a1b95b76f0e4a45f55d019375cb0c744.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49
 DISCLOSURES Joshua A. Hirsch, MD Consulting Fees – Intratech Medical LTD. , Medtronic Cardio. Vascular, Inc.
DISCLOSURES Joshua A. Hirsch, MD Consulting Fees – Intratech Medical LTD. , Medtronic Cardio. Vascular, Inc.
 Acute Stroke Intervention: Part 3 Imaging (basic-->advanced for triage) Joshua A. Hirsch, MD FSIR Albert Yoo MD Vice Chief Interventional Care Director : Interventional Neuroradiology/Endovascular Neurosurgery Chief: Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Prof: Harvard Medical School MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Acute Stroke Intervention: Part 3 Imaging (basic-->advanced for triage) Joshua A. Hirsch, MD FSIR Albert Yoo MD Vice Chief Interventional Care Director : Interventional Neuroradiology/Endovascular Neurosurgery Chief: Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Prof: Harvard Medical School MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Disclosures: stroke Consultant and shareholder: Intratech Steering Committee: MERCI Registry--all honoraria donated to charity (NERF) Co-investigator on all IA stroke studies MGH is participating in. Some slides provided by industry Discussion will include off label use of product MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Disclosures: stroke Consultant and shareholder: Intratech Steering Committee: MERCI Registry--all honoraria donated to charity (NERF) Co-investigator on all IA stroke studies MGH is participating in. Some slides provided by industry Discussion will include off label use of product MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
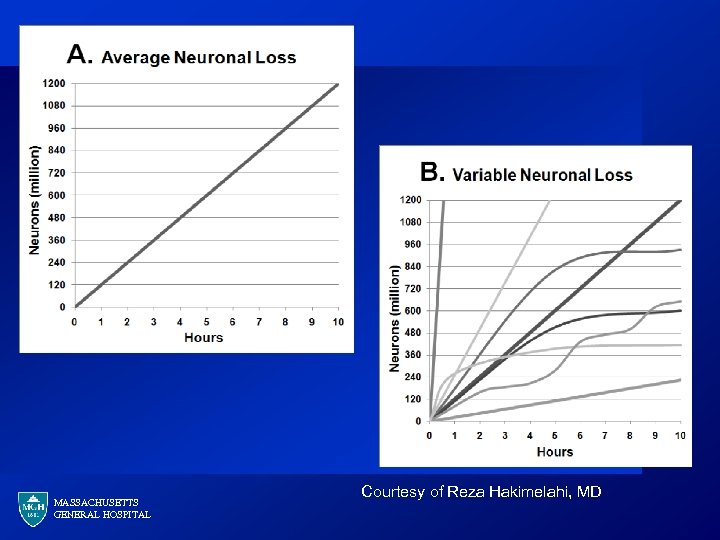
 Stroke Physiology · · · After acute proximal artery occlusion, there is a characteristic progression of neuronal death Currently, time = surrogate for the extent of brain injury Imaging seeks to individualize treatment decisions MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Stroke Physiology · · · After acute proximal artery occlusion, there is a characteristic progression of neuronal death Currently, time = surrogate for the extent of brain injury Imaging seeks to individualize treatment decisions MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
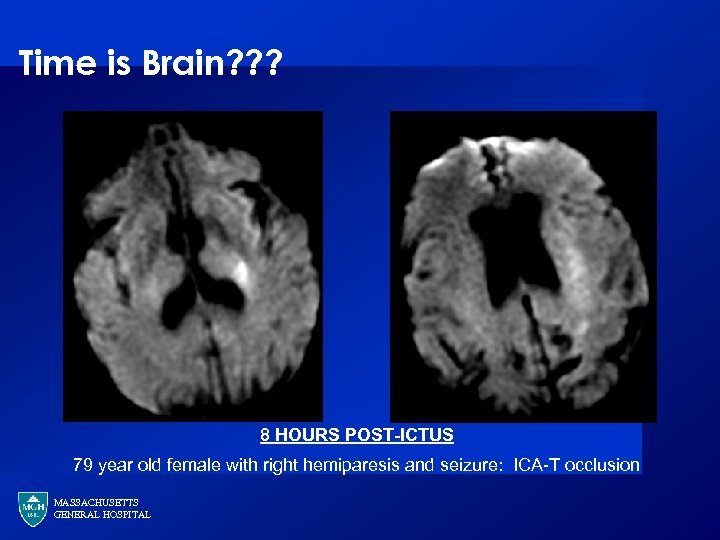 Time is Brain? ? ? 8 HOURS POST-ICTUS 79 year old female with right hemiparesis and seizure: ICA-T occlusion MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Time is Brain? ? ? 8 HOURS POST-ICTUS 79 year old female with right hemiparesis and seizure: ICA-T occlusion MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Time is Brain? ? ? 2. 5 HOURS POST-ICTUS 74 year old male with right hemiparesis and aphasia: ICA-T occlusion MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Time is Brain? ? ? 2. 5 HOURS POST-ICTUS 74 year old male with right hemiparesis and aphasia: ICA-T occlusion MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Courtesy of Reza Hakimelahi, MD
MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Courtesy of Reza Hakimelahi, MD
