7795eccbc3ee021f5d7f659faf645c85.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36

Displayable Reports (DRPT) ACCA IHE Workshop 2007 Harry Solomon, GE Healthcare IHE-Cardiology Technical & Planning Committees 3/19/2018 1
Typical Cardiology Reports 2

Typical Report Supported by EMR History: 35 yo white female with a history of inappropriate sinus tachycardia presents for sinus node modification. Mrs. Edmonds had a history of a rapid heart rate for the past three to four years which is usally initiated by activity/exercise. These episodes of rapid heart rate have occassionally been associated with presyncope/dizzy spells. The patient has not suffered any injuries from these episodes. She has previously been evaluated by Dr. Schutzman with the Care Group - who has attempted control of her heart rate with multiple medical regiments including beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers. The patient could not tolerate either of the classes of medications. The patient had a normal ECHO and an unremarkable Holter Monitor. She subsequently had a an Event Monitor which showed several episodes of sinus tachycardia up to rate of 150 bpm. She then underwent a Tilt Table Test on October 3, 2006 to differentiate between inappropriate sinus tachycardia and postural tachycardia syndrome. Her Tilt was postive for NCS without any evidence of POTS. Past medical history significant for gallbladder and thyroid surgery - not on synthroid currently. Informed consent detailing risks and benefits of the procedure was obtained from the patient and witnessed on the day of the procedure. Physical: Normal cardiovascular exam, without evidence of congestive heart failure. Normal jugular venous pressure and carotids, regular rhythm with no murmur, no gallop. Normal symmetrical pulses, no edema. Lab Data: No significant abnormalities. Procedure: After prepping and draping and effecting local anesthesia with lidocaine, catheters were inserted as follows: A 5 F quadripolar catheter was advanced from the left femoral vein ( Tri. Port) to the high right atrium. A 6 F deflectable quadripolar catheter was advance from the left femoral vein ( Tri. Port) to the A-V junction (His bundle). A 5 F quadripolar catheter was advanced from the left femoral vein ( Tri. Port) to the right ventricular apex. A 7 F deflectable decapolar catheter was placed from the right femoral vein to the coronary sinus. A 7 F EPT ablation catheter was advanced from the right femoral vein for mapping and ablation. A 4 F sheath was placed into the left femoral artery for blood pressure monitoring. Twelve surface ECG leads and intracardiac electrograms from the above locations were recorded during the study. Medications administered: propofol, total 1341 mg IV fentanyl, total 100 mcg IV promethazine, total 25 mg IV isoproterenol, up to 2. 5 mcg/min infusion At the end of the study, the catheters were removed and hemostasis achieved using direct pressure. Results: The spontaneous rhythm was sinus with ventricular cycle length 968 ms. The P wave duration was 79 ms nl <100), ( with no atrial abnormality; the PR interval was 151 ms ( 120 -200); the QRS duration was 71 ms ( nl nl, 80 -120), showing no conduction disturbance with an axis of 45° and QT interval 368 ms ( nl, 390 -440); the corrected QT [Bazett’s formula] was 374 ms. There was no evidence of a previous MI or delta waves. 3

How do we cross the chasm between the graphically rich cardiology reports and the limited capabilities of EMR systems? How do we bring electronic reports to environments that do not yet support them at all? 4

