bb873768ab9e2fd4c28977a0e805243c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Diseases of the Renal System KNH 413
Diseases of the Renal System KNH 413
 CKD - Renal Replacement Therapy Hemodialysis (HD) or Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) Type based on underlying kidney disease and co-morbid factors Both require selective, permeable membrane Allows passage of water and small molecules
CKD - Renal Replacement Therapy Hemodialysis (HD) or Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) Type based on underlying kidney disease and co-morbid factors Both require selective, permeable membrane Allows passage of water and small molecules
 CKD - Renal Replacement Therapy Hemodialysis (HD) Membrane is manmade dialyzer Preferred access site – AVF, AVG Typical regimen
CKD - Renal Replacement Therapy Hemodialysis (HD) Membrane is manmade dialyzer Preferred access site – AVF, AVG Typical regimen
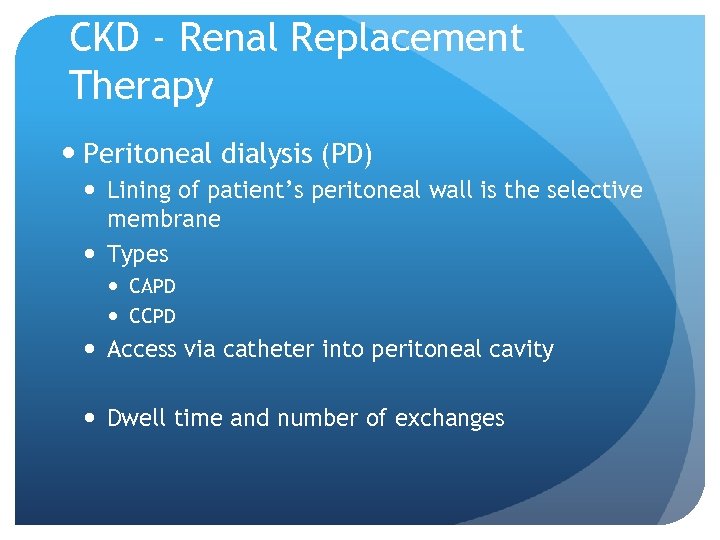 CKD - Renal Replacement Therapy Peritoneal dialysis (PD) Lining of patient’s peritoneal wall is the selective membrane Types CAPD CCPD Access via catheter into peritoneal cavity Dwell time and number of exchanges
CKD - Renal Replacement Therapy Peritoneal dialysis (PD) Lining of patient’s peritoneal wall is the selective membrane Types CAPD CCPD Access via catheter into peritoneal cavity Dwell time and number of exchanges
 CKD - Stages 1 & 2 Nutrition Therapy Focus on co-morbid conditions: diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, progression of CVD K/DOQI guidelines for GFR ≤ 20 SGA every 1– 3 mo. Dietary interviews and food intake Protein: . 6 -. 75 g/kg Energy: 30 -35 kcal/kg
CKD - Stages 1 & 2 Nutrition Therapy Focus on co-morbid conditions: diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, progression of CVD K/DOQI guidelines for GFR ≤ 20 SGA every 1– 3 mo. Dietary interviews and food intake Protein: . 6 -. 75 g/kg Energy: 30 -35 kcal/kg
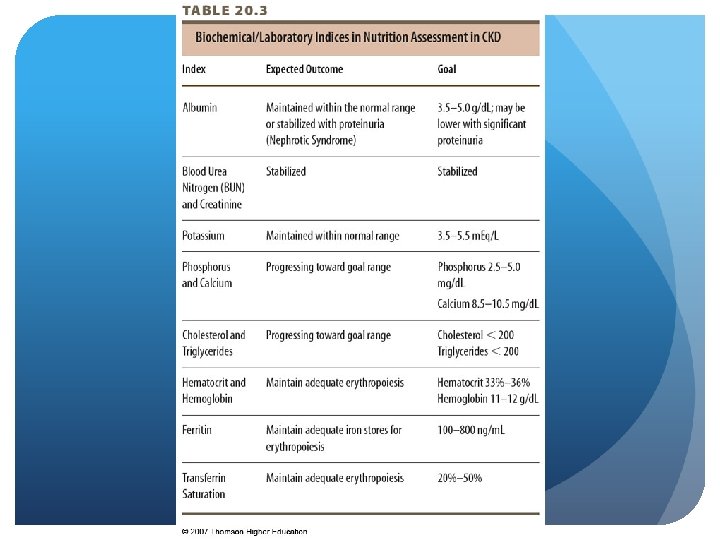
 CKD - Stages 3 & 4 Nutrition Therapy See ADA guidelines Nutrition assessment recommendations Nutrient recommendations Protein, energy, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, calcium, vitamins, minerals, fluid may need adjustment Emphasize usual foods
