Digestive_system_Part_2_med_2014.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 36
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Intestine LIVER PANCREAS 2
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Intestine LIVER PANCREAS 2
 Small intestine Functions: • digestion – by enzimes from liver, pancreas, and enterocytes (Membrane and luminal digestion) • absorption – by enterocytes
Small intestine Functions: • digestion – by enzimes from liver, pancreas, and enterocytes (Membrane and luminal digestion) • absorption – by enterocytes
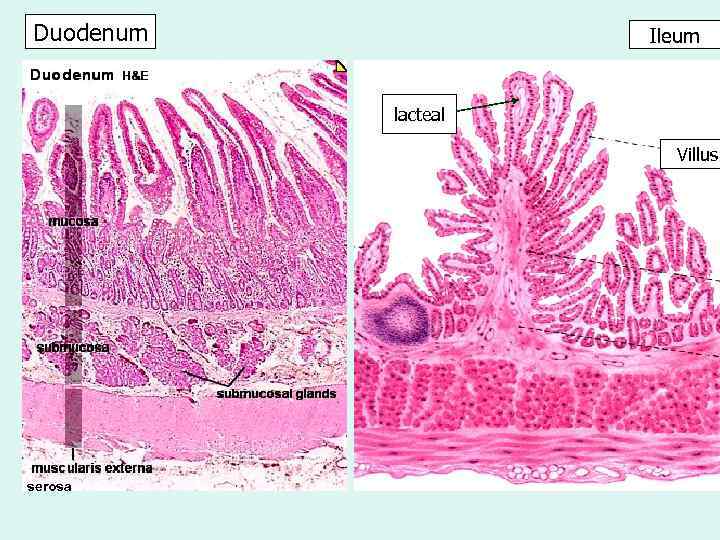 Duodenum Ileum lacteal Villus serosa
Duodenum Ileum lacteal Villus serosa
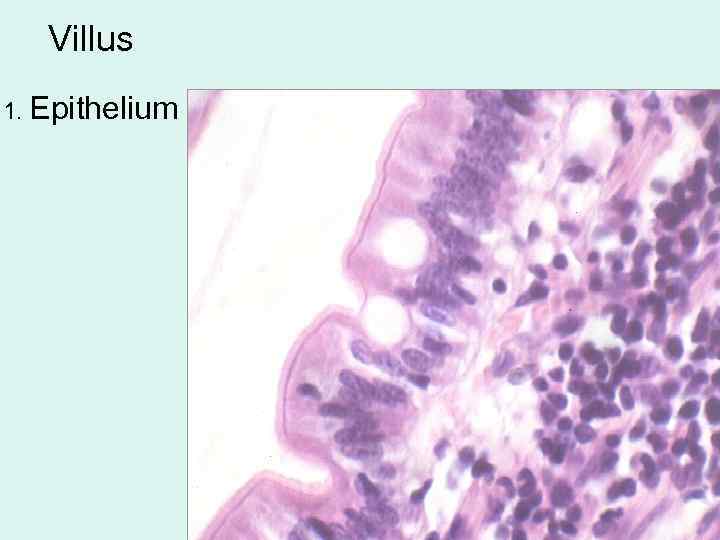 Villus 1. Epithelium
Villus 1. Epithelium
 Epithelium: simple columnar. Cells: 1. Enterocytes -- Columnar absorptive cells -have microvilli = brush border for absorption of digested food. 2. Goblet cells produce a protective mucus. Lamina propria: Connective tissue, has fenestrated capillaries and central lacteal - lymphatic capillary Lymphocytes and plasma cells are very numerous.
Epithelium: simple columnar. Cells: 1. Enterocytes -- Columnar absorptive cells -have microvilli = brush border for absorption of digested food. 2. Goblet cells produce a protective mucus. Lamina propria: Connective tissue, has fenestrated capillaries and central lacteal - lymphatic capillary Lymphocytes and plasma cells are very numerous.