DRPT Premises PDF is a prevalent output format for reporting applications Design must support independent reporting apps We can control (more or less) what happens in the department Provide a variety of mechanisms for integration to systems outside the department (since we can’t control them) 5
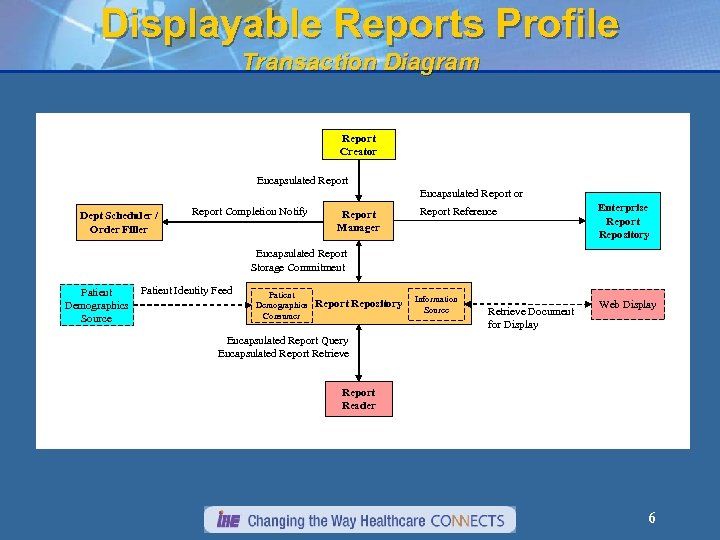
Displayable Reports Profile Transaction Diagram Report Creator Encapsulated Report or Dept Scheduler / Order Filler Report Completion Notify Report Manager Report Reference Enterprise Report Repository Encapsulated Report Storage Commitment Patient Demographics Source Patient Identity Feed Patient Demographics Consumer Report Repository Information Source Retrieve Document for Display Web Display Encapsulated Report Query Encapsulated Report Retrieve Report Reader 6

Displayable Reports Profile Actors Report Creator – A system that generates and transmits clinical reports (the reporting app). Report Manager – A system that manages the status of reporting, and distributes reports to report repositories (the department info system). Report Repository – A departmental system that receives reports and stores them for long-term access (may leverage the PACS. Enterprise Report Repository – A system that receives reports and/or references (pointers) to reports, and stores them for access throughout the healthcare enterprise (the EMR). Report Reader – A system that can query/retrieve and view reports encoded as DICOM objects (an imaging workstation). 7
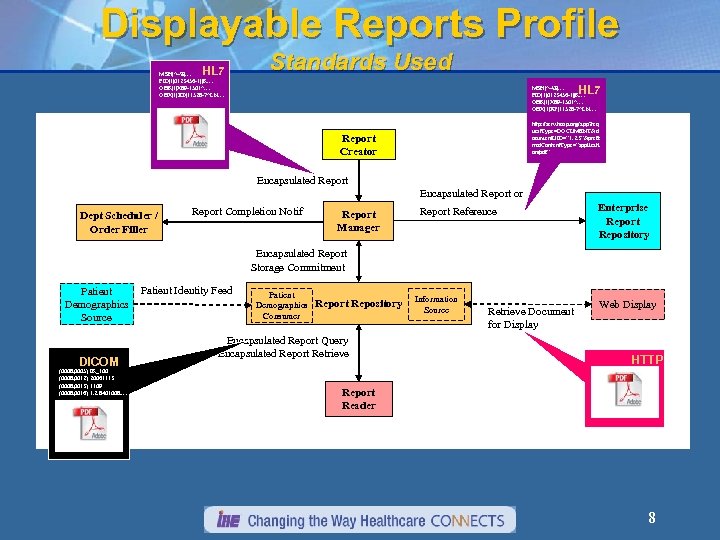
Displayable Reports Profile HL 7 MSH|^~$|… PID|1|0123456‑ 1||R… OBR|1|X 89‑ 1501^… OBX|1|ED|11528 -7^LN… Standards Used HL 7 MSH|^~$|… PID|1|0123456‑ 1||R… OBR|1|X 89‑ 1501^… OBX|1|RP|11528 -7^LN… OBX|1|ED|11528 -7^LN… http: //serv. hosp. org/app? req uest. Type=DOCUMENT&d ocument. UID=” 1. 2. 3”&prefe rred. Content. Type=”applicati on/pdf” Report Creator Encapsulated Report or Dept Scheduler / Order Filler Report Completion Notif Report Manager Report Reference Enterprise Report Repository Encapsulated Report Storage Commitment Patient Demographics Source DICOM (0008, 0005) IR_100 (0008, 0012) 20061113 (0008, 0013) 1109 (0008, 0016) 1. 2. 8401008. … Patient Identity Feed Patient Demographics Consumer Report Repository Encapsulated Report Query Encapsulated Report Retrieve Information Source Retrieve Document for Display Web Display HTTP Report Reader 8

