dae1850589a702b5785342bc323c1283.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx WLAN-Cellular Interworking Rajesh S. Pazhyannur GTSS, Motorola Submission 1
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx WLAN-Cellular Interworking Rajesh S. Pazhyannur GTSS, Motorola Submission 1
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Contributors • • Chad Fors Natarajan Johanna Wild All from GTSS, Motorola • Contact Address Rajesh S. Pazhyannur, QA 6283@email. mot. com Submission 2 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Contributors • • Chad Fors Natarajan Johanna Wild All from GTSS, Motorola • Contact Address Rajesh S. Pazhyannur, QA 6283@email. mot. com Submission 2 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Outline • • Introduction Architectural Approaches Standardization Efforts Experiences from Feasibility Study Submission 3 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Outline • • Introduction Architectural Approaches Standardization Efforts Experiences from Feasibility Study Submission 3 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Introduction • WLAN Segments need picture – Public Hotspots • Airports, Cafes, etc – Enterprises – Residences • Primary Focus – Public Hotspots and Cellular Data Systems – Integrated “Data” Services need picture • Important Area not Discussed – Integrating Enterprise WLAN with Cellular Voice Submission 4 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Introduction • WLAN Segments need picture – Public Hotspots • Airports, Cafes, etc – Enterprises – Residences • Primary Focus – Public Hotspots and Cellular Data Systems – Integrated “Data” Services need picture • Important Area not Discussed – Integrating Enterprise WLAN with Cellular Voice Submission 4 November 21, 2002
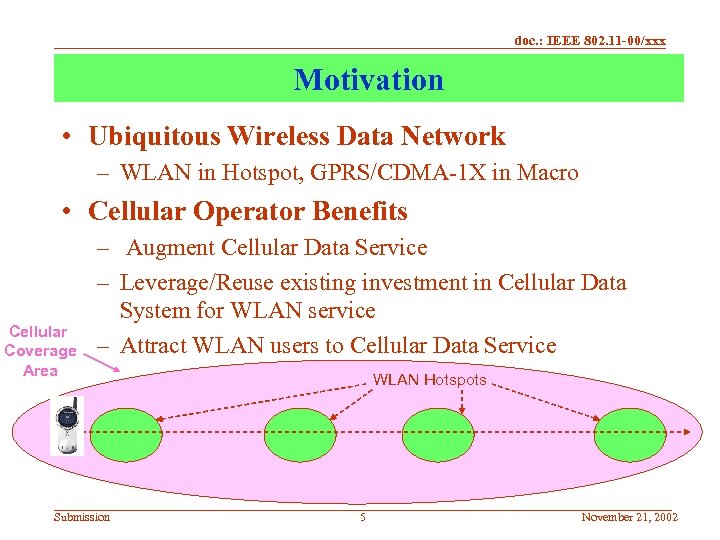 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Motivation • Ubiquitous Wireless Data Network – WLAN in Hotspot, GPRS/CDMA-1 X in Macro • Cellular Operator Benefits Cellular Coverage Area – Augment Cellular Data Service – Leverage/Reuse existing investment in Cellular Data System for WLAN service – Attract WLAN users to Cellular Data Service Submission WLAN Hotspots 5 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Motivation • Ubiquitous Wireless Data Network – WLAN in Hotspot, GPRS/CDMA-1 X in Macro • Cellular Operator Benefits Cellular Coverage Area – Augment Cellular Data Service – Leverage/Reuse existing investment in Cellular Data System for WLAN service – Attract WLAN users to Cellular Data Service Submission WLAN Hotspots 5 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx High-Level Requirements • Authentication – authentication provided by cellular operator – “common” authentication • Billing – Single Bill based on combined data usage • Session Mobility – Handoff between WLAN and Cellular • Support WLAN Roaming – Third Party owned WLAN Hotspots • Access to Applications from WLAN – IMS (Messaging) Submission 6 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx High-Level Requirements • Authentication – authentication provided by cellular operator – “common” authentication • Billing – Single Bill based on combined data usage • Session Mobility – Handoff between WLAN and Cellular • Support WLAN Roaming – Third Party owned WLAN Hotspots • Access to Applications from WLAN – IMS (Messaging) Submission 6 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Architectural Approaches Submission 7 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Architectural Approaches Submission 7 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx WLAN-Cellular Integration • Multiple Approaches – – Submission Loosely coupled architecture Tightly coupled architecture No coupling Proprietary architectures (vendor-specific solutions) 8 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx WLAN-Cellular Integration • Multiple Approaches – – Submission Loosely coupled architecture Tightly coupled architecture No coupling Proprietary architectures (vendor-specific solutions) 8 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Tight and Loose Coupling • Tight Coupling – Hierarchical relationship between WLAN and Cellular • WLAN as an alternate access network • WLAN traffic routed through cellular core network • Loose Coupling – WLAN as peer IP access network – Maintain distinct systems for bearer traffic – Reuse AAA services for WLAN Submission 9 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Tight and Loose Coupling • Tight Coupling – Hierarchical relationship between WLAN and Cellular • WLAN as an alternate access network • WLAN traffic routed through cellular core network • Loose Coupling – WLAN as peer IP access network – Maintain distinct systems for bearer traffic – Reuse AAA services for WLAN Submission 9 November 21, 2002
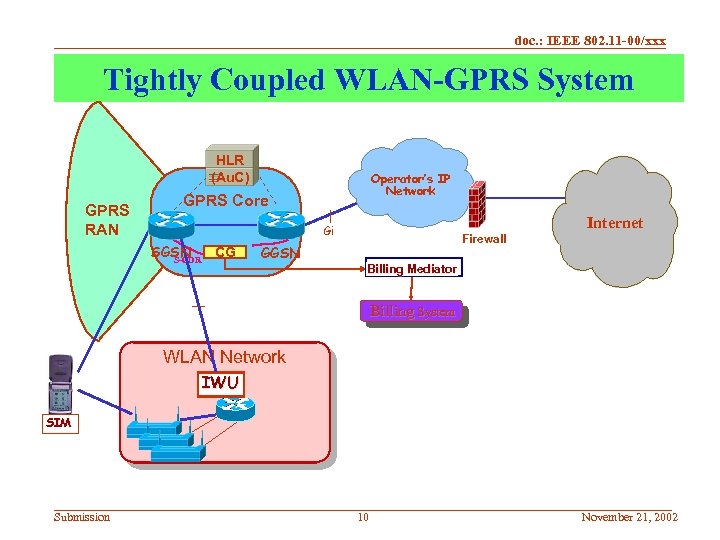 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Tightly Coupled WLAN-GPRS System HLR (Au. C) GPRS RAN Operator’s IP Network GPRS Core Internet Gi SGSN CG S-CDR Firewall GGSN Billing Mediator Billing System WLAN Network IWU SIM Submission 10 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Tightly Coupled WLAN-GPRS System HLR (Au. C) GPRS RAN Operator’s IP Network GPRS Core Internet Gi SGSN CG S-CDR Firewall GGSN Billing Mediator Billing System WLAN Network IWU SIM Submission 10 November 21, 2002
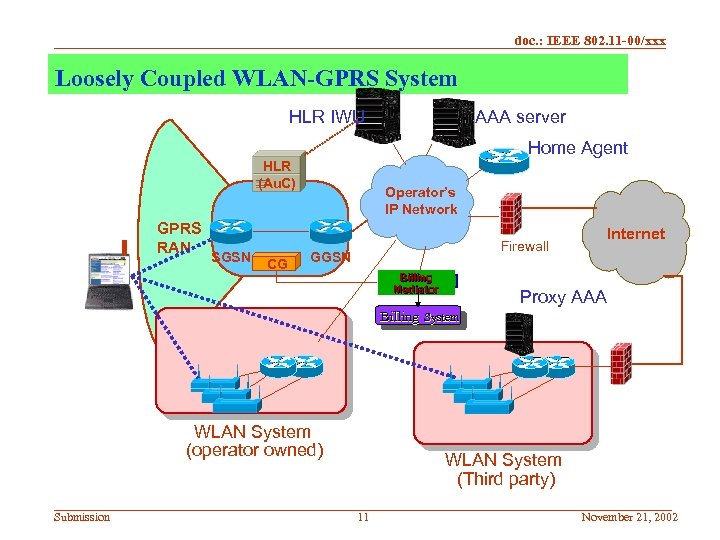 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Loosely Coupled WLAN-GPRS System HLR IWU AAA server Home Agent HLR (Au. C) GPRS RAN SGSN CG Operator’s IP Network Firewall GGSN Billing Mediator Internet Proxy AAA Billing System WLAN System (operator owned) Submission WLAN System (Third party) 11 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Loosely Coupled WLAN-GPRS System HLR IWU AAA server Home Agent HLR (Au. C) GPRS RAN SGSN CG Operator’s IP Network Firewall GGSN Billing Mediator Internet Proxy AAA Billing System WLAN System (operator owned) Submission WLAN System (Third party) 11 November 21, 2002
