6 DNA damage p53 TNF Cell death.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 110
 DNA Damage Signaling
DNA Damage Signaling
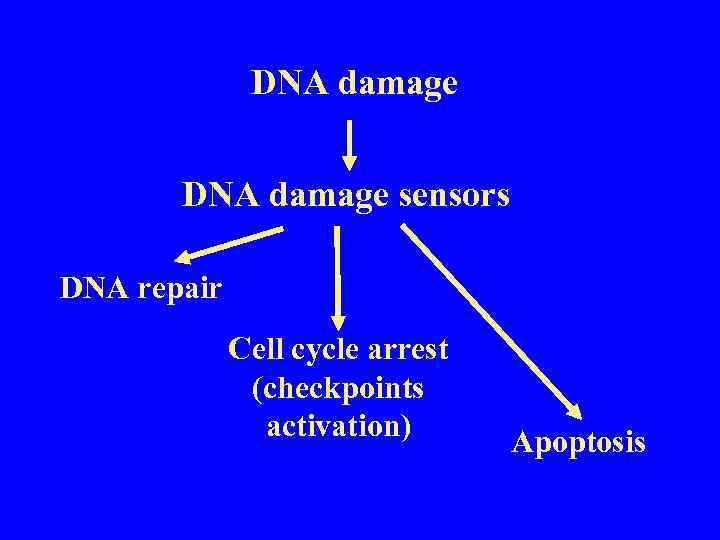 DNA damage sensors DNA repair Cell cycle arrest (checkpoints activation) Apoptosis
DNA damage sensors DNA repair Cell cycle arrest (checkpoints activation) Apoptosis
 PI 3 K-related protein kinases in DNA damage signaling ATM DNA-PK ATR
PI 3 K-related protein kinases in DNA damage signaling ATM DNA-PK ATR
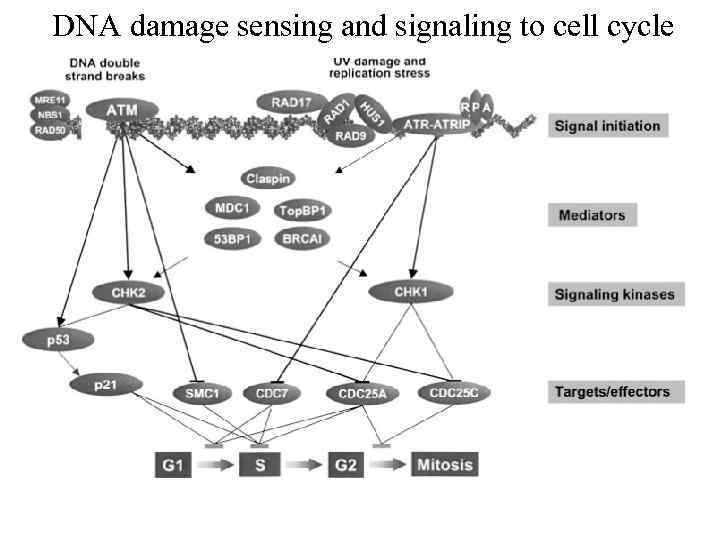 DNA damage sensing and signaling to cell cycle
DNA damage sensing and signaling to cell cycle
 DNA repair pathways by iniciation - Global Genomic Repair (GGR), including Replication-coupled repair (connected to stalled replication fork signaling, replicative stress signaling) - Transcription-coupled repair - Diferentiation-associated repair
DNA repair pathways by iniciation - Global Genomic Repair (GGR), including Replication-coupled repair (connected to stalled replication fork signaling, replicative stress signaling) - Transcription-coupled repair - Diferentiation-associated repair
 DNA repair pathways by type of DNA damage Single-strand damage repair Double-strand damage repair
DNA repair pathways by type of DNA damage Single-strand damage repair Double-strand damage repair
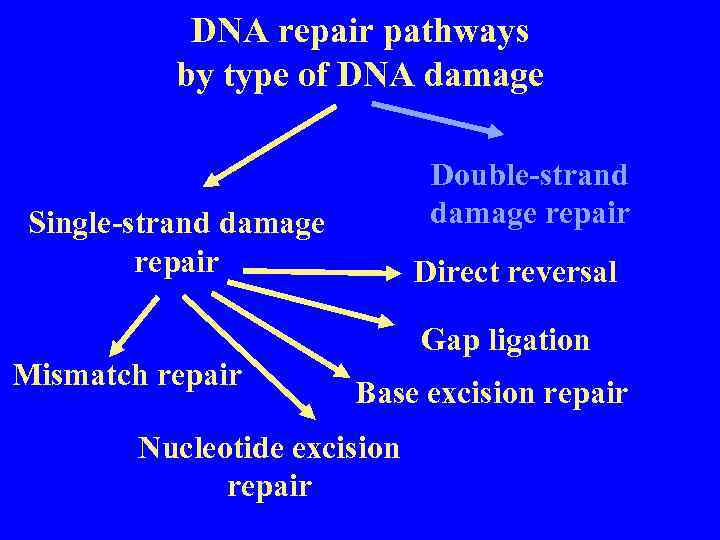 DNA repair pathways by type of DNA damage Double-strand damage repair Single-strand damage repair Mismatch repair Direct reversal Gap ligation Base excision repair Nucleotide excision repair
DNA repair pathways by type of DNA damage Double-strand damage repair Single-strand damage repair Mismatch repair Direct reversal Gap ligation Base excision repair Nucleotide excision repair
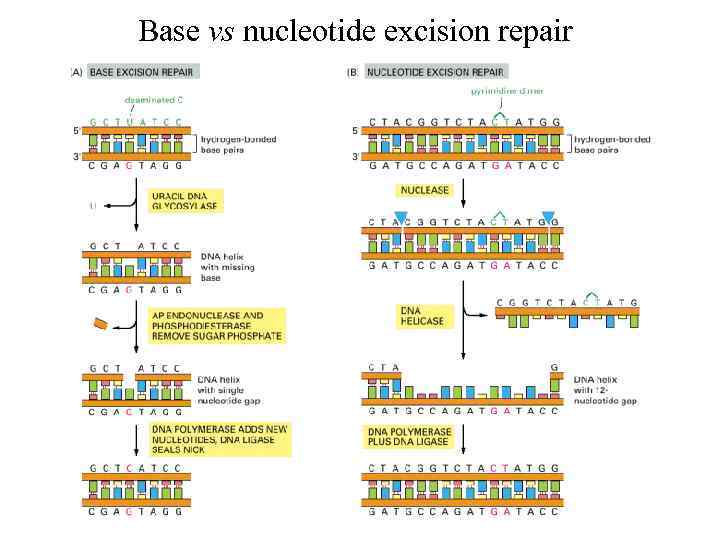 Base vs nucleotide excision repair
Base vs nucleotide excision repair
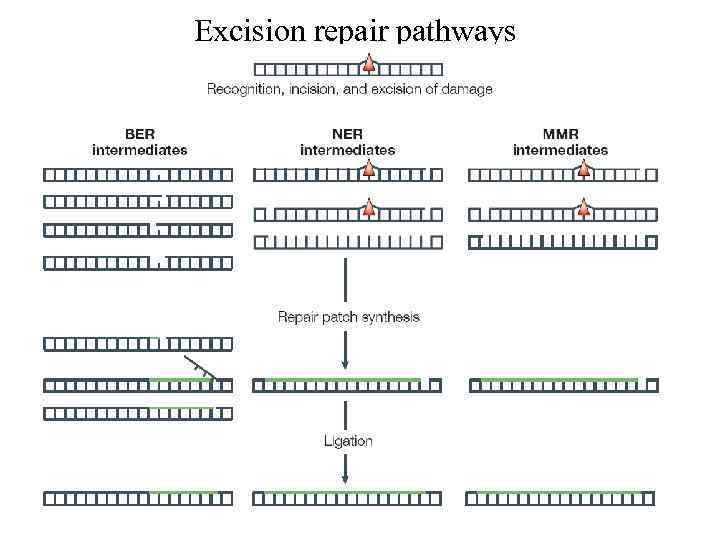 Excision repair pathways
Excision repair pathways
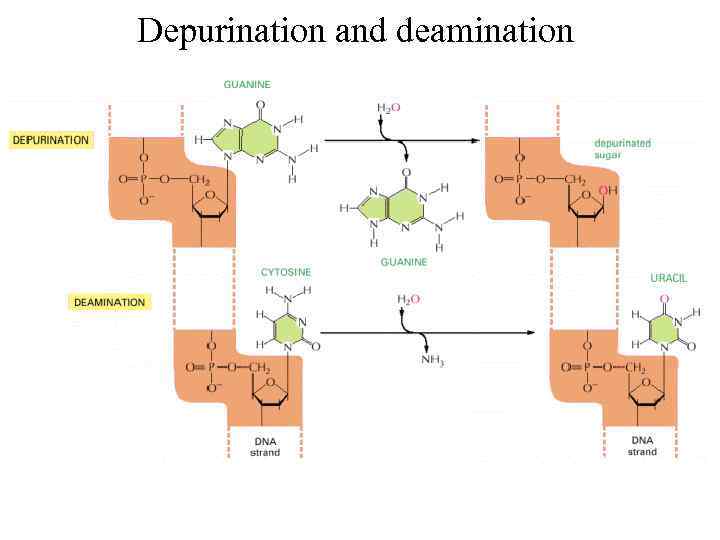 Depurination and deamination
Depurination and deamination
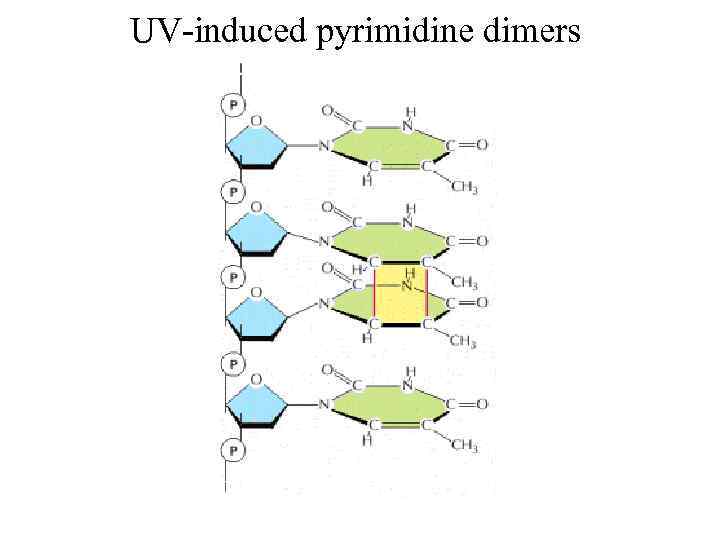 UV-induced pyrimidine dimers
UV-induced pyrimidine dimers
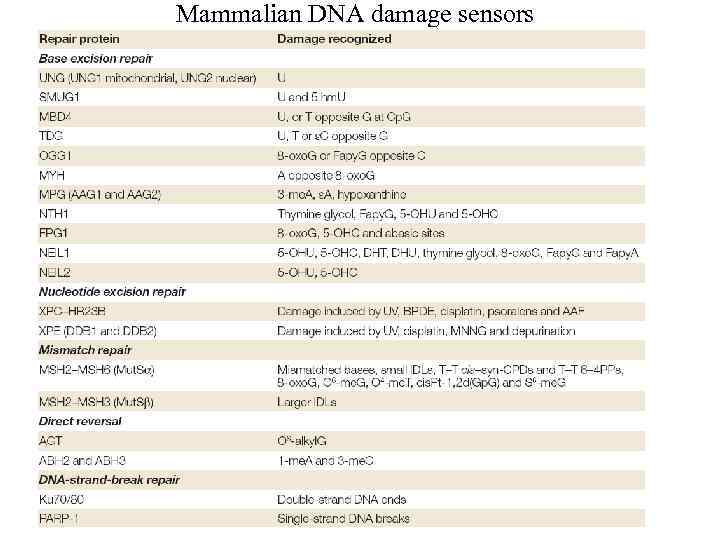 Mammalian DNA damage sensors
Mammalian DNA damage sensors
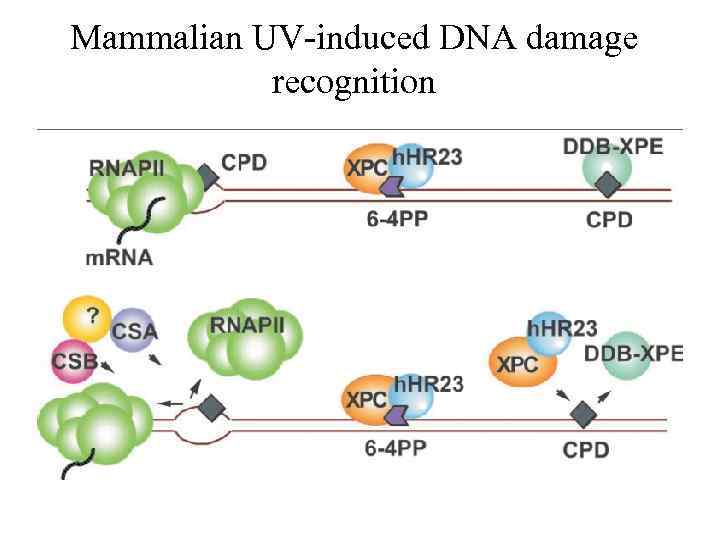 Mammalian UV-induced DNA damage recognition
Mammalian UV-induced DNA damage recognition
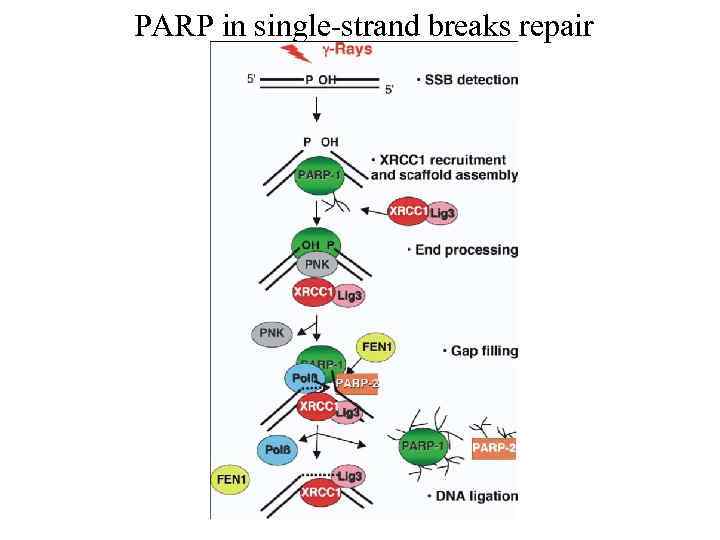 PARP in single-strand breaks repair
PARP in single-strand breaks repair