Profile Status Demonstrated in 2006 Currently being reworked to use most recent HL 7 message definitions Re-release for trial implementation in June 2007 9

Implications for RFPs Reporting apps – Department info systems – Cardiology PACS – Imaging workstations – EMR and clinical workstations – 10

11

IHE for Regional Health Information Networks – XDS and Related Profiles ACCA IHE Workshop 2007 Harry Solomon, GE Healthcare IHE-Cardiology Technical & Planning Committees 3/19/2018 12
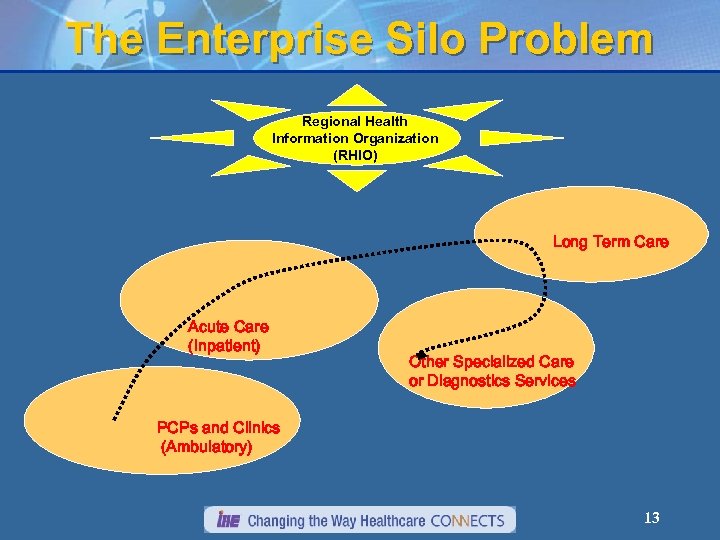
The Enterprise Silo Problem Regional Health Information Organization (RHIO) Long Term Care Acute Care (Inpatient) Other Specialized Care or Diagnostics Services PCPs and Clinics (Ambulatory) 13

RHIOs – an emerging trend 85+% of healthcare encounters in local home area Regional markets often limited to 2 -5 major IDNs, facilitating agreement among all players Social factors favor regional business agreements Regional markets may be assisted by state initiatives Regional Health Information Organizations (RHIOs) recognized as the preferred model for EHR data sharing by US Dept. of Health and Human Services 14

