c690370f7db81759907624fa8f5b16e8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Discourse, coherence and anaphora resolution Lecture 16 1
Discourse, coherence and anaphora resolution Lecture 16 1
 What is discourse? l l 2 Any piece of text consisting of more than one sentence Until now our lectures revolved mainly around topics concerning word-level or sentencelevel analysis.
What is discourse? l l 2 Any piece of text consisting of more than one sentence Until now our lectures revolved mainly around topics concerning word-level or sentencelevel analysis.
 Discourse phenomena l Anaphora resolution – l Types of noun phrases – – – 3 The Tin Woodman went to Emerald City to see the Wizard of Oz and ask for a heart. After he asked for it, the Woodman waited for the Wizard’s response. Indefinite: Julia has a cat. Some cat entered the house. Definite: The cat is brown. Pronoun: It doesn’t eat much.
Discourse phenomena l Anaphora resolution – l Types of noun phrases – – – 3 The Tin Woodman went to Emerald City to see the Wizard of Oz and ask for a heart. After he asked for it, the Woodman waited for the Wizard’s response. Indefinite: Julia has a cat. Some cat entered the house. Definite: The cat is brown. Pronoun: It doesn’t eat much.
 l Coherence – – l John hid Bill’s car keys. [the reason he did this was that] He was drunk. ? ? John hid Bill’s car keys. [How are these sentences related? ] He likes spinach. Coherence relations – explanation or cause – contrast or concession 4
l Coherence – – l John hid Bill’s car keys. [the reason he did this was that] He was drunk. ? ? John hid Bill’s car keys. [How are these sentences related? ] He likes spinach. Coherence relations – explanation or cause – contrast or concession 4
 Discourse connectives l Cue phrases, discourse markers – – John hid Bill’s car keys because he was drunk. – 5 Because, although, but, for example, yet, and [We can’t win] [but we must keep trying] contrast
Discourse connectives l Cue phrases, discourse markers – – John hid Bill’s car keys because he was drunk. – 5 Because, although, but, for example, yet, and [We can’t win] [but we must keep trying] contrast
![Implicit and explicit discourse relations I took my umbrella this morning. [because] The forecast Implicit and explicit discourse relations I took my umbrella this morning. [because] The forecast](https://present5.com/presentation/c690370f7db81759907624fa8f5b16e8/image-6.jpg) Implicit and explicit discourse relations I took my umbrella this morning. [because] The forecast was rain in the afternoon. She is never late for meetings. [but] He always arrives 10 minutes late. She woke up early. [afterward] She had breakfast and went for a walk in the park. 6