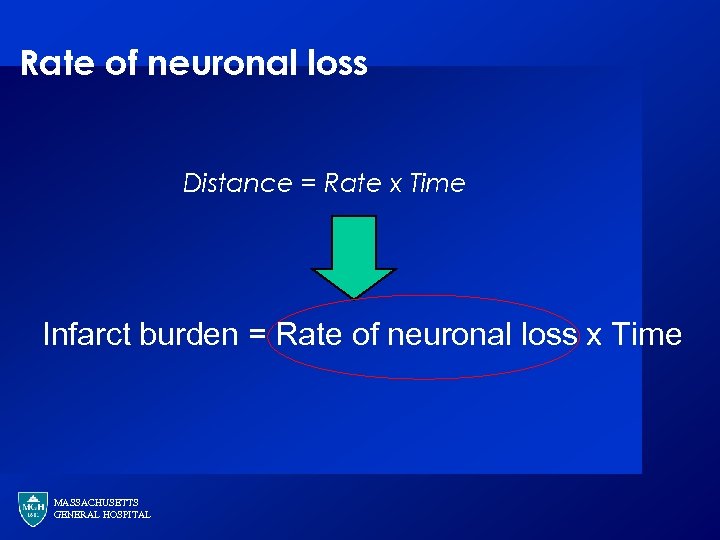 Rate of neuronal loss Distance = Rate x Time Infarct burden = Rate of neuronal loss x Time MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Rate of neuronal loss Distance = Rate x Time Infarct burden = Rate of neuronal loss x Time MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
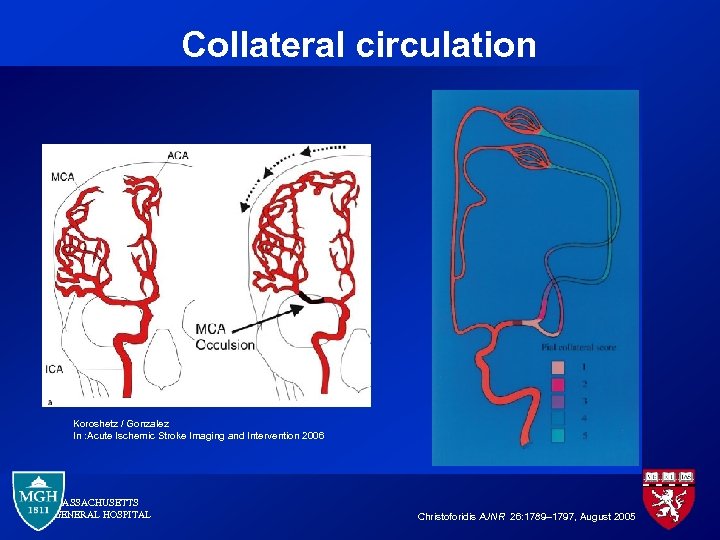 Collateral circulation Koroshetz / Gonzalez In : Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging and Intervention 2006 MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Christoforidis AJNR 26: 1789– 1797, August 2005
Collateral circulation Koroshetz / Gonzalez In : Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging and Intervention 2006 MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Christoforidis AJNR 26: 1789– 1797, August 2005
 Key imaging questions · · Is there a hemorrhage? NCCT ≥ MRI Is there a vessel occlusion? CTA > MRA How much is dead? DWI > NCCT (? CTA SI, ? CTP) How much is at risk? Perfusion imaging? ? MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Key imaging questions · · Is there a hemorrhage? NCCT ≥ MRI Is there a vessel occlusion? CTA > MRA How much is dead? DWI > NCCT (? CTA SI, ? CTP) How much is at risk? Perfusion imaging? ? MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Basic Imaging Physics · · · CT has one intrinsic contrast mechanism = differences in electron density MRI can image many different physical properties of protons: density, T 1 & T 2 relaxation times, diffusivity For both CT and MRI, contrast can be given to assess perfusion characteristics in the ischemic bed MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Basic Imaging Physics · · · CT has one intrinsic contrast mechanism = differences in electron density MRI can image many different physical properties of protons: density, T 1 & T 2 relaxation times, diffusivity For both CT and MRI, contrast can be given to assess perfusion characteristics in the ischemic bed MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
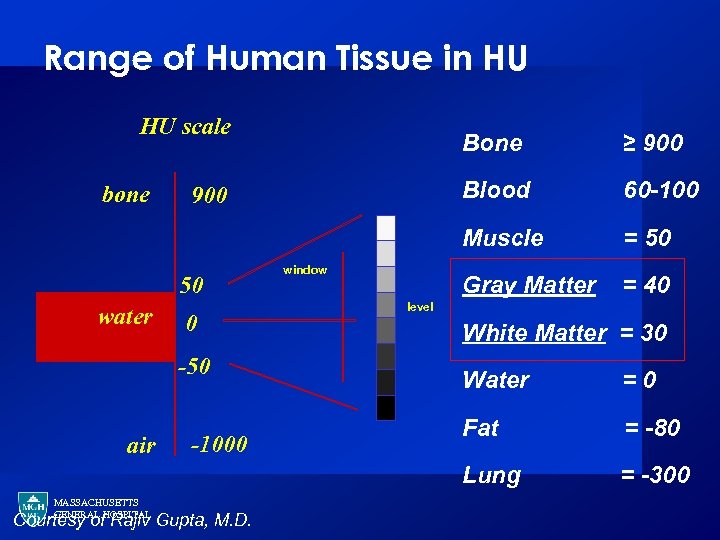 Range of Human Tissue in HU HU scale 50 water Blood 0 -50 window 60 -100 = 50 Gray Matter 900 ≥ 900 Muscle bone Bone = 40 level White Matter = 30 MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL -1000 Courtesy of Rajiv Gupta, M. D. =0 Fat = -80 Lung air Water = -300
Range of Human Tissue in HU HU scale 50 water Blood 0 -50 window 60 -100 = 50 Gray Matter 900 ≥ 900 Muscle bone Bone = 40 level White Matter = 30 MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL -1000 Courtesy of Rajiv Gupta, M. D. =0 Fat = -80 Lung air Water = -300
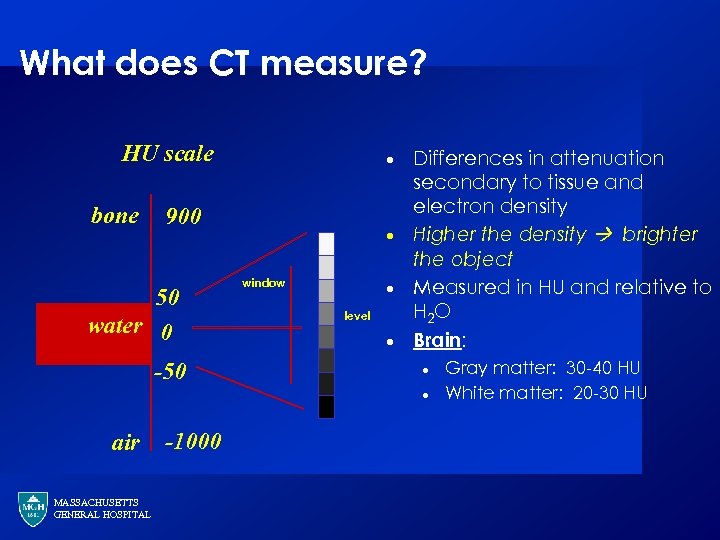 What does CT measure? HU scale bone · 900 50 water 0 -50 · window · level · Differences in attenuation secondary to tissue and electron density Higher the density brighter the object Measured in HU and relative to H 2 O Brain: · · air MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL -1000 Gray matter: 30 -40 HU White matter: 20 -30 HU
What does CT measure? HU scale bone · 900 50 water 0 -50 · window · level · Differences in attenuation secondary to tissue and electron density Higher the density brighter the object Measured in HU and relative to H 2 O Brain: · · air MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL -1000 Gray matter: 30 -40 HU White matter: 20 -30 HU
