43047079a9447bb3a407fa57ee97c8c1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Project: IEEE P 802. 15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) Submission Title: [Solutions-to-LOS-mm. W-WPAN] Date Submitted: [July, 2006] Source: [Yozo Shoji, Ryuhei Funada, Hirokazu Sawada, Chang-Soon Choi, Katsuyoshi Sato, Hiroshi Harada , Shuzo Kato] Company [National Institute of Information and Communications Technology] Address [3 -4, Hikarino-Oka, Yokosuka, Kanagawa, 239 -0847, Japan] Voice: [+81. 46. 847. 5083], FAX: [+81. 46. 847. 5296], E-Mail: [shu. kato@nict. go. jp] Re: [] Abstract: [This contribution discusses technologies to realize LOS communications in mm. W WPAN. ] Purpose: [Contribution to mm. W TG 3 c meeting. ] Notice: This document has been prepared to assist the IEEE P 802. 15. It is offered as a basis for discussion and is not binding on the contributing individual(s) or organization(s). The material in this document is subject to change in form and content after further study. The contributor(s) reserve(s) the right to add, amend or withdraw material contained herein. Release: The contributor acknowledges and accepts that this contribution becomes the property of IEEE and may be made publicly available by P 802. 15. Submission 1
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Project: IEEE P 802. 15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANs) Submission Title: [Solutions-to-LOS-mm. W-WPAN] Date Submitted: [July, 2006] Source: [Yozo Shoji, Ryuhei Funada, Hirokazu Sawada, Chang-Soon Choi, Katsuyoshi Sato, Hiroshi Harada , Shuzo Kato] Company [National Institute of Information and Communications Technology] Address [3 -4, Hikarino-Oka, Yokosuka, Kanagawa, 239 -0847, Japan] Voice: [+81. 46. 847. 5083], FAX: [+81. 46. 847. 5296], E-Mail: [shu. kato@nict. go. jp] Re: [] Abstract: [This contribution discusses technologies to realize LOS communications in mm. W WPAN. ] Purpose: [Contribution to mm. W TG 3 c meeting. ] Notice: This document has been prepared to assist the IEEE P 802. 15. It is offered as a basis for discussion and is not binding on the contributing individual(s) or organization(s). The material in this document is subject to change in form and content after further study. The contributor(s) reserve(s) the right to add, amend or withdraw material contained herein. Release: The contributor acknowledges and accepts that this contribution becomes the property of IEEE and may be made publicly available by P 802. 15. Submission 1
