4d8d744fc8560e45d8411aa901ddf3fb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Do Lifestyle Variables Help Predict Consumer Confidence? Dr. Michael A. Merz San Jose State University Global Conference on Business and Finance, Kailua-Kona, Hawaii January 03, 2018

• Introduction • The Meaning and Importance of Consumer Confidence • Why is a Micro-Level Perspective on Consumer Confidence Important? • Antecedents to Consumer Confidence • Methodology • Results • Conclusion

Introduction • Anticipating future consumer spending and saving behavior is key in today’s marketplace (e. g. , Lawson et al. 2001). • Early predictions of consumer consumption behavior focused solely on objective economic variables (e. g. , income, interest rate, inflation rate). • Katona (1951, 1960) suggested that consumer expenditures depend on consumers’ ability to buy and on their willingness to buy -> more subjective, psychological factors (support for this reasoning can also be Development e. g. , Batra and Ray 1986). found in marketing; of several indexes that aim at measuring consumer confidence/sentiment as an indication of the future course of the national economy (Curtin 1982; Linden 1982; Roper 1982).

Introduction While several (good) indexes of consumer confidence exist (e. g. , The University of Michigan’s Survey Research Center’s ICS or The Conference Board’s CCI), prior research suggests that an integration of psychographic or lifestyle variables may help understand the undercurrents and dynamics of consumer confidence (e. g. , Andreasen 1984; Didow et al. 1983; Iguzquiza 1996; Lawson et al. 2001; Wells 1975). Our purpose: • Develop a consumer confidence index that integrates lifestyle variables; • Demonstrate that this index helps understand the undercurrents and dynamics of consumer confidence. • Note: We do not claim that our index is better than existing indexes!

Meaning and Importance of Consumer Confidence • Consumer confidence (CC) is the general mood of consumers, ranging from optimism and confidence to pessimism and uncertainty (Curtin 2002; Mc. Whinney 2005). • In marketing and consumer behavior, CC has been found to be an important determinant of buying and consumption behavior (e. g. , Howard and Sheth 1969; Laroche and Kim 1995; Laroche et al. 1996; White et al. 1991; Barone, Miniard, and Romeo 2000). • Important: CC indexes do not measure the absolute level of CC at any given time; rather, they are intended to measure change (Curtin 1982) and as such the relative degree of optimism on the state of the economy (Mc. Whinney 2005).
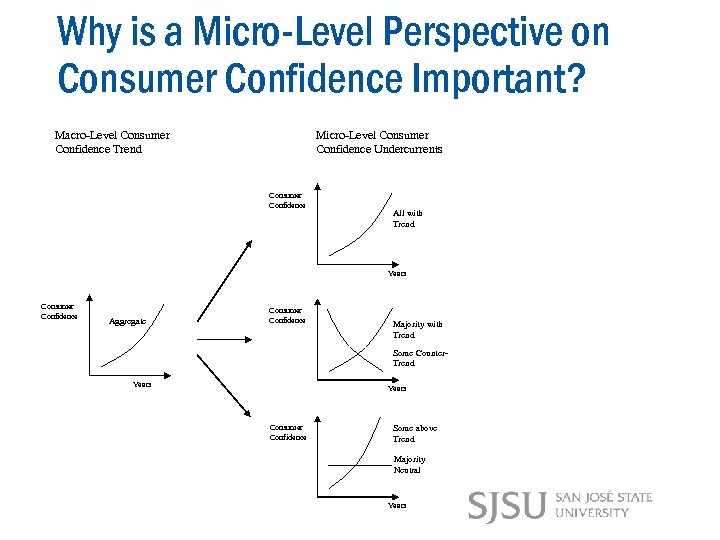