Implicit and explicit discourse relations I took my umbrella this morning. [because] The forecast was rain in the afternoon. She is never late for meetings. [but] He always arrives 10 minutes late. She woke up early. [afterward] She had breakfast and went for a walk in the park. 6
 Ambiguity of discourse connectives They have not spoken to each other since they argued last fall. (Temporal) I assumed you were not coming since you never replied to the invitation. (Causal) 7
Ambiguity of discourse connectives They have not spoken to each other since they argued last fall. (Temporal) I assumed you were not coming since you never replied to the invitation. (Causal) 7
 Penn Discourse Tree Bank l l 8 Annotated explicit and implicit discourse relations Each relation is annotated with its sense
Penn Discourse Tree Bank l l 8 Annotated explicit and implicit discourse relations Each relation is annotated with its sense
 In a general text, what is the proportion of explicit versus implicit relations? 9
In a general text, what is the proportion of explicit versus implicit relations? 9
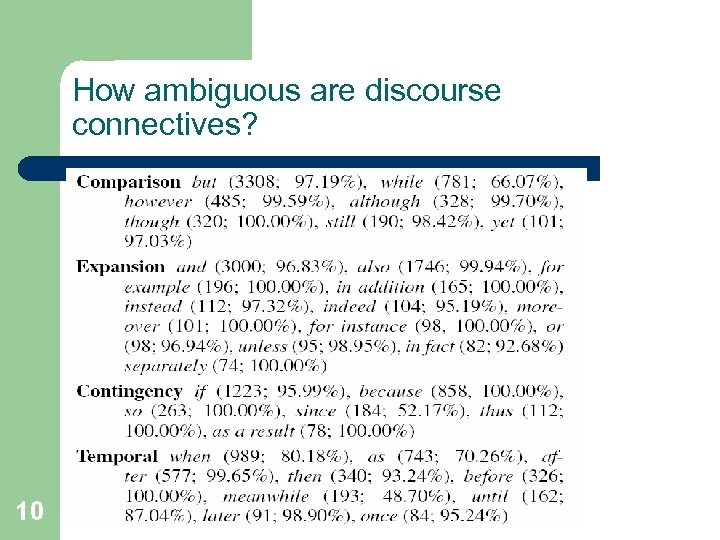 How ambiguous are discourse connectives? 10
How ambiguous are discourse connectives? 10
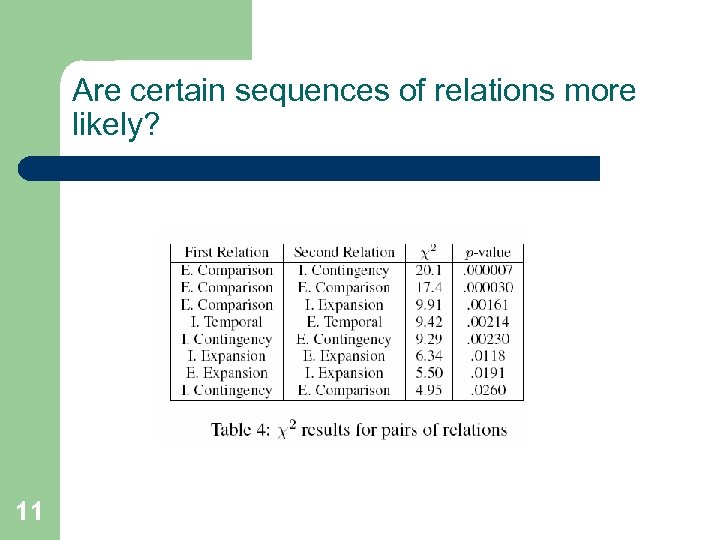 Are certain sequences of relations more likely? 11
Are certain sequences of relations more likely? 11
 l l 12 In order to interpret (understand) discourse automatically, the problem of identification and disambiguation of discourse relations needs to be addressed. What else?
l l 12 In order to interpret (understand) discourse automatically, the problem of identification and disambiguation of discourse relations needs to be addressed. What else?
 Reference resolution l 13 Victoria Chen, Chief Financial Officer of Megabucks Banking Corp since 2004, saw her pay jump 20%, to $1. 3 million, as the 37 year-old also became the Denver-based financial-services company’s president. It has been ten years since she came to Megabucks from rival Lotsabucks.
Reference resolution l 13 Victoria Chen, Chief Financial Officer of Megabucks Banking Corp since 2004, saw her pay jump 20%, to $1. 3 million, as the 37 year-old also became the Denver-based financial-services company’s president. It has been ten years since she came to Megabucks from rival Lotsabucks.
