5c89eebf428b403b1e16c7f1a9c45da4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 Dipartimento di Neuroscienze Università degli Studi di Torino e Istituto Nazionale di Neuroscienze Torino www. personalweb. unito. it / fabrizio. benedetti
Dipartimento di Neuroscienze Università degli Studi di Torino e Istituto Nazionale di Neuroscienze Torino www. personalweb. unito. it / fabrizio. benedetti
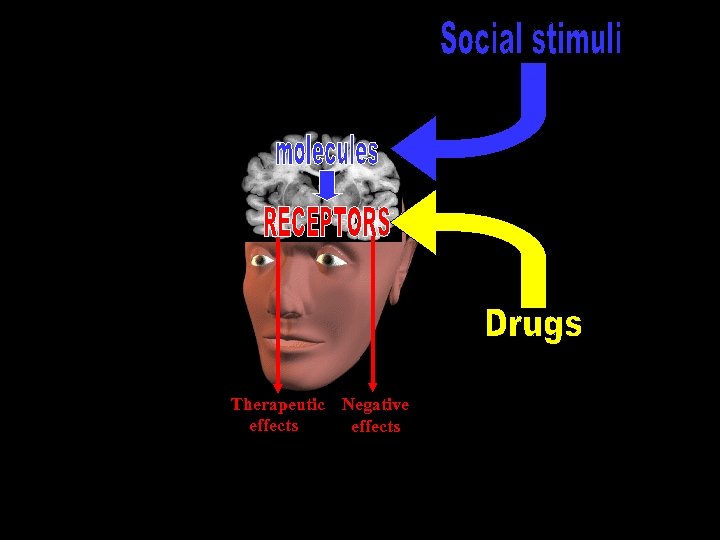 Therapeutic Negative effects
Therapeutic Negative effects
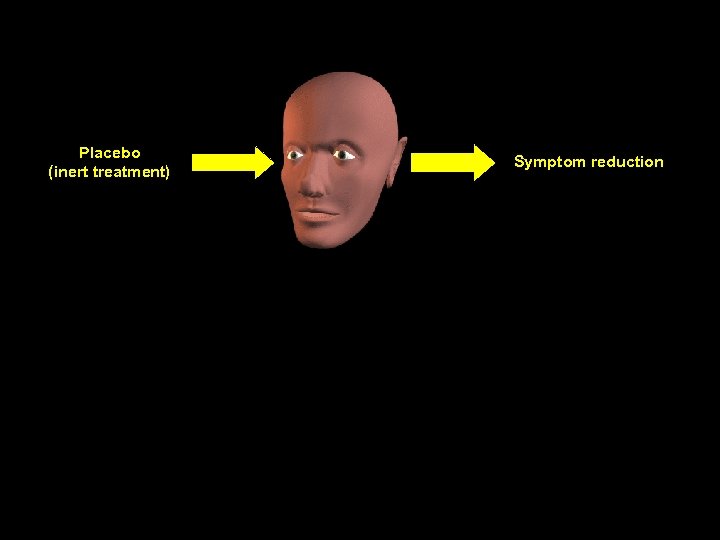 Placebo (inert treatment) Symptom reduction spontaneous remission others regression to the mean conditioning cognitive factors
Placebo (inert treatment) Symptom reduction spontaneous remission others regression to the mean conditioning cognitive factors
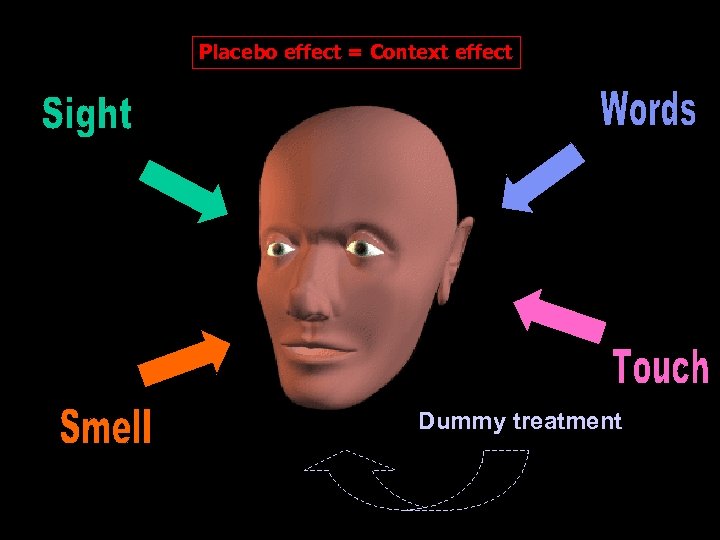 Placebo effect = Context effect Dummy treatment Medical treatment
Placebo effect = Context effect Dummy treatment Medical treatment
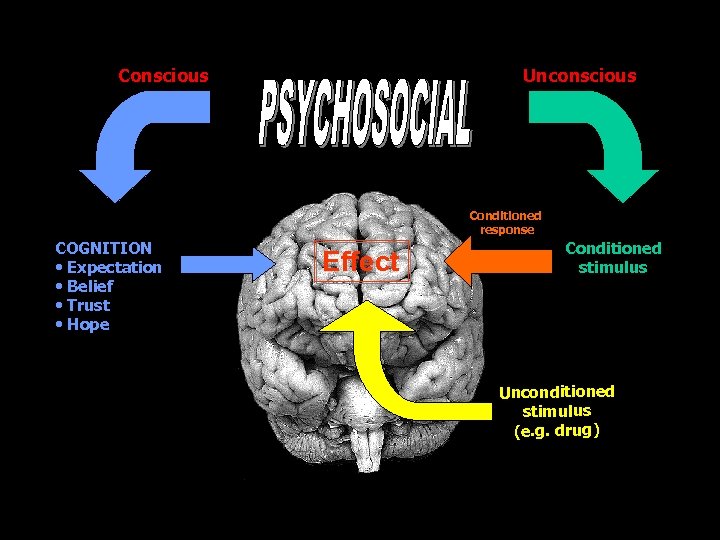 Conscious Unconscious Conditioned response COGNITION • Expectation • Belief • Trust • Hope Effect Conditioned stimulus Unconditioned stimulus (e. g. drug)
Conscious Unconscious Conditioned response COGNITION • Expectation • Belief • Trust • Hope Effect Conditioned stimulus Unconditioned stimulus (e. g. drug)
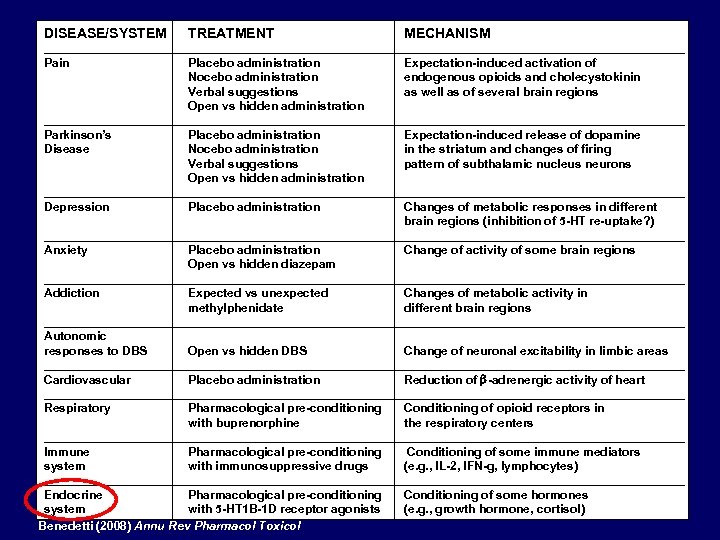
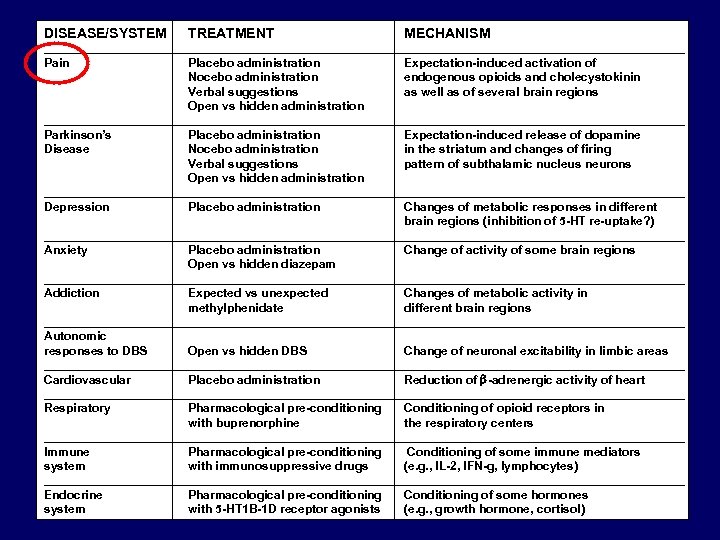 DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol)
DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol)
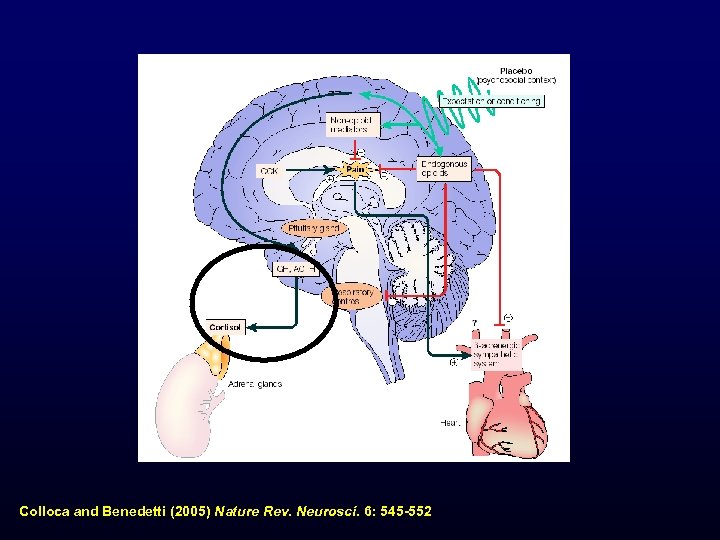
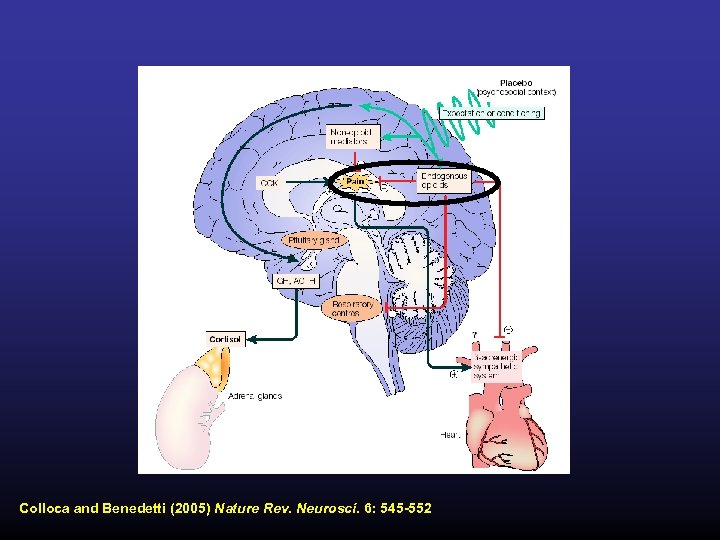 Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
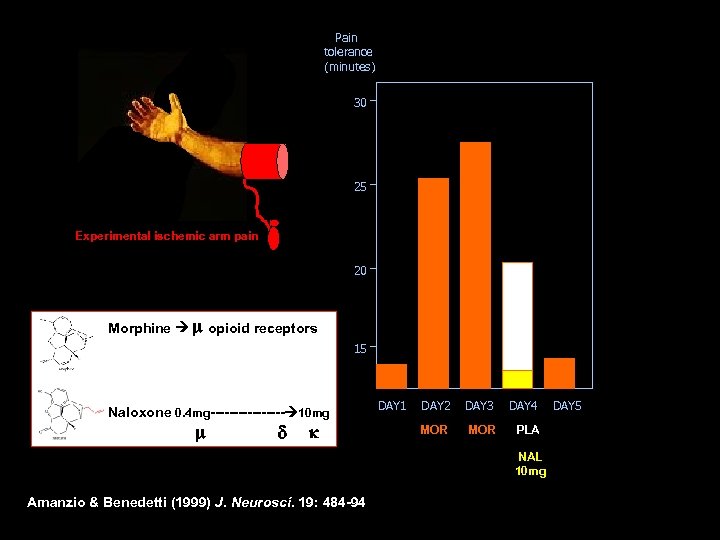 Pain tolerance (minutes) 30 25 Experimental ischemic arm pain 20 Morphine m opioid receptors 15 Naloxone 0. 4 mg-------- 10 mg m d k DAY 1 DAY 2 DAY 3 DAY 4 MOR PLA NAL 10 mg Amanzio & Benedetti (1999) J. Neurosci. 19: 484 -94 DAY 5
Pain tolerance (minutes) 30 25 Experimental ischemic arm pain 20 Morphine m opioid receptors 15 Naloxone 0. 4 mg-------- 10 mg m d k DAY 1 DAY 2 DAY 3 DAY 4 MOR PLA NAL 10 mg Amanzio & Benedetti (1999) J. Neurosci. 19: 484 -94 DAY 5
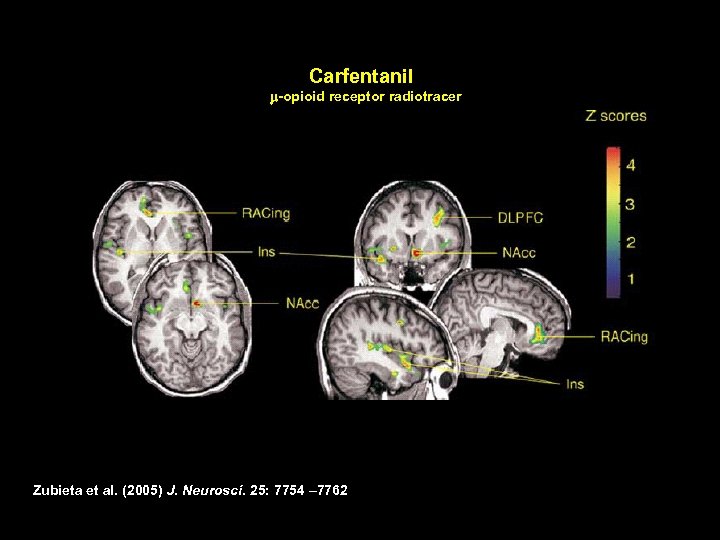 Carfentanil m-opioid receptor radiotracer Zubieta et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25: 7754 – 7762
Carfentanil m-opioid receptor radiotracer Zubieta et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25: 7754 – 7762
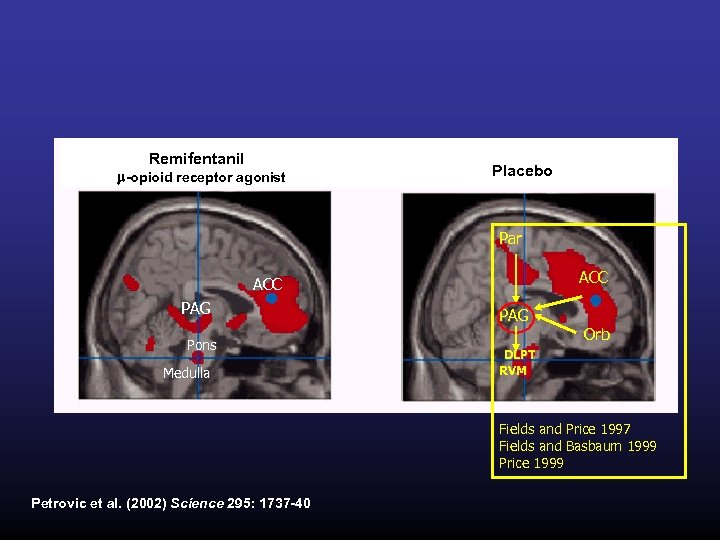 Remifentanil m-opioid receptor agonist Placebo Par ACC PAG Pons Medulla PAG Orb DLPT RVM Fields and Price 1997 Fields and Basbaum 1999 Price 1999 Petrovic et al. (2002) Science 295: 1737 -40
Remifentanil m-opioid receptor agonist Placebo Par ACC PAG Pons Medulla PAG Orb DLPT RVM Fields and Price 1997 Fields and Basbaum 1999 Price 1999 Petrovic et al. (2002) Science 295: 1737 -40
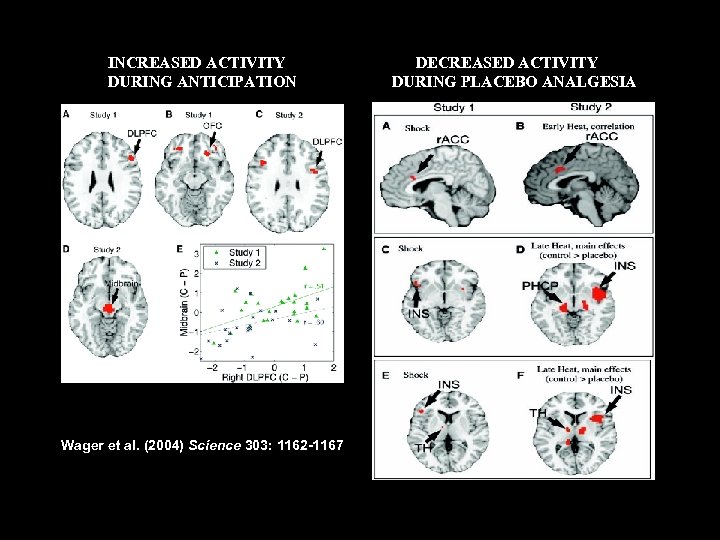 INCREASED ACTIVITY DURING ANTICIPATION Wager et al. (2004) Science 303: 1162 -1167 DECREASED ACTIVITY DURING PLACEBO ANALGESIA
INCREASED ACTIVITY DURING ANTICIPATION Wager et al. (2004) Science 303: 1162 -1167 DECREASED ACTIVITY DURING PLACEBO ANALGESIA
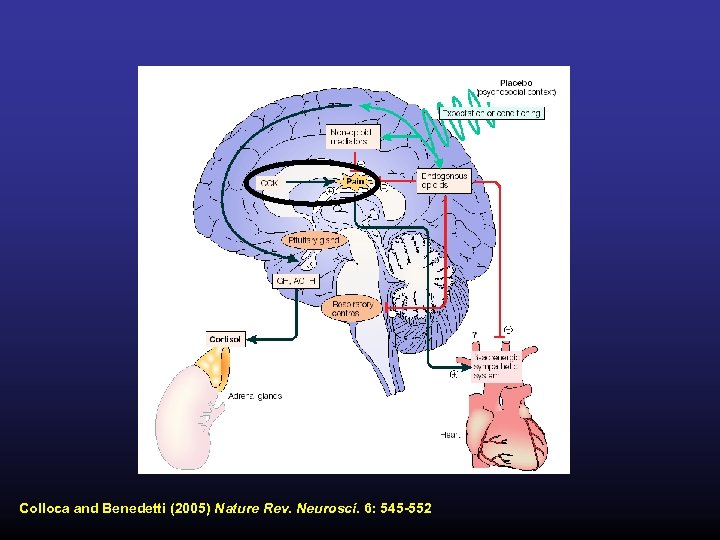 Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
