fee147bd880526ca4c888ae75cd4d5d0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17

Distributed Framework for Automatic Facial Mark Detection Graduate Operating Systems-CSE 60641 Nisha Srinivas and Tao Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering nsriniva, txu 1@nd. edu 1

Introduction • What is Biometrics? – Face, iris, fingerprint etc. – Face is a popular biometric • Non-invasive Different type of Biometric. – Identical twins have a high degree of facial similarity. • Fine details on the face like facial marks are used to distinguish between identical twins. – Automatic facial mark detector: detects facial marks and extracts facial mark features. 2

Automatic Facial Mark Detector Independent of results from other images Convert Images Face Contour Points Crop face Images Detect facial marks 3

Objective • Drawbacks of the Automatic Facial Mark Detector – Slow • Size of the dataset • Size of each image in the dataset • Run time of algorithms is long • Executing it sequentially • Objective: – To design a distributed framework for the automatic facial mark detector. • To improve computation time • To obtain scalability 4
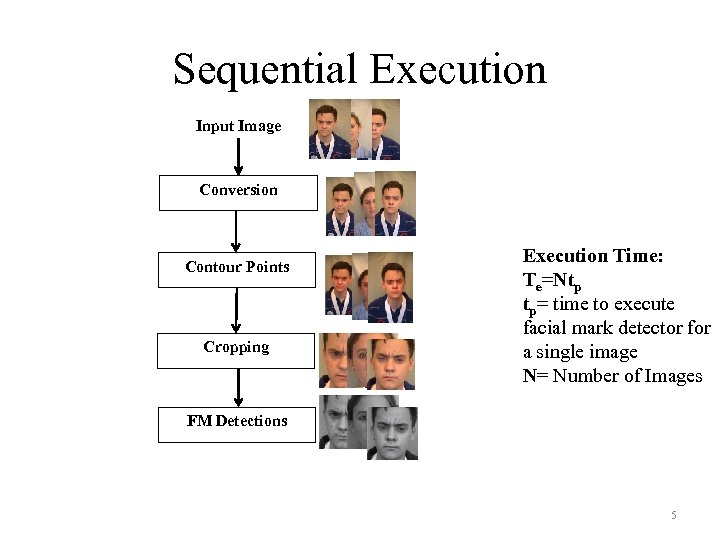
Sequential Execution Input Image Conversion Contour Points Cropping Execution Time: Te=Ntp tp= time to execute facial mark detector for a single image N= Number of Images FM Detections 5
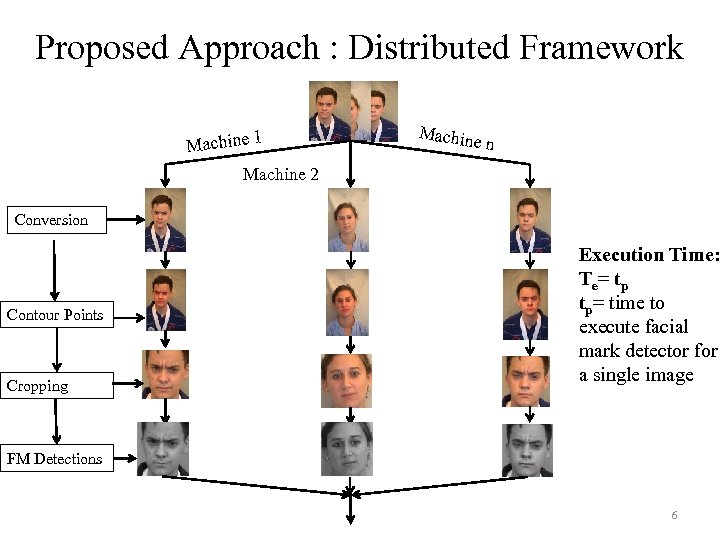
Proposed Approach : Distributed Framework Machine 1 Machine n Machine 2 Conversion Contour Points Cropping Execution Time: T e = tp tp= time to execute facial mark detector for a single image FM Detections 6