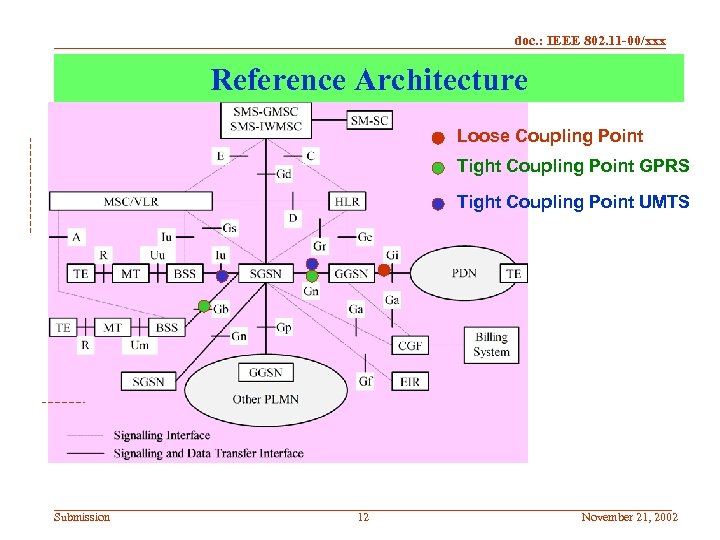 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Reference Architecture Loose Coupling Point Tight Coupling Point GPRS Tight Coupling Point UMTS Submission 12 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Reference Architecture Loose Coupling Point Tight Coupling Point GPRS Tight Coupling Point UMTS Submission 12 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx No Coupling • Maintain separate systems • Two separate services – Separate sign-on for WLAN and Cellular Data – Separate bills Submission 13 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx No Coupling • Maintain separate systems • Two separate services – Separate sign-on for WLAN and Cellular Data – Separate bills Submission 13 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Standardization Efforts Submission 14 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Standardization Efforts Submission 14 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Standardization Groups • 3 GPP – GPRS and UMTS Systems – One year ago – Interworking Scenarios Document • 3 GPP 2 – CDMA 1 X Systems – 4 Q, 2002 – Stage 1 Document • IETF – Authentication/Security, Mobility Submission 15 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Standardization Groups • 3 GPP – GPRS and UMTS Systems – One year ago – Interworking Scenarios Document • 3 GPP 2 – CDMA 1 X Systems – 4 Q, 2002 – Stage 1 Document • IETF – Authentication/Security, Mobility Submission 15 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx 3 GPP and WLAN • Feasibility Study Highlights • Six Interworking scenarios – Incremental Functionality • Interworking based on IP as common layer – Independent of WLAN radio technology • Reuse standard WLAN mechanisms Submission 16 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx 3 GPP and WLAN • Feasibility Study Highlights • Six Interworking scenarios – Incremental Functionality • Interworking based on IP as common layer – Independent of WLAN radio technology • Reuse standard WLAN mechanisms Submission 16 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx 3 GPP • Six Scenarios for WLAN-Cellular Interworking – Scenario 1: Common Billing and Customer Care – Scenario 2: 3 GPP system based Access Control and Charging – Scenario 3: Access to 3 GPP system PS based services – Scenario 4: Service Continuity – Scenario 5: Seamless services – Scenario 6: Access to 3 GPP CS Services • Currently Focused on Scenarios 2 and 3 • Advocating a Loose Coupling Architecture Submission 17 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx 3 GPP • Six Scenarios for WLAN-Cellular Interworking – Scenario 1: Common Billing and Customer Care – Scenario 2: 3 GPP system based Access Control and Charging – Scenario 3: Access to 3 GPP system PS based services – Scenario 4: Service Continuity – Scenario 5: Seamless services – Scenario 6: Access to 3 GPP CS Services • Currently Focused on Scenarios 2 and 3 • Advocating a Loose Coupling Architecture Submission 17 November 21, 2002