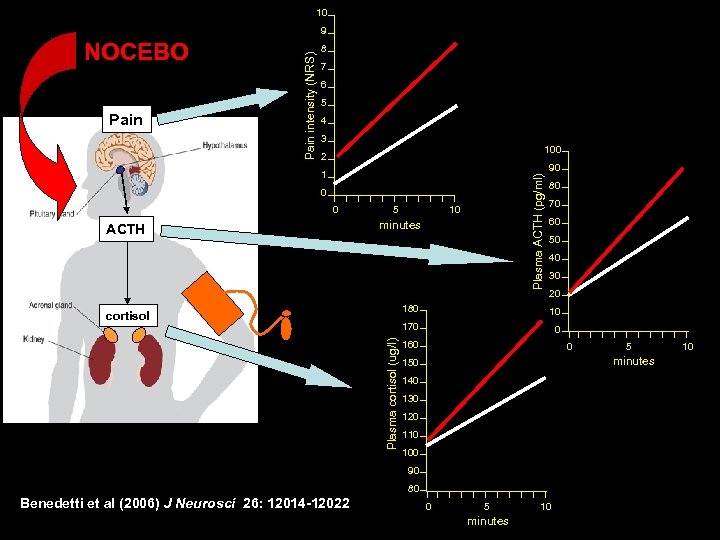 10 NOCEBO Pain intensity (NRS) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 100 2 90 Plasma ACTH (pg/ml) 1 0 0 ACTH 5 10 minutes 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 180 Plasma cortisol (ug/l) 10 170 cortisol 0 160 0 minutes 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 Benedetti et al (2006) J Neurosci 26: 12014 -12022 5 0 5 minutes 10 10
10 NOCEBO Pain intensity (NRS) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 100 2 90 Plasma ACTH (pg/ml) 1 0 0 ACTH 5 10 minutes 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 180 Plasma cortisol (ug/l) 10 170 cortisol 0 160 0 minutes 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 Benedetti et al (2006) J Neurosci 26: 12014 -12022 5 0 5 minutes 10 10
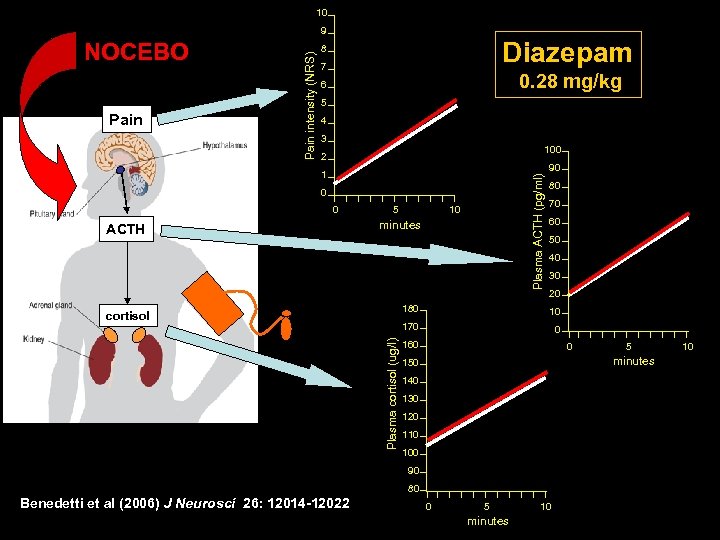 10 NOCEBO Pain intensity (NRS) 9 Diazepam 8 7 0. 28 mg/kg 6 5 4 3 100 2 90 Plasma ACTH (pg/ml) 1 0 0 ACTH 5 10 minutes 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 180 Plasma cortisol (ug/l) 10 170 cortisol 0 160 0 minutes 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 Benedetti et al (2006) J Neurosci 26: 12014 -12022 5 0 5 minutes 10 10
10 NOCEBO Pain intensity (NRS) 9 Diazepam 8 7 0. 28 mg/kg 6 5 4 3 100 2 90 Plasma ACTH (pg/ml) 1 0 0 ACTH 5 10 minutes 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 180 Plasma cortisol (ug/l) 10 170 cortisol 0 160 0 minutes 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 Benedetti et al (2006) J Neurosci 26: 12014 -12022 5 0 5 minutes 10 10
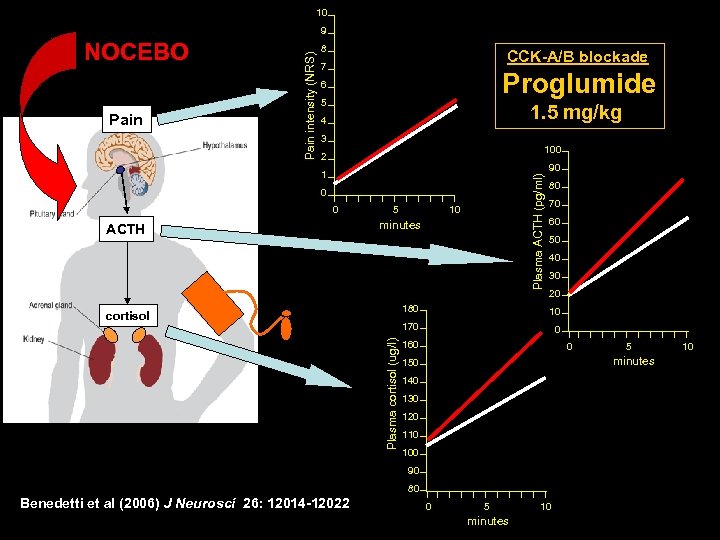 10 NOCEBO Pain intensity (NRS) 9 8 CCK-A/B blockade 7 Proglumide 6 5 1. 5 mg/kg 4 3 100 2 90 Plasma ACTH (pg/ml) 1 0 0 ACTH 5 10 minutes 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 180 Plasma cortisol (ug/l) 10 170 cortisol 0 160 0 minutes 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 Benedetti et al (2006) J Neurosci 26: 12014 -12022 5 0 5 minutes 10 10
10 NOCEBO Pain intensity (NRS) 9 8 CCK-A/B blockade 7 Proglumide 6 5 1. 5 mg/kg 4 3 100 2 90 Plasma ACTH (pg/ml) 1 0 0 ACTH 5 10 minutes 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 180 Plasma cortisol (ug/l) 10 170 cortisol 0 160 0 minutes 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 Benedetti et al (2006) J Neurosci 26: 12014 -12022 5 0 5 minutes 10 10
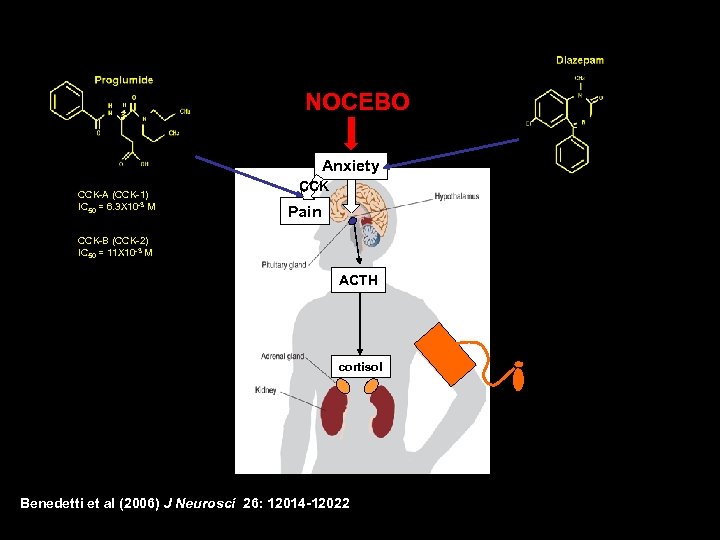 NOCEBO Anxiety CCK-A (CCK-1) IC 50 = 6. 3 X 10 -3 M CCK Pain CCK-B (CCK-2) IC 50 = 11 X 10 -3 M ACTH cortisol Benedetti et al (2006) J Neurosci 26: 12014 -12022
NOCEBO Anxiety CCK-A (CCK-1) IC 50 = 6. 3 X 10 -3 M CCK Pain CCK-B (CCK-2) IC 50 = 11 X 10 -3 M ACTH cortisol Benedetti et al (2006) J Neurosci 26: 12014 -12022
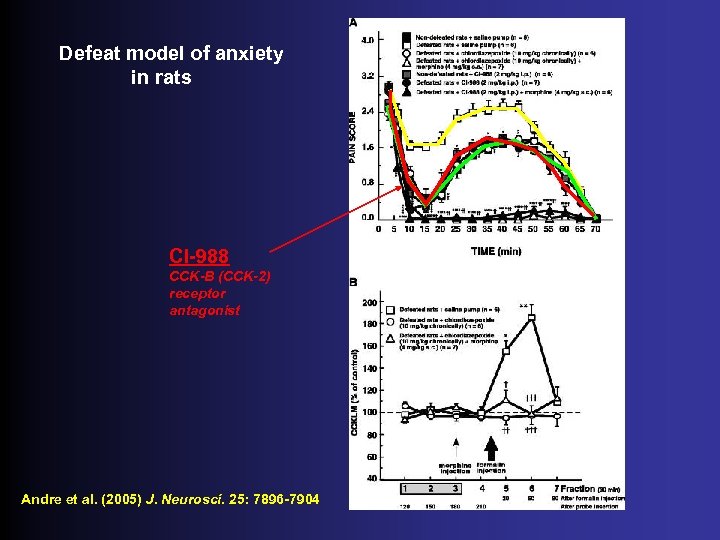 Defeat model of anxiety in rats CI-988 CCK-B (CCK-2) receptor antagonist Andre et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25: 7896 -7904
Defeat model of anxiety in rats CI-988 CCK-B (CCK-2) receptor antagonist Andre et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25: 7896 -7904
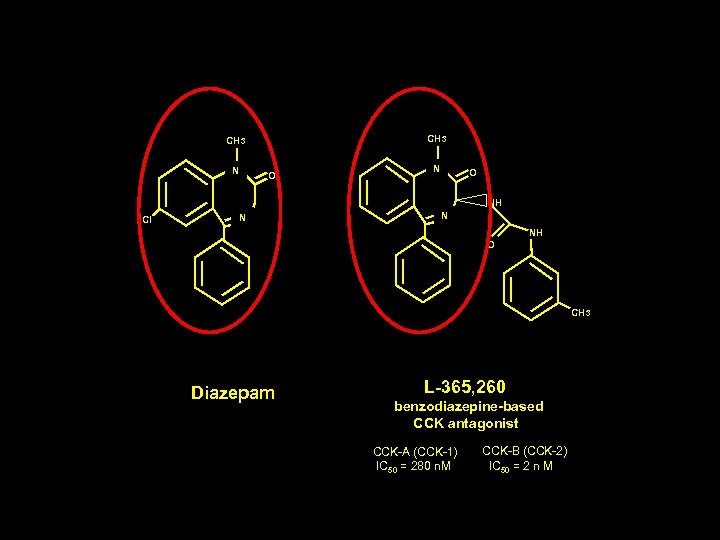 CH 3 N O NH Cl N N NH O CH 3 Diazepam L-365, 260 benzodiazepine-based CCK antagonist CCK-A (CCK-1) IC 50 = 280 n. M CCK-B (CCK-2) IC 50 = 2 n M
CH 3 N O NH Cl N N NH O CH 3 Diazepam L-365, 260 benzodiazepine-based CCK antagonist CCK-A (CCK-1) IC 50 = 280 n. M CCK-B (CCK-2) IC 50 = 2 n M