Why is a Micro-Level Perspective on Consumer Confidence Important? Macro-Level Consumer Confidence Trend Micro-Level Consumer Confidence Undercurrents Consumer Confidence All with Trend Years Consumer Confidence Aggregate Consumer Confidence Majority with Trend Some Counter. Trend Years Consumer Confidence Some above Trend Majority Neutral Years
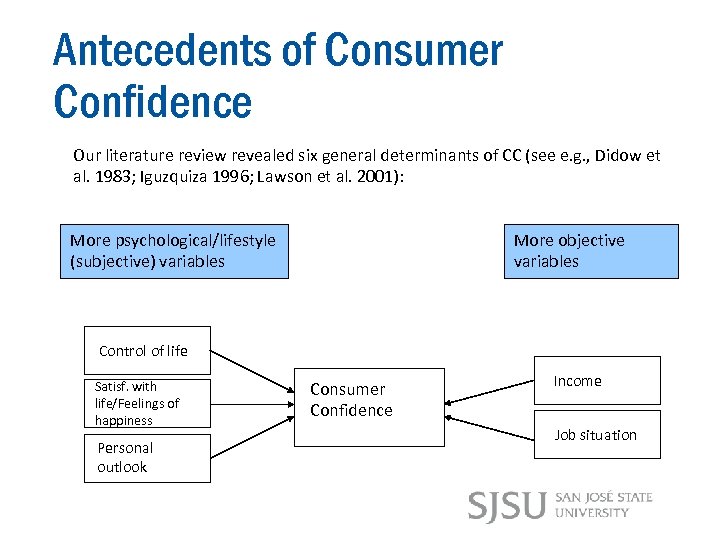
Antecedents of Consumer Confidence Our literature review revealed six general determinants of CC (see e. g. , Didow et al. 1983; Iguzquiza 1996; Lawson et al. 2001): More psychological/lifestyle (subjective) variables More objective variables Control of life Satisf. with life/Feelings of happiness Personal outlook Consumer Confidence Income Job situation

Methodology • Secondary data analysis • 2001 DDB Life Style Study • annual survey conducted by DDB Worldwide • survey consists of 830 different items • mail panel answered by more than 3, 000 people • response rate > 80% • survey findings representative of US consumers • The use of the DDB items offers several advantages (e. g. , only items included that highly correlate with consumer behavior)
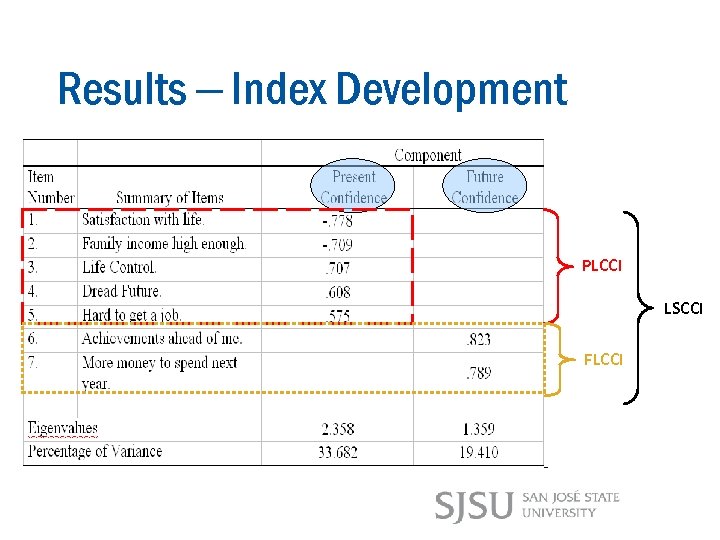
Results – Index Development PLCCI LSCCI FLCCI
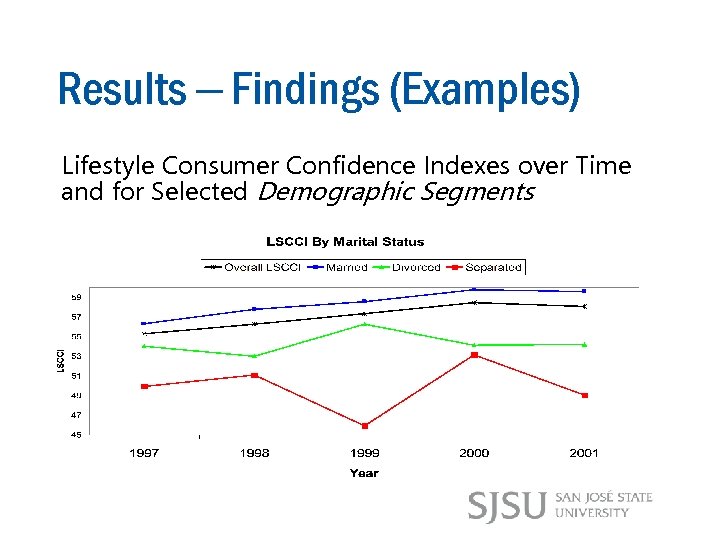
Results – Findings (Examples) Lifestyle Consumer Confidence Indexes over Time and for Selected Demographic Segments
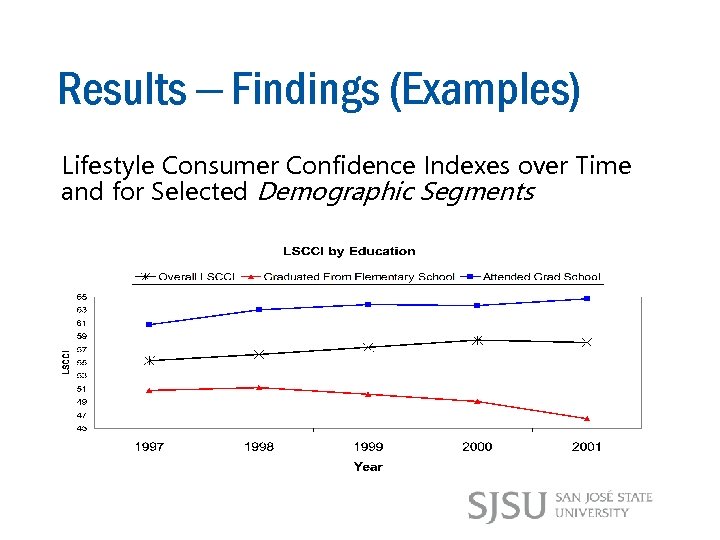