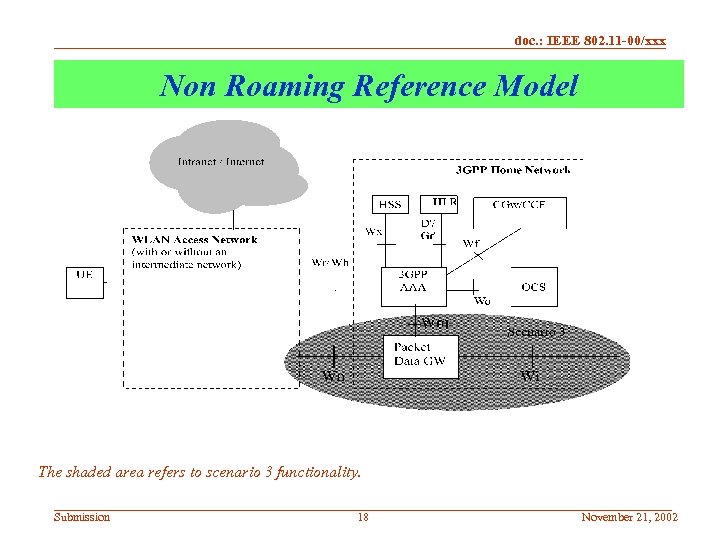 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Non Roaming Reference Model The shaded area refers to scenario 3 functionality. Submission 18 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Non Roaming Reference Model The shaded area refers to scenario 3 functionality. Submission 18 November 21, 2002
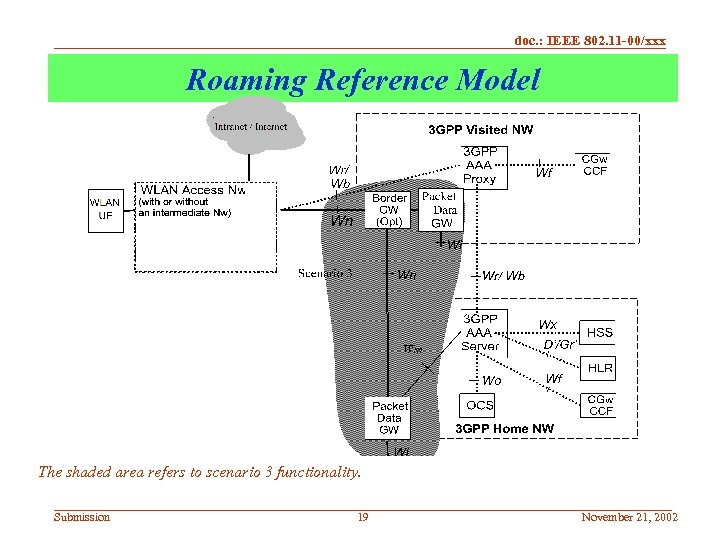 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Roaming Reference Model The shaded area refers to scenario 3 functionality. Submission 19 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Roaming Reference Model The shaded area refers to scenario 3 functionality. Submission 19 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Network Selection • Access Point may have relationship with multiple 3 GPP Network Providers • User wishes to choose the service operator Operator 1 Operator 2 Operator 3 Submission 20 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Network Selection • Access Point may have relationship with multiple 3 GPP Network Providers • User wishes to choose the service operator Operator 1 Operator 2 Operator 3 Submission 20 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Potential Solutions • WLAN based Solutions 1. Multiple SSIDs in the beacon 2. Round Robin SSIDs 3. Multiple BSSIDs: – One Beacon per SSID • EAP Based Solution – Prior to Authentication, probe the AP for Systems supported Submission 21 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Potential Solutions • WLAN based Solutions 1. Multiple SSIDs in the beacon 2. Round Robin SSIDs 3. Multiple BSSIDs: – One Beacon per SSID • EAP Based Solution – Prior to Authentication, probe the AP for Systems supported Submission 21 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Motorola Feasibility Study • Advanced Technology Effort – – CDMA-1 X and GPRS Loosely Coupled Architecture Investigate implementation issues Evaluate commercial offering • Focus on Functionality – EAP-SIM – Roaming and Session Mobility – Accounting and Single Bill Submission 22 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Motorola Feasibility Study • Advanced Technology Effort – – CDMA-1 X and GPRS Loosely Coupled Architecture Investigate implementation issues Evaluate commercial offering • Focus on Functionality – EAP-SIM – Roaming and Session Mobility – Accounting and Single Bill Submission 22 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx EAP-SIM • Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) has a long history – Smart card that is removable from the phone equipment – Used to authenticate GSM/GPRS users • EAP-SIM enables WLAN authentication based on SIM • Why EAP-SIM? – Cellular Operators like it !! • Single Point of Provisioning • Leverage existing resources and assets – GSM users are conversant with SIM – Provides a degree of security within the 802. 