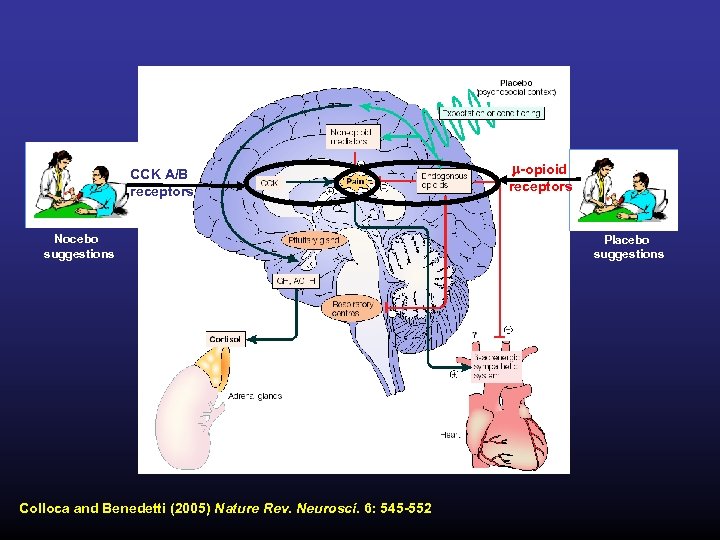 CCK A/B receptors Nocebo suggestions Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552 m-opioid receptors Placebo suggestions
CCK A/B receptors Nocebo suggestions Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552 m-opioid receptors Placebo suggestions
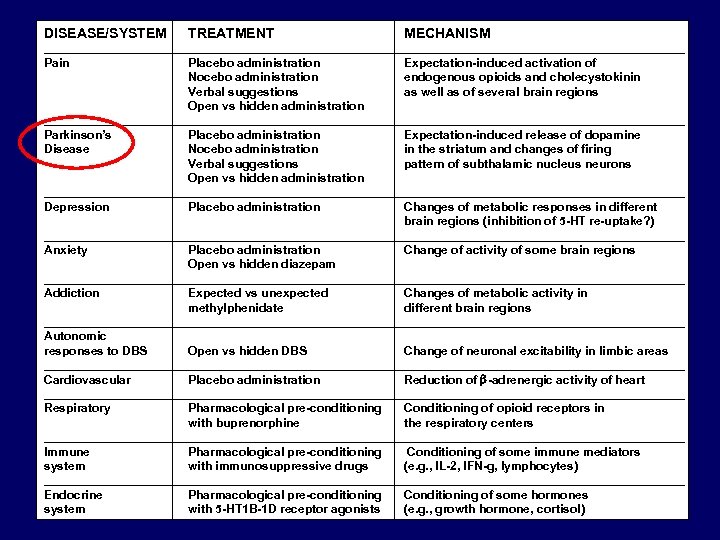 DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol)
DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol)
 Video by Pollo and Benedetti from the DATABASE of Nature Med 2005 table. mpg. 2005
Video by Pollo and Benedetti from the DATABASE of Nature Med 2005 table. mpg. 2005
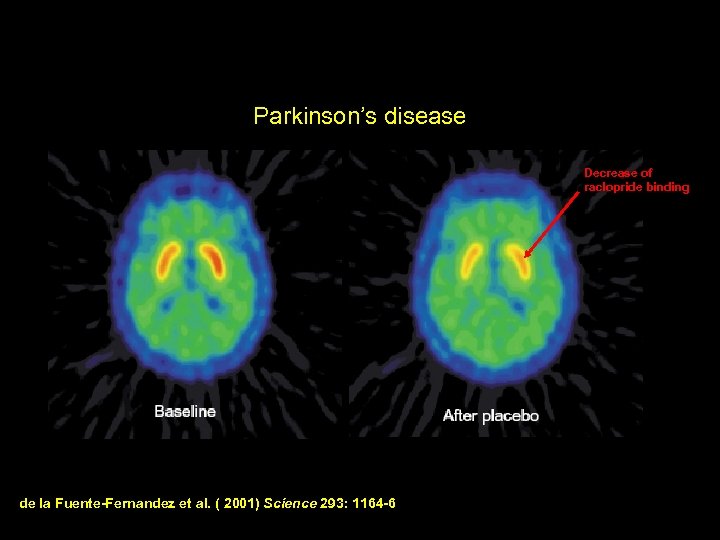 Parkinson’s disease Decrease of raclopride binding de la Fuente-Fernandez et al. ( 2001) Science 293: 1164 -6
Parkinson’s disease Decrease of raclopride binding de la Fuente-Fernandez et al. ( 2001) Science 293: 1164 -6
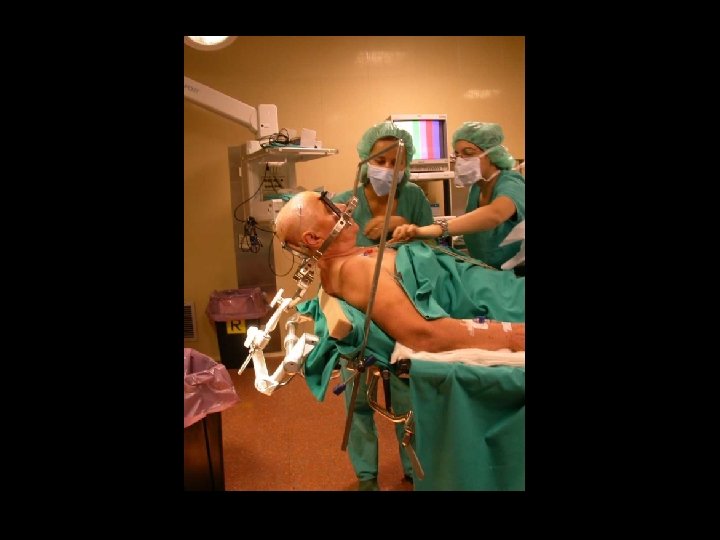
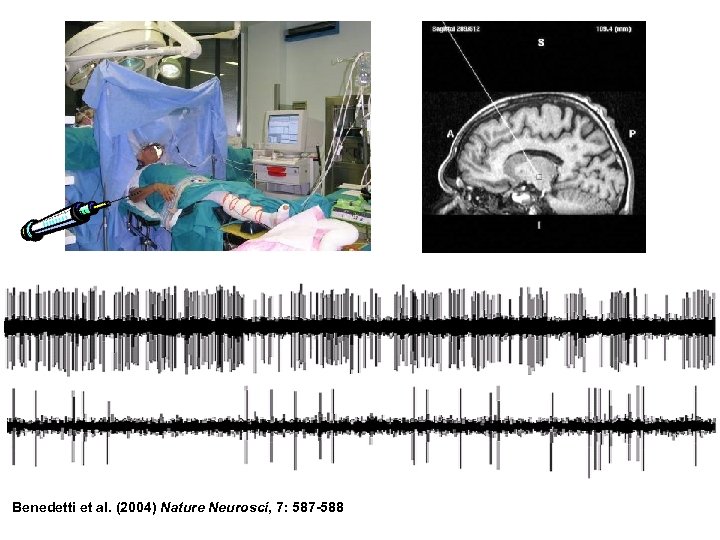 Benedetti et al. (2004) Nature Neurosci, 7: 587 -588
Benedetti et al. (2004) Nature Neurosci, 7: 587 -588
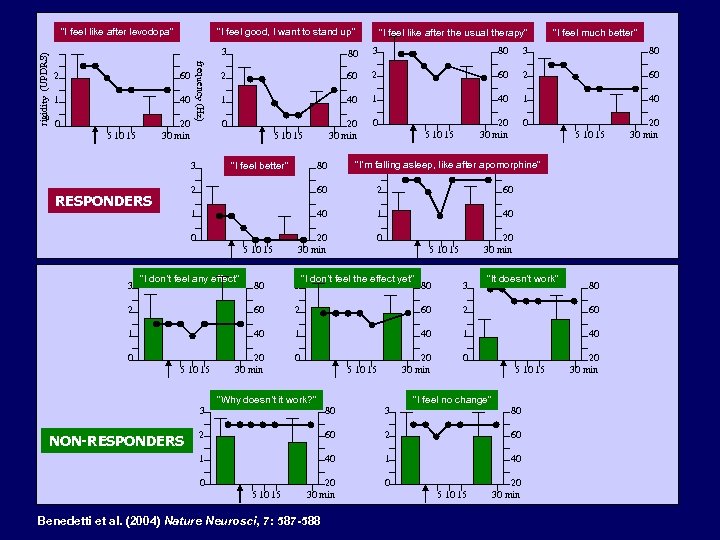 “I feel good, I want to stand up” “I feel like after the usual therapy” “I feel much better” 3 2 60 1 40 0 20 30 min 5 10 15 frequency (Hz) rigidity (UPDRS) “I feel like after levodopa” 80 3 80 2 60 1 40 20 30 min 0 0 5 10 15 “I feel better” 3 5 10 15 “I’m falling asleep, like after apomorphine” 3 80 2 60 1 RESPONDERS 40 1 40 20 30 min 0 0 5 10 15 3 80 5 10 15 “I don’t feel any effect” 80 3 2 60 1 20 30 min 5 10 15 “I don’t feel the effect yet” “It doesn’t work” 5 10 15 3 3 2 60 40 0 80 1 40 20 30 min 0 5 10 15 “Why doesn’t it work? ” 5 10 15 “I feel no change” 3 2 60 1 NON-RESPONDERS 80 40 1 40 20 30 min 0 0 5 10 15 Benedetti et al. (2004) Nature Neurosci, 7: 587 -588 5 10 15 80 20 30 min
“I feel good, I want to stand up” “I feel like after the usual therapy” “I feel much better” 3 2 60 1 40 0 20 30 min 5 10 15 frequency (Hz) rigidity (UPDRS) “I feel like after levodopa” 80 3 80 2 60 1 40 20 30 min 0 0 5 10 15 “I feel better” 3 5 10 15 “I’m falling asleep, like after apomorphine” 3 80 2 60 1 RESPONDERS 40 1 40 20 30 min 0 0 5 10 15 3 80 5 10 15 “I don’t feel any effect” 80 3 2 60 1 20 30 min 5 10 15 “I don’t feel the effect yet” “It doesn’t work” 5 10 15 3 3 2 60 40 0 80 1 40 20 30 min 0 5 10 15 “Why doesn’t it work? ” 5 10 15 “I feel no change” 3 2 60 1 NON-RESPONDERS 80 40 1 40 20 30 min 0 0 5 10 15 Benedetti et al. (2004) Nature Neurosci, 7: 587 -588 5 10 15 80 20 30 min
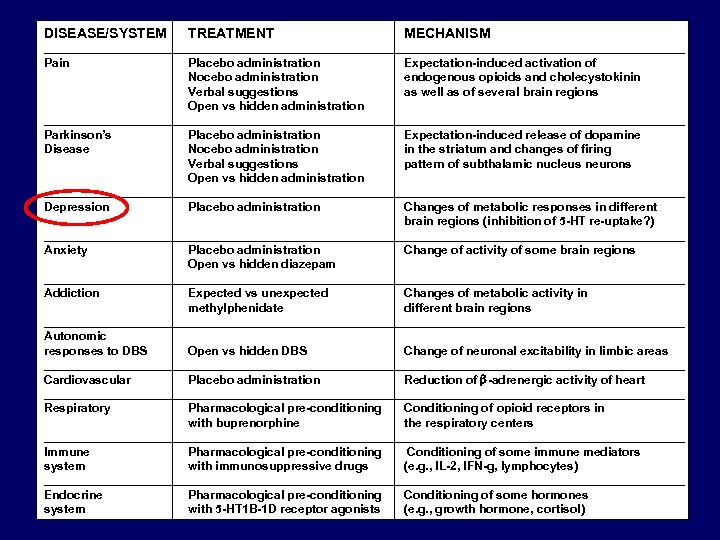 DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol)
DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol)
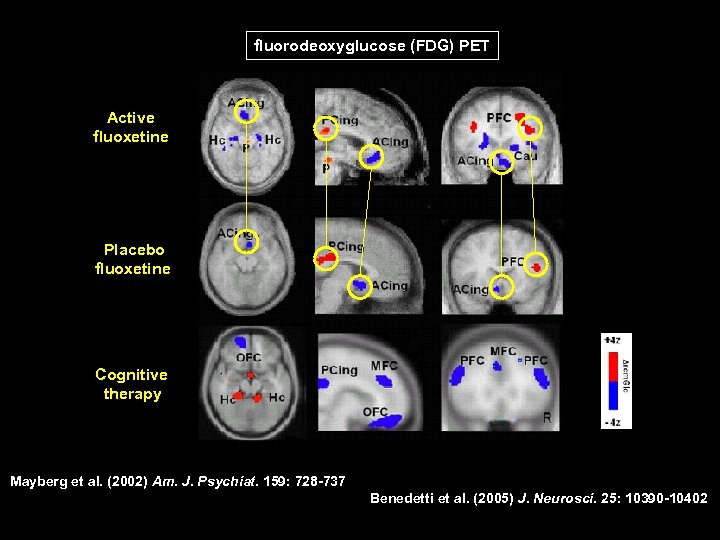 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET Active fluoxetine Placebo fluoxetine Cognitive therapy Mayberg et al. (2002) Am. J. Psychiat. 159: 728 -737 Benedetti et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25: 10390 -10402
fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET Active fluoxetine Placebo fluoxetine Cognitive therapy Mayberg et al. (2002) Am. J. Psychiat. 159: 728 -737 Benedetti et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25: 10390 -10402
