67180e0ece7689979dd4da979ae5efb1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 70

Digital natives. Digital immigrants. Libraries. The challenge faced by libraries in reaching out to born digital Tefko Saracevic, Ph. D http: //comminfo. rutgers. edu/~tefko/ tefkos@rutgers. edu Tefko Saracevic 1

What? Part I – The BIG picture Social forces Part II – The LIBRARY Challenges & responses 1. Digital natives, digital immigrants 2. Contemporary technology & society 3. Digital information resources 4. Web access 5. Information literacy 6. Social media 7. Conclusions Are young people (digital natives) really different? Tefko Saracevic How are library services for digital natives handled? 2

1. What do we mean? Definitions Digital natives Digital immigrants • Persons for whom digital • Individuals who grew up technologies already without digital existed when they were technology and adopted born, and hence had grown it later up with digital technology – also called “born digital” “net generation” “millenials” Generational differences expressed in technological terms Tefko Saracevic 3
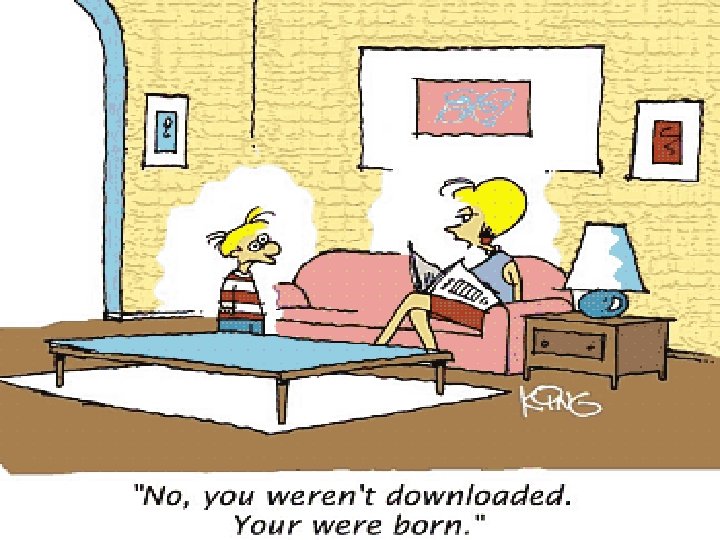

4
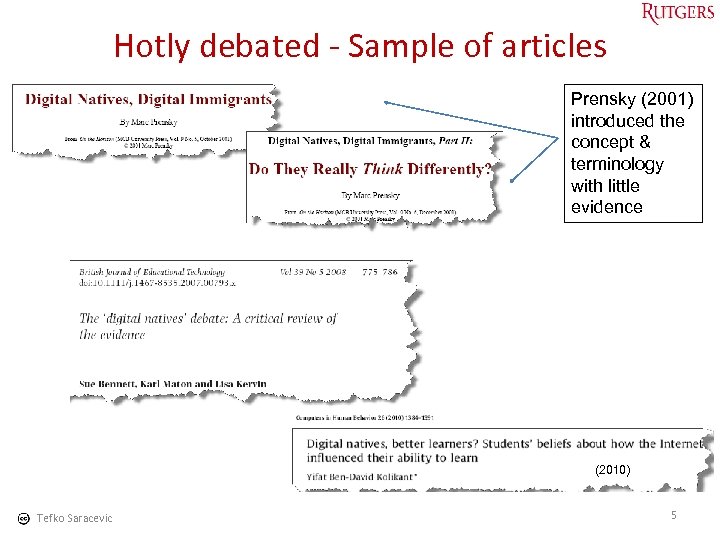
Hotly debated - Sample of articles Prensky (2001) introduced the concept & terminology with little evidence (2010) Tefko Saracevic 5

Growing number of studies – Sample of articles (2010) (2009) (2010) Tefko Saracevic 6
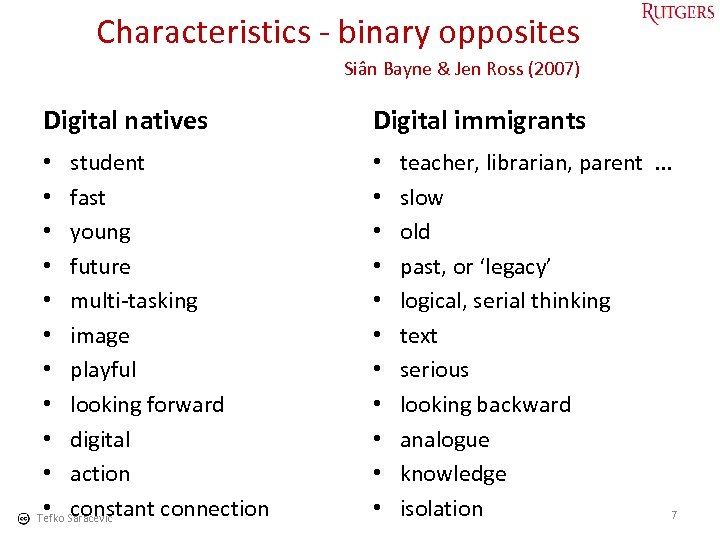
Characteristics - binary opposites Siân Bayne & Jen Ross (2007) Digital natives Digital immigrants • student • fast • young • future • multi-tasking • image • playful • looking forward • digital • action • constant connection Tefko Saracevic • • • teacher, librarian, parent . . . slow old past, or ‘legacy’ logical, serial thinking text serious looking backward analogue knowledge isolation 7
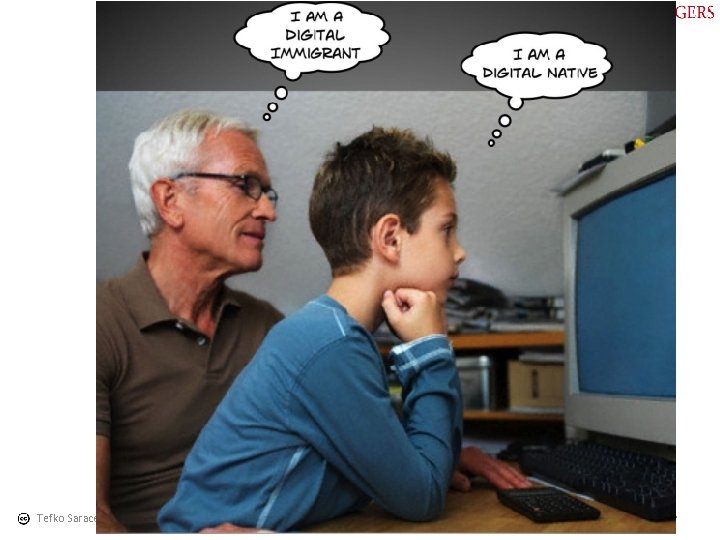

