61060ca52dbff27dac6a5767b7cc90fd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Digital Terrestrial Television <DVB-T Ver. >
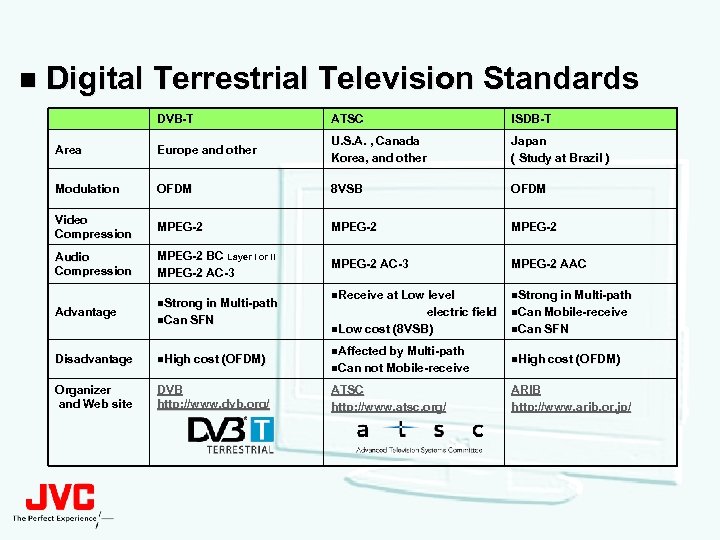
n Digital Terrestrial Television Standards DVB-T ATSC ISDB-T Area Europe and other U. S. A. , Canada Korea, and other Japan ( Study at Brazil ) Modulation OFDM 8 VSB OFDM Video Compression MPEG-2 Audio Compression MPEG-2 BC Layer I or II MPEG-2 AC-3 MPEG-2 AAC n. Receive at Low level n. Strong in Multi-path electric field n. Low cost (8 VSB) n. Can Mobile-receive Advantage n. Strong in Multi-path n. Can SFN Disadvantage n. High cost (OFDM) Organizer and Web site DVB http: //www. dvb. org/ n. Affected by Multi-path n. Can not Mobile-receive ATSC http: //www. atsc. org/ n. Can SFN n. High cost (OFDM) ARIB http: //www. arib. or. jp/
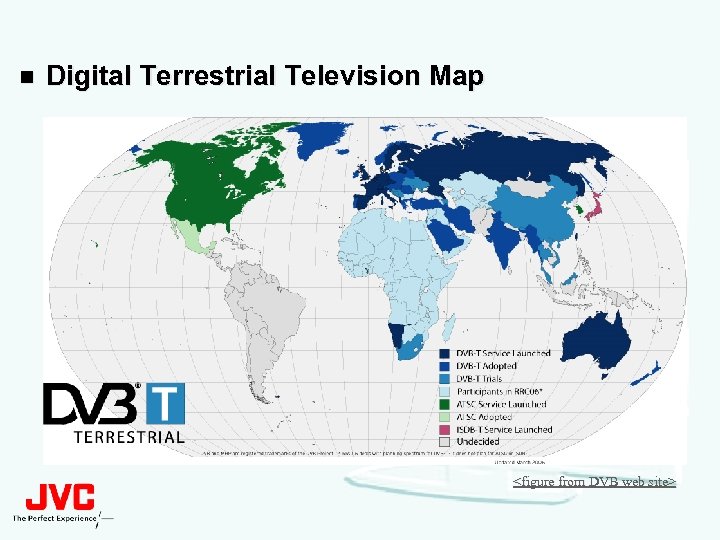
n Digital Terrestrial Television Map <figure from DVB web site>
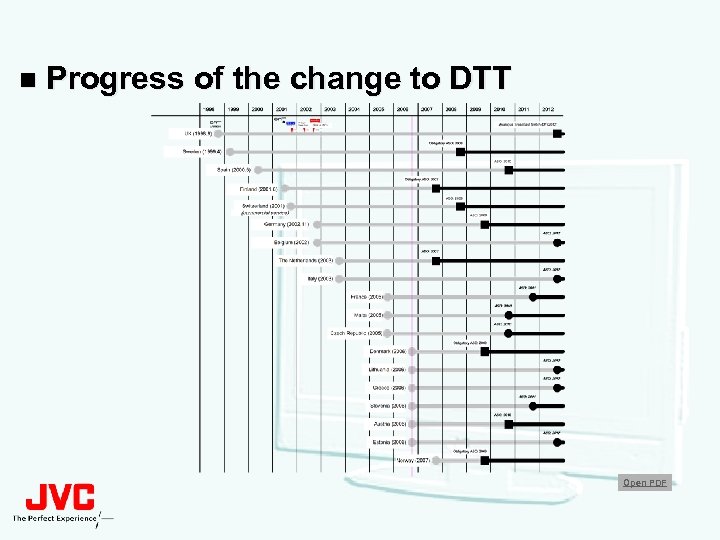