IHE’s approach for RHIOs Common technical specification for local, regional, diseasespecific, or national health information exchange Enable document-based search and exchange between EHR systems, ancillary IT systems (lab, pharmacy, payers), and personal health record systems Incrementally build on (do not replace) existing healthcare business models, including models of “data custodianship” Avoid the pitfalls of “rampant featurism” – keep it simple IHE Cross-Enterprise Document Sharing (XDS) introduced in 2005 Adopted as primary foundation for HITSP Interoperability Specifications in 2006 15
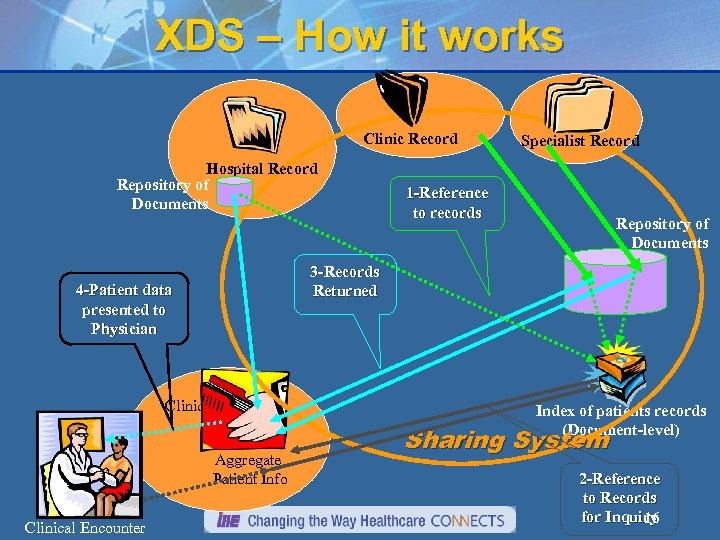
XDS – How it works Clinic Record Hospital Record Repository of Documents 1 -Reference to records Repository of Documents 3 -Records Returned 4 -Patient data presented to Physician Clinical IT System Aggregate Patient Info Clinical Encounter Specialist Record Index of patients records (Document-level) Sharing System 2 -Reference to Records for Inquiry 16
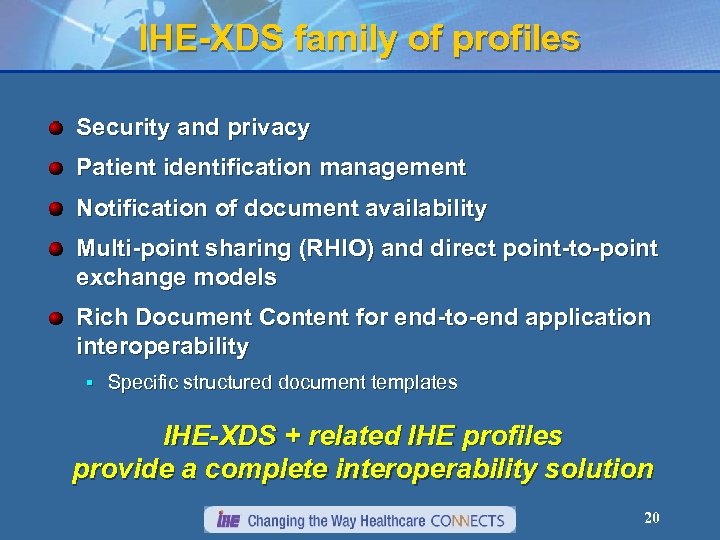
IHE-XDS family of profiles Security and privacy Patient identification management Notification of document availability Multi-point sharing (RHIO) and direct point-to-point exchange models Rich Document Content for end-to-end application interoperability § Specific structured document templates IHE-XDS + related IHE profiles provide a complete interoperability solution 20