Tefko Saracevic 8

Controversy about digital natives Claims – Assumptions on the one hand Critiques on the other hand • Generational stereotyping • As native speakers of – reality: claims/assumptions digital language, young DO NOT reflect it people think and – oversimplified: should be process information in understood in diversity an entirely different way rather than dichotomy from previous • Assumes that all young generations people are wired digital • Because of that they masters who use have biological brain technology mysteriously changes • No scientific evidence 9 Tefko Saracevic

Examples of digital natives in action Tefko Saracevic 10

a few more. . . Tefko Saracevic 11
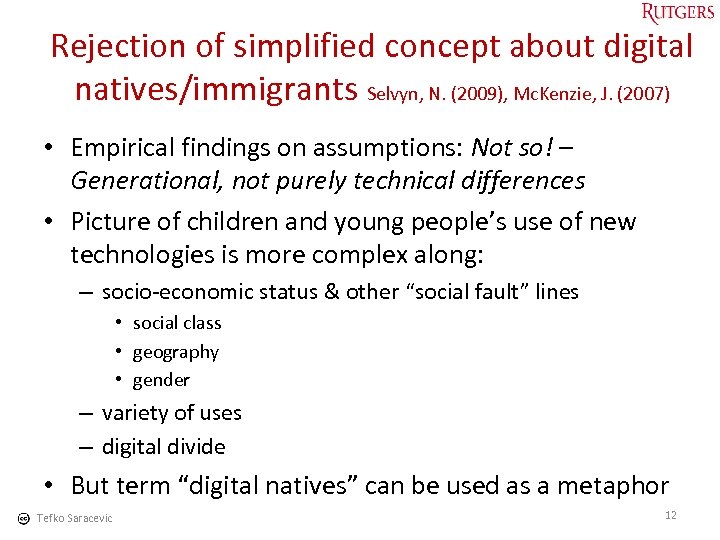
Rejection of simplified concept about digital natives/immigrants Selvyn, N. (2009), Mc. Kenzie, J. (2007) • Empirical findings on assumptions: Not so! – Generational, not purely technical differences • Picture of children and young people’s use of new technologies is more complex along: – socio-economic status & other “social fault” lines • social class • geography • gender – variety of uses – digital divide • But term “digital natives” can be used as a metaphor Tefko Saracevic 12

13

2. Contemporary technology Web 2. 0 • Information and communication technology and web design that aims to enhance creativity & information sharing in a new way Lets people • • Interact Connect Collaborate Share Contribute Inform Using variety of media – text, audio, video, images Tefko Saracevic 14
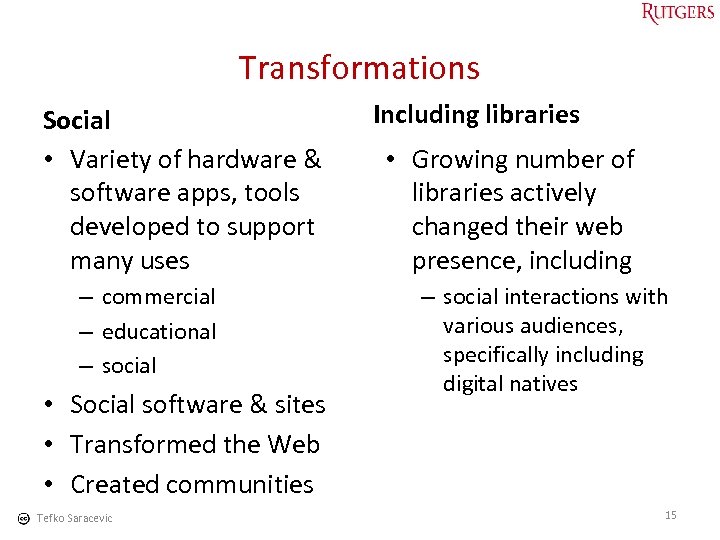
Transformations Social • Variety of hardware & software apps, tools developed to support many uses – commercial – educational – social • Social software & sites • Transformed the Web • Created communities Tefko Saracevic Including libraries • Growing number of libraries actively changed their web presence, including – social interactions with various audiences, specifically including digital natives 15

Another view of transformations Tefko Saracevic 16
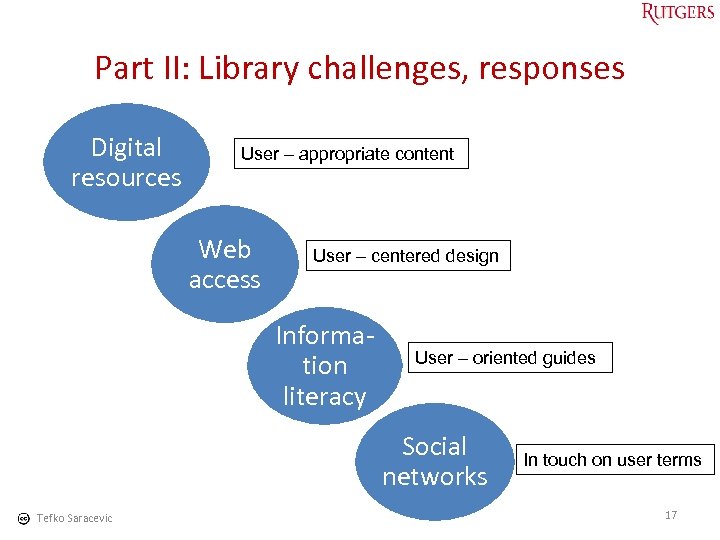
Part II: Library challenges, responses Digital resources User – appropriate content Web access User – centered design Information literacy User – oriented guides Social networks Tefko Saracevic In touch on user terms 17

