c0642b92c9669b6752e56313bb190a2f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Direct Digital Radiography or Direct Capture Radiography Bushong Ch. 27

Late 1990’s n A new approach to imaging appeared n DR or Direct Capture imaging n Too early to tell which system will prevail

Directed Digital Radiography (DDR) Directed digital radiography, a term used to describe total electronic imaging capturing. Eliminates the need for an image plate altogether.
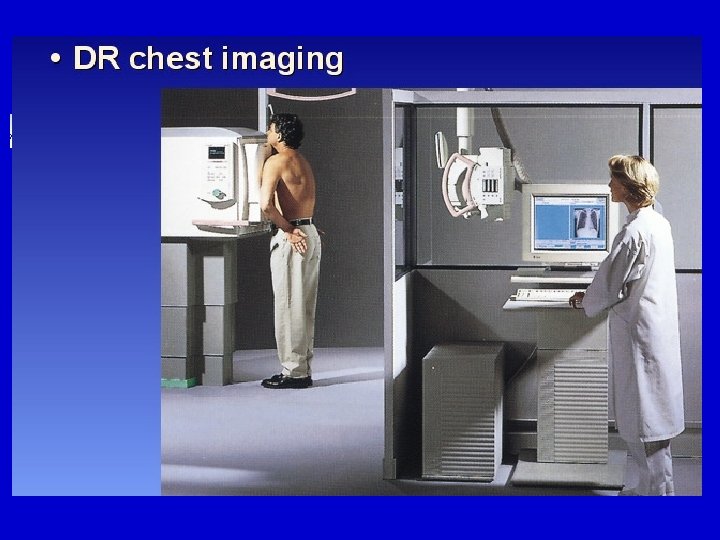

DDR Systems

IMAGE CAPTURE CR n n PSP – photostimulable phosphor plate REPLACES FILM IN THE CASSETTE DR – NO CASSETTE – PHOTONS n n n CAPTURED DIRECTLY ONTO A TRANSISTOR SENT DIRECTLY TO A MONITOR

