91e4beffbb3e46c68c699861dd6961fc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Do. DAF Maintenance Update (v 2. 03) 5 Jan 2012 Do. DAF Team
Do. DAF Maintenance Update (v 2. 03) 5 Jan 2012 Do. DAF Team
 Outline • Recap of the Do. DAF Configuration Management Process • CM Plan (CMP) • ASRG, FAC, and Do. DAF-DM 2 WG • CM Processes Overview • CM “Business” Rules • Changes for 2. 03 • Formal coordination review plan 2
Outline • Recap of the Do. DAF Configuration Management Process • CM Plan (CMP) • ASRG, FAC, and Do. DAF-DM 2 WG • CM Processes Overview • CM “Business” Rules • Changes for 2. 03 • Formal coordination review plan 2
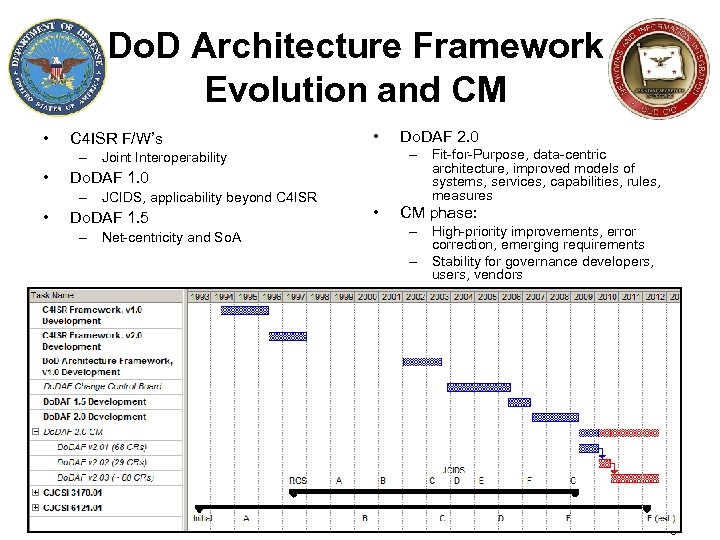 Do. D Architecture Framework Evolution and CM • C 4 ISR F/W’s • – Fit-for-Purpose, data-centric architecture, improved models of systems, services, capabilities, rules, measures – Joint Interoperability • Do. DAF 1. 0 – JCIDS, applicability beyond C 4 ISR • Do. DAF 1. 5 – Net-centricity and So. A Do. DAF 2. 0 • CM phase: – High-priority improvements, error correction, emerging requirements – Stability for governance developers, users, vendors 3
Do. D Architecture Framework Evolution and CM • C 4 ISR F/W’s • – Fit-for-Purpose, data-centric architecture, improved models of systems, services, capabilities, rules, measures – Joint Interoperability • Do. DAF 1. 0 – JCIDS, applicability beyond C 4 ISR • Do. DAF 1. 5 – Net-centricity and So. A Do. DAF 2. 0 • CM phase: – High-priority improvements, error correction, emerging requirements – Stability for governance developers, users, vendors 3
 Do. DAF is Under Formal CM • Configuration Identification • Organizational roles, responsibilities, and interactions • Do. DAF-DM 2 CM Processes and Procedures • Do. DAF-DM 2 CM Business Rules • Configuration Status Accounting 4
Do. DAF is Under Formal CM • Configuration Identification • Organizational roles, responsibilities, and interactions • Do. DAF-DM 2 CM Processes and Procedures • Do. DAF-DM 2 CM Business Rules • Configuration Status Accounting 4
 Configuration Identification 1. Do. DAF Viewpoint Definitions. Conventions for the construction, interpretation and use of architecture views and associated architecture models. 2. Do. DAF Model Specifications from which architecture views representing an architecture are composed. 3. Glossary. Defines all non-demotic terms used in Do. DAF and the Do. DAF Meta Model. 4. DM 2. Consists of a Conceptual Data Model (CDM) diagram and narrative description, a Logical Data Model (LDM) in an UML file adapted to IDEAS and a narrative description, and Physical Exchange Specification (PES) XML Schema Descriptions. • NOTE that introductory, tutorial, document outlining, and web navigation documentation is considered under control of the Do. DAF Journal editorial team and not subject to formal CM in scope of this plan. 5