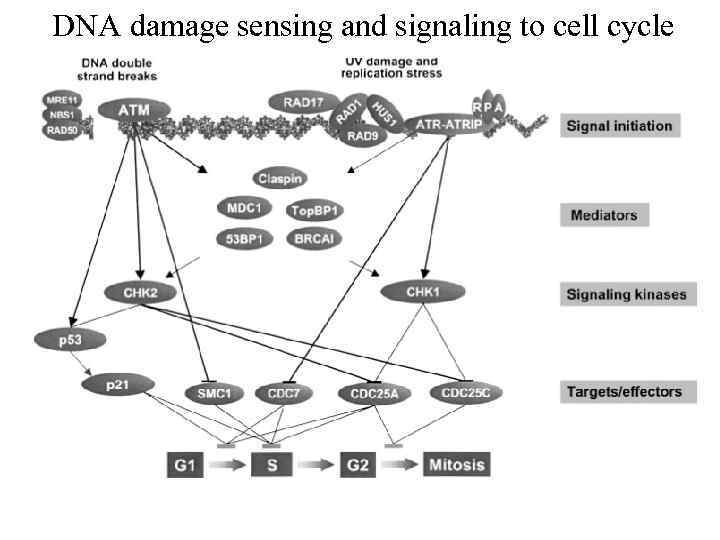 DNA damage sensing and signaling to cell cycle
DNA damage sensing and signaling to cell cycle
 ATR activation ATRIP — esssential regulatory subunit For activation reguires RPA (binds to ss. DNA) and TOPBP 1 (usually binds to Rad 9 -Rad 1 -Hus 1 complex detecting ss-ds. DNA border) Timeless and Tipin (Circadian clock proteins) and BRCA 1 needed for ATR activation or signaling. Activated in responce to: - NER - Stalled replication fork - Fanconi anemia pathway - ATM activation or strand resection in DSB (in S/G 2) - Mismatch repair (via Msh 2) Has functions in normal replication
ATR activation ATRIP — esssential regulatory subunit For activation reguires RPA (binds to ss. DNA) and TOPBP 1 (usually binds to Rad 9 -Rad 1 -Hus 1 complex detecting ss-ds. DNA border) Timeless and Tipin (Circadian clock proteins) and BRCA 1 needed for ATR activation or signaling. Activated in responce to: - NER - Stalled replication fork - Fanconi anemia pathway - ATM activation or strand resection in DSB (in S/G 2) - Mismatch repair (via Msh 2) Has functions in normal replication
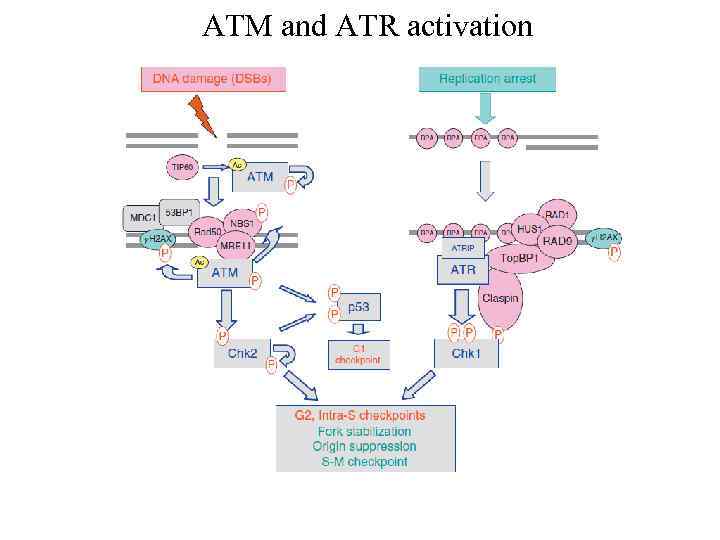 ATM and ATR activation
ATM and ATR activation
 ATR functions - cell cycle arrest (S, G 1, G 2) - preventing firing of late replication origins (Cdc 45 binding) 12 in S - ? prevention of lycenzing in G 1 (Cdt 1 degradation) - stabilizing stressed replication forks in S - promoting DNA repair and restart of replication - apoptosos induction - functions in normal replication
ATR functions - cell cycle arrest (S, G 1, G 2) - preventing firing of late replication origins (Cdc 45 binding) 12 in S - ? prevention of lycenzing in G 1 (Cdt 1 degradation) - stabilizing stressed replication forks in S - promoting DNA repair and restart of replication - apoptosos induction - functions in normal replication
 ATR substrates Rad 17, Claspin — for Chk 1 binding Chk 1 — for cell cycle arrest p 53 — for cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, repair Siah 1 — for HIPK 2 stabilisation to p 53 Hus 1, ATRIP, RPA, Top. BP 1 — feedback E 2 F 1 — for cell cycle arrest Cdc 7 -DBF 4, Mll 1 — blocking firing of later origins (also via Cdc 25) BRCA 1, Mdc 1, H 2 AX — usually by ATM for HR PLK (via Claspin and Mcm 2, for Chk 1 inactivation)
