a0f804748a567bffc2c43b50e9f31da5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Discriminative analysis of mi. RNAs with the mi. RCURY™ platform Niels Tolstrup nt@exiqon. com 2007
Discriminative analysis of mi. RNAs with the mi. RCURY™ platform Niels Tolstrup nt@exiqon. com 2007
 Overview • mi. RNA (!? ) • LNA – oligo design • mi. RNA research • towards research automation
Overview • mi. RNA (!? ) • LNA – oligo design • mi. RNA research • towards research automation
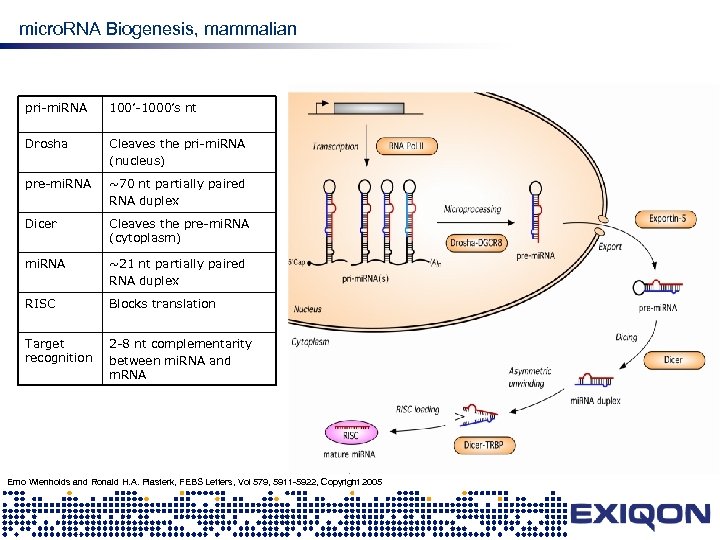 micro. RNA Biogenesis, mammalian pri-mi. RNA 100’-1000’s nt Drosha Cleaves the pri-mi. RNA (nucleus) pre-mi. RNA ~70 nt partially paired RNA duplex Dicer Cleaves the pre-mi. RNA (cytoplasm) mi. RNA ~21 nt partially paired RNA duplex RISC Blocks translation Target recognition 2 -8 nt complementarity between mi. RNA and m. RNA Erno Wienholds and Ronald H. A. Plasterk, FEBS Letters, Vol 579, 5911 -5922, Copyright 2005 mi. RNA
micro. RNA Biogenesis, mammalian pri-mi. RNA 100’-1000’s nt Drosha Cleaves the pri-mi. RNA (nucleus) pre-mi. RNA ~70 nt partially paired RNA duplex Dicer Cleaves the pre-mi. RNA (cytoplasm) mi. RNA ~21 nt partially paired RNA duplex RISC Blocks translation Target recognition 2 -8 nt complementarity between mi. RNA and m. RNA Erno Wienholds and Ronald H. A. Plasterk, FEBS Letters, Vol 579, 5911 -5922, Copyright 2005 mi. RNA