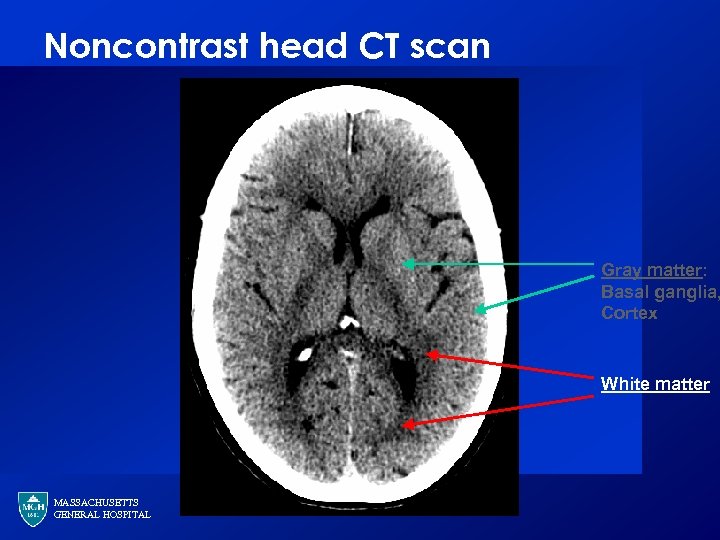 Noncontrast head CT scan Gray matter: Basal ganglia, Cortex White matter MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Noncontrast head CT scan Gray matter: Basal ganglia, Cortex White matter MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 · Is there a hemorrhage? MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
· Is there a hemorrhage? MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
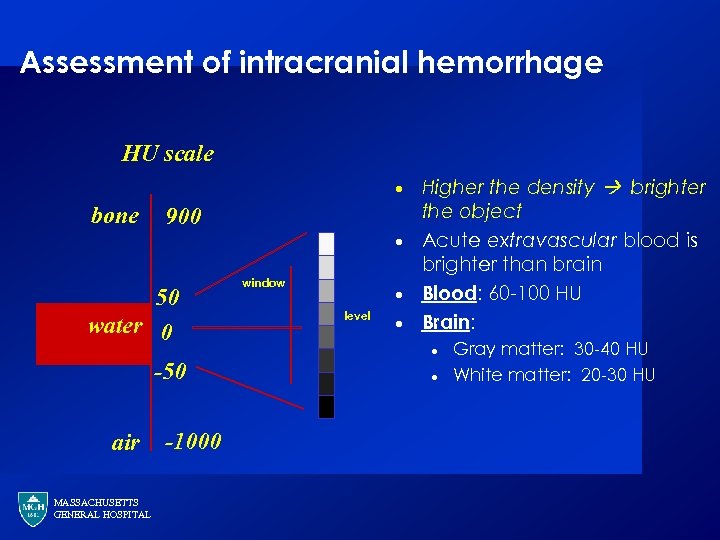 Assessment of intracranial hemorrhage HU scale · bone 900 · 50 water 0 -50 air MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL -1000 window · level · Higher the density brighter the object Acute extravascular blood is brighter than brain Blood: 60 -100 HU Brain: · · Gray matter: 30 -40 HU White matter: 20 -30 HU
Assessment of intracranial hemorrhage HU scale · bone 900 · 50 water 0 -50 air MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL -1000 window · level · Higher the density brighter the object Acute extravascular blood is brighter than brain Blood: 60 -100 HU Brain: · · Gray matter: 30 -40 HU White matter: 20 -30 HU
 Traditional Imaging of Acute Stroke: Non-Contrast CT Exclude intracranial hemorrhage: Hemorrhagic (non-ischemic) stroke Subarachnoid Bleed (aneurysmal rupture) MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Courtesy of Stuart Pomerantz, M. D. Parenchymal Hematoma (e. g. hypertensive bleed)
Traditional Imaging of Acute Stroke: Non-Contrast CT Exclude intracranial hemorrhage: Hemorrhagic (non-ischemic) stroke Subarachnoid Bleed (aneurysmal rupture) MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Courtesy of Stuart Pomerantz, M. D. Parenchymal Hematoma (e. g. hypertensive bleed)
 Hemorrhagic conversion of ischemic stroke · · Important complication of AIS and treatment Occurs in the ischemic bed MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Hemorrhagic conversion of ischemic stroke · · Important complication of AIS and treatment Occurs in the ischemic bed MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 · Is there a vessel occlusion? MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
· Is there a vessel occlusion? MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 CT Angiography · Important tool for rapidly and accurately assessing location of vessel occlusion · · · Is there a lesion amenable to interventional stroke therapy? Prognostic implications: ICA-T vs. M 1 vs. M 2 May provide added value to the evaluation of the brain parenchyma · More sensitive assessment of the brain parenchyma MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
CT Angiography · Important tool for rapidly and accurately assessing location of vessel occlusion · · · Is there a lesion amenable to interventional stroke therapy? Prognostic implications: ICA-T vs. M 1 vs. M 2 May provide added value to the evaluation of the brain parenchyma · More sensitive assessment of the brain parenchyma MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Neuro-CTA is our study of choice for all Emergent Neurovascular Indications · Intracranial Vasculature · · · Acute ischemic stroke Intracranial stenosis Aneurysms AVMs Venous Thrombosis Courtesy of Stuart MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL Pomerantz, HOSPITAL M. D.