ATR substrates Rad 17, Claspin — for Chk 1 binding Chk 1 — for cell cycle arrest p 53 — for cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, repair Siah 1 — for HIPK 2 stabilisation to p 53 Hus 1, ATRIP, RPA, Top. BP 1 — feedback E 2 F 1 — for cell cycle arrest Cdc 7 -DBF 4, Mll 1 — blocking firing of later origins (also via Cdc 25) BRCA 1, Mdc 1, H 2 AX — usually by ATM for HR PLK (via Claspin and Mcm 2, for Chk 1 inactivation)
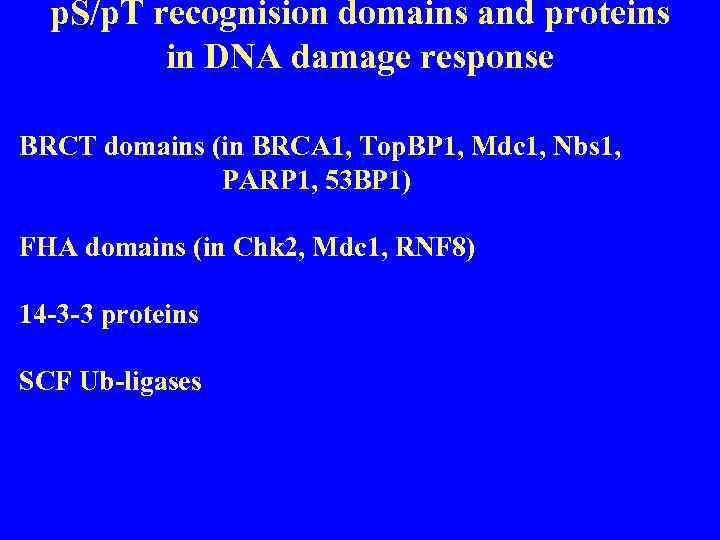 p. S/p. T recognision domains and proteins in DNA damage response BRCT domains (in BRCA 1, Top. BP 1, Mdc 1, Nbs 1, PARP 1, 53 BP 1) FHA domains (in Chk 2, Mdc 1, RNF 8) 14 -3 -3 proteins SCF Ub-ligases
p. S/p. T recognision domains and proteins in DNA damage response BRCT domains (in BRCA 1, Top. BP 1, Mdc 1, Nbs 1, PARP 1, 53 BP 1) FHA domains (in Chk 2, Mdc 1, RNF 8) 14 -3 -3 proteins SCF Ub-ligases
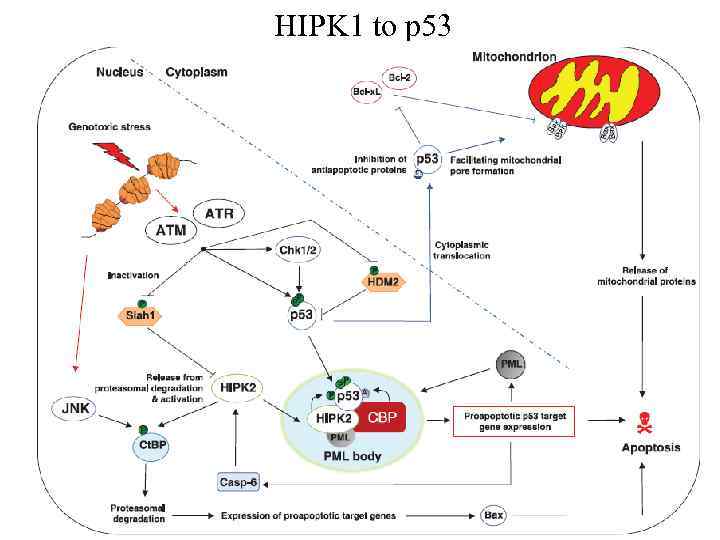 HIPK 1 to p 53
HIPK 1 to p 53
 Chk 1 substrates Cdc 25 A (degradation) — for cell cycle arrest Cdc 25 C (inactivation) — for cell cycle arrest Wee 1 p 53 — for cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, repair BRCA 2, Rad 51 — for HR
Chk 1 substrates Cdc 25 A (degradation) — for cell cycle arrest Cdc 25 C (inactivation) — for cell cycle arrest Wee 1 p 53 — for cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, repair BRCA 2, Rad 51 — for HR
 Transcription-coupled repair To NER — via CSA, CSB, XAB 2 To MMR — via Mlh 1, Msh 2 To BER — via CSA, CSB, BRCA 1
Transcription-coupled repair To NER — via CSA, CSB, XAB 2 To MMR — via Mlh 1, Msh 2 To BER — via CSA, CSB, BRCA 1
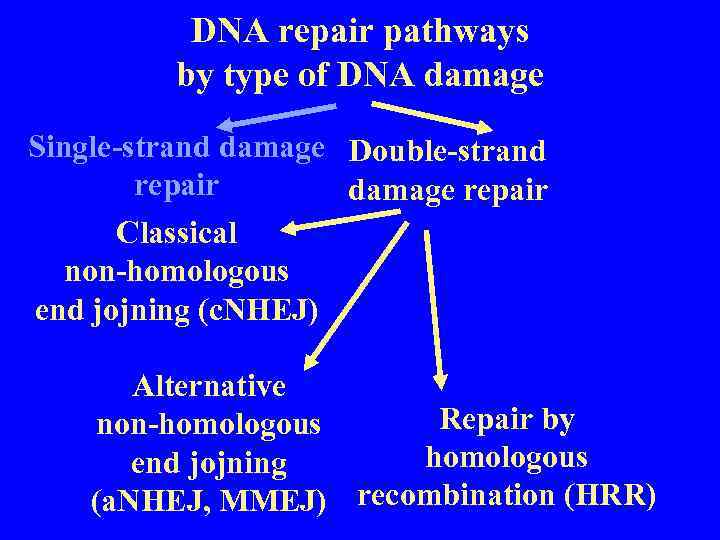 DNA repair pathways by type of DNA damage Single-strand damage Double-strand repair damage repair Classical non-homologous end jojning (c. NHEJ) Alternative Repair by non-homologous end jojning (a. NHEJ, MMEJ) recombination (HRR)
DNA repair pathways by type of DNA damage Single-strand damage Double-strand repair damage repair Classical non-homologous end jojning (c. NHEJ) Alternative Repair by non-homologous end jojning (a. NHEJ, MMEJ) recombination (HRR)
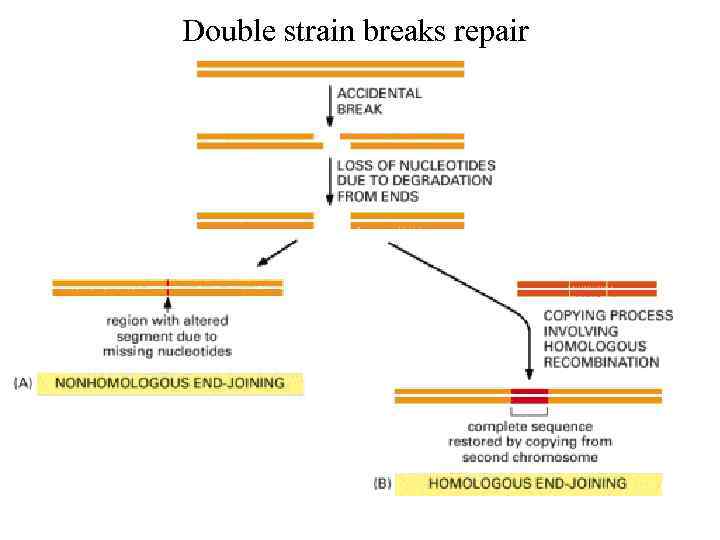 Double strain breaks repair
Double strain breaks repair
 Double-strand damage - Double-strand breaks (competing pathways: Ku-DNA-PK (c. NHEJ) and PARP-ATM (HR, a. NHEJ) - RAG-induced breaks (i. e, V(D)J recombination) — c. NHEJ via DNA-PK - Stalled-replication fork-induced breaks - Single-strand to double-strand break conversion - Interstrand crosslinks (detection by Fanconi anemia pathway — first to ATR)