 How complex is the mi. RNA world? mi. RNA • 4584 mi. RNAs identified in vertebrates, invertebrates and plants – mi. RNA Registry 9. 2, May 2007 • Many mi. RNAs are phylogenetically conserved • At least one third of the human genes may be regulated by mi. RNAs* • The number of human (vertebrate) mi. RNA genes up to 1000** • An average of 100 target sites per mi. RNA*** • Human mi. RNA genes are frequently located in cancer-associated genomic regions and in viral infection • Perturbed mi. RNA expression observed in human cancers Many mi. RNAs potentially useful as biomarkers for disease diagnostics *Lewis et al. 2005, Cell 120, 15 -20; **Berezikov et al. 2005, Cell 120, 21 -24 ***Brennecke et al. 2005, PLo. S Biology
How complex is the mi. RNA world? mi. RNA • 4584 mi. RNAs identified in vertebrates, invertebrates and plants – mi. RNA Registry 9. 2, May 2007 • Many mi. RNAs are phylogenetically conserved • At least one third of the human genes may be regulated by mi. RNAs* • The number of human (vertebrate) mi. RNA genes up to 1000** • An average of 100 target sites per mi. RNA*** • Human mi. RNA genes are frequently located in cancer-associated genomic regions and in viral infection • Perturbed mi. RNA expression observed in human cancers Many mi. RNAs potentially useful as biomarkers for disease diagnostics *Lewis et al. 2005, Cell 120, 15 -20; **Berezikov et al. 2005, Cell 120, 21 -24 ***Brennecke et al. 2005, PLo. S Biology