• Implementation – Combination of Makeflow, Worker Queue , Condor • Condor is a distributed environment which makes use of idle resources on remote computers. • Work Queue is a fault tolerant framework. – Master/Worker framework. – Manages Condor • Makeflow – Distributed computing abstraction – Runs computations on WQ – The computations have dependencies that are represented by directed acyclic graph (DAG). 7
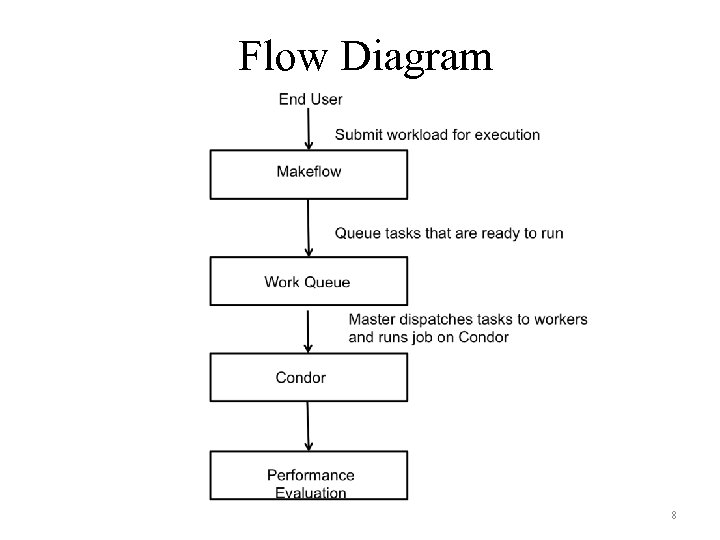
Flow Diagram 8

Performance Metrics • We evaluate the performance of the distributed framework by computing the following metrics – Total execution time – Node Efficiency – Scalability • Weak scaling: Number of jobs proportional to number of images in dataset. • Strong scaling: Number of jobs is varied by keeping the number of images in the dataset a constant. 9

