c3476cd190ebee03390e1e7b2d7c8dc1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9

Distribution of Resources SOL WG. 9 b

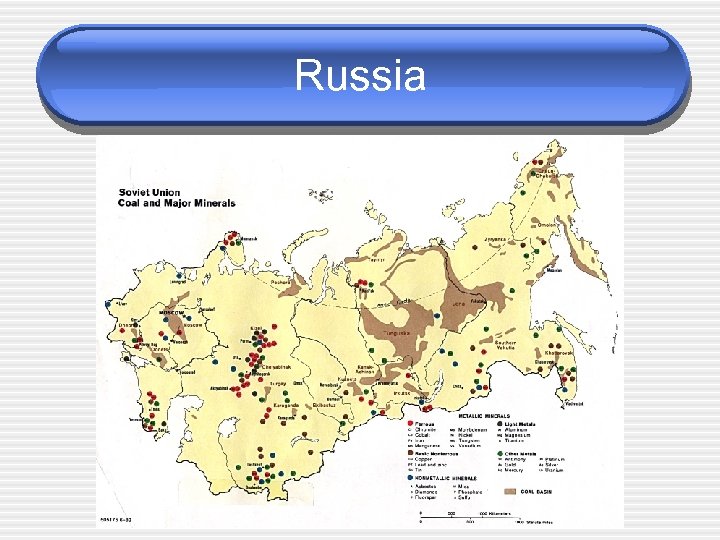
Resource Distribution • Countries do not have the same types A. B. and amounts of resources. Here are some examples: Japan - A highly industrialized country despite its lack of natural resources. Russia - Many natural resources that are difficult to extract due to weather, distance, and lack of infrastructure.

Resource Distribution C. United States - Abundant natural resources, diversified economy, and specialized industries. D. Cote d’ Ivoire - Limited natural resources. Country must exchange cash crops for manufactured goods. E. Switzerland - Limited natural resources but the country has a global service industry.
Russia

Cote d’Ivoire • Cote d’Ivoire is the worlds largest producer of cocoa beans and a significant producer of coffee and palm oil. However, around 68% of the population works in agriculture. In comparison, about. 6% of the labor force in the United States works in agriculture.

Switzerland • Labor force by occupation in Switzerland: • agriculture 4. 6%, industry 26. 3%, services 69. 1% Switzerland has large banking and tourism industries

Effects of Unequal Distribution • Since countries do not have all of the • resources they need they usually specialize in goods and services that the country can market for a profit. Countries engage in exchange of goods and services. (sell what you can and buy what you can’t produce)

Comparative Advantage • Comparative advantage is when a country exports goods and services that they can produce at a lower relative cost than other countries.

Why do Countries Trade? • To import goods and services that you • need To export goods and services that you can market for a profit
c3476cd190ebee03390e1e7b2d7c8dc1.ppt