Configuration Identification 1. Do. DAF Viewpoint Definitions. Conventions for the construction, interpretation and use of architecture views and associated architecture models. 2. Do. DAF Model Specifications from which architecture views representing an architecture are composed. 3. Glossary. Defines all non-demotic terms used in Do. DAF and the Do. DAF Meta Model. 4. DM 2. Consists of a Conceptual Data Model (CDM) diagram and narrative description, a Logical Data Model (LDM) in an UML file adapted to IDEAS and a narrative description, and Physical Exchange Specification (PES) XML Schema Descriptions. • NOTE that introductory, tutorial, document outlining, and web navigation documentation is considered under control of the Do. DAF Journal editorial team and not subject to formal CM in scope of this plan. 5
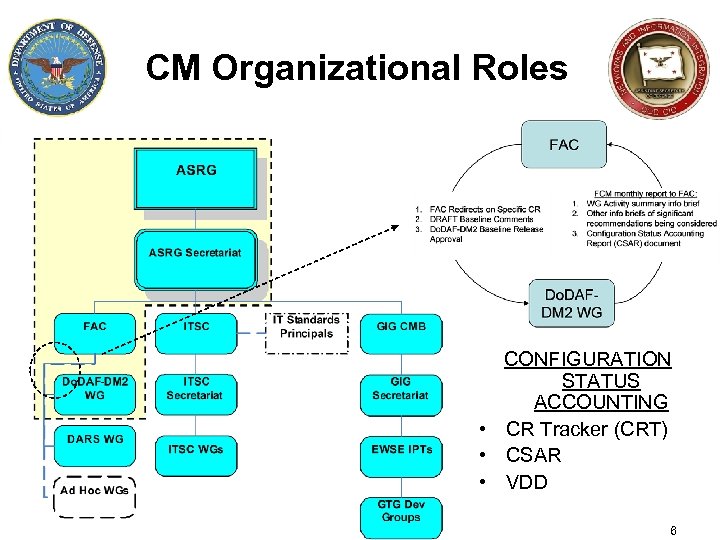 CM Organizational Roles CONFIGURATION STATUS ACCOUNTING • CR Tracker (CRT) • CSAR • VDD 6
CM Organizational Roles CONFIGURATION STATUS ACCOUNTING • CR Tracker (CRT) • CSAR • VDD 6
 CMP Processes • CR Processing and Configuration Status Reporting • Baseline Process 7
CMP Processes • CR Processing and Configuration Status Reporting • Baseline Process 7
 CMP Business Rules 1. Terms and Definitions 2. Aliases 3. Core Process Requirement 4. Aggregation Rule 5. Subtype Rule 6. Typed Relationships 7. Attributes and Properties 8. Do. DAF Model Specification 9. Information Pedigree 10. Security Classification Marking 8
CMP Business Rules 1. Terms and Definitions 2. Aliases 3. Core Process Requirement 4. Aggregation Rule 5. Subtype Rule 6. Typed Relationships 7. Attributes and Properties 8. Do. DAF Model Specification 9. Information Pedigree 10. Security Classification Marking 8
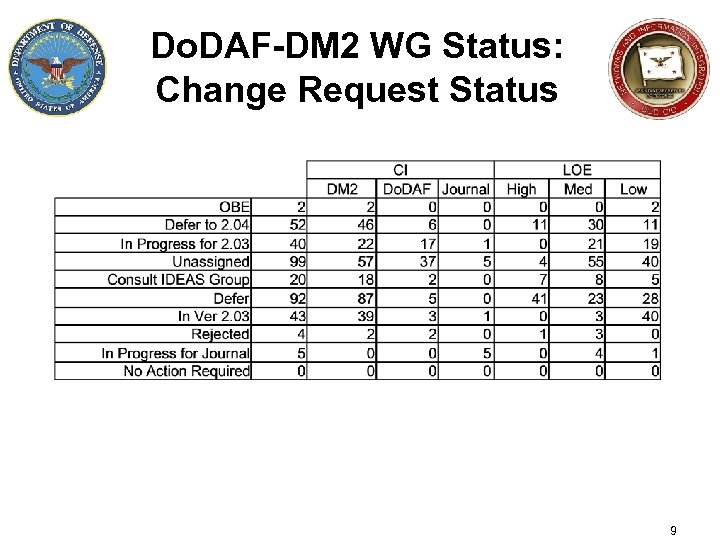 Do. DAF-DM 2 WG Status: Change Request Status 9
Do. DAF-DM 2 WG Status: Change Request Status 9
 Packaging for Formal CM • Vol. I – DM 2 Conceptual Model – Do. DAF Viewpoints & Models • Vol. II – – DM 2 Logical DM Do. DAF Model Specs Do. DAF Glossary Sparx. EAP DM 2 • Vol. III – DM 2 Physical DM: PES – Sparx. EAP IDEAS Foundation 10
Packaging for Formal CM • Vol. I – DM 2 Conceptual Model – Do. DAF Viewpoints & Models • Vol. II – – DM 2 Logical DM Do. DAF Model Specs Do. DAF Glossary Sparx. EAP DM 2 • Vol. III – DM 2 Physical DM: PES – Sparx. EAP IDEAS Foundation 10
 Changes for v 2. 03 • TECHEDITS • Normative parts separated from informative parts – Normative parts subject to formal coordination with Do. D Components – Informative parts moved to Do. DAF Journal • Document + Webpages • Major DM 2 CR’s: – Rules and Desired Effects: 1. Their Descriptions are produced by rule and goal-setting authorities 2. They are consumed by Activities (ala Controls in IDEF 0) 3. Conforming Activities are subtypes – Information resource flow was simplified into flatter type structure so it would be logically correct and consistent with other Resource Flows, e. g. , • Aircraft 123 on my scope Î {all reports on A/C 123} Ì {TADIL-J 3. 