d6730879aa053934b33dd715fe3765bf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Directory Workshop Parallel Sessions Rob Banz, Univ. of Maryland, Baltimore County Tom Barton, University of Memphis Keith Hazelton, University of Wisconsin, Madison 02 Feb 2002 Richard Jones, University of Colorado, Boulder 02 February 2002
Overview Interactive tour of directory design & implementation issues: • Data flow from source systems through enterprise directory to applications • Infrastructure services provided to applications & service platforms • Directory enabled applications • Groups • Metadirectories & affiliated directories 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 2
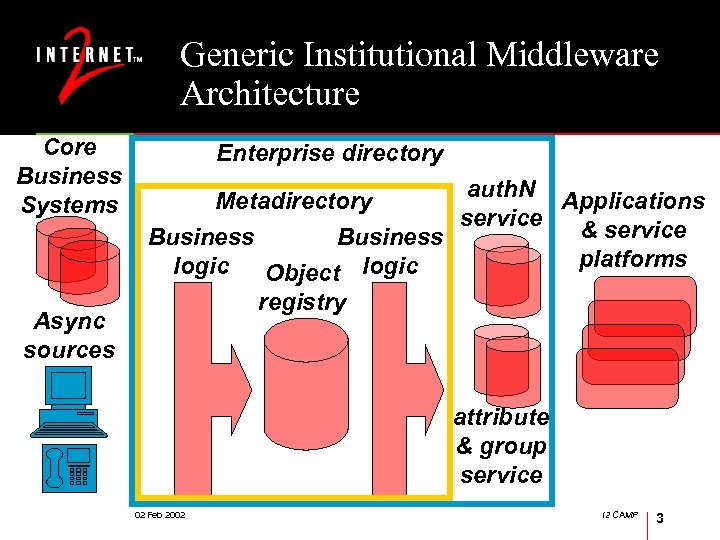
Generic Institutional Middleware Architecture Core Business Systems Async sources Enterprise directory auth. N Applications Metadirectory service & service Business platforms logic Object registry attribute & group service 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 3

Source(s) of Identity What is the system of record for identity data? (trick question) (A) Several. Some of HRS, SIS, Academic Personnel, Med School, Law School, Telecommunications Management System, Alumni System, Library, … are sources, and others must be reconciled. (B) All core business systems obtain identity data from the object registry. Answer B may prove to be fundamental to having substantial online services & programs… 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 4

Managed Objects • Objects that describe: • People • Groups • Aliases, Roles, Affiliations • Network devices • Security policies • Network services • Org structure • Application specific objects • The object classes and source data to populate them are determined by the applications to be directory enabled, with institutional policy folded in. 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 5
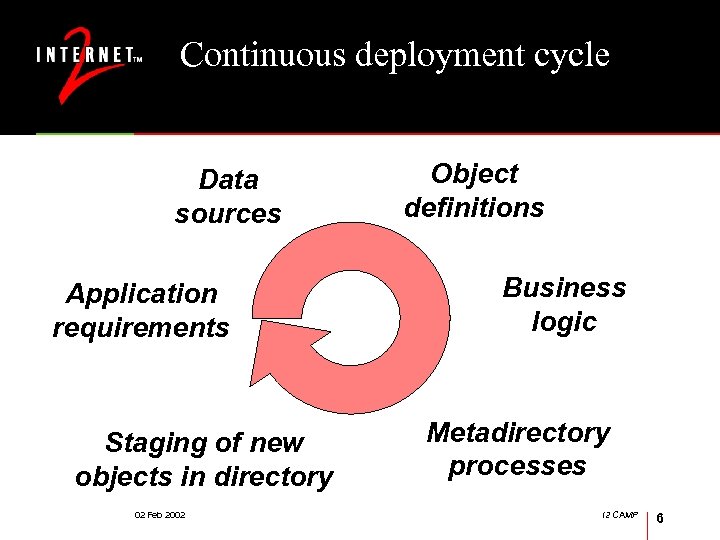
Continuous deployment cycle Data sources Application requirements Staging of new objects in directory 02 Feb 2002 Object definitions Business logic Metadirectory processes I 2 CAMP 6

Authentication Service Models • Several authentication services may need to be provided “on the front end”: RADIUS, LDAP, Kerberos, Web. ISO, basic auth, …. • Best practice to work towards is to base them all on a strong system such as Kerberos or PKI, implementing backend callouts from other auth. N services where possible. • (and of course ensure basic auth is only done over encrypted channels in the meanwhile!) 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 7

Attribute & group services facilitate… • Customization – application UI tailored to user’s affiliation with the organization. • Personalization – application UI tailored to user’s preferences. • General authorization (but especially affiliation based auth. Z). • Group messaging. • Naming services (for unix at least). 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 8

