1e48428e1370ad3de6bc2b20fffd192c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 HEW Usage Models for Backhauls and Floor Automation Date: 2013 -07 -15 Authors: Name Affiliations Address Phone email Minho Cheong ETRI 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejoen, Korea +82 42 860 5635 minho@etri. re. kr Hyoung Jin Kwon ETRI 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejoen, Korea +82 42 860 1698 kwonjin@etri. re. kr Jae Seung Lee ETRI 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejoen, Korea +82 42 860 1326 jasonlee@etri. re. kr Sok-Kyu Lee ETRI 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejoen, Korea +82 42 860 5919 sk-lee@etri. re. kr Submission Slide 1 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 HEW Usage Models for Backhauls and Floor Automation Date: 2013 -07 -15 Authors: Name Affiliations Address Phone email Minho Cheong ETRI 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejoen, Korea +82 42 860 5635 minho@etri. re. kr Hyoung Jin Kwon ETRI 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejoen, Korea +82 42 860 1698 kwonjin@etri. re. kr Jae Seung Lee ETRI 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejoen, Korea +82 42 860 1326 jasonlee@etri. re. kr Sok-Kyu Lee ETRI 161 Gajeong-dong, Yuseong-Gu, Daejoen, Korea +82 42 860 5919 sk-lee@etri. re. kr Submission Slide 1 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 May 2013 Abstract This document describes additional complementary usage models for HEW. Submission Slide 2 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 May 2013 Abstract This document describes additional complementary usage models for HEW. Submission Slide 2 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
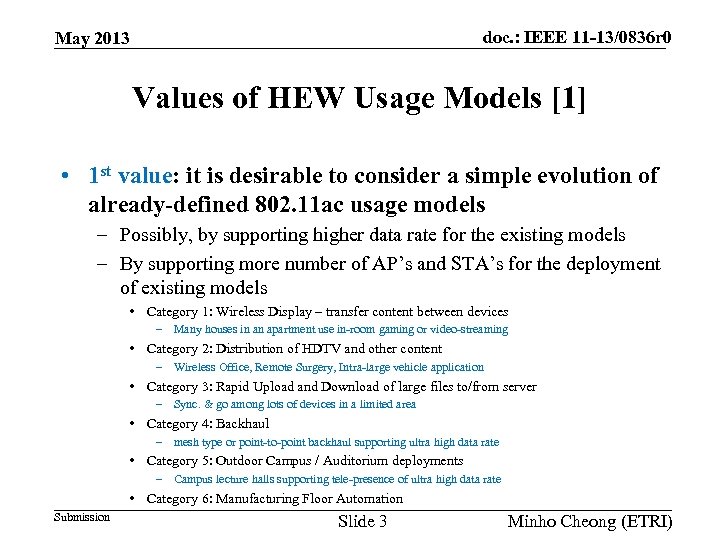 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 May 2013 Values of HEW Usage Models [1] • 1 st value: it is desirable to consider a simple evolution of already-defined 802. 11 ac usage models – Possibly, by supporting higher data rate for the existing models – By supporting more number of AP’s and STA’s for the deployment of existing models • Category 1: Wireless Display – transfer content between devices – Many houses in an apartment use in-room gaming or video-streaming • Category 2: Distribution of HDTV and other content – Wireless Office, Remote Surgery, Intra-large vehicle application • Category 3: Rapid Upload and Download of large files to/from server – Sync. & go among lots of devices in a limited area • Category 4: Backhaul – mesh type or point-to-point backhaul supporting ultra high data rate • Category 5: Outdoor Campus / Auditorium deployments – Campus lecture halls supporting tele-presence of ultra high data rate • Category 6: Manufacturing Floor Automation Submission Slide 3 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 May 2013 Values of HEW Usage Models [1] • 1 st value: it is desirable to consider a simple evolution of already-defined 802. 11 ac usage models – Possibly, by supporting higher data rate for the existing models – By supporting more number of AP’s and STA’s for the deployment of existing models • Category 1: Wireless Display – transfer content between devices – Many houses in an apartment use in-room gaming or video-streaming • Category 2: Distribution of HDTV and other content – Wireless Office, Remote Surgery, Intra-large vehicle application • Category 3: Rapid Upload and Download of large files to/from server – Sync. & go among lots of devices in a limited area • Category 4: Backhaul – mesh type or point-to-point backhaul supporting ultra high data rate • Category 5: Outdoor Campus / Auditorium deployments – Campus lecture halls supporting tele-presence of ultra high data rate • Category 6: Manufacturing Floor Automation Submission Slide 3 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
