42d29e5a7630eb5475faf47ab293da92.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Distributed System 電機四 陳伯翰 b 90901011

Distributed System Structures outline Definition Characterisic Process migration Distributed file system Topology Grid

Definition 不共用memory,clock的一群 processors. Loosely coupled by communication network. (remote) 如手機連到電腦編輯通訊錄

History & Feature History – Uni-processor Supercomputer – Parallel – Distributed System – Collaborative … the Grid Feature – Inherently layered architecture – Shared, heterogeneous, distributed resources

Grid Computing - Application Global weather analysis DNA breakdown Particle Physics

為什麼要DS Resource sharing - CPU , disks, , memory -data (e. g. , file systems, databases, etc. )
Types of Distributed O. S. Network operating system – Remote login( long dis access) – Remote file transfer(not transparent) Distributed operating system – Data migration Only necessary – Process migration
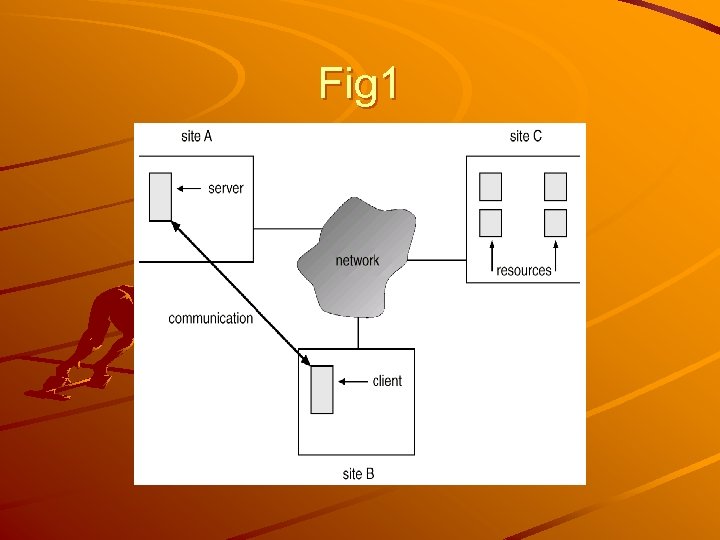
Fig 1

Definition Characterisic Process migration Distributed file system Topology Grid

特色 Resource sharing – Ex. Printer , high-speed array processor Computation speedup – Load sharing. Automated load sharing. Reliability – Correct site fails. Instead of dependence. – Detect , Recovery from fails.

Challenges Heterogeneity – Networks, OS, hardware, language Openness – Documents and specifications Security – Encryption, DOS( denial of service ) Scalability – Data should be structured hierarchically

Challenges (con ‘t) Failure handling – Any process, computer fails indep Robustness – Detect(handshake) – reconfigure (emergency process) – Recover(rejoint)

Trade off Scalability – It is potential to combine all the three by distributed system 集中式和自主化的trade-off Use thread to deal with each host each process , or even each push and pop.

Definition Characterisic Process migration Distributed file system Topology Grid

Process migration Load balancing Computation speedup Hardware preference Software preference Scheduler Ex. Java applet

Concurrent No happened before relation. Each process has independent effect on the whole implementation.
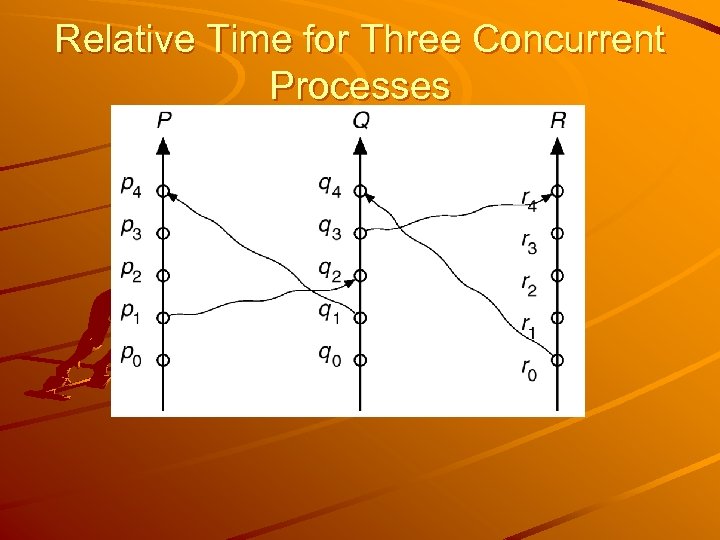
Relative Time for Three Concurrent Processes

Distributed Mutual Exclusion (DME) Assumptions – Each process has a critical section that requires mutual exclusion. .

Distributed Mutual Exclusion (DME) Centralized approach Fully distributed approach Token-passing approach

Definition Characterisic Process migration Distributed file system Topology Grid
DFS Distributed file system (DFS) – a distributed implementation of a file system, where multiple users share files and storage resources. remotely located, smaller storage spaces. constituent storage spaces and sets of files
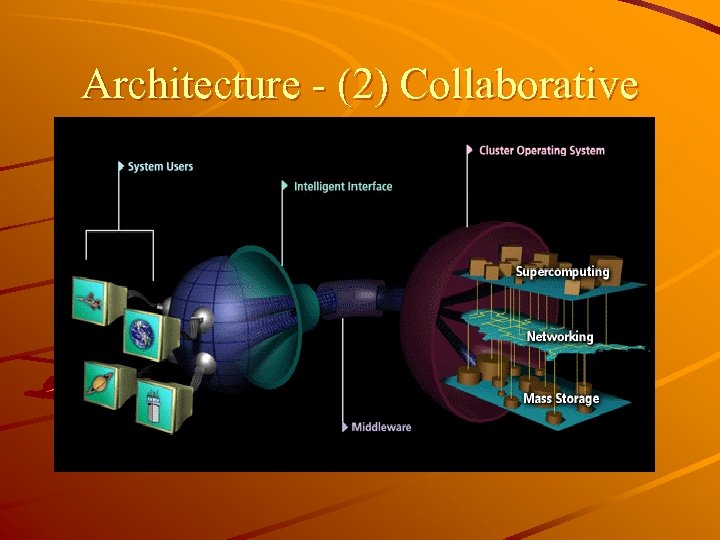
Architecture - (2) Collaborative

DFS Structure Service Server – service software running on a single machine. Client – process that can invoke a service using a set of operations that forms its client interface.