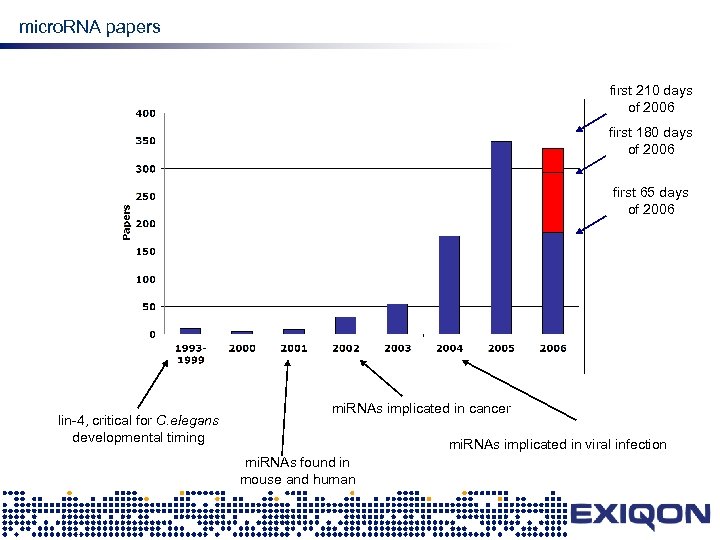 mi. RNA micro. RNA papers first 210 days of 2006 first 180 days of 2006 first 65 days of 2006 lin-4, critical for C. elegans developmental timing mi. RNAs implicated in cancer mi. RNAs implicated in viral infection mi. RNAs found in mouse and human
mi. RNA micro. RNA papers first 210 days of 2006 first 180 days of 2006 first 65 days of 2006 lin-4, critical for C. elegans developmental timing mi. RNAs implicated in cancer mi. RNAs implicated in viral infection mi. RNAs found in mouse and human
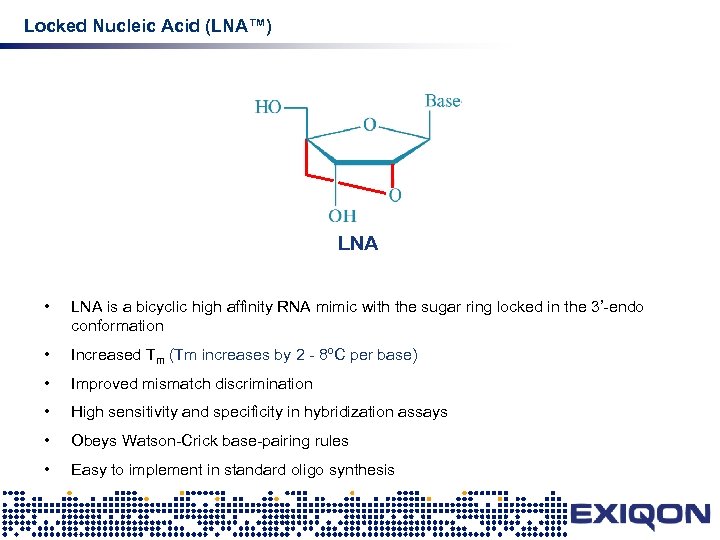 Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA™) LNA • LNA is a bicyclic high affinity RNA mimic with the sugar ring locked in the 3’-endo conformation • Increased Tm (Tm increases by 2 - 8ºC per base) • Improved mismatch discrimination • High sensitivity and specificity in hybridization assays • Obeys Watson-Crick base-pairing rules • Easy to implement in standard oligo synthesis
Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA™) LNA • LNA is a bicyclic high affinity RNA mimic with the sugar ring locked in the 3’-endo conformation • Increased Tm (Tm increases by 2 - 8ºC per base) • Improved mismatch discrimination • High sensitivity and specificity in hybridization assays • Obeys Watson-Crick base-pairing rules • Easy to implement in standard oligo synthesis