Neuro-CTA is our study of choice for all Emergent Neurovascular Indications · Intracranial Vasculature · · · Acute ischemic stroke Intracranial stenosis Aneurysms AVMs Venous Thrombosis Courtesy of Stuart MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL Pomerantz, HOSPITAL M. D.
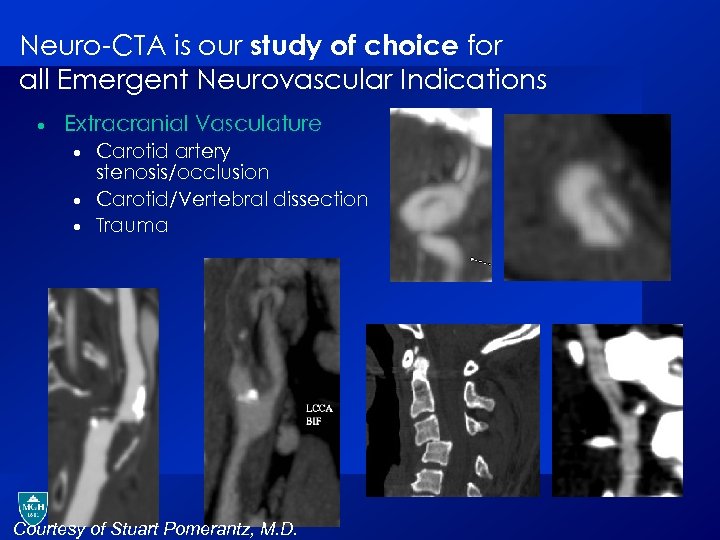 Neuro-CTA is our study of choice for all Emergent Neurovascular Indications · Extracranial Vasculature · · · Carotid artery stenosis/occlusion Carotid/Vertebral dissection Trauma MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Courtesy of Stuart Pomerantz, M. D.
Neuro-CTA is our study of choice for all Emergent Neurovascular Indications · Extracranial Vasculature · · · Carotid artery stenosis/occlusion Carotid/Vertebral dissection Trauma MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Courtesy of Stuart Pomerantz, M. D.
 Neuro-CTA: Why? · · · · Accurate Fast Widespread availability of scanners Not prone to artifactual signal dropout like MRI Non-invasive High-resolution Preservation of bone detail MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Courtesy of Stuart Pomerantz, M. D.
Neuro-CTA: Why? · · · · Accurate Fast Widespread availability of scanners Not prone to artifactual signal dropout like MRI Non-invasive High-resolution Preservation of bone detail MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Courtesy of Stuart Pomerantz, M. D.