A client interface for a file service is formed by a set of primitive file operations (create, delete, read, write). Client interface of a DFS should be transparent, i. e. , not distinguish between local and remote files.

Naming and Transparency Naming – mapping between logical and physical objects. Multilevel mapping – abstraction of a file that hides the details of how and where on the disk the file is actually stored. A transparent DFS hides the location where in the network the file is stored.

Definition Characterisic Process migration Distributed file system Topology Grid

Topology Installation cost Communication cost( delay time) Availability( reliability) Partially connected network Routing , split , cost.
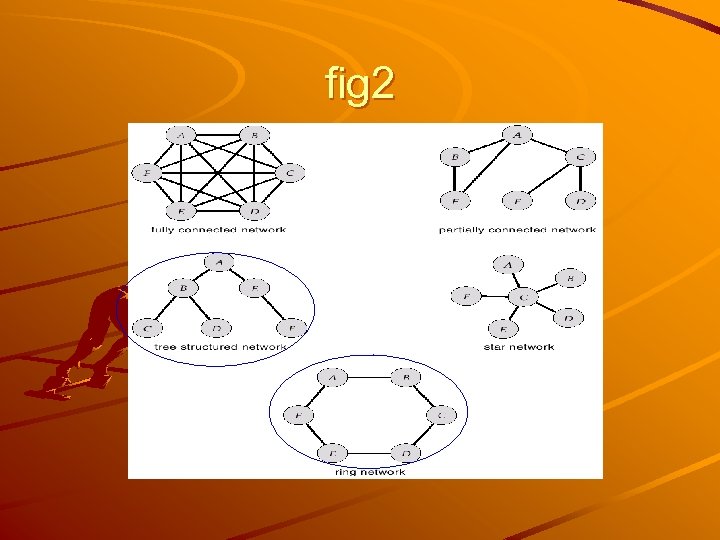
fig 2
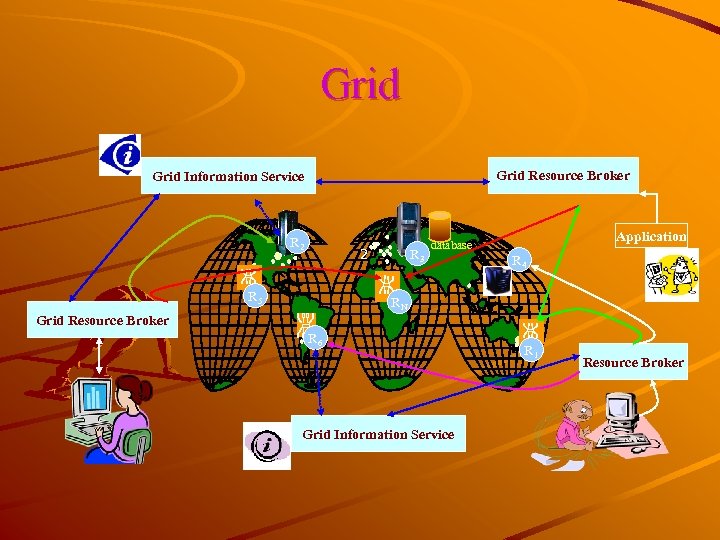
Grid Resource Broker Grid Information Service R 2 2 R 5 R 3 Application database R 4 RN Grid Resource Broker R 6 Grid Information Service R 1 Resource Broker
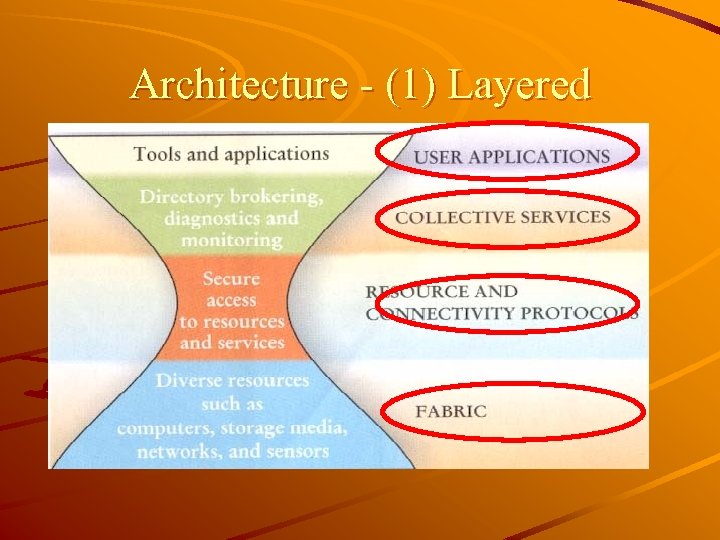
Architecture - (1) Layered

Conclude the Grid The Grid solving that requires high performance computing using widely distributed, heterogeneous resources. Topology The Grid inherently layered architecture that provides for common services and a diversity of middleware that supports building distributed, large-scale, systems.

謝謝大家
42d29e5a7630eb5475faf47ab293da92.ppt