -psychiatric disorders -legal problems -stress -career advice -marital breakdown -help finding a GP
DHAS - 2 • ‘No problem is too serious or too trivial!’ • Problems: -alcoholism -physical illness -drug addiction -financial -psychiatric disorders -legal problems -stress -career advice -marital breakdown -help finding a GP
 Victorian Doctors’ Health Program (VDHP) • Began 2001 - joint initiative of Medical Board of Victoria and AMA (Vic. Branch) • Independent body - confidential service • Program based on north american model: -education and prevention -early identification and intervention -evaluation and treatment -rehabilitation and monitoring
Victorian Doctors’ Health Program (VDHP) • Began 2001 - joint initiative of Medical Board of Victoria and AMA (Vic. Branch) • Independent body - confidential service • Program based on north american model: -education and prevention -early identification and intervention -evaluation and treatment -rehabilitation and monitoring
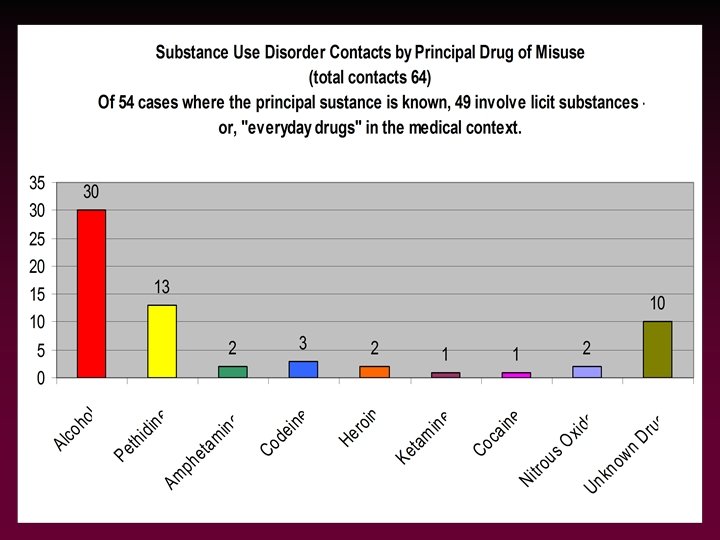
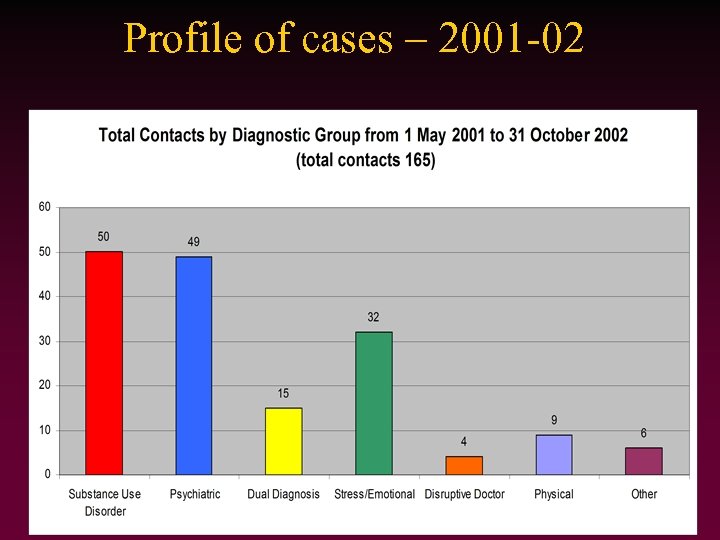 Profile of cases – 2001 -02 • (Insert report of Level of involvement)
Profile of cases – 2001 -02 • (Insert report of Level of involvement)
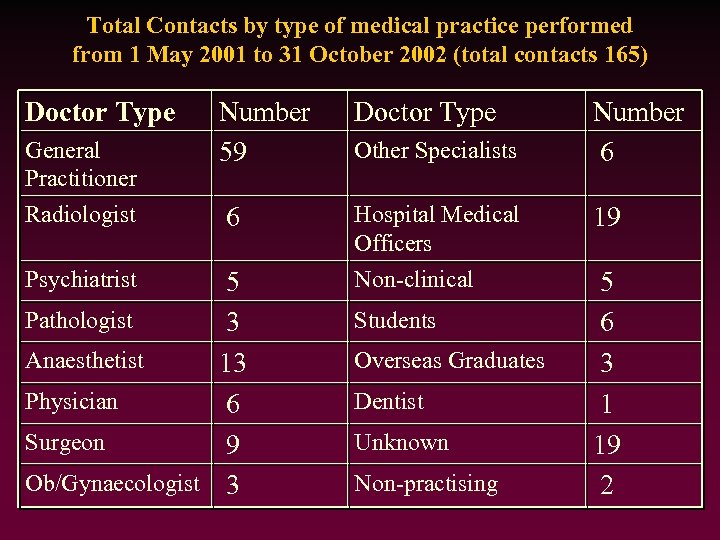 Total Contacts by type of medical practice performed from 1 May 2001 to 31 October 2002 (total contacts 165) Doctor Type General Practitioner Radiologist Psychiatrist Number 59 Doctor Type 6 Hospital Medical Officers Non-clinical 5 Pathologist 3 Anaesthetist 13 Physician 6 Surgeon 9 Ob/Gynaecologist 3 Other Specialists Students Overseas Graduates Dentist Unknown Non-practising Number 6 19 5 6 3 1 19 2
Total Contacts by type of medical practice performed from 1 May 2001 to 31 October 2002 (total contacts 165) Doctor Type General Practitioner Radiologist Psychiatrist Number 59 Doctor Type 6 Hospital Medical Officers Non-clinical 5 Pathologist 3 Anaesthetist 13 Physician 6 Surgeon 9 Ob/Gynaecologist 3 Other Specialists Students Overseas Graduates Dentist Unknown Non-practising Number 6 19 5 6 3 1 19 2
 VDHP - Service - 1 • Referral: -self (voluntary-self or family) -Board Mandated (referred by medical board) • Team: -Full-time doctor/director -2 Counsellors
VDHP - Service - 1 • Referral: -self (voluntary-self or family) -Board Mandated (referred by medical board) • Team: -Full-time doctor/director -2 Counsellors
 VDHP - Service - 2 • • Intervention Assessment and referral Case management Aftercare and monitoring Support and monitoring groups Family support Advocacy - work, MPBV, Courts
VDHP - Service - 2 • • Intervention Assessment and referral Case management Aftercare and monitoring Support and monitoring groups Family support Advocacy - work, MPBV, Courts
