89b1ab89075f9f1ea242f515513f587f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Digital Broadcast Technology Development Presented by John Yip Chief Engineer RTHK 2006. 12. 06 1
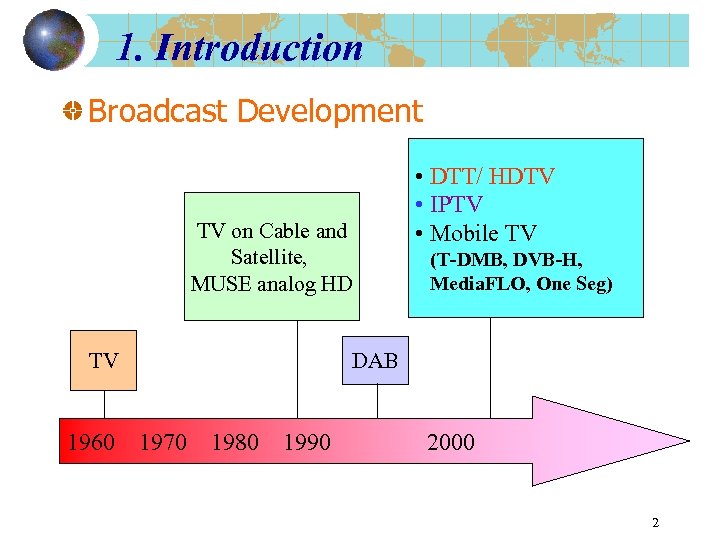
1. Introduction Broadcast Development TV on Cable and Satellite, MUSE analog HD (T-DMB, DVB-H, Media. FLO, One Seg) DAB TV 1960 • DTT/ HDTV • IPTV • Mobile TV 1970 1980 1990 2000 2
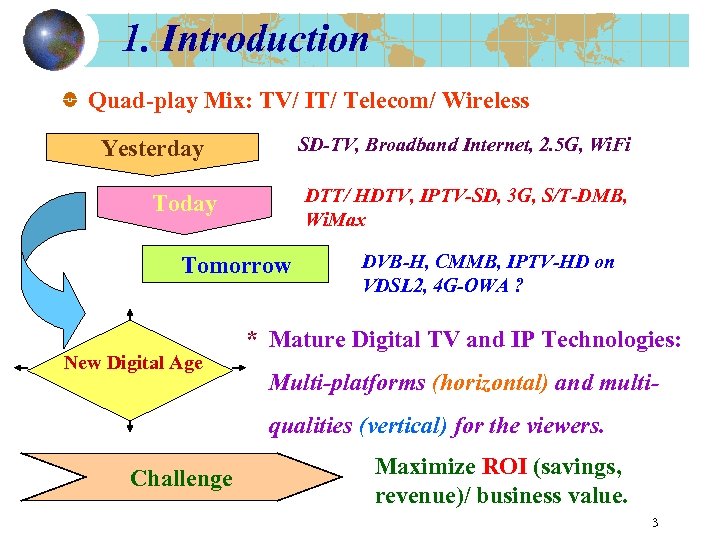
1. Introduction Quad-play Mix: TV/ IT/ Telecom/ Wireless SD-TV, Broadband Internet, 2. 5 G, Wi. Fi Yesterday DTT/ HDTV, IPTV-SD, 3 G, S/T-DMB, Wi. Max Today Tomorrow New Digital Age DVB-H, CMMB, IPTV-HD on VDSL 2, 4 G-OWA ? * Mature Digital TV and IP Technologies: Multi-platforms (horizontal) and multiqualities (vertical) for the viewers. Challenge Maximize ROI (savings, revenue)/ business value. 3

1. Introduction Convergence Converging technologies lead to a divergence of viewers’ choices. Quality: traded-off against mobility, transmission costs. Video bitrates, from 0. 2 Mbps (for mobile phones) to over 100 Mbps for HDTV. Quality vs user cost, but technologies provide flexibility, improvements. 4