n Progress of the change to DTT Open PDF
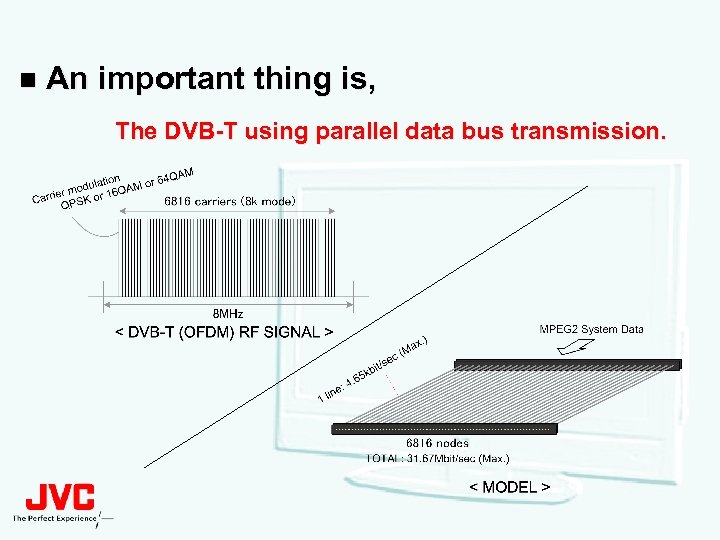
n An important thing is, The DVB-T using parallel data bus transmission.
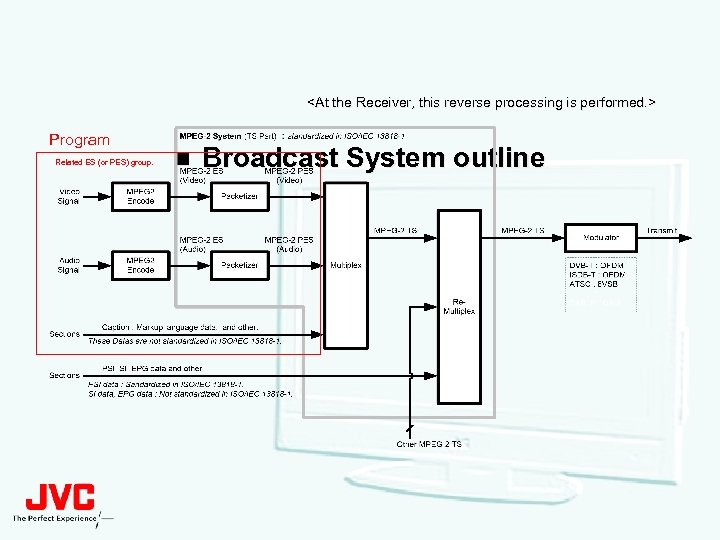
<At the Receiver, this reverse processing is performed. > Program Related ES (or PES) group. n Broadcast System outline
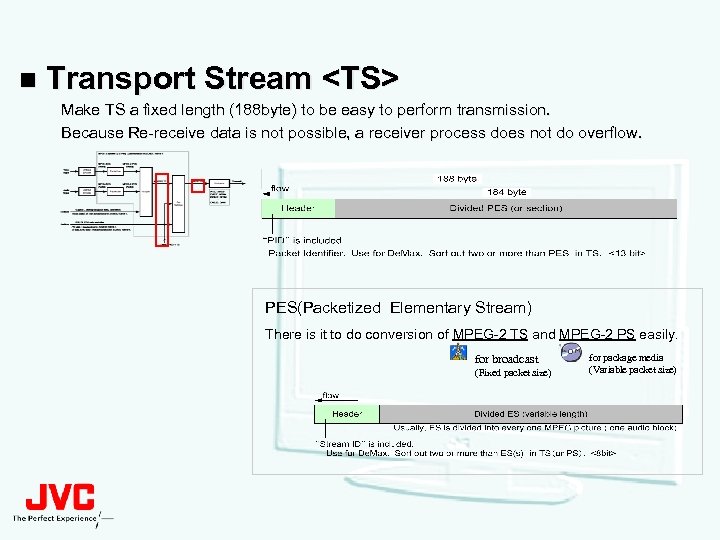
n Transport Stream <TS> Make TS a fixed length (188 byte) to be easy to perform transmission. Because Re-receive data is not possible, a receiver process does not do overflow. PES(Packetized Elementary Stream) There is it to do conversion of MPEG-2 TS and MPEG-2 PS easily. for broadcast (Fixed packet size) for package media (Variable packet size)
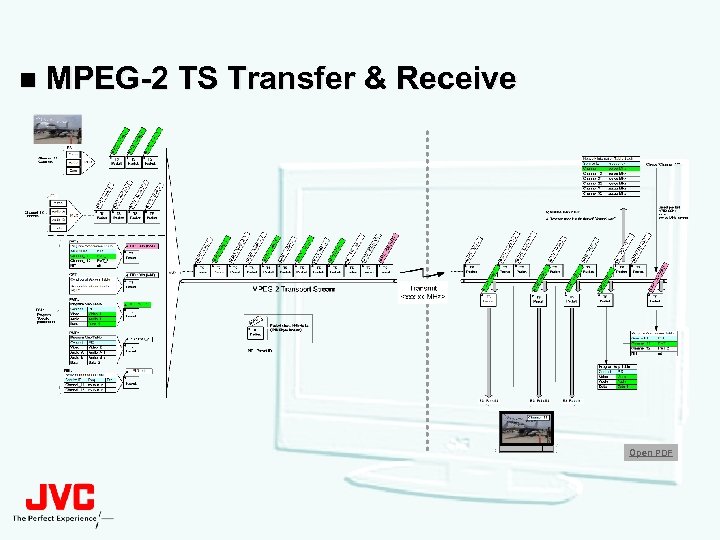
n MPEG-2 TS Transfer & Receive Open PDF
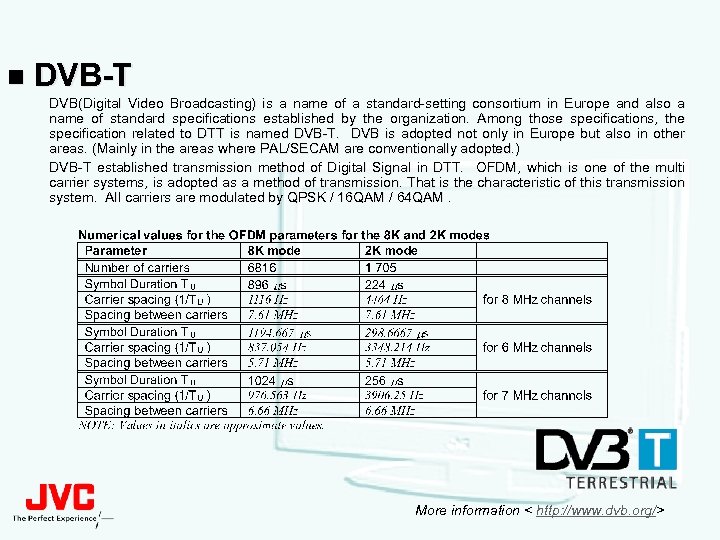