 VDHP - Service - 3 Case Management, Aftercare and Monitoring Program ‘CAMP’ Agreement 1. Abstinence 6. Support groups agreement AA, NA, VDHP 2. Treating doctor 7. Workplace monitoring 3. General Practitioner 8. Self-medication 4. Psychiatrist prohibited 5. Counsellor 9. Restricted prescribing
VDHP - Service - 3 Case Management, Aftercare and Monitoring Program ‘CAMP’ Agreement 1. Abstinence 6. Support groups agreement AA, NA, VDHP 2. Treating doctor 7. Workplace monitoring 3. General Practitioner 8. Self-medication 4. Psychiatrist prohibited 5. Counsellor 9. Restricted prescribing
 Initiatives - DMHIC Doctors’ Mental Health Implementation Committee • Produced ‘Doctors Mental Health Policy’ • Strategies for: -Area health services -Medical colleges -Medical schools -Rural divisions of General Practice • Website: www. dmh. org. au
Initiatives - DMHIC Doctors’ Mental Health Implementation Committee • Produced ‘Doctors Mental Health Policy’ • Strategies for: -Area health services -Medical colleges -Medical schools -Rural divisions of General Practice • Website: www. dmh. org. au
 Physician Health Programs in the United States
Physician Health Programs in the United States
 History - US • 1958 - Physician addiction recognised. • 1973 - ‘The Sick Physician’ (JAMA. 1973; 223: 684 -7) • 1974 - Legislation developed. • 1975 - Physicians Health Conference • Late 1970’s - Several articles published • 1980 - 51 medical societies had programs • 1990 - Federation of State Physician Health Programs, Inc. (FSPHP)
History - US • 1958 - Physician addiction recognised. • 1973 - ‘The Sick Physician’ (JAMA. 1973; 223: 684 -7) • 1974 - Legislation developed. • 1975 - Physicians Health Conference • Late 1970’s - Several articles published • 1980 - 51 medical societies had programs • 1990 - Federation of State Physician Health Programs, Inc. (FSPHP)
 Structure - US - 1 State Physician Health Programs • Independent state programs • Program Structure: -education and prevention -early identification and intervention -evaluation and treatment -rehabilitation and monitoring • Consultation and communication
Structure - US - 1 State Physician Health Programs • Independent state programs • Program Structure: -education and prevention -early identification and intervention -evaluation and treatment -rehabilitation and monitoring • Consultation and communication
 Structure - US - 2 State Physician Health Programs • Operated by: -medical society -licensing agency -independent body -other • Funding: -medical society -insurance companies -licensing agency -participant fees -hospital donations -private donations