CKD - Stages 3 & 4 Nutrition Therapy See ADA guidelines Nutrition assessment recommendations Nutrient recommendations Protein, energy, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, calcium, vitamins, minerals, fluid may need adjustment Emphasize usual foods
 CKD - Stages 3 & 4 Outcome measures Clinical Biochemical Anthropometrics Clinical signs and symptoms Behavioral Meal planning, meeting nutrient needs, awareness of food/drug interactions, exercise
CKD - Stages 3 & 4 Outcome measures Clinical Biochemical Anthropometrics Clinical signs and symptoms Behavioral Meal planning, meeting nutrient needs, awareness of food/drug interactions, exercise
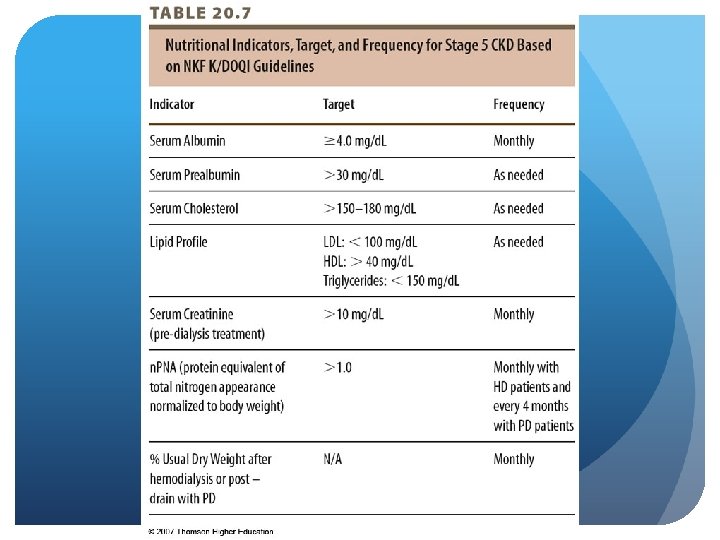
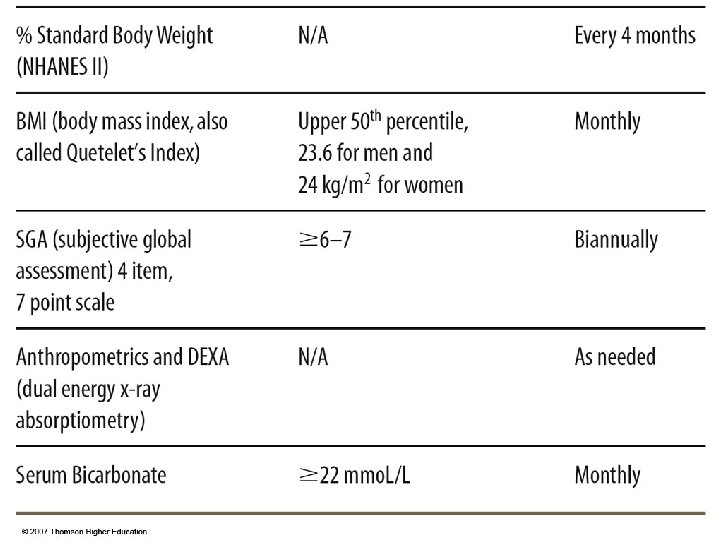
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Assessment On dialysis – measures not different Dietary intake Biochemical: serum albumin Goals: meet nutritional requirements, prevent malnutrition, minimize uremia, minimize complications Maintain blood pressure, fluid status
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Assessment On dialysis – measures not different Dietary intake Biochemical: serum albumin Goals: meet nutritional requirements, prevent malnutrition, minimize uremia, minimize complications Maintain blood pressure, fluid status
 © 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth
© 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention HD – high in protein, control intake of potassium, phosphorus, fluids and sodium PD – more liberalized; higher in pro. , sodium, potassium and fluid, limit phosphorus nutrients to monitor
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention HD – high in protein, control intake of potassium, phosphorus, fluids and sodium PD – more liberalized; higher in pro. , sodium, potassium and fluid, limit phosphorus nutrients to monitor
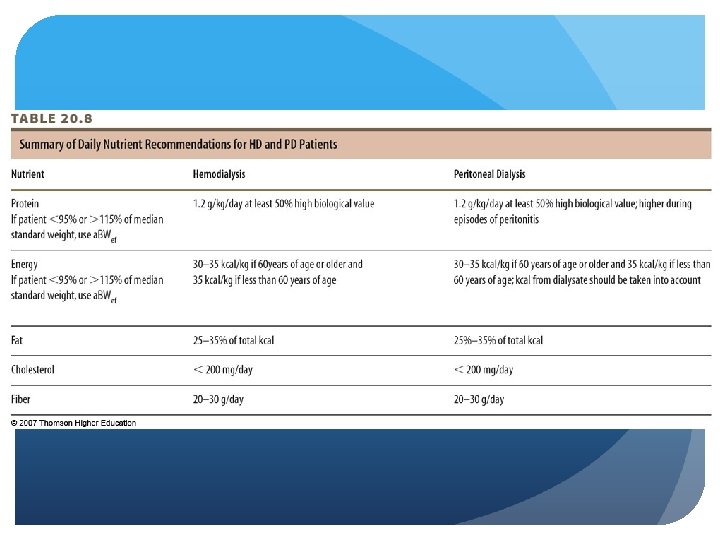
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Protein - 1. 2 g/kg (HD), at least 50% HBV PD same except during peritonitis
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Protein - 1. 2 g/kg (HD), at least 50% HBV PD same except during peritonitis
