fde80c5fc6b0b48617702ac09ed5c4c0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28

Digital Video Library Network • Supervisor: Prof. Michael Lyu • Student: Ma Chak Kei, Jacky

Introduction • Overview • System Architecture – – Video Server Indexing Server Query Server Client Applications • Related Technology

Overview • Make large video library to be searchable information resources • Video – Captures the experience of society – News, TV, Movie…etc • Search and Discovery – Automated extraction of knowledge from video – Integration of speech, image, and natural language understanding for library creation and exploration

Information Retrieval • Given a large collection of multimedia records, find similar/interesting things – Allow fast, approximate queries – Find rules/patterns • Similarity search – Find pairs of documents that are similar – Find medical cases similar to Smith’s – Find pairs of stocks that move in sync

Application Areas • Education and training • Consumer and business access to news and information of interest • Entertainment • Interactive television • Meeting/corporate memory • Video conferences

Diverse Technologies • • • Image Understanding Scene Understanding Speech Recognition Metadata/Entity Extraction Natural Language Processing More… – Database, Network, User Interface. . .
System Architecture • Component Based – High Extensibility – High Availability – High Performance • Workstation or Distributed Systems over Internet
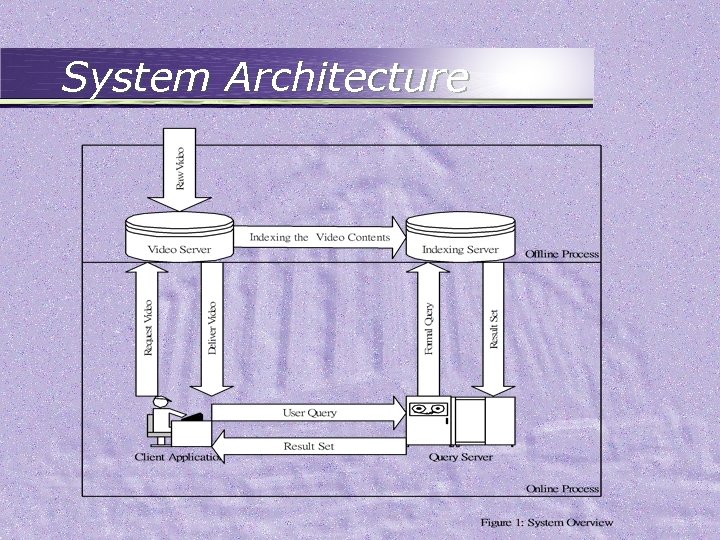
System Architecture
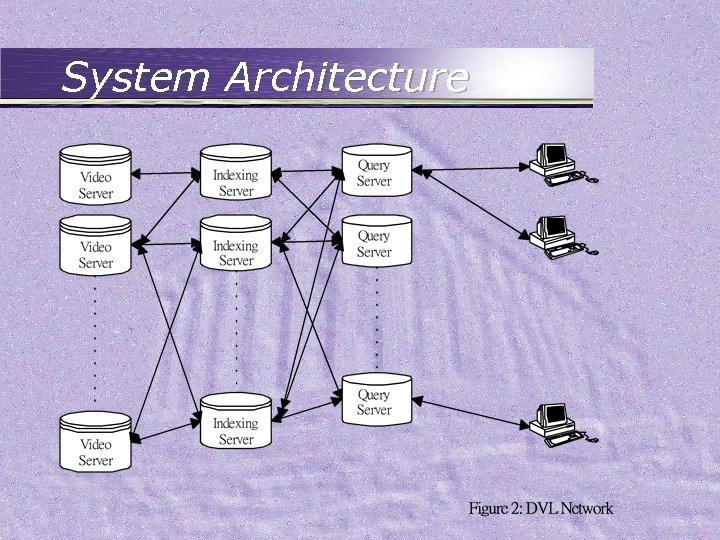
System Architecture

Video Server • Specialized in capturing, storing, and delivery videos • Dual with different video sources • Features: – Video Storage – Meta-Media Attributes – Video Delivery