2 msg} exists spatio-temporally usable in, e. g. , SV-6 a set – Capability made a subtype of Property so that it is the set of Tasks performed under Conditions that meet certain performance standards (Measures) • Makes Capability comparison and dependencies more direct (simple set operations) – Distinguished that Guidance influences Activity from Rules that control Activity – Added So. A Joint Action concept – Continued work on distinguishing Roles (within scope of EA) from types of Persons (outside scope of EA) 11
Changes for v 2. 03 • TECHEDITS • Normative parts separated from informative parts – Normative parts subject to formal coordination with Do. D Components – Informative parts moved to Do. DAF Journal • Document + Webpages • Major DM 2 CR’s: – Rules and Desired Effects: 1. Their Descriptions are produced by rule and goal-setting authorities 2. They are consumed by Activities (ala Controls in IDEF 0) 3. Conforming Activities are subtypes – Information resource flow was simplified into flatter type structure so it would be logically correct and consistent with other Resource Flows, e. g. , • Aircraft 123 on my scope Î {all reports on A/C 123} Ì {TADIL-J 3. 2 msg} exists spatio-temporally usable in, e. g. , SV-6 a set – Capability made a subtype of Property so that it is the set of Tasks performed under Conditions that meet certain performance standards (Measures) • Makes Capability comparison and dependencies more direct (simple set operations) – Distinguished that Guidance influences Activity from Rules that control Activity – Added So. A Joint Action concept – Continued work on distinguishing Roles (within scope of EA) from types of Persons (outside scope of EA) 11
 Marine Corps - Led TECHEDIT Team • Marine Corps commented on many incorrect, ambiguous, and inconsistent statements – After working on this for several meetings, the WG requested a rewrite rather than line-by-line fixes • SPAWAR noted many undefined and inconsistent terms in the Do. DAF model • A long-standing CR asked for a DM 2 diagram for each Do. DAF model as in Do. DAF 1. x documents 12
Marine Corps - Led TECHEDIT Team • Marine Corps commented on many incorrect, ambiguous, and inconsistent statements – After working on this for several meetings, the WG requested a rewrite rather than line-by-line fixes • SPAWAR noted many undefined and inconsistent terms in the Do. DAF model • A long-standing CR asked for a DM 2 diagram for each Do. DAF model as in Do. DAF 1. x documents 12
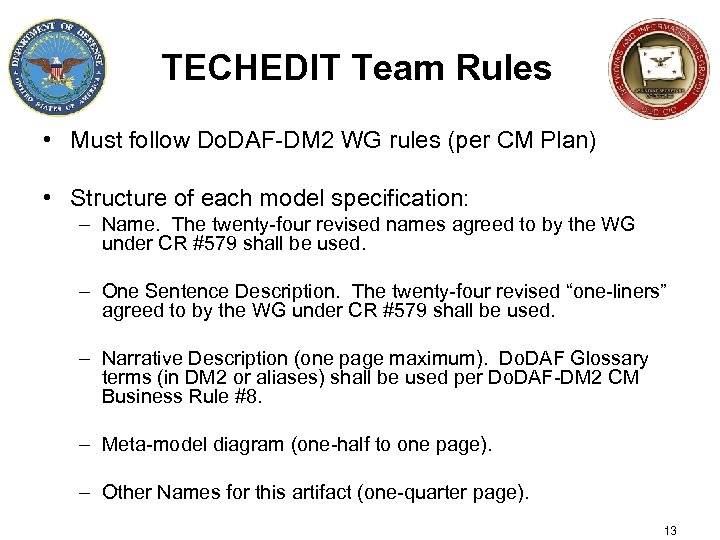 TECHEDIT Team Rules • Must follow Do. DAF-DM 2 WG rules (per CM Plan) • Structure of each model specification: – Name. The twenty-four revised names agreed to by the WG under CR #579 shall be used. – One Sentence Description. The twenty-four revised “one-liners” agreed to by the WG under CR #579 shall be used. – Narrative Description (one page maximum). Do. DAF Glossary terms (in DM 2 or aliases) shall be used per Do. DAF-DM 2 CM Business Rule #8. – Meta-model diagram (one-half to one page). – Other Names for this artifact (one-quarter page). 13