Dataset and System Specifications • Twin face images were collected at the Twins Days Festival in Twinsburg, Ohio in August 2009. • High Resolution Images: 4310 rows x 2868 columns • Total Number of Images: 800 – Dataset size based on attributes: [206 200 250 144] • Notre Dame Condor Pool: ~(700 cores) 10
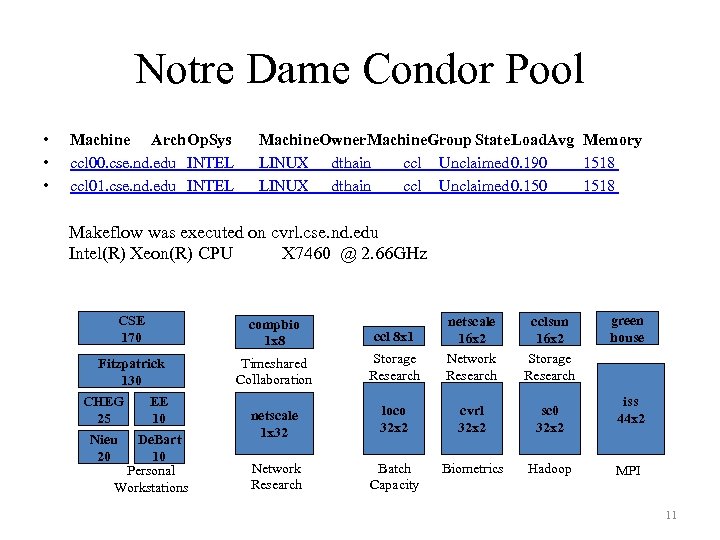
Notre Dame Condor Pool • • • Machine Arch. Op. Sys ccl 00. cse. nd. edu INTEL ccl 01. cse. nd. edu INTEL Machine. Owner. Machine. Group State. Load. Avg Memory LINUX dthain ccl Unclaimed 0. 190 1518 LINUX dthain ccl Unclaimed 0. 150 1518 Makeflow was executed on cvrl. cse. nd. edu Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU X 7460 @ 2. 66 GHz CSE 170 compbio 1 x 8 ccl 8 x 1 Fitzpatrick 130 Timeshared Collaboration CHEG 25 Nieu 20 EE 10 De. Bart 10 Personal Workstations Storage Research netscale 16 x 2 Network Research cclsun 16 x 2 Storage Research netscale 1 x 32 loco 32 x 2 cvrl 32 x 2 sc 0 32 x 2 Network Research Batch Capacity Biometrics Hadoop green house iss 44 x 2 MPI 11
Experiments • Experiment 1 – Comparison of total execution time between the distributed framework and sequential framework. – Submit N jobs to Condor by keeping the dataset constant. – Number of jobs workers for distributed framework= {10, 50, 100, 150, 200} – Dataset Size= 206 – Executed on the Notre Dame Condor Pool. 12
• Experiment 2 – To evaluate node efficiency – Analyze the time taken for a single job to complete on a machine in the Notre Dame Condor Pool. • Experiment 3 – To evaluate scalability of the AFMD • Weak scaling: Number of jobs proportional to number of images in dataset. • Strong scaling: Number of jobs is varied by keeping the number of images in the dataset a constant. 13
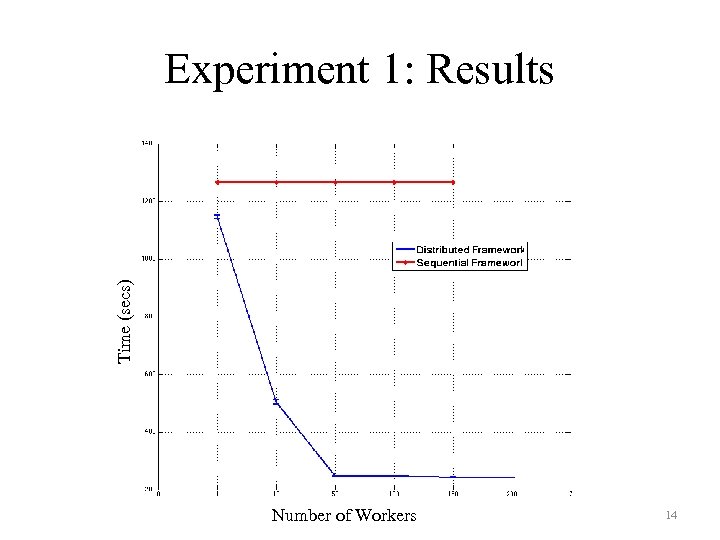
Time (secs) Experiment 1: Results Number of Workers 14
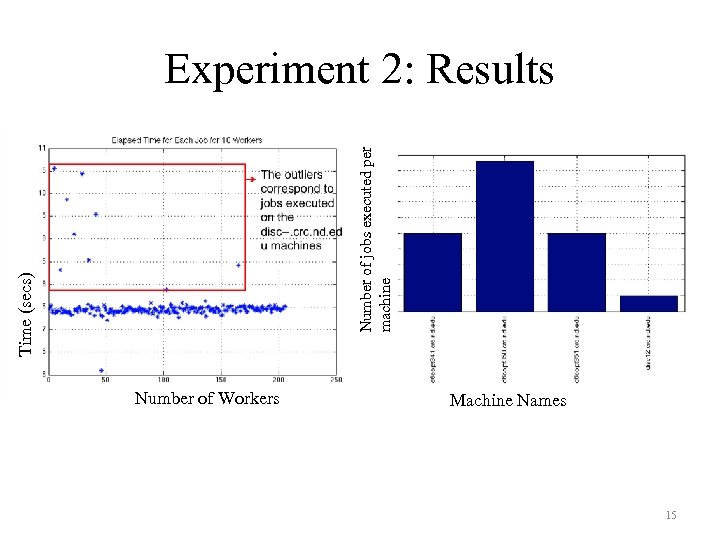
Time (secs) Number of jobs executed per machine Experiment 2: Results Number of Workers Machine Names 15
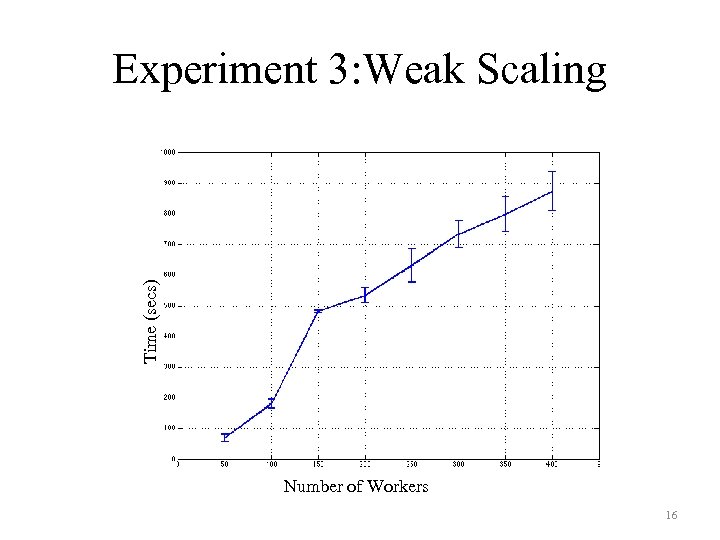
Time (secs) Experiment 3: Weak Scaling Number of Workers 16

Conclusion • Designed and implemented a distributed framework for a Automatic facial mark detector. • It was implemented using Makeflow, Work Queue and Condor. • Performance of the distributed framework is significantly better. 17
fee147bd880526ca4c888ae75cd4d5d0.ppt