Structure - US - 2 State Physician Health Programs • Operated by: -medical society -licensing agency -independent body -other • Funding: -medical society -insurance companies -licensing agency -participant fees -hospital donations -private donations
 Structure - US - 3 State Physician Health Programs • Staff: -paid vs volunteers • Conditions monitored: -chemical dependency -physical illness -stress management -mental health -behavioural problems -malpractice -sexual misconduct/boundary violations
Structure - US - 3 State Physician Health Programs • Staff: -paid vs volunteers • Conditions monitored: -chemical dependency -physical illness -stress management -mental health -behavioural problems -malpractice -sexual misconduct/boundary violations
 Structure - US - 4 State Physician Health Programs • Who can get help: -physicians -medical students -nurses -pharmacists -veterinarians -families of physicians -physician assistants -dentists -podiatrists
Structure - US - 4 State Physician Health Programs • Who can get help: -physicians -medical students -nurses -pharmacists -veterinarians -families of physicians -physician assistants -dentists -podiatrists
 Services - US - Alabama • • • Established 1991 24 hour help line, email Website: www. alabamaphp. org ~30 Educational programs Family support: www. recoveringtogether. com • Interstate and international activity
Services - US - Alabama • • • Established 1991 24 hour help line, email Website: www. alabamaphp. org ~30 Educational programs Family support: www. recoveringtogether. com • Interstate and international activity
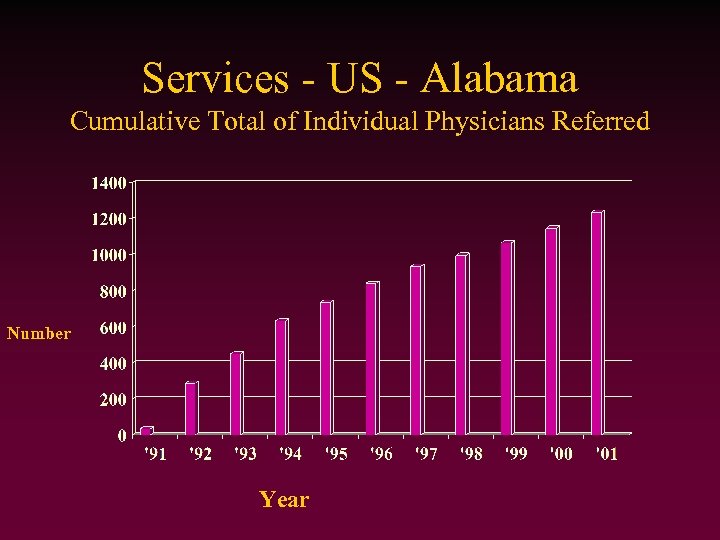 Services - US - Alabama Cumulative Total of Individual Physicians Referred Number Year
Services - US - Alabama Cumulative Total of Individual Physicians Referred Number Year
 Initiatives - Alabama • Educational programs • Family program www. recoveringtogether. com • Phoenix 2000 - Professionals Health Programs Management Software
Initiatives - Alabama • Educational programs • Family program www. recoveringtogether. com • Phoenix 2000 - Professionals Health Programs Management Software
 US Conference - 2004 • 2004 International Conference on Physician Health - October 13 -16 ‘Successes and challenges in creating a healthy culture in medicine’ www. ama-assn. org/go/phc
US Conference - 2004 • 2004 International Conference on Physician Health - October 13 -16 ‘Successes and challenges in creating a healthy culture in medicine’ www. ama-assn. org/go/phc
 Canada
Canada
 History - Canada • 1998 - CMA policy on ‘Physician health and well-being’. • 2001 - Canadian Physician Health Network • 2003 - CMA Centre for Physician Health and Well-being.
History - Canada • 1998 - CMA policy on ‘Physician health and well-being’. • 2001 - Canadian Physician Health Network • 2003 - CMA Centre for Physician Health and Well-being.