 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Summary LOS Millimeter Wave Systems are Preferable and Feasible Millimeter wave systems: n Power-limited but not band-limited – 10 m. W by regulations and device capability Should enjoy wide bandwidth for low cost terminal implementation 2. Higher directivity Lead to: -Transmission range of LOS millimeter systems: superior -Simple modulation and FEC: Applicable Selectable or beam forming antenna will solve a potential issue of “professional installation” in LOS systems Submission 2
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Summary LOS Millimeter Wave Systems are Preferable and Feasible Millimeter wave systems: n Power-limited but not band-limited – 10 m. W by regulations and device capability Should enjoy wide bandwidth for low cost terminal implementation 2. Higher directivity Lead to: -Transmission range of LOS millimeter systems: superior -Simple modulation and FEC: Applicable Selectable or beam forming antenna will solve a potential issue of “professional installation” in LOS systems Submission 2
 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Several Important Factors in IEEE 802. 15. 3 c WPAN Standardization n Limited transmission power (10 m. W) and High free-space loss - Low received signal levels expected n High directivity in 60 GHz propagation - Difficult to expect strong diffracted or reflected received signals n Target data rate of over 2 Gbps - Sensitive to multipath fading n Device performance – Immature? - Larger phase noise, limited PA output power (non-linearity ) Submission 3
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Several Important Factors in IEEE 802. 15. 3 c WPAN Standardization n Limited transmission power (10 m. W) and High free-space loss - Low received signal levels expected n High directivity in 60 GHz propagation - Difficult to expect strong diffracted or reflected received signals n Target data rate of over 2 Gbps - Sensitive to multipath fading n Device performance – Immature? - Larger phase noise, limited PA output power (non-linearity ) Submission 3
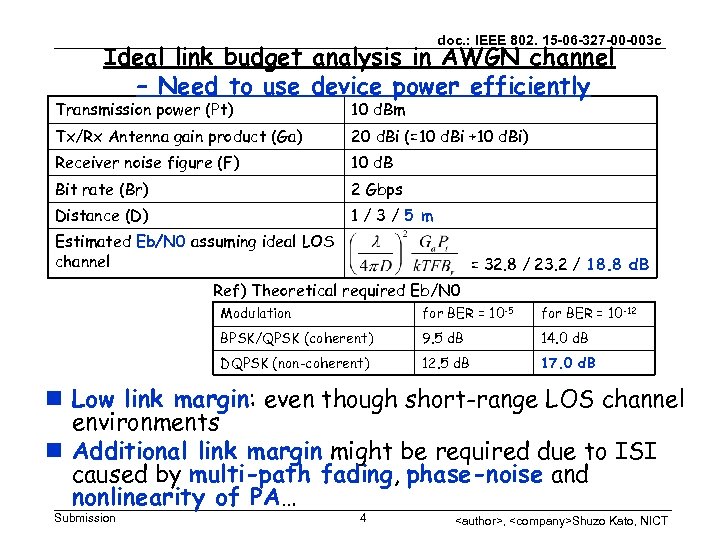 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Ideal link budget analysis in AWGN channel – Need to use device power efficiently Transmission power (Pt) 10 d. Bm Tx/Rx Antenna gain product (Ga) 20 d. Bi (=10 d. Bi +10 d. Bi) Receiver noise figure (F) 10 d. B Bit rate (Br) 2 Gbps Distance (D) 1/3/5 m Estimated Eb/N 0 assuming ideal LOS channel = 32. 8 / 23. 2 / 18. 8 d. B Ref) Theoretical required Eb/N 0 Modulation for BER = 10 -5 for BER = 10 -12 BPSK/QPSK (coherent) 9. 5 d. B 14. 0 d. B DQPSK (non-coherent) 12. 5 d. B 17. 0 d. B n Low link margin: even though short-range LOS channel environments n Additional link margin might be required due to ISI caused by multi-path fading, phase-noise and nonlinearity of PA… Submission 4