 · CTA is highly accurate · · · Sensitivity 98. 4%, Specificity 98. 1% vs DSA · (Lev MH et al, JCAT 2001) High inter-observer reliability MRA (3 D TOF) performs reasonably well · · · Sensitivity 84 -87%, Specificity 85 -98% vs DSA Moderate inter-observer reliability Less accurate for more distal occlusions MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
· CTA is highly accurate · · · Sensitivity 98. 4%, Specificity 98. 1% vs DSA · (Lev MH et al, JCAT 2001) High inter-observer reliability MRA (3 D TOF) performs reasonably well · · · Sensitivity 84 -87%, Specificity 85 -98% vs DSA Moderate inter-observer reliability Less accurate for more distal occlusions MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 · How much tissue is dead? And how much is at risk? MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
· How much tissue is dead? And how much is at risk? MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
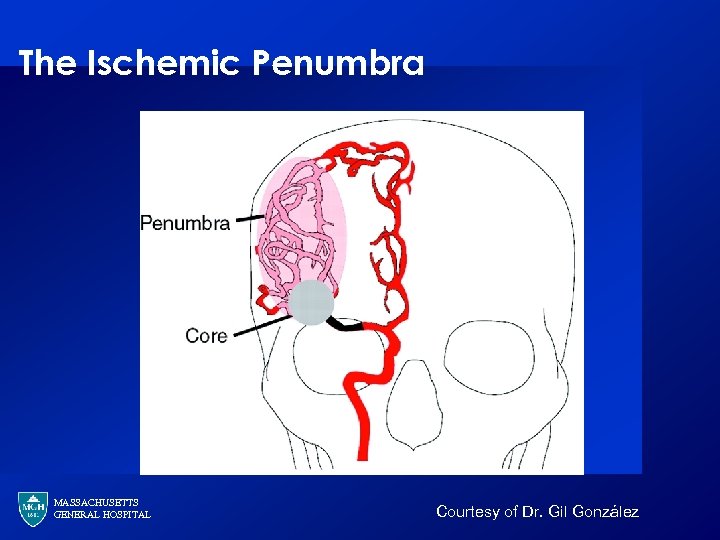 The Ischemic Penumbra MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Courtesy of Dr. Gil González
The Ischemic Penumbra MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Courtesy of Dr. Gil González
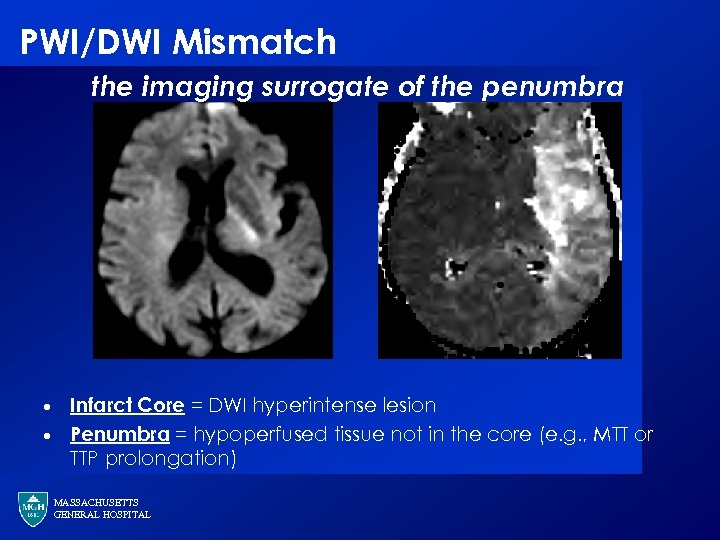 PWI/DWI Mismatch the imaging surrogate of the penumbra · · Infarct Core = DWI hyperintense lesion Penumbra = hypoperfused tissue not in the core (e. g. , MTT or TTP prolongation) MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
PWI/DWI Mismatch the imaging surrogate of the penumbra · · Infarct Core = DWI hyperintense lesion Penumbra = hypoperfused tissue not in the core (e. g. , MTT or TTP prolongation) MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Selection for IAT · · PWI/DWI mismatch is not discriminatory in the setting of large vessel occlusion – volume of MCA territory is ~300 cm 3 In our opinion, the more important question: How much is dead on arrival? · This is best assessed on DWI lesion MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Selection for IAT · · PWI/DWI mismatch is not discriminatory in the setting of large vessel occlusion – volume of MCA territory is ~300 cm 3 In our opinion, the more important question: How much is dead on arrival? · This is best assessed on DWI lesion MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Importance of Infarct Volume · Final infarct volume is the best predictor of clinical outcome. MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Importance of Infarct Volume · Final infarct volume is the best predictor of clinical outcome. MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Stroke 2003; 34: 2426 -35 MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Stroke 2003; 34: 2426 -35 MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Selection for IAT · · · PWI/DWI mismatch is not discriminatory in the setting of large vessel occlusion – volume of MCA territory is 300 cm 3 The more important question: What is dead on arrival? DWI lesion An acute infarct volume threshold of 70 cm 3 has a high specificity for predicting a poor outcome (Sanak et al. 2006) MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Selection for IAT · · · PWI/DWI mismatch is not discriminatory in the setting of large vessel occlusion – volume of MCA territory is 300 cm 3 The more important question: What is dead on arrival? DWI lesion An acute infarct volume threshold of 70 cm 3 has a high specificity for predicting a poor outcome (Sanak et al. 2006) MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
