sveta_dihybrid_slide.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
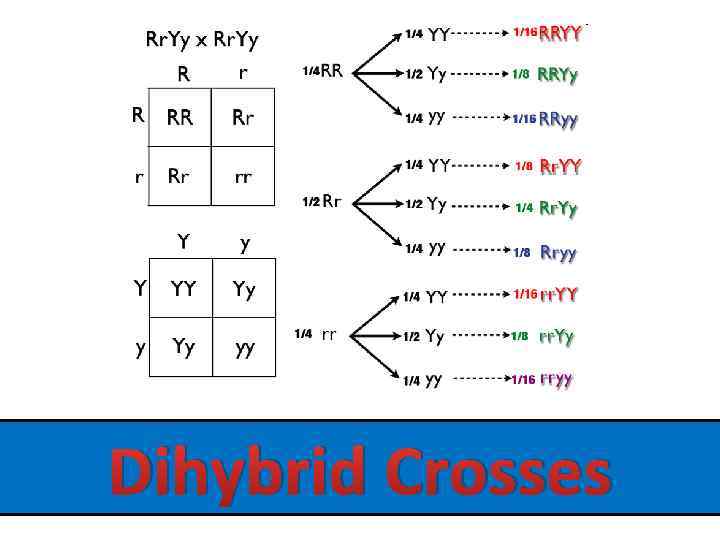
Dihybrid Crosses
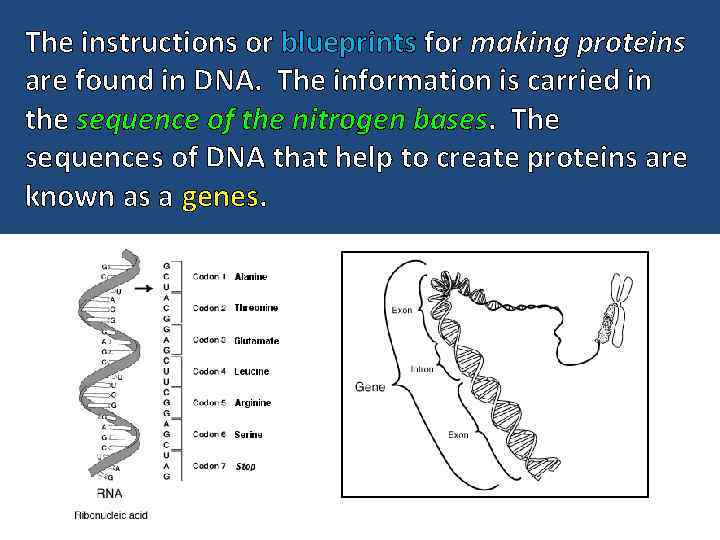
The instructions or blueprints for making proteins are found in DNA. The information is carried in the sequence of the nitrogen bases. The sequences of DNA that help to create proteins are known as a genes.

The different versions of a gene are called alleles. You would find the eye color gene in the same place for everyone, but some people have the allele for green eyes and some people have the allele for blue eyes.
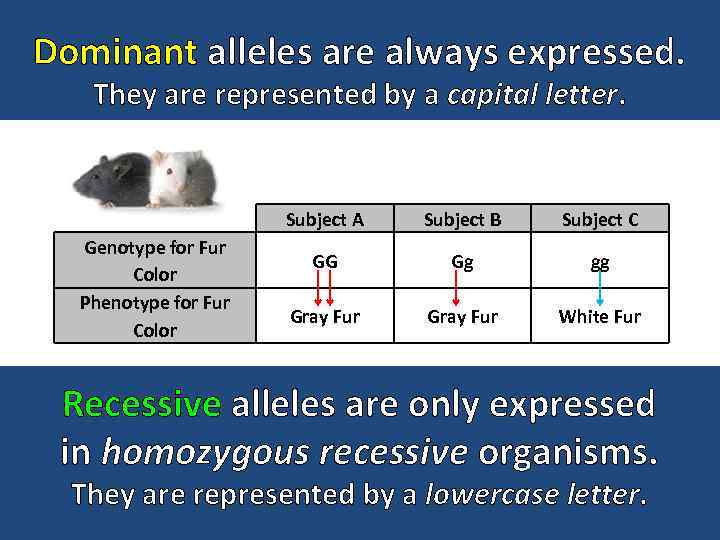
Dominant alleles are always expressed. They are represented by a capital letter. Subject A Genotype for Fur Color Phenotype for Fur Color Subject B Subject C GG Gg gg Gray Fur White Fur Recessive alleles are only expressed in homozygous recessive organisms. They are represented by a lowercase letter.