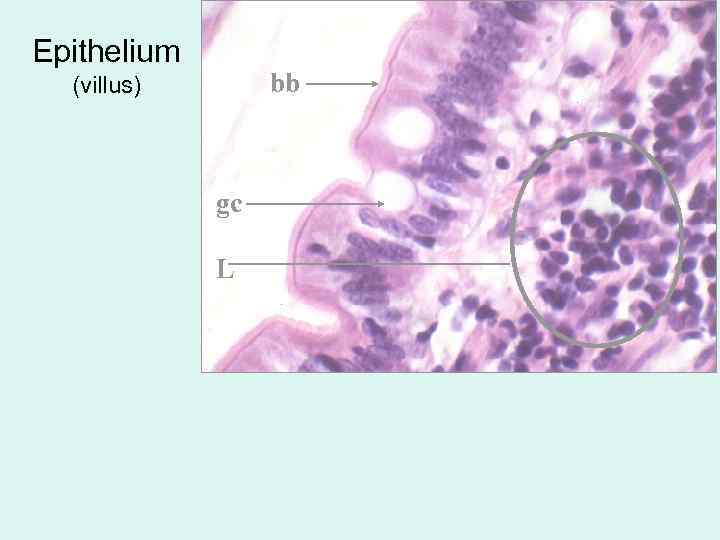 Epithelium bb (villus) gc L
Epithelium bb (villus) gc L
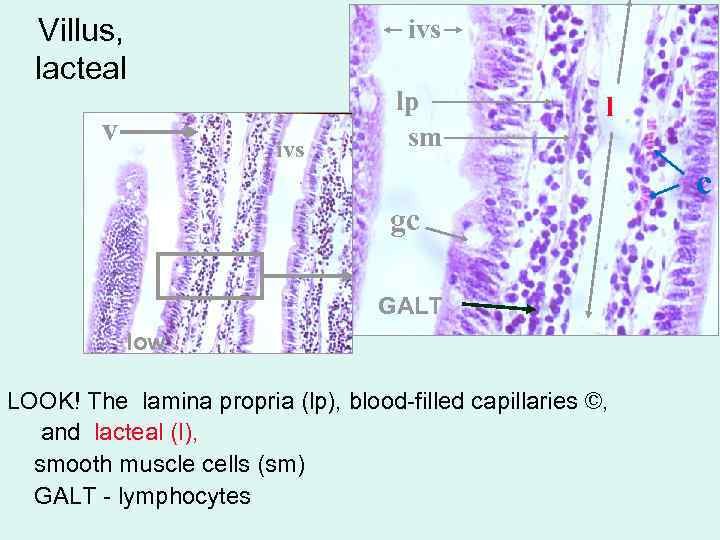 Villus, lacteal v ivs lp sm l gc GALT low LOOK! The lamina propria (lp), blood-filled capillaries ©, and lacteal (l), smooth muscle cells (sm) GALT - lymphocytes c
Villus, lacteal v ivs lp sm l gc GALT low LOOK! The lamina propria (lp), blood-filled capillaries ©, and lacteal (l), smooth muscle cells (sm) GALT - lymphocytes c
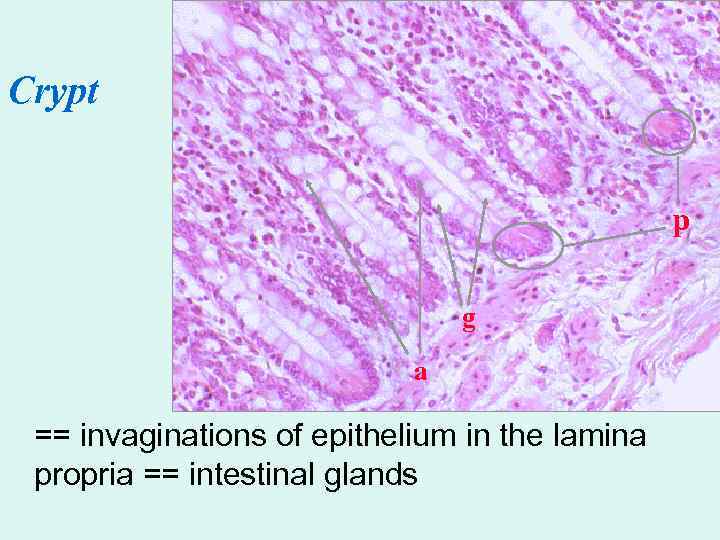 Crypt p g a == invaginations of epithelium in the lamina propria == intestinal glands
Crypt p g a == invaginations of epithelium in the lamina propria == intestinal glands
 Epithelium of crypt 1. Goblet and 2. absorptive cells. 3. the granule-containing Paneth cells - produce Lysozyme (. at the bottom • 4. enteroendocrine cells • 5. undifferentiated stem cells
Epithelium of crypt 1. Goblet and 2. absorptive cells. 3. the granule-containing Paneth cells - produce Lysozyme (. at the bottom • 4. enteroendocrine cells • 5. undifferentiated stem cells
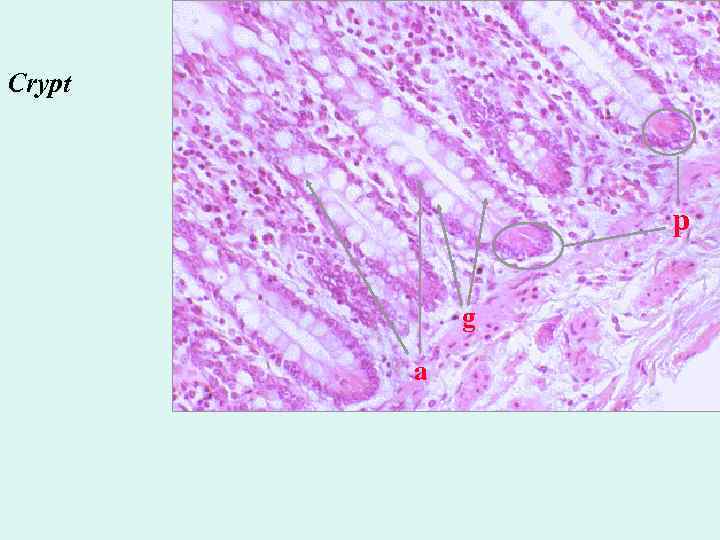 Crypt p g a
Crypt p g a
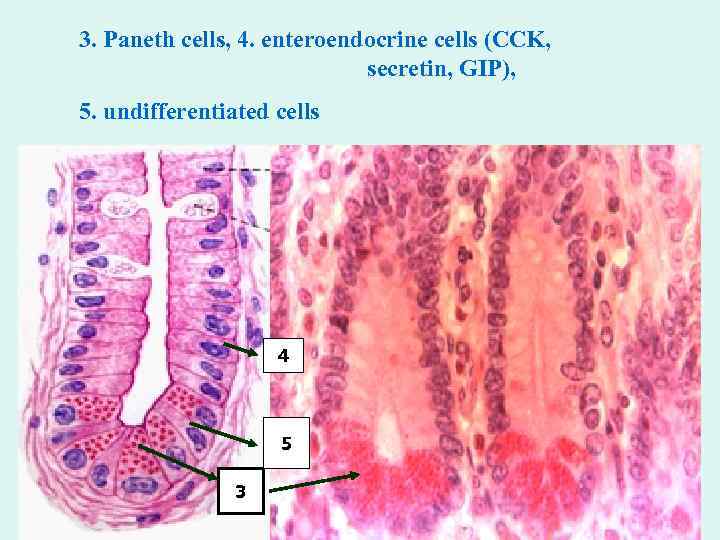 3. Paneth cells, 4. enteroendocrine cells (CCK, secretin, GIP), 5. undifferentiated cells 4 5 3
3. Paneth cells, 4. enteroendocrine cells (CCK, secretin, GIP), 5. undifferentiated cells 4 5 3