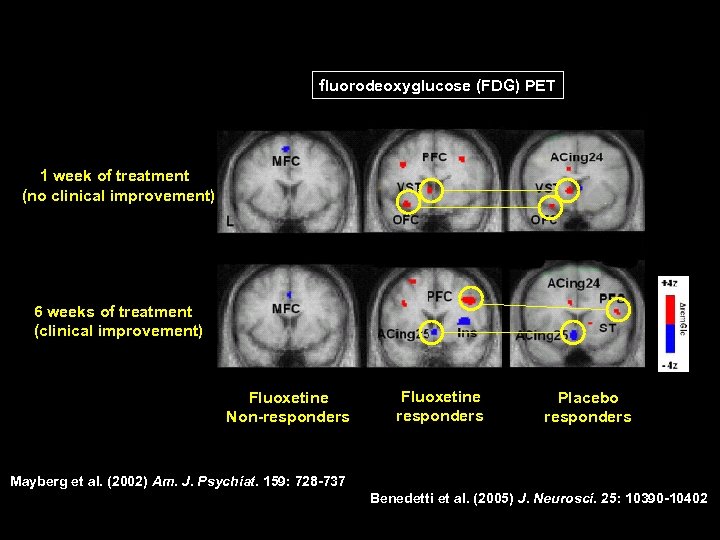 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET 1 week of treatment (no clinical improvement) 6 weeks of treatment (clinical improvement) Fluoxetine Non-responders Fluoxetine responders Placebo responders Mayberg et al. (2002) Am. J. Psychiat. 159: 728 -737 Benedetti et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25: 10390 -10402
fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET 1 week of treatment (no clinical improvement) 6 weeks of treatment (clinical improvement) Fluoxetine Non-responders Fluoxetine responders Placebo responders Mayberg et al. (2002) Am. J. Psychiat. 159: 728 -737 Benedetti et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25: 10390 -10402
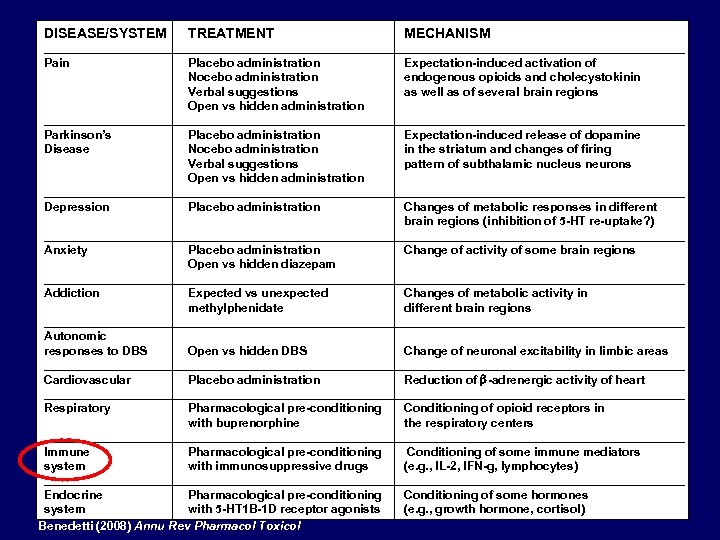 DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol) Benedetti (2008) Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol
DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol) Benedetti (2008) Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol
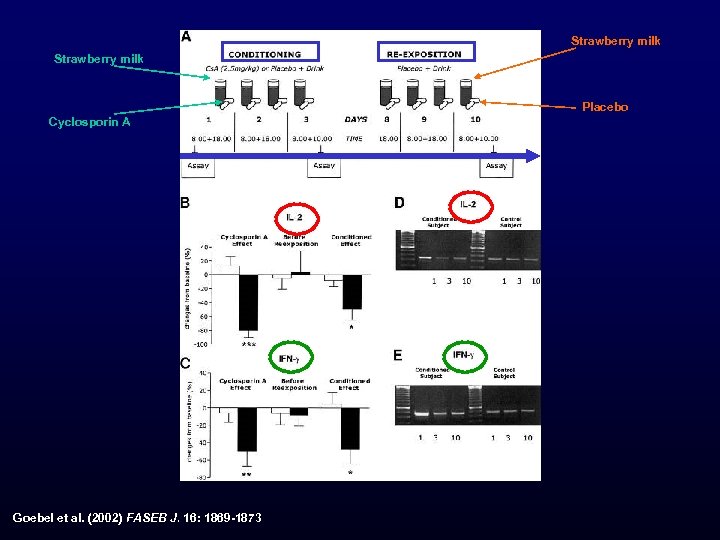 Strawberry milk Placebo Cyclosporin A Goebel et al. (2002) FASEB J. 16: 1869 -1873
Strawberry milk Placebo Cyclosporin A Goebel et al. (2002) FASEB J. 16: 1869 -1873
 DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol) Benedetti (2008) Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol
DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol) Benedetti (2008) Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol
 Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
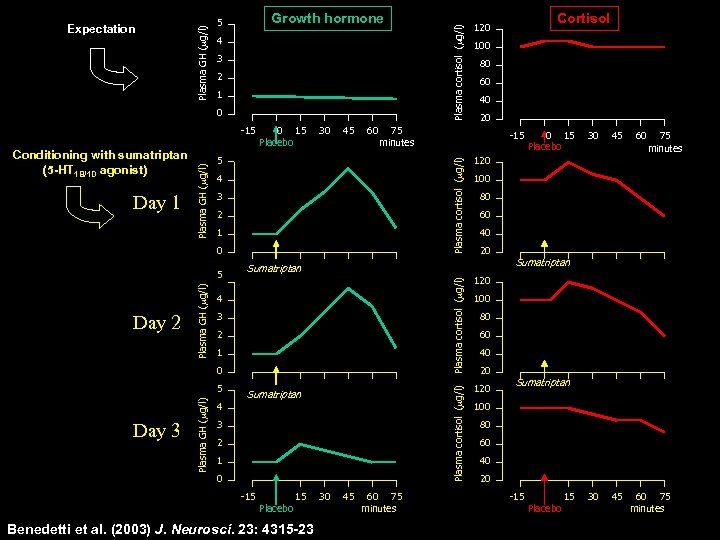 Growth hormone 5 4 3 2 1 0 Day 1 0 15 Placebo 30 45 60 5 4 3 2 1 0 Plasma GH (mg/l) Day 3 60 40 20 Sumatriptan 3 2 1 0 -15 Placebo 15 Benedetti et al. (2003) J. Neurosci. 23: 4315 -23 30 45 60 75 minutes 0 15 Placebo 30 45 60 75 minutes 120 100 80 60 40 20 Plasma cortisol (mg/l) 3 4 80 -15 Sumatriptan 4 5 100 120 Sumatriptan 120 Plasma cortisol (mg/l) Day 2 Plasma GH (mg/l) 5 Cortisol 120 75 minutes Plasma cortisol (mg/l) Conditioning with sumatriptan (5 -HT 1 B/1 D agonist) Plasma GH (mg/l) -15 Plasma cortisol (mg/l) Plasma GH (mg/l) Expectation 100 80 60 40 20 Sumatriptan 100 80 60 40 20 -15 Placebo 15 60 75 minutes
Growth hormone 5 4 3 2 1 0 Day 1 0 15 Placebo 30 45 60 5 4 3 2 1 0 Plasma GH (mg/l) Day 3 60 40 20 Sumatriptan 3 2 1 0 -15 Placebo 15 Benedetti et al. (2003) J. Neurosci. 23: 4315 -23 30 45 60 75 minutes 0 15 Placebo 30 45 60 75 minutes 120 100 80 60 40 20 Plasma cortisol (mg/l) 3 4 80 -15 Sumatriptan 4 5 100 120 Sumatriptan 120 Plasma cortisol (mg/l) Day 2 Plasma GH (mg/l) 5 Cortisol 120 75 minutes Plasma cortisol (mg/l) Conditioning with sumatriptan (5 -HT 1 B/1 D agonist) Plasma GH (mg/l) -15 Plasma cortisol (mg/l) Plasma GH (mg/l) Expectation 100 80 60 40 20 Sumatriptan 100 80 60 40 20 -15 Placebo 15 60 75 minutes
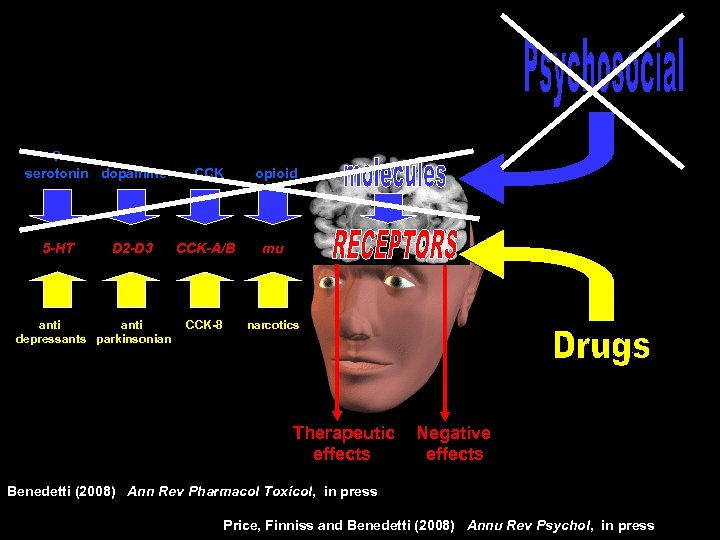 ? serotonin dopamine 5 -HT D 2 -D 3 anti depressants parkinsonian CCK opioid CCK-A/B mu CCK-8 narcotics Therapeutic effects Negative effects Benedetti (2008) Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, in press Price, Finniss and Benedetti (2008) Annu Rev Psychol, in press