1. Introduction Content is King + Customer is Queen Compelling contents can drive people to buy new technologies, e. g. sports. People’s habits/ life styles are then gradually changed by the new technologies. General Trends - Ubiquitous: anywhere, anytime, desired form Mobility increases Threshold of acceptable quality dropping Networked environment eg office, home Time-shifted viewing/ listening eg PVR, ipod Interactive 5
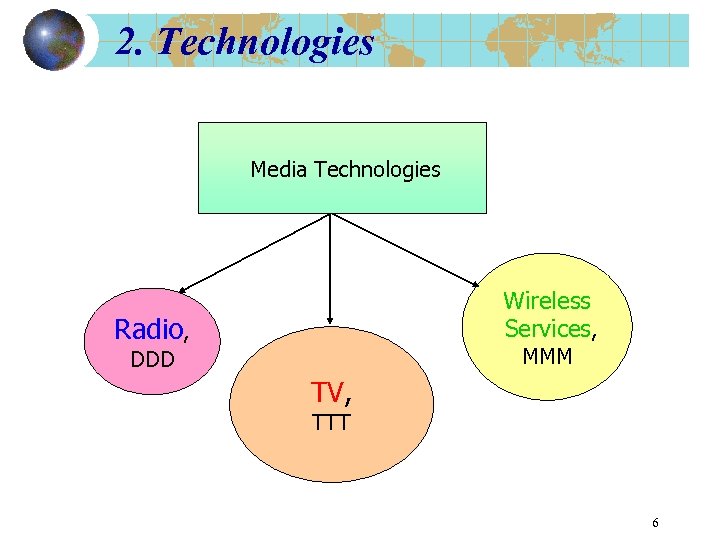
2. Technologies Media Technologies Wireless Services, Radio, MMM DDD TV, TTT 6

2. Technologies - Radio : DAB, DRM, DMB DAB (Digital Audio Broadcasting) A technology for multi-channel audio broadcasts. Based on European Eureka-147 standard, developed in mid 1990’s. DRM (Digital Radio Mondiale) An open-source platform for digital radio broadcasting in AM, SW or FM bands. Fits within existing AM channel bandwidth. DMB (or T-DMB, Digital Multimedia Broadcasting) A digital system for sending data, radio and TV to mobile devices such as mobile phones. Developed by S. Korea (TDMB, S-DMB). DAB-compatible. 7

2. Technologies - TV TV - DTT (Digital Terrestrial TV) Using digital technology to provide - more channels (SDTV) and/ or - better picture (HDTV) and sound (surround) through a TV antenna eg on top of the roof, instead of using cable, satellite or internet. 8