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Energy to prevent catabolism; needs slightly higher PD - account for kcal in dialysate Caloric load 24 -27 kcal/kg/day average intake
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Energy to prevent catabolism; needs slightly higher PD - account for kcal in dialysate Caloric load 24 -27 kcal/kg/day average intake
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Adjusted Edema-Free Body Weight should be used to calculate body weight for calculating protein and kcal For those < 95% or > 115% median standard weight NHANESII For maintenance in HD and PD pts. Obtained postdialysis for HD pts. , and after drainage for PD patients
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Adjusted Edema-Free Body Weight should be used to calculate body weight for calculating protein and kcal For those < 95% or > 115% median standard weight NHANESII For maintenance in HD and PD pts. Obtained postdialysis for HD pts. , and after drainage for PD patients
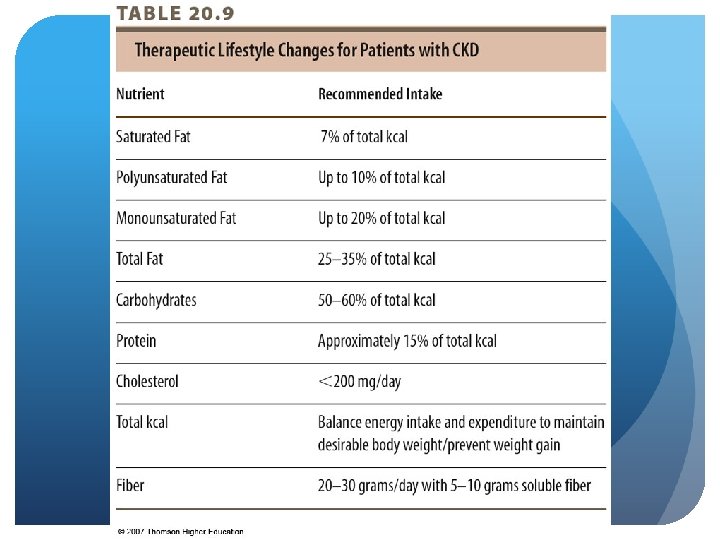
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Fat - increased risk for CAD and stroke HD typically have normal LDL, HDL, TG PD higher TC, LDL, TG Recommend TLC diet guidelines for both
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Fat - increased risk for CAD and stroke HD typically have normal LDL, HDL, TG PD higher TC, LDL, TG Recommend TLC diet guidelines for both
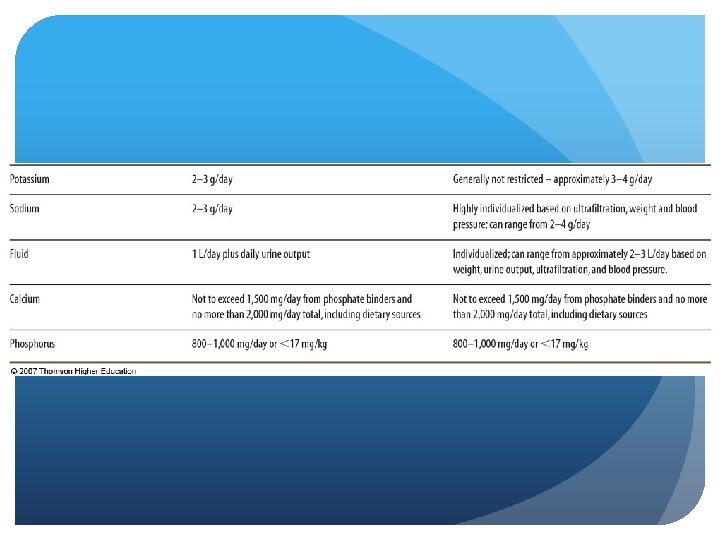
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Fluid and Sodium highly individualized based on residual urine output and dialysis modality Interdialytic weight gain (HD) should not exceed 5% of body weight 2 gram sodium diet Not more than 1 L fluid daily If urine output > 1 L/day sodium and fluid can be liberalized to 2 -4 g and 2 L
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Fluid and Sodium highly individualized based on residual urine output and dialysis modality Interdialytic weight gain (HD) should not exceed 5% of body weight 2 gram sodium diet Not more than 1 L fluid daily If urine output > 1 L/day sodium and fluid can be liberalized to 2 -4 g and 2 L