? serotonin dopamine 5 -HT D 2 -D 3 anti depressants parkinsonian CCK opioid CCK-A/B mu CCK-8 narcotics Therapeutic effects Negative effects Benedetti (2008) Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol, in press Price, Finniss and Benedetti (2008) Annu Rev Psychol, in press
 Benedetti et al. (1995) Lancet 346: 1231
Benedetti et al. (1995) Lancet 346: 1231
 en dd i h Benedetti et al. (1995) Lancet 346: 1231 ug dr
en dd i h Benedetti et al. (1995) Lancet 346: 1231 ug dr
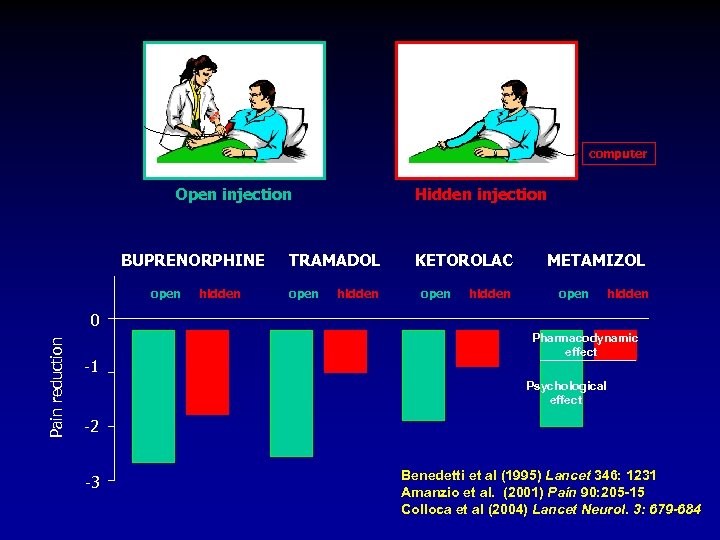 computer Open injection BUPRENORPHINE open hidden Hidden injection TRAMADOL open hidden KETOROLAC open hidden METAMIZOL open hidden Pain reduction 0 -1 Pharmacodynamic effect Psychological effect -2 -3 Benedetti et al (1995) Lancet 346: 1231 Amanzio et al. (2001) Pain 90: 205 -15 Colloca et al (2004) Lancet Neurol. 3: 679 -684
computer Open injection BUPRENORPHINE open hidden Hidden injection TRAMADOL open hidden KETOROLAC open hidden METAMIZOL open hidden Pain reduction 0 -1 Pharmacodynamic effect Psychological effect -2 -3 Benedetti et al (1995) Lancet 346: 1231 Amanzio et al. (2001) Pain 90: 205 -15 Colloca et al (2004) Lancet Neurol. 3: 679 -684
 TRIAL P 2 (Colloca and Benedetti, Nature Rev Neurosci 6: 545 -552, 2005) Is metamizol (300 mg) effective in post-thymectomy pain? Open metamizol injection group (N=10) Hidden metamizol injection group (N=10) Informed consent “You will receive metamizol but you don’t know when” Double blind
TRIAL P 2 (Colloca and Benedetti, Nature Rev Neurosci 6: 545 -552, 2005) Is metamizol (300 mg) effective in post-thymectomy pain? Open metamizol injection group (N=10) Hidden metamizol injection group (N=10) Informed consent “You will receive metamizol but you don’t know when” Double blind
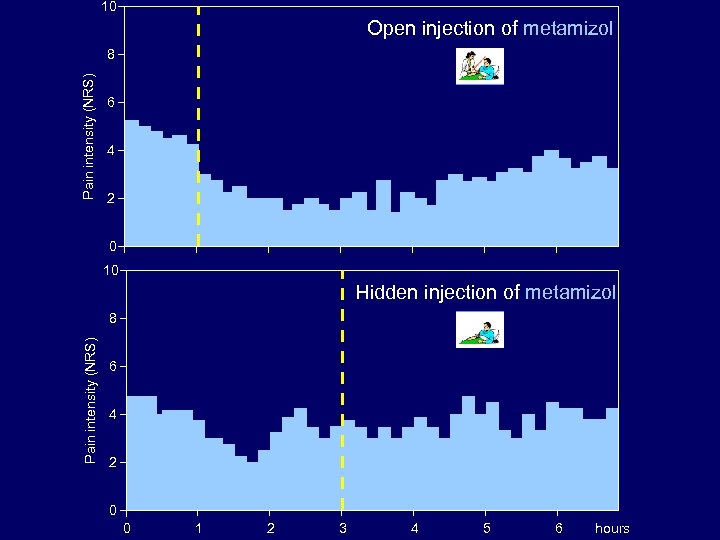 10 Open injection of metamizol Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 10 Hidden injection of metamizol Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 hours
10 Open injection of metamizol Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 10 Hidden injection of metamizol Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 hours
 TRIAL 1 (Colloca et al. Lancet Neurol 3: 679 -684, 2004) Is morphine (0. 14 mg/kg) effective in post-thoracotomy pain? Open morphine injection group (N=21) Hidden morphine injection group (N=21) Informed consent “You will receive morphine but you don’t know when” Double blind
TRIAL 1 (Colloca et al. Lancet Neurol 3: 679 -684, 2004) Is morphine (0. 14 mg/kg) effective in post-thoracotomy pain? Open morphine injection group (N=21) Hidden morphine injection group (N=21) Informed consent “You will receive morphine but you don’t know when” Double blind
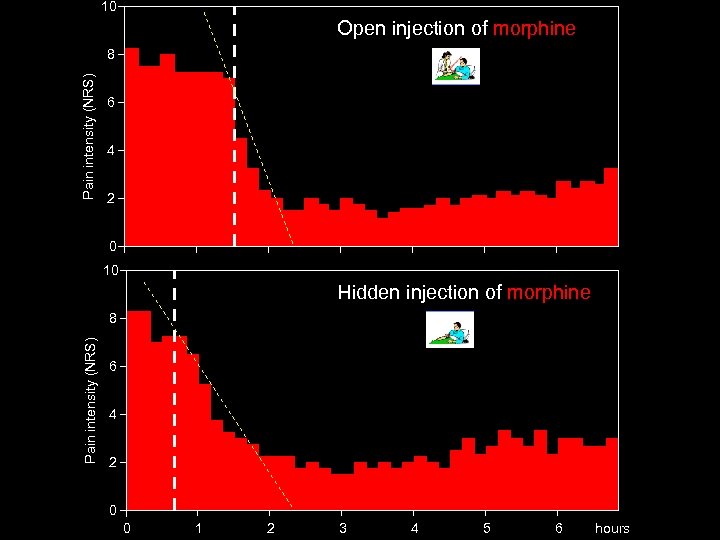 10 Open injection of morphine Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 10 Hidden injection of morphine Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 hours
10 Open injection of morphine Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 10 Hidden injection of morphine Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 hours
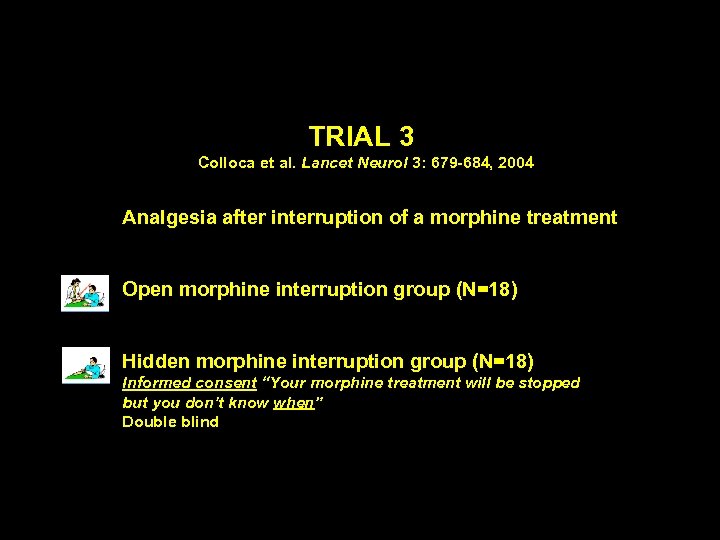 TRIAL 3 Colloca et al. Lancet Neurol 3: 679 -684, 2004 Analgesia after interruption of a morphine treatment Open morphine interruption group (N=18) Hidden morphine interruption group (N=18) Informed consent “Your morphine treatment will be stopped but you don’t know when” Double blind