TECHEDIT Team Rules • Must follow Do. DAF-DM 2 WG rules (per CM Plan) • Structure of each model specification: – Name. The twenty-four revised names agreed to by the WG under CR #579 shall be used. – One Sentence Description. The twenty-four revised “one-liners” agreed to by the WG under CR #579 shall be used. – Narrative Description (one page maximum). Do. DAF Glossary terms (in DM 2 or aliases) shall be used per Do. DAF-DM 2 CM Business Rule #8. – Meta-model diagram (one-half to one page). – Other Names for this artifact (one-quarter page). 13
 OV-2 As-Is Text is lengthy… but doesn’t actually ever get around to unambiguously specifying content for an OV-2 model… 14
OV-2 As-Is Text is lengthy… but doesn’t actually ever get around to unambiguously specifying content for an OV-2 model… 14
 TECHEDIT Example (pg 1 of 2) SHALLS & MAYS 15
TECHEDIT Example (pg 1 of 2) SHALLS & MAYS 15
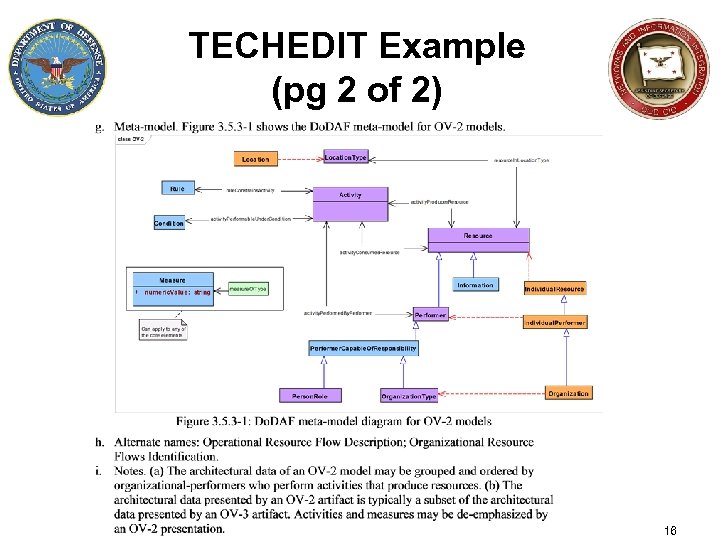 TECHEDIT Example (pg 2 of 2) 16
TECHEDIT Example (pg 2 of 2) 16
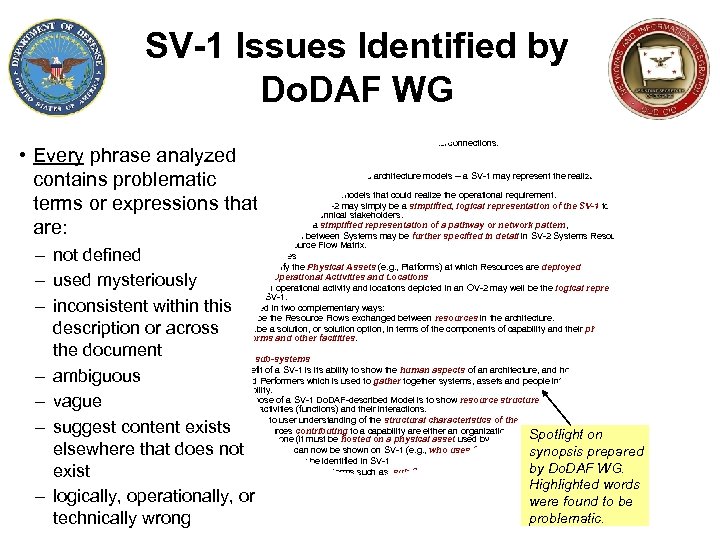 SV-1 Issues Identified by Do. DAF WG • • • Name: Systems Interface Description One liner: The identification of systems, system items, and their interconnections. Description: – composition and interaction of Systems – links together the operational and systems architecture models -- a SV-1 may represent the realization of a requirement specified in an OV-2 – there may be many alternative SV models that could realize the operational requirement. – in an “As-Is” architecture, the OV-2 may simply be a simplified, logical representation of the SV-1 to allow communication of key Resource Flows to non-technical stakeholders. – A System Resource Flow is a simplified representation of a pathway or network pattern, – Note that Resource Flows between Systems may be further specified in detail in SV-2 Systems Resource Flow Description and SV-6 Systems Resource Flow Matrix. – Sub-System assemblies – SV-1 may also identify the Physical Assets (e. g. , Platforms) at which Resources are deployed – optionally overlay Operational Activities and Locations – In many cases, an operational activity and locations depicted in an OV-2 may well be the logical representation of the resource that is shown in SV-1. – The SV-1 is used in two complementary ways: • Describe the Resource Flows exchanged between resources in the architecture. • Describe a solution, or solution option, in terms of the components of capability and their physical integration on platforms and other facilities. Detailed Description: – Systems and sub-systems – The real benefit of a SV-1 is its ability to show the human aspects of an architecture, and how