1 X framework – Being standardized within IETF Submission 23 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx EAP-SIM • Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) has a long history – Smart card that is removable from the phone equipment – Used to authenticate GSM/GPRS users • EAP-SIM enables WLAN authentication based on SIM • Why EAP-SIM? – Cellular Operators like it !! • Single Point of Provisioning • Leverage existing resources and assets – GSM users are conversant with SIM – Provides a degree of security within the 802. 1 X framework – Being standardized within IETF Submission 23 November 21, 2002
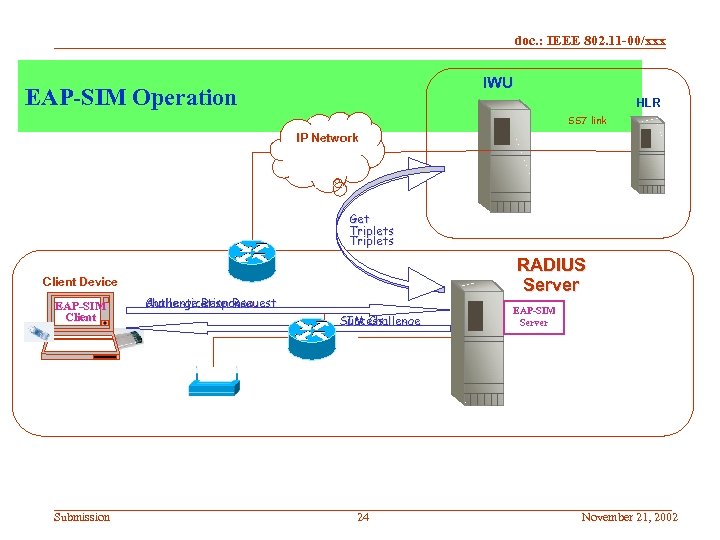 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx IWU EAP-SIM Operation HLR SS 7 link IP Network Get Triplets RADIUS Server Client Device EAP-SIM Client Submission Challenge Response Authentication Request Success SIM Challenge 24 EAP-SIM Server November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx IWU EAP-SIM Operation HLR SS 7 link IP Network Get Triplets RADIUS Server Client Device EAP-SIM Client Submission Challenge Response Authentication Request Success SIM Challenge 24 EAP-SIM Server November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx EAP-SIM Issues • How are SIM Cards administered? – Single SIM versus Multiple SIM • How does the WLAN user connect to SIM card? – WLAN card is integrated with SIM – WLAN device (PDA, etc) connected to SIM dongle through USB – WLAN device has a sleeve to insert SIM (just like phones) Submission 25 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx EAP-SIM Issues • How are SIM Cards administered? – Single SIM versus Multiple SIM • How does the WLAN user connect to SIM card? – WLAN card is integrated with SIM – WLAN device (PDA, etc) connected to SIM dongle through USB – WLAN device has a sleeve to insert SIM (just like phones) Submission 25 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx WLAN-Cellular Handover • Handover is accomplished through MIP • Requires Following Components – MIP Client – MIP Home Agent • How does it work? – – – Submission Mobile is assigned a Home Address. When Mobile is away from home, it acquires a Care-of-address Mobile IP Client registers Care-of-address with Home Agent All IP packets destined to Home Address are intercepted by Home Agent forwards IP packets to Care-of-Address As Mobile Moves between WLAN and Cellular • Care-of-Address Changes but Home Address remains same • TCP/UDP Sessions based on Home Address are unaffected between handoffs 26 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx WLAN-Cellular Handover • Handover