 Digital Archive Policies and Trusted Digital Repositories Mac. Kenzie Smith, MIT Libraries Reagan Moore, San Diego Supercomputer Center ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 1
Digital Archive Policies and Trusted Digital Repositories Mac. Kenzie Smith, MIT Libraries Reagan Moore, San Diego Supercomputer Center ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 1
 What is the Problem? n Need to extract local collection management policies from software to be more discoverable, configurable n Need to standardize ILM policies to support sharing across systems within a preservation environment n Need to define metadata to audit ILM operations and achieve trust in a scalable, automated way ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 2
What is the Problem? n Need to extract local collection management policies from software to be more discoverable, configurable n Need to standardize ILM policies to support sharing across systems within a preservation environment n Need to define metadata to audit ILM operations and achieve trust in a scalable, automated way ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 2
 ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 3
©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 3
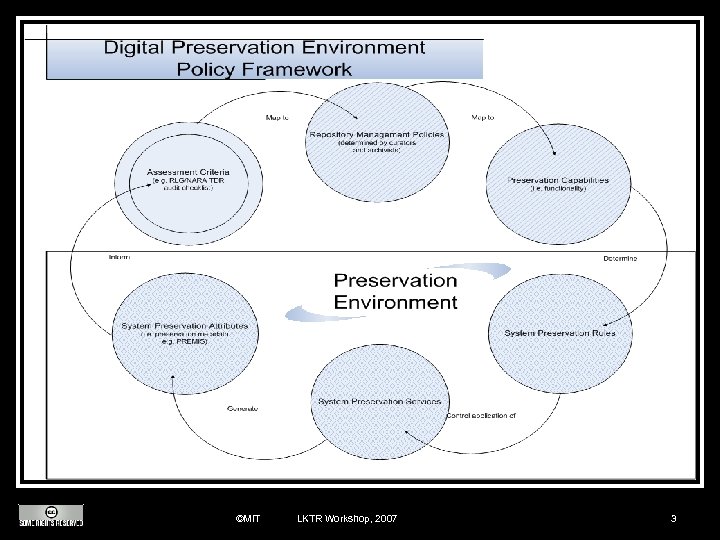
 Policy Framework Based on NARA/RLG TDR checklist categories: n Organization, environment and legal policies n Community and usability policies n Process and Procedure policies n Technology and Infrastructure policies ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 4
Policy Framework Based on NARA/RLG TDR checklist categories: n Organization, environment and legal policies n Community and usability policies n Process and Procedure policies n Technology and Infrastructure policies ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 4
 Policy Encoding n Looked at lots of schemas and approaches n XACML and BPEL too limited n n Ponder and KAo. S too risky n n Single purpose (access control, rights management, workflow, etc. ) Research projects that are no longer active Rule. ML and Rei (N 3) RDF ontology best fit n Selected Rei ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 5
Policy Encoding n Looked at lots of schemas and approaches n XACML and BPEL too limited n n Ponder and KAo. S too risky n n Single purpose (access control, rights management, workflow, etc. ) Research projects that are no longer active Rule. ML and Rei (N 3) RDF ontology best fit n Selected Rei ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 5
 Policy Exchange n Repository management system – DIPs n n n METS (also looked at XFDU, IMS CP, DIDL, etc. ) encapsulate content files, metadata, provenance, and policies Virtual storage system – SIPs n n enforce policies based on locally-implemented rules produce state information (metadata) auditable by archivist over time ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 6
Policy Exchange n Repository management system – DIPs n n n METS (also looked at XFDU, IMS CP, DIDL, etc. ) encapsulate content files, metadata, provenance, and policies Virtual storage system – SIPs n n enforce policies based on locally-implemented rules produce state information (metadata) auditable by archivist over time ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 6
 Rule Definition n Based on assessment criteria (e. g. TDR checklist) n local preservation policies n preservation system functional capabilities n n Implemented as n Rules controlling micro-services with associated persistent state information ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 7
Rule Definition n Based on assessment criteria (e. g. TDR checklist) n local preservation policies n preservation system functional capabilities n n Implemented as n Rules controlling micro-services with associated persistent state information ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 7
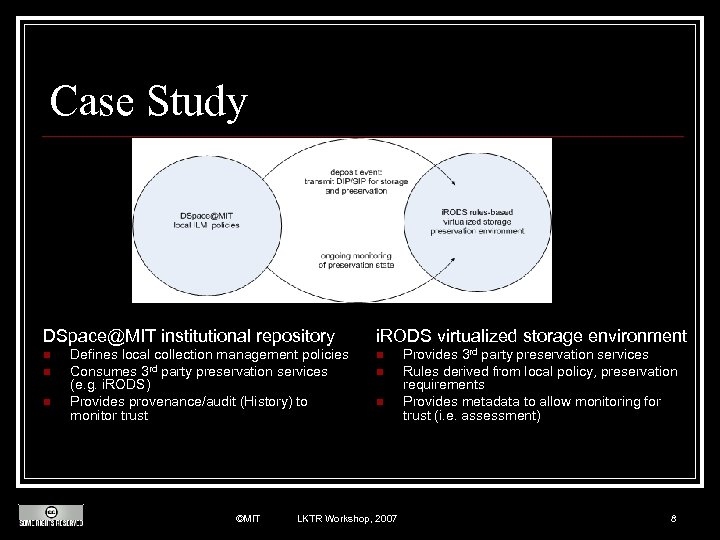 Case Study DSpace@MIT institutional repository n n n Defines local collection management policies Consumes 3 rd party preservation services (e. g. i. RODS) Provides provenance/audit (History) to monitor trust ©MIT i. RODS virtualized storage environment n n n LKTR Workshop, 2007 Provides 3 rd party preservation services Rules derived from local policy, preservation requirements Provides metadata to allow monitoring for trust (i. e. assessment) 8
Case Study DSpace@MIT institutional repository n n n Defines local collection management policies Consumes 3 rd party preservation services (e. g. i. RODS) Provides provenance/audit (History) to monitor trust ©MIT i. RODS virtualized storage environment n n n LKTR Workshop, 2007 Provides 3 rd party preservation services Rules derived from local policy, preservation requirements Provides metadata to allow monitoring for trust (i. e. assessment) 8
 Rule-based Preservation Policies n Generated Rules n Event-Condition-Actions n i. e. set of micro-services or other rules n Each micro-service corresponds to operations on a record at a remote storage location n Each micro-service has a recovery procedure to handle remote system failure or unavailability n Persistent state information is saved to track the outcome from applying the rule ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 9
Rule-based Preservation Policies n Generated Rules n Event-Condition-Actions n i. e. set of micro-services or other rules n Each micro-service corresponds to operations on a record at a remote storage location n Each micro-service has a recovery procedure to handle remote system failure or unavailability n Persistent state information is saved to track the outcome from applying the rule ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 9
 Self-consistency and Closure n For every required preservation attribute (authenticity and integrity) are their assessment criteria? n For every assessment criterion, does there exist preservation metadata? n Are the properties of the preservation environment also preserved? ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 10
Self-consistency and Closure n For every required preservation attribute (authenticity and integrity) are their assessment criteria? n For every assessment criterion, does there exist preservation metadata? n Are the properties of the preservation environment also preserved? ©MIT LKTR Workshop, 2007 10