 Definitions Reference: use of linguistic expressions (her, Chen) to denote an entity or individual Reference resolution: the task of determining what entities are referred to by which linguistic expressions l A natural language expression used to perform reference is called a referring expression, and the entity that is referred to is called the referent. 14
Definitions Reference: use of linguistic expressions (her, Chen) to denote an entity or individual Reference resolution: the task of determining what entities are referred to by which linguistic expressions l A natural language expression used to perform reference is called a referring expression, and the entity that is referred to is called the referent. 14
 l l Reference to an entity that has been previously introduced into the discourse is called anaphora. l 15 Two referring expressions that are used to refer to the same entity are said to corefer Coreference resolution is the task of finding referring expressions in a text that refer to the same entity (coreference chains)
l l Reference to an entity that has been previously introduced into the discourse is called anaphora. l 15 Two referring expressions that are used to refer to the same entity are said to corefer Coreference resolution is the task of finding referring expressions in a text that refer to the same entity (coreference chains)
 Features for pronominal anaphora resolution l Number agreement – – l l 16 John has a Ford Falcon. It is red ? ? John has a Ford Falcon. They are red. John has three cars. They are red. ? ? John has three cars. It is red. Person agreement Gender agreement
Features for pronominal anaphora resolution l Number agreement – – l l 16 John has a Ford Falcon. It is red ? ? John has a Ford Falcon. They are red. John has three cars. They are red. ? ? John has three cars. It is red. Person agreement Gender agreement
 Preferences in pronoun interpretation Salience l Recency – l Grammatical role: – l l typically entities mentioned in subject position are more salient than those mentioned in object position Repeated mention Selectional restrictions – 17 pronoun antecedents have been mentioned nearby in the text. John parked his car in the garage after driving it around for hours.