Double-strand damage - Double-strand breaks (competing pathways: Ku-DNA-PK (c. NHEJ) and PARP-ATM (HR, a. NHEJ) - RAG-induced breaks (i. e, V(D)J recombination) — c. NHEJ via DNA-PK - Stalled-replication fork-induced breaks - Single-strand to double-strand break conversion - Interstrand crosslinks (detection by Fanconi anemia pathway — first to ATR)
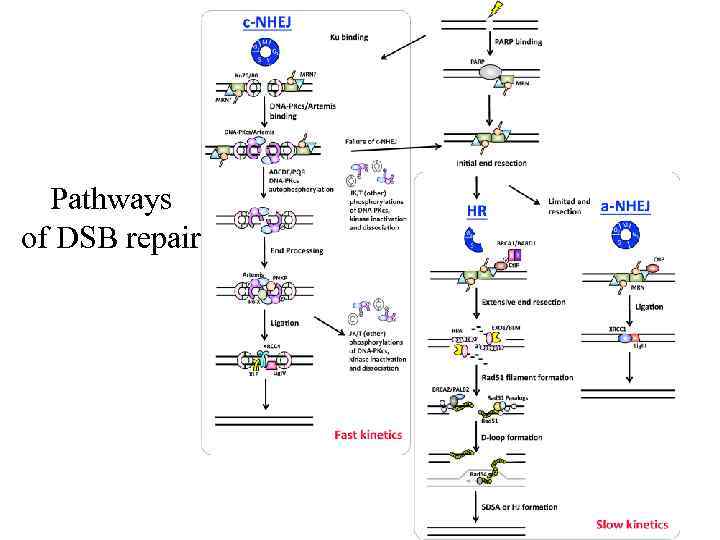 Pathways of DSB repair
Pathways of DSB repair
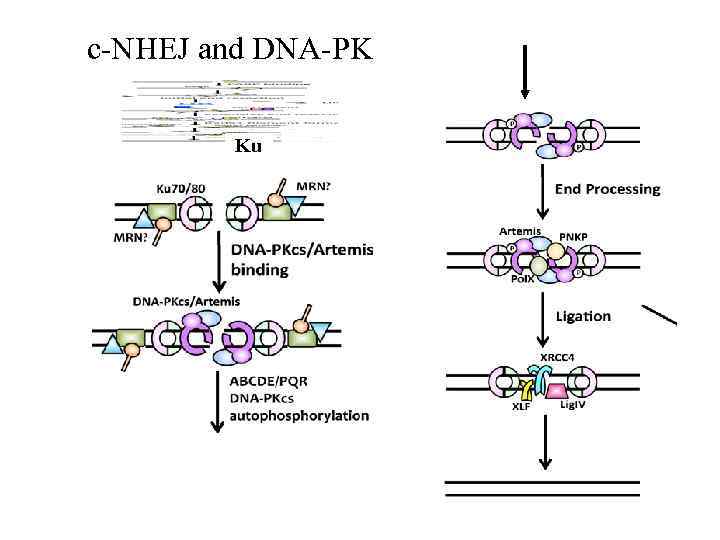 c-NHEJ and DNA-PK Ku
c-NHEJ and DNA-PK Ku
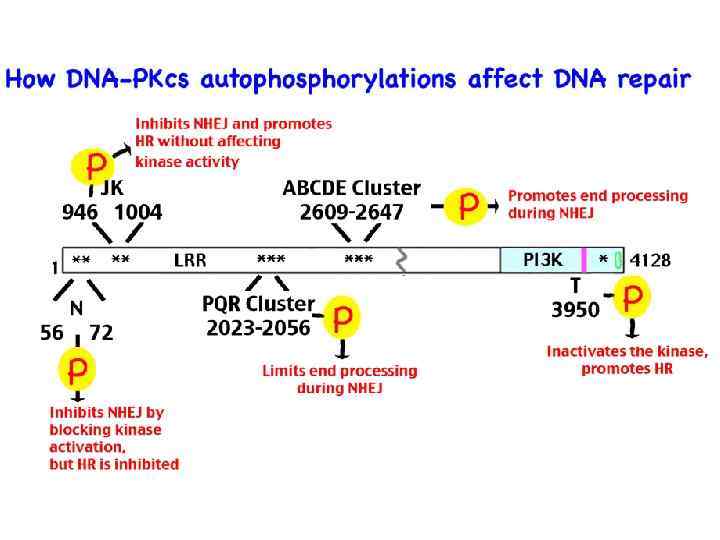
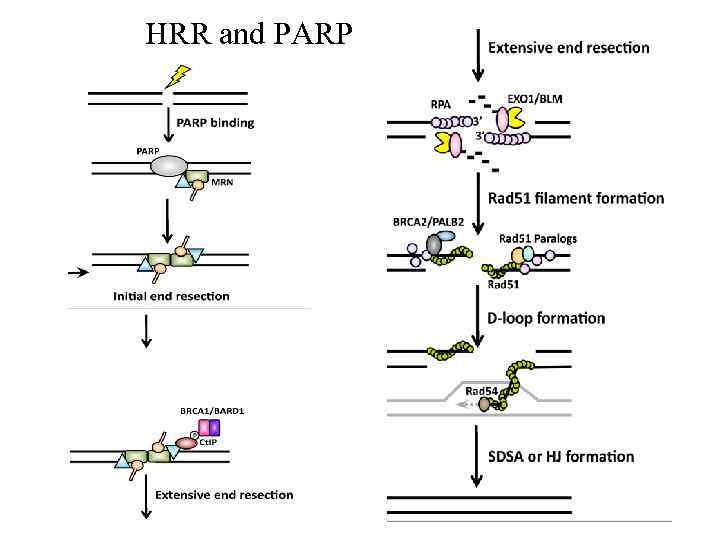 HRR and PARP
HRR and PARP
 ATM activation Mre 11 -Rad 50 -Nbs 1 complex binds DSB and activates ATM. Inactive dimeric ATM → trans-autophosphorylation → active monomeric ATM Activated in responce to double-strand breaks γH 2 AX, BRCA 1, Mdc 1, 53 BP 1 help in activation (positive feedback)
ATM activation Mre 11 -Rad 50 -Nbs 1 complex binds DSB and activates ATM. Inactive dimeric ATM → trans-autophosphorylation → active monomeric ATM Activated in responce to double-strand breaks γH 2 AX, BRCA 1, Mdc 1, 53 BP 1 help in activation (positive feedback)
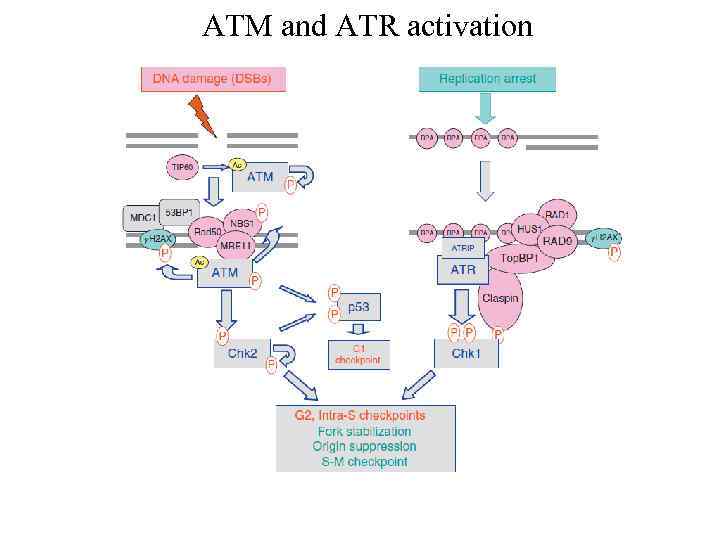 ATM and ATR activation
ATM and ATR activation
 ATM substrates H 2 AX — for Mdc 1 and other binding Mdc 1 — for γH 2 AX spreading (interacts with Nbs 1 in MRN) and further complex formation Chk 2 — for cell cycle arrest (dimerisation via FHAdomain and autophosphorylation) 53 BP 1 — for p 53 binding (via γH 2 AX) Mdm 2, Mdm. X — for p 53 stabilisation p 53 — for cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, repair Siah 1 — for HIPK 2 stabilisation to p 53 BRCA 1, 2 — for HR (via γH 2 AX) Nbs 1 (MRN complex) Smc 1 (cohesin)
ATM substrates H 2 AX — for Mdc 1 and other binding Mdc 1 — for γH 2 AX spreading (interacts with Nbs 1 in MRN) and further complex formation Chk 2 — for cell cycle arrest (dimerisation via FHAdomain and autophosphorylation) 53 BP 1 — for p 53 binding (via γH 2 AX) Mdm 2, Mdm. X — for p 53 stabilisation p 53 — for cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, repair Siah 1 — for HIPK 2 stabilisation to p 53 BRCA 1, 2 — for HR (via γH 2 AX) Nbs 1 (MRN complex) Smc 1 (cohesin)
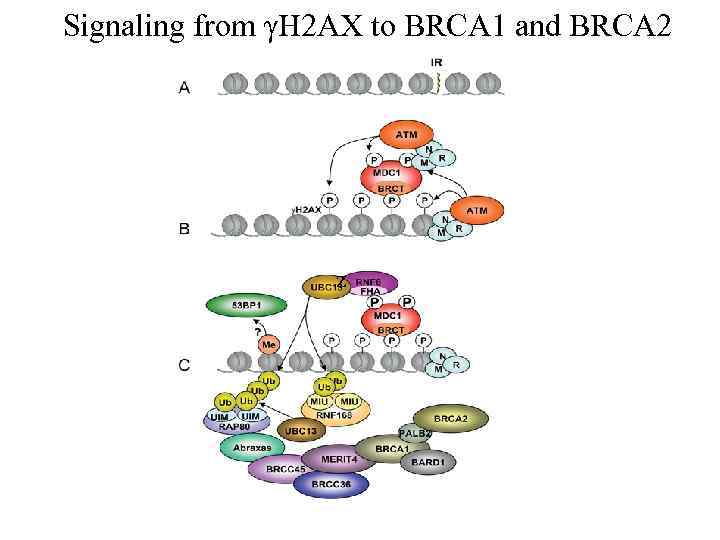 Signaling from γH 2 AX to BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 z
Signaling from γH 2 AX to BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 z
 Chk 2 substrates Cdc 25 A (degradation) — for cell cycle arrest Cdc 25 C (inactivation) — for cell cycle arrest p 53 — for cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, repair Mdm. X — for p 53 stabilisation (Chk 2) BRCA 1 — for HR Fox. M 1, E 2 F 1