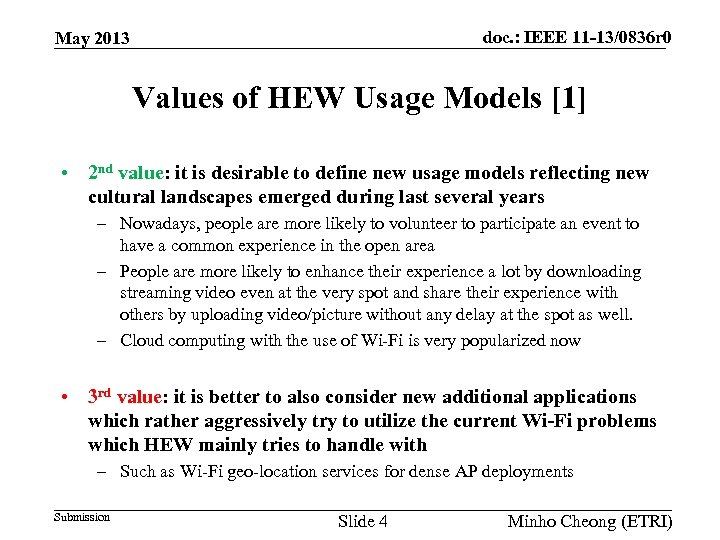 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 May 2013 Values of HEW Usage Models [1] • 2 nd value: it is desirable to define new usage models reflecting new cultural landscapes emerged during last several years – Nowadays, people are more likely to volunteer to participate an event to have a common experience in the open area – People are more likely to enhance their experience a lot by downloading streaming video even at the very spot and share their experience with others by uploading video/picture without any delay at the spot as well. – Cloud computing with the use of Wi-Fi is very popularized now • 3 rd value: it is better to also consider new additional applications which rather aggressively try to utilize the current Wi-Fi problems which HEW mainly tries to handle with – Such as Wi-Fi geo-location services for dense AP deployments Submission Slide 4 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 May 2013 Values of HEW Usage Models [1] • 2 nd value: it is desirable to define new usage models reflecting new cultural landscapes emerged during last several years – Nowadays, people are more likely to volunteer to participate an event to have a common experience in the open area – People are more likely to enhance their experience a lot by downloading streaming video even at the very spot and share their experience with others by uploading video/picture without any delay at the spot as well. – Cloud computing with the use of Wi-Fi is very popularized now • 3 rd value: it is better to also consider new additional applications which rather aggressively try to utilize the current Wi-Fi problems which HEW mainly tries to handle with – Such as Wi-Fi geo-location services for dense AP deployments Submission Slide 4 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
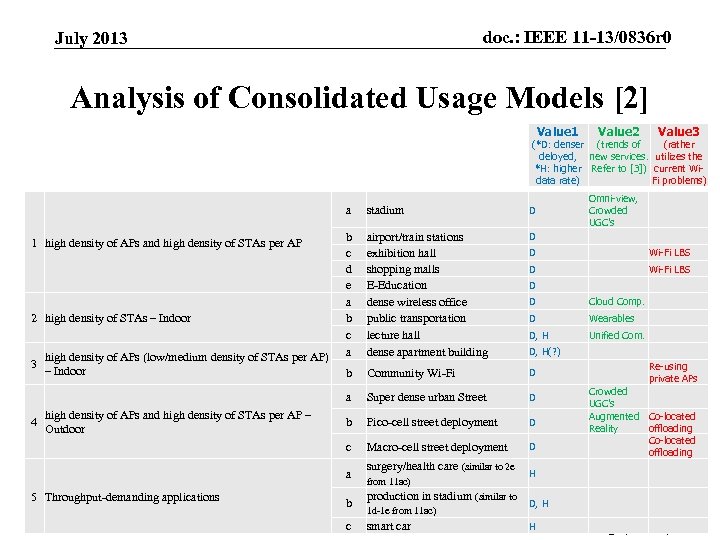 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Analysis of Consolidated Usage Models [2] Value 1 Value 2 Value 3 (*D: denser (trends of (rather deloyed, new services. utilizes the *H: higher Refer to [3]) current Widata rate) Fi problems) a high density of APs (low/medium density of STAs per AP) 3 – Indoor 4 high density of APs and high density of STAs per AP – Outdoor b c d e a b c a airport/train stations exhibition hall shopping malls E-Education dense wireless office public transportation lecture hall dense apartment building b Community Wi-Fi D Super dense urban Street D b Pico-cell street deployment D Macro-cell street deployment D Submission D Wi-Fi LBS D D Cloud Comp. D Wearables D, H Unified Com. D, H(? ) Re-using private APs Crowded UGC’s Augmented Co-located Reality offloading Co-located offloading surgery/health care (similar to 2 e H from 11 ac) production in stadium (similar to D, H b 1 d-1 e from 11 ac) H c smart car Slide 5 Minho Cheong (ETRI) a 5 Throughput-demanding applications Omni-view, Crowded UGC’s D c 2 high density of STAs – Indoor D a 1 high density of APs and high density of STAs per AP stadium
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Analysis of Consolidated Usage Models [2] Value 1 Value 2 Value 3 (*D: denser (trends of (rather deloyed, new services. utilizes the *H: higher Refer to [3]) current Widata rate) Fi problems) a high density of APs (low/medium density of STAs per AP) 3 – Indoor 4 high density of APs and high density of STAs per AP – Outdoor b c d e a b c a airport/train stations exhibition hall shopping malls E-Education dense wireless office public transportation lecture hall dense apartment building b Community Wi-Fi D Super dense urban Street D b Pico-cell street deployment D Macro-cell street deployment D Submission D Wi-Fi LBS D D Cloud Comp. D Wearables D, H Unified Com. D, H(? ) Re-using private APs Crowded UGC’s Augmented Co-located Reality offloading Co-located offloading surgery/health care (similar to 2 e H from 11 ac) production in stadium (similar to D, H b 1 d-1 e from 11 ac) H c smart car Slide 5 Minho Cheong (ETRI) a 5 Throughput-demanding applications Omni-view, Crowded UGC’s D c 2 high density of STAs – Indoor D a 1 high density of APs and high density of STAs per AP stadium