 Structure - Canada • Independent provincial/territorial programs • Funding sources: -Medical association -College of Physicians and Surgeons -other • Independent of government • CPHN and CMA Centre
Structure - Canada • Independent provincial/territorial programs • Funding sources: -Medical association -College of Physicians and Surgeons -other • Independent of government • CPHN and CMA Centre
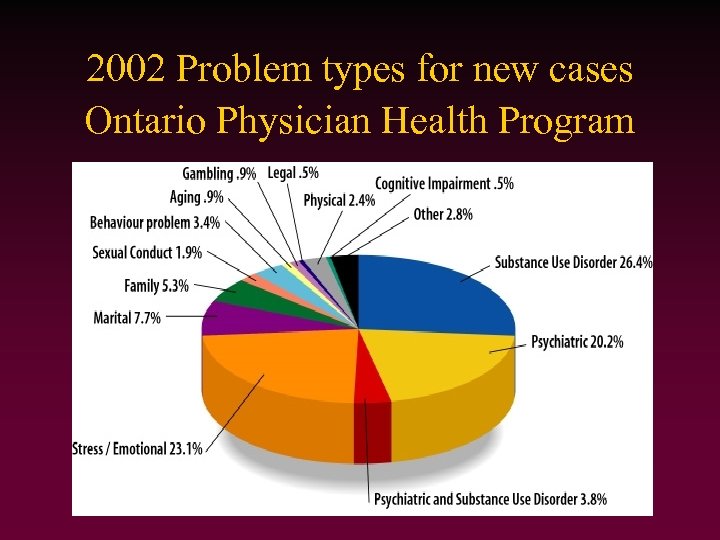 2002 Problem types for new cases Ontario Physician Health Program
2002 Problem types for new cases Ontario Physician Health Program
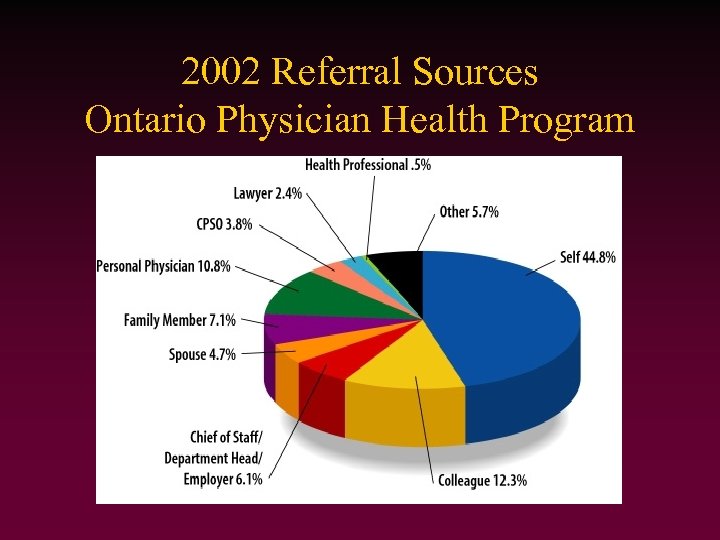 2002 Referral Sources Ontario Physician Health Program
2002 Referral Sources Ontario Physician Health Program
 Services - Canada - Alberta - 1 • Physician and Family Support Program • Physicians, residents, medical students and immediate family members. • Toll-free 24 -hour-number • Website • Educational program • Information resource
Services - Canada - Alberta - 1 • Physician and Family Support Program • Physicians, residents, medical students and immediate family members. • Toll-free 24 -hour-number • Website • Educational program • Information resource
 Services - Canada - Alberta - 2 Physician and Family Support Program • Staff: -Clinical director -Director -5 Assessment physicians -Project manager -Administrative assistant and resource staff
Services - Canada - Alberta - 2 Physician and Family Support Program • Staff: -Clinical director -Director -5 Assessment physicians -Project manager -Administrative assistant and resource staff
 Services - Canada - Alberta - 3 • Research - Stress and Burnout Study -2002 • Resources - General Medical Checklist - Psychiatry Checklist - Goals for Healthy Living - Life Balance Assessment • Newsletter • Education - retreats, seminars, workshops
Services - Canada - Alberta - 3 • Research - Stress and Burnout Study -2002 • Resources - General Medical Checklist - Psychiatry Checklist - Goals for Healthy Living - Life Balance Assessment • Newsletter • Education - retreats, seminars, workshops



 Spain
Spain
 Integral Care Programme for Sick Physicians (PAIMM) • Regional program - Catalonia • 1998 - Joint initiative: -Department of Health -Social Security of Regional Government -Medical Council of Catalonia • Managed by Barcelona Medical Council • Funded jointly by above groups
Integral Care Programme for Sick Physicians (PAIMM) • Regional program - Catalonia • 1998 - Joint initiative: -Department of Health -Social Security of Regional Government -Medical Council of Catalonia • Managed by Barcelona Medical Council • Funded jointly by above groups
 PAIMM - Structure • Philosophy based on Code of Conduct-1999 • Mental disorders &/or addictive behaviours • Free to physicians on the Catalan Register • Also those whose Medical council or local government has agreement with PAIMM.