Results – Findings (Examples) Lifestyle Consumer Confidence Indexes over Time and for Selected Demographic Segments
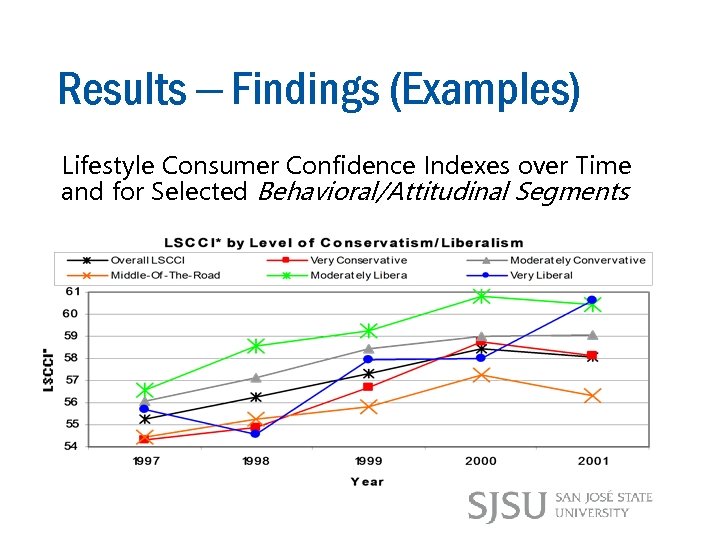
Results – Findings (Examples) Lifestyle Consumer Confidence Indexes over Time and for Selected Behavioral/Attitudinal Segments
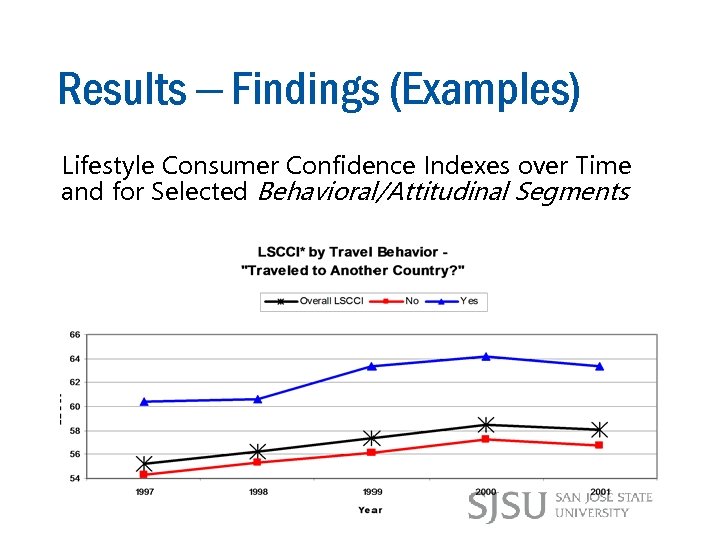
Results – Findings (Examples) Lifestyle Consumer Confidence Indexes over Time and for Selected Behavioral/Attitudinal Segments
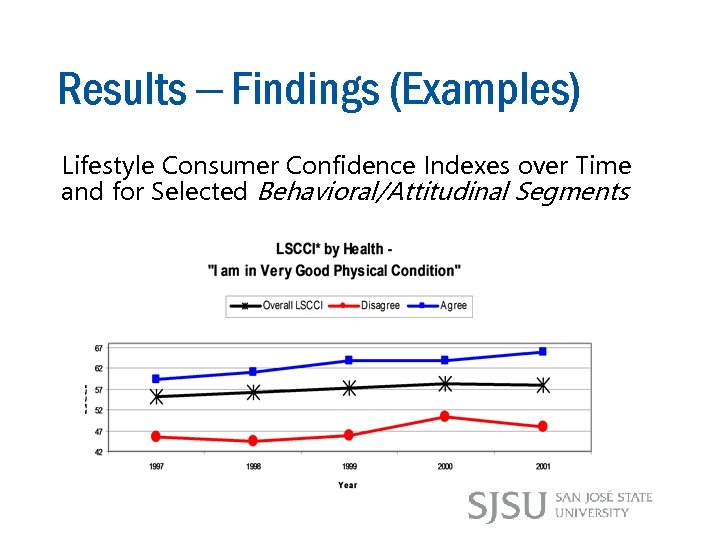
Results – Findings (Examples) Lifestyle Consumer Confidence Indexes over Time and for Selected Behavioral/Attitudinal Segments
Conclusion CC varies across different segments. -> track undercurrents Across-segment differences over time may take on different paths. -> track dynamics Existence of very turbulent segments -> track unstable segments whose levels of confidence fluctuate from year to year. The LSCCI helps discover challenging segments that: (1) are low in CC in a particular year, (2) demonstrate a continuously decreasing path, and (3) are very unstable over time. Important for several public policy agencies (e. g. , Federal Reserve System).
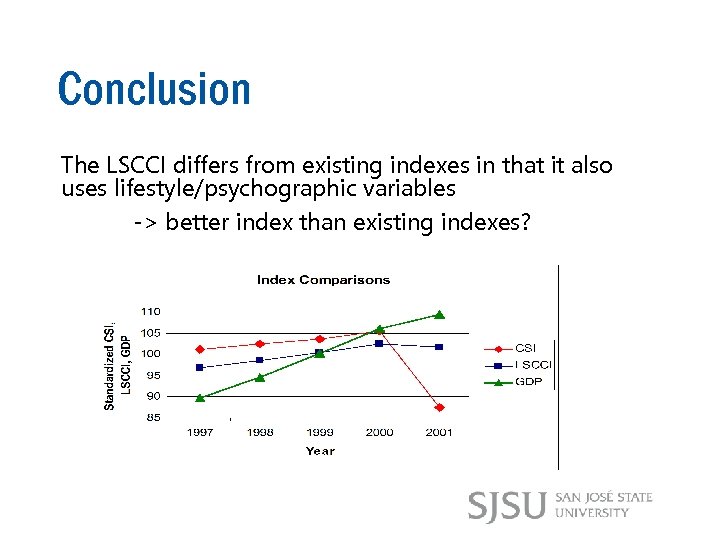
Conclusion The LSCCI differs from existing indexes in that it also uses lifestyle/psychographic variables -> better index than existing indexes?

Thank you for your attention! ?
4d8d744fc8560e45d8411aa901ddf3fb.ppt