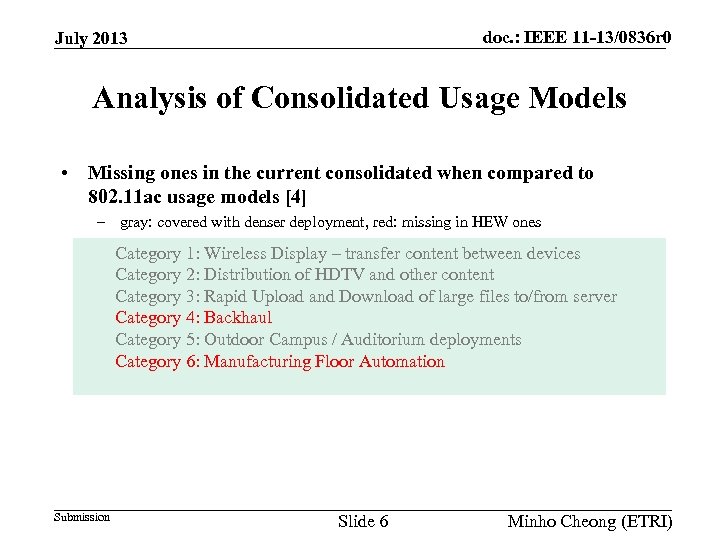 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Analysis of Consolidated Usage Models • Missing ones in the current consolidated when compared to 802. 11 ac usage models [4] – gray: covered with denser deployment, red: missing in HEW ones Category 1: Wireless Display – transfer content between devices Category 2: Distribution of HDTV and other content Category 3: Rapid Upload and Download of large files to/from server Category 4: Backhaul Category 5: Outdoor Campus / Auditorium deployments Category 6: Manufacturing Floor Automation Submission Slide 6 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Analysis of Consolidated Usage Models • Missing ones in the current consolidated when compared to 802. 11 ac usage models [4] – gray: covered with denser deployment, red: missing in HEW ones Category 1: Wireless Display – transfer content between devices Category 2: Distribution of HDTV and other content Category 3: Rapid Upload and Download of large files to/from server Category 4: Backhaul Category 5: Outdoor Campus / Auditorium deployments Category 6: Manufacturing Floor Automation Submission Slide 6 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
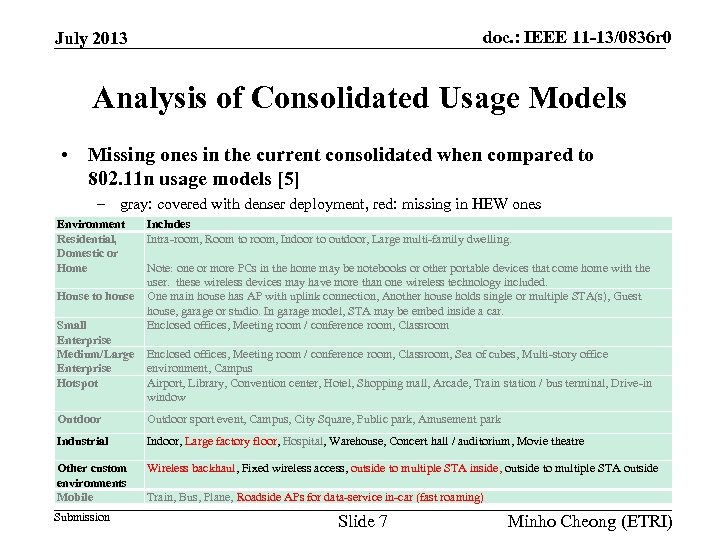 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Analysis of Consolidated Usage Models • Missing ones in the current consolidated when compared to 802. 11 n usage models [5] – gray: covered with denser deployment, red: missing in HEW ones Environment Residential, Domestic or Home House to house Small Enterprise Medium/Large Enterprise Hotspot Includes Intra-room, Room to room, Indoor to outdoor, Large multi-family dwelling. Note: one or more PCs in the home may be notebooks or other portable devices that come home with the user. these wireless devices may have more than one wireless technology included. One main house has AP with uplink connection, Another house holds single or multiple STA(s), Guest house, garage or studio. In garage model, STA may be embed inside a car. Enclosed offices, Meeting room / conference room, Classroom, Sea of cubes, Multi-story office environment, Campus Airport, Library, Convention center, Hotel, Shopping mall, Arcade, Train station / bus terminal, Drive-in window Outdoor sport event, Campus, City Square, Public park, Amusement park Industrial Indoor, Large factory floor, Hospital, Warehouse, Concert hall / auditorium, Movie theatre Other custom environments Mobile Wireless backhaul, Fixed wireless access, outside to multiple STA inside, outside to multiple STA outside Submission Train, Bus, Plane, Roadside APs for data-service in-car (fast roaming) Slide 7 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Analysis of Consolidated Usage Models • Missing ones in the current consolidated when compared to 802. 11 n usage models [5] – gray: covered with denser deployment, red: missing in HEW ones Environment Residential, Domestic or Home House to house Small Enterprise Medium/Large Enterprise Hotspot Includes Intra-room, Room to room, Indoor to outdoor, Large multi-family dwelling. Note: one or more PCs in the home may be notebooks or other portable devices that come home with the user. these wireless devices may have more than one wireless technology included. One main house has AP with uplink connection, Another house holds single or multiple STA(s), Guest house, garage or studio. In garage model, STA may be embed inside a car. Enclosed offices, Meeting room / conference room, Classroom, Sea of cubes, Multi-story office environment, Campus Airport, Library, Convention center, Hotel, Shopping mall, Arcade, Train station / bus terminal, Drive-in window Outdoor sport event, Campus, City Square, Public park, Amusement park Industrial Indoor, Large factory floor, Hospital, Warehouse, Concert hall / auditorium, Movie theatre Other custom environments Mobile Wireless backhaul, Fixed wireless access, outside to multiple STA inside, outside to multiple STA outside Submission Train, Bus, Plane, Roadside APs for data-service in-car (fast roaming) Slide 7 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Suggestion • It is desirable to add backhaul and floor automation with denser deployment to the HEW usage models, because denser deployment will be as much limiting factor on performance of those as others. 1 high density of APs and high density of STAs per AP 2 high density of STAs – Indoor 3 high density of APs (low/medium density of STAs per AP) – Indoor high density of APs and high density of STAs per AP – 4 Outdoor 5 Throughput-demanding applications Submission a b c d e f a b c d a b stadium airport/train stations exhibition hall shopping malls E-Education Multi-media mesh backhaul dense wireless office public transportation lecture hall Manufacturing floor automation dense apartment building Community Wi-Fi a Super dense urban Street b Pico-cell street deployment c a b Macro-cell street deployment surgery/health care (similar to 2 e from 11 ac) production in stadium (similar to 1 d-1 e from 11 ac) c smart car Slide 8 d Point-to-point backhaul Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Suggestion • It is desirable to add backhaul and floor automation with denser deployment to the HEW usage models, because denser deployment will be as much limiting factor on performance of those as others. 1 high density of APs and high density of STAs per AP 2 high density of STAs – Indoor 3 high density of APs (low/medium density of STAs per AP) – Indoor high density of APs and high density of STAs per AP – 4 Outdoor 5 Throughput-demanding applications Submission a b c d e f a b c d a b stadium airport/train stations exhibition hall shopping malls E-Education Multi-media mesh backhaul dense wireless office public transportation lecture hall Manufacturing floor automation dense apartment building Community Wi-Fi a Super dense urban Street b Pico-cell street deployment c a b Macro-cell street deployment surgery/health care (similar to 2 e from 11 ac) production in stadium (similar to 1 d-1 e from 11 ac) c smart car Slide 8 d Point-to-point backhaul Minho Cheong (ETRI)
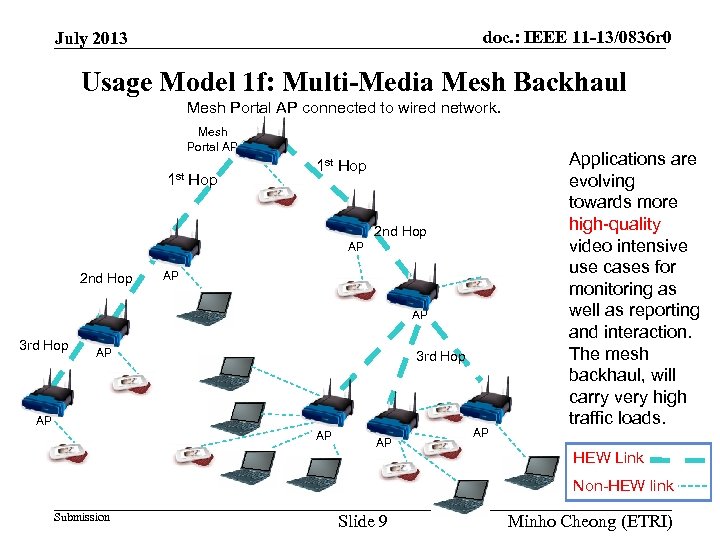 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Usage Model 1 f: Multi-Media Mesh Backhaul Mesh Portal AP connected to wired network. Mesh Portal AP 1 st Hop 2 nd Hop AP AP 3 rd Hop AP AP Applications are evolving towards more high-quality video intensive use cases for monitoring as well as reporting and interaction. The mesh backhaul, will carry very high traffic loads. HEW Link Non-HEW link Submission Slide 9 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Usage Model 1 f: Multi-Media Mesh Backhaul Mesh Portal AP connected to wired network. Mesh Portal AP 1 st Hop 2 nd Hop AP AP 3 rd Hop AP AP Applications are evolving towards more high-quality video intensive use cases for monitoring as well as reporting and interaction. The mesh backhaul, will carry very high traffic loads. HEW Link Non-HEW link Submission Slide 9 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Usage Model 1 f: Multi-Media Mesh Backhaul Pre-Conditions: Mesh topology with one Mesh Portal AP with wired link to a network such as the Internet. An example topology could be up to 3 hops from Mesh Portal AP and 1~10 clients per AP. APs provide mesh routing with simultaneous access for clients. Mesh Portal AP also provide connectivity for clients. Application: Traffic is both outbound and inbound for data, high-quality video and voice. Data may include scheduled hard-drive backups of many PCs. Video is high definition compressed video using, for example, a VHD high compressed video (100 Mbps) or HD video (20 Mbps). High definition voice may be using a codec like GIPS i. PMC-wb or G 729. 1. Environment: Mesh backhaul for hot spot, enterprise, small office/home office, campus, and municipal deployments. Line of Sight as well as NLOS. There is some unmanageable interference in the area. Hops with a 50 to 200 m separation from each other. Submission Traffic Conditions: Mesh Portal AP VHT interface reaches capacity limits with an equal amount of inbound and outbound traffic. Packets may be aggregated. Use Case: 1. User on client devices looks up a program on electronic program guide. 2. User selects a video. 3. High Quality Compressed Video is delivered/uploaded over the wireless network for a period of two hours. 4. User may pause video during 2 hour period then resume watching. 5. Upload/downloading a file while watching the movie is a background task that is not likely to be interrupted. 6. Task is complete when user stops watching the video. 7. The video from multiple clients is aggregated up through the mesh network through the Mesh Portal AP. Slide 10 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Usage Model 1 f: Multi-Media Mesh Backhaul Pre-Conditions: Mesh topology with one Mesh Portal AP with wired link to a network such as the Internet. An example topology could be up to 3 hops from Mesh Portal AP and 1~10 clients per AP. APs provide mesh routing with simultaneous access for clients. Mesh Portal AP also provide connectivity for clients. Application: Traffic is both outbound and inbound for data, high-quality video and voice. Data may include scheduled hard-drive backups of many PCs. Video is high definition compressed video using, for example, a VHD high compressed video (100 Mbps) or HD video (20 Mbps). High definition voice may be using a codec like GIPS i. PMC-wb or G 729. 1. Environment: Mesh backhaul for hot spot, enterprise, small office/home office, campus, and municipal deployments. Line of Sight as well as NLOS. There is some unmanageable interference in the area. Hops with a 50 to 200 m separation from each other. Submission Traffic Conditions: Mesh Portal AP VHT interface reaches capacity limits with an equal amount of inbound and outbound traffic. Packets may be aggregated. Use Case: 1. User on client devices looks up a program on electronic program guide. 2. User selects a video. 3. High Quality Compressed Video is delivered/uploaded over the wireless network for a period of two hours. 4. User may pause video during 2 hour period then resume watching. 5. Upload/downloading a file while watching the movie is a background task that is not likely to be interrupted. 6. Task is complete when user stops watching the video. 7. The video from multiple clients is aggregated up through the mesh network through the Mesh Portal AP. Slide 10 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 July 2013 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 Usage Model 2 d: Manufacturing Floor Automation Pre-Conditions: Multiple WLAN networks are operational in manufacturing space that has hundreds to thousands of individual tasks happening each minute. Many of these tasks require communications. Application: All types of information required to run large manufacturing floor. Large variances in data transfer size, time sensitivity, and reliability exist. Here are some examples: • Streaming of live or CAD video requires high throughput, time sensitive, and reliable transfers: VHD compressed video (100 Mbps, <20 ms jitter/delay, <1. 0 E-7 PER) or HD compressed video (20 Mbps, <50 ms jitter/delay, <1. 0 E-5 PER) or SD compressed video (5 Mbps, <200 ms jitter/delay, <1. 0 E-4 PER) • Voice requires lower bandwidth and time sensitive transfers; reliability is less of a concern: standard quality voice streams (<50 Kbps, <10 ms jitter/delay, <1. 0 E-2 PER). 30 calls yields aggregate bandwidth requirement of 1. 5 Mbps. • Machine-machine communications, robotic material handling requires high reliability but is less time sensitive. • Data loading machines is high bandwidth but low in time sensitivity. Application layer protocols would ensure reliability. Environment: Communications are within a large metallic building with 100 m x 100 m for 1000 devices. 4 WLAN AP’s are separated each other by equal distance of 50 in the building. High reverberation, long propagation distances (10’s~100’s meters), long delay spreads. Constantly moving equipment changing RF propagation channel model. Submission Slide 11 Traffic Conditions: 1000 independent links and data streams with varying Qo. S, reliability, and throughput, requirements. Aggregate data flows range into multiple Gbps requirements for each BSS. Use Case: 1. Multiple systems in factory; starting, stopping, and flowing network traffic in a largely asynchronous environment with the use of multiple WLAN BSS’s. 2. Some data flows have significant integrity requirements (large material-handling machines; cranes, crawlers, etc. ) 3. Some data flows have significant Qo. S requirements (Vo. IP, Video streams, etc. ) 4. Factory is VERY electrically noisy; spark-gap noise (electric motors, etc. ), microwave ovens, other technologies (RFID, RTLS, etc. ), and competing 802. x wireless systems such as 802. 15. 4 g Zig. Bee’s. Minho Cheong (ETRI)
July 2013 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 Usage Model 2 d: Manufacturing Floor Automation Pre-Conditions: Multiple WLAN networks are operational in manufacturing space that has hundreds to thousands of individual tasks happening each minute. Many of these tasks require communications. Application: All types of information required to run large manufacturing floor. Large variances in data transfer size, time sensitivity, and reliability exist. Here are some examples: • Streaming of live or CAD video requires high throughput, time sensitive, and reliable transfers: VHD compressed video (100 Mbps, <20 ms jitter/delay, <1. 0 E-7 PER) or HD compressed video (20 Mbps, <50 ms jitter/delay, <1. 0 E-5 PER) or SD compressed video (5 Mbps, <200 ms jitter/delay, <1. 0 E-4 PER) • Voice requires lower bandwidth and time sensitive transfers; reliability is less of a concern: standard quality voice streams (<50 Kbps, <10 ms jitter/delay, <1. 0 E-2 PER). 30 calls yields aggregate bandwidth requirement of 1. 5 Mbps. • Machine-machine communications, robotic material handling requires high reliability but is less time sensitive. • Data loading machines is high bandwidth but low in time sensitivity. Application layer protocols would ensure reliability. Environment: Communications are within a large metallic building with 100 m x 100 m for 1000 devices. 4 WLAN AP’s are separated each other by equal distance of 50 in the building. High reverberation, long propagation distances (10’s~100’s meters), long delay spreads. Constantly moving equipment changing RF propagation channel model. Submission Slide 11 Traffic Conditions: 1000 independent links and data streams with varying Qo. S, reliability, and throughput, requirements. Aggregate data flows range into multiple Gbps requirements for each BSS. Use Case: 1. Multiple systems in factory; starting, stopping, and flowing network traffic in a largely asynchronous environment with the use of multiple WLAN BSS’s. 2. Some data flows have significant integrity requirements (large material-handling machines; cranes, crawlers, etc. ) 3. Some data flows have significant Qo. S requirements (Vo. IP, Video streams, etc. ) 4. Factory is VERY electrically noisy; spark-gap noise (electric motors, etc. ), microwave ovens, other technologies (RFID, RTLS, etc. ), and competing 802. x wireless systems such as 802. 15. 4 g Zig. Bee’s. Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Usage Model 5 d: Point-to-Point Backhaul HEW Link Submission Slide 12 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Usage Model 5 d: Point-to-Point Backhaul HEW Link Submission Slide 12 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Usage Model 5 d: Point-to-Point Backhaul Pre-Conditions: Networks (wired or wireless) are be connected via a point-to-point link. The individual networks can support hundreds of users with a wide array of traffic requirements that will only be limited by the HEW link capabilities. Environment: Point-to-point link distance is 50 meters to 200 meters. Typically locations are Line of Sight. There is some unmanageable interference around the area. Application: Traffic is bidirectional and is comprised of data, voice, high-quality video and data. Data may include scheduled hard-drive backups of many PCs. High Definition Video is compressed using something like a VHD high compressed video (100 Mbps) or HD video (20 Mbps). High definition voice may be using a codec like GIPS i. PMC-wb or G 729. 1. Each building may hundreds of end users. Consider the case of up to 50 users requiring multi-media connectivity through the point-to-point link at any given moment in time. (50% for VHD, 50% for HD) Aggregate of 50 users = (20 M*25 users + 100 M*25 users) = 3. 0 Gbps throughput. Traffic Conditions: Point-to-point link can carry traffic with multiple Qo. S categories. End of each link is heavily loaded with equal amount of traffic in both directions. Use Case: 1. Two builds are on opposite sides of a rail road track. The building owner has no rights to lay a wire in the ground between buildings. 2. Owner sets up a wireless HEW link between the buildings. 3. Users can now take advantage multi-media applications spanning both buildings. Submission Slide 13 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Usage Model 5 d: Point-to-Point Backhaul Pre-Conditions: Networks (wired or wireless) are be connected via a point-to-point link. The individual networks can support hundreds of users with a wide array of traffic requirements that will only be limited by the HEW link capabilities. Environment: Point-to-point link distance is 50 meters to 200 meters. Typically locations are Line of Sight. There is some unmanageable interference around the area. Application: Traffic is bidirectional and is comprised of data, voice, high-quality video and data. Data may include scheduled hard-drive backups of many PCs. High Definition Video is compressed using something like a VHD high compressed video (100 Mbps) or HD video (20 Mbps). High definition voice may be using a codec like GIPS i. PMC-wb or G 729. 1. Each building may hundreds of end users. Consider the case of up to 50 users requiring multi-media connectivity through the point-to-point link at any given moment in time. (50% for VHD, 50% for HD) Aggregate of 50 users = (20 M*25 users + 100 M*25 users) = 3. 0 Gbps throughput. Traffic Conditions: Point-to-point link can carry traffic with multiple Qo. S categories. End of each link is heavily loaded with equal amount of traffic in both directions. Use Case: 1. Two builds are on opposite sides of a rail road track. The building owner has no rights to lay a wire in the ground between buildings. 2. Owner sets up a wireless HEW link between the buildings. 3. Users can now take advantage multi-media applications spanning both buildings. Submission Slide 13 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
![doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 References [1] 11 -13 -0554 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 References [1] 11 -13 -0554](https://present5.com/presentation/1e48428e1370ad3de6bc2b20fffd192c/image-14.jpg) doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 References [1] 11 -13 -0554 -00 -0 hew-Usage-models-for-HEW [2] 11 -13 -0657 -03 -0 hew-sg-usage-models-andrequirements-liaison-with-wfa [3] 11 -13 -0514 -00 -0 hew-usage-scenarios-and-applications [4] 11 -03 -0802 -23 -000 n-usage-models [5] 11 -09 -0161 -02 -00 ac-802 -11 ac-usage-model-document Submission Slide 14 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 References [1] 11 -13 -0554 -00 -0 hew-Usage-models-for-HEW [2] 11 -13 -0657 -03 -0 hew-sg-usage-models-andrequirements-liaison-with-wfa [3] 11 -13 -0514 -00 -0 hew-usage-scenarios-and-applications [4] 11 -03 -0802 -23 -000 n-usage-models [5] 11 -09 -0161 -02 -00 ac-802 -11 ac-usage-model-document Submission Slide 14 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Appendix Submission Slide 15 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Appendix Submission Slide 15 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Brief Review of 802. 11 ac Usage Models • Category 1: Wireless Display – transfer content between devices a. b. c. d. e. Submission Desktop Display at home or enterprise In room projection from PC to TV at home or projector in conference room within an enterprise In room Gaming – video display from game machine and peer-topeer connectivity for hand-held controllers Streaming from a camcorder to a display (live or stored content) Broadcast TV Field Pick Up Slide 16 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Brief Review of 802. 11 ac Usage Models • Category 1: Wireless Display – transfer content between devices a. b. c. d. e. Submission Desktop Display at home or enterprise In room projection from PC to TV at home or projector in conference room within an enterprise In room Gaming – video display from game machine and peer-topeer connectivity for hand-held controllers Streaming from a camcorder to a display (live or stored content) Broadcast TV Field Pick Up Slide 16 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Brief Review of 802. 11 ac Usage Models • Category 2: Distribution of HDTV and other content a. Lightly compressed video streaming around the entire home (100 s of Mbps) b. Compressed video streaming in a room or throughout a home c. Intra-Large-Vehicle (e. g. airplane) Applications • • d. e. Submission Video streaming of 30 -40 movies, 100 s of TV channels to up to 300 people with individual play/rewind control over each stream Streams are ~5 Mbps each. 300*5 Mbps=1. 5 Gbps Wireless Networking for Office Remote Medical Assistance via Wireless Networks Slide 17 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Brief Review of 802. 11 ac Usage Models • Category 2: Distribution of HDTV and other content a. Lightly compressed video streaming around the entire home (100 s of Mbps) b. Compressed video streaming in a room or throughout a home c. Intra-Large-Vehicle (e. g. airplane) Applications • • d. e. Submission Video streaming of 30 -40 movies, 100 s of TV channels to up to 300 people with individual play/rewind control over each stream Streams are ~5 Mbps each. 300*5 Mbps=1. 5 Gbps Wireless Networking for Office Remote Medical Assistance via Wireless Networks Slide 17 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Brief Review of 802. 11 ac Usage Models • Category 3: Rapid Upload and Download of large files to/from server a. Rapid Sync-n-Go file transfer – camera to PC (10 s of MB per pic), video kiosk b. Picture-by-picture viewing - displaying digital pictures (jpegs, raw files) from a remote storage device to laptop or TV c. Airplane docking – as airplane pulls up to the boarding gate: • plane down loads sensor (mechanic info, flight performance, maintenance) & flight information (e. g. crew, passenger info, flight plan) • plane uploads next flight information and new videos d. Movie Content Download to Car as it pulls into garage e. Police / Surveillance Car Upload • Submission Upload several 10 s of GB of data (Video Surveillance footage) from surveillance car to content server police station Slide 18 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Brief Review of 802. 11 ac Usage Models • Category 3: Rapid Upload and Download of large files to/from server a. Rapid Sync-n-Go file transfer – camera to PC (10 s of MB per pic), video kiosk b. Picture-by-picture viewing - displaying digital pictures (jpegs, raw files) from a remote storage device to laptop or TV c. Airplane docking – as airplane pulls up to the boarding gate: • plane down loads sensor (mechanic info, flight performance, maintenance) & flight information (e. g. crew, passenger info, flight plan) • plane uploads next flight information and new videos d. Movie Content Download to Car as it pulls into garage e. Police / Surveillance Car Upload • Submission Upload several 10 s of GB of data (Video Surveillance footage) from surveillance car to content server police station Slide 18 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Brief Review of 802. 11 ac Usage Models • Category 4: Backhaul a. Multi-Media Mesh Backhaul • • • b. Submission Hotspot Enterprise Small Office or Home Campus-wide deployments Municipal deployments Point-to-Point Backhaul Slide 19 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Brief Review of 802. 11 ac Usage Models • Category 4: Backhaul a. Multi-Media Mesh Backhaul • • • b. Submission Hotspot Enterprise Small Office or Home Campus-wide deployments Municipal deployments Point-to-Point Backhaul Slide 19 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
 doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Brief Review of 802. 11 ac Usage Models • Category 5: Outdoor Campus / Auditorium deployments a. b. • Video Demos or Tele-presence in Auditoriums/Lecture Halls Public Safety Mesh Category 6: Manufacturing Floor Automation – Factory floor within large metallic buildings. Applications have a large variance in data transfer size, time sensitivity, and reliability. Submission Slide 20 Minho Cheong (ETRI)
doc. : IEEE 11 -13/0836 r 0 July 2013 Brief Review of 802. 11 ac Usage Models • Category 5: Outdoor Campus / Auditorium deployments a. b. • Video Demos or Tele-presence in Auditoriums/Lecture Halls Public Safety Mesh Category 6: Manufacturing Floor Automation – Factory floor within large metallic buildings. Applications have a large variance in data transfer size, time sensitivity, and reliability. Submission Slide 20 Minho Cheong (ETRI)