TRIAL 3 Colloca et al. Lancet Neurol 3: 679 -684, 2004 Analgesia after interruption of a morphine treatment Open morphine interruption group (N=18) Hidden morphine interruption group (N=18) Informed consent “Your morphine treatment will be stopped but you don’t know when” Double blind
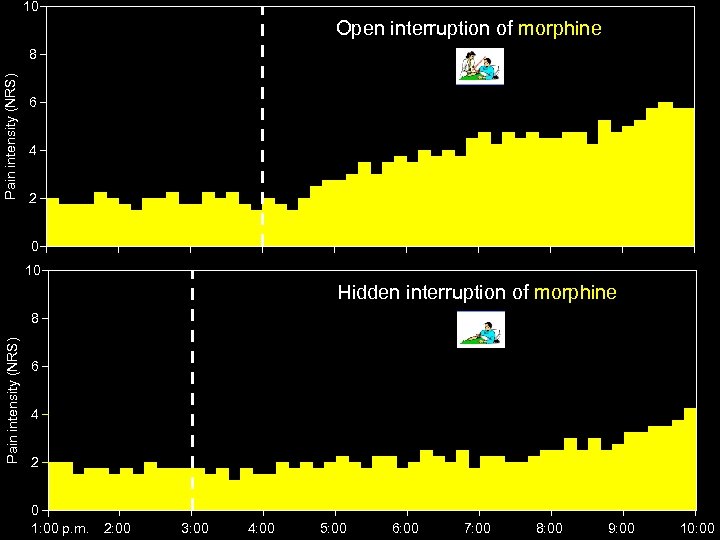 10 Open interruption of morphine Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 10 Hidden interruption of morphine Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 1: 00 p. m. 2: 00 3: 00 4: 00 5: 00 6: 00 7: 00 8: 00 9: 00 10: 00
10 Open interruption of morphine Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 10 Hidden interruption of morphine Pain intensity (NRS) 8 6 4 2 0 1: 00 p. m. 2: 00 3: 00 4: 00 5: 00 6: 00 7: 00 8: 00 9: 00 10: 00
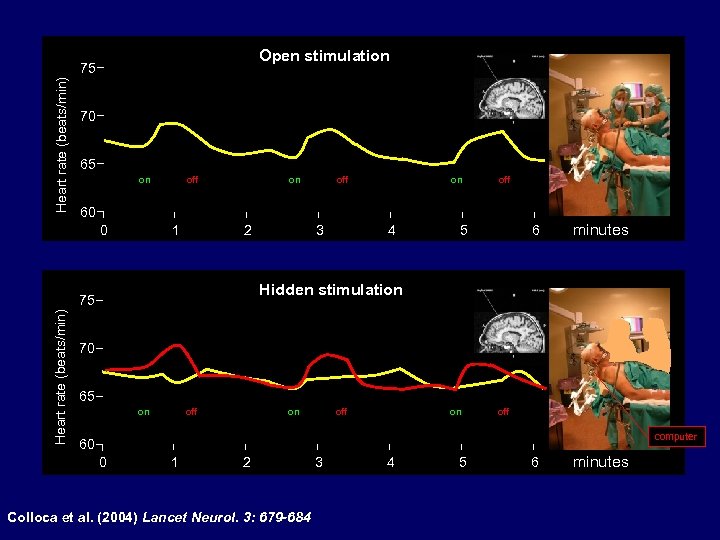 Open stimulation Heart rate (beats/min) 75 70 65 on on off 60 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 minutes Hidden stimulation 75 Heart rate (beats/min) on off 70 65 on on off off computer 60 0 1 2 Colloca et al. (2004) Lancet Neurol. 3: 679 -684 3 4 5 6 minutes
Open stimulation Heart rate (beats/min) 75 70 65 on on off 60 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 minutes Hidden stimulation 75 Heart rate (beats/min) on off 70 65 on on off off computer 60 0 1 2 Colloca et al. (2004) Lancet Neurol. 3: 679 -684 3 4 5 6 minutes
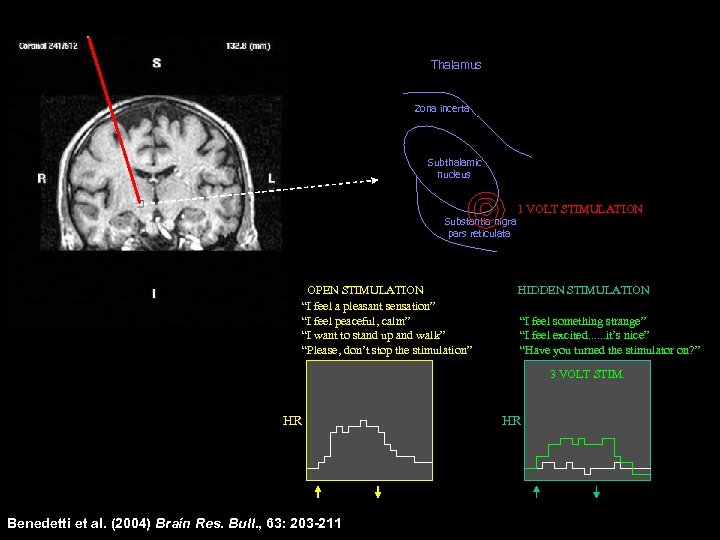 Thalamus Zona incerta Subthalamic nucleus Substantia nigra pars reticulata OPEN STIMULATION “I feel a pleasant sensation” “I feel peaceful, calm” “I want to stand up and walk” “Please, don’t stop the stimulation” 1 VOLT STIMULATION HIDDEN STIMULATION “I feel nothing” “I feel something strange” “I feel excited. . . it’s nice” “Have you turned the stimulator on? ” 3 VOLT STIM. HR Benedetti et al. (2004) Brain Res. Bull. , 63: 203 -211 HR
Thalamus Zona incerta Subthalamic nucleus Substantia nigra pars reticulata OPEN STIMULATION “I feel a pleasant sensation” “I feel peaceful, calm” “I want to stand up and walk” “Please, don’t stop the stimulation” 1 VOLT STIMULATION HIDDEN STIMULATION “I feel nothing” “I feel something strange” “I feel excited. . . it’s nice” “Have you turned the stimulator on? ” 3 VOLT STIM. HR Benedetti et al. (2004) Brain Res. Bull. , 63: 203 -211 HR
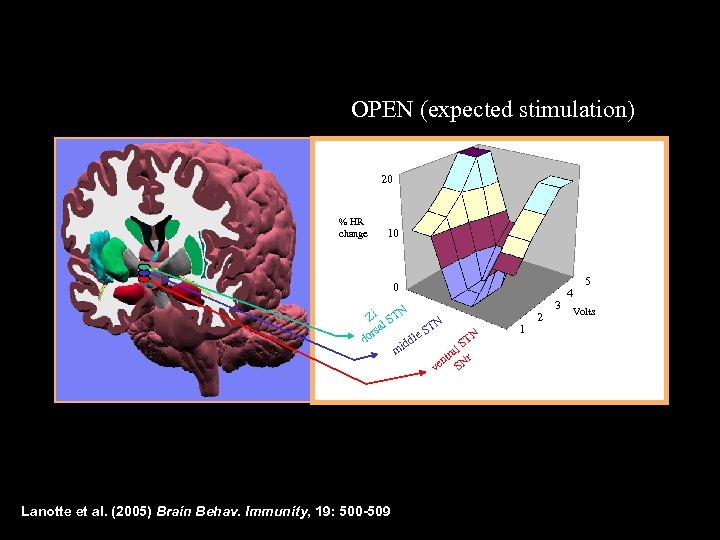 OPEN (expected stimulation) 20 % HR change 10 0 Zi STN l TN rsa e. S N l do ST idd l m tra r en SN v Lanotte et al. (2005) Brain Behav. Immunity, 19: 500 -509 1 2 3 5 4 Volts
OPEN (expected stimulation) 20 % HR change 10 0 Zi STN l TN rsa e. S N l do ST idd l m tra r en SN v Lanotte et al. (2005) Brain Behav. Immunity, 19: 500 -509 1 2 3 5 4 Volts
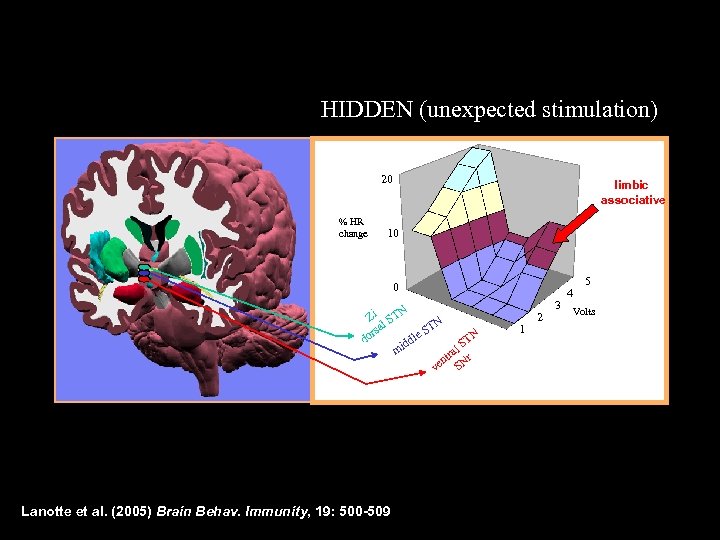 HIDDEN (unexpected stimulation) 20 % HR change limbic associative 10 0 Zi STN l TN rsa e. S N l do ST idd l m tra r en SN v Lanotte et al. (2005) Brain Behav. Immunity, 19: 500 -509 1 2 3 5 4 Volts
HIDDEN (unexpected stimulation) 20 % HR change limbic associative 10 0 Zi STN l TN rsa e. S N l do ST idd l m tra r en SN v Lanotte et al. (2005) Brain Behav. Immunity, 19: 500 -509 1 2 3 5 4 Volts
 How can the recent neurobiological advances on placebos affect current clinical trials and clinical practice?
