e994a4785a387859b544a19b12b5fbbc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 DO-254 Trends and Efficient Methods for Hardware Verification MAPLD 2009 Presentation Session D: Design and Verification Tools and Methodologies
DO-254 Trends and Efficient Methods for Hardware Verification MAPLD 2009 Presentation Session D: Design and Verification Tools and Methodologies
 Agenda • Introduction • Challenges with Verification in Hardware for • • DO-254/CTS Solution s HDL Simulation s In-Hardware Simulation with requirements traceability s Hardware Output Validation s Independent Tool Qualification Key Benefits of DO-254/CTS MAPLD 2009 – Session D 2
Agenda • Introduction • Challenges with Verification in Hardware for • • DO-254/CTS Solution s HDL Simulation s In-Hardware Simulation with requirements traceability s Hardware Output Validation s Independent Tool Qualification Key Benefits of DO-254/CTS MAPLD 2009 – Session D 2
 Designing for DO-254 Compliance The DO-254 specification imposes many additional requirements in the following areas: • System Aspects of Hardware Design Assurance Defining system safety processes and system development assurance levels (A, B, C, D, E) • Planning Process Development of hardware plans used to control the development of the hardware item • Hardware Design Process Requirements capturing, design and implementation of the hardware item • Validation and Verification Process Provides assurance that the requirements are correct, complete and hardware item implementation meets those requirements • Configuration Management Focuses on configuration management objectives and activities (configuration identification, baseline establishment, problem reporting and tracking, change control etc). MAPLD 2009 – Session D 3
Designing for DO-254 Compliance The DO-254 specification imposes many additional requirements in the following areas: • System Aspects of Hardware Design Assurance Defining system safety processes and system development assurance levels (A, B, C, D, E) • Planning Process Development of hardware plans used to control the development of the hardware item • Hardware Design Process Requirements capturing, design and implementation of the hardware item • Validation and Verification Process Provides assurance that the requirements are correct, complete and hardware item implementation meets those requirements • Configuration Management Focuses on configuration management objectives and activities (configuration identification, baseline establishment, problem reporting and tracking, change control etc). MAPLD 2009 – Session D 3
 Verification tool position in DO-254 compliant process • Verification in Hardware with Requirements Traceability Objective: Fast and reliable design verification process accepted by the certification authorities Addresses: Chapter 6. 2 (Verification Process) of DO-254 specification • Tool Qualification Process Objective: Independent Simulation Tool Qualification Addresses: Chapter 11. 4 (Tool Assessment and Qualification) of DO-254 specification MAPLD 2009 – Session D 4