Digital resources Digital INFORMATION resources In libraries General • Part of the collection • Information records in • Many e (digital) forms digital form, as opposed – books (e. Books) to analog – used to accomplish, support, help activities requiring information – – e. Journals videos images audio • Either digitized from analog or born digital Tefko Saracevic 18

Concentration I will concentrate here on e. Books in some depth recognizing that there are other digital information resources of great importance for library users of all generations – I will mention them only Tefko Saracevic 19

And now from print books (p. Books) onto electronic books (e. Books) • No sculpture, yet, commemorating e. Books • But e. Books are the fastest & most massive globally spreading books in book history – e. g. Book sculpture - commemorating invention of modern printing Walk of ideas, Berlin Tefko Saracevic a virtual fair July, 4 to Aug. 4, 2010 , featuring over 3, 000 e. Books; org. by World Public Library - Michael Hart (Gutenberg Project) 20
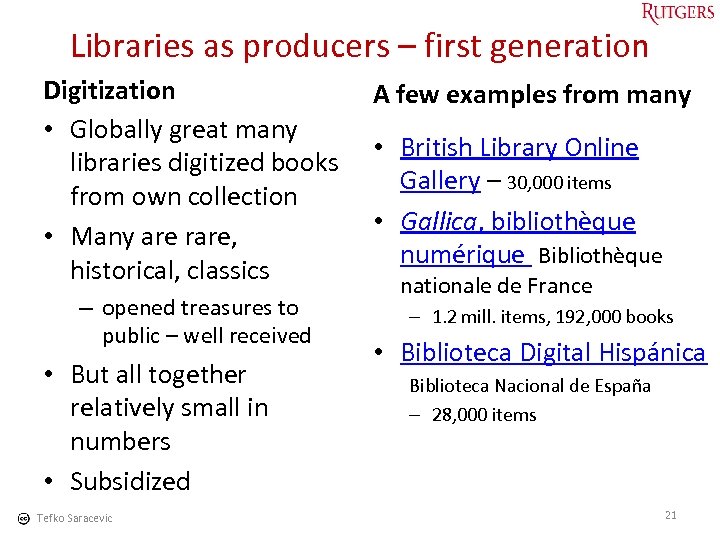
Libraries as producers – first generation Digitization • Globally great many libraries digitized books from own collection • Many are rare, historical, classics – opened treasures to public – well received • But all together relatively small in numbers • Subsidized Tefko Saracevic A few examples from many • British Library Online Gallery – 30, 000 items • Gallica, bibliothèque numérique Bibliothèque nationale de France – 1. 2 mill. items, 192, 000 books • Biblioteca Digital Hispánica Biblioteca Nacional de España – 28, 000 items 21

Mass digitization projects – second generation Major projects Pioneered • Industrial scale of e. Book • Project Gutenberg digitization – first, gave ideas to all – innovative • applications of technologies • a number of partnerships with libraries • Raised many issues & disagreements • Global reach & involvement Tefko Saracevic – about 140, 000 books • Million Book Project – global cooperation – about 1. 7 mill. books • Google Books – largest; international – many libraries & even countries cooperate – about 12 mill. books 22
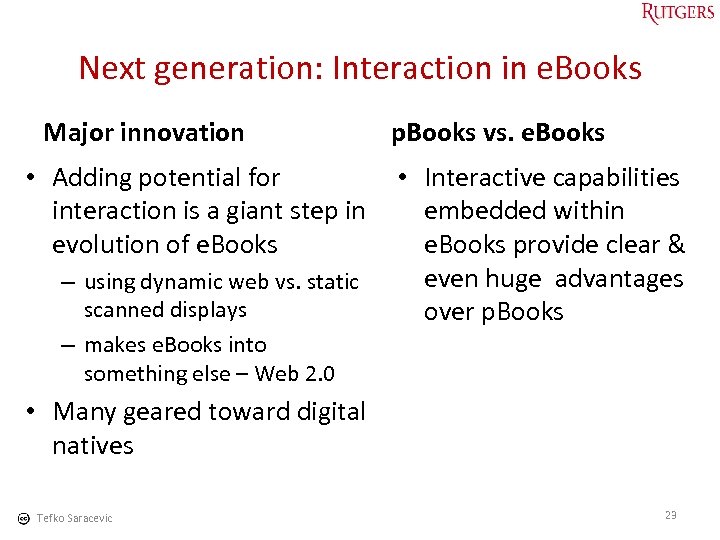
Next generation: Interaction in e. Books Major innovation p. Books vs. e. Books • Adding potential for • Interactive capabilities interaction is a giant step in embedded within evolution of e. Books provide clear & even huge advantages – using dynamic web vs. static scanned displays over p. Books – makes e. Books into something else – Web 2. 0 • Many geared toward digital natives Tefko Saracevic 23

Vendors (aggregators) What? • Bring together e. Books from different sources & publishers & make it available to libraries & others • Some do it via specific software or apps • Provide books by subscription, license, payment, and free Tefko Saracevic Who? • Large, universal ones taking the role of superbookstores – with some interactivity • Smaller, more specialized, aimed at specific markets, topics – particularly libraries & similar institutions – many most innovative, lots of interactivity 24

Sample of vendors … all online only Giants with global reach • Amazon – a super store & bookstore, e- & p. Books – mid 2010: for every 100 p. Books sold, 180 e. Books were sold • i. Books – Apple repeating the music formula to books, some digitized heritage books (e. g. Project Gutenberg) + current; many for digital natives (While we do not call them “vendors” or “aggregators” that is what they are) Tefko Saracevic Specialized or niche • ebrary “get the most out of your digital content. ” Several interactive capabilities for e. Books • Class. Zone – large global text book publisher turned to e. Books. Extensive interactive e-texts for middle & high schools – geared toward digital natives. – interactive learning: “Textbooks come to life. ” • They became the way for libraries to get & manage e -resources of all kinds 25
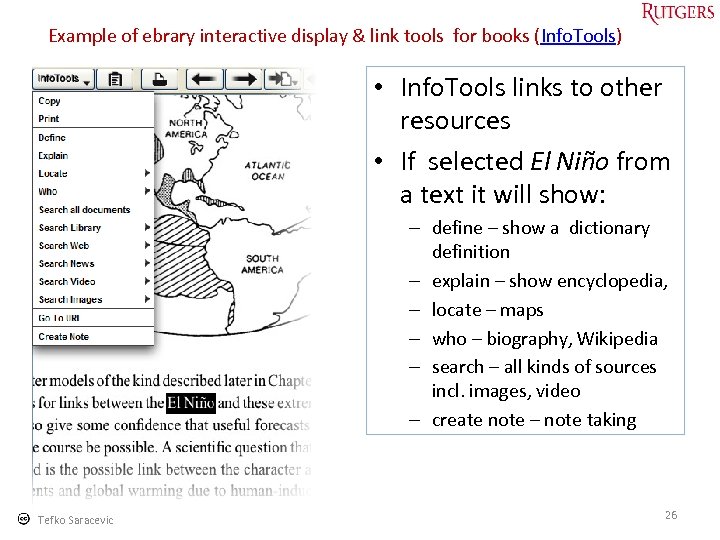
Example of ebrary interactive display & link tools for books (Info. Tools) • Info. Tools links to other resources • If selected El Niño from a text it will show: – define – show a dictionary definition – explain – show encyclopedia, – locate – maps – who – biography, Wikipedia – search – all kinds of sources incl. images, video – create note – note taking Tefko Saracevic 26
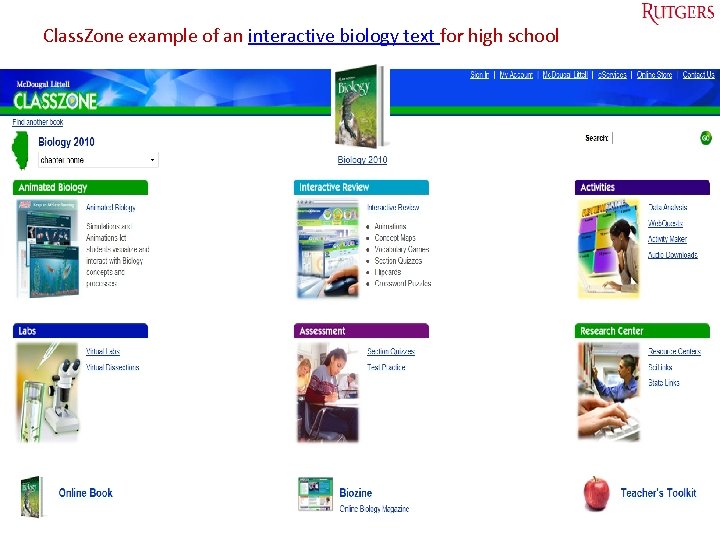
Class. Zone example of an interactive biology text for high school Tefko Saracevic 27

Libraries and e. Books Digitized old(er) books • Support tradition, culture – enlarge collection – attract interest for “buried” treasures – provide resources for education, scholarship • Major political point for justifying subsidy • Many libraries have a large number Tefko Saracevic Newly published • Support modernity – current demands • Why buy or license? – – – provide innovative services possible for multi locations circulate as other books go with digital natives for some no alternative 28

e. Book advantages for libraries Operations • Can’t be stolen, lost, mis-shelved • Automatic circulation • No additional space • Management easier – software from vendors • Circulated as other books Access • 24/7 from anyplace – but often restricted to own users (university, city) • High demand books easily managed – p. Book= single concurrent user; e. Book = many • Merges with other services – print, audio, video Very popular with users, particularly digital natives Tefko Saracevic 29

e. Book disadvantages for libraries Economics Balancing • Lots of €€€, $$$ … • With print collection • Funding a challenge – still the major part for all libraries • Technology investments • Still a good proportion still high of users are not there • New competencies, yet – digital divide (re)education needed – for both librarians & users Mind-set changes needed & hard to achieve Tefko Saracevic 30

Digital natives and e. Books Digital Tools for reading e. Books • Part of their universe • Becoming better & ubiquitous – young predominate, but not only young • Changing patterns how people read in general – devices: Kindle, i. Pad, Nook – software: Adobe Digital Editions. . . • Integrated with life • But information literacy • e. Books are just books – to be read anywhere for great many still low – & search for information Tefko Saracevic 31

Example of an e. Book read by a digital native anywhere Ally reading her book at a football game where her sister was a goalie (score 3: 3) Tefko Saracevic 32

Web access Versions of libraries – bricks & clicks Library as physical place • Physical building – physical collection, tools – social, collaborative, learning places for users • Physical access to organized materials in the place • Prisoner of physicality Tefko Saracevic Library as virtual space • Digital space/place – digital collection – access tools – quite different • Interaction beyond searching & browsing • Virtual access to organized digital resources any place • Prisoner of technology Great many libraries are hybrid 33
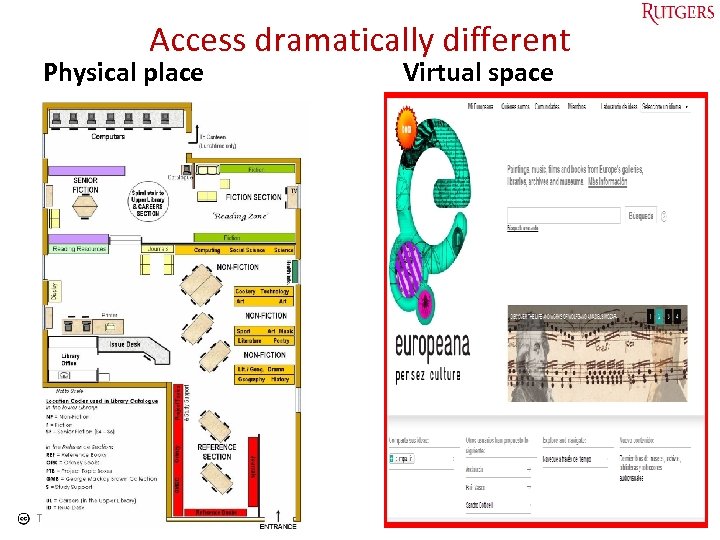
Access dramatically different Physical place Tefko Saracevic Virtual space 34
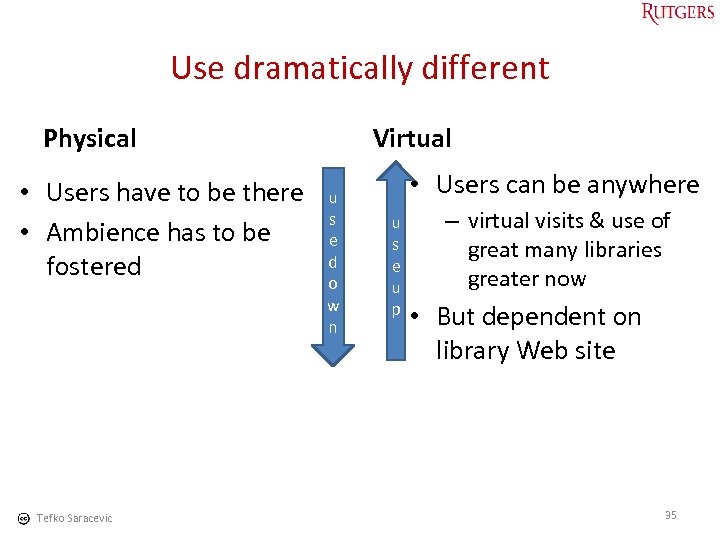
Use dramatically different Physical • Users have to be there • Ambience has to be fostered Tefko Saracevic Virtual u s e d o w n • Users can be anywhere u s e u p – virtual visits & use of great many libraries greater now • But dependent on library Web site 35

Library Web pages: where users meet the library Good design absolutely critical for effective use Major design criteria • User-centered design For digital natives • Functional, clear, – needs, wants, & limitations appealing, utilitarian of end users are given extensive attention – organized by user tasks, frequency, characteristics – search made clear – aesthetics & graphics • Flexibility, efficiency in use • Expected high usability • Valid for all kinds of users Tefko Saracevic For many libraries: a new world 36
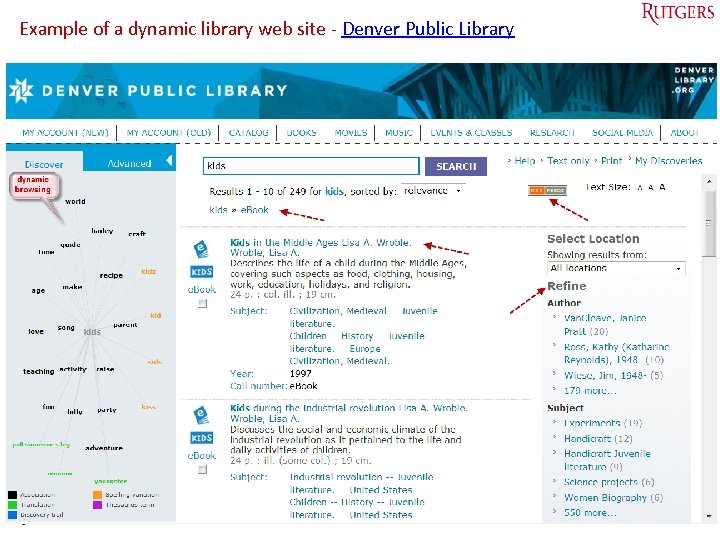
Example of a dynamic library web site - Denver Public Library Tefko Saracevic 37
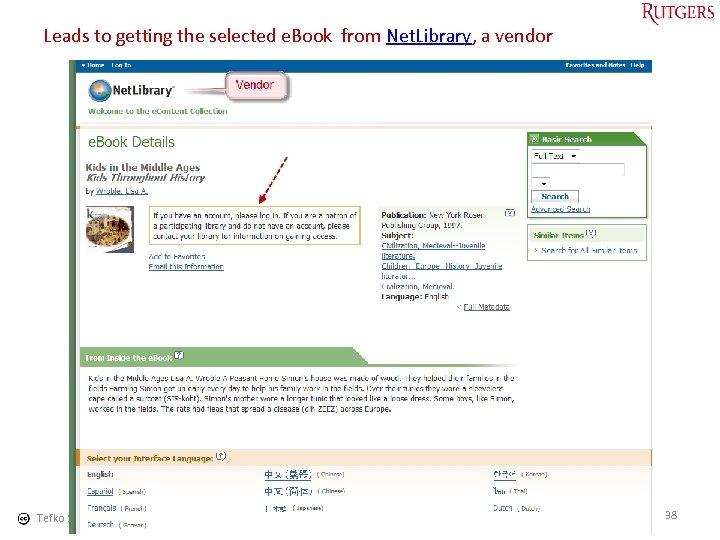
Leads to getting the selected e. Book from Net. Library, a vendor Tefko Saracevic 38
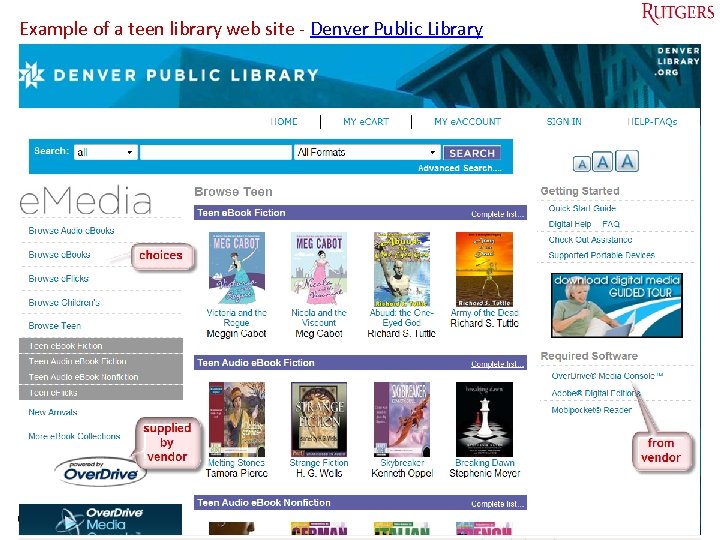
Example of a teen library web site - Denver Public Library Tefko Saracevic 39