n DVB-T DVB(Digital Video Broadcasting) is a name of a standard-setting consortium in Europe and also a name of standard specifications established by the organization. Among those specifications, the specification related to DTT is named DVB-T. DVB is adopted not only in Europe but also in other areas. (Mainly in the areas where PAL/SECAM are conventionally adopted. ) DVB-T established transmission method of Digital Signal in DTT. OFDM, which is one of the multi carrier systems, is adopted as a method of transmission. That is the characteristic of this transmission system. All carriers are modulated by QPSK / 16 QAM / 64 QAM. More information < http: //www. dvb. org/>
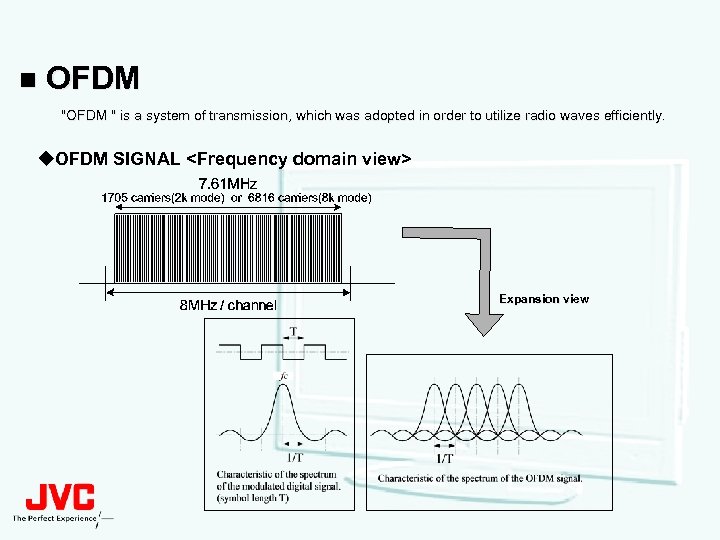
n OFDM " is a system of transmission, which was adopted in order to utilize radio waves efficiently. u. OFDM SIGNAL <Frequency domain view> Expansion view
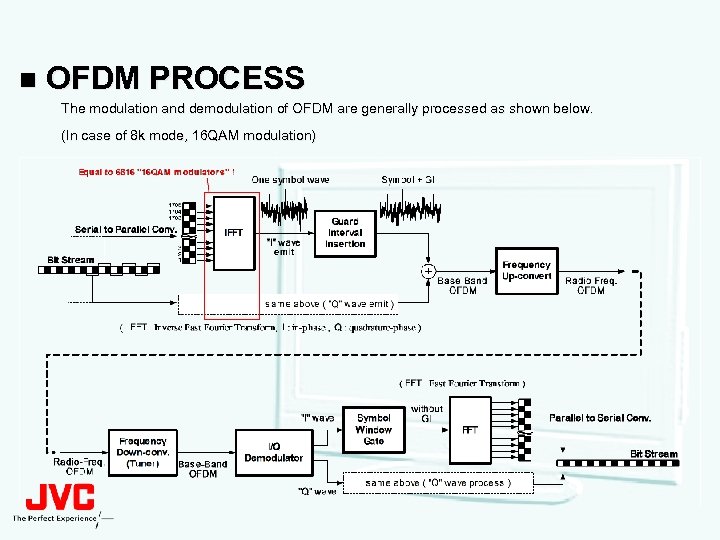
n OFDM PROCESS The modulation and demodulation of OFDM are generally processed as shown below. (In case of 8 k mode, 16 QAM modulation)