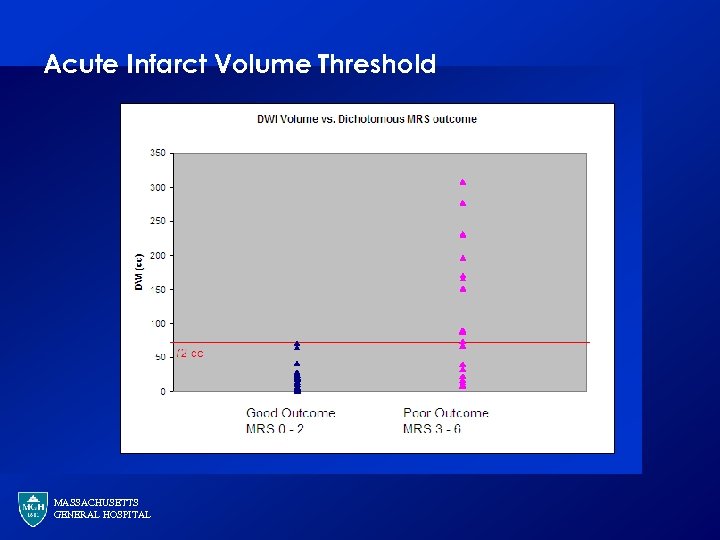 Acute Infarct Volume Threshold MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Acute Infarct Volume Threshold MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Various measures of the core infarct · · MRI DWI (best estimate) NCCT CTA source images CT perfusion MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Various measures of the core infarct · · MRI DWI (best estimate) NCCT CTA source images CT perfusion MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 MRI DWI · · Considered the gold standard for depicting the infarct core Identifies restricted diffusivity of water, which is thought to be related to energy failure cytotoxic edema Highly sensitive (91 -100%) and specific (86 -100%) within the first 6 hrs of stroke onset Similar accuracy to 11 C flumazenil PET, a reliable marker of neuronal integrity MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
MRI DWI · · Considered the gold standard for depicting the infarct core Identifies restricted diffusivity of water, which is thought to be related to energy failure cytotoxic edema Highly sensitive (91 -100%) and specific (86 -100%) within the first 6 hrs of stroke onset Similar accuracy to 11 C flumazenil PET, a reliable marker of neuronal integrity MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
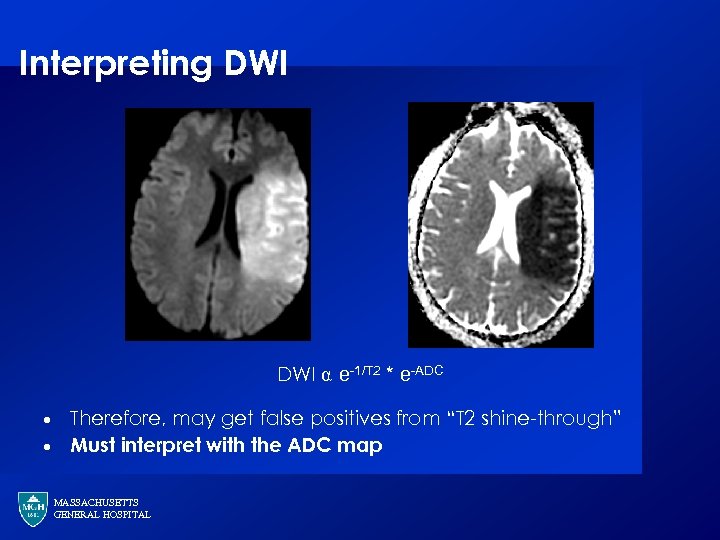 Interpreting DWI ⍺ e-1/T 2 * e-ADC · · Therefore, may get false positives from “T 2 shine-through” Must interpret with the ADC map MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Interpreting DWI ⍺ e-1/T 2 * e-ADC · · Therefore, may get false positives from “T 2 shine-through” Must interpret with the ADC map MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 NCCT detection of acute infarction · · · 0 -3 hrs: cytotoxic edema – not much change in overall tissue water content > 3 -6 hrs: vasogenic edema Δ HU ⍺ (degree of edema) · For every 1% ↑ in tissue H 2 O, X-ray attenuation ↓ by 3 -5% (or ~2. 5 HU) MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
NCCT detection of acute infarction · · · 0 -3 hrs: cytotoxic edema – not much change in overall tissue water content > 3 -6 hrs: vasogenic edema Δ HU ⍺ (degree of edema) · For every 1% ↑ in tissue H 2 O, X-ray attenuation ↓ by 3 -5% (or ~2. 5 HU) MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 NCCT signs of acute ischemia · Basal Insular Cortex ganglia ribbon Loss of gray-white matter differentiation: · · · MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL “Insular ribbon” Basal ganglia Cortex
NCCT signs of acute ischemia · Basal Insular Cortex ganglia ribbon Loss of gray-white matter differentiation: · · · MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL “Insular ribbon” Basal ganglia Cortex
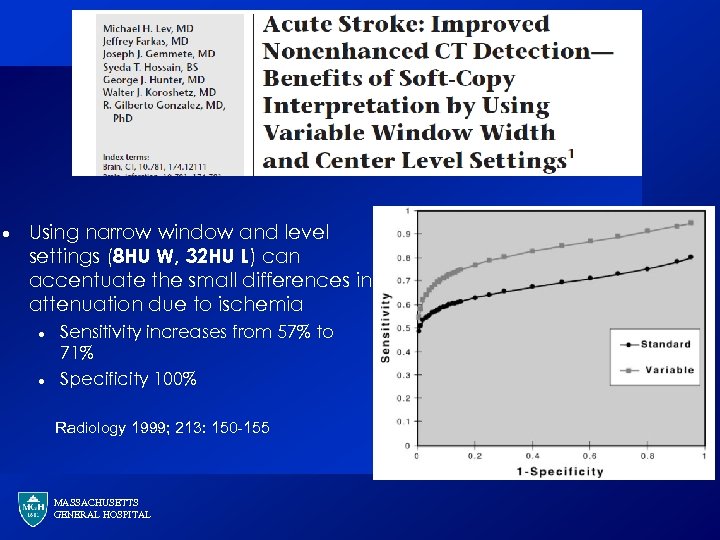 · Using narrow window and level settings (8 HU W, 32 HU L) can accentuate the small differences in attenuation due to ischemia · · Sensitivity increases from 57% to 71% Specificity 100% Radiology 1999; 213: 150 -155 MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