DIRECT RADIOGRAPHY n n n uses a transistor receiver (like bucky) that captures and converts x-ray energy directly into digital signal seen immediately on monitor then sent to PACS/ printer/ other workstations FOR VIEWING
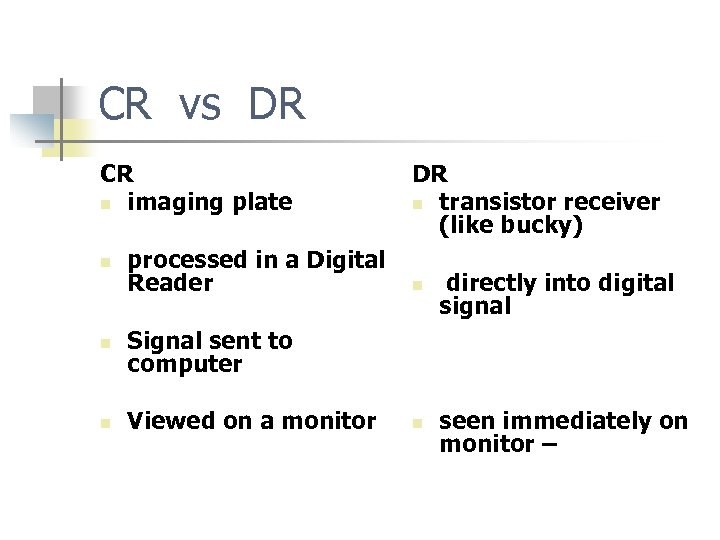
CR vs DR CR n imaging plate n processed in a Digital Reader n Viewed on a monitor n directly into digital signal n seen immediately on monitor – Signal sent to computer n DR n transistor receiver (like bucky)
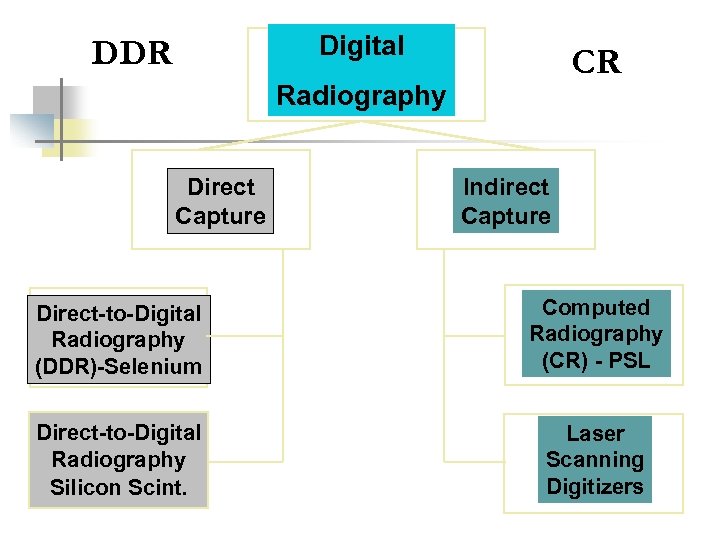
Digital DDR CR Radiography Direct Capture Indirect Capture Direct-to-Digital Radiography (DDR)-Selenium Computed Radiography (CR) - PSL Direct-to-Digital Radiography Silicon Scint. Laser Scanning Digitizers
Two types of DDR systems n n Both are based on the thin-film transistor as an active matrix array (AMA) Built the size of a conventional S/F receptor
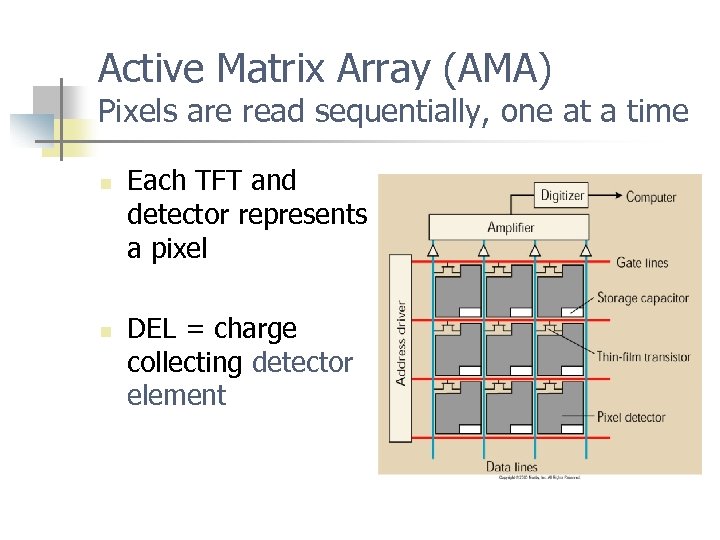
Active Matrix Array (AMA) Pixels are read sequentially, one at a time n n Each TFT and detector represents a pixel DEL = charge collecting detector element
DEL Digital Value n Digital Value depends on: n n Charge collected by DEL. Bit depth 10 bit = 1 – 1024 12 bit =1 - 4096
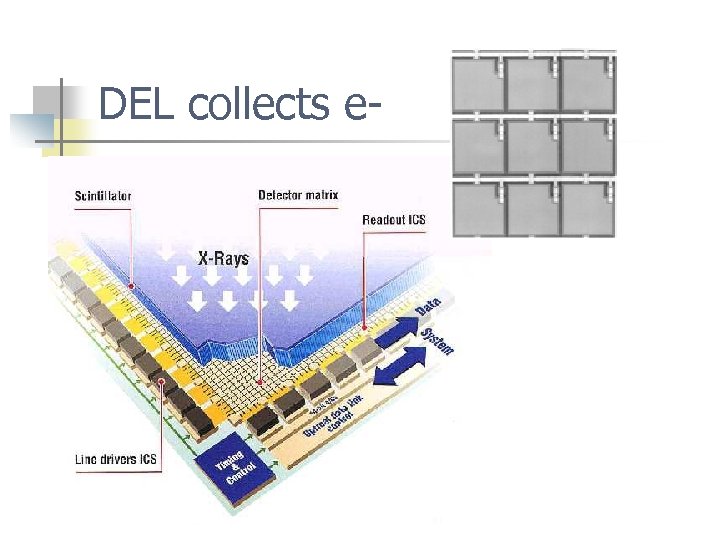
DEL collects e-

Unlike CR plates, only the exposed pixels contribute to the image data base. n One exposure = Detector Readout
DDR using cesium iodide scintillation phosphors n n n Cs. I is coated over an active matrix array (AMA) of amorphus silicon (a-Si) photodiodes Amorphus means without shape Photodiodes are used to detect light or measure its intensity also called a charge coupled device (CCD)