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Fluid and Sodium PD – based on ultrafiltration; 2 -2. 5 kg fluid/day Fluid 2 L Sodium 2 -4 g Fluid overload: shortness of breath, htn. , CHF, edema
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Fluid and Sodium PD – based on ultrafiltration; 2 -2. 5 kg fluid/day Fluid 2 L Sodium 2 -4 g Fluid overload: shortness of breath, htn. , CHF, edema

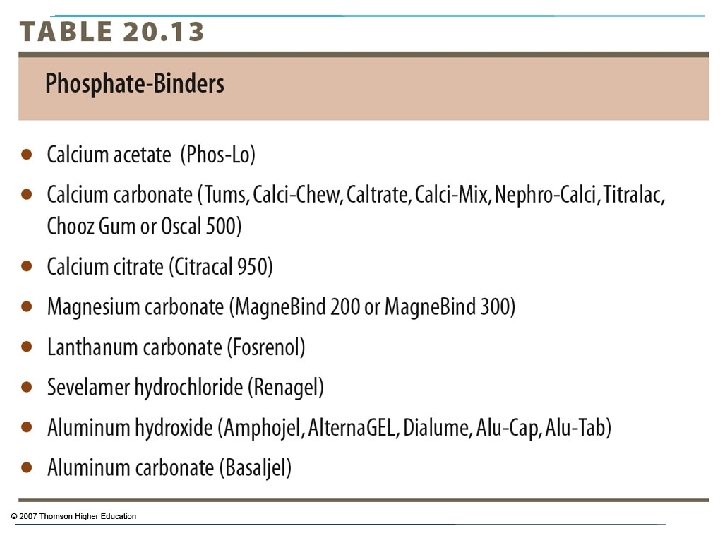
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Phosphorus Hyperphospatemia - GFR 20 -30 m. L/min Dietary phosphorus restriction: 800 -1000 mg/day, < 17 mg/kg body IBW Phosphate binders; calcium salts Limit calcium intake
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Phosphorus Hyperphospatemia - GFR 20 -30 m. L/min Dietary phosphorus restriction: 800 -1000 mg/day, < 17 mg/kg body IBW Phosphate binders; calcium salts Limit calcium intake
 © 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth
© 2007 Thomson - Wadsworth
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Calcium requirements higher in CKD Restrict foods high in calcium Take supplements on empty stomach Limit to 2000 mg/day from all sources
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Calcium requirements higher in CKD Restrict foods high in calcium Take supplements on empty stomach Limit to 2000 mg/day from all sources
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Vitamin Supplementation Water-soluble vitamins Daily requirements “Renal” vitamins include B 12, folic acid, vitamin C Avoid high doses of vitamins A & C May need vitamin K if on antibiotics
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Vitamin Supplementation Water-soluble vitamins Daily requirements “Renal” vitamins include B 12, folic acid, vitamin C Avoid high doses of vitamins A & C May need vitamin K if on antibiotics
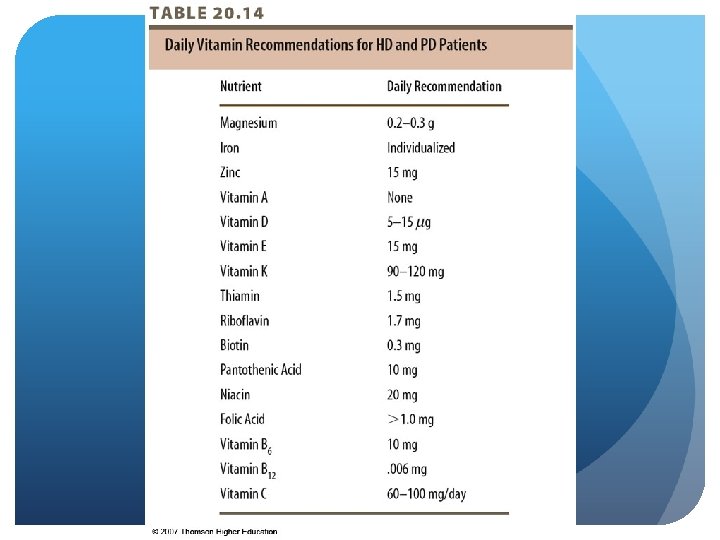
 CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Mineral supplementation Avoid Mg-containing phosphate binders, antacids, and supplements Iron Zinc
CKD - Stage 5 Nutrition Intervention Mineral supplementation Avoid Mg-containing phosphate binders, antacids, and supplements Iron Zinc