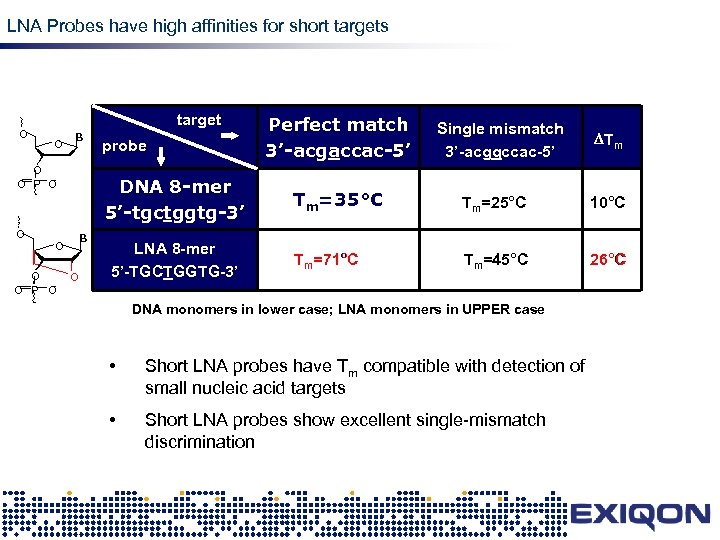 LNA Probes have high affinities for short targets O target O B O O P O O DNA 8 -mer 5’-tgctggtg-3’ B O O O P O probe O LNA 8 -mer 5’-TGCTGGTG-3’ Perfect match 3’-acgaccac-5’ LNA Single mismatch 3’-acggccac-5’ Tm Tm=35°C Tm=25°C 10°C Tm=71°C Tm=45°C 26°C DNA monomers in lower case; LNA monomers in UPPER case • Short LNA probes have Tm compatible with detection of small nucleic acid targets • Short LNA probes show excellent single-mismatch discrimination
LNA Probes have high affinities for short targets O target O B O O P O O DNA 8 -mer 5’-tgctggtg-3’ B O O O P O probe O LNA 8 -mer 5’-TGCTGGTG-3’ Perfect match 3’-acgaccac-5’ LNA Single mismatch 3’-acggccac-5’ Tm Tm=35°C Tm=25°C 10°C Tm=71°C Tm=45°C 26°C DNA monomers in lower case; LNA monomers in UPPER case • Short LNA probes have Tm compatible with detection of small nucleic acid targets • Short LNA probes show excellent single-mismatch discrimination
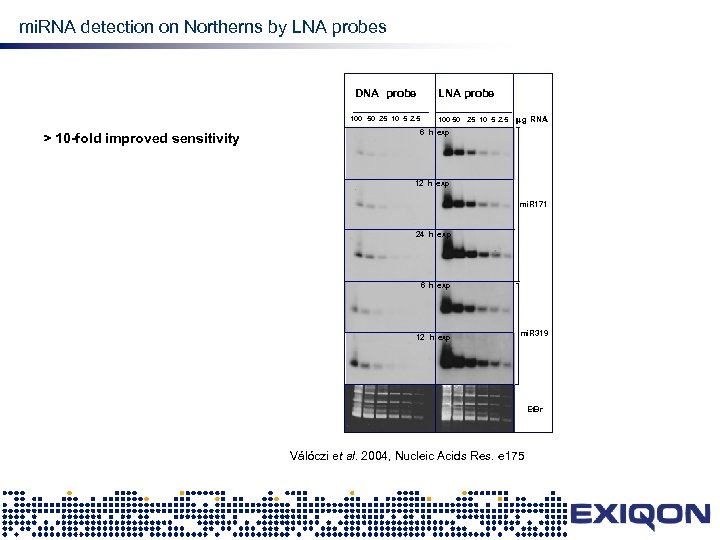 LNA mi. RNA detection on Northerns by LNA probes DNA probe 100 50 25 10 5 2. 5 > 10 -fold improved sensitivity LNA probe 100 50 25 10 5 2. 5 mg RNA 6 h exp 12 h exp mi. R 171 24 h ex p 6 h exp 12 h exp mi. R 319 Et. Br Válóczi et al. 2004, Nucleic Acids Res. e 175
LNA mi. RNA detection on Northerns by LNA probes DNA probe 100 50 25 10 5 2. 5 > 10 -fold improved sensitivity LNA probe 100 50 25 10 5 2. 5 mg RNA 6 h exp 12 h exp mi. R 171 24 h ex p 6 h exp 12 h exp mi. R 319 Et. Br Válóczi et al. 2004, Nucleic Acids Res. e 175