these interact with Systems. – Capability and Performers which is used to gather together systems, assets and people into a configuration, which can meet a specific capability. – A primary purpose of a SV-1 Do. DAF-described Model is to show resource structure, i. e. , identify the primary sub-systems, performer and activities (functions) and their interactions. – SV-1 contributes to user understanding of the structural characteristics of the capability. – The physical resources contributing to a capability are either an organizational resource or a physical asset, i. e. , a system Spotlight on cannot contribute alone (it must be hosted on a physical asset used by an organizational resource of both). – Organizational aspects can now be shown on SV-1 (e. g. , who uses System). synopsis prepared – Resource structures may be identified in SV-1 by terms often WG. – Do. DAF does not specifically use terms such as, sub-System and component as these Do. DAF denote a position relative to a structural hierarchy. Highlighted words – Any System may combine hardware and software or these can be treated as separate (sub) Systems. Do. DAF V 2. 0 includes human factors (as Personnel Types and a type of Performer). Should an architectwere describe ato be which has human wish to found System elements, then Systems, Personnel Types and Performers should be used to wrap the human and system elements together. – optionally be annotated with Operational Activities, Capabilities, and/or Locations originally specified in OV-2 problematic. • Every phrase analyzed contains problematic terms or expressions that are: – not defined – used mysteriously – inconsistent within this description or across • the document – ambiguous – vague – suggest content exists elsewhere that does not exist – logically, operationally, or technically wrong 17
SV-1 Issues Identified by Do. DAF WG • • • Name: Systems Interface Description One liner: The identification of systems, system items, and their interconnections. Description: – composition and interaction of Systems – links together the operational and systems architecture models -- a SV-1 may represent the realization of a requirement specified in an OV-2 – there may be many alternative SV models that could realize the operational requirement. – in an “As-Is” architecture, the OV-2 may simply be a simplified, logical representation of the SV-1 to allow communication of key Resource Flows to non-technical stakeholders. – A System Resource Flow is a simplified representation of a pathway or network pattern, – Note that Resource Flows between Systems may be further specified in detail in SV-2 Systems Resource Flow Description and SV-6 Systems Resource Flow Matrix. – Sub-System assemblies – SV-1 may also identify the Physical Assets (e. g. , Platforms) at which Resources are deployed – optionally overlay Operational Activities and Locations – In many