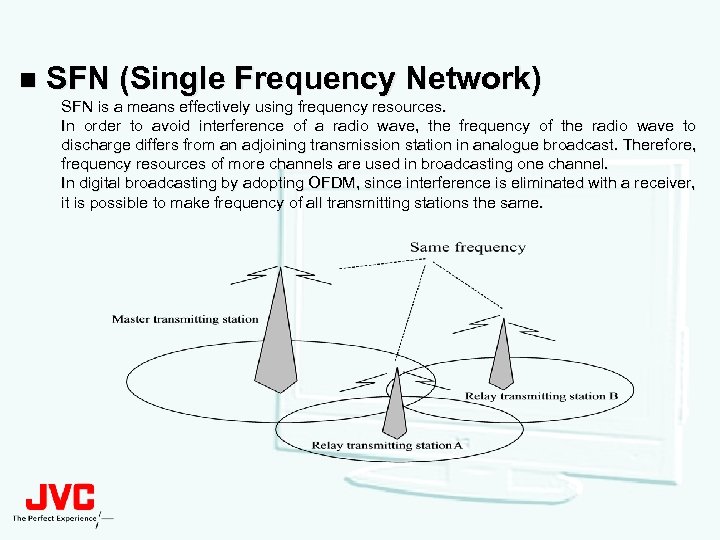
n SFN (Single Frequency Network) SFN is a means effectively using frequency resources. In order to avoid interference of a radio wave, the frequency of the radio wave to discharge differs from an adjoining transmission station in analogue broadcast. Therefore, frequency resources of more channels are used in broadcasting one channel. In digital broadcasting by adopting OFDM, since interference is eliminated with a receiver, it is possible to make frequency of all transmitting stations the same.
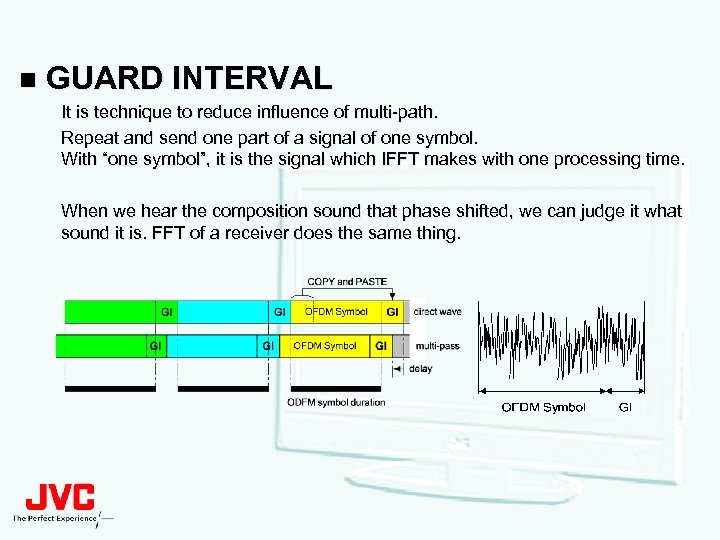
n GUARD INTERVAL It is technique to reduce influence of multi-path. Repeat and send one part of a signal of one symbol. With “one symbol”, it is the signal which IFFT makes with one processing time. When we hear the composition sound that phase shifted, we can judge it what sound it is. FFT of a receiver does the same thing.
61060ca52dbff27dac6a5767b7cc90fd.ppt