Preferences in pronoun interpretation Salience l Recency – l Grammatical role: – l l typically entities mentioned in subject position are more salient than those mentioned in object position Repeated mention Selectional restrictions – 17 pronoun antecedents have been mentioned nearby in the text. John parked his car in the garage after driving it around for hours.
 Relation to summarization l 18 Revisions that improve cohesion in multidocument summaries: a preliminary study (2002) Jahna C. Otterbacher, Dragomir R. Radev, Airong Luo. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Automatic Summarization
Relation to summarization l 18 Revisions that improve cohesion in multidocument summaries: a preliminary study (2002) Jahna C. Otterbacher, Dragomir R. Radev, Airong Luo. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Automatic Summarization
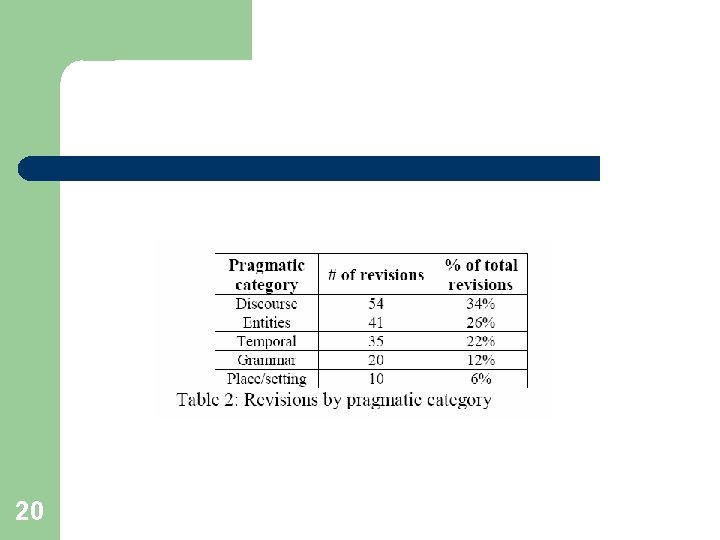
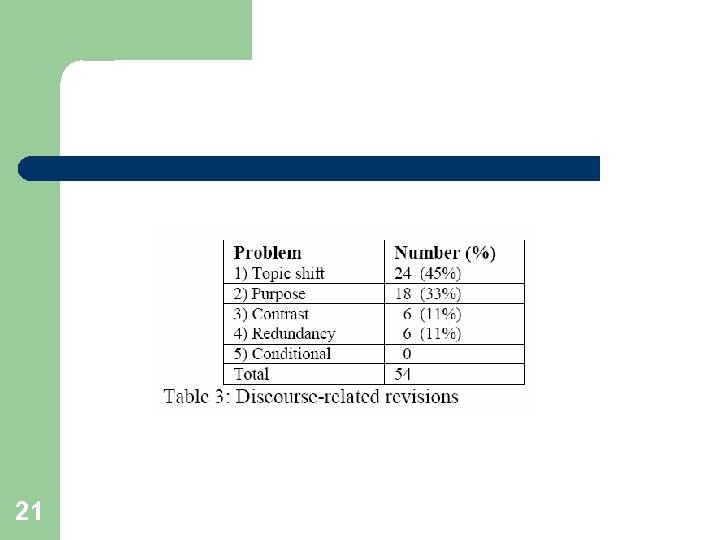
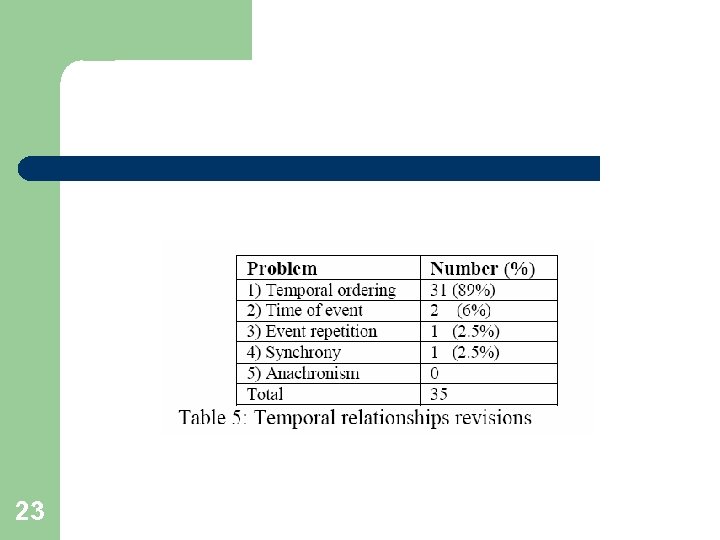
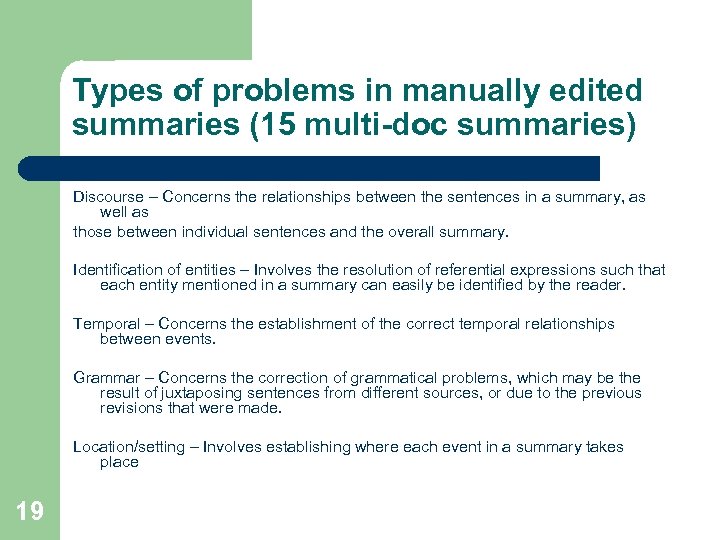 Types of problems in manually edited summaries (15 multi-doc summaries) Discourse – Concerns the relationships between the sentences in a summary, as well as those between individual sentences and the overall summary. Identification of entities – Involves the resolution of referential expressions such that each entity mentioned in a summary can easily be identified by the reader. Temporal – Concerns the establishment of the correct temporal relationships between events. Grammar – Concerns the correction of grammatical problems, which may be the result of juxtaposing sentences from different sources, or due to the previous revisions that were made. Location/setting – Involves establishing where each event in a summary takes place 19
Types of problems in manually edited summaries (15 multi-doc summaries) Discourse – Concerns the relationships between the sentences in a summary, as well as those between individual sentences and the overall summary. Identification of entities – Involves the resolution of referential expressions such that each entity mentioned in a summary can easily be identified by the reader. Temporal – Concerns the establishment of the correct temporal relationships between events. Grammar – Concerns the correction of grammatical problems, which may be the result of juxtaposing sentences from different sources, or due to the previous revisions that were made. Location/setting – Involves establishing where each event in a summary takes place 19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23