Verification tool position in DO-254 compliant process • Verification in Hardware with Requirements Traceability Objective: Fast and reliable design verification process accepted by the certification authorities Addresses: Chapter 6. 2 (Verification Process) of DO-254 specification • Tool Qualification Process Objective: Independent Simulation Tool Qualification Addresses: Chapter 11. 4 (Tool Assessment and Qualification) of DO-254 specification MAPLD 2009 – Session D 4
 Design Verification for DO-254 “Since the results depend on the models and scenarios employed, simulation results alone cannot be used for the purpose of certification credit without supporting evidence of their validity. ” Chapter 6. 3. 2 DO-254 Specification, Apr 19, 2000. Verification methods, such as tests, simulation , prototyping, analyses and reviews, should be selected and performed. Verification in Simulator Chapter 6. 2. 2 DO-254 Specification, Apr 19, 2000. Verification in Hardware MAPLD 2009 – Session D 5
Design Verification for DO-254 “Since the results depend on the models and scenarios employed, simulation results alone cannot be used for the purpose of certification credit without supporting evidence of their validity. ” Chapter 6. 3. 2 DO-254 Specification, Apr 19, 2000. Verification methods, such as tests, simulation , prototyping, analyses and reviews, should be selected and performed. Verification in Simulator Chapter 6. 2. 2 DO-254 Specification, Apr 19, 2000. Verification in Hardware MAPLD 2009 – Session D 5
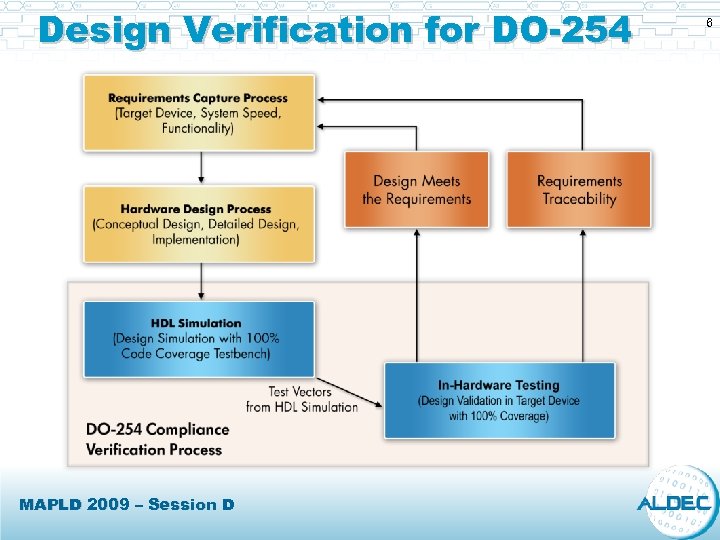 Design Verification for DO-254 MAPLD 2009 – Session D 6
Design Verification for DO-254 MAPLD 2009 – Session D 6
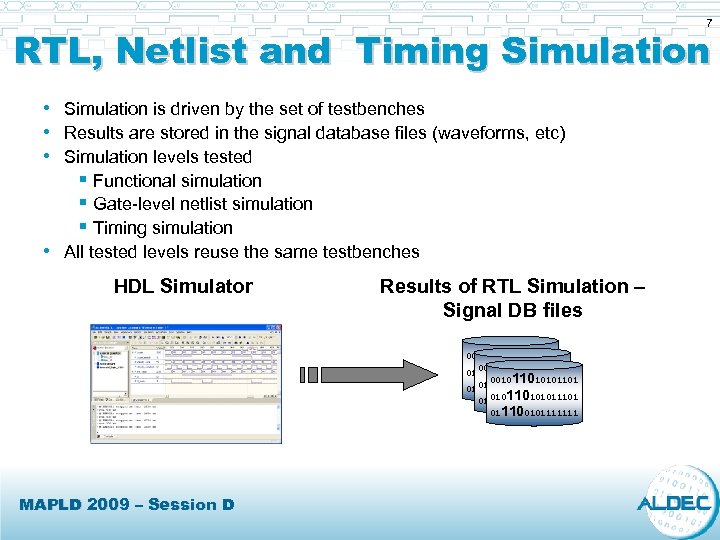 7 RTL, Netlist and Timing Simulation • Simulation is driven by the set of testbenches • Results are stored in the signal database files (waveforms, etc) • Simulation levels tested § Functional simulation § Gate-level netlist simulation § Timing simulation • All tested levels reuse the same testbenches HDL Simulator Results of RTL Simulation – Signal DB files 00101101010110101011101 0010110101011101 011100101111111 MAPLD 2009 – Session D
7 RTL, Netlist and Timing Simulation • Simulation is driven by the set of testbenches • Results are stored in the signal database files (waveforms, etc) • Simulation levels tested § Functional simulation § Gate-level netlist simulation § Timing simulation • All tested levels reuse the same testbenches HDL Simulator Results of RTL Simulation – Signal DB files 00101101010110101011101 0010110101011101 011100101111111 MAPLD 2009 – Session D
 Analysis Tools Complementing HDL Simulation • Code Coverage § Line and Branch coverage § Toggle coverage § Expression coverage • Code Linting § Coding Styles rules § Design Style rules § Synthesis rules MAPLD 2009 – Session D Feature-rich HDL Simulators 8
Analysis Tools Complementing HDL Simulation • Code Coverage § Line and Branch coverage § Toggle coverage § Expression coverage • Code Linting § Coding Styles rules § Design Style rules § Synthesis rules MAPLD 2009 – Session D Feature-rich HDL Simulators 8
 Traditional Testing in Hardware • Real-time stimuli are streaming through the design inputs • Design outputs (FPGA) are connected to another discrete components on the board Challenges • Limited access to design inputs • Covering all test points • Capturing and recording the outputs • Requirements traceability • Automating the testing • Special analysis is used to prove the coverage of all testing points MAPLD 2009 – Session D 9