Example of a children library web site - Denver Public Library Tefko Saracevic 40
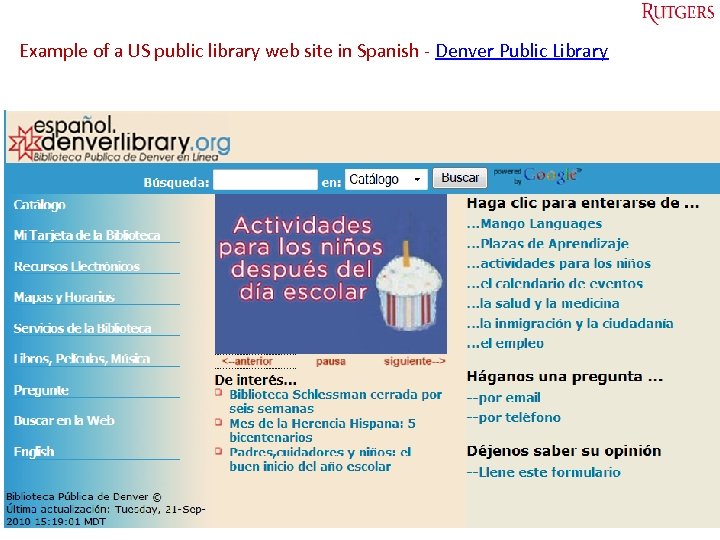
Example of a US public library web site in Spanish - Denver Public Library Tefko Saracevic 41

Over. Drive : Example of a vendor providing variety of resources & apps for libraries, schools etc. for access & variety of users, digital natives included Tefko Saracevic 42
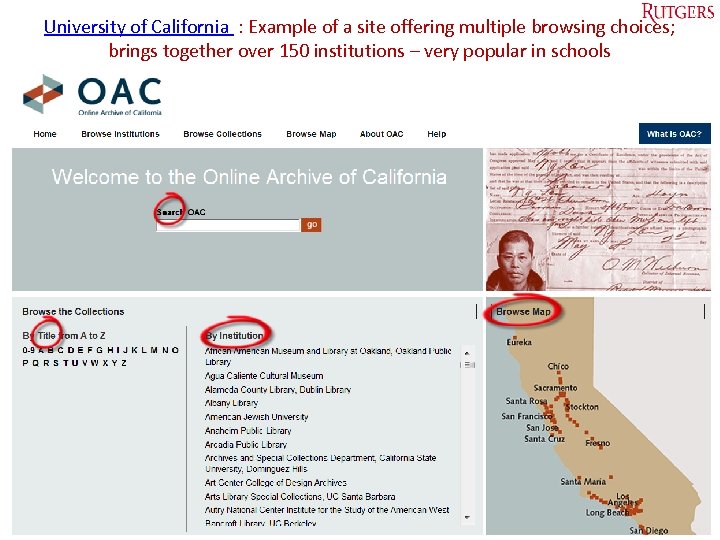
University of California : Example of a site offering multiple browsing choices; brings together over 150 institutions – very popular in schools Tefko Saracevic 43
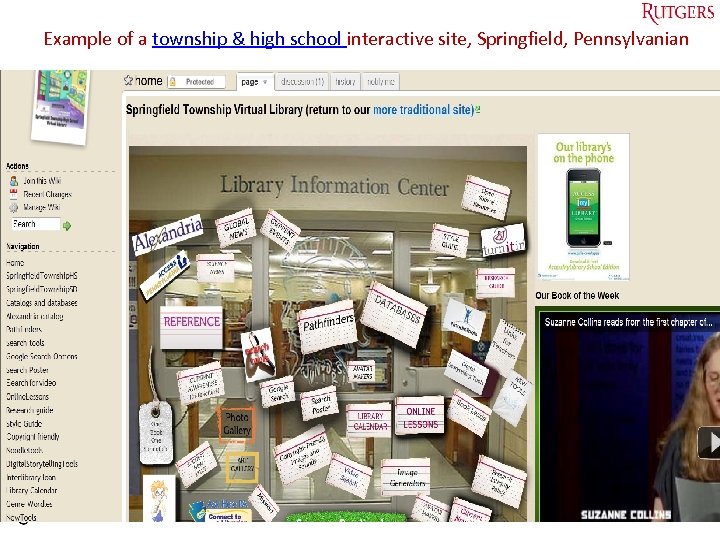
Example of a township & high school interactive site, Springfield, Pennsylvanian Tefko Saracevic 44

Among others it leads to this site where kids can click on their choice Tefko Saracevic 45
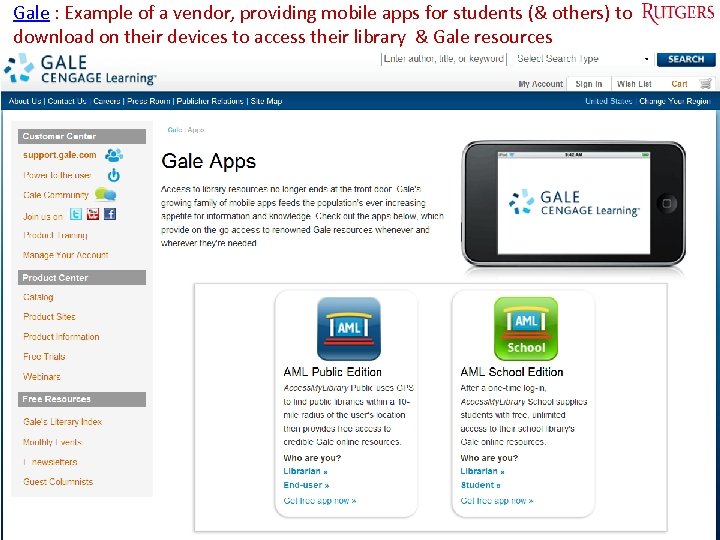
Gale : Example of a vendor, providing mobile apps for students (& others) to download on their devices to access their library & Gale resources Tefko Saracevic 46

Information literacy What do we mean? Contemporary approach: Digital literacy • Ability to use digital technology, communication tools or networks effectively • A person’s ability to perform tasks effectively in a digital environment • Tech savvy is not automatically digitally literate Tefko Saracevic Information literacy • Ability to locate, understand, use & evaluate information in multiple formats from a wide range of sources using a computing device – for problem solving, decision making, learning, even enjoying 47

Goals for information literacy efforts Recognition Competencies • Accurate, trustworthy, • Identify potential verifiable information is sources of information basis for intelligent • Access these sources decision making, • Evaluate sources & problem solving, information learning • Organize information • Integrate for application, learning Geared toward digital resources & specific audiences, e. g. digital natives 48 Tefko Saracevic