Video Storage • Store segmented video in digital formats • Video segmentation – Using low-level visual features – Using multimedia cues • Semantic segmentation – Using audio, visual, textual signals at different stages – For Example: use audio feature to separate speech and commercials; then use text analysis to do story-level segmentation – Require knowledge on the video source

Meta-Media Attributes • For information – related to but not “within” the video – impossible to be extracted from the video • Five baisc types – – – Production feature Media feature Text description Intellectual property information References

Video Delivery • Main concern: – number of current clients – quality of services • Streaming protocol – reduce the latency for starting the video – exploit the error tolerance nature of video • Qo. S – User perspective – Application perspective – Transmission perspective
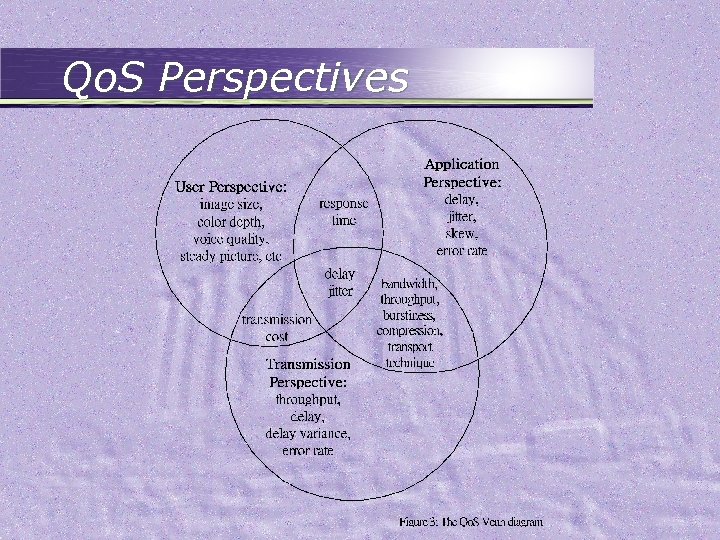
Qo. S Perspectives
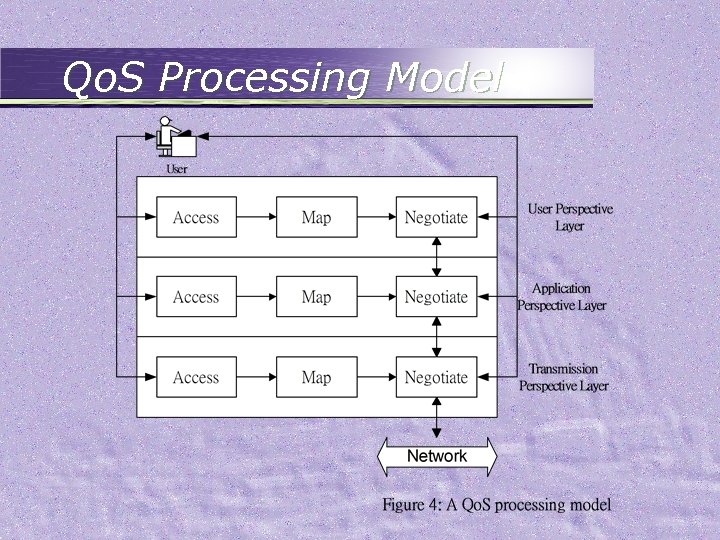
Qo. S Processing Model

Indexing Server • Specialized in indexing the video for retrieval use • Features to be indexed – Textual Information – Physical Features – Semantic Features • Advanced indexing on – Video caption – Company logo – Face recognition