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Ideal link budget analysis in AWGN channel – Need to use device power efficiently Transmission power (Pt) 10 d. Bm Tx/Rx Antenna gain product (Ga) 20 d. Bi (=10 d. Bi +10 d. Bi) Receiver noise figure (F) 10 d. B Bit rate (Br) 2 Gbps Distance (D) 1/3/5 m Estimated Eb/N 0 assuming ideal LOS channel = 32. 8 / 23. 2 / 18. 8 d. B Ref) Theoretical required Eb/N 0 Modulation for BER = 10 -5 for BER = 10 -12 BPSK/QPSK (coherent) 9. 5 d. B 14. 0 d. B DQPSK (non-coherent) 12. 5 d. B 17. 0 d. B n Low link margin: even though short-range LOS channel environments n Additional link margin might be required due to ISI caused by multi-path fading, phase-noise and nonlinearity of PA… Submission 4
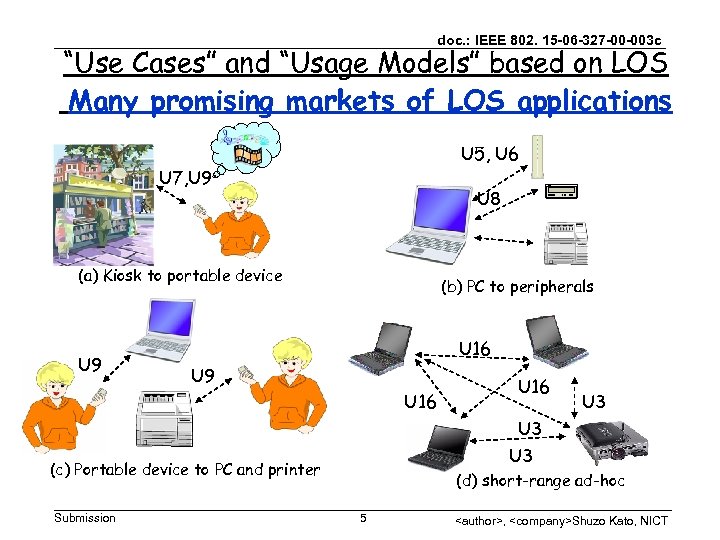 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c “Use Cases” and “Usage Models” based on LOS Many promising markets of LOS applications U 5, U 6 U 7, U 9 U 8 (a) Kiosk to portable device U 9 (b) PC to peripherals U 16 U 9 U 16 U 3 U 3 (c) Portable device to PC and printer Submission (d) short-range ad-hoc 5
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c “Use Cases” and “Usage Models” based on LOS Many promising markets of LOS applications U 5, U 6 U 7, U 9 U 8 (a) Kiosk to portable device U 9 (b) PC to peripherals U 16 U 9 U 16 U 3 U 3 (c) Portable device to PC and printer Submission (d) short-range ad-hoc 5
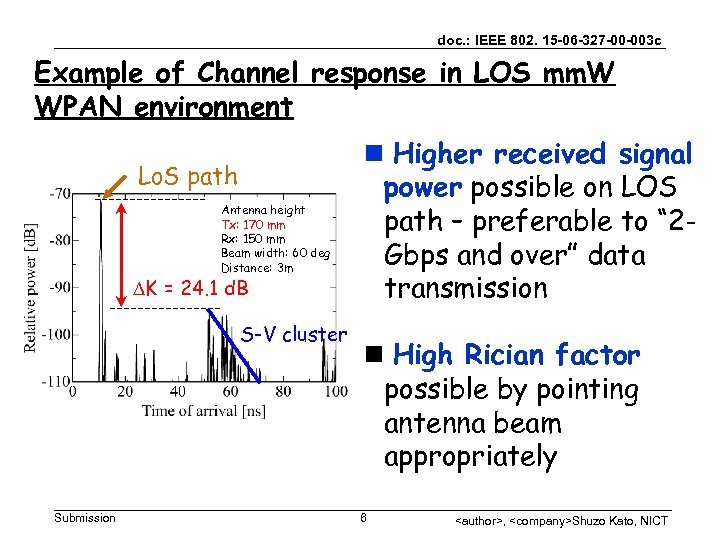 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Example of Channel response in LOS mm. W WPAN environment Lo. S path Antenna height Tx: 170 mm Rx: 150 mm Beam width: 60 deg Distance: 3 m DK = 24. 1 d. B S-V cluster Submission n Higher received signal power possible on LOS path – preferable to “ 2 Gbps and over” data transmission n High Rician factor possible by pointing antenna beam appropriately 6
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Example of Channel response in LOS mm. W WPAN environment Lo. S path Antenna height Tx: 170 mm Rx: 150 mm Beam width: 60 deg Distance: 3 m DK = 24. 1 d. B S-V cluster Submission n Higher received signal power possible on LOS path – preferable to “ 2 Gbps and over” data transmission n High Rician factor possible by pointing antenna beam appropriately 6
 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c A potential issue of “professional installation” in LOS systems n The use of LOS - strong received signal path is preferable in mm. W WPAN communications - How can the mm. W device with highdirectivity antenna catch and track the LOS path? May “professional installation” required? May require miniaturized “adaptive” antenna for consumer product applications Submission 7
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c A potential issue of “professional installation” in LOS systems n The use of LOS - strong received signal path is preferable in mm. W WPAN communications - How can the mm. W device with highdirectivity antenna catch and track the LOS path? May “professional installation” required? May require miniaturized “adaptive” antenna for consumer product applications Submission 7