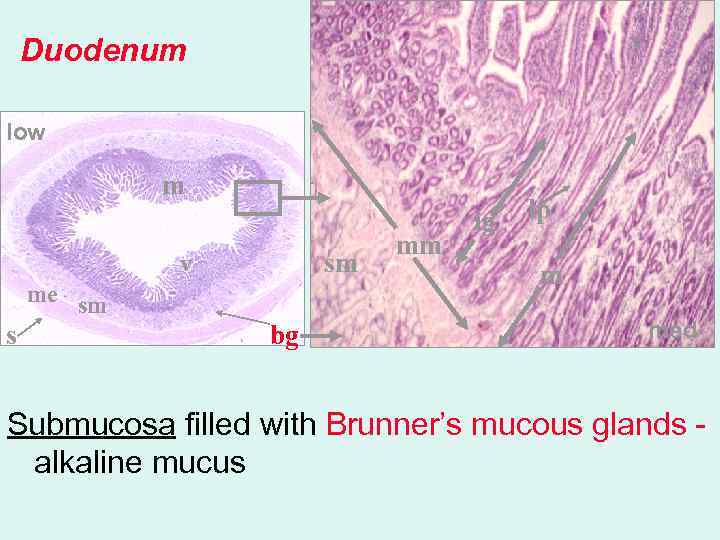 v Duodenum low m v sm v me sm s bg mm ig lp m med Submucosa filled with Brunner’s mucous glands alkaline mucus
v Duodenum low m v sm v me sm s bg mm ig lp m med Submucosa filled with Brunner’s mucous glands alkaline mucus
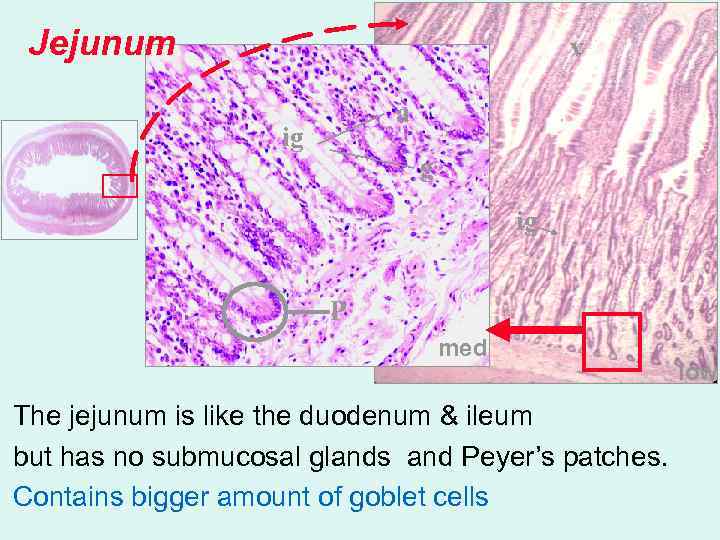 Jejunum v a ig g ig P med The jejunum is like the duodenum & ileum but has no submucosal glands and Peyer’s patches. Contains bigger amount of goblet cells low
Jejunum v a ig g ig P med The jejunum is like the duodenum & ileum but has no submucosal glands and Peyer’s patches. Contains bigger amount of goblet cells low
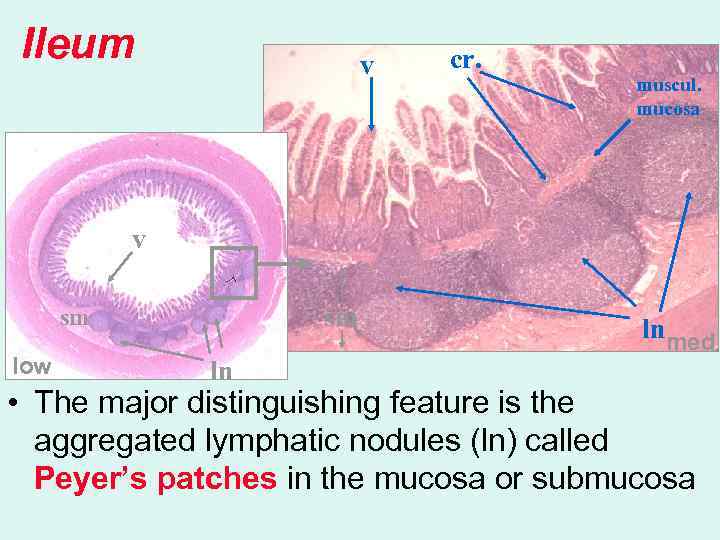 Ileum v cr. muscul. mucosa v sm sm low ln lnmed • The major distinguishing feature is the aggregated lymphatic nodules (ln) called Peyer’s patches in the mucosa or submucosa
Ileum v cr. muscul. mucosa v sm sm low ln lnmed • The major distinguishing feature is the aggregated lymphatic nodules (ln) called Peyer’s patches in the mucosa or submucosa
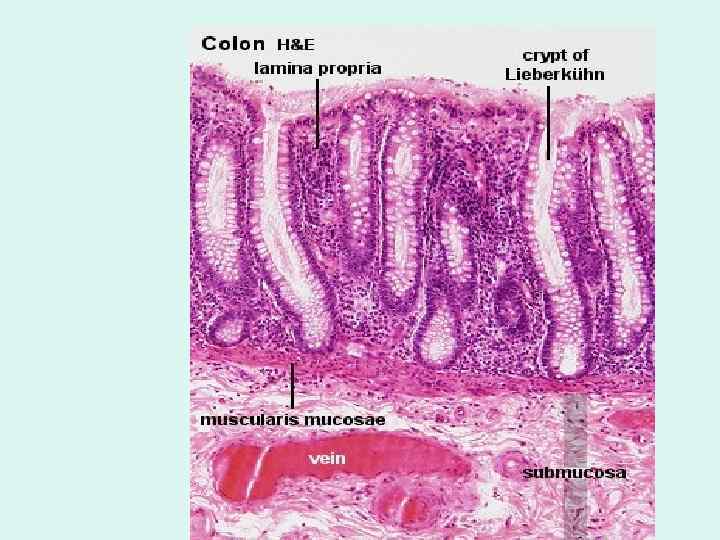
 Large intestine (bowal) - general • Function = Reabsorbtion of water and electrolytes + Elimination of wastes • Inner lining - permanent internal folds of its mucosa + submucosa called plicae circulares and crypts. • Its mucosa lacks of villi. • muscularis externa: The inner circular layer is uniform but the outer longitudinal layer has 3 thicker bands, the taenia coli. • where the colon faces the abdominal cavity there is a serosa.