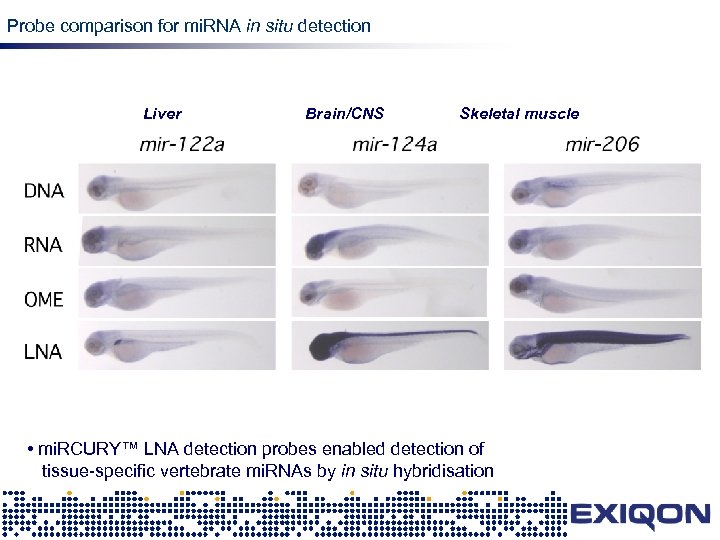 Probe comparison for mi. RNA in situ detection Liver Brain/CNS LNA Skeletal muscle • mi. RCURY™ LNA detection probes enabled detection of tissue-specific vertebrate mi. RNAs by in situ hybridisation
Probe comparison for mi. RNA in situ detection Liver Brain/CNS LNA Skeletal muscle • mi. RCURY™ LNA detection probes enabled detection of tissue-specific vertebrate mi. RNAs by in situ hybridisation
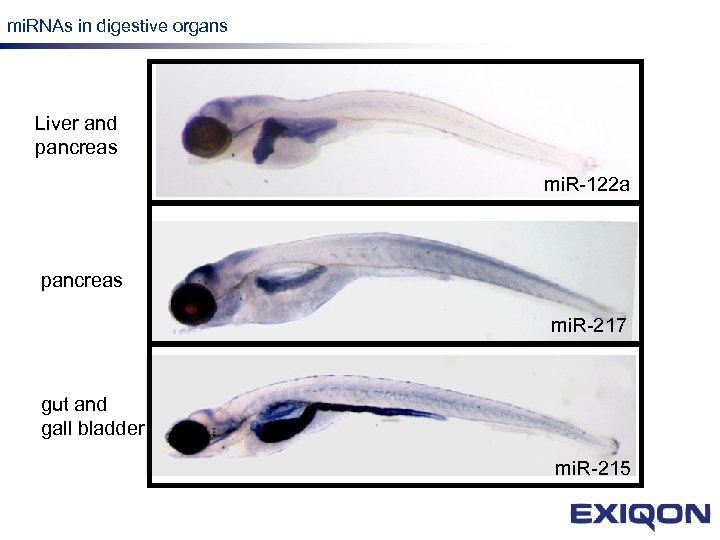 mi. RNAs in digestive organs LNA Liver and pancreas mi. R-122 a pancreas mi. R-217 gut and gall bladder mi. R-215
mi. RNAs in digestive organs LNA Liver and pancreas mi. R-122 a pancreas mi. R-217 gut and gall bladder mi. R-215
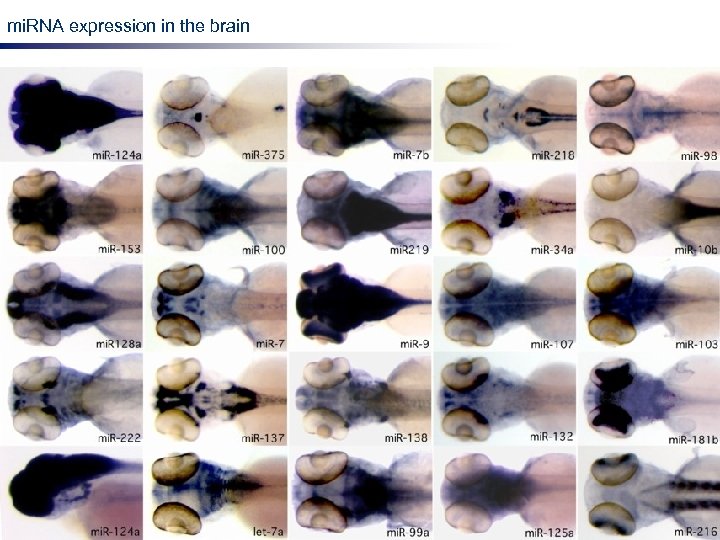 mi. RNA expression in the brain LNA
mi. RNA expression in the brain LNA
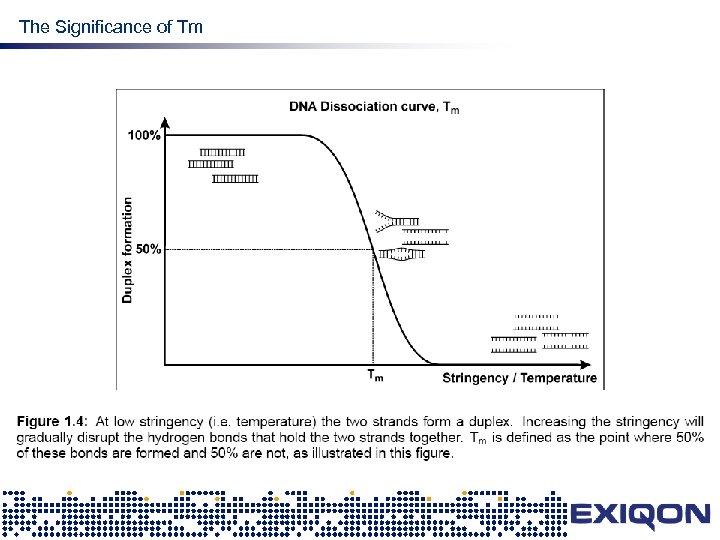 The Significance of Tm design
The Significance of Tm design
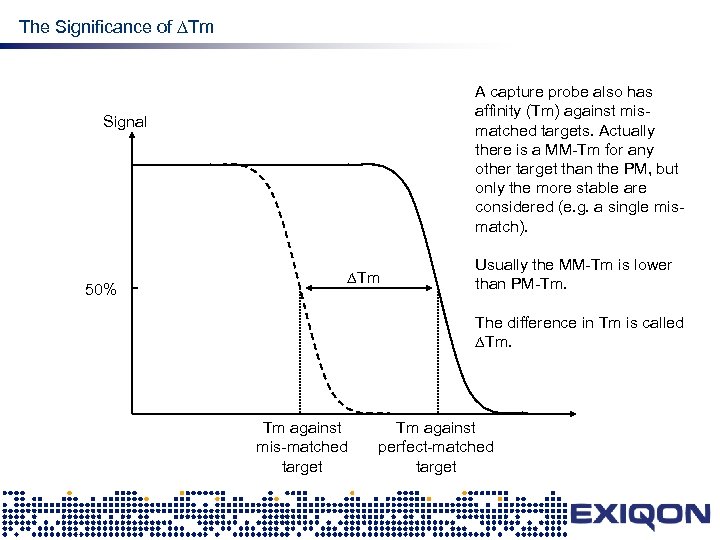 The Significance of Tm design A capture probe also has affinity (Tm) against mismatched targets. Actually there is a MM-Tm for any other target than the PM, but only the more stable are considered (e. g. a single mismatch). Signal 50% Tm Usually the MM-Tm is lower than PM-Tm. The difference in Tm is called Tm. Tm against mis-matched target Tm against perfect-matched target