Chk 2 substrates Cdc 25 A (degradation) — for cell cycle arrest Cdc 25 C (inactivation) — for cell cycle arrest p 53 — for cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, repair Mdm. X — for p 53 stabilisation (Chk 2) BRCA 1 — for HR Fox. M 1, E 2 F 1
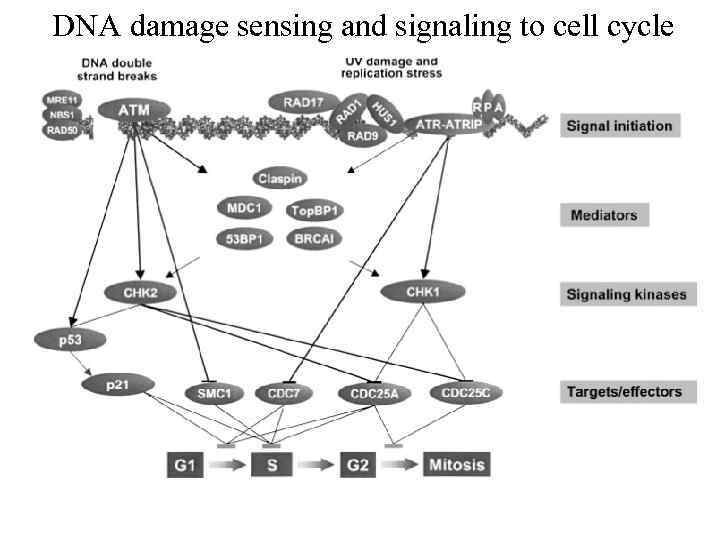 DNA damage sensing and signaling to cell cycle
DNA damage sensing and signaling to cell cycle
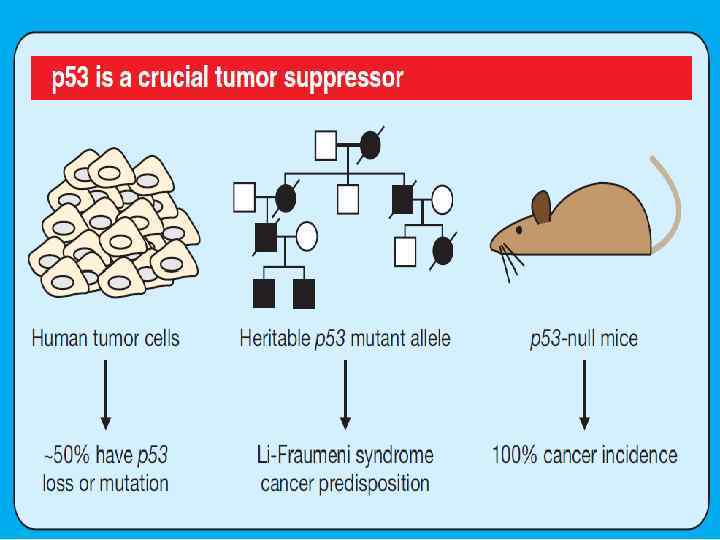
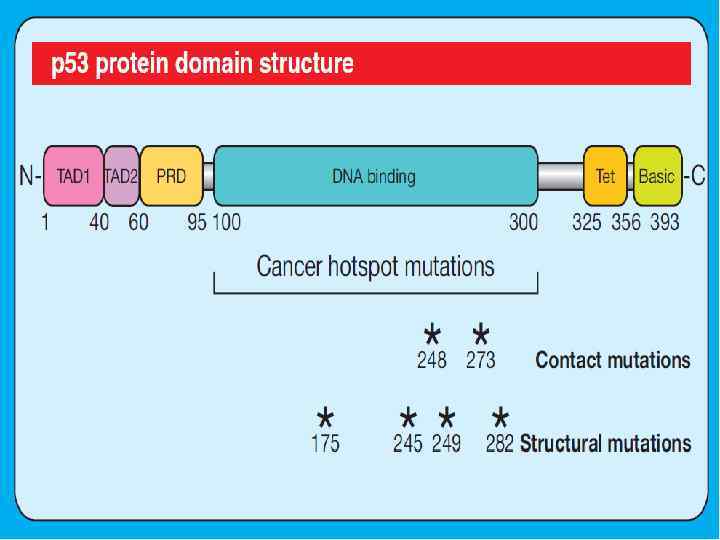
 p 53
p 53
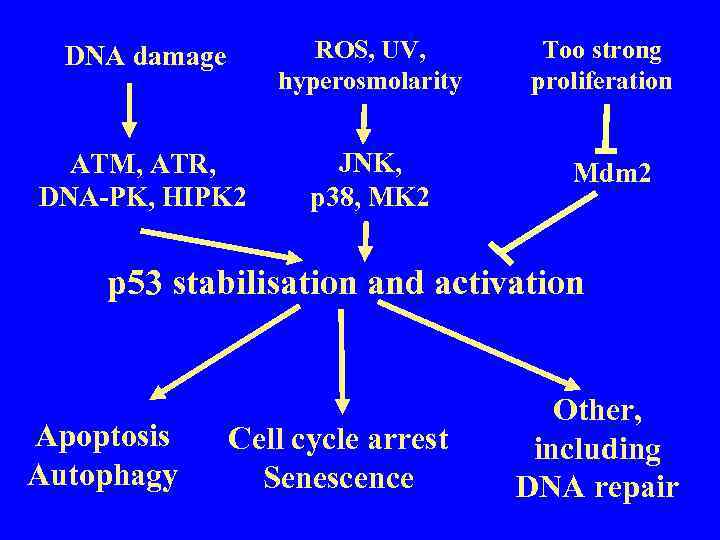 DNA damage ROS, UV, hyperosmolarity ATM, ATR, DNA-PK, HIPK 2 JNK, p 38, MK 2 Too strong proliferation Mdm 2 p 53 stabilisation and activation Apoptosis Autophagy Cell cycle arrest Senescence Other, including DNA repair
DNA damage ROS, UV, hyperosmolarity ATM, ATR, DNA-PK, HIPK 2 JNK, p 38, MK 2 Too strong proliferation Mdm 2 p 53 stabilisation and activation Apoptosis Autophagy Cell cycle arrest Senescence Other, including DNA repair
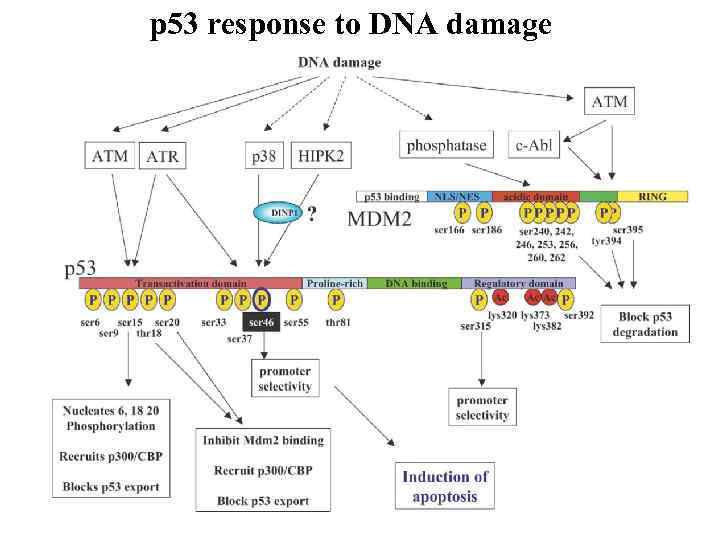 p 53 response to DNA damage
p 53 response to DNA damage
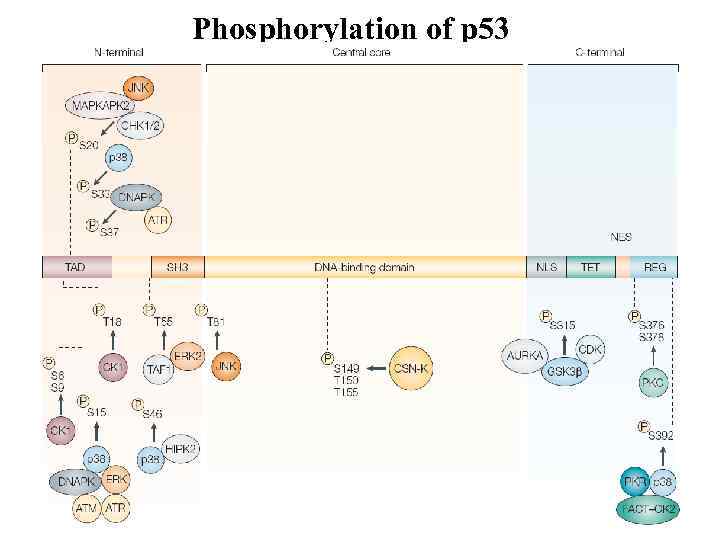 Phosphorylation of p 53
Phosphorylation of p 53
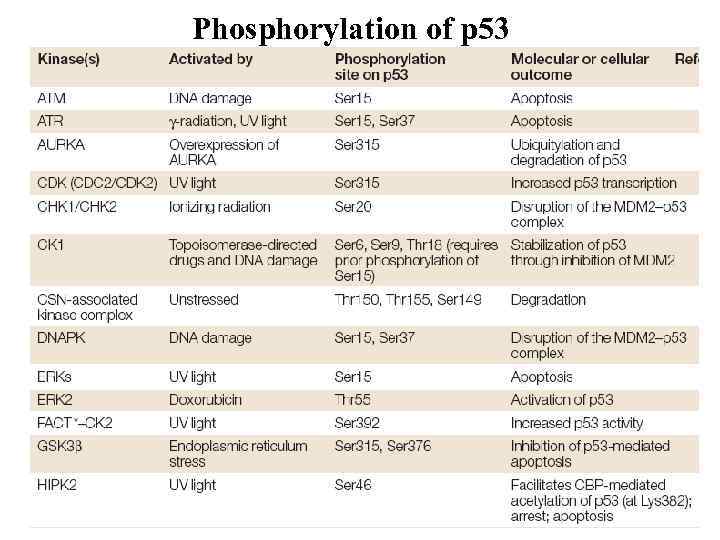 Phosphorylation of p 53
Phosphorylation of p 53
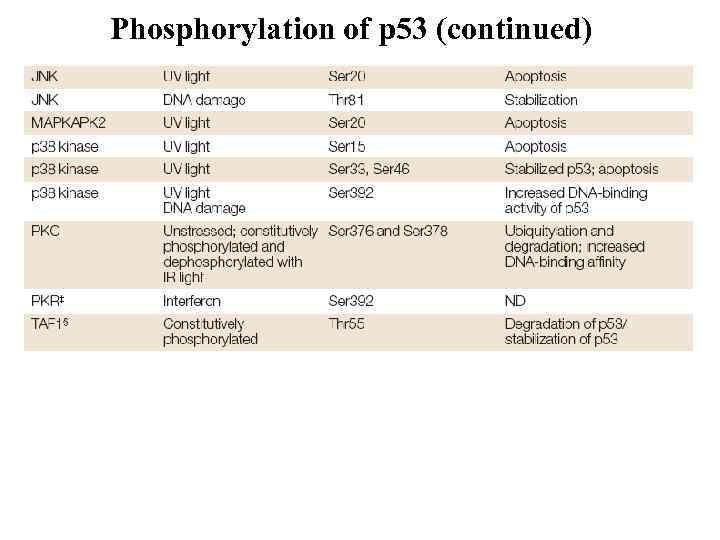 Phosphorylation of p 53 (continued)
Phosphorylation of p 53 (continued)
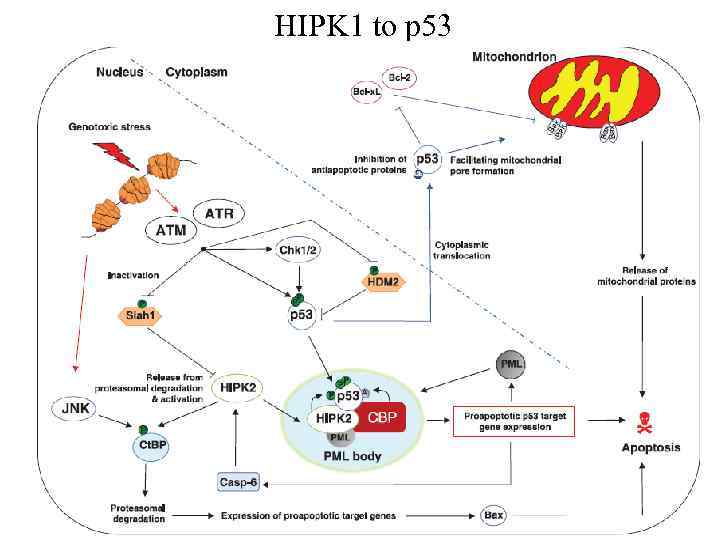 HIPK 1 to p 53
HIPK 1 to p 53
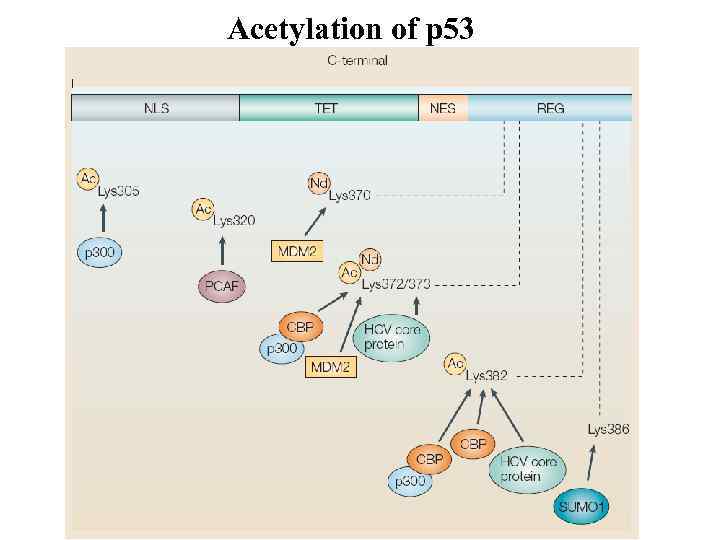 Acetylation of p 53
Acetylation of p 53
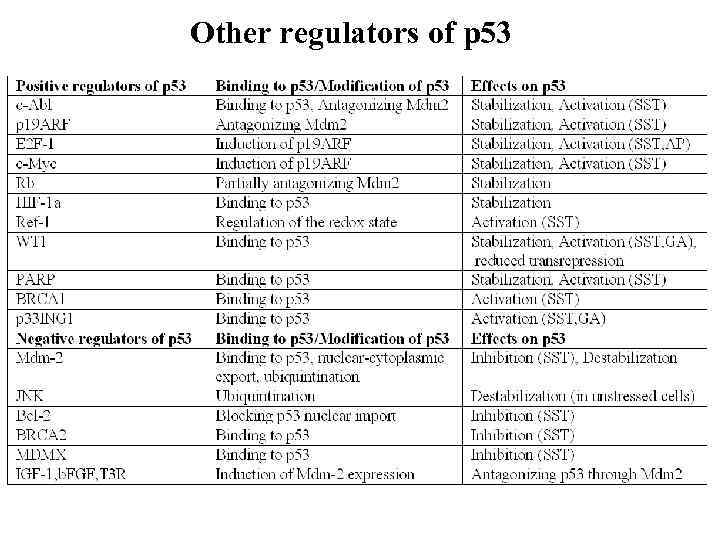 Other regulators of p 53
Other regulators of p 53
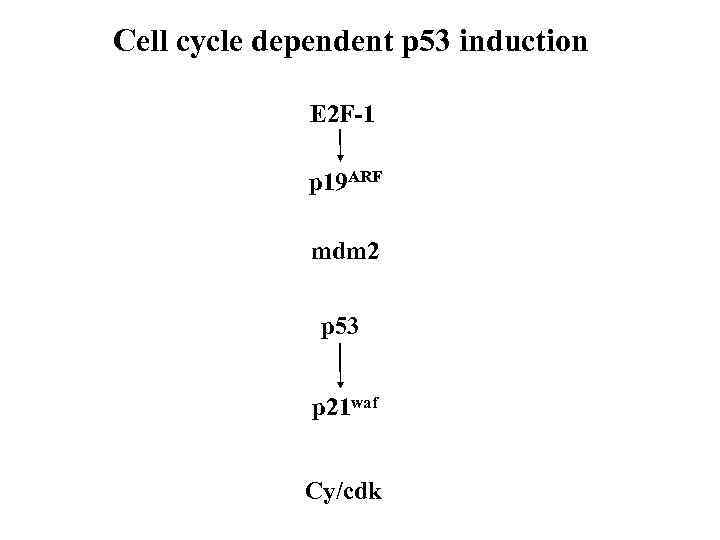 Cell cycle dependent p 53 induction E 2 F-1 p 19 ARF mdm 2 p 53 p 21 waf Cy/cdk
Cell cycle dependent p 53 induction E 2 F-1 p 19 ARF mdm 2 p 53 p 21 waf Cy/cdk
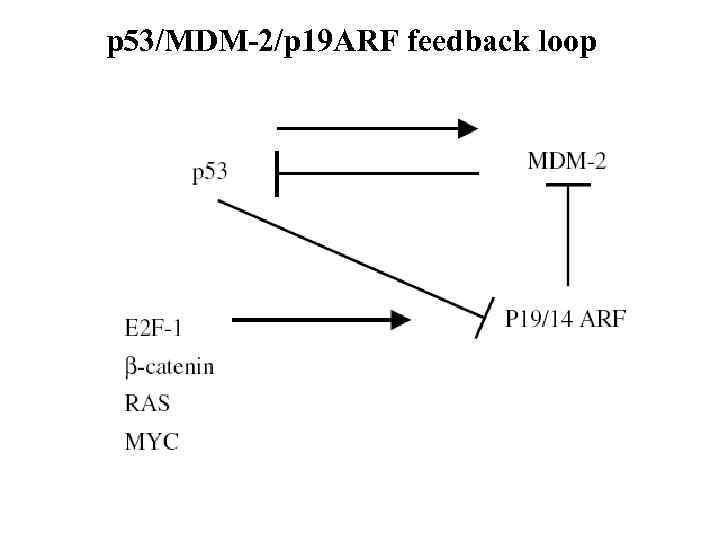 p 53/MDM-2/p 19 ARF feedback loop
p 53/MDM-2/p 19 ARF feedback loop
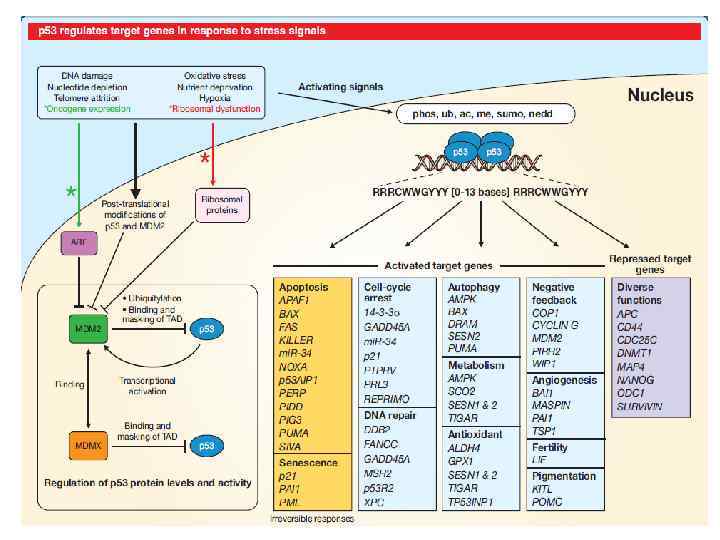
 DNA excision repair proteins induced by p 53 - p 48/DDB 2 (XPE/UV-DDB component) - XPC - GADD 45
DNA excision repair proteins induced by p 53 - p 48/DDB 2 (XPE/UV-DDB component) - XPC - GADD 45
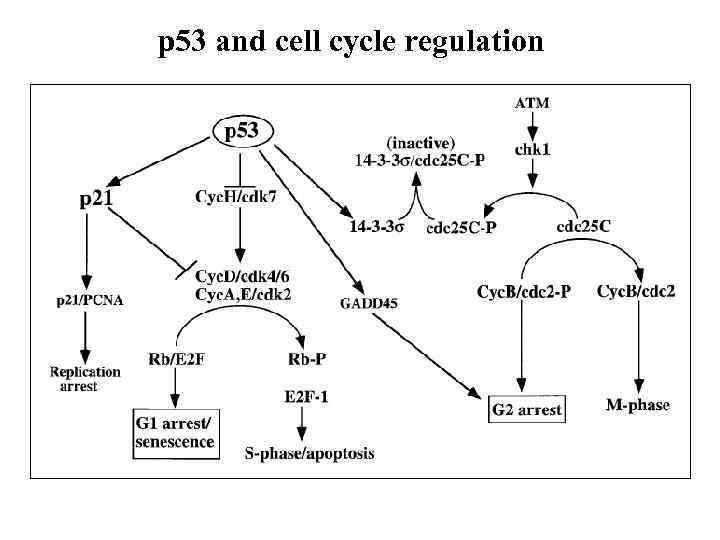 p 53 and cell cycle regulation
p 53 and cell cycle regulation
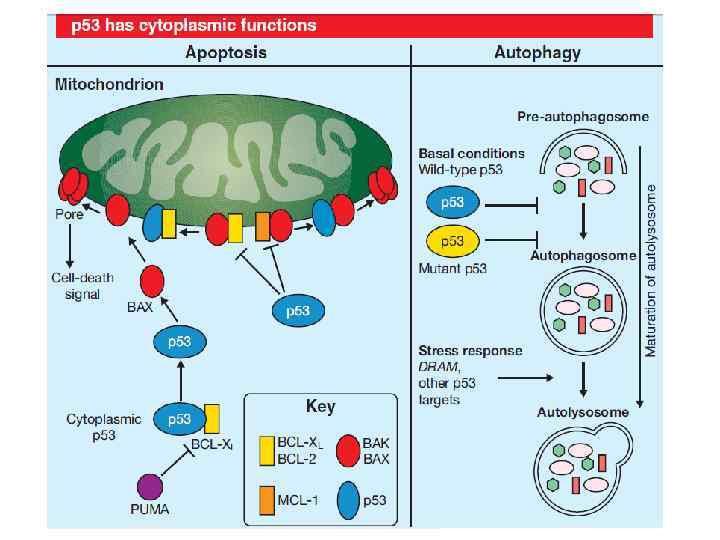
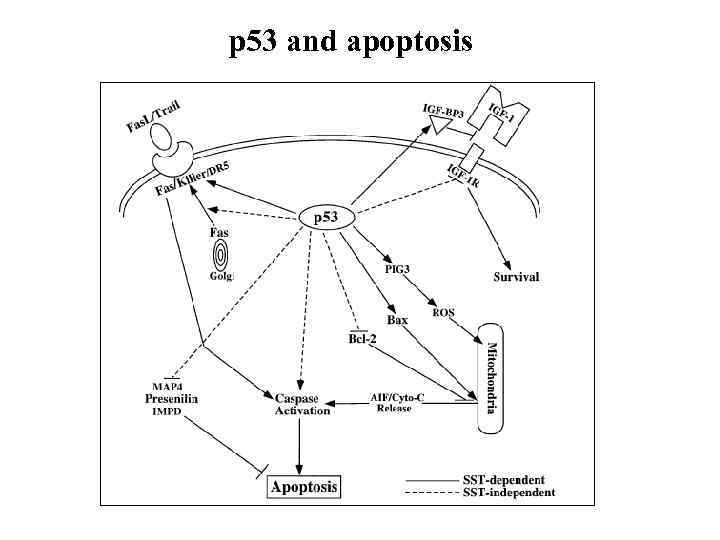 p 53 and apoptosis
p 53 and apoptosis