Large intestine (bowal) - general • Function = Reabsorbtion of water and electrolytes + Elimination of wastes • Inner lining - permanent internal folds of its mucosa + submucosa called plicae circulares and crypts. • Its mucosa lacks of villi. • muscularis externa: The inner circular layer is uniform but the outer longitudinal layer has 3 thicker bands, the taenia coli. • where the colon faces the abdominal cavity there is a serosa.
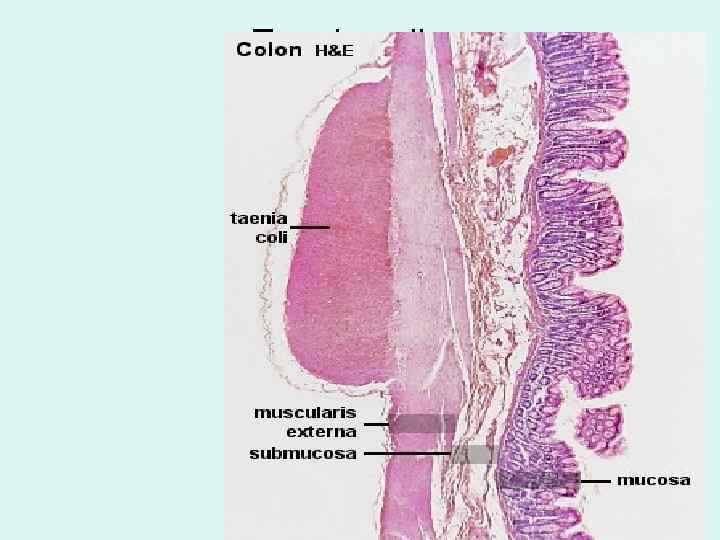 Taenia coli
Taenia coli
 High. Magn.
High. Magn.
 Liver & Gall Bladder
Liver & Gall Bladder
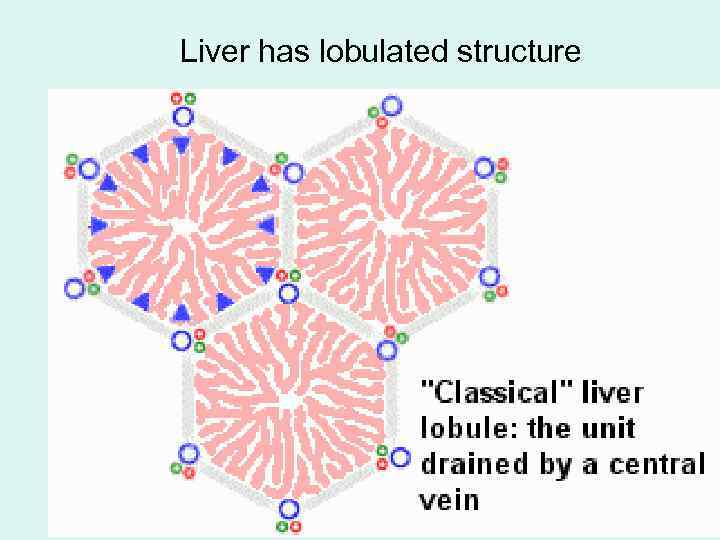 Liver has lobulated structure
Liver has lobulated structure
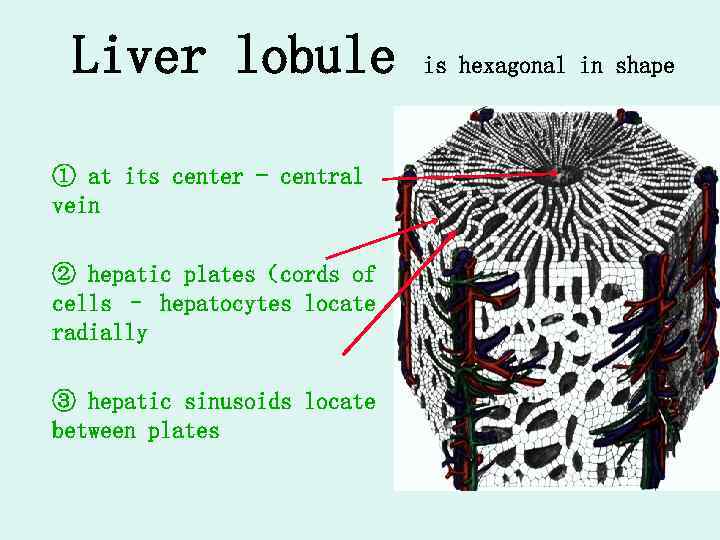 Liver lobule ① at its center - central vein ② hepatic plates(cords of cells – hepatocytes locate radially ③ hepatic sinusoids locate between plates is hexagonal in shape
Liver lobule ① at its center - central vein ② hepatic plates(cords of cells – hepatocytes locate radially ③ hepatic sinusoids locate between plates is hexagonal in shape
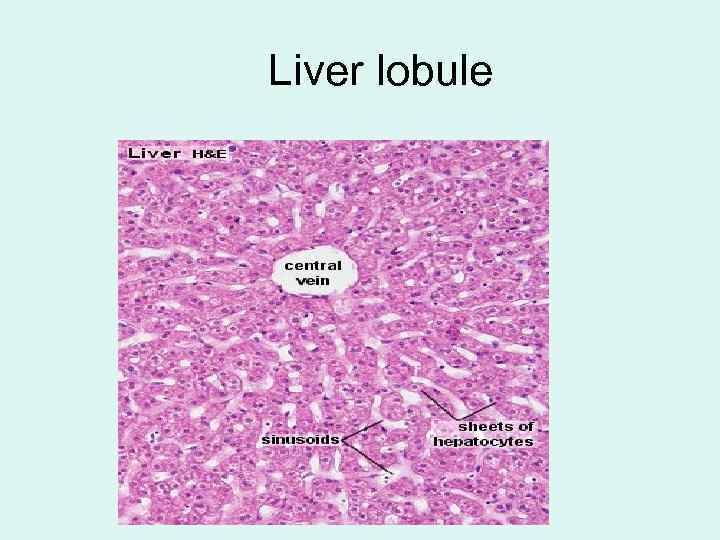 Liver lobule
Liver lobule