The Significance of Tm design A capture probe also has affinity (Tm) against mismatched targets. Actually there is a MM-Tm for any other target than the PM, but only the more stable are considered (e. g. a single mismatch). Signal 50% Tm Usually the MM-Tm is lower than PM-Tm. The difference in Tm is called Tm. Tm against mis-matched target Tm against perfect-matched target
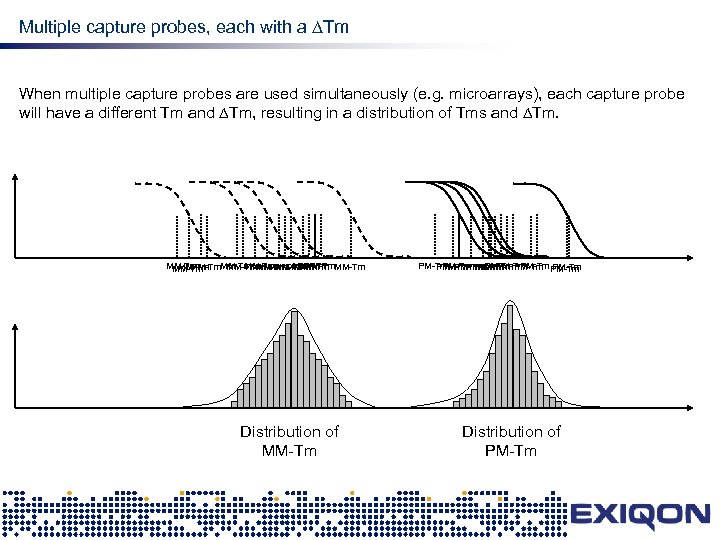 Multiple capture probes, each with a Tm design When multiple capture probes are used simultaneously (e. g. microarrays), each capture probe will have a different Tm and Tm, resulting in a distribution of Tms and Tm. MM-Tm MM-Tm MM-Tm Distribution of MM-Tm PM-Tm PM-Tm PM-Tm PM-Tm Distribution of PM-Tm
Multiple capture probes, each with a Tm design When multiple capture probes are used simultaneously (e. g. microarrays), each capture probe will have a different Tm and Tm, resulting in a distribution of Tms and Tm. MM-Tm MM-Tm MM-Tm Distribution of MM-Tm PM-Tm PM-Tm PM-Tm PM-Tm Distribution of PM-Tm
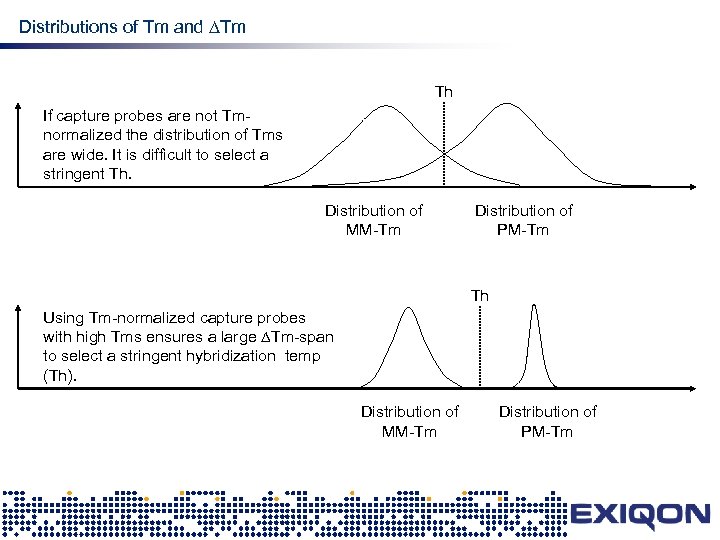 Distributions of Tm and Tm design Th If capture probes are not Tmnormalized the distribution of Tms are wide. It is difficult to select a stringent Th. Distribution of MM-Tm Distribution of PM-Tm Th Using Tm-normalized capture probes with high Tms ensures a large Tm-span to select a stringent hybridization temp (Th). Distribution of MM-Tm Distribution of PM-Tm
Distributions of Tm and Tm design Th If capture probes are not Tmnormalized the distribution of Tms are wide. It is difficult to select a stringent Th. Distribution of MM-Tm Distribution of PM-Tm Th Using Tm-normalized capture probes with high Tms ensures a large Tm-span to select a stringent hybridization temp (Th). Distribution of MM-Tm Distribution of PM-Tm
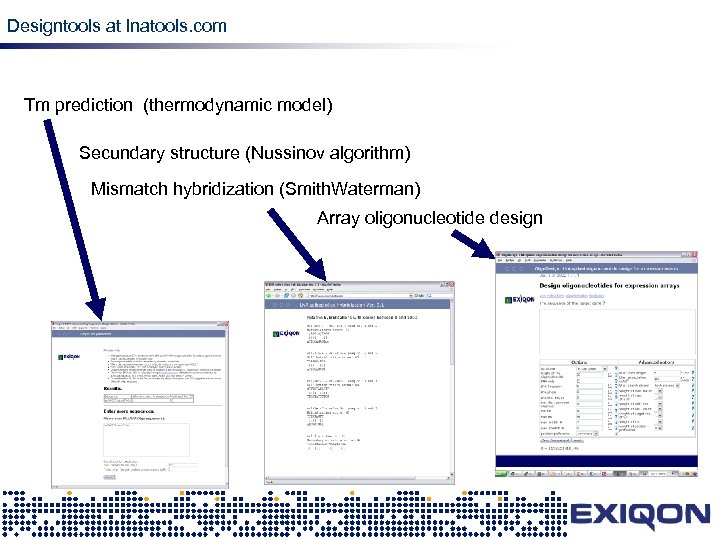 Designtools at lnatools. com design Tm prediction (thermodynamic model) Secundary structure (Nussinov algorithm) Mismatch hybridization (Smith. Waterman) Array oligonucleotide design
Designtools at lnatools. com design Tm prediction (thermodynamic model) Secundary structure (Nussinov algorithm) Mismatch hybridization (Smith. Waterman) Array oligonucleotide design
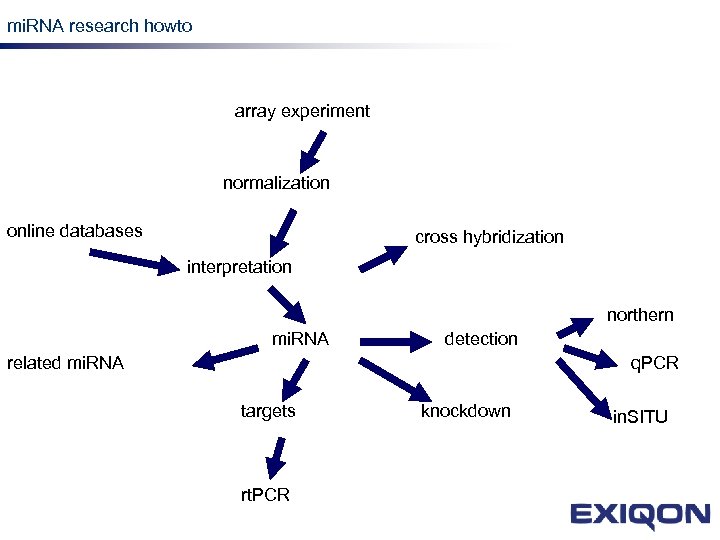 mi. RNA research howto mi. RNA research array experiment normalization online databases cross hybridization interpretation northern mi. RNA detection related mi. RNA q. PCR targets rt. PCR knockdown in. SITU
mi. RNA research howto mi. RNA research array experiment normalization online databases cross hybridization interpretation northern mi. RNA detection related mi. RNA q. PCR targets rt. PCR knockdown in. SITU
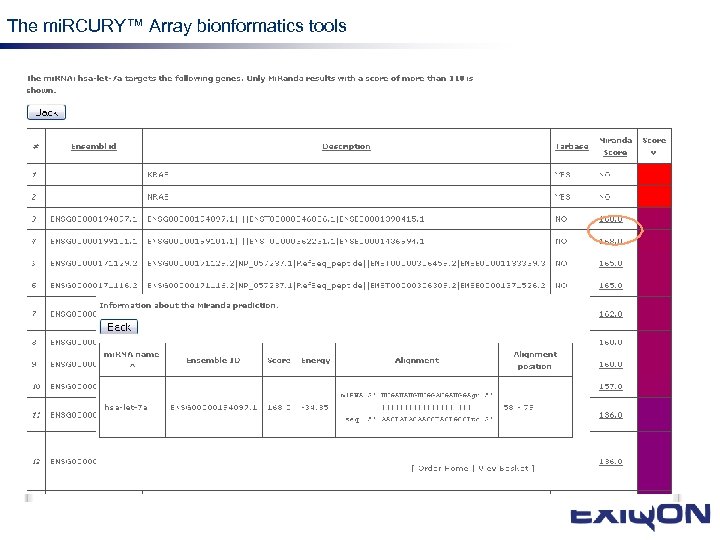 The mi. RCURY™ Array bionformatics tools mi. RNA research
The mi. RCURY™ Array bionformatics tools mi. RNA research
 Future mi. RNA research Automated research
Future mi. RNA research Automated research
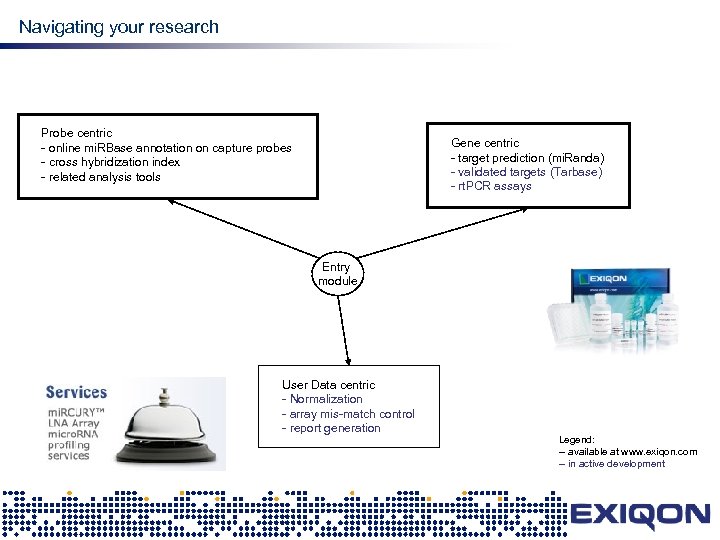 mi. RNA research Navigating your research Probe centric - online mi. RBase annotation on capture probes - cross hybridization index - related analysis tools Gene centric - target prediction (mi. Randa) - validated targets (Tarbase) - rt. PCR assays Entry module User Data centric - Normalization - array mis-match control - report generation Legend: -- available at www. exiqon. com -- in active development
mi. RNA research Navigating your research Probe centric - online mi. RBase annotation on capture probes - cross hybridization index - related analysis tools Gene centric - target prediction (mi. Randa) - validated targets (Tarbase) - rt. PCR assays Entry module User Data centric - Normalization - array mis-match control - report generation Legend: -- available at www. exiqon. com -- in active development
 Thanks Exiqon bioinformatics: Jacob B. Nielsen, Niels B. Jensen, Bing Zhang, Mette Jørgensen, Jesper Salomon Manager R&D: Søren Møller S&M Web team: Marie-Louise Lunn, Anders K. Rosengren Exiqon: all employees
Thanks Exiqon bioinformatics: Jacob B. Nielsen, Niels B. Jensen, Bing Zhang, Mette Jørgensen, Jesper Salomon Manager R&D: Søren Møller S&M Web team: Marie-Louise Lunn, Anders K. Rosengren Exiqon: all employees


