ba15435dcadf8997db0068f6cf6f37af.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Dissolved Oxygen The Good Gas
Dissolved Oxygen The Good Gas
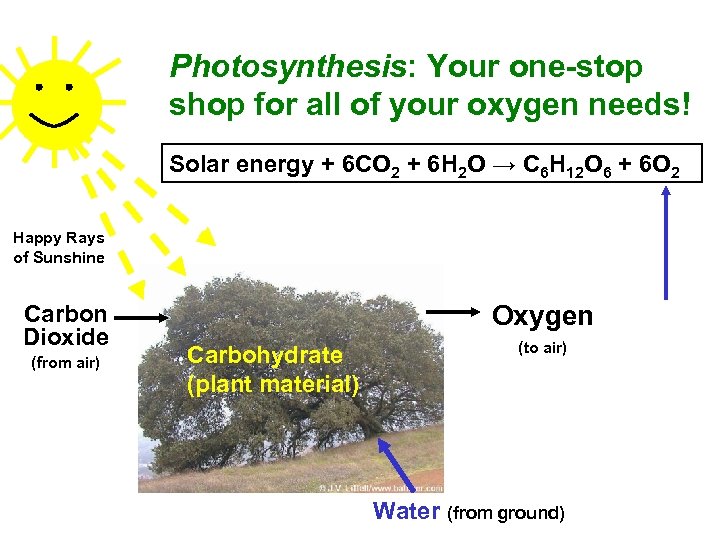 Photosynthesis: Your one-stop shop for all of your oxygen needs! Solar energy + 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 Happy Rays of Sunshine Carbon Dioxide (from air) Oxygen Carbohydrate (plant material) (to air) Water (from ground)
Photosynthesis: Your one-stop shop for all of your oxygen needs! Solar energy + 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 Happy Rays of Sunshine Carbon Dioxide (from air) Oxygen Carbohydrate (plant material) (to air) Water (from ground)
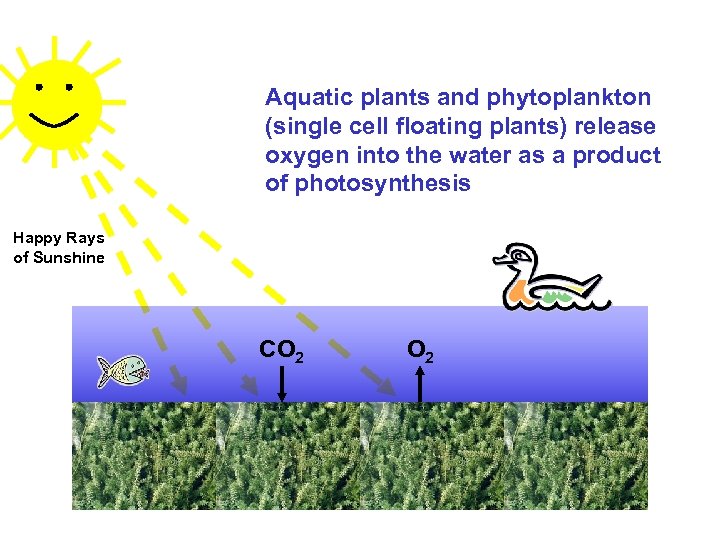 Aquatic plants and phytoplankton (single cell floating plants) release oxygen into the water as a product of photosynthesis Happy Rays of Sunshine CO 2
Aquatic plants and phytoplankton (single cell floating plants) release oxygen into the water as a product of photosynthesis Happy Rays of Sunshine CO 2
 Phytoplankton (single cell plants) – are the base of the aquatic food web and provide most of the aquatic oxygen.
Phytoplankton (single cell plants) – are the base of the aquatic food web and provide most of the aquatic oxygen.
 Submerged aquatic plants can provide shelter for young fish as well as house an abundant food supply.
Submerged aquatic plants can provide shelter for young fish as well as house an abundant food supply.