Traditional Testing in Hardware • Real-time stimuli are streaming through the design inputs • Design outputs (FPGA) are connected to another discrete components on the board Challenges • Limited access to design inputs • Covering all test points • Capturing and recording the outputs • Requirements traceability • Automating the testing • Special analysis is used to prove the coverage of all testing points MAPLD 2009 – Session D 9
 In-Hardware Simulation at Target Speed Test Vectors Generation INPUT • Design under test – provided by customer, unaltered • Testbench for DUT – RTL TB is used TOOLS • HDL Simulator – Aldec or third party • Test Vectors Dumping module (PLI) ACTIONS • Running RTL simulation • Test vectors generation OUTPUT • • MAPLD 2009 – Session D Golden Vectors – RTL simulation output Input (Test) Vectors – RTL test vectors to be used for in-hardware simulation 10
In-Hardware Simulation at Target Speed Test Vectors Generation INPUT • Design under test – provided by customer, unaltered • Testbench for DUT – RTL TB is used TOOLS • HDL Simulator – Aldec or third party • Test Vectors Dumping module (PLI) ACTIONS • Running RTL simulation • Test vectors generation OUTPUT • • MAPLD 2009 – Session D Golden Vectors – RTL simulation output Input (Test) Vectors – RTL test vectors to be used for in-hardware simulation 10
 In-Hardware Simulation at Target Speed 11 At Speed Testing INPUT • Design under test – programs the boards • Input Vectors – RTL test vectors TOOLS • Verification Tool (VT) – controls in-hw simulation • Mother Board – simulation control logic • Daughter Board with a target device ACTIONS • Programming target FPGA • In-hardware testing at the target speed (MHz) • Recording hardware test output OUTPUT • MAPLD 2009 – Session D Output Vectors – result of in-hardware simulation
In-Hardware Simulation at Target Speed 11 At Speed Testing INPUT • Design under test – programs the boards • Input Vectors – RTL test vectors TOOLS • Verification Tool (VT) – controls in-hw simulation • Mother Board – simulation control logic • Daughter Board with a target device ACTIONS • Programming target FPGA • In-hardware testing at the target speed (MHz) • Recording hardware test output OUTPUT • MAPLD 2009 – Session D Output Vectors – result of in-hardware simulation
 Hardware Output Validation • Visual analysis of hardware recorded waveforms • Comparing hardware output with RTL (golden) output s graphically as waveform files s as two text files MAPLD 2009 – Session D 12
Hardware Output Validation • Visual analysis of hardware recorded waveforms • Comparing hardware output with RTL (golden) output s graphically as waveform files s as two text files MAPLD 2009 – Session D 12
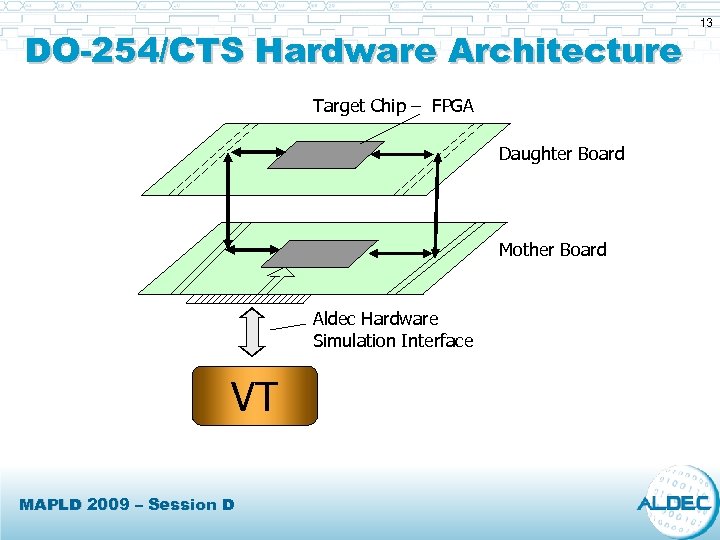 DO-254/CTS Hardware Architecture Target Chip – FPGA Daughter Board Mother Board Aldec Hardware Simulation Interface VT MAPLD 2009 – Session D 13
DO-254/CTS Hardware Architecture Target Chip – FPGA Daughter Board Mother Board Aldec Hardware Simulation Interface VT MAPLD 2009 – Session D 13
 DO-254/CTS Practical Application Design Parameters
DO-254/CTS Practical Application Design Parameters