gg The combination of alleles is known as the organism’s genotype. (e. g. heterozygous or homozygous dominant) Subject A Genotype for Fur Color Phenotype for Fur Color Subject B Subject C GG Gg gg Gray Fur White Fur The physical appearance caused by the expression of the alleles is the phenotype. (e. g. having gray fur or white fur)
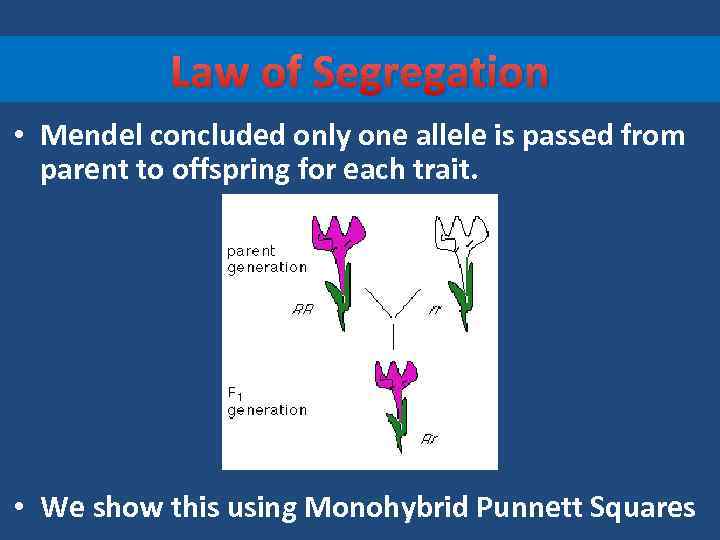
Law of Segregation • Mendel concluded only one allele is passed from parent to offspring for each trait. • We show this using Monohybrid Punnett Squares
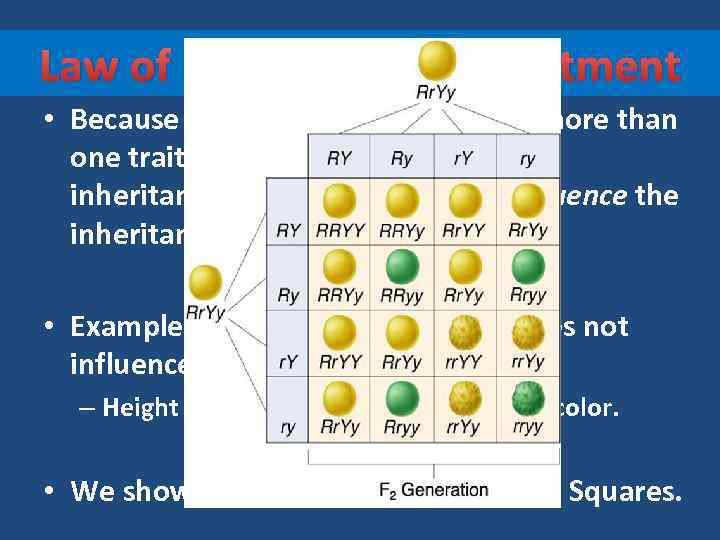
Law of Independent Assortment • Because organisms are made up of more than one trait, Mendel concluded that the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of a second trait. • Example: Height of the pea plant does not influence the color of the peas – Height is independently assorted from color. • We show this using Dihybrid Punnett Squares.