XD* Content Profiles Medical Summary – encounter notes, discharge summary Imaging – exchange of image links Emergency Department Referral Pre-procedure History and Physical Scanned Documents Personal Health Records Basic Patient Privacy Consents Laboratory Reports All from Patient Care Coordination Domain, except Imaging (Radiology) and Laboratory (Laboratory Domain) 21
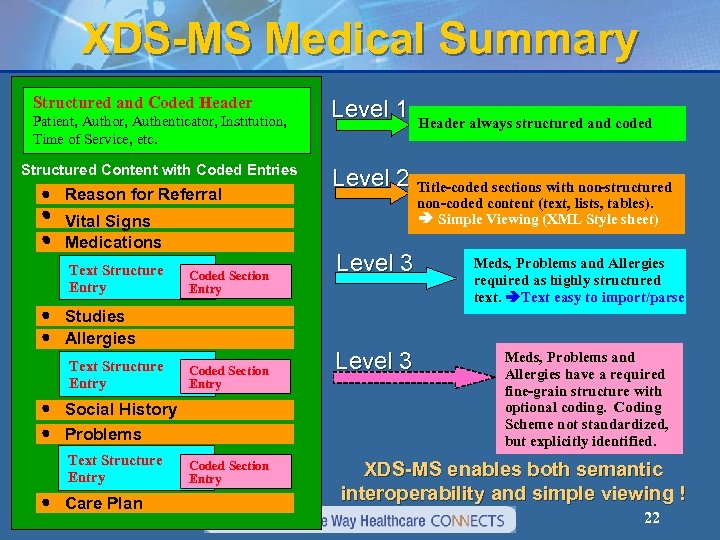
XDS-MS Medical Summary Structured and Coded Header Patient, Author, Authenticator, Institution, Time of Service, etc. Structured Content with Coded Entries · Reason for Referral · Vital Signs · Medications Text Structure Entry Coded Section Entry · Studies · Allergies Text Structure Entry Coded Section Entry · Social History · Problems Text Structure Entry · Care Plan Coded Section Entry Level 1 Header always structured and coded Level 2 Title-coded sections with non-structured non-coded content (text, lists, tables). Simple Viewing (XML Style sheet) Level 3 Meds, Problems and Allergies required as highly structured text. Text easy to import/parse Meds, Problems and Allergies have a required fine-grain structure with optional coding. Coding Scheme not standardized, but explicitly identified. XDS-MS enables both semantic interoperability and simple viewing ! 22
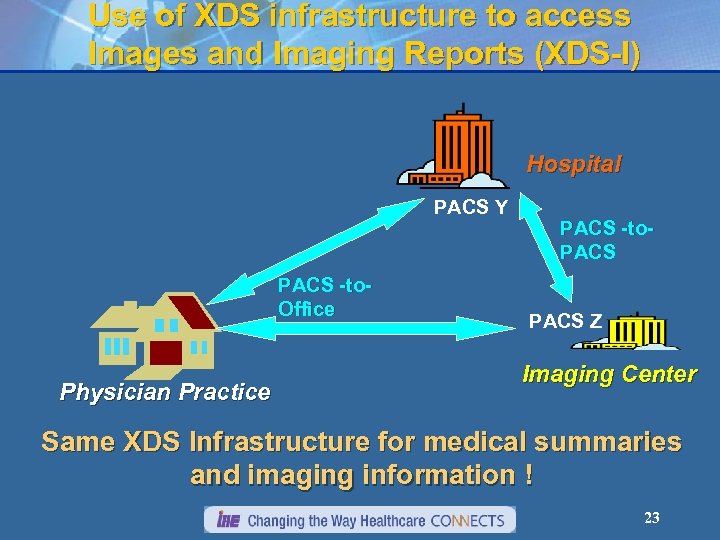
Use of XDS infrastructure to access Images and Imaging Reports (XDS-I) Hospital PACS Y PACS -to. Office Physician Practice PACS -to. PACS Z Imaging Center Same XDS Infrastructure for medical summaries and imaging information ! 23
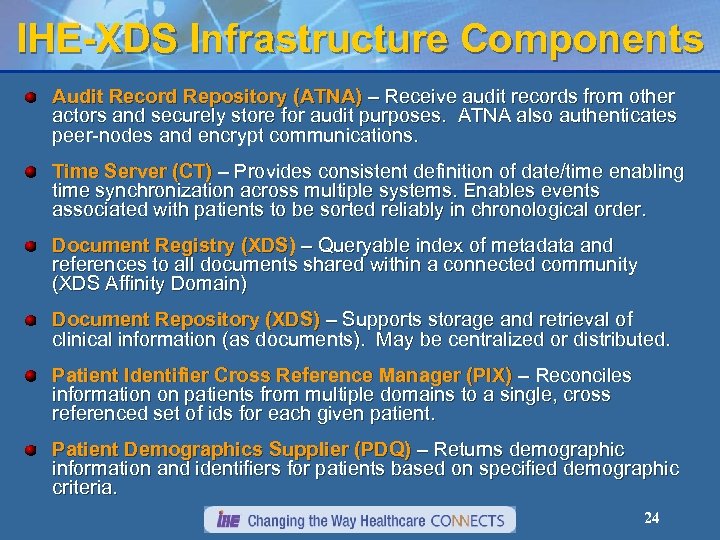