2. Technologies - TV TV - HDTV (High Definition TV) 16 x 9 aspect ratio. Studio Standard: 1080/50 i in 50 Hz countries (HK/China). 720/50 p is also used in Europe, Australia. Transmission standard: country-dependent. Picture information about 5 times that of conventional TV Needs critical camera focusing and attention to the wide aspect ratio. OB can use fewer cameras. Compatibility with 4 x 3 SDTV: some down-convert to 14 x 9 or 13 x 9. 9
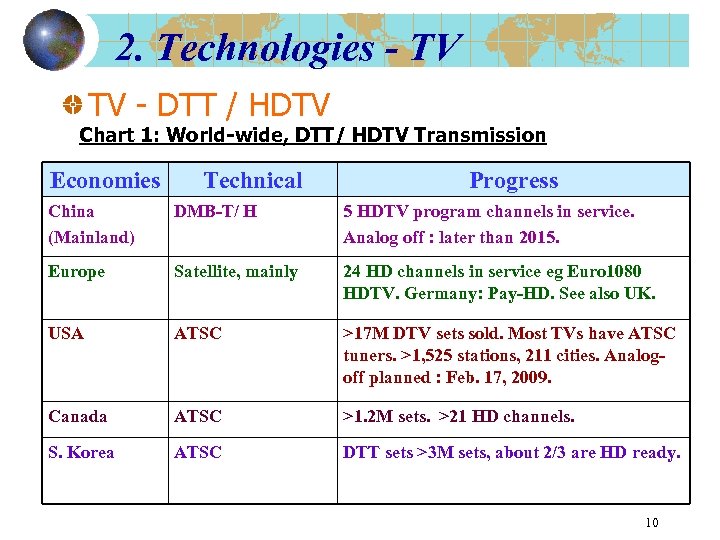
2. Technologies - TV TV - DTT / HDTV Chart 1: World-wide, DTT/ HDTV Transmission Economies Technical Progress China (Mainland) DMB-T/ H 5 HDTV program channels in service. Analog off : later than 2015. Europe Satellite, mainly 24 HD channels in service eg Euro 1080 HDTV. Germany: Pay-HD. See also UK. USA ATSC >17 M DTV sets sold. Most TVs have ATSC tuners. >1, 525 stations, 211 cities. Analogoff planned : Feb. 17, 2009. Canada ATSC >1. 2 M sets. >21 HD channels. S. Korea ATSC DTT sets >3 M sets, about 2/3 are HD ready. 10
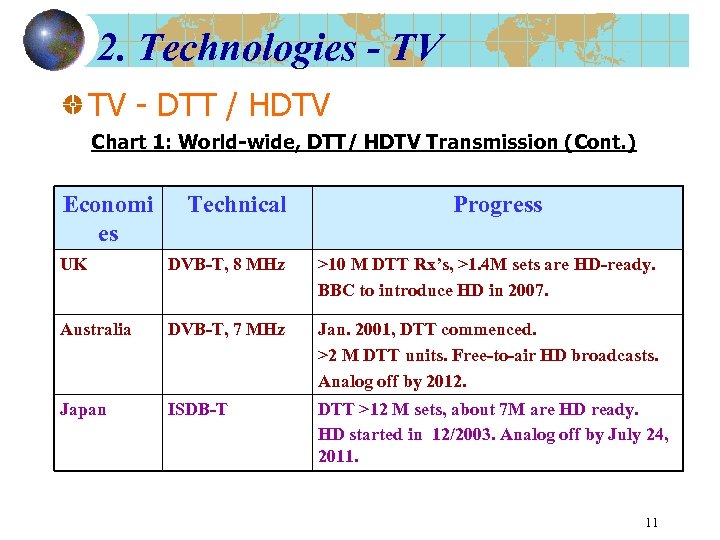
2. Technologies - TV TV - DTT / HDTV Chart 1: World-wide, DTT/ HDTV Transmission (Cont. ) Economi es Technical Progress UK DVB-T, 8 MHz >10 M DTT Rx’s, >1. 4 M sets are HD-ready. BBC to introduce HD in 2007. Australia DVB-T, 7 MHz Jan. 2001, DTT commenced. >2 M DTT units. Free-to-air HD broadcasts. Analog off by 2012. Japan ISDB-T DTT >12 M sets, about 7 M are HD ready. HD started in 12/2003. Analog off by July 24, 2011. 11
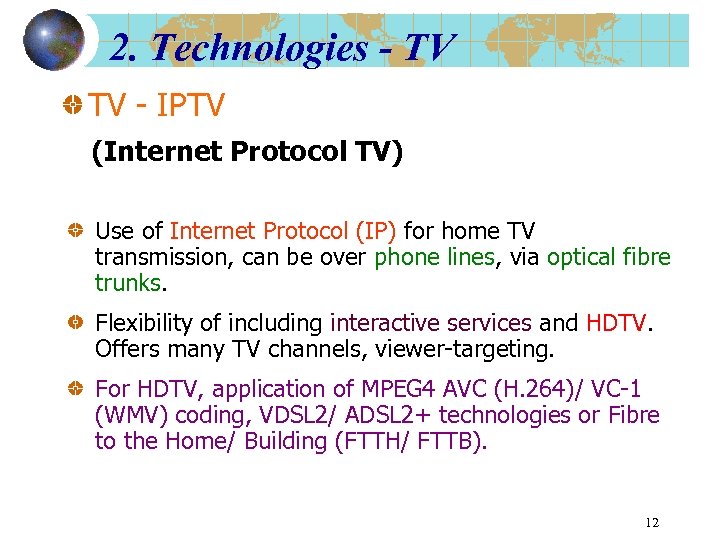
2. Technologies - TV TV - IPTV (Internet Protocol TV) Use of Internet Protocol (IP) for home TV transmission, can be over phone lines, via optical fibre trunks. Flexibility of including interactive services and HDTV. Offers many TV channels, viewer-targeting. For HDTV, application of MPEG 4 AVC (H. 264)/ VC-1 (WMV) coding, VDSL 2/ ADSL 2+ technologies or Fibre to the Home/ Building (FTTH/ FTTB). 12