is accomplished through MIP • Requires Following Components – MIP Client – MIP Home Agent • How does it work? – – – Submission Mobile is assigned a Home Address. When Mobile is away from home, it acquires a Care-of-address Mobile IP Client registers Care-of-address with Home Agent All IP packets destined to Home Address are intercepted by Home Agent forwards IP packets to Care-of-Address As Mobile Moves between WLAN and Cellular • Care-of-Address Changes but Home Address remains same • TCP/UDP Sessions based on Home Address are unaffected between handoffs 26 November 21, 2002
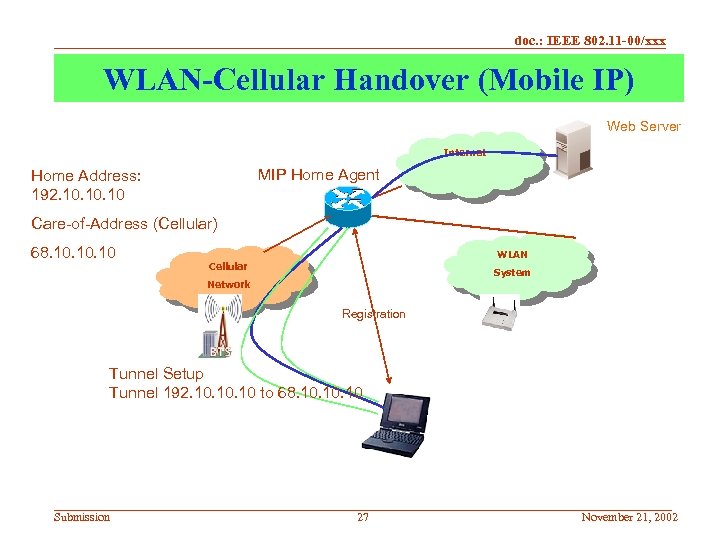 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx WLAN-Cellular Handover (Mobile IP) Web Server Internet MIP Home Agent Home Address: 192. 10. 10 Care-of-Address (Cellular) 68. 10. 10 WLAN Cellular System Network Registration Tunnel Setup Tunnel 192. 10. 10 to 68. 10. 10 Submission 27 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx WLAN-Cellular Handover (Mobile IP) Web Server Internet MIP Home Agent Home Address: 192. 10. 10 Care-of-Address (Cellular) 68. 10. 10 WLAN Cellular System Network Registration Tunnel Setup Tunnel 192. 10. 10 to 68. 10. 10 Submission 27 November 21, 2002
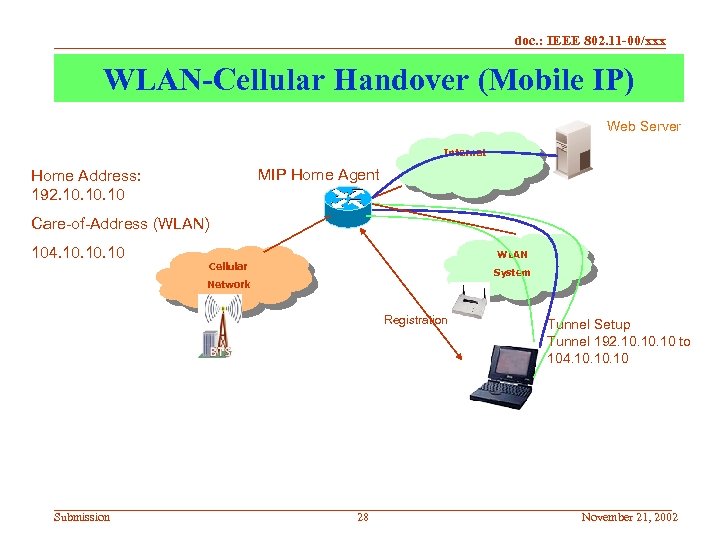 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx WLAN-Cellular Handover (Mobile IP) Web Server Internet MIP Home Agent Home Address: 192. 10. 10 Care-of-Address (WLAN) 104. 10. 10 WLAN Cellular System Network Registration Submission 28 Tunnel Setup Tunnel 192. 10. 10 to 104. 10. 10 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx WLAN-Cellular Handover (Mobile IP) Web Server Internet MIP Home Agent Home Address: 192. 10. 10 Care-of-Address (WLAN) 104. 10. 10 WLAN Cellular System Network Registration Submission 28 Tunnel Setup Tunnel 192. 10. 10 to 104. 10. 10 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Session Mobility Issues • • Support for Mobile IP in Cellular Systems NATs and Firewalls Interaction between VPN and MIP Clients MIP Handover Performance Submission 29 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Session Mobility Issues • • Support for Mobile IP in Cellular Systems NATs and Firewalls Interaction between VPN and MIP Clients MIP Handover Performance Submission 29 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Interaction between VPN and MIP • VPN Clients intolerant of changes in Route Table – – • Assume VPN over MIP – – • Any Change in route table usually resets the VPN Force VPN Re-authentication MIP running on top of WLAN Move out of WLAN coverage into Cellular Acquire IP address from Cellular. MIP handover from WLAN to Cellular Workarounds 1. 