IHE-XDS Infrastructure Components Audit Record Repository (ATNA) – Receive audit records from other actors and securely store for audit purposes. ATNA also authenticates peer-nodes and encrypt communications. Time Server (CT) – Provides consistent definition of date/time enabling time synchronization across multiple systems. Enables events associated with patients to be sorted reliably in chronological order. Document Registry (XDS) – Queryable index of metadata and references to all documents shared within a connected community (XDS Affinity Domain) Document Repository (XDS) – Supports storage and retrieval of clinical information (as documents). May be centralized or distributed. Patient Identifier Cross Reference Manager (PIX) – Reconciles information on patients from multiple domains to a single, cross referenced set of ids for each given patient. Patient Demographics Supplier (PDQ) – Returns demographic information and identifiers for patients based on specified demographic criteria. 24
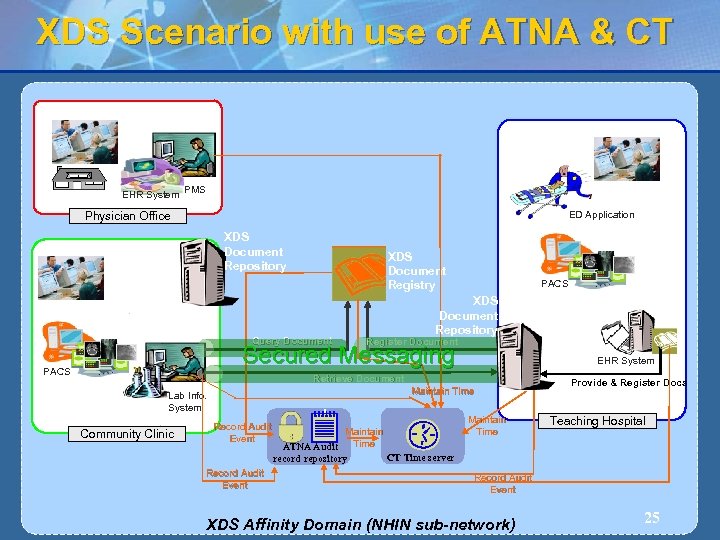
XDS Scenario with use of ATNA & CT EHR System PMS ED Application Physician Office XDS Document Repository XDS Document Registry Query Document PACS XDS Document Repository Register Document Secured Messaging PACS EHR System Retrieve Document Maintain Time Lab Info. System Community Clinic Record Audit Event Maintain ATNA Audit Time CT Time server record repository Maintain Time Provide & Register Docs Teaching Hospital Record Audit Event XDS Affinity Domain (NHIN sub-network) 25
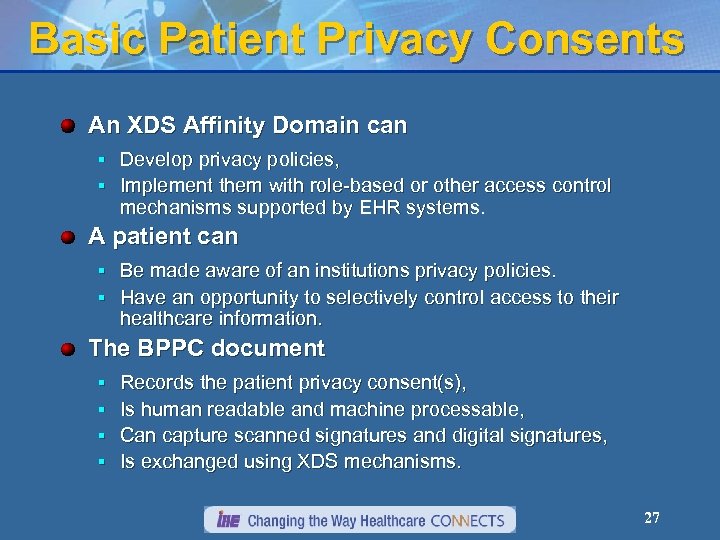
Basic Patient Privacy Consents An XDS Affinity Domain can § Develop privacy policies, § Implement them with role-based or other access control mechanisms supported by EHR systems. A patient can § Be made aware of an institutions privacy policies. § Have an opportunity to selectively control access to their healthcare information. The BPPC document § § Records the patient privacy consent(s), Is human readable and machine processable, Can capture scanned signatures and digital signatures, Is exchanged using XDS mechanisms. 27