2. Technologies - Mobile TV Broadcast to hand-sets (mobile phones, PDAs), notebook PCs, etc. Interactive and audio services. T-DMB (Terrestrial-DMB) Evolved from DAB. Allows video, audio and data to be transmitted to mobile devices. More efficient audio coding. Backward compatible with DAB audio (MUSICAM). DVB-H (Digital Video Broadcasting – Handheld) Tailored for transmitting multiple TV channels to mobile devices. Time-slicing technology conserves battery power of mobile devices. 13

3. HDTV and Economics * Chicken vs egg; (govt. + industry) vs consumers; content creation vs consumption; market size vs consumers’ costs. * Economics: predictive of a rapid roll-out of costly digital HDTV. • AI (Affordability Index) = Normalized (GDP * GDP-per-capita) (using PPP) GDP --> size of economy --> strength for driving technology/ content creation. GDP-per-capita --> consumer’s ability buy new devices/ contents. 14
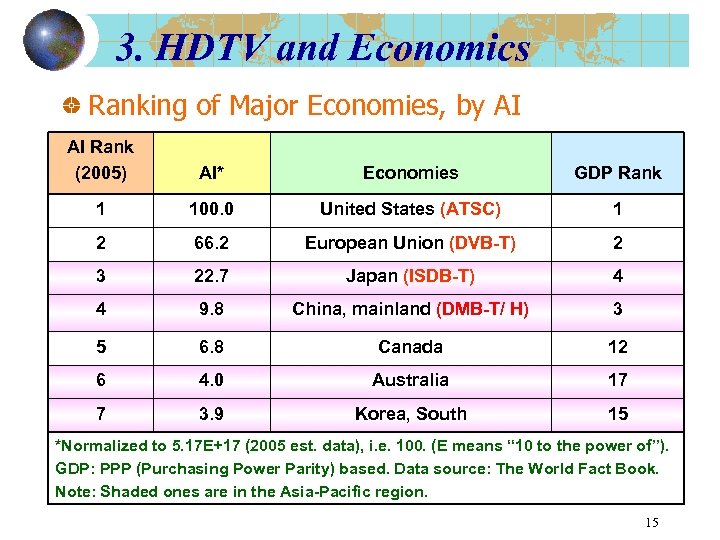
3. HDTV and Economics Ranking of Major Economies, by AI AI Rank (2005) AI* Economies GDP Rank 1 100. 0 United States (ATSC) 1 2 66. 2 European Union (DVB-T) 2 3 22. 7 Japan (ISDB-T) 4 4 9. 8 China, mainland (DMB-T/ H) 3 5 6. 8 Canada 12 6 4. 0 Australia 17 7 3. 9 Korea, South 15 *Normalized to 5. 17 E+17 (2005 est. data), i. e. 100. (E means “ 10 to the power of”). GDP: PPP (Purchasing Power Parity) based. Data source: The World Fact Book. Note: Shaded ones are in the Asia-Pacific region. 15
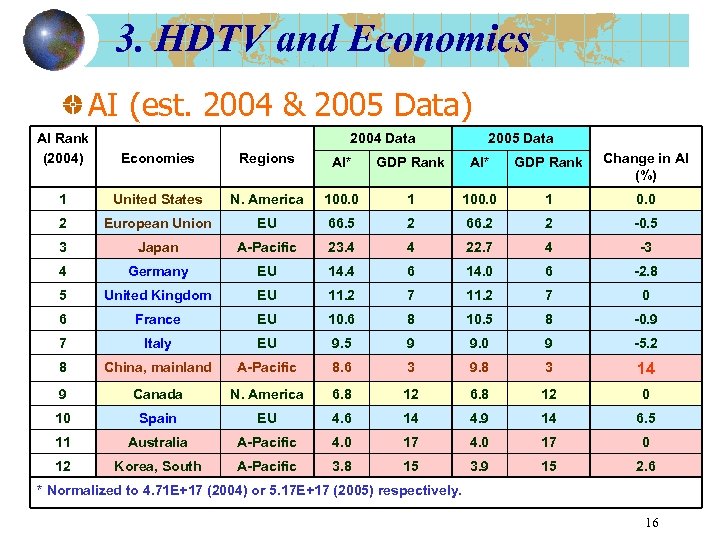
3. HDTV and Economics AI (est. 2004 & 2005 Data) AI Rank (2004) 2004 Data 2005 Data Economies Regions AI* GDP Rank Change in AI (%) 1 United States N. America 100. 0 1 0. 0 2 European Union EU 66. 5 2 66. 2 2 -0. 5 3 Japan A-Pacific 23. 4 4 22. 7 4 -3 4 Germany EU 14. 4 6 14. 0 6 -2. 8 5 United Kingdom EU 11. 2 7 0 6 France EU 10. 6 8 10. 5 8 -0. 9 7 Italy EU 9. 5 9 9. 0 9 -5. 2 8 China, mainland A-Pacific 8. 6 3 9. 8 3 14 9 Canada N. America 6. 8 12 0 10 Spain EU 4. 6 14 4. 9 14 6. 5 11 Australia A-Pacific 4. 0 17 0 12 Korea, South A-Pacific 3. 8 15 3. 9 15 2. 6 * Normalized to 4. 71 E+17 (2004) or 5. 17 E+17 (2005) respectively. 16
3. HDTV and Economics Observations from AI (affordability index) data: USA, Europe, Japan established DTT/ HDTV standards (ATSC, DVB-T, ISDB-T). China (mainland) has recently established a standard in Aug. , 2006. AI of 9. 8 seems to be the minimum threshold. In Europe, the ranking order is Germany, UK, France, followed by Italy/ Spain. For Europe, a wide-coverage technology such as satellites is beneficial (in fact, satellites are prevalent). HDTV activity is most intense in economies with an AI index >= 3. 8 (2004 data) or 3. 9 (2005 data), approx. AI ranking for the top economies has not changed a lot over 2004 -2005. (For Hong Kong, AI = 1. 7 (2004) and 1. 8 (2005); synergy with mainland China is an important factor. ) 17