DDR steps using cesium iodide n n n Exit x-rays interact with Cs. I scintillation phosphor to produce light The light interact with the a-Si to produce a signal The TFT stores the signal until readout, one pixel at a time
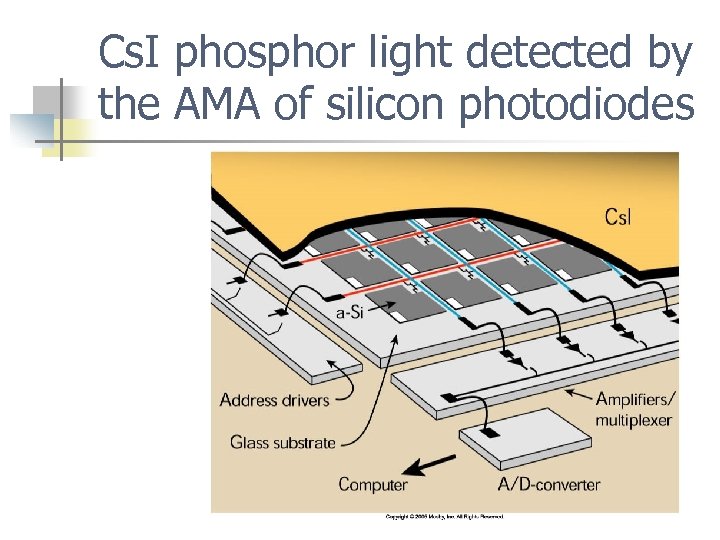
Cs. I phosphor light detected by the AMA of silicon photodiodes

DDR only using amorphous selenium (a-Se) n n The exit x-ray photon interact with the a -Si (detector element/DEL). Photon energy is trapped on detector (signal) The TFT stores the signal until readout, one pixel at a time
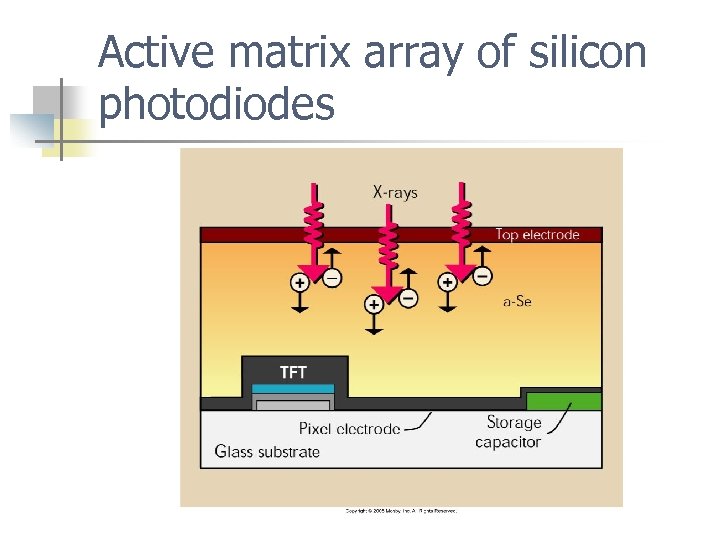
Active matrix array of silicon photodiodes