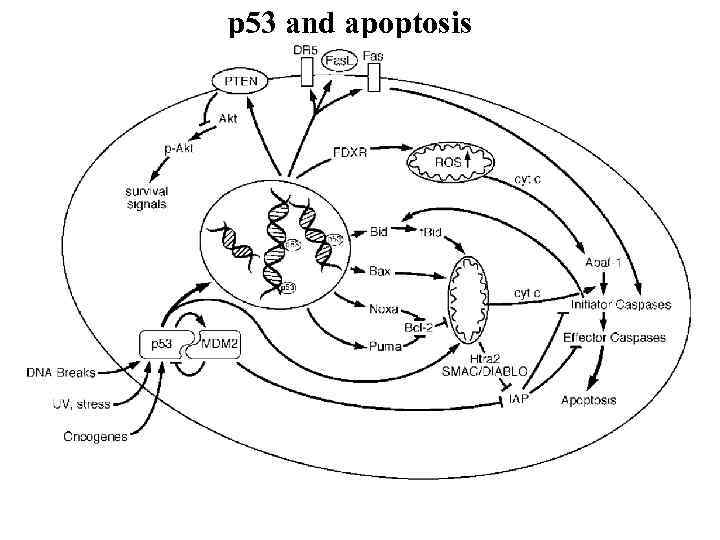 p 53 and apoptosis
p 53 and apoptosis
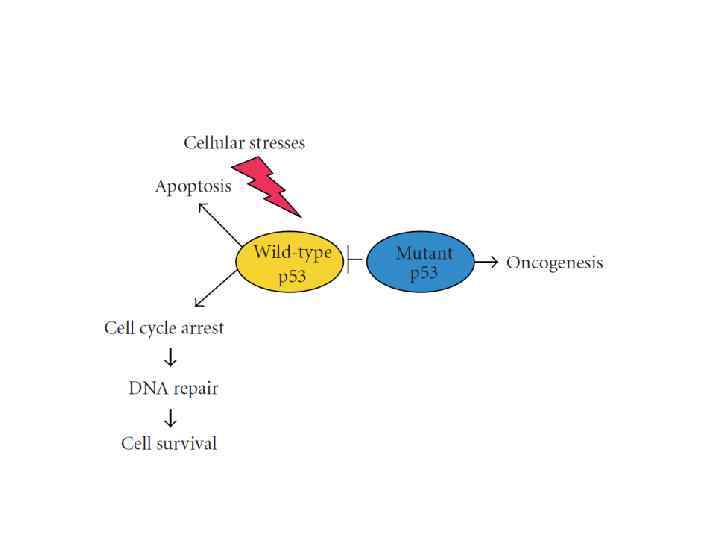
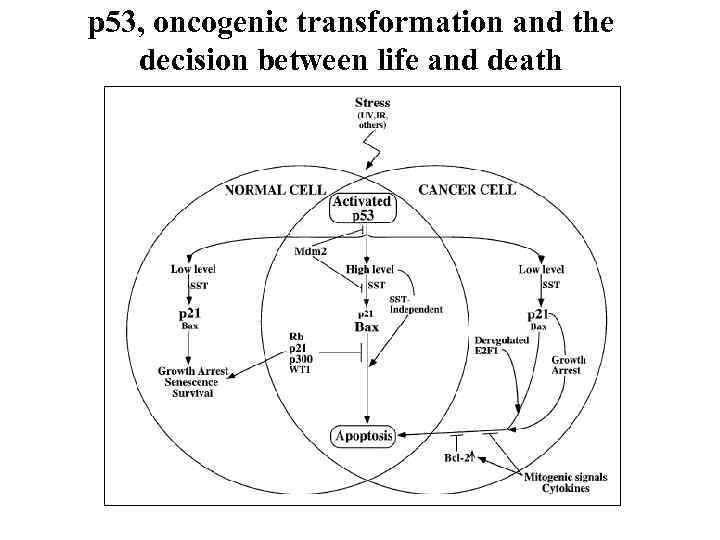 p 53, oncogenic transformation and the decision between life and death
p 53, oncogenic transformation and the decision between life and death
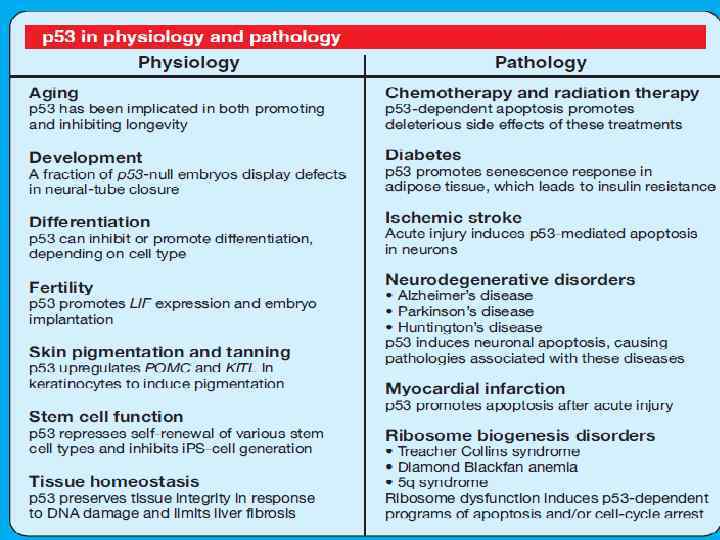
 Other functions - Inhibits angiogenesis (thrombospondin expression) - Inhibits glycolysis (TIGAR), promotes oxidative phosphorylation (SCO 2) - Stimulates embrio implantation (LIF expression) -Pro- or antioxidative features
Other functions - Inhibits angiogenesis (thrombospondin expression) - Inhibits glycolysis (TIGAR), promotes oxidative phosphorylation (SCO 2) - Stimulates embrio implantation (LIF expression) -Pro- or antioxidative features
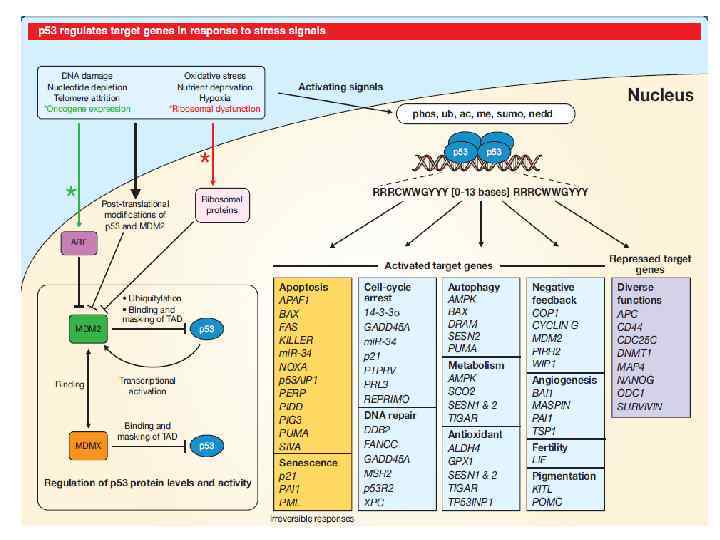
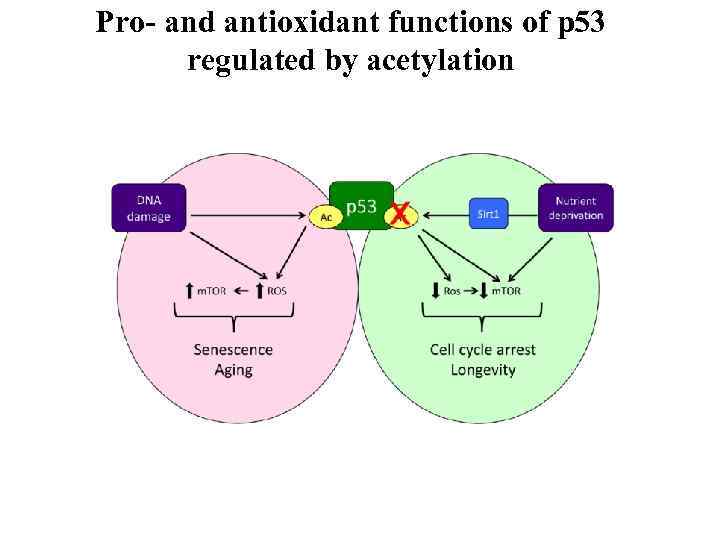 Pro- and antioxidant functions of p 53 regulated by acetylation
Pro- and antioxidant functions of p 53 regulated by acetylation
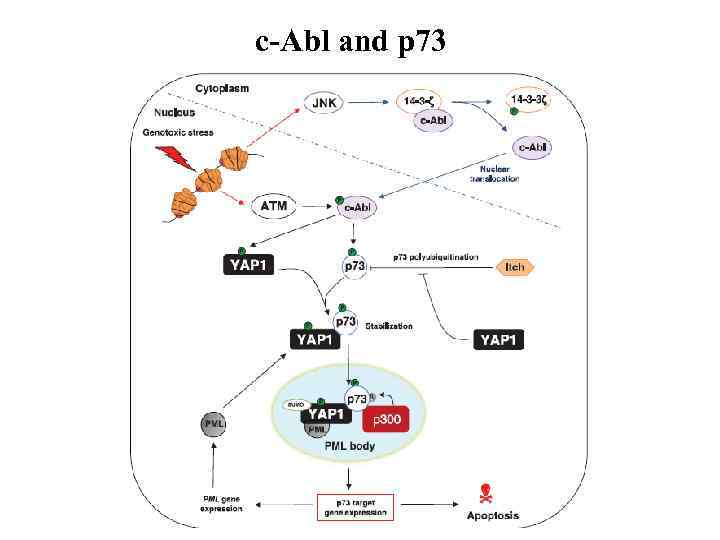 c-Abl and p 73
c-Abl and p 73
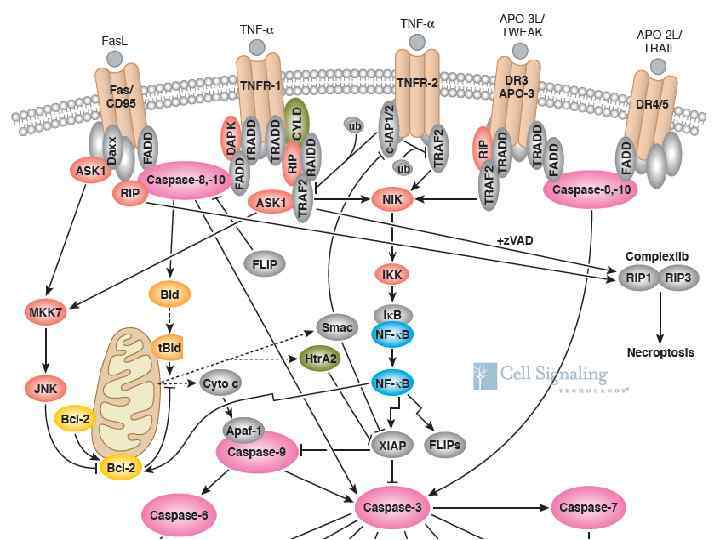
 TNFR-family and IL-1 R-family receptors
TNFR-family and IL-1 R-family receptors
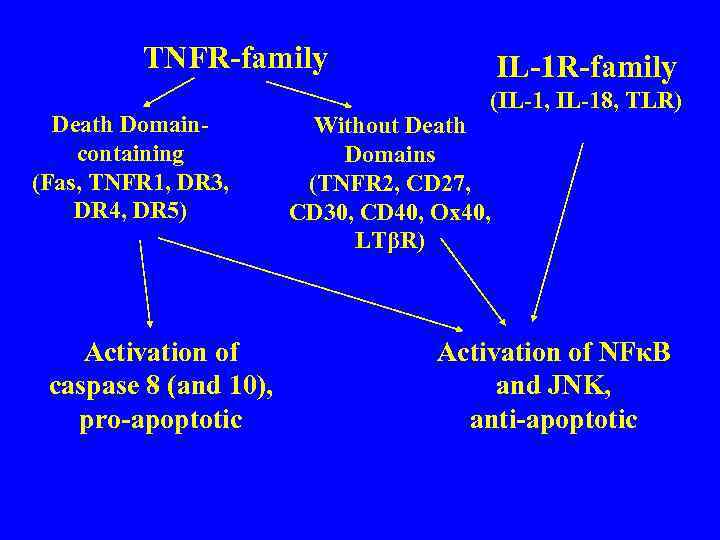 TNFR-family Death Domaincontaining (Fas, TNFR 1, DR 3, DR 4, DR 5) Activation of caspase 8 (and 10), pro-apoptotic IL-1 R-family (IL-1, IL-18, TLR) Without Death Domains (TNFR 2, CD 27, CD 30, CD 40, Ox 40, LTβR) Activation of NFκB and JNK, anti-apoptotic
TNFR-family Death Domaincontaining (Fas, TNFR 1, DR 3, DR 4, DR 5) Activation of caspase 8 (and 10), pro-apoptotic IL-1 R-family (IL-1, IL-18, TLR) Without Death Domains (TNFR 2, CD 27, CD 30, CD 40, Ox 40, LTβR) Activation of NFκB and JNK, anti-apoptotic
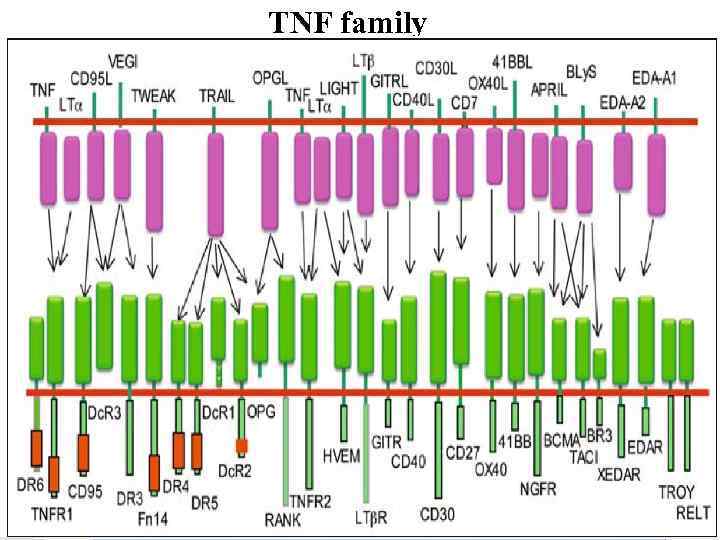 TNF family
TNF family
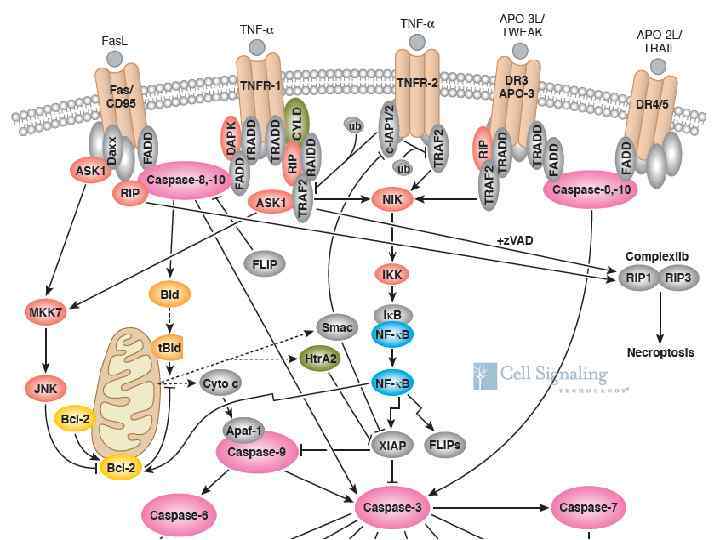
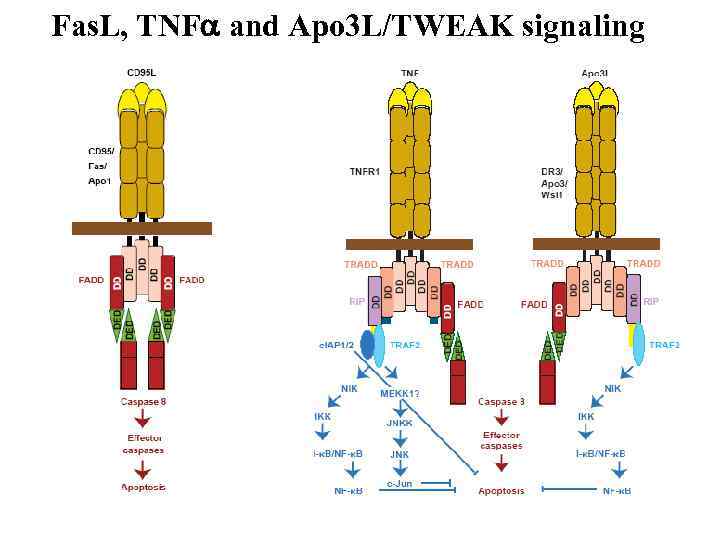 Fas. L, TNF and Apo 3 L/TWEAK signaling
Fas. L, TNF and Apo 3 L/TWEAK signaling
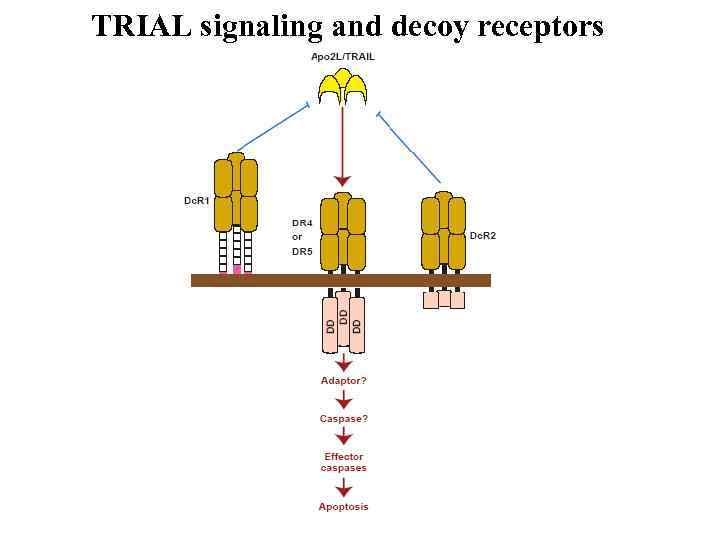 TRIAL signaling and decoy receptors
TRIAL signaling and decoy receptors
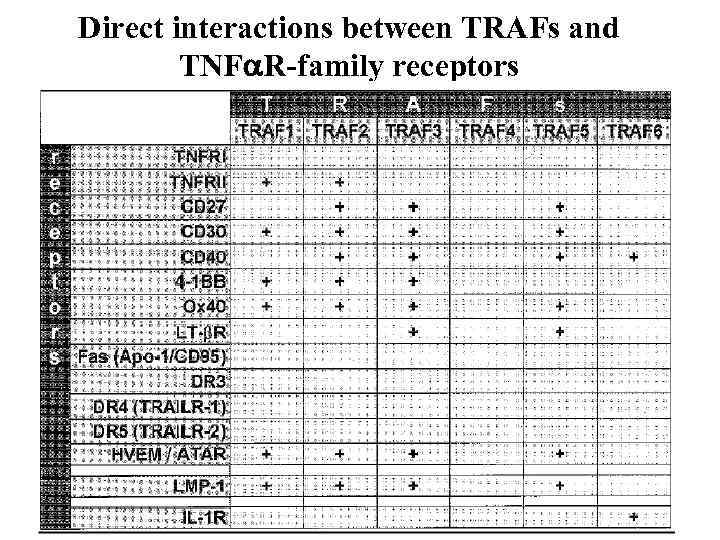 Direct interactions between TRAFs and TNF R-family receptors
Direct interactions between TRAFs and TNF R-family receptors
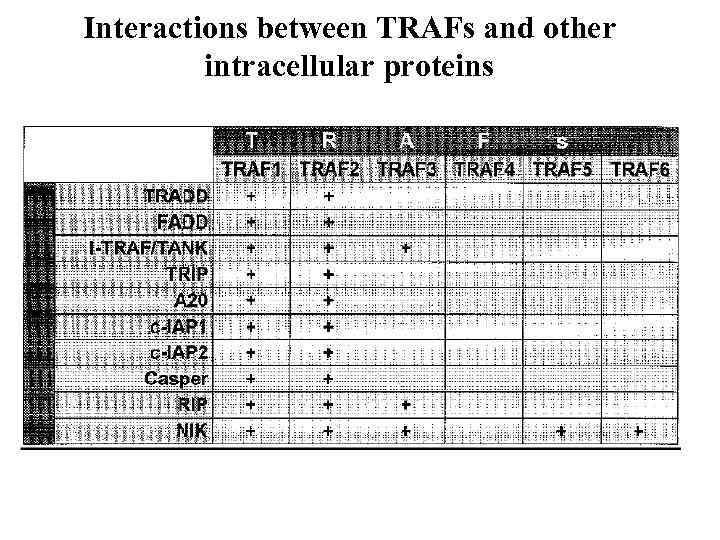 Interactions between TRAFs and other intracellular proteins
Interactions between TRAFs and other intracellular proteins
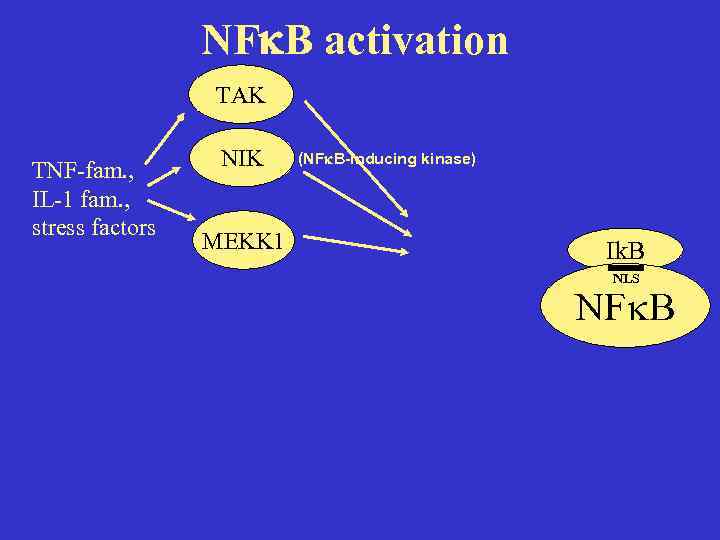 NF B activation TAK TNF-fam. , IL-1 fam. , stress factors NIK MEKK 1 (NF B-inducing kinase) Ik. B NLS NF B