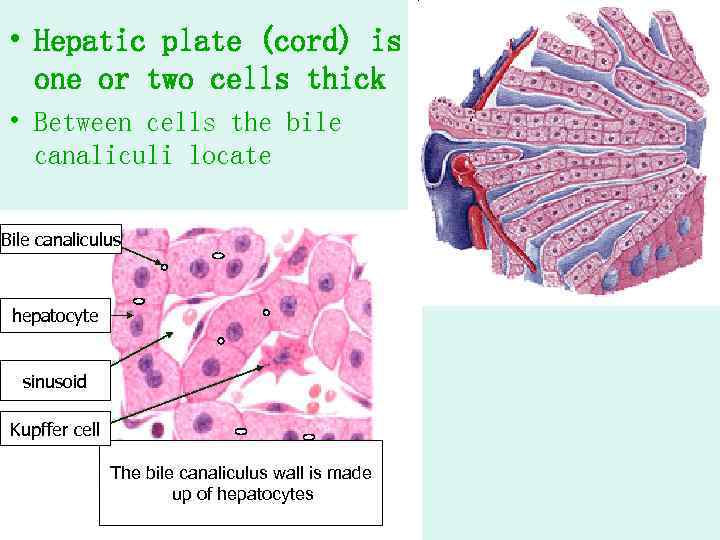 • Hepatic plate (cord) is one or two cells thick • Between cells the bile canaliculi locate Bile canaliculus hepatocyte sinusoid Kupffer cell The bile canaliculus wall is made up of hepatocytes
• Hepatic plate (cord) is one or two cells thick • Between cells the bile canaliculi locate Bile canaliculus hepatocyte sinusoid Kupffer cell The bile canaliculus wall is made up of hepatocytes
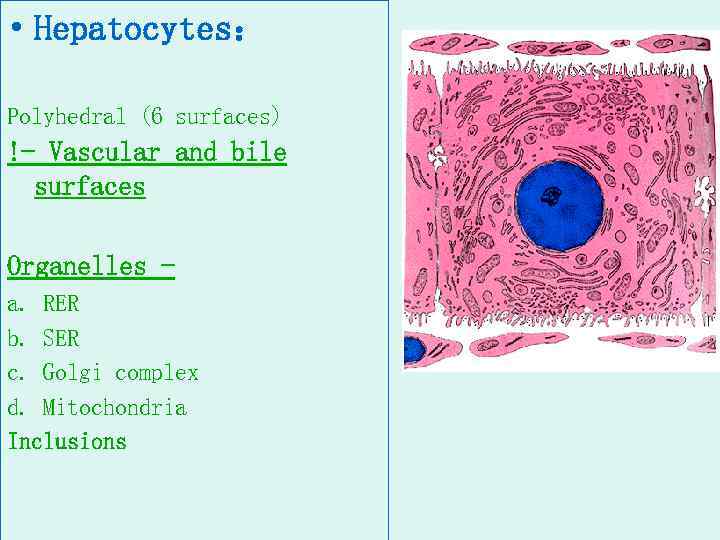 • Hepatocytes: Polyhedral (6 surfaces) !- Vascular and bile surfaces Organelles a. RER b. SER c. Golgi complex d. Mitochondria Inclusions
• Hepatocytes: Polyhedral (6 surfaces) !- Vascular and bile surfaces Organelles a. RER b. SER c. Golgi complex d. Mitochondria Inclusions
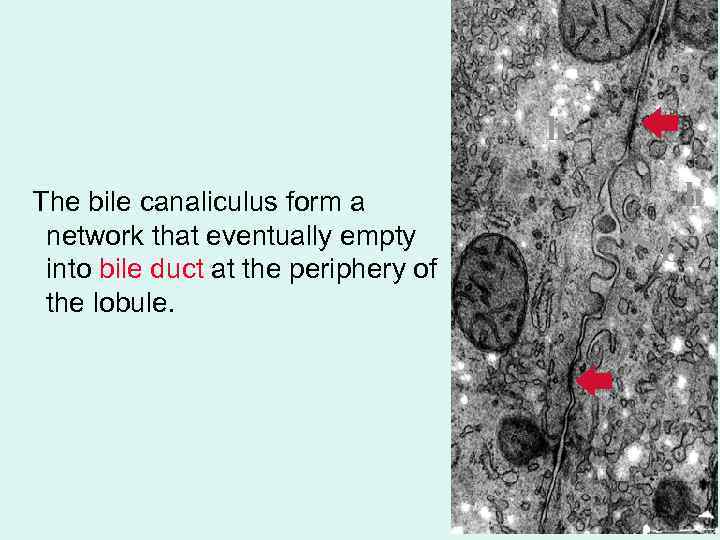 h The bile canaliculus form a network that eventually empty into bile duct at the periphery of the lobule. h b
h The bile canaliculus form a network that eventually empty into bile duct at the periphery of the lobule. h b
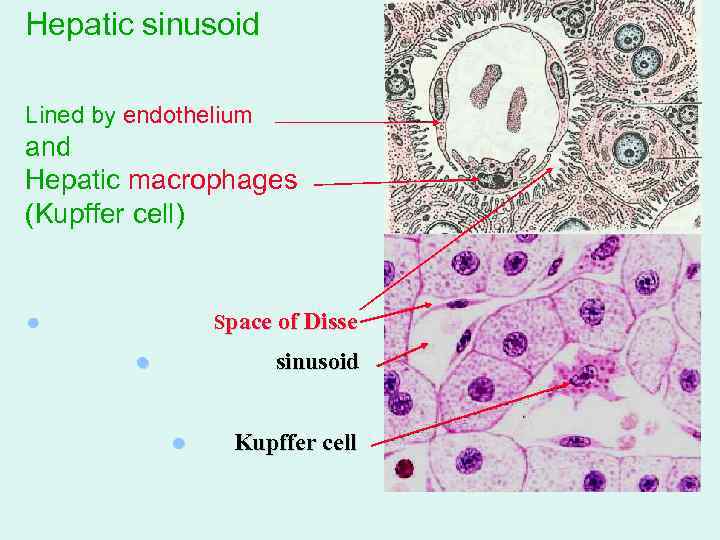 Hepatic sinusoid Lined by endothelium and Hepatic macrophages (Kupffer cell) Space of Disse l sinusoid l l Kupffer cell
Hepatic sinusoid Lined by endothelium and Hepatic macrophages (Kupffer cell) Space of Disse l sinusoid l l Kupffer cell