Advantages/Disadvantages n Cs. I phosphors have high detective quantum efficiency (DQE) = lower patient dose n n DQE = % of x-rays absorbed by the phosphors a-Se only: there is no spreading of light in the phosphor = better spatial resolution
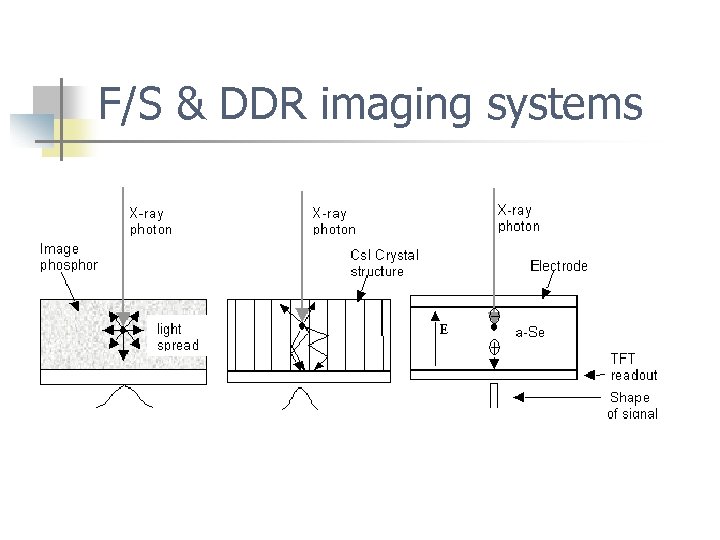
F/S & DDR imaging systems
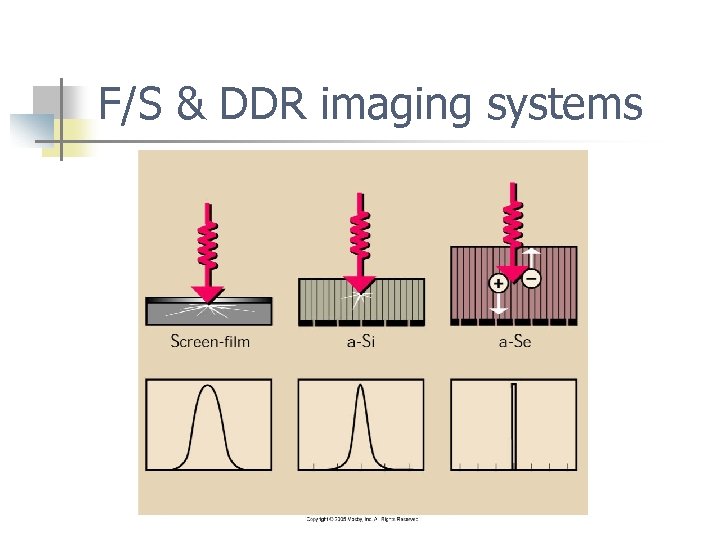
F/S & DDR imaging systems

Image Resolution – (how sharply is the image seen) CR & DR n 4000 x 4000 n image only as good a monitor* n n n 525 vs 1000 line more pixels = more memory needed to store resolution dependent on pixel size n n n CR 2 - 5 lp/mm RAD 3 -6 lp/mm DR 3 - 5 lp/mm IMAGE APPEARS SHARPER BECAUSE CONTRAST CAN BE ADJUSTED BY THE COMPUTER – (DIFFERENCES IN DENSITY)

Image Resolution
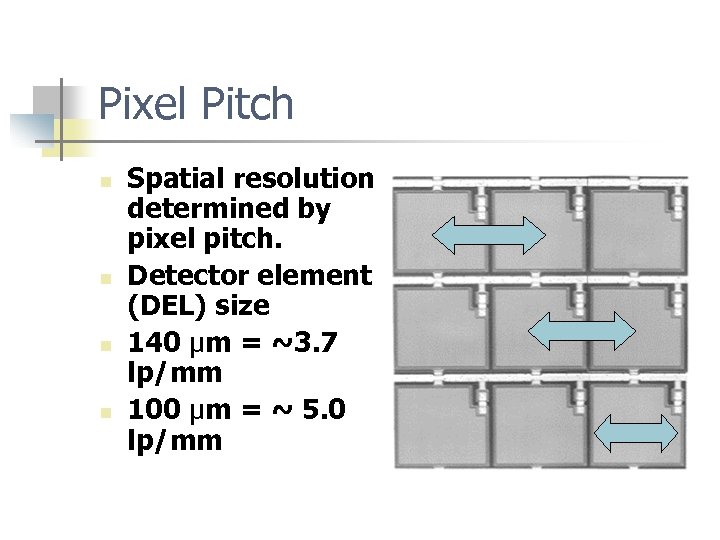
Pixel Pitch n n Spatial resolution determined by pixel pitch. Detector element (DEL) size 140 μm = ~3. 7 lp/mm 100 μm = ~ 5. 0 lp/mm
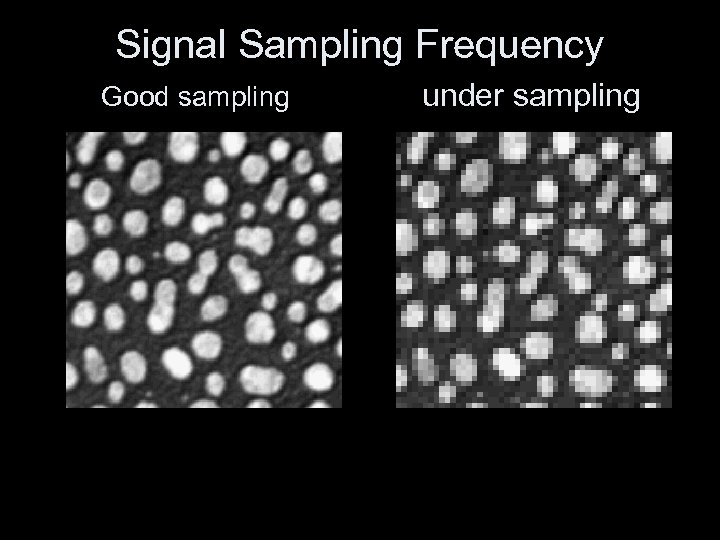
Signal Sampling Frequency Good sampling under sampling