Textual Information • Includes: – Provided meta-media attributes – Generated script by automatic speech recognition • Tradition information retrieval for text documents – – – Lexical analysis Removal of stopwords Stemming Selection of index terms Construction of term categorization structures
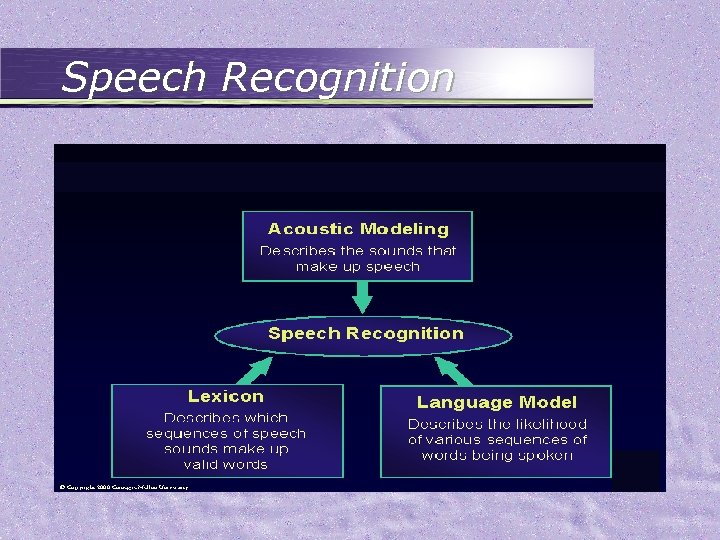
Speech Recognition

Physical Features • Low-level objects and associated features • Features indexed – – – Color Texture Shape Motion Spatiotemporal structures

Extract Physical Features • Segment the video into separate shots – Consistent background scene – Extract salient video regions and video objects • Index video objects with features mentioned • Advanced video object extraction in MPEG-4

Semantic Features • More intuitive and direct then physical features • Probabilistic graphic model – By Hidden Markov Model (HMM) to investigate the combination of input features that represent an object – Identify events, objects, and sites – Using multimedia training data – Limit the lifetime of objects to the shot’s duration – Compute probabilities of P(car AND road| segment of multimedia data) – Higher level HMM between different objects (Markov chain Monte Carlo method)
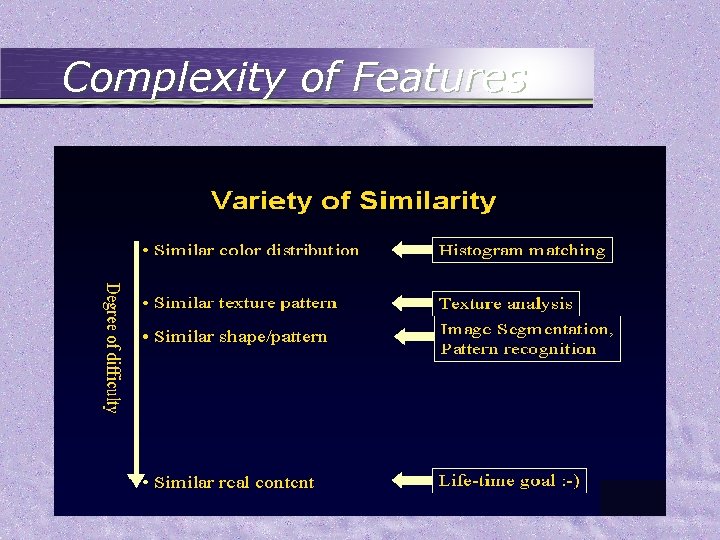
Complexity of Features

Query Server • • Transform user query to formal queries Natural language processing Ranking of results Different IR Models: – Boolean Model – Vector Model – Probabilistic Model • Have knowledge of individual Indexing Servers • Multimedia Portals!

Client Applications • Basic functionality: – Query – Presentation of Results – Video Playback • Additional functionality: – Linkage to external database – Manipulation of video

MPEG 4 • Standard to address multimedia contents – Represent units of aural, visual or audiovisual content as “media objects” – Natural or synthetic origin – Compose the scene by description of media objects • Support Qo. S in a media-object level • Indexing of media-object become easy

MPEG 7 • Standard to describe the multimedia content data with some degree of interpretation of the semantics • Act as the interface for multimedia applications – e. g. Between Video Server and Indexing Server

Conclusion • Challenges – – – Multilingual Processing Cognitive Processing Library Interoperability Intellectual Property Security Issues

Thank you
fde80c5fc6b0b48617702ac09ed5c4c0.ppt