 Oxygen: A Soluble Gas H 2 O O 2 O 2 H 2 O O 2 H O H 2 O 2 H 2 O
Oxygen: A Soluble Gas H 2 O O 2 O 2 H 2 O O 2 H O H 2 O 2 H 2 O
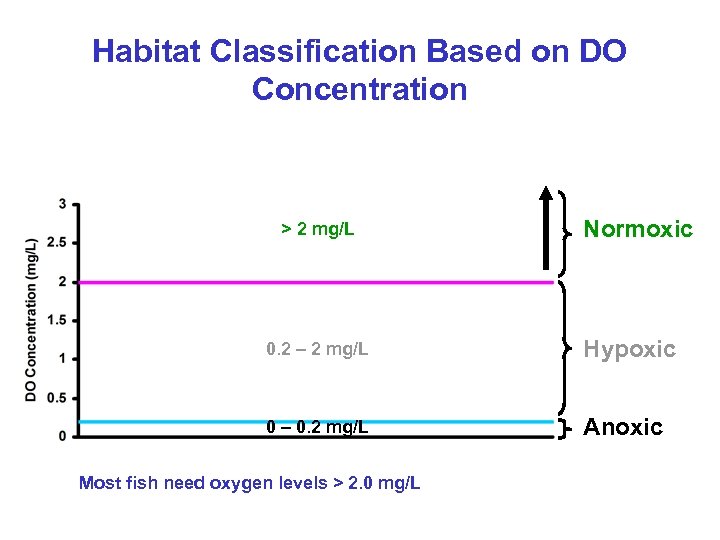 Habitat Classification Based on DO Concentration > 2 mg/L Normoxic 0. 2 – 2 mg/L Hypoxic 0 – 0. 2 mg/L Anoxic Most fish need oxygen levels > 2. 0 mg/L
Habitat Classification Based on DO Concentration > 2 mg/L Normoxic 0. 2 – 2 mg/L Hypoxic 0 – 0. 2 mg/L Anoxic Most fish need oxygen levels > 2. 0 mg/L
 Respiration: How we, the animals, use oxygen (and plants too!) C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 → 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + energy (in form of ATP) Carbohydrate + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy Oxygen in CO 2 and H 2 O out Energy out n te i ra Previous Meal Car hyd bo
Respiration: How we, the animals, use oxygen (and plants too!) C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 → 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + energy (in form of ATP) Carbohydrate + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy Oxygen in CO 2 and H 2 O out Energy out n te i ra Previous Meal Car hyd bo