Implications for RFPs Department info systems – Cardiology PACS – EMR and clinical workstations – 28

29

The US Federal Landscape for Health Information Technology ONCHIT, HITSP, CCHIT ACCA IHE Workshop 2007 Harry Solomon, GE Healthcare IHE-Cardiology Technical & Planning Committees 3/19/2018 30

The current initiative Executive Order 13, 335 (2004) § Most Americans to have an EHR by 2014 § Establish DHHS Office of National Coordinator for Health IT American Health Information Community (2005) § Make policy recommendations to HHS Secretary § Identify ‘early breakthrough’ priorities: • Initial set: Biosurveillance, Consumer Empowerment, EHRs, Chronic Disease ONCHIT contracts in four programmatic areas (2005) § Standards harmonization (HITSP) § Security and privacy policy (HISPC) § System certification (CCHIT) § Prototype National Health Information Networks (NHIN) 31
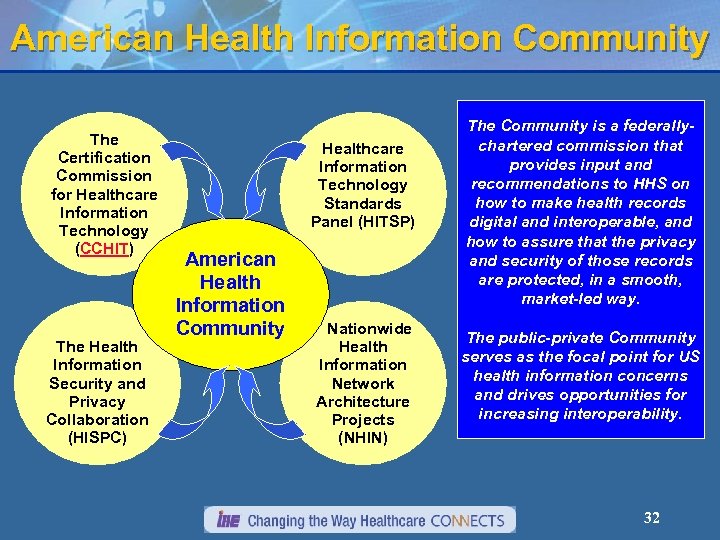
American Health Information Community The Certification Commission for Healthcare Information Technology (CCHIT) The Health Information Security and Privacy Collaboration (HISPC) Healthcare Information Technology Standards Panel (HITSP) American Health Information Community Nationwide Health Information Network Architecture Projects (NHIN) The Community is a federallychartered commission that provides input and recommendations to HHS on how to make health records digital and interoperable, and how to assure that the privacy and security of those records are protected, in a smooth, market-led way. The public-private Community serves as the focal point for US health information concerns and drives opportunities for increasing interoperability. 32

Federal HIT Projects HITSP delivers first set of Interoperability Specifications (2006) § § Based on three AHIC breakthrough priorities Using IHE Profiles for 80% of technical content CCHIT completes first round of certifications (2006) § Ambulatory EMR systems Four NHIN contractors begin implementation of 12 prototype RHIOs § 9 of 12 are based on IHE Profiles HISPC to deliver report (April 2007) § Recommendations on security and privacy regulations (federal and state) 33