2. Submission Integrated MIP and VPN Make VPN more “tolerant” of changes 30 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Interaction between VPN and MIP • VPN Clients intolerant of changes in Route Table – – • Assume VPN over MIP – – • Any Change in route table usually resets the VPN Force VPN Re-authentication MIP running on top of WLAN Move out of WLAN coverage into Cellular Acquire IP address from Cellular. MIP handover from WLAN to Cellular Workarounds 1. 2. Submission Integrated MIP and VPN Make VPN more “tolerant” of changes 30 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Support for Mobile IP in Cellular Systems • 3 GPP 2 has incorporated MIP – PDSN behaves as FA, Handsets have MIP clients • 3 GPP does not require MIP – Some GGSN providers have MIP capability • Is FA Care-of-Address Registration important? Submission 31 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Support for Mobile IP in Cellular Systems • 3 GPP 2 has incorporated MIP – PDSN behaves as FA, Handsets have MIP clients • 3 GPP does not require MIP – Some GGSN providers have MIP capability • Is FA Care-of-Address Registration important? Submission 31 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx NATs and Firewalls • Private IP addresses are a problem for MIP – MIP Clients can register with Home Agent – Home Agent tunnels packets to Private IP address (not the NATted public IP address) • Potential Workarounds: – IETF is working on numerous NAT Traversal drafts. • Tunnel MIP packets within UDP packets • Firewalls may block tunneled packets – Mobile IP uses IP-in-IP tunnels between HA and Client • Potential Workaround – Use GRE for tunneling – Change firewall policy to allow MIP packets Submission 32 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx NATs and Firewalls • Private IP addresses are a problem for MIP – MIP Clients can register with Home Agent – Home Agent tunnels packets to Private IP address (not the NATted public IP address) • Potential Workarounds: – IETF is working on numerous NAT Traversal drafts. • Tunnel MIP packets within UDP packets • Firewalls may block tunneled packets – Mobile IP uses IP-in-IP tunnels between HA and Client • Potential Workaround – Use GRE for tunneling – Change firewall policy to allow MIP packets Submission 32 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Handoff Delays • Handoff Delays are still “large” (~4 secs) • Sources of delay – IP address assignment (DHCP) and authentication – Detection of Loss of WLAN coverage – Cellular Data call-setup • Impact of Delay (> 4 sec) on Applications – Some FTP clients will “hang” – Streaming Clients sometimes “freeze” • Adjusting buffer size has “mixed” effect Submission 33 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Handoff Delays • Handoff Delays are still “large” (~4 secs) • Sources of delay – IP address assignment (DHCP) and authentication – Detection of Loss of WLAN coverage – Cellular Data call-setup • Impact of Delay (> 4 sec) on Applications – Some FTP clients will “hang” – Streaming Clients sometimes “freeze” • Adjusting buffer size has “mixed” effect Submission 33 November 21, 2002