 CO 2: A Soluble Gas Too! CO 2 O CO 2 2 H 2 O O 2 CO 2 O 2 H O H 2 O 2 H 2 O CO 2 H 2 O
CO 2: A Soluble Gas Too! CO 2 O CO 2 2 H 2 O O 2 CO 2 O 2 H O H 2 O 2 H 2 O CO 2 H 2 O
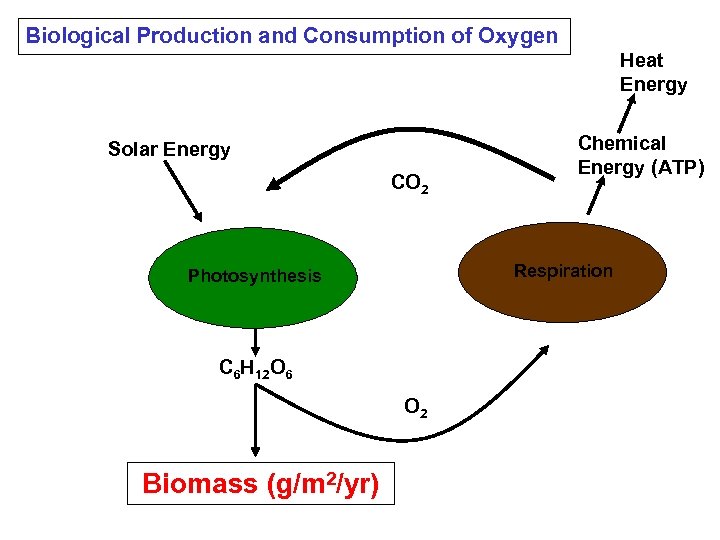 Biological Production and Consumption of Oxygen Heat Energy Solar Energy CO 2 Respiration Photosynthesis C 6 H 12 O 6 O 2 Biomass (g/m 2/yr) Chemical Energy (ATP)
Biological Production and Consumption of Oxygen Heat Energy Solar Energy CO 2 Respiration Photosynthesis C 6 H 12 O 6 O 2 Biomass (g/m 2/yr) Chemical Energy (ATP)
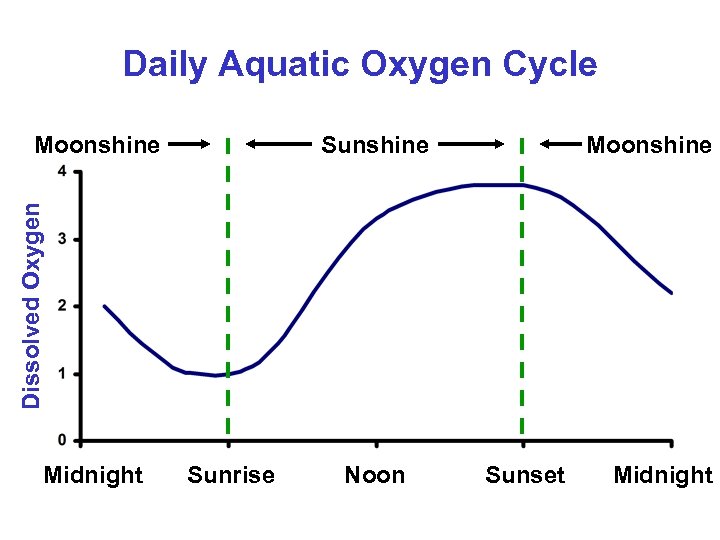 Daily Aquatic Oxygen Cycle Sunshine Moonshine Dissolved Oxygen Moonshine Midnight Sunrise Noon Sunset Midnight
Daily Aquatic Oxygen Cycle Sunshine Moonshine Dissolved Oxygen Moonshine Midnight Sunrise Noon Sunset Midnight
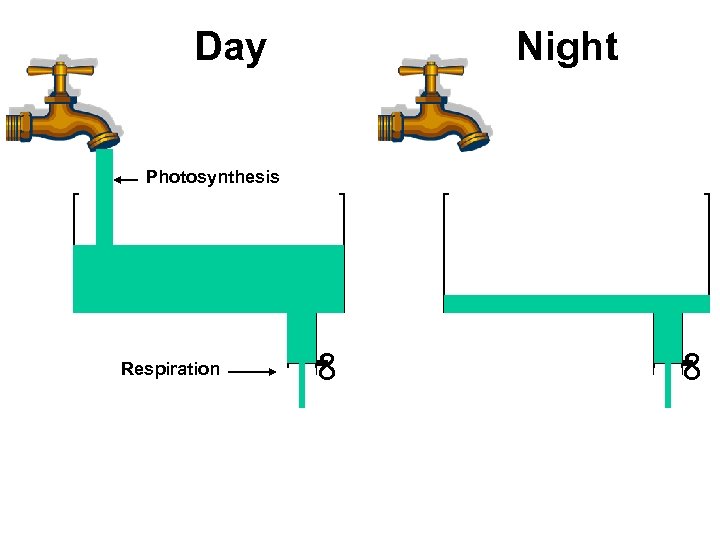 Day Night Photosynthesis ∞ ∞ Respiration
Day Night Photosynthesis ∞ ∞ Respiration
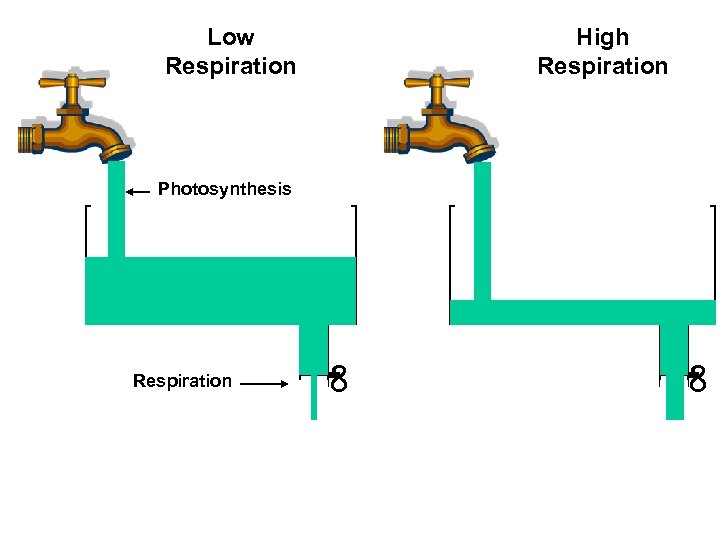 Low Respiration High Respiration Photosynthesis ∞ ∞ Respiration
Low Respiration High Respiration Photosynthesis ∞ ∞ Respiration
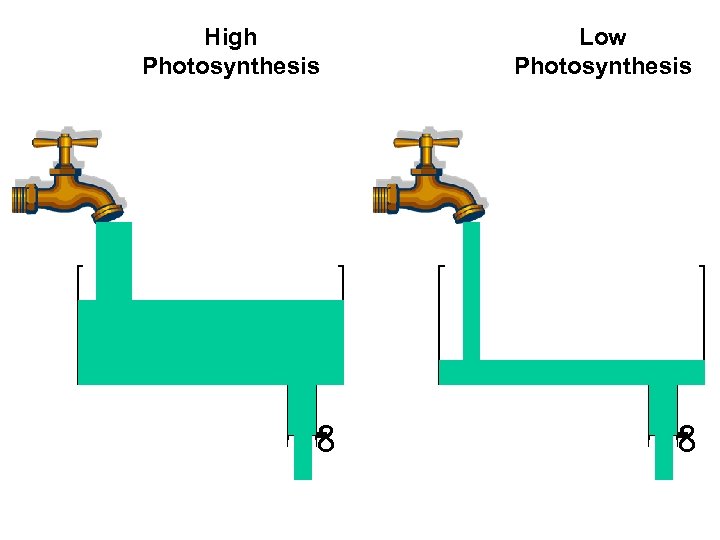 High Photosynthesis Low Photosynthesis ∞ ∞
High Photosynthesis Low Photosynthesis ∞ ∞
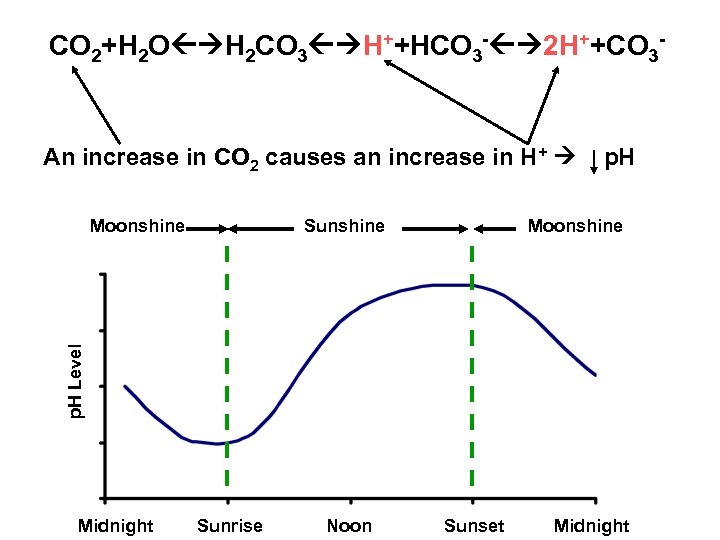 CO 2+H 2 O H 2 CO 3 H++HCO 3 - 2 H++CO 3 - An increase in CO 2 causes an increase in H+ Sunshine Moonshine p. H Level Moonshine p. H Midnight Sunrise Noon Sunset Midnight
CO 2+H 2 O H 2 CO 3 H++HCO 3 - 2 H++CO 3 - An increase in CO 2 causes an increase in H+ Sunshine Moonshine p. H Level Moonshine p. H Midnight Sunrise Noon Sunset Midnight
 Decomposition – Not good for DO • Decomposer organisms (mainly bacteria) consume oxygen – Sometimes consume oxygen faster than plants can produce it, even during the middle of the day! • A sudden increase in organic matter (think leaf litter) can create a spike in decomposition activity – especially if it is hot – Hurricanes not only add organic matter to our waterways, but also stir up the sediment. – Can cause fish kills!!
Decomposition – Not good for DO • Decomposer organisms (mainly bacteria) consume oxygen – Sometimes consume oxygen faster than plants can produce it, even during the middle of the day! • A sudden increase in organic matter (think leaf litter) can create a spike in decomposition activity – especially if it is hot – Hurricanes not only add organic matter to our waterways, but also stir up the sediment. – Can cause fish kills!!
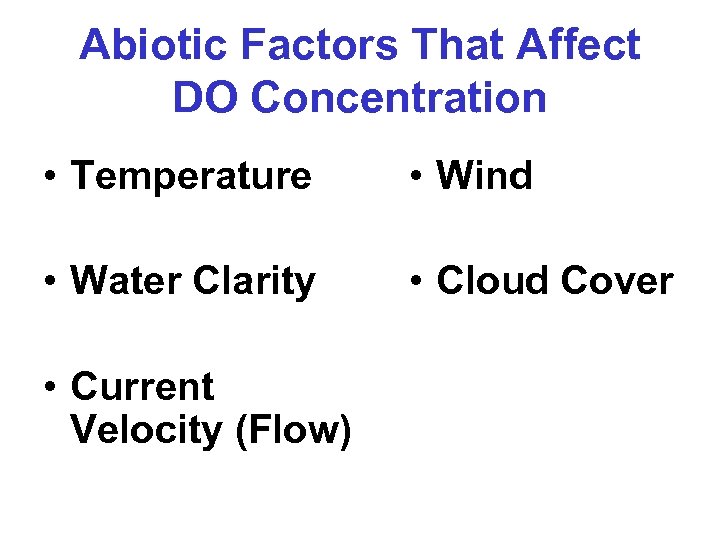 Abiotic Factors That Affect DO Concentration • Temperature • Wind • Water Clarity • Cloud Cover • Current Velocity (Flow)
Abiotic Factors That Affect DO Concentration • Temperature • Wind • Water Clarity • Cloud Cover • Current Velocity (Flow)
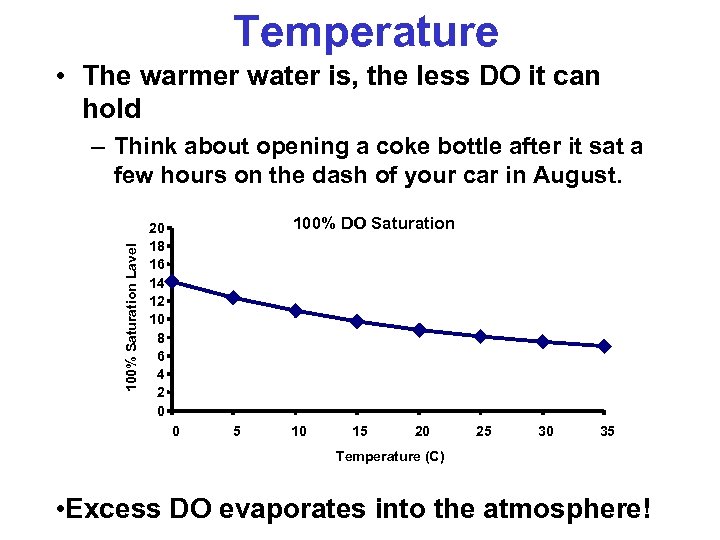 Temperature • The warmer water is, the less DO it can hold 100% Saturation Lavel – Think about opening a coke bottle after it sat a few hours on the dash of your car in August. 100% DO Saturation 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Temperature (C) • Excess DO evaporates into the atmosphere!
Temperature • The warmer water is, the less DO it can hold 100% Saturation Lavel – Think about opening a coke bottle after it sat a few hours on the dash of your car in August. 100% DO Saturation 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Temperature (C) • Excess DO evaporates into the atmosphere!
 Oxygen Can Diffuse Out of or Into the Water Column Atmosphere Oxygen diffuses out of water column Oxygen diffuses into water column Oxygen > 100% Saturation Oxygen < 100% Saturation Water Column
Oxygen Can Diffuse Out of or Into the Water Column Atmosphere Oxygen diffuses out of water column Oxygen diffuses into water column Oxygen > 100% Saturation Oxygen < 100% Saturation Water Column
 Wind Stirs in atmospheric oxygen
Wind Stirs in atmospheric oxygen
 Current Velocity • The faster water flows, the more atmospheric oxygen is mixed into the water.
Current Velocity • The faster water flows, the more atmospheric oxygen is mixed into the water.
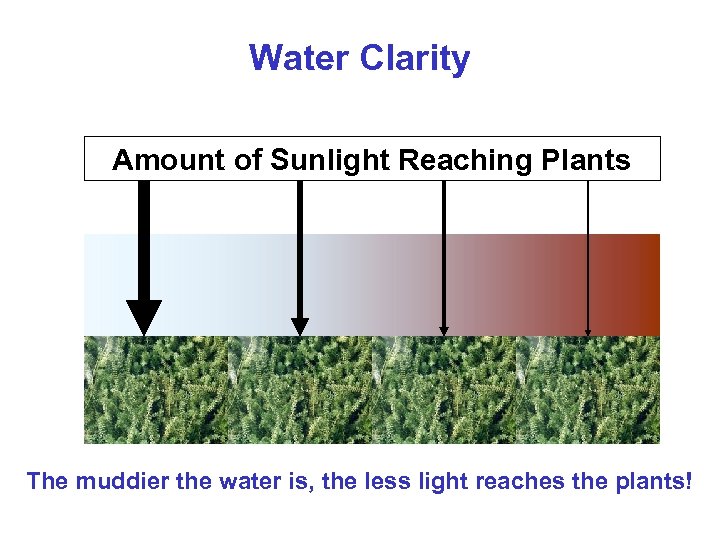 Water Clarity Amount of Sunlight Reaching Plants The muddier the water is, the less light reaches the plants!
Water Clarity Amount of Sunlight Reaching Plants The muddier the water is, the less light reaches the plants!
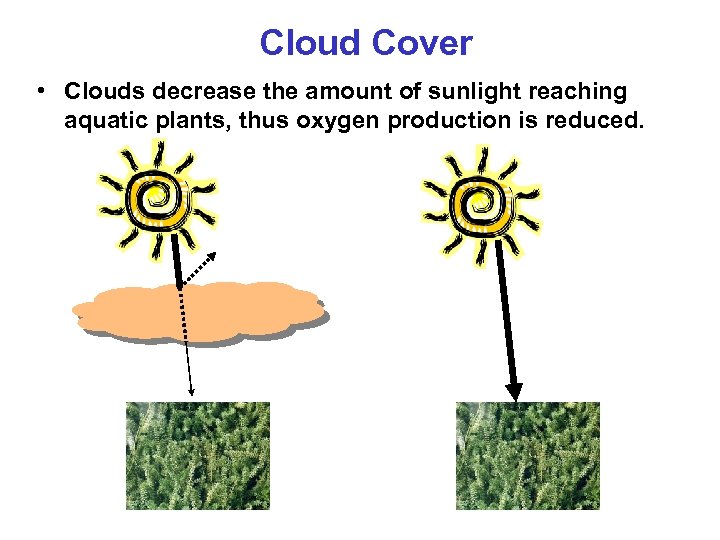 Cloud Cover • Clouds decrease the amount of sunlight reaching aquatic plants, thus oxygen production is reduced.
Cloud Cover • Clouds decrease the amount of sunlight reaching aquatic plants, thus oxygen production is reduced.