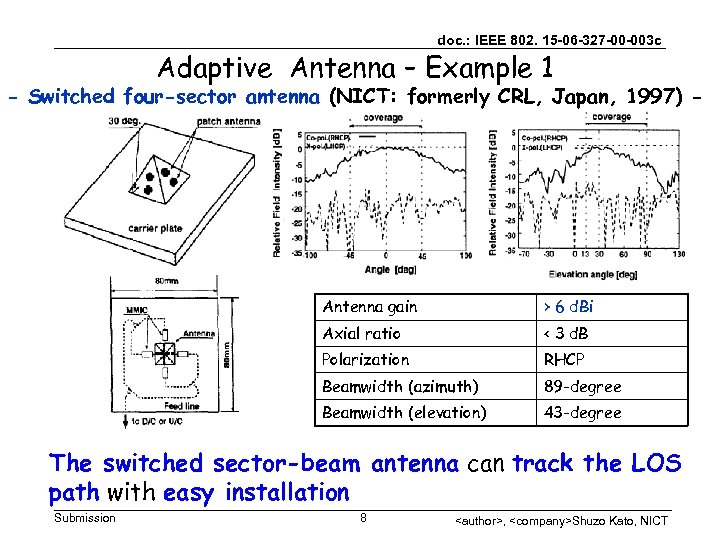 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Adaptive Antenna – Example 1 - Switched four-sector antenna (NICT: formerly CRL, Japan, 1997) - Antenna gain > 6 d. Bi Axial ratio < 3 d. B Polarization RHCP Beamwidth (azimuth) 89 -degree Beamwidth (elevation) 43 -degree The switched sector-beam antenna can track the LOS path with easy installation Submission 8
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Adaptive Antenna – Example 1 - Switched four-sector antenna (NICT: formerly CRL, Japan, 1997) - Antenna gain > 6 d. Bi Axial ratio < 3 d. B Polarization RHCP Beamwidth (azimuth) 89 -degree Beamwidth (elevation) 43 -degree The switched sector-beam antenna can track the LOS path with easy installation Submission 8
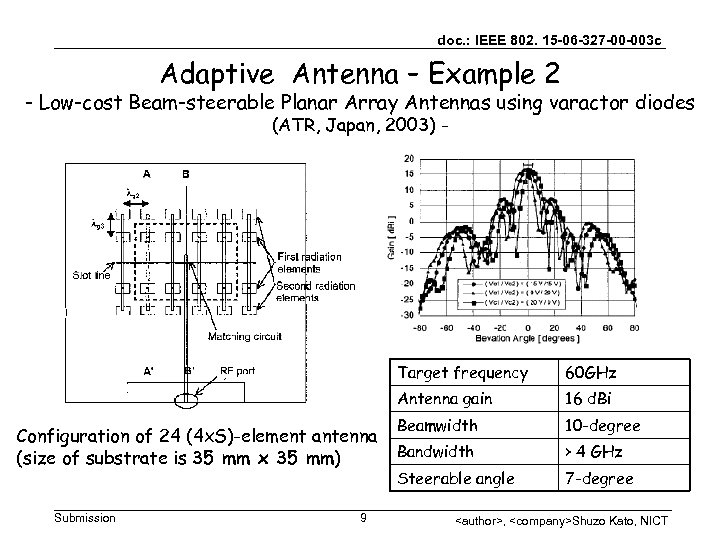 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Adaptive Antenna – Example 2 - Low-cost Beam-steerable Planar Array Antennas using varactor diodes (ATR, Japan, 2003) - Target frequency Antenna gain Configuration of 24 (4 x. S)-element antenna (size of substrate is 35 mm x 35 mm) Submission 9 60 GHz 16 d. Bi Beamwidth 10 -degree Bandwidth > 4 GHz Steerable angle 7 -degree
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Adaptive Antenna – Example 2 - Low-cost Beam-steerable Planar Array Antennas using varactor diodes (ATR, Japan, 2003) - Target frequency Antenna gain Configuration of 24 (4 x. S)-element antenna (size of substrate is 35 mm x 35 mm) Submission 9 60 GHz 16 d. Bi Beamwidth 10 -degree Bandwidth > 4 GHz Steerable angle 7 -degree
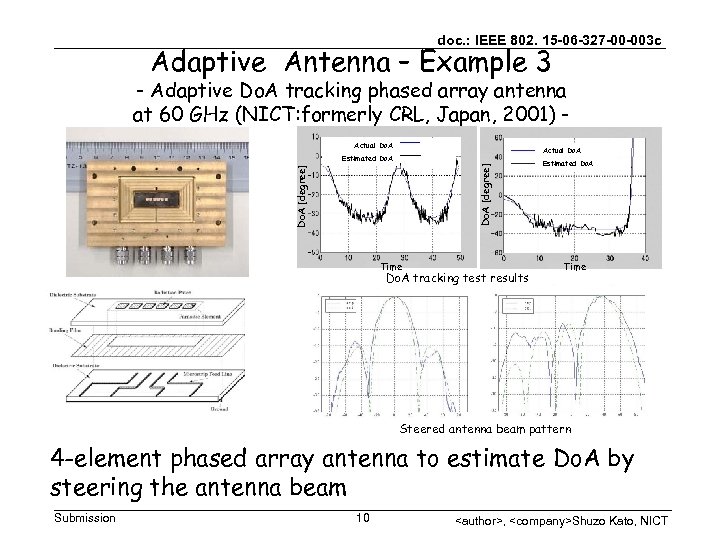 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Adaptive Antenna – Example 3 - Adaptive Do. A tracking phased array antenna at 60 GHz (NICT: formerly CRL, Japan, 2001) Actual Do. A [degree] Estimated Do. A Time Do. A tracking test results Estimated Do. A Time Steered antenna beam pattern 4 -element phased array antenna to estimate Do. A by steering the antenna beam Submission 10
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Adaptive Antenna – Example 3 - Adaptive Do. A tracking phased array antenna at 60 GHz (NICT: formerly CRL, Japan, 2001) Actual Do. A [degree] Estimated Do. A Time Do. A tracking test results Estimated Do. A Time Steered antenna beam pattern 4 -element phased array antenna to estimate Do. A by steering the antenna beam Submission 10