Punnett Squares: Dihybrid Cross A dihybrid cross involves making predictions about two traits. To do this, we will make a Punnett square for each trait. G G B b G GG GG B BB Bb g Gg Gg b Bb bb GGBb (male) × Gg. Bb (female)
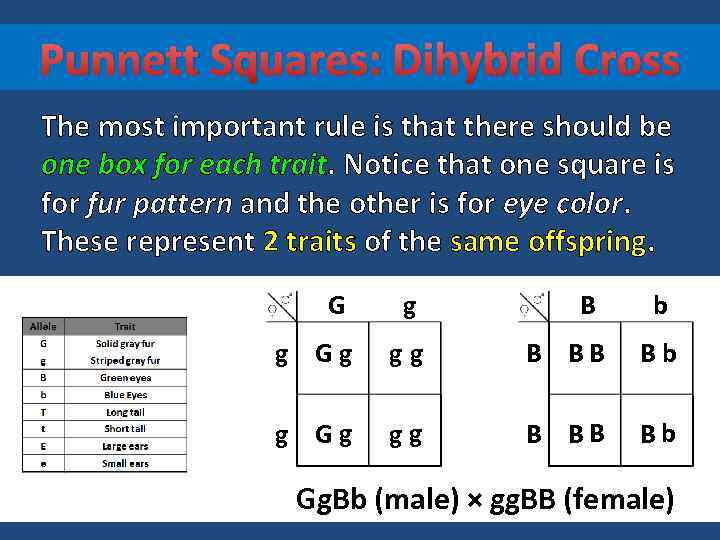
Punnett Squares: Dihybrid Cross The most important rule is that there should be one box for each trait. Notice that one square is for fur pattern and the other is for eye color. These represent 2 traits of the same offspring. G g B b g Gg gg B BB Bb Gg. Bb (male) × gg. BB (female)

What trait will appear in ALL of the offspring? Solid Gray Fur Only 75% of the offspring will have green eyes. G Solid G GG Gray g Fur Solid Gg Gray Fur G Solid GG Gray Fur Solid Gg Gray Fur B b B Green BB eyes Green Bb eyes bb eyes b Blue GGBb (male) × Gg. Bb (female)
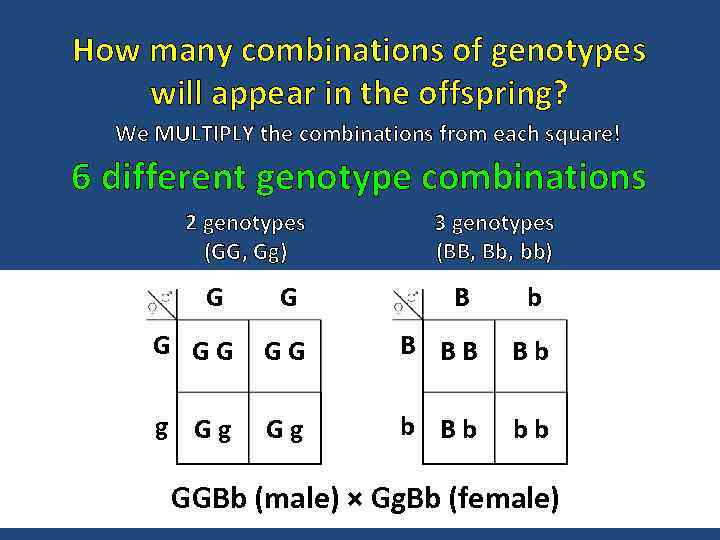
How many combinations of genotypes will appear in the offspring? We MULTIPLY the combinations from each square! 6 different genotype combinations 2 genotypes (GG, Gg) G 3 genotypes (BB, Bb, bb) G B b G GG GG B BB Bb g Gg Gg b Bb bb GGBb (male) × Gg. Bb (female)