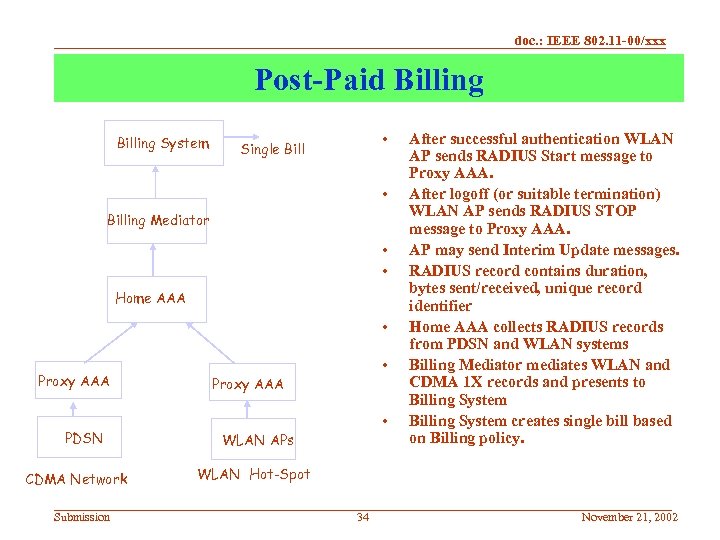 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Post-Paid Billing System • Single Bill • Billing Mediator • • Home AAA • Proxy AAA PDSN CDMA Network Submission • Proxy AAA • WLAN APs After successful authentication WLAN AP sends RADIUS Start message to Proxy AAA. After logoff (or suitable termination) WLAN AP sends RADIUS STOP message to Proxy AAA. AP may send Interim Update messages. RADIUS record contains duration, bytes sent/received, unique record identifier Home AAA collects RADIUS records from PDSN and WLAN systems Billing Mediator mediates WLAN and CDMA 1 X records and presents to Billing System creates single bill based on Billing policy. WLAN Hot-Spot 34 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Post-Paid Billing System • Single Bill • Billing Mediator • • Home AAA • Proxy AAA PDSN CDMA Network Submission • Proxy AAA • WLAN APs After successful authentication WLAN AP sends RADIUS Start message to Proxy AAA. After logoff (or suitable termination) WLAN AP sends RADIUS STOP message to Proxy AAA. AP may send Interim Update messages. RADIUS record contains duration, bytes sent/received, unique record identifier Home AAA collects RADIUS records from PDSN and WLAN systems Billing Mediator mediates WLAN and CDMA 1 X records and presents to Billing System creates single bill based on Billing policy. WLAN Hot-Spot 34 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Billing Issues • Accounting Records in WLAN Systems – No standards unlike 3 GPP and 3 GPP 2 – Perhaps WECA (? ? ) – 3 GPP 2 uses RADIUS accounting records • Quite different from what APs provide Submission 35 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Billing Issues • Accounting Records in WLAN Systems – No standards unlike 3 GPP and 3 GPP 2 – Perhaps WECA (? ? ) – 3 GPP 2 uses RADIUS accounting records • Quite different from what APs provide Submission 35 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Key Conclusions • WLAN-Cellular Interworking is relatively easy to implement – Most components for Scenarios 1 -4 exist – Does not affect 3 GPP and 3 GPP 2 systems in any significant manner – High Reuse between 3 GPP and 3 GPP 2 Systems • Combination Devices may be potential trigger! – Combination PC cards – Dual-Mode WLAN-Cellular Phones Submission 36 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Key Conclusions • WLAN-Cellular Interworking is relatively easy to implement – Most components for Scenarios 1 -4 exist – Does not affect 3 GPP and 3 GPP 2 systems in any significant manner – High Reuse between 3 GPP and 3 GPP 2 Systems • Combination Devices may be potential trigger! – Combination PC cards – Dual-Mode WLAN-Cellular Phones Submission 36 November 21, 2002
 doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Backup Submission 37 November 21, 2002
doc. : IEEE 802. 11 -00/xxx Backup Submission 37 November 21, 2002