Applied in libraries • • • Online tutorials for given subjects Online tutorials for given activities Webinars (Web seminars) Suggestions on making information literacy courses Evaluation tools Tefko Saracevic 49
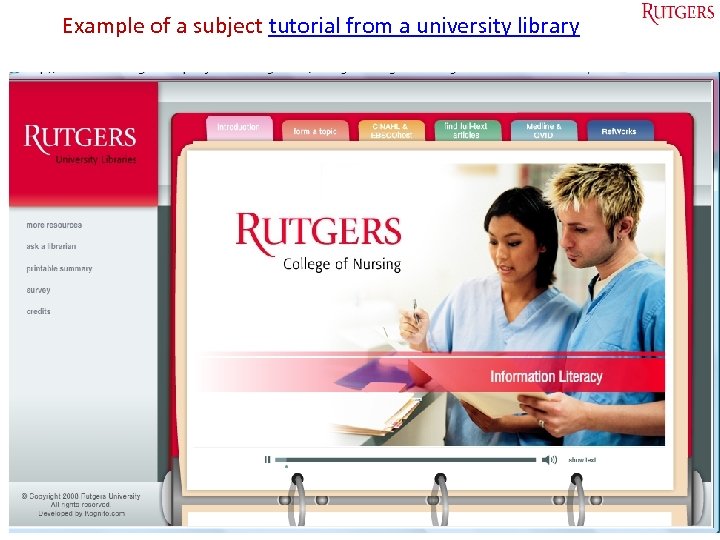
Example of a subject tutorial from a university library Tefko Saracevic 50
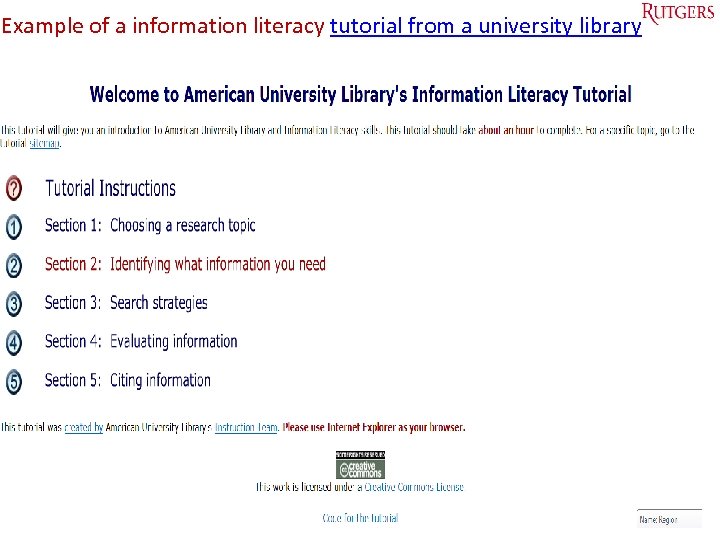
Example of a information literacy tutorial from a university library Tefko Saracevic 51

Example of a library research tutorial from Cornell University library Tefko Saracevic 52
Example of a regular Webinar about solving information problems Tefko Saracevic 53
Example of a video on making of information literacy tutorials (from Slideshare) Tefko Saracevic 54

Social networks • Sites that focus on building online communities of people who: – share interests – activities – explore interests & activities of others What do we mean? Results • Developing a culture of critique & debate • Much freer expression • For education: – educational tools – back to student driven model of medieval Europe? (José Ortega y Gasset) Many sites emerged & disappeared, few big ones dominate Tefko Saracevic 55

56
Means for: • Collaborating: – Wikis • Expressing, responding: – Blogs • Communicating: – Twitter – Facebook – My. Space • RSS (Really Simple Syndication) – updating Tefko Saracevic • Sharing: – Dropbox – Flickr – You. Tube • Bookmarking: – Delicious • Subject guides – many libraries & others • Instant messaging (IM) – many reference services Enhance human connections – but. . . 57

58

Library applications • Transition the way • Making the library site services are delivered to more interactive users • Increase the flow of • Marketing & promoting information from users library services to library • Many libraries • Connect with users: participate in e. g. – blogging (list of library blogs) – social media (Social networking librarian) Tefko Saracevic 59
Example of social media in a public library – Denver Public Library Tefko Saracevic 60
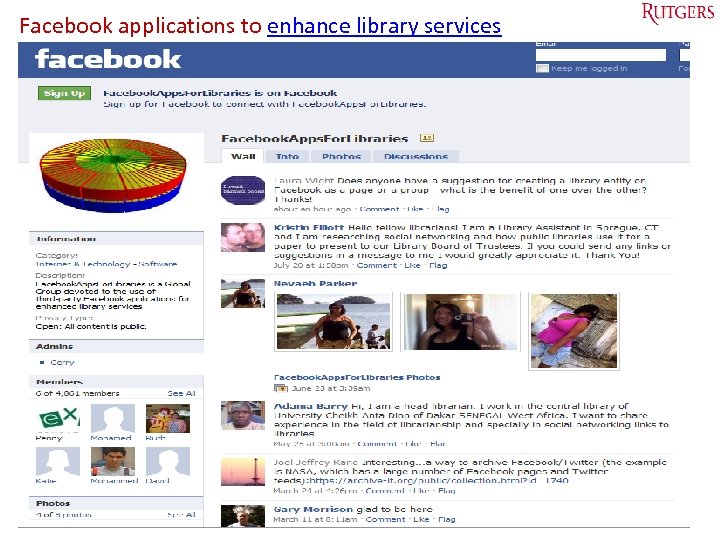
Facebook applications to enhance library services Tefko Saracevic 61
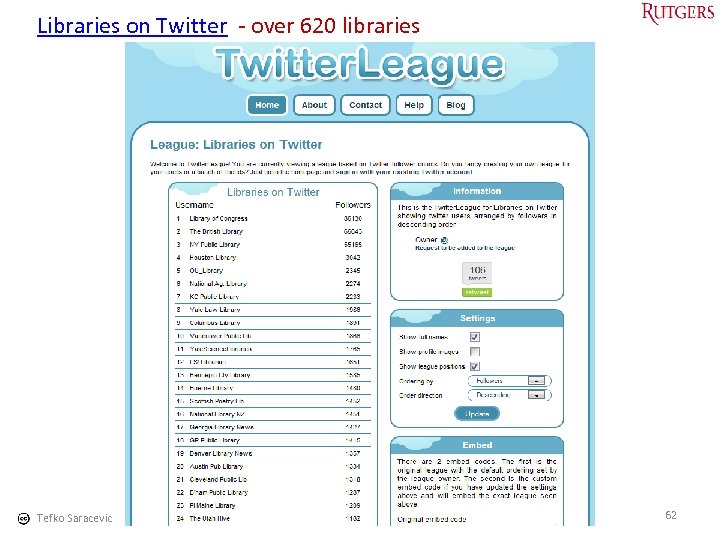
Libraries on Twitter - over 620 libraries Tefko Saracevic 62
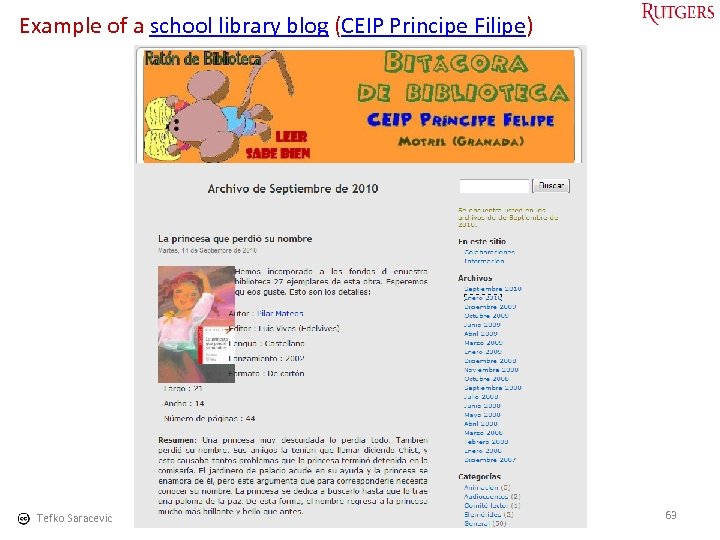
Example of a school library blog (CEIP Principe Filipe) Tefko Saracevic 63
And a video Librarians do Gaga ( Information School, University of Washington) Tefko Saracevic 64