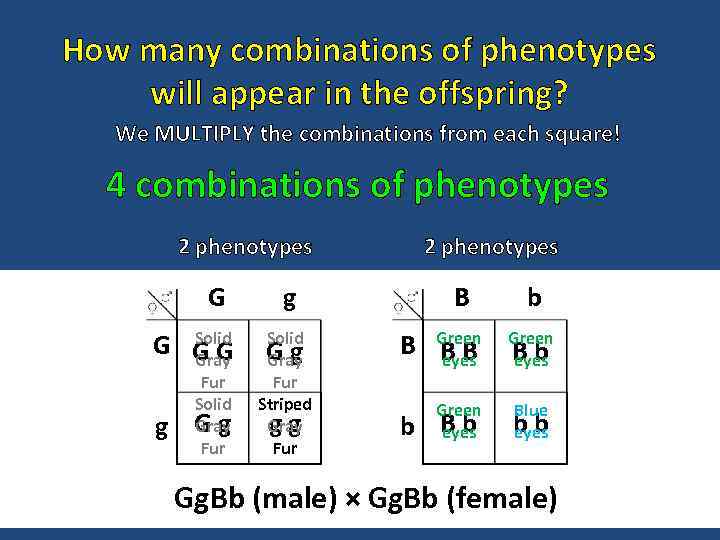
How many combinations of phenotypes will appear in the offspring? We MULTIPLY the combinations from each square! 4 combinations of phenotypes 2 phenotypes G Solid G GG Gray g Fur Solid Gg Gray Fur 2 phenotypes g Solid Gg Gray Fur Striped gg Gray Fur B b B Green BB eyes Green Bb eyes bb eyes b Blue Gg. Bb (male) × Gg. Bb (female)
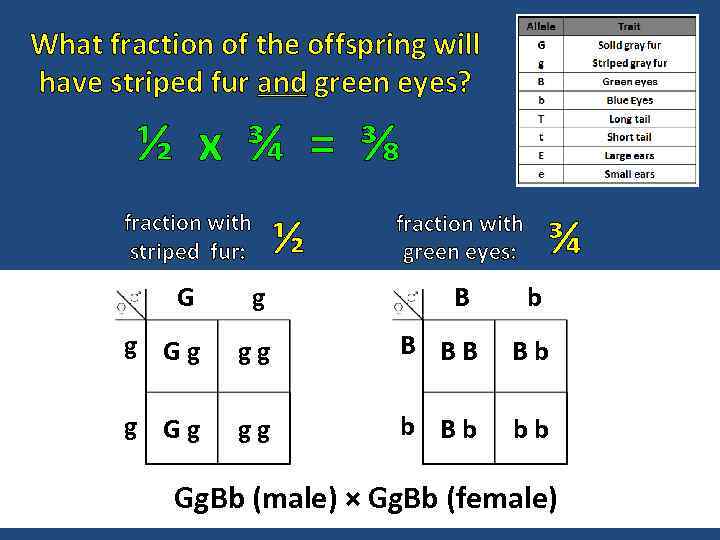
What fraction of the offspring will have striped fur and green eyes? ½ x ¾ = ⅜ fraction with striped fur: ½ ¾ fraction with green eyes: G g B b g Gg gg B BB Bb g Gg gg b Bb bb Gg. Bb (male) × Gg. Bb (female)
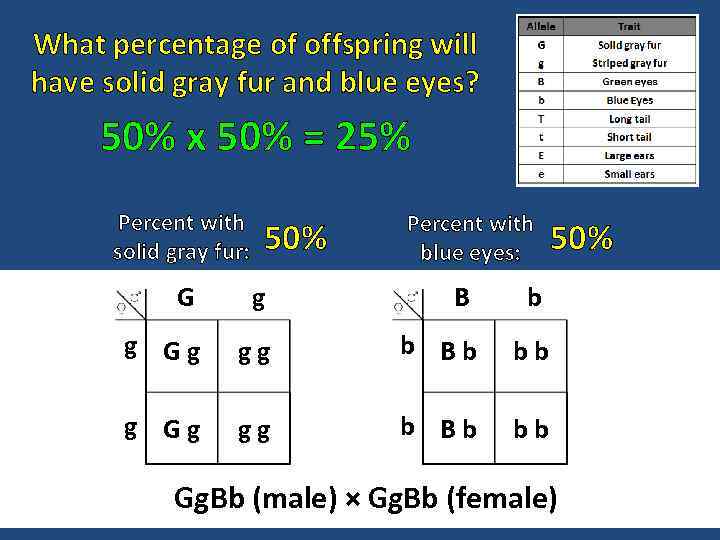
What percentage of offspring will have solid gray fur and blue eyes? 50% x 50% = 25% Percent with solid gray fur: 50% Percent with blue eyes: G g B b g Gg gg b Bb bb g Gg gg b Bb 50% bb Gg. Bb (male) × Gg. Bb (female)
sveta_dihybrid_slide.ppt