NF B activation TAK TNF-fam. , IL-1 fam. , stress factors NIK MEKK 1 (NF B-inducing kinase) Ik. B NLS NF B
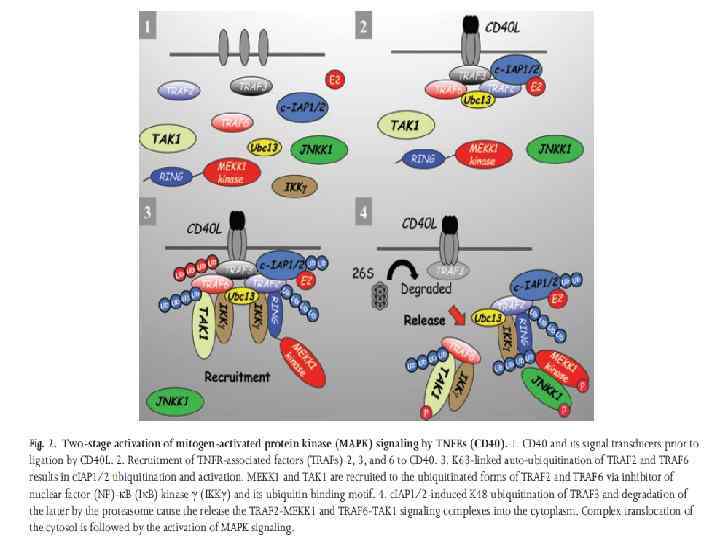
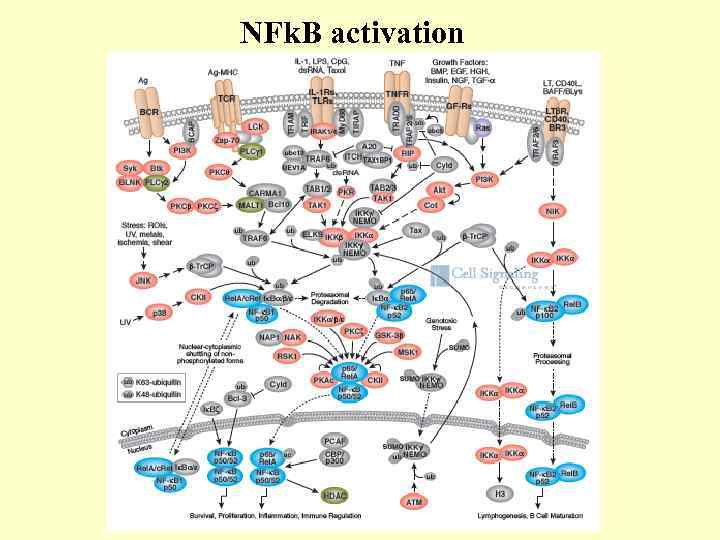 NFk. B activation
NFk. B activation
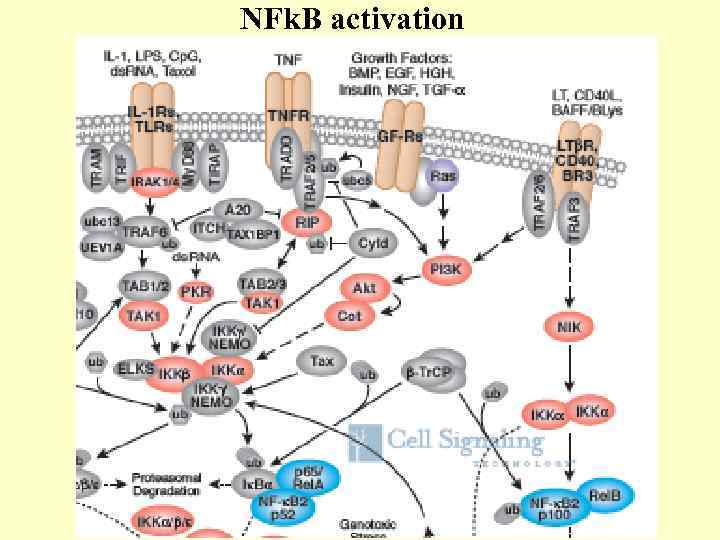 NFk. B activation
NFk. B activation
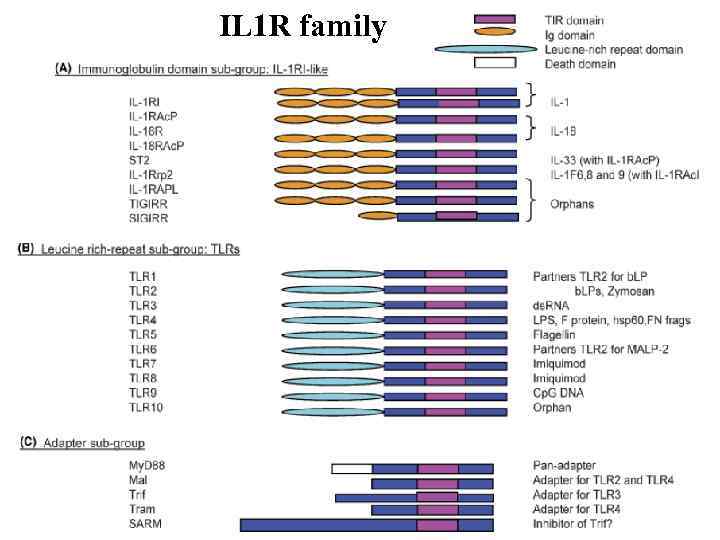 IL 1 R family
IL 1 R family
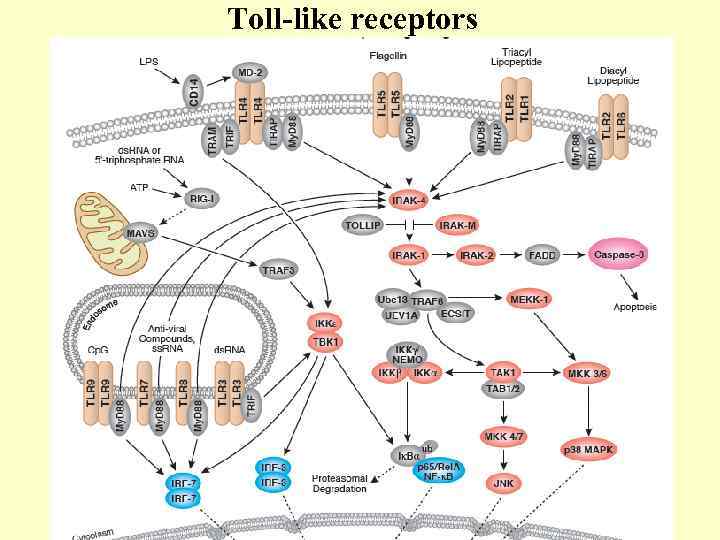 Toll-like receptors
Toll-like receptors

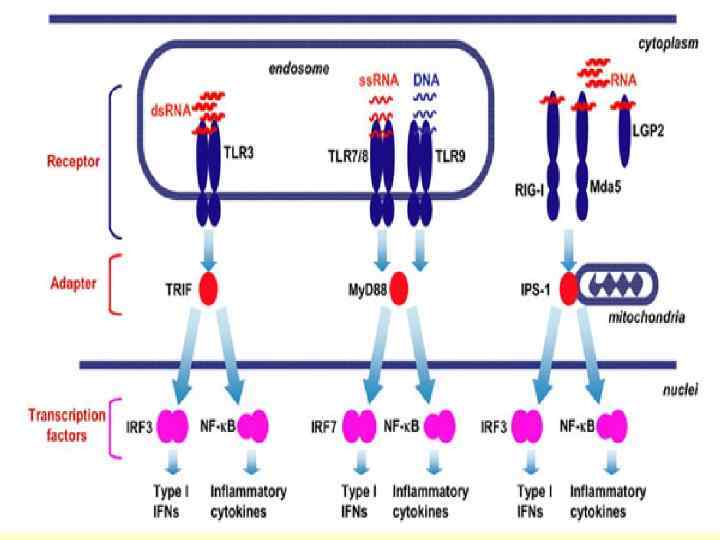
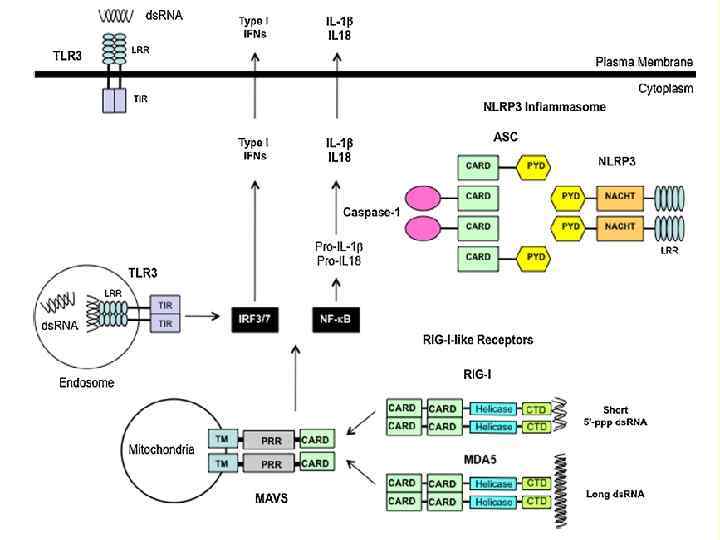
 Apoptosis
Apoptosis
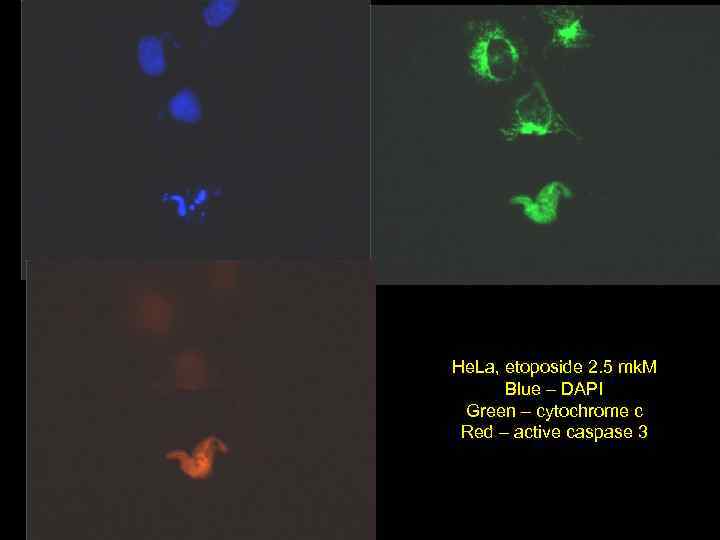 He. La, etoposide 2. 5 mk. M Blue – DAPI Green – cytochrome c Red – active caspase 3
He. La, etoposide 2. 5 mk. M Blue – DAPI Green – cytochrome c Red – active caspase 3
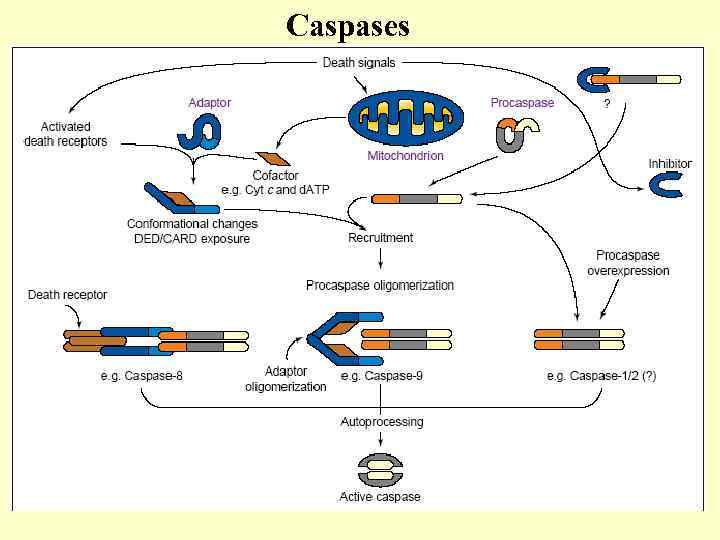 Caspases
Caspases
 Apoptotic caspases Initiatory – caspases 8 (and 10), 9, 2, 12(? ) Executive – caspases 3, 7 and 6
Apoptotic caspases Initiatory – caspases 8 (and 10), 9, 2, 12(? ) Executive – caspases 3, 7 and 6
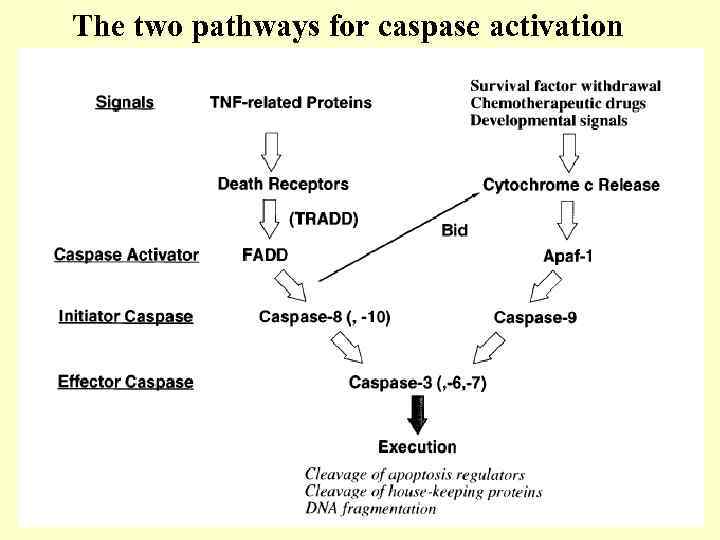 The two pathways for caspase activation
The two pathways for caspase activation
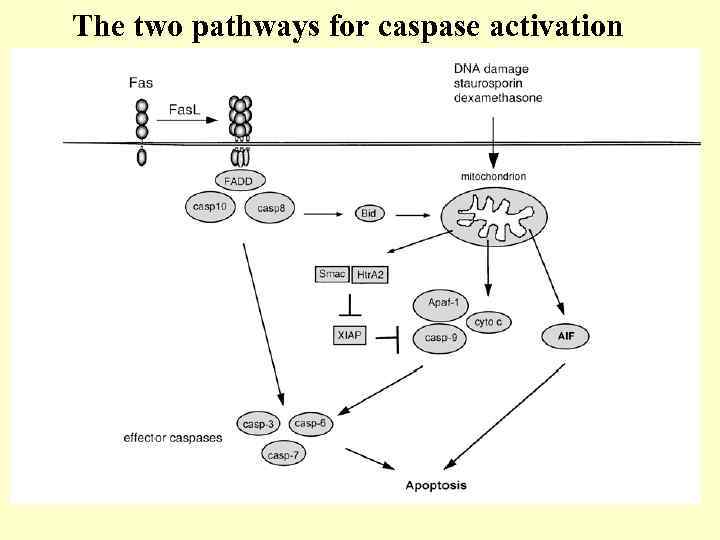 The two pathways for caspase activation
The two pathways for caspase activation
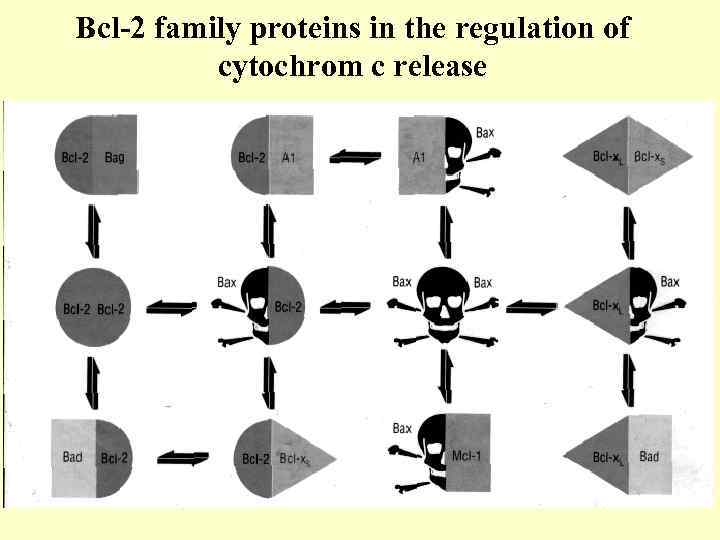 Bcl-2 family proteins in the regulation of cytochrom c release
Bcl-2 family proteins in the regulation of cytochrom c release
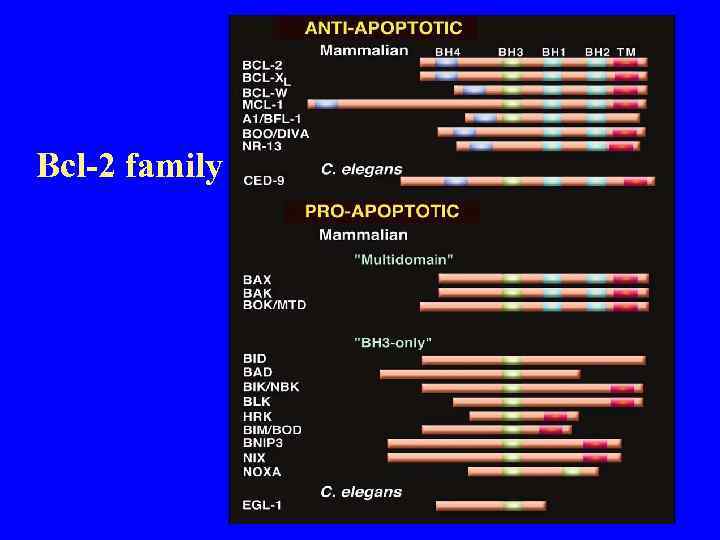 Bcl-2 family
Bcl-2 family
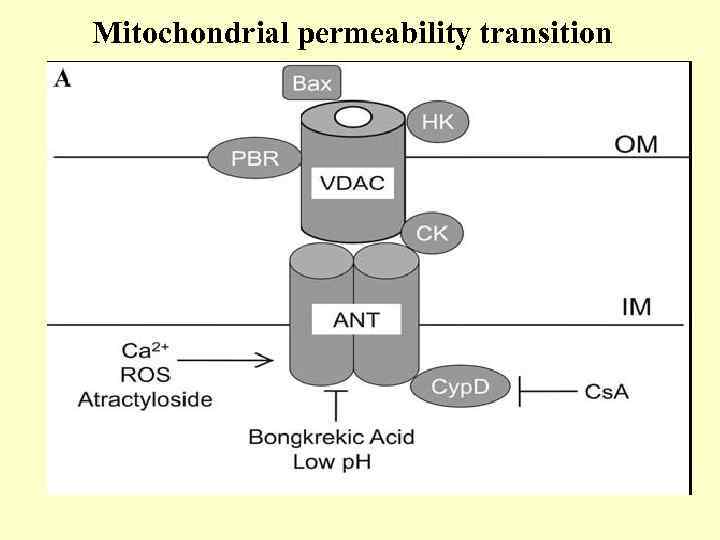 Mitochondrial permeability transition
Mitochondrial permeability transition
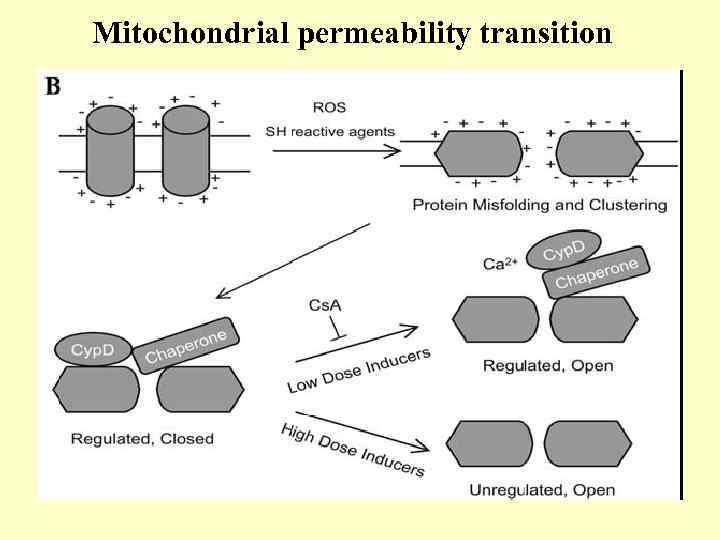 Mitochondrial permeability transition
Mitochondrial permeability transition
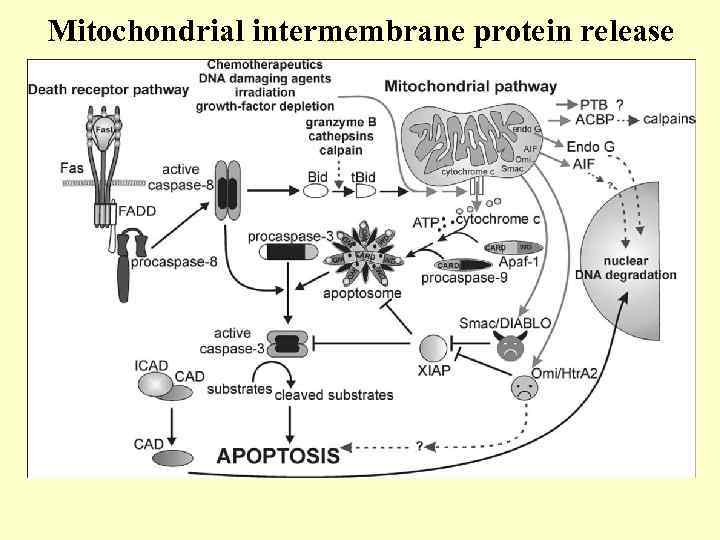 Mitochondrial intermembrane protein release
Mitochondrial intermembrane protein release
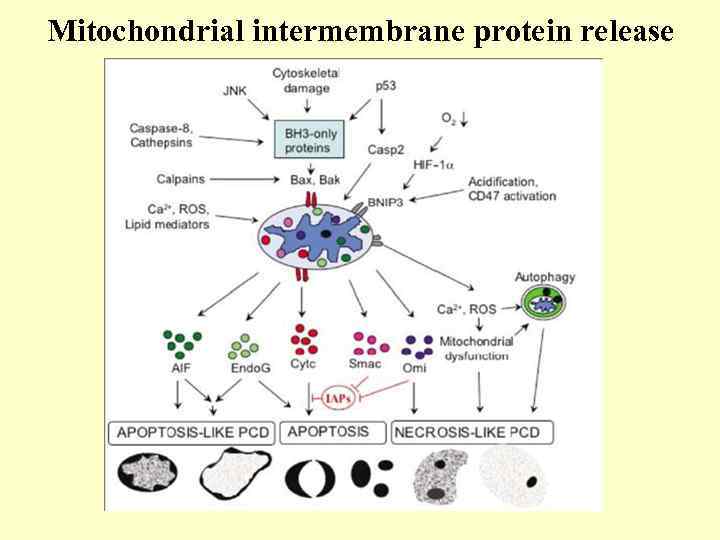 Mitochondrial intermembrane protein release
Mitochondrial intermembrane protein release
 Some inhibitors of caspase activation - IAPs (IAP 1, 2, survivin, XIAP) (for caspase 9) -FLIP, BAR, ARC (for caspase 8)
Some inhibitors of caspase activation - IAPs (IAP 1, 2, survivin, XIAP) (for caspase 9) -FLIP, BAR, ARC (for caspase 8)
 Some more important apoptosis inducers -Caspase 2 -Nuclear Daxx -Nur 77 -p 73 -Ceramide and sphingosine
Some more important apoptosis inducers -Caspase 2 -Nuclear Daxx -Nur 77 -p 73 -Ceramide and sphingosine