cases, an operational activity and locations depicted in an OV-2 may well be the logical representation of the resource that is shown in SV-1. – The SV-1 is used in two complementary ways: • Describe the Resource Flows exchanged between resources in the architecture. • Describe a solution, or solution option, in terms of the components of capability and their physical integration on platforms and other facilities. Detailed Description: – Systems and sub-systems – The real benefit of a SV-1 is its ability to show the human aspects of an architecture, and how these interact with Systems. – Capability and Performers which is used to gather together systems, assets and people into a configuration, which can meet a specific capability. – A primary purpose of a SV-1 Do. DAF-described Model is to show resource structure, i. e. , identify the primary sub-systems, performer and activities (functions) and their interactions. – SV-1 contributes to user understanding of the structural characteristics of the capability. – The physical resources contributing to a capability are either an organizational resource or a physical asset, i. e. , a system Spotlight on cannot contribute alone (it must be hosted on a physical asset used by an organizational resource of both). – Organizational aspects can now be shown on SV-1 (e. g. , who uses System). synopsis prepared – Resource structures may be identified in SV-1 by terms often WG. – Do. DAF does not specifically use terms such as, sub-System and component as these Do. DAF denote a position relative to a structural hierarchy. Highlighted words – Any System may combine hardware and software or these can be treated as separate (sub) Systems. Do. DAF V 2. 0 includes human factors (as Personnel Types and a type of Performer). Should an architectwere describe ato be which has human wish to found System elements, then Systems, Personnel Types and Performers should be used to wrap the human and system elements together. – optionally be annotated with Operational Activities, Capabilities, and/or Locations originally specified in OV-2 problematic. • Every phrase analyzed contains problematic terms or expressions that are: – not defined – used mysteriously – inconsistent within this description or across • the document – ambiguous – vague – suggest content exists elsewhere that does not exist – logically, operationally, or technically wrong 17
 SV-1 Content Guidance for Template and Descriptions • Several distinct pieces are currently described. They should be refactored: 1. SV-1 a Interface Description. The SV-1 a shows interfaces (Resource Flows) between Systems, Services, and/or Person Types. 2. SV-1 b Perfomer Configuration Diagram. Interface Description plus composition (whole-parts) of Resources involved. If Locations are involved in the configuration, relationships to Resources. 