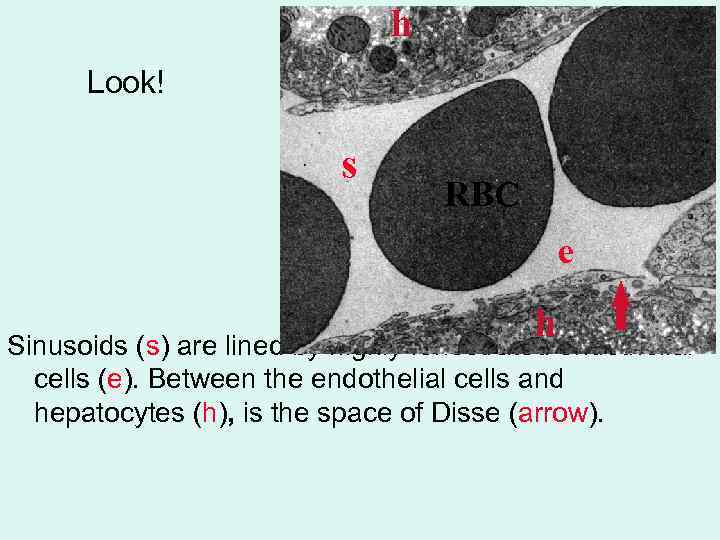 h Look! s RBC e h endothelial Sinusoids (s) are lined by highly fenestrated cells (e). Between the endothelial cells and hepatocytes (h), is the space of Disse (arrow).
h Look! s RBC e h endothelial Sinusoids (s) are lined by highly fenestrated cells (e). Between the endothelial cells and hepatocytes (h), is the space of Disse (arrow).
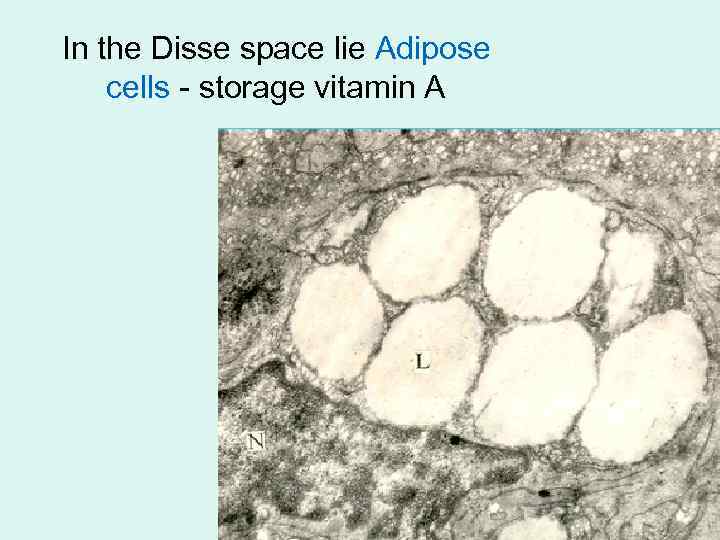 In the Disse space lie Adipose cells - storage vitamin A
In the Disse space lie Adipose cells - storage vitamin A
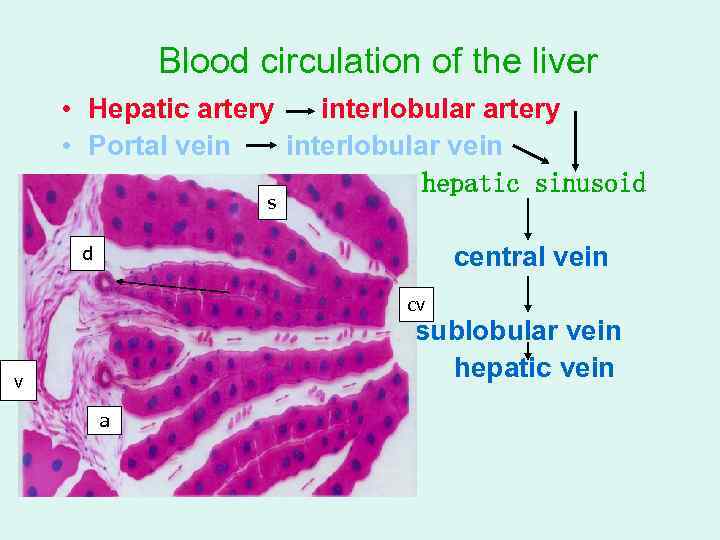 Blood circulation of the liver • Hepatic artery interlobular artery • Portal vein interlobular vein • hepatic sinusoid s v • d • cv • • a central vein cv sublobular vein hepatic vein
Blood circulation of the liver • Hepatic artery interlobular artery • Portal vein interlobular vein • hepatic sinusoid s v • d • cv • • a central vein cv sublobular vein hepatic vein
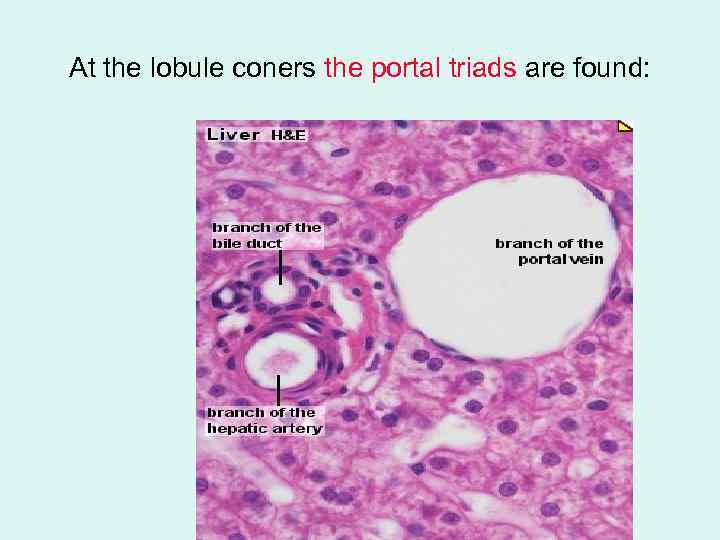 At the lobule coners the portal triads are found:
At the lobule coners the portal triads are found:
 Pancreas -mixed gland • Functions: – Exocrine • • Trypsinogen, peptidase Amylase Lipase Deoxyribonuclease, ribonuclease – Endocrine
Pancreas -mixed gland • Functions: – Exocrine • • Trypsinogen, peptidase Amylase Lipase Deoxyribonuclease, ribonuclease – Endocrine
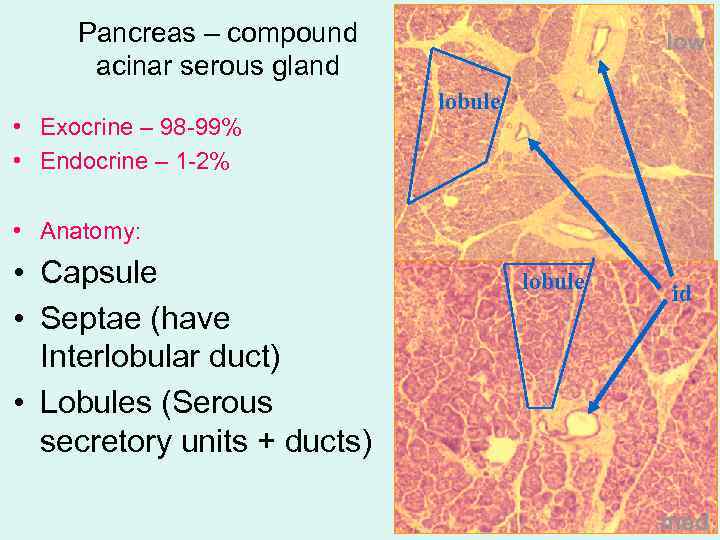 Pancreas – compound acinar serous gland • Exocrine – 98 -99% • Endocrine – 1 -2% low lobule • Anatomy: • Capsule • Septae (have Interlobular duct) • Lobules (Serous secretory units + ducts) lobule id med
Pancreas – compound acinar serous gland • Exocrine – 98 -99% • Endocrine – 1 -2% low lobule • Anatomy: • Capsule • Septae (have Interlobular duct) • Lobules (Serous secretory units + ducts) lobule id med
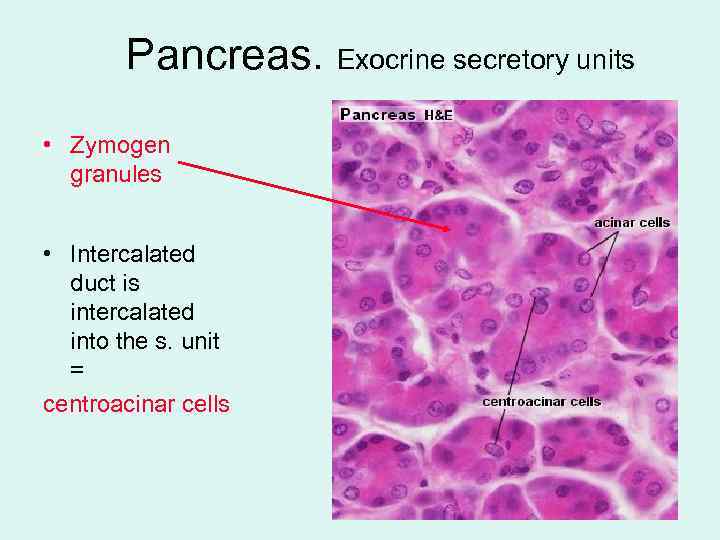 Pancreas. Exocrine secretory units • Zymogen granules • Intercalated duct is intercalated into the s. unit = centroacinar cells
Pancreas. Exocrine secretory units • Zymogen granules • Intercalated duct is intercalated into the s. unit = centroacinar cells
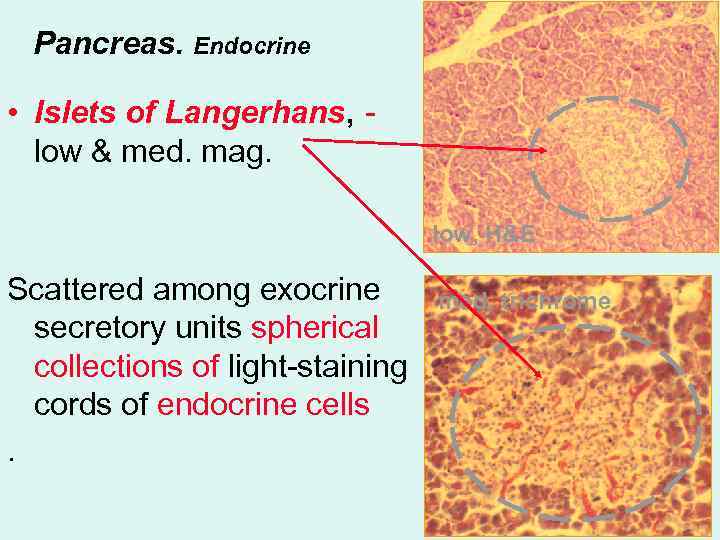 Pancreas. Endocrine • Islets of Langerhans, low & med. mag. low, H&E Scattered among exocrine secretory units spherical collections of light-staining cords of endocrine cells. med, trichrome