· Using narrow window and level settings (8 HU W, 32 HU L) can accentuate the small differences in attenuation due to ischemia · · Sensitivity increases from 57% to 71% Specificity 100% Radiology 1999; 213: 150 -155 MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
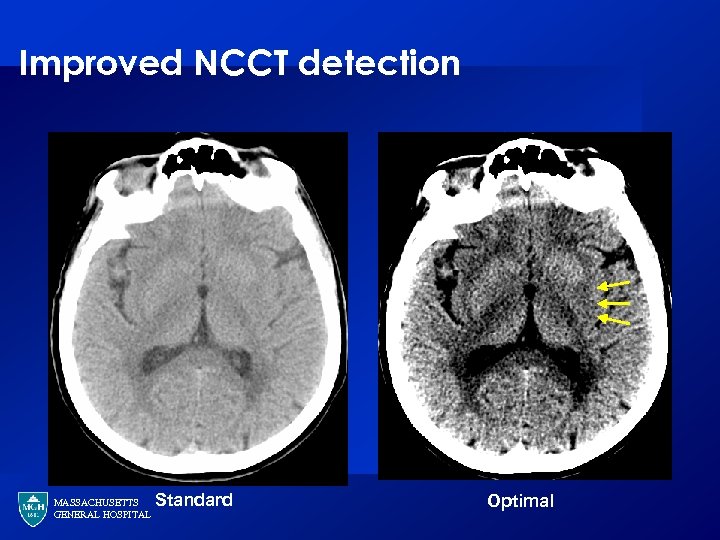 Improved NCCT detection MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Standard Optimal
Improved NCCT detection MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Standard Optimal
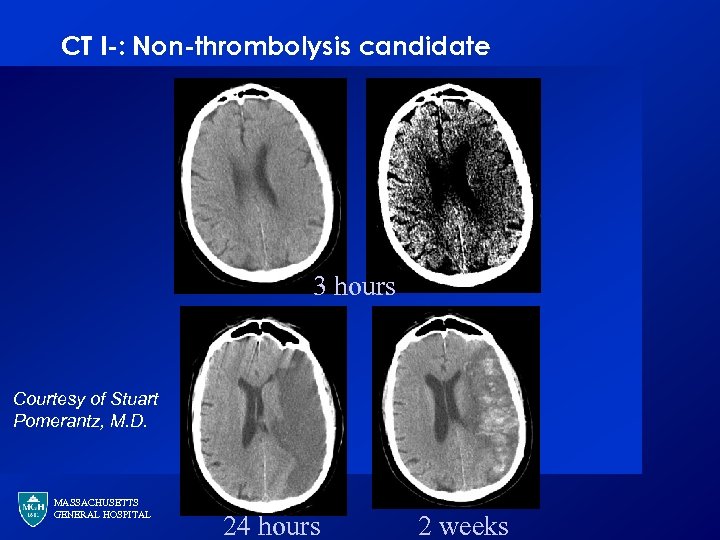 CT I-: Non-thrombolysis candidate 3 hours Courtesy of Stuart Pomerantz, M. D. MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL 24 hours 2 weeks
CT I-: Non-thrombolysis candidate 3 hours Courtesy of Stuart Pomerantz, M. D. MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL 24 hours 2 weeks
 NCCT has poor sensitivity · · CT is much less sensitive than MRI for detection of acute infarction (75% sensitivity 1) Has comparable specificity (>90%) 1 Barber PA, et al. Stroke. 1999; 30: 2059 -65. MG, et al. Neurology. 2000; 54: 1557 -61. 2 Lansberg MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
NCCT has poor sensitivity · · CT is much less sensitive than MRI for detection of acute infarction (75% sensitivity 1) Has comparable specificity (>90%) 1 Barber PA, et al. Stroke. 1999; 30: 2059 -65. MG, et al. Neurology. 2000; 54: 1557 -61. 2 Lansberg MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
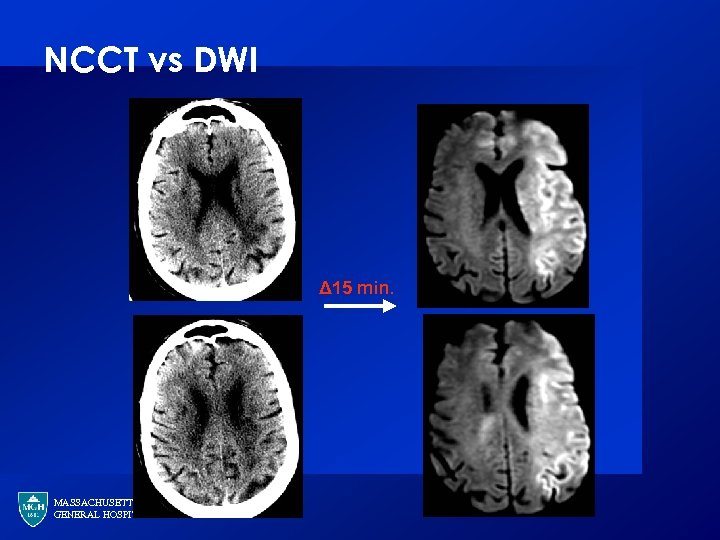 NCCT vs DWI Δ 15 min. MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
NCCT vs DWI Δ 15 min. MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 CTA source images · · Parenchymal evaluation performed on CT angiography Hypodensity is related to decreased tissue constrast Under steady state conditions, the hypodense lesion approximates the CBV (Hamberg et al, AJNR 1996) Images viewed on narrow windows (W: 30 HU, L: 30 HU) MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
CTA source images · · Parenchymal evaluation performed on CT angiography Hypodensity is related to decreased tissue constrast Under steady state conditions, the hypodense lesion approximates the CBV (Hamberg et al, AJNR 1996) Images viewed on narrow windows (W: 30 HU, L: 30 HU) MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
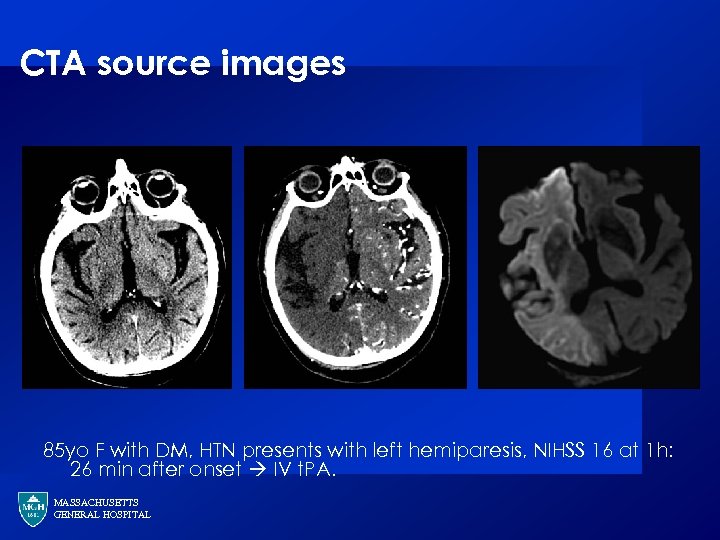 CTA source images MGH 85 yo F with DM, HTN presents with left hemiparesis, NIHSS 16 at 1 h: 26 min after onset IV t. PA. MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
CTA source images MGH 85 yo F with DM, HTN presents with left hemiparesis, NIHSS 16 at 1 h: 26 min after onset IV t. PA. MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 CTA-SI ≈ DWI · Schramm et al. (Stroke 2002; 33: 2426 -2432): · · 20 AIS pts underwent CTA and DWI within 6 hrs of onset (interval, 0. 55± 0. 25 hrs) 16/20 had vessel occlusion CTA-SI lesion volume significantly correlated with DWI lesion volume (r=0. 922, p<0. 0001) This is a complex problem and “improvements” in image acquisition raise ? s about the utility of this technique broadly MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
CTA-SI ≈ DWI · Schramm et al. (Stroke 2002; 33: 2426 -2432): · · 20 AIS pts underwent CTA and DWI within 6 hrs of onset (interval, 0. 55± 0. 25 hrs) 16/20 had vessel occlusion CTA-SI lesion volume significantly correlated with DWI lesion volume (r=0. 922, p<0. 0001) This is a complex problem and “improvements” in image acquisition raise ? s about the utility of this technique broadly MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
 Dynamic perfusion imaging · · Requires IV contrast injected at high rate Images are rapidly acquired from a slab of tissue to monitor the first pass transit of the contrast bolus Post-processing of the images (usually deconvolution with an arterial input function) produces maps of tissue-level perfusion: CBV, CBF and MTT For CT perfusion, region of CBV depression estimates the infarct core MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Dynamic perfusion imaging · · Requires IV contrast injected at high rate Images are rapidly acquired from a slab of tissue to monitor the first pass transit of the contrast bolus Post-processing of the images (usually deconvolution with an arterial input function) produces maps of tissue-level perfusion: CBV, CBF and MTT For CT perfusion, region of CBV depression estimates the infarct core MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
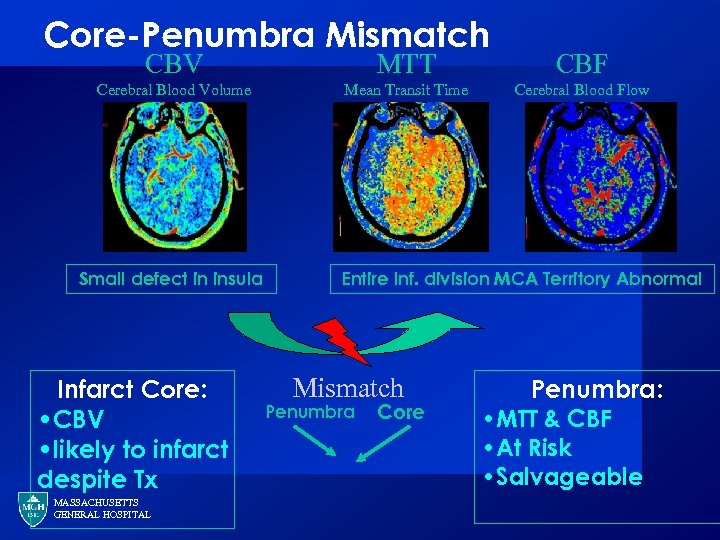 Core-Penumbra Mismatch CBV MTT CBF Cerebral Blood Volume Mean Transit Time Cerebral Blood Flow Small defect in insula Infarct Core: • CBV • likely to infarct despite Tx MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Entire Inf. division MCA Territory Abnormal Mismatch Penumbra Core Penumbra: • MTT & CBF • At Risk • Salvageable
Core-Penumbra Mismatch CBV MTT CBF Cerebral Blood Volume Mean Transit Time Cerebral Blood Flow Small defect in insula Infarct Core: • CBV • likely to infarct despite Tx MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Entire Inf. division MCA Territory Abnormal Mismatch Penumbra Core Penumbra: • MTT & CBF • At Risk • Salvageable
 Successful Thrombolysis: Infarct Limited Mostly to Ischemic Core (CBV) CBV MTT CBF Mismatch Majority of penumbra salvaged MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Penumbra Core Courtesy of Stuart Pomerantz, M. D. DWI
Successful Thrombolysis: Infarct Limited Mostly to Ischemic Core (CBV) CBV MTT CBF Mismatch Majority of penumbra salvaged MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL Penumbra Core Courtesy of Stuart Pomerantz, M. D. DWI
 Conclusion: “Part 3” and “ 3 part series” · Advanced neurovascular imaging allows for dramatic improvement in the triage of stroke · · This is a work in progress but absolutely critical Understanding the power of that imaging and coupling it to the treatment advances allows for best possible treatments at any given time. Device development for endovascular Rx continues to push forward Taken together, these are powerful trends for the continued improvement in our ability to Rx acute ischemic stroke! MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL
Conclusion: “Part 3” and “ 3 part series” · Advanced neurovascular imaging allows for dramatic improvement in the triage of stroke · · This is a work in progress but absolutely critical Understanding the power of that imaging and coupling it to the treatment advances allows for best possible treatments at any given time. Device development for endovascular Rx continues to push forward Taken together, these are powerful trends for the continued improvement in our ability to Rx acute ischemic stroke! MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL