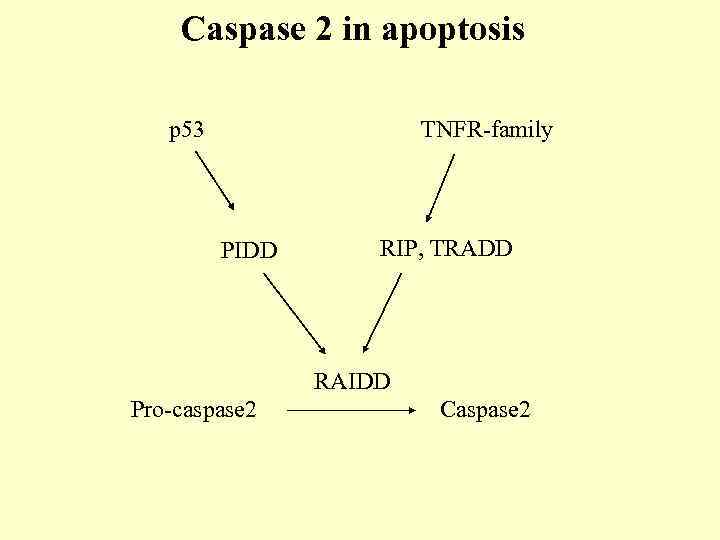 Caspase 2 in apoptosis p 53 TNFR-family PIDD RIP, TRADD RAIDD Pro-caspase 2 Caspase 2
Caspase 2 in apoptosis p 53 TNFR-family PIDD RIP, TRADD RAIDD Pro-caspase 2 Caspase 2
 Some more apoptosis inducers -Caspase 2 -Nuclear Daxx -Nur 77 -p 73 -Ceramide and sphingosine
Some more apoptosis inducers -Caspase 2 -Nuclear Daxx -Nur 77 -p 73 -Ceramide and sphingosine
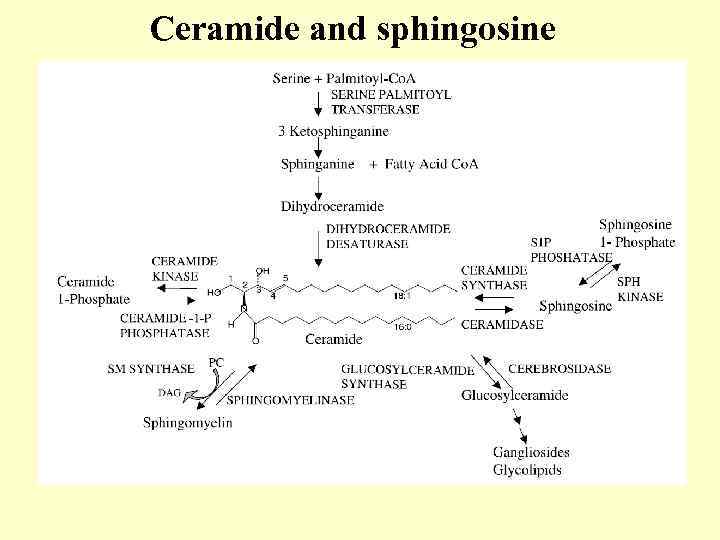 Ceramide and sphingosine
Ceramide and sphingosine
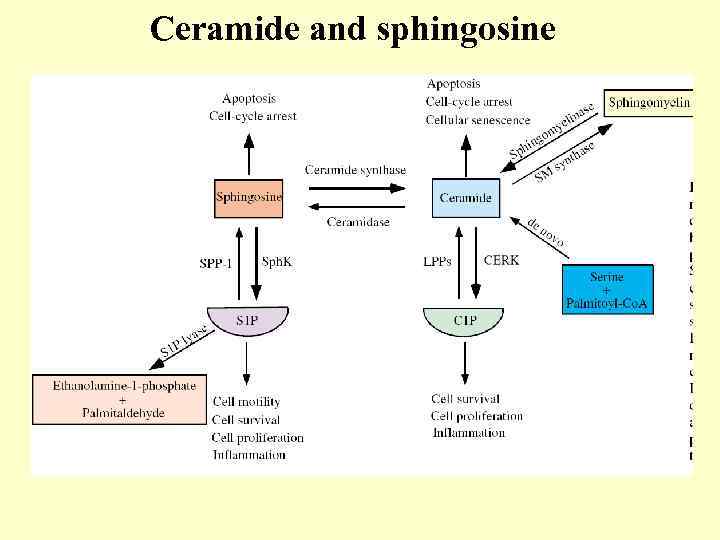 Ceramide and sphingosine
Ceramide and sphingosine
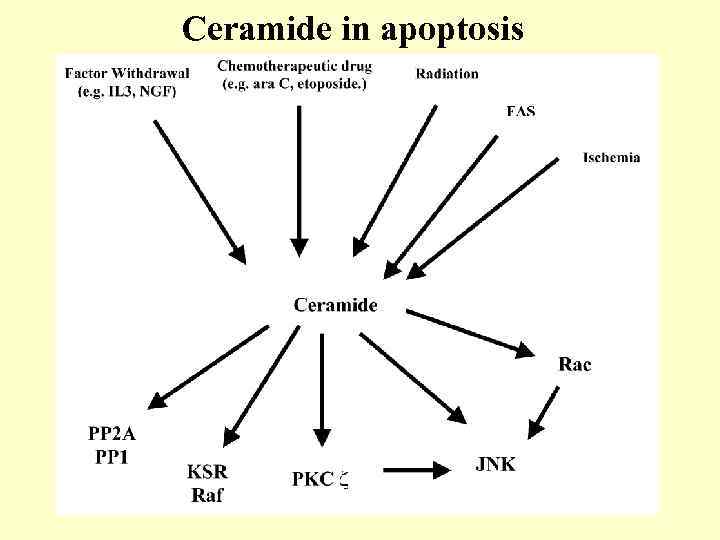 Ceramide in apoptosis
Ceramide in apoptosis
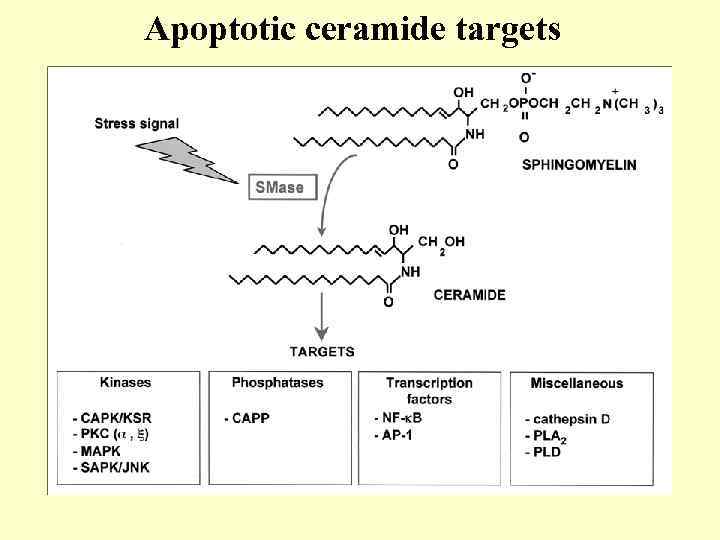 Apoptotic ceramide targets
Apoptotic ceramide targets
 Non-apoptotic cell death
Non-apoptotic cell death
 Non-apoptotic cell death variants - Caspase-independent apoptosis-like processes - Autophagy (type II programmed cell death) - Necrosis - Mitotic catastrophe
Non-apoptotic cell death variants - Caspase-independent apoptosis-like processes - Autophagy (type II programmed cell death) - Necrosis - Mitotic catastrophe
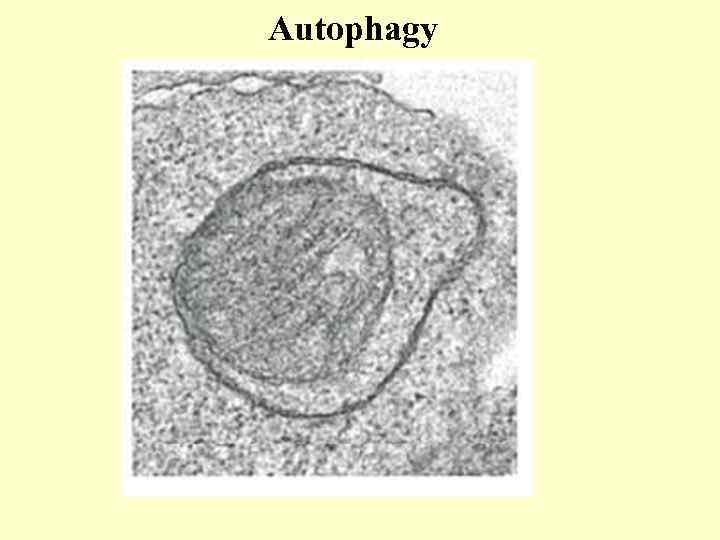 Autophagy
Autophagy
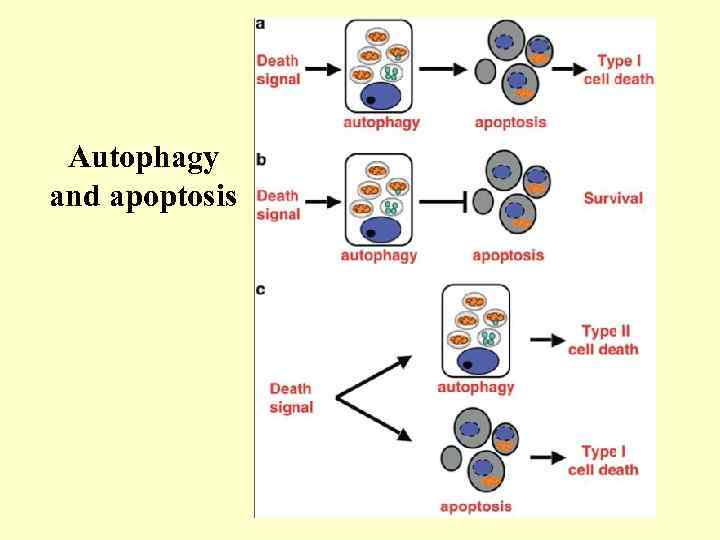 Autophagy and apoptosis
Autophagy and apoptosis
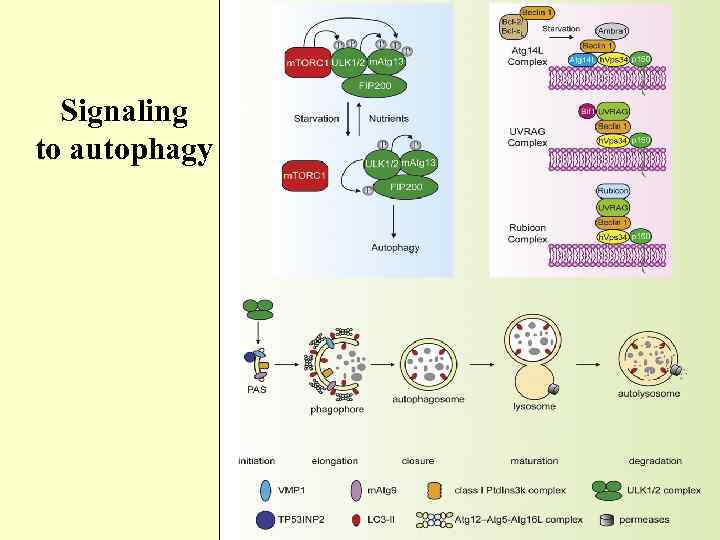 Signaling to autophagy
Signaling to autophagy
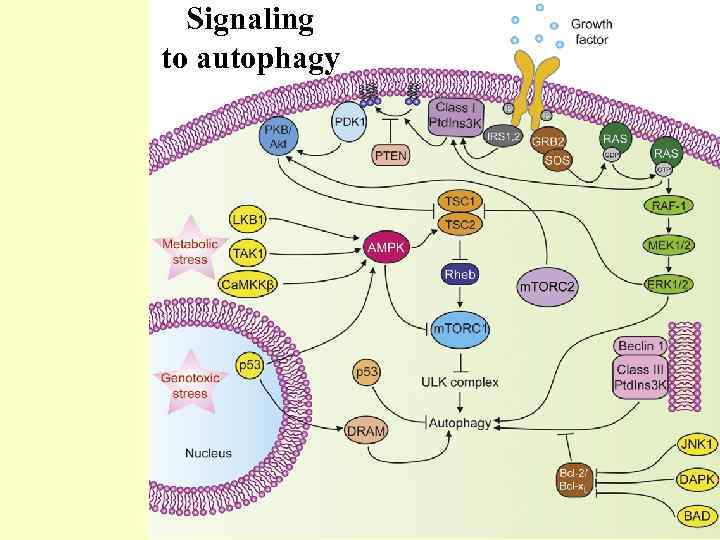 Signaling to autophagy
Signaling to autophagy
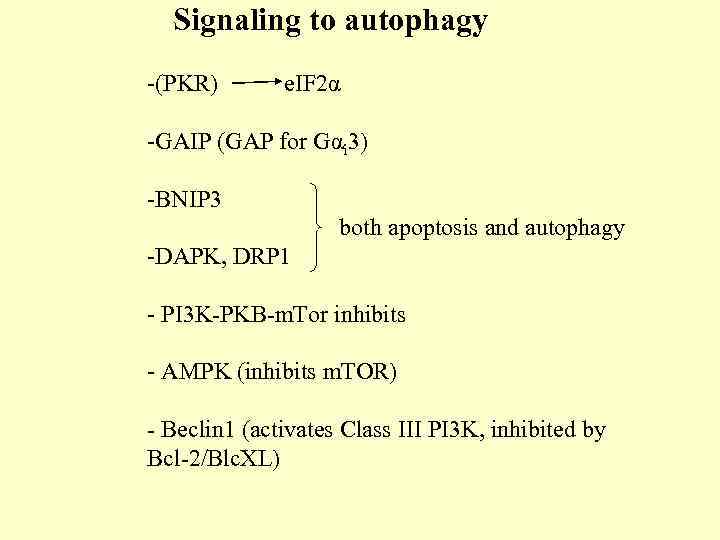 Signaling to autophagy -(PKR) e. IF 2α -GAIP (GAP for Gαi 3) -BNIP 3 both apoptosis and autophagy -DAPK, DRP 1 - PI 3 K-PKB-m. Tor inhibits - AMPK (inhibits m. TOR) - Beclin 1 (activates Class III PI 3 K, inhibited by Bcl-2/Blc. XL)
Signaling to autophagy -(PKR) e. IF 2α -GAIP (GAP for Gαi 3) -BNIP 3 both apoptosis and autophagy -DAPK, DRP 1 - PI 3 K-PKB-m. Tor inhibits - AMPK (inhibits m. TOR) - Beclin 1 (activates Class III PI 3 K, inhibited by Bcl-2/Blc. XL)
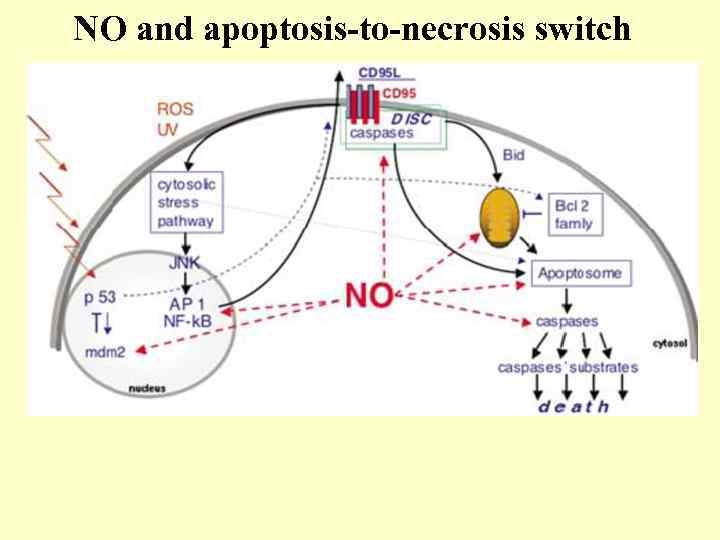 NO and apoptosis-to-necrosis switch
NO and apoptosis-to-necrosis switch
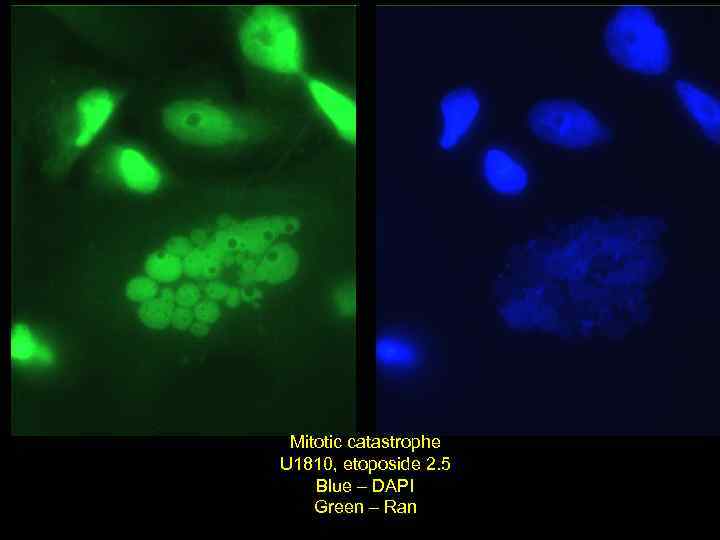 Mitotic catastrophe U 1810, etoposide 2. 5 Blue – DAPI Green – Ran
Mitotic catastrophe U 1810, etoposide 2. 5 Blue – DAPI Green – Ran
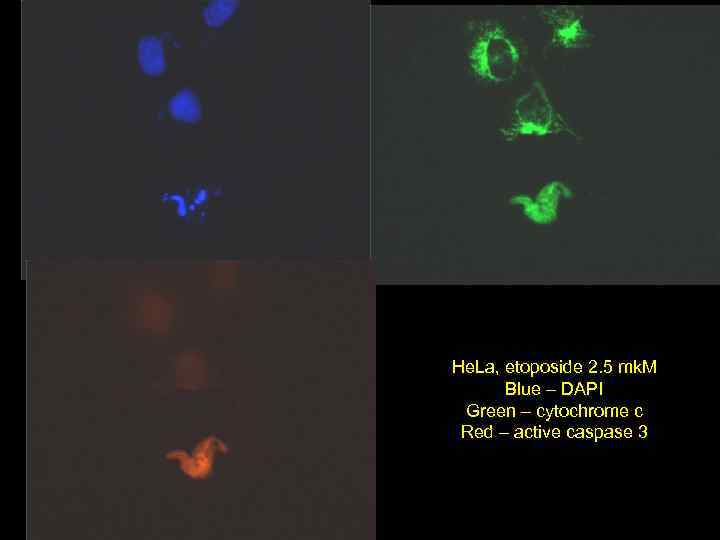 He. La, etoposide 2. 5 mk. M Blue – DAPI Green – cytochrome c Red – active caspase 3
He. La, etoposide 2. 5 mk. M Blue – DAPI Green – cytochrome c Red – active caspase 3