Pancreas. Endocrine • Islets of Langerhans, low & med. mag. low, H&E Scattered among exocrine secretory units spherical collections of light-staining cords of endocrine cells. med, trichrome
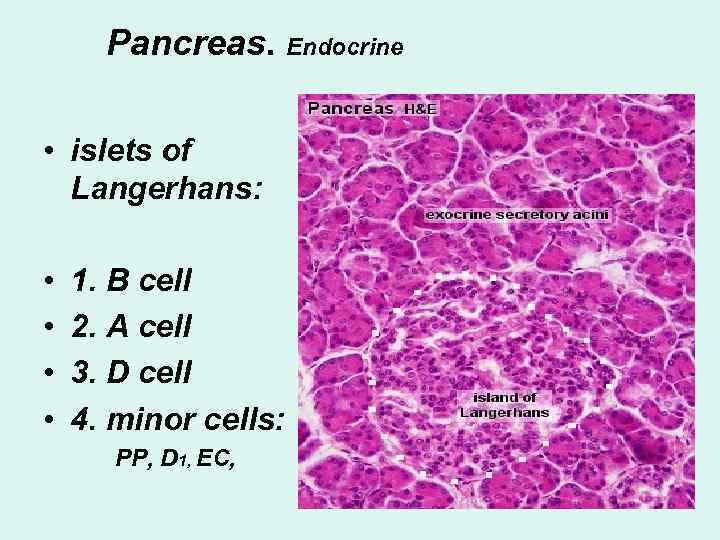 Pancreas. Endocrine • islets of Langerhans: • • 1. B cell 2. A cell 3. D cell 4. minor cells: PP, D 1, EC,
Pancreas. Endocrine • islets of Langerhans: • • 1. B cell 2. A cell 3. D cell 4. minor cells: PP, D 1, EC,
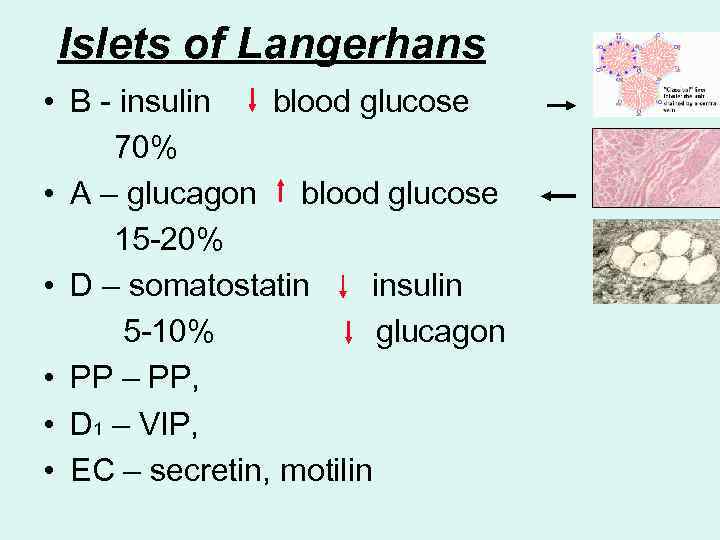 Islets of Langerhans • B - insulin blood glucose 70% • A – glucagon blood glucose 15 -20% • D – somatostatin insulin 5 -10% glucagon • PP – PP, • D 1 – VIP, • EC – secretin, motilin
Islets of Langerhans • B - insulin blood glucose 70% • A – glucagon blood glucose 15 -20% • D – somatostatin insulin 5 -10% glucagon • PP – PP, • D 1 – VIP, • EC – secretin, motilin
 Control question • Group, name • 1. Compare Duodenum, Ileum and Colon Transversum • 2. Liver: Blood supply. (What peculiar in the blood supply of the Liver? )
Control question • Group, name • 1. Compare Duodenum, Ileum and Colon Transversum • 2. Liver: Blood supply. (What peculiar in the blood supply of the Liver? )