 Summary doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c LOS Millimeter Wave Systems are Preferable and Feasible 1. Power-limited but not band-limited systems – 10 m. W by regulations and device capability Should enjoy wide bandwidth for low cost terminal implementation 2. Higher directivity at 60 GHz Transmission range of LOS millimeter systems: superior Simple modulation and FEC: Applicable Less need for complicated modulation schemes which may have to loose 10 d. B PA output back off and 10 to 20 d. B in link budget due to no LOS signals assumed Selectable or beam forming antenna will solve a potential issue of “professional installation” in LOS systems Commercial LOS millimeter wave systems in Japanese market already Submission 11
Summary doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c LOS Millimeter Wave Systems are Preferable and Feasible 1. Power-limited but not band-limited systems – 10 m. W by regulations and device capability Should enjoy wide bandwidth for low cost terminal implementation 2. Higher directivity at 60 GHz Transmission range of LOS millimeter systems: superior Simple modulation and FEC: Applicable Less need for complicated modulation schemes which may have to loose 10 d. B PA output back off and 10 to 20 d. B in link budget due to no LOS signals assumed Selectable or beam forming antenna will solve a potential issue of “professional installation” in LOS systems Commercial LOS millimeter wave systems in Japanese market already Submission 11
 doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Millimeter Wave Commercialization Consortium Established n Millimeter wave Commercialization (MMWC) Consortium has been established for LOS communications in Japan n This MMWC Consortium is currently composed of (15 +3) institutes and open for non-Japanese institutes as well n The purpose of this consortium is to promote LOS millimeter wave communications systems which have already been in commercial use in Japan and will share significant part of millimeter wave applications n The Agreement in Japanese is available at http: //yrp. co. jp/yrprdc/facilities 060621/index. html and its English version will be available soon ( no later than the end of July) Submission 12
doc. : IEEE 802. 15 -06 -327 -00 -003 c Millimeter Wave Commercialization Consortium Established n Millimeter wave Commercialization (MMWC) Consortium has been established for LOS communications in Japan n This MMWC Consortium is currently composed of (15 +3) institutes and open for non-Japanese institutes as well n The purpose of this consortium is to promote LOS millimeter wave communications systems which have already been in commercial use in Japan and will share significant part of millimeter wave applications n The Agreement in Japanese is available at http: //yrp. co. jp/yrprdc/facilities 060621/index. html and its English version will be available soon ( no later than the end of July) Submission 12