How can the recent neurobiological advances on placebos affect current clinical trials and clinical practice?
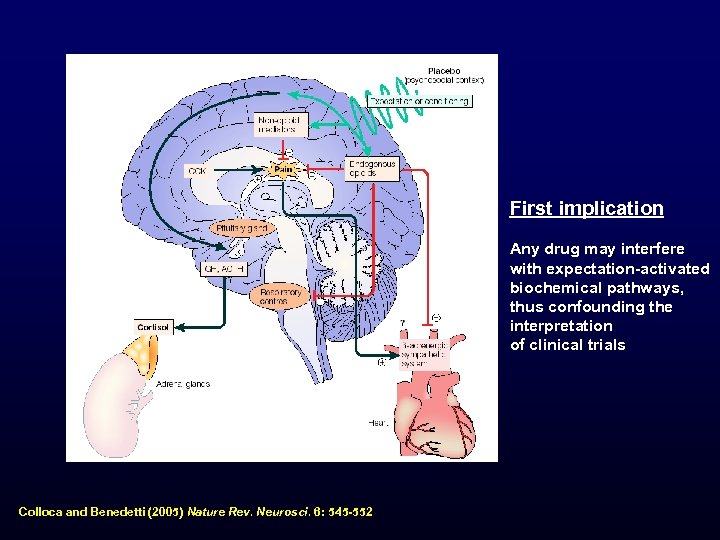 First implication Any drug may interfere with expectation-activated biochemical pathways, thus confounding the interpretation of clinical trials Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
First implication Any drug may interfere with expectation-activated biochemical pathways, thus confounding the interpretation of clinical trials Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
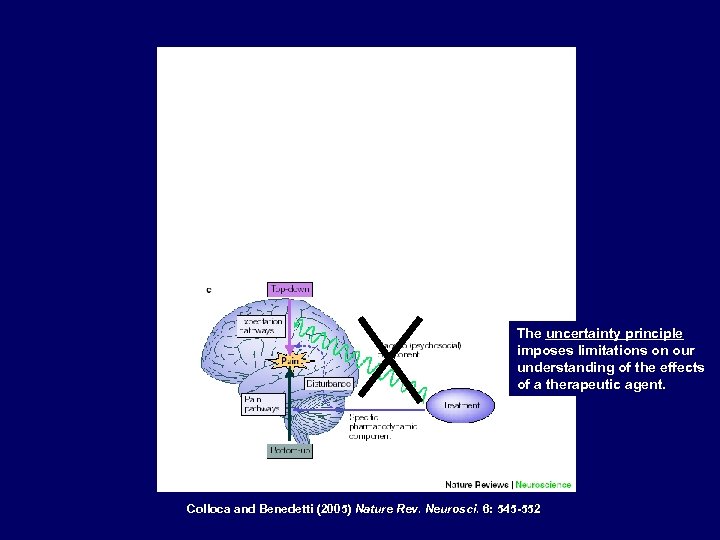 Benedetti et al. (1995) Lancet 346: 1231 The uncertainty principle imposes limitations on our understanding of the effects of a therapeutic agent. Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
Benedetti et al. (1995) Lancet 346: 1231 The uncertainty principle imposes limitations on our understanding of the effects of a therapeutic agent. Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
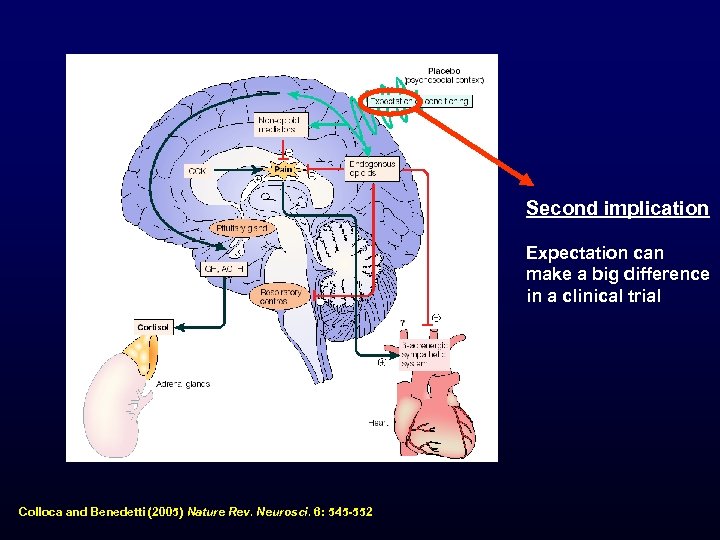 Second implication Expectation can make a big difference in a clinical trial Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
Second implication Expectation can make a big difference in a clinical trial Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
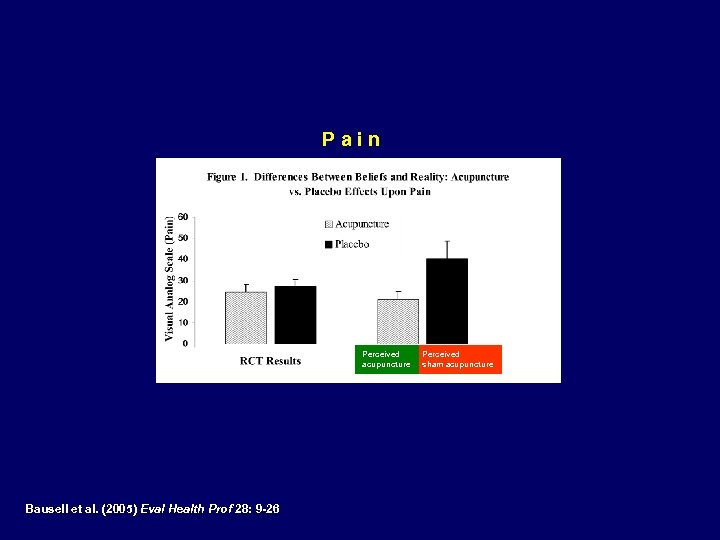 Pain Perceived acupuncture Bausell et al. (2005) Eval Health Prof 28: 9 -26 Perceived sham acupuncture
Pain Perceived acupuncture Bausell et al. (2005) Eval Health Prof 28: 9 -26 Perceived sham acupuncture
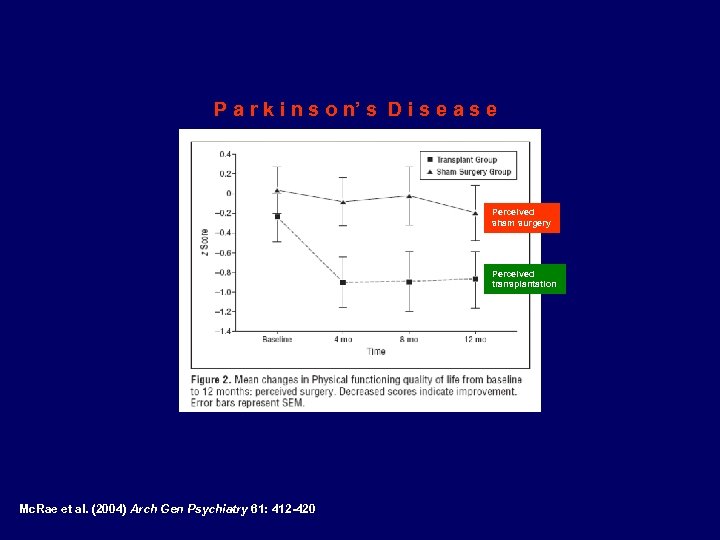 P a r k i n s o n’ s D i s e a s e Perceived sham surgery Perceived transplantation Mc. Rae et al. (2004) Arch Gen Psychiatry 61: 412 -420
P a r k i n s o n’ s D i s e a s e Perceived sham surgery Perceived transplantation Mc. Rae et al. (2004) Arch Gen Psychiatry 61: 412 -420
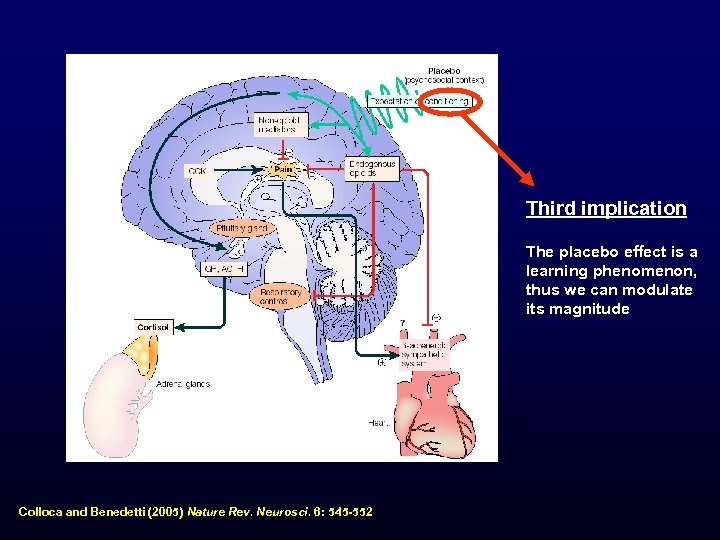 Third implication The placebo effect is a learning phenomenon, thus we can modulate its magnitude Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
Third implication The placebo effect is a learning phenomenon, thus we can modulate its magnitude Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
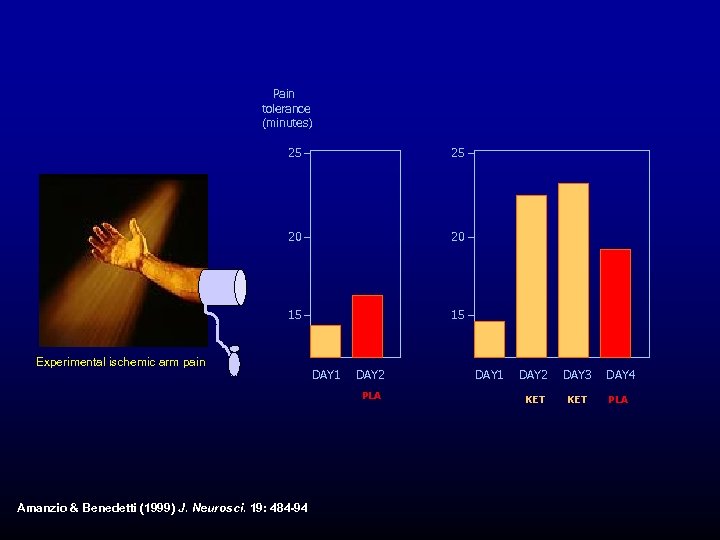 Pain tolerance (minutes) 25 25 20 20 15 15 Experimental ischemic arm pain DAY 1 DAY 2 PLA Amanzio & Benedetti (1999) J. Neurosci. 19: 484 -94 DAY 1 DAY 2 DAY 3 KET DAY 4 PLA
Pain tolerance (minutes) 25 25 20 20 15 15 Experimental ischemic arm pain DAY 1 DAY 2 PLA Amanzio & Benedetti (1999) J. Neurosci. 19: 484 -94 DAY 1 DAY 2 DAY 3 KET DAY 4 PLA
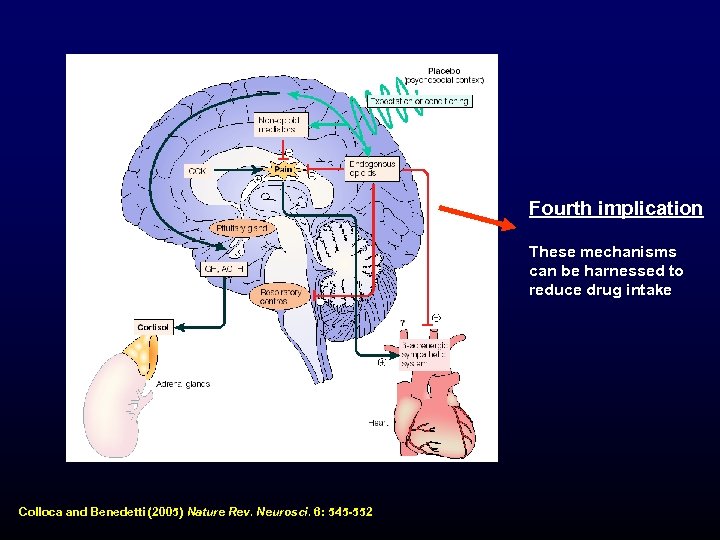 Fourth implication These mechanisms can be harnessed to reduce drug intake Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
Fourth implication These mechanisms can be harnessed to reduce drug intake Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
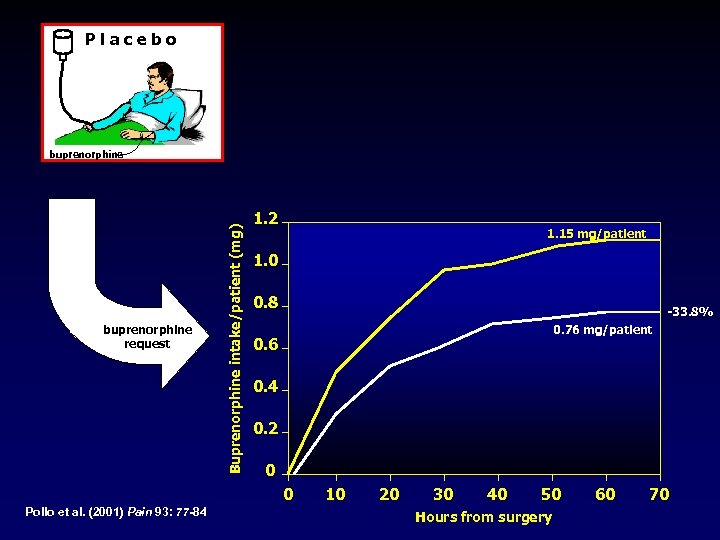 Placebo buprenorphine request Buprenorphine intake/patient (mg) buprenorphine 1. 2 1. 15 mg/patient 1. 0 0. 8 -33. 8% 0. 76 mg/patient 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 0 Pollo et al. (2001) Pain 93: 77 -84 10 20 30 40 50 Hours from surgery 60 70
Placebo buprenorphine request Buprenorphine intake/patient (mg) buprenorphine 1. 2 1. 15 mg/patient 1. 0 0. 8 -33. 8% 0. 76 mg/patient 0. 6 0. 4 0. 2 0 0 Pollo et al. (2001) Pain 93: 77 -84 10 20 30 40 50 Hours from surgery 60 70
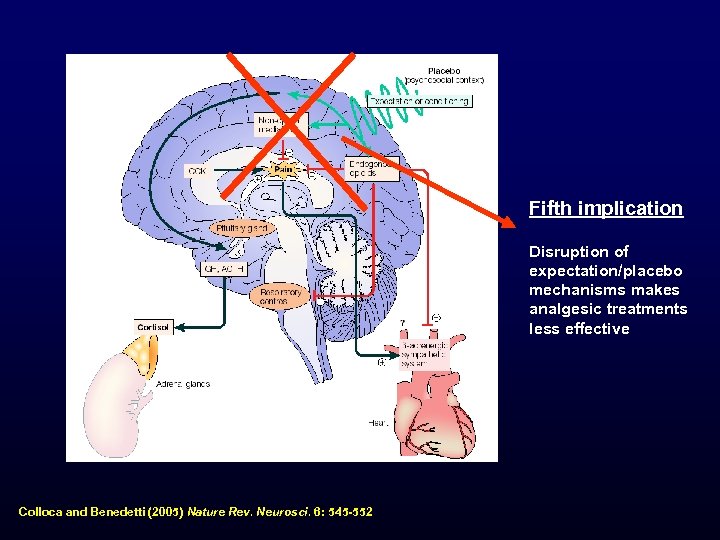 Fifth implication Disruption of expectation/placebo mechanisms makes analgesic treatments less effective Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
Fifth implication Disruption of expectation/placebo mechanisms makes analgesic treatments less effective Colloca and Benedetti (2005) Nature Rev. Neurosci. 6: 545 -552
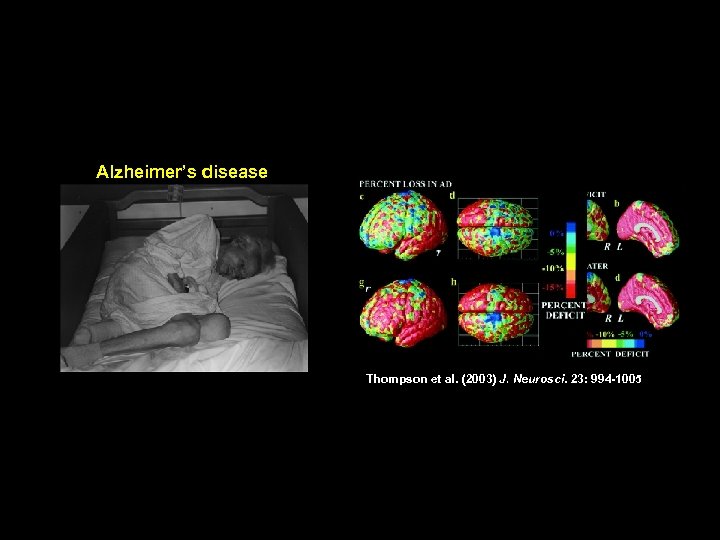 Alzheimer’s disease Thompson et al. (2003) J. Neurosci. 23: 994 -1005
Alzheimer’s disease Thompson et al. (2003) J. Neurosci. 23: 994 -1005