DR n n Initial expense high very low dose to pt – image quality of 100 s using a 400 s technique Therfore ¼ the dose needed to make the image
Flat Panel TFT Detectors n n n n Have to be very careful with terminology One vendor claims: “Detector has sharpness of 100 speed screen” May be true: TFT detectors can have very sharp edges due to DEL alignment But ! Spatial resolution is not as good as 100 speed screen. TFT detector = 3. 4 lp/mm 100 speed screen = 8 – 10 lp/mm
TFT Array Detectors n n n Detector is refreshed after exposure If no exposures are produced. . . detector refreshed every 30 – 45 sec Built in AEC, An ion chamber between grid and detector
Patient Dose n n n Important factors that affect patient dose DQE: when using Cs. I systems Both systems “fill factor” n n The percentage of the pixel face that contains the x-ray detector. Fill factor is approximately 80%
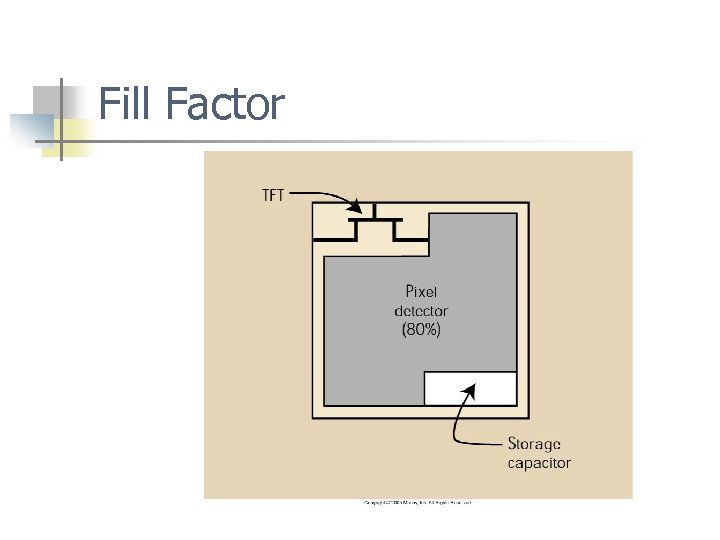
Fill Factor
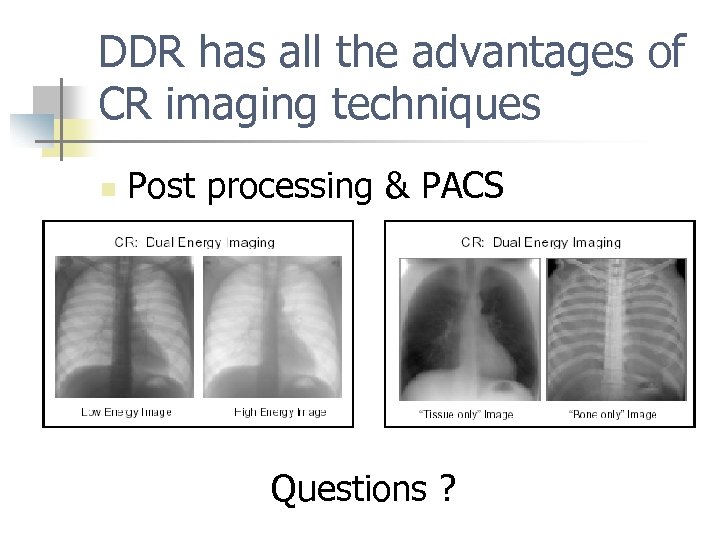
DDR has all the advantages of CR imaging techniques n Post processing & PACS Questions ?
c0642b92c9669b6752e56313bb190a2f.ppt