HITSP Technical Committees Focus on AHIC Breakthrough Areas Biosurveillance -- Transmit essential ambulatory care and emergency department visit, utilization, and lab result data from electronically enabled health care delivery and public health systems in standardized anonymized format to authorized public health agencies with less than one day lag time. Consumer Empowerment -- Deploy to targeted populations a prepopulated, consumer-directed and secure electronic registration summary. Deploy a widely available pre-populated medication history linked to the registration summary. Electronic Health Records -- Deploy standardized, widely available, secure solutions for accessing laboratory results and interpretations in a patientcentric manner for clinical care by authorized parties. Chronic Care – Ensure that widespread use of secure messaging, as appropriate, is fostered as a means of communication between clinicians and patients about care delivery 34
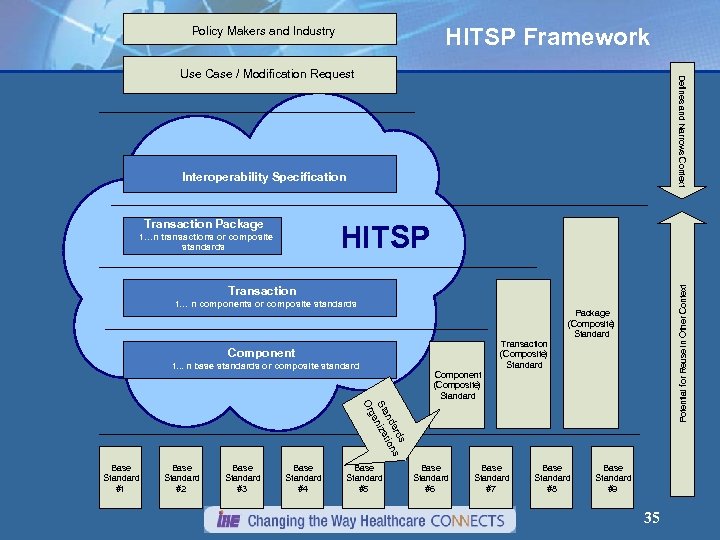
HITSP Framework Policy Makers and Industry Defines and Narrows Context Use Case / Modification Request Interoperability Specification Transaction Package Potential for Reuse in Other Context HITSP 1…n transactions or composite standards Transaction 1… n components or composite standards Package (Composite ) Standard Transaction (Composite ) Standard Component 1. . . n base standards or composite standard Component (Composite ) Standard rd s da t ions an St n i za ga Or Base Standard #1 Base Standard #2 Base Standard #3 Base Standard #4 Base Standard #5 Base Standard #6 Base Standard #7 Base Standard #8 Base Standard #9 35

IHE and HITSP Interoperability Specifications for 3 use cases use 8 IHE profiles EHR - Access to Lab results Historical Results: XDS + NAV + XDS-Lab + PIX + PDQ § Lab to Ordering Provider: HL 7 V 2. 5 msg with some differences with Lab-3 transaction from LSWF. § Consumer Empowerment Doc Sharing: XDS + PIX + PDQ § Reg/Med History: Not finalized but will be CDA/CCD. XPHR-TI version to be aligned on CCD when final is on the HITSP path. § Biosurveillance Doc Sharing track: XDS, XDS-Lab, XDS-I, XDS-MS § Anonimization: PIX + PDQ (with extensions) § Capture: RFD § Messaging track, no use of IHE profiles § 36

CCHIT within HHS Health IT Strategy American Health Information Community Chaired by HHS Secretary Mike Leavitt Office of the National Coordinator Project Officers Standards Harmonization Contractor NHIN Prototype Contractors Privacy/Security Solutions Contractor Strategic Direction + Breakthrough Use Cases Harmonized Standards Network Architecture Privacy Policies CCHIT: Compliance Certification Contractor Certification Criteria + Inspection Process for EHRs and Networks Accelerated adoption of robust, interoperable, privacy-enhancing Health IT Governance and Consensus Process Engaging Public and Private Sector Stakeholders 38

Scope of Work Under HHS Contract Phase I (Oct 05 – Sep 06) § Develop, pilot test, and assess certification of EHR products for ambulatory care settings Phase II (Oct 06 – Sep 07) § Develop, pilot test, and assess certification of EHR products for inpatient care settings As defined by HITSP Interop Specs (80% IHE) Phase III (Oct 07 – Sep 08) § Develop, pilot test, and assess certification of infrastructure or network components through which EHRs interoperate This will include cardiology Scope Expansion (effective Oct 06) § Address specialized EHR needs 39

Implications of Certification Likely requirement (2009 -10) for all health IT purchased with federal funds to be certified by CCHIT under HITSP Interoperability Specs § How far will that go regarding HIT used in treatment of CMS patients? HITSP Interoperability Specs are IHE! 40

41
7795eccbc3ee021f5d7f659faf645c85.ppt