Application Examples 1 • White & blue pages: find contact info for persons and departments • SMTP routing • Mailbox access & personalization • Group messaging • Calendar auth. N, customization (calendar roles), personalization. 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 9
Application Examples 2 • Web basic auth. N, auth. Z: “require user”, “require group”, and “require filter”. • Course management system: auth. N, customization, personalization. • Portal: ditto • Generic application server (egs, EJB, J 2 EE): ditto + auth. Z. • Specialized application server (egs, Brio, Cognos, Right. Now, ARS, …): auth. N, auth. Z. 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 10

Application Examples 3 • Account self-maintenance (password, PIN, email, personal URL, pager, …) • E-provisioning – automated account management. Basic life cycle for accounts and access privileges. • Unix naming services 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 11

Application examples 4 • NAS auth. N, auth. Z, customization. • Proxy access • Network auto-registration • Computer lab (& desktop) auth. N, auth. Z, customization, personalization. • Integration of LAN specific directory… 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 12

Active Directory • As application specific directory (for LAN management), needs accounts to be synchronized from institutional directory service. A metadirectory problem? • Want groups too (for LAN management)? ? • AD as enterprise directory? 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 13

Types of groups: how sourced • Institutional • Automated • Manual • Delegated • Personal • Joinable 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 14

Types of groups: content • Enterprise (e. g. all faculty, staff & students; all nonexempt employees) • Departmental (e. g. History Dept staff; all dept heads and above in College of Education) • Academic (e. g. students in PHYS 101 section 001 Spring 2002; all seniors in MIS) • Application specific (e. g. persons permitted to run special Brio queries; answerers for questions about the Law program) • Activity specific (e. g. Chess Club; Helpdesk Team) 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 15
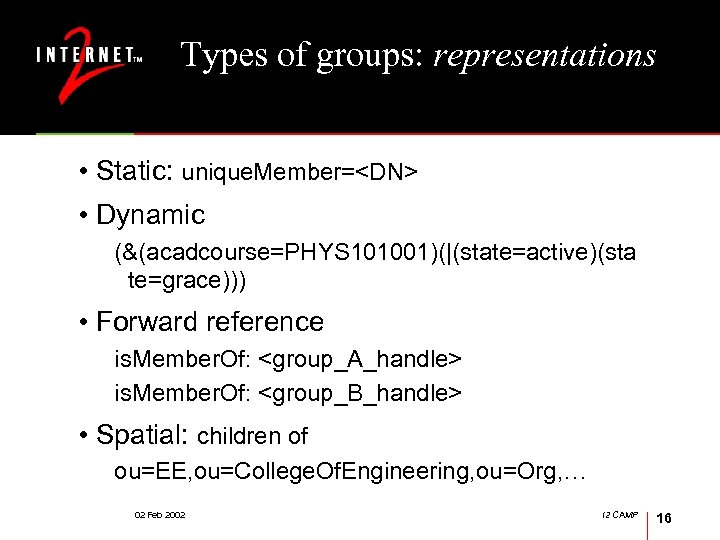
Types of groups: representations • Static: unique. Member=<DN> • Dynamic (&(acadcourse=PHYS 101001)(|(state=active)(sta te=grace))) • Forward reference is. Member. Of: <group_A_handle> is. Member. Of: <group_B_handle> • Spatial: children of ou=EE, ou=College. Of. Engineering, ou=Org, … 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 16

Groups: techniques & issues • Naming & location • Group math • Referential integrity • Privacy • Aging • Delegated management • Forward referencing 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 17

Groups: choosing a representation • how the group information is to be maintained • how it is to be most commonly accessed (e. g. , is X a member of, list all members, …) • interactions between the type of representation, the nature of the group (such as size and privacy requirements), and capabilities of the particular directory service agent (DSA) being used. 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 18

Metadirectories: why? • Replication solves some problems but not all • You will need directories with • special ACLs • special objects or attributes • handling multicampus issues • etc • You WILL end up running multiple (different) directories. How? . . . 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 19
Metadirectory: what it is & isn’t • An overworked term • Not just a meta-database (not necessarily a directory!) • Data transformation among data sources and directories including identity management, organizational policy, and eprovisioning. 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 20
Metadirectory tools • Meta. Merge--a metatool (use free to higher ed) to solve metadirectory problems. • Examples: • Move data from a person registry to the enterprise directory • Transform data from enterprise directory to special application directory • Do. DHE 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 21

Affiliated directories • Trying to characterize the problem is itself a problem! E. g. s: • currency of information in a personal address book • Maintaining integrity of PI contact information at granting agencies • Verification/currency of data outside of the bounds of a unified enterprise directory. • The things that flow out to target repositories are data + metadata bundles 02 Feb 2002 I 2 CAMP 22
d6730879aa053934b33dd715fe3765bf.ppt