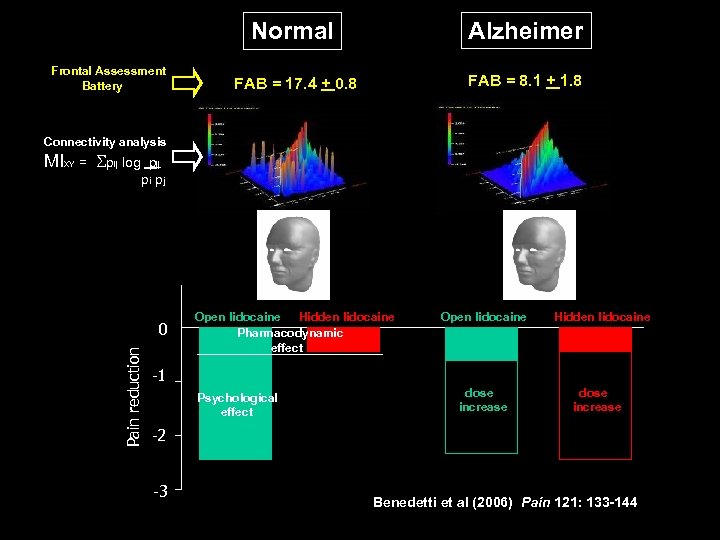 Normal Frontal Assessment Battery Alzheimer FAB = 17. 4 + 0. 8 FAB = 8. 1 + 1. 8 Connectivity analysis MIXY = Spij log pij pi pj Pain reduction 0 Open lidocaine Hidden lidocaine Pharmacodynamic effect Open lidocaine Hidden lidocaine -1 Psychological effect dose increase -2 -3 Benedetti et al (2006) Pain 121: 133 -144
Normal Frontal Assessment Battery Alzheimer FAB = 17. 4 + 0. 8 FAB = 8. 1 + 1. 8 Connectivity analysis MIXY = Spij log pij pi pj Pain reduction 0 Open lidocaine Hidden lidocaine Pharmacodynamic effect Open lidocaine Hidden lidocaine -1 Psychological effect dose increase -2 -3 Benedetti et al (2006) Pain 121: 133 -144
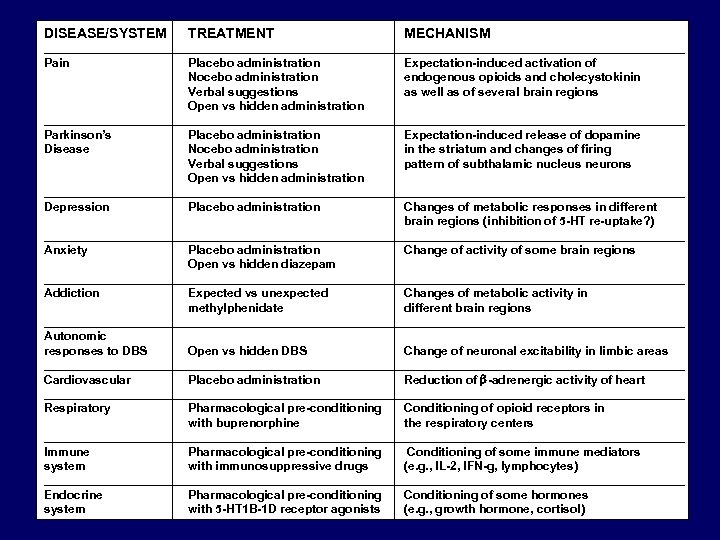 DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol)
DISEASE/SYSTEM TREATMENT MECHANISM ________________________________________________ Pain Placebo administration Expectation-induced activation of Nocebo administration endogenous opioids and cholecystokinin Verbal suggestions as well as of several brain regions Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Parkinson’s Placebo administration Expectation-induced release of dopamine Disease Nocebo administration in the striatum and changes of firing Verbal suggestions pattern of subthalamic nucleus neurons Open vs hidden administration ________________________________________________ Depression Placebo administration Changes of metabolic responses in different brain regions (inhibition of 5 -HT re-uptake? ) ________________________________________________ Anxiety Placebo administration Change of activity of some brain regions Open vs hidden diazepam ________________________________________________ Addiction Expected vs unexpected Changes of metabolic activity in methylphenidate different brain regions ________________________________________________ Autonomic responses to DBS Open vs hidden DBS Change of neuronal excitability in limbic areas ________________________________________________ Cardiovascular Placebo administration Reduction of b-adrenergic activity of heart ________________________________________________ Respiratory Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of opioid receptors in with buprenorphine the respiratory centers ________________________________________________ Immune Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some immune mediators system with immunosuppressive drugs (e. g. , IL-2, IFN-g, lymphocytes) ________________________________________________ Endocrine Pharmacological pre-conditioning Conditioning of some hormones system with 5 -HT 1 B-1 D receptor agonists (e. g. , growth hormone, cortisol)
 Department of Neuroscience University of Turin Medical School and National Institute of Neuroscience Turin, Italy www. personalweb. unito. it / fabrizio. benedetti NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Antonella Pollo Luana Colloca PSYCHOLOGY Martina Amanzio Claudia Arduino Sara Costa NEUROLOGY Bruno Bergamasco Leonardo Lopiano Innocenzo Rainero Giovanni Asteggiano Luisella Tarenzi Elena Torre NEUROSURGERY BIOENGINEERING Sergio Vighetti Michele Lanotte Antonio Melcarne SURGERY Giuliano Maggi Caterina Casadio Anna Arslanian RESPIRATORY PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Sergio Baldi
Department of Neuroscience University of Turin Medical School and National Institute of Neuroscience Turin, Italy www. personalweb. unito. it / fabrizio. benedetti NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Antonella Pollo Luana Colloca PSYCHOLOGY Martina Amanzio Claudia Arduino Sara Costa NEUROLOGY Bruno Bergamasco Leonardo Lopiano Innocenzo Rainero Giovanni Asteggiano Luisella Tarenzi Elena Torre NEUROSURGERY BIOENGINEERING Sergio Vighetti Michele Lanotte Antonio Melcarne SURGERY Giuliano Maggi Caterina Casadio Anna Arslanian RESPIRATORY PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Sergio Baldi