PAIMM - Structure • Philosophy based on Code of Conduct-1999 • Mental disorders &/or addictive behaviours • Free to physicians on the Catalan Register • Also those whose Medical council or local government has agreement with PAIMM.
 PAIMM - Services • • • Health care Social assistance Legal support Job-related assistance Programmes: -mental disorders, dual pathologies, addictive disorders, maintenance and personalised programmes
PAIMM - Services • • • Health care Social assistance Legal support Job-related assistance Programmes: -mental disorders, dual pathologies, addictive disorders, maintenance and personalised programmes
 PAIMM - Services Clinical Unit • • Confidential location Assumed name of physician Confidentiality guaranteed Programs: -clinical -ambulatory -residential
PAIMM - Services Clinical Unit • • Confidential location Assumed name of physician Confidentiality guaranteed Programs: -clinical -ambulatory -residential
 PAIMM - Services Clinical Unit • Medical Team: -2 attending physicians (Psychiatrists) -5 further specialists -2 consultants -3 physicians on duty rota -3 psychologists -4 fully-qualified nurses -nursing assistants
PAIMM - Services Clinical Unit • Medical Team: -2 attending physicians (Psychiatrists) -5 further specialists -2 consultants -3 physicians on duty rota -3 psychologists -4 fully-qualified nurses -nursing assistants
 PAIMM - Services Clinical Unit • Facilities: -13 single rooms-bathroom, TV, video, desk -nurses office, dining room, recreation room -day centre and ambulatory treatment areas -gymnasium, study with computers/internet -Complementary services - massage, hairdresser, manicure, chiropodist, films
PAIMM - Services Clinical Unit • Facilities: -13 single rooms-bathroom, TV, video, desk -nurses office, dining room, recreation room -day centre and ambulatory treatment areas -gymnasium, study with computers/internet -Complementary services - massage, hairdresser, manicure, chiropodist, films

 Summary • There is a problem • It has been recognised around the world • It has been addressed in a variety of ways: -formal PHPs with organised funding and support, volunteer help-lines, web-based, 1: 1, group and peer support, disciplinary procedures, national vs local programs • Many depend heavily on volunteers
Summary • There is a problem • It has been recognised around the world • It has been addressed in a variety of ways: -formal PHPs with organised funding and support, volunteer help-lines, web-based, 1: 1, group and peer support, disciplinary procedures, national vs local programs • Many depend heavily on volunteers
 The key…. . develop a service tailored to your physicians’ needs with the resources you have available
The key…. . develop a service tailored to your physicians’ needs with the resources you have available
 and…. . finding a generous source of funding!
and…. . finding a generous source of funding!
 Challenges to us all. . . -funding -confidentiality -research and data collection -assessing effectiveness of services -prevention and education -changing the culture of medicine. . .
Challenges to us all. . . -funding -confidentiality -research and data collection -assessing effectiveness of services -prevention and education -changing the culture of medicine. . .
 “We need to accept (rather than constantly rediscovering) that we know enough about the main causes of high stress levels in doctors to address the principal organisational stressors using primary preventive interventions” J Firth-Cozens, BMJ 2003; 326: 670 -671
“We need to accept (rather than constantly rediscovering) that we know enough about the main causes of high stress levels in doctors to address the principal organisational stressors using primary preventive interventions” J Firth-Cozens, BMJ 2003; 326: 670 -671

 Acknowledgements Dr Jolyon Oxley - Honorary Secretary NCSSD, UK Dr Michael Crawford - Imperial College, London Dr Rhona Mac. Donald - Editor - BMJ Careers Dr Lizzie Miller - Doctors Support Network Dr Sue Elliston - Nth Wales Doctors Support Service Dr Douglas Fowlie - CHITS Dr R Brown, Physician Health Program, US Dr M Kaufmann, Physician Health Program, Canada Dr Phil Thomson, DHAS, Australia
Acknowledgements Dr Jolyon Oxley - Honorary Secretary NCSSD, UK Dr Michael Crawford - Imperial College, London Dr Rhona Mac. Donald - Editor - BMJ Careers Dr Lizzie Miller - Doctors Support Network Dr Sue Elliston - Nth Wales Doctors Support Service Dr Douglas Fowlie - CHITS Dr R Brown, Physician Health Program, US Dr M Kaufmann, Physician Health Program, Canada Dr Phil Thomson, DHAS, Australia