 Tool Assessment and Qualification Process “Independent assessment of a design tool’s output may include a manual review of the tool outputs or may include a comparison against the outputs of a separate tool capable of performing the same verification activity as the tool being assessed. Chapter 11. 4. 1. 3, DO-254 Specification, Apr 19, 2000. Tool Assessment and Qualification Process (ch. 11. 4): 1. Identify the Tool (name, source, version, environment etc). 2. Identify the Process the Tool Supports (design or verification process). 3. Is the tool independently assessed? If the tool output is independently assessed, then no further assessment is necessary A tool assessment should be performed prior to the use of a tool. Source: chapter 11. 4 of DO-254/ED 80 Specification MAPLD 2009 – Session D 15
Tool Assessment and Qualification Process “Independent assessment of a design tool’s output may include a manual review of the tool outputs or may include a comparison against the outputs of a separate tool capable of performing the same verification activity as the tool being assessed. Chapter 11. 4. 1. 3, DO-254 Specification, Apr 19, 2000. Tool Assessment and Qualification Process (ch. 11. 4): 1. Identify the Tool (name, source, version, environment etc). 2. Identify the Process the Tool Supports (design or verification process). 3. Is the tool independently assessed? If the tool output is independently assessed, then no further assessment is necessary A tool assessment should be performed prior to the use of a tool. Source: chapter 11. 4 of DO-254/ED 80 Specification MAPLD 2009 – Session D 15
 Independent Tool Assessment with DO-254/CTS Comparing output of RTL and HW simulations RTL Verification MAPLD 2009 – Session D Validates RTL simulation results • In-Hardware Simulation • Validates Hardware simulation results * In addition, set of the hardware diagnostic tests is provided to qualify Aldec’s hardware simulation tool 16
Independent Tool Assessment with DO-254/CTS Comparing output of RTL and HW simulations RTL Verification MAPLD 2009 – Session D Validates RTL simulation results • In-Hardware Simulation • Validates Hardware simulation results * In addition, set of the hardware diagnostic tests is provided to qualify Aldec’s hardware simulation tool 16
 Summary: DO-254 CTS • Functional and at-speed verification of the design implementation in the target FPGA device • No extra circuits are added to the target device • Testing unaltered original design • RTL simulation test vectors used – no need to create separate vectors for hardware testing • In-Hardware Simulation results recorded in the waveformat for convenient analysis and archival • Automated output validation • Complete traceability of all design requirements • Fully automated script driven testing environment MAPLD 2009 – Session D 17
Summary: DO-254 CTS • Functional and at-speed verification of the design implementation in the target FPGA device • No extra circuits are added to the target device • Testing unaltered original design • RTL simulation test vectors used – no need to create separate vectors for hardware testing • In-Hardware Simulation results recorded in the waveformat for convenient analysis and archival • Automated output validation • Complete traceability of all design requirements • Fully automated script driven testing environment MAPLD 2009 – Session D 17