3. HDTV and Economics Expanded List showing Rollouts AI Rank AI* Economies GDP Rank GDP/ capita Rank HDTV sets (est. M) Pop. (est. M) TVH (est. M) HDTV sets / capita (est. %) HDTV sets / TVH (est. %) 1 100 United States 1 2 17 296 110 5. 7 15. 4 2 66. 5 European Union 2 32 457 3 23. 4 Japan 4 21 7 127 47. 5 5. 5 14. 7 4 14. 4 Germany 6 24 82 34. 2 5 11. 2 United Kingdom 7 19 1. 4 60 24. 3 2. 3 5. 8 6 10. 6 France 8 23 61 23 7 9. 5 Italy 9 30 58 21 8 8. 6 China, mainland 3 121 1, 306 330 9 6. 8 Canada 12 15 1. 2 33 12 3. 6 10. 0 10 4. 6 Spain 14 39 40 13. 1 11 4. 0 Australia 17 17 1 20 7. 3 5 18 13. 7

3. HDTV and Economics Factors: Accelerating HDTV Other factors impact on HDTV rollout: regulatory, pricing, marketing, etc. Propelling Factor (HDF) = M (r, p, m, o)*(GDP*GDP-per-capita) - where GDP is based on the PPP method, and (GDP*GDP-per-capita) = Affordability factor, M is a function of regulatory/ pricing/ marketing/ other factors For 0=<M<1 : retarding; For M>1 : accelerating As (HDTV sets-per-capita, %) increases with HDF, hence M is proportional to (HDTV sets-per-capita, %) divided by AI. 19