3. SV-1 c Functional Allocation. Activities (System Functions) performed by Systems, Services, and Person Types. 4. SV-1 d Organizational Resources. Shows Resources that are part of (wholepart) Organizations. 5. SV-1 e Organizational Dependencies. Shows Organizations whose Activities are reified by System Functions (Activities) performed by Performer Configurations. 6. All views should show traceability to higher-order reifications, other views that constitute requirements, and/or other non-view requirements. This should be restated for just about every model. 7. Systems relationship to Capabilities – already in SV-5. 18
SV-1 Content Guidance for Template and Descriptions • Several distinct pieces are currently described. They should be refactored: 1. SV-1 a Interface Description. The SV-1 a shows interfaces (Resource Flows) between Systems, Services, and/or Person Types. 2. SV-1 b Perfomer Configuration Diagram. Interface Description plus composition (whole-parts) of Resources involved. If Locations are involved in the configuration, relationships to Resources. 3. SV-1 c Functional Allocation. Activities (System Functions) performed by Systems, Services, and Person Types. 4. SV-1 d Organizational Resources. Shows Resources that are part of (wholepart) Organizations. 5. SV-1 e Organizational Dependencies. Shows Organizations whose Activities are reified by System Functions (Activities) performed by Performer Configurations. 6. All views should show traceability to higher-order reifications, other views that constitute requirements, and/or other non-view requirements. This should be restated for just about every model. 7. Systems relationship to Capabilities – already in SV-5. 18
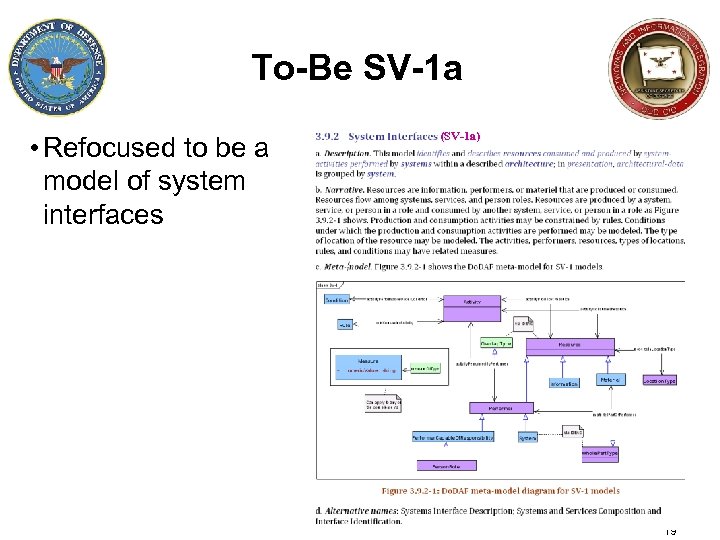 To-Be SV-1 a • Refocused to be a model of system interfaces (SV-1 a) 19
To-Be SV-1 a • Refocused to be a model of system interfaces (SV-1 a) 19
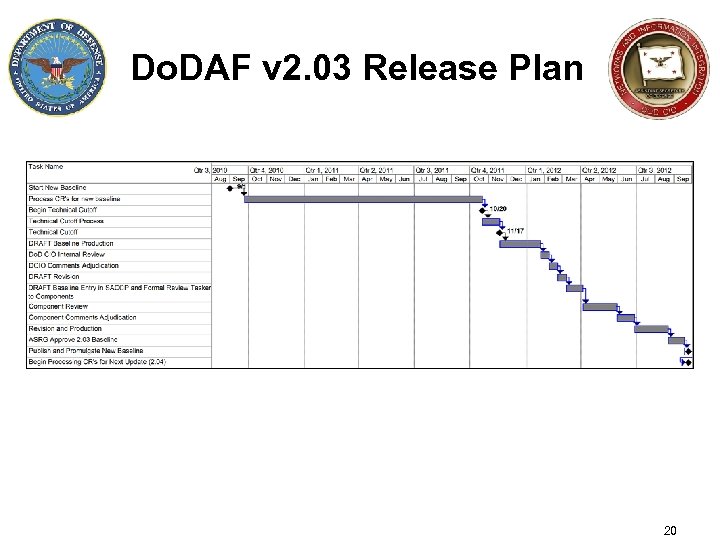 Do. DAF v 2. 03 Release Plan 20
Do. DAF v 2. 03 Release Plan 20
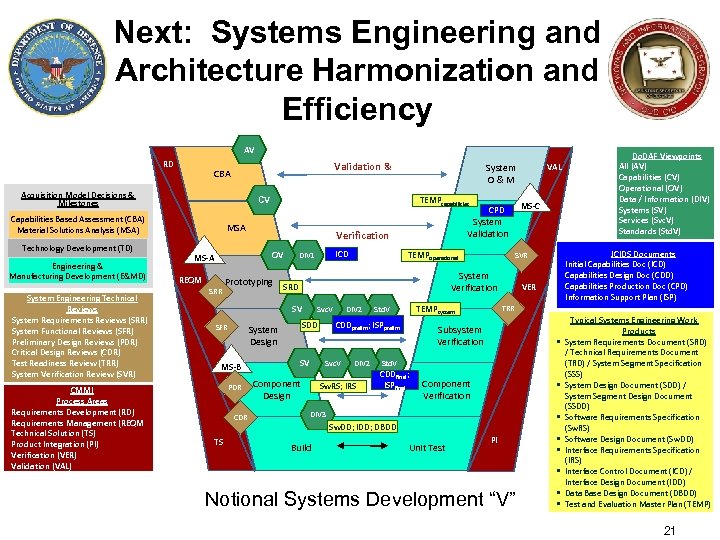 Next: Systems Engineering and Architecture Harmonization and Efficiency AV RD Validation & CBA Acquisition Model Decisions & Milestones Engineering & Manufacturing Development (E&MD) System Engineering Technical Reviews System Requirements Reviews (SRR) System Functional Reviews (SFR) Preliminary Design Reviews (PDR) Critical Design Reviews (CDR) Test Readiness Review (TRR) System Verification Review (SVR) CMMI Process Areas Requirements Development (RD) Requirements Management (REQM Technical Solution (TS) Product Integration (PI) Verification (VER) Validation (VAL) TEMPcapabilities CV Capabilities Based Assessment (CBA) Material Solutions Analysis (MSA) Technology Development (TD) System O&M MSA REQM SRR Prototyping PDR CDR TS Svc. V Component Design TEMPsystem Std. V CDDprelim; ISPprelim SDD SV DIV 2 Sw. RS; IRS VER TRR Subsystem Verification • Std. V CDDfinal; ISPfinal Component Verification • DIV 3 • Sw. DD; IDD; DBDD Build Unit Test Do. DAF Viewpoints All (AV) Capabilities (CV) Operational (OV) Data / Information (DIV) Systems (SV) Services (Svc. V) Standards (Std. V) JCIDS Documents Initial Capabilities Doc (ICD) Capabilities Design Doc (CDD) Capabilities Production Doc (CPD) Information Support Plan (ISP) SVR System Verification System Design MS-B TEMPoperational SRD SV SFR ICD DIV 1 MS-C CPD System Validation Verification OV MS-A VAL PI • • • Notional Systems Development “V” • • Typical Systems Engineering Work Products System Requirements Document (SRD) / Technical Requirements Document (TRD) / System Segment Specification (SSS) System Design Document (SDD) / System Segment Design Document (SSDD) Software Requirements Specification (Sw. RS) Software Design Document (Sw. DD) Interface Requirements Specification (IRS) Interface Control Document (ICD) / Interface Design Document (IDD) Data Base Design Document (DBDD) Test and Evaluation Master Plan (TEMP) 21
Next: Systems Engineering and Architecture Harmonization and Efficiency AV RD Validation & CBA Acquisition Model Decisions & Milestones Engineering & Manufacturing Development (E&MD) System Engineering Technical Reviews System Requirements Reviews (SRR) System Functional Reviews (SFR) Preliminary Design Reviews (PDR) Critical Design Reviews (CDR) Test Readiness Review (TRR) System Verification Review (SVR) CMMI Process Areas Requirements Development (RD) Requirements Management (REQM Technical Solution (TS) Product Integration (PI) Verification (VER) Validation (VAL) TEMPcapabilities CV Capabilities Based Assessment (CBA) Material Solutions Analysis (MSA) Technology Development (TD) System O&M MSA REQM SRR Prototyping PDR CDR TS Svc. V Component Design TEMPsystem Std. V CDDprelim; ISPprelim SDD SV DIV 2 Sw. RS; IRS VER TRR Subsystem Verification • Std. V CDDfinal; ISPfinal Component Verification • DIV 3 • Sw. DD; IDD; DBDD Build Unit Test Do. DAF Viewpoints All (AV) Capabilities (CV) Operational (OV) Data / Information (DIV) Systems (SV) Services (Svc. V) Standards (Std. V) JCIDS Documents Initial Capabilities Doc (ICD) Capabilities Design Doc (CDD) Capabilities Production Doc (CPD) Information Support Plan (ISP) SVR System Verification System Design MS-B TEMPoperational SRD SV SFR ICD DIV 1 MS-C CPD System Validation Verification OV MS-A VAL PI • • • Notional Systems Development “V” • • Typical Systems Engineering Work Products System Requirements Document (SRD) / Technical Requirements Document (TRD) / System Segment Specification (SSS) System Design Document (SDD) / System Segment Design Document (SSDD) Software Requirements Specification (Sw. RS) Software Design Document (Sw. DD) Interface Requirements Specification (IRS) Interface Control Document (ICD) / Interface Design Document (IDD) Data Base Design Document (DBDD) Test and Evaluation Master Plan (TEMP) 21
 Questions? 22
Questions? 22