7. Conclusions Digital natives – digital immigrants • Generational changes happened throughout history • We should be mindful of the changes in technological “lifeworld” of digital natives – but avoid excesses in the debate - such as claiming substantial transformation of social relations - & – concentrate on enhancing our understandings of the realities of technology use in contemporary society (Selvyn, 2009) • It is not threatening at all – could be used for advantage • But digital divide - have and have nots - is real for all generations & must be taken into account Tefko Saracevic 65
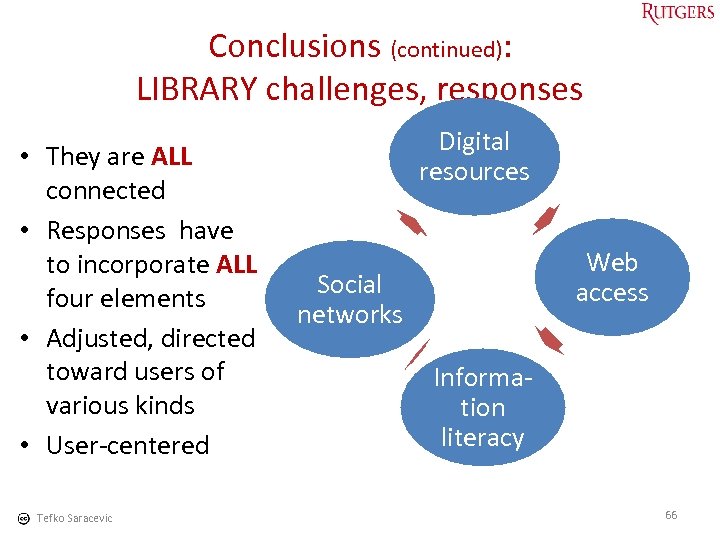
Conclusions (continued): LIBRARY challenges, responses • They are ALL connected • Responses have to incorporate ALL four elements • Adjusted, directed toward users of various kinds • User-centered Tefko Saracevic Digital resources Web access Social networks Information literacy 66

This presentation in Wordle Tefko Saracevic 67

Thank you for inviting me! Tefko Saracevic 68

Bibliography Bennett, S. , Maton, K. , & Kervin, L. (2008) The 'digital natives' debate: A critical review of the evidence. British Journal of Educational Technology, 39 (5), 775 -786. Brown, A. L. (blog). Social networking librarian. Exploring social networking and technology in libraries. Available at: http: //socialnetworkinglibrarian. com/ Fernandez-Villavicencio, N. G. (2010) Helping students become literate in a digital, networking-based society: A literature review and discussion, The International Information & Library Review, 42(2), 124 -136. Kolikant, Y. B. -D. (2010. Digital natives, better learners? Students' beliefs about how the Internet influenced their ability to learn. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1384 -1391. Mc. Kenzie, J. (2007) Digital Nativism, Digital Delusions and Digital Deprivation. From Now On: The Educational technology Journal , 17(2). Available at: http: //www. fno. org/nov 07/nativism. html Prensky, M (2001). Digital Natives, Digital Immigrants On the Horizon, 9 (5) Available at: http: //www. marcprensky. com/writing/Prensky%20 -%20 Digital%20 Natives, %20 Digital%20 Immigrants%20%20 Part 1. pdf Prensky, M (2001). Digital Natives, Digital Immigrants, Part II: Do They Really Think Differently? On the Horizon, 9(6) Available at: http: //www. marcprensky. com/writing/Prensky%20%20 Digital%20 Natives, %20 Digital%20 Immigrants%20 -%20 Part 2. pdf Selvyn, N. The digital native – myth and reality (2009) Aslib Proceedings: New Information Perspectives, 61(4), 364 -379. Wong, M. (n. d. ) Great web design tips Available at http: //www. great-web-design-tips. com/ Tefko Saracevic 69

For download • This presentation can be found at my site: http: //comminfo. rutgers. edu/~tefko/articles. htm Tefko Saracevic 70
67180e0ece7689979dd4da979ae5efb1.ppt