3. HDTV and Economics Factors: Accelerating HDTV (cont. ) Propelling Factor (HDF) = M (r, p, m, o)*(GDP*GDP-per-capita) On breaking down function M : HDF = (Ar * Ap * Am * Ao) * (GDP*GDP-per-capita) Strategic factors to foster HD development: Ar, Ap, Am, Ao 20

3. HDTV and Economics Factors: Accelerating HDTV (cont. ) Ar – regulatory, mandating early rollout/ early cessation of analog TV, built-in digital tuners in TV sets, HD on-air quota, spectrum allotments, licensing regime, standardization; Ap – subsidies by governments/ operators, assisting viewers eg on HDTV STB; Am – Promotional/ marketing campaigns, to promote viewers’ awareness; Ao –leapfrog into HD (eg Canada and S. Korea, using ATSC, have achieved fast rollouts), adopting HDV/ low-cost EFP production, D-cinemas/ communal/ public viewing. 21

4. CD • DC Model Supply Contents (HD) Consumption Delivery eg. Terrestrial, IPTV, etc. Display Contents (IPTV is just one more method for delivering HDTV but it is not affected by spectrum scarcity. IT technologies are used in the delivery process to connect the contents to the services. ) 22

5. IP TV and Economics IPTV (HD, SD) and Economics IPTV-HD is subject to the economics of HDTV. However, for IPTV-SD content production is less expensive than that of HDTV. Consumer spending power is an important issue. ROI for the operators is critical. The upgrading and roll-out of a highbandwidth and scalable network is a major investment. Population density is an influencing factor. Is Hong Kong no. 1 ? Propelling Factor (IPTF) = Mi (r, p, m, o) * (GDP-per-sq. km) Equation applies to targeted cities, for IPTV-SD. 23

6. Mobile TV and Economics Content production is far less expensive than that of HDTV. Affordability is an issue : hardware and content costs, plus high functional obsolescence (short replacement cycles). Terrain is an issue (HK being one example. ) Propelling Factor (MTF) = Mm (r, p, m, o) * T * (GDP-per-capita) where T = Terrain factor, 0 < T =< 1. Terrain factor is technology (VHF, UHF, satellite) and frequencyband dependent, for targeted Cities. 24

7. Influencing Factors IPTV: no spectrum issues. Other factors may also apply, such as consumer behaviour. (H/ M/ L = high/ medium/ low impact) 25

8. Status of Digital Broadcast Technologies Sets (in M), world-wide Main Areas DAB >5 United Kingdom HDTV > 30 USA, Japan IPTV-SD >5 Hong Kong, France Mobile TV > 2. 5 S. Korea (T-DMB) Internet Users > 1, 100 USA, China, Japan Broadband Users > 200 USA, Japan, S. Korea Sources : wilkipedia, internetworldstat. com, etc. 26

9. Convergence, HK On digital broadcast technologies; not FMC. HK: >67% broadband penetration, >131% mobile subscriber penetration, and >2 M 2. 5 G/3 G mobile users. Leading with >0. 7 M IPTV subscribers and high mobile penetration. Lots of potential. Synergy with mainland China on DTT/ HDTV development: HK has one of the highest GDP/ capita and mainland China is near the top in GDP. HK can help accelerate HDTV roll-outs. Chinese CMMB mobile standard uses STi. Mi for S-CMMB and T-CMMB (terrestrial gap fillers), 30 -3000 MHz. HK, with high rise buildings and rough terrain, is very challenging for mobile TV using wide-area transmission ie T-CMMB or DVB-H (unlike cellular 3 G). FTA may be less problematic. 27

10. Summary TTT (Triple TV Technologies) and digital sound broadcasting developments are perplexing but interesting. Techno-economic equations and an AI index have been introduced to enhance the understanding of world-wide developments. Technological development and economics are closely related. Other factors such as regulatory, pricing, marketing and even terrain exert influences on growth. Technological diffusion in broadcasting depends a lot on content and consumer behaviour; operators have to evaluate techno-economic and market factors in order to succeed. 28

“HDTV Development” paper published (searchable on Google, Yahoo HK ), “IPTV Development” available in late Dec. 2006. ~The End~ Thank You! yipjcs@rthk. org. hk 29
89b1ab89075f